18 VALENCE BOND THEORY
|
|
|
- Michael Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 18 VALENCE BOND THEORY - an attempt to explain why molecules behave in the way that the VSEPR model predicts. - Describes the formation of bonds in terms of the OVERLAP of ORBITALS from the bonding atoms. Bonds are formed when two atoms are close enough together so that their ORBITALS OVERLAP (share the same space). Each SET of overlapping orbitals can contain at most a total of TWO electrons. So, two orbitals with one electron each may bond. An orbital with two electrons can only bond with an EMPTY orbital (This is called a COORDINATE COVALENT BOND.) These 1s orbitals overlap to form what we call a "sigma bond" with overlap BETWEEN the two atomic nuclei.
2 19 Hybridization - Look at carbon's electron configuration: You would expect that carbon would form several different kinds of bonds in a molecule like methane. But, methane's bonds are experimentally all identical. How does carbon form the four equivalent C-H bonds we see in methane? We observe that these bonds are IDENTICAL! Same bond energy, distance, and angle.
3 20 - In valence bond theory, atomic orbitals can COMBINE to make new orbitals that can then go on to bond with other molecules. - When orbitals combine to make HYBRID ORBITALS,... The overall NUMBER OF ORBITALS does not change. The overall NUMBER OF ELECTRONS around the atom does not change The energy of the orbitals is between the energies of the orbitals that combine. These sp3 orbitals were formed from the combination of carbon's original 2s and 2p orbitals. These orbitals are all identical, and are spread degrees apart from one another. Hybrid orbitals are named from the orbitals that go into making the hybrid. 2s + 3 2p orbitals = "sp3"! OpenStax: See page 422 for a picture of hybrid orbitals.
4 21 Types of hybrid orbitals: Hybrid type sp Number of orbitals 2 Molecular shape linear sp2 3 trigonal planar sp3 4 tetrahedral (or derivatives) sp3d 5 trigonal bipyramidal (or derivatives) sp3d2 6 octahedral (or derivatives) OpenStax: See page 422 for a fancier version of this chart!
5 22 MULTIPLE BONDS and VALENCE BOND THEORY - Valence bond theory provides an explanation of multiple (double and triple) bonding that explains some interesting observations about these kinds of bonds. ethylene Each carbon has a TRIGONAL PLANAR geometry. This suggests that the carbons are "sp2 hybridized". One unchanged 2p orbital Three sp2 hybrids that are 120 degrees apart "Original" unbonded carbon atom Carbon atom with sp2 hybrid orbitals
6 23 sp2 hybrid orbitals in BLUE 2p orbital in RED OpenStax: See page 425 The 2p orbitals overlap above and below the axis between the two carbon atoms. This OFF-AXIS overlap is called a PI BOND. The sp2 hybrid orbitals overlap ON THE AXIS between the two carbon atoms. This bond is called a SIGMA BOND. As you can see, the carbon-carbon double bond in ethylene is made up of TWO DIFFERENT KINDS OF BONDS!
7 24 Some notes on sigma and pi bonds: SIGMA bonds are formed when orbitals overlap along the axis between two atoms. These bonds have good overlap between the bonding orbitals, meaning that they are strong. Single bonds are always sigma bonds. Double and triple bonds contain one sigma bond each. PI bonds are formed when off-axis orbitals (usually p orbitals) overlap. Since the overlapping orbitals do not face each other as in the sigma bond, the overlap in pi bonds tends to be poorer than in sigma bonds, As a result, pi bonds tend to be weaker than sigma bonds. Double bonds contain a single pi bond, and triple bonds contain two pi bonds. Experimentally, we observe that the bond energy of the C=C bond is less than the bond energy of two C-C bonds. This suggests that the second bond in a double bond is different from the first! Molecules may rotate around SIGMA bonds, since rotation around the axis between two atoms will not affect the overlap and break the bond. Off-axis PI BONDS prevent rotation because rotation would break the pi bond.
8 25 ROTATION, ISOMERS, and VALENCE BOND THEORY - Consider this molecule: "1,2-dichloroethane"... are these two structures different? No! The molecule is free to rotate around the C-C single (sigma) bond, and we do not observe two different versions of 1,2-dichloroethane. Both of the forms drawn above are equivalent.
9 26 The molecule is free to rotate about the carbon-carbon bond!
10 27... now consider "1,2-dichloroethene":... are these two structures different? YES! The two carbon atoms in these structures are held together by a DOUBLE BOND, which contains a pi bond. The molecule cannot rotate around the C=C double bond without breaking the pi bond, so the form with the two chlorine atoms on opposite sides cannot freely flip over to the form with the chlorine atoms on the same side. These two Lewis structures actually represent DIFFERENT MOLECULES. They are called ISOMERS, since they have the same chemical formula but different arrangements of atoms.
11 28 For this rotation to take place, the PI BOND must break and then re-form!
12 29 trans 1,2-dichloroethene BOILING POINT: 47.5 C POLARITY: NONPOLAR (0 D dipole moment) DENSITY: 1.26 g/ml cis 1,2-dichloroethene BOILING POINT: 60.3 C POLARITY: POLAR (1.9 D dipole moment) DENSITY: 1.28 g/ml * As you can see, some of the properties of these two molecules are very different! The presence of the pi bond (part of the double bond) in each of these molecules means conversion from one form to the other requires a chemical reaction instead of a simple rotation. * Double (and triple) bonds prevent rotation and "fix" the structure of a molecule. This is easily explained by valence bond theory!
13 30 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines until they hit another gas molecule or the walls of the container. * There are no attractive or repulsive forces between gas molecules except during a collision. * When gas molecules collide, energy may be transferred, but no energy is lost as heat. * The temperature of a gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules. Gases are FLUID, COMPRESSIBLE, and DIFFUSE (NOT DENSE)! variable volume! - The properties of different gases are very similar to one another. At moderate conditions, different gases obey the simple IDEAL GAS EQUATION.
14 31 LIQUIDS * Molecules are much closer together than in the gas phase. * Molecules are free to move around each other, but there is much less freedom of motion than in the gas phase * Molecules in the liquid state are held together by attractive forces that we will call INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Liquids are FLUID, DENSE, and INCOMPRESSIBLE! fixed volume! - The properties of different liquids are often very different from one another, Compare liquids like water and motor oil, which are different enough so that they won't readily mix with one another!
15 32 SOLIDS * Molecules are usually packed closer together in the solid phase than in the gas or liquid phases. * Molecules are not free to move around each other as in the liquid phase. Molecular/atomic motion in the solid phase is limited to vibration. * Most solids have a regular structure - unlike liquids or gases. This structure is called a CRYSTAL LATTICE. * Molecules are held together by INTERMOLECULAR FORCES. These are usually stronger than in the liquid phase. Solids are RIGID, DENSE, and INCOMPRESSIBLE! - As for the liquids, the properties of different solids often differ considerably. Compare a sample of candle wax to a sample of quartz.
Polar? * POLAR BONDS? YES. C=O should be polar. * GEOMETRY? LINEAR geometry, with the oxygens 180 degrees apart, so NONPOLAR.
 16 Examples: Polar? * POLAR BONDS? YES. Large electronegativity difference beween C and F. * GEOMETRY? Tetrahedral. All these bonds are arranged symmetrically around the carbon, so electrons can't be pulled
16 Examples: Polar? * POLAR BONDS? YES. Large electronegativity difference beween C and F. * GEOMETRY? Tetrahedral. All these bonds are arranged symmetrically around the carbon, so electrons can't be pulled
Some notes on sigma and pi bonds:
 Some notes on sigma and pi bonds: SIGMA bonds are formed when orbitals overlap along the axis between two atoms. These bonds have good overlap between the bonding orbitals, meaning that they are strong.
Some notes on sigma and pi bonds: SIGMA bonds are formed when orbitals overlap along the axis between two atoms. These bonds have good overlap between the bonding orbitals, meaning that they are strong.
- A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged.
 POLARITY and shape: - A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged. POLARITY influences several easily observable properties. -
POLARITY and shape: - A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged. POLARITY influences several easily observable properties. -
These carbon atoms have TETRAHEDRAL geometry.
 12 VSEPR and large molecules - Large molecules have more than one "center" atom - Describe the molecule by describing the shape around each "center". Each of the three carbon centers is TETRAHEDRAL, since
12 VSEPR and large molecules - Large molecules have more than one "center" atom - Describe the molecule by describing the shape around each "center". Each of the three carbon centers is TETRAHEDRAL, since
- A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged.
 14 POLARITY and shape: - A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged. POLARITY influences several easily observable properties.
14 POLARITY and shape: - A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged. POLARITY influences several easily observable properties.
SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES
 30 SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines
30 SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines
SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES
 30 SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines
30 SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines
SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES
 30 SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines
30 SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS - Here's a brief review of the atomic picture or gases, liquids, and solids GASES * Gas molecules are small compared to the space between them. * Gas molecules move in straight lines
Valence Bond Theory - Description
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Two bonds Two
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Two bonds Two
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity. Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity. Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity
 Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity When there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms, then the bond between them is polar. It is possible for a molecule to contain polar bonds, but
Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity When there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms, then the bond between them is polar. It is possible for a molecule to contain polar bonds, but
CHAPTER TEN MOLECULAR GEOMETRY MOLECULAR GEOMETRY V S E P R CHEMICAL BONDING II: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY AND HYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS
 CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
Lewis Dot Structures for Methane, CH 4 The central C atom is bonded by single bonds (-) to 4 individual H atoms
 Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Lecture 17 - Covalent Bonding. Lecture 17 - VSEPR and Molecular Shape. Lecture 17 - Introduction. Lecture 17 - VSEPR and Molecular Shape
 Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent Compounds Lecture 17 Using the Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory to predict molecular shapes Molecular shape and polarity
Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent Compounds Lecture 17 Using the Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory to predict molecular shapes Molecular shape and polarity
Hybridization of Orbitals
 Hybridization of Orbitals Structure & Properties of Matter 1 Atomic Orbitals and Bonding Previously: Electron configurations Lewis structures Bonding Shapes of molecules Now: How do atoms form covalent
Hybridization of Orbitals Structure & Properties of Matter 1 Atomic Orbitals and Bonding Previously: Electron configurations Lewis structures Bonding Shapes of molecules Now: How do atoms form covalent
Organic Chemistry. Review Information for Unit 1. VSEPR Hybrid Orbitals Polar Molecules
 rganic hemistry Review Information for Unit 1 VSEPR ybrid rbitals Polar Molecules VSEPR The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR) can be used to predict the geometry around a particular atom
rganic hemistry Review Information for Unit 1 VSEPR ybrid rbitals Polar Molecules VSEPR The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR) can be used to predict the geometry around a particular atom
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding
 Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Chapter 10. Geometry
 Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces. Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2
 1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Chapter 9
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Chapter 8. Molecular Shapes. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) What Determines the Shape of a Molecule?
 PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Shapes Chapter 8 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Figure 8.2 The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of bonding
PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Shapes Chapter 8 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Figure 8.2 The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of bonding
Hybridisation of Atomic Orbitals
 Lecture 7 CHEM101 Hybridisation of Atomic Orbitals Dr. Noha Osman Learning Outcomes Understand the valence bond theory Understand the concept of hybridization. Understand the different types of orbital
Lecture 7 CHEM101 Hybridisation of Atomic Orbitals Dr. Noha Osman Learning Outcomes Understand the valence bond theory Understand the concept of hybridization. Understand the different types of orbital
Andrew Rosen *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same
 *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP 2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has
*Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP 2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has
Molecular Geometry. Dr. Williamson s Molecular Geometry Notes. VSEPR: Definition of Terms. Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version
 Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry. Dr. Williamson s Molecular Geometry Notes. VSEPR: Definition of Terms. VSEPR: Electronic Geometries VSEPR
 Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1 Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1 Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
Molecular Structure. Valence Bond Theory Overlap of atomic orbitals is a covalent bond that joins atoms together to form a molecule
 Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Valence Bond
Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Valence Bond
Localized Electron Model
 Localized Electron Model Models for Chemical Bonding Localized electron model (Valence bond model) Molecular orbital model Localized Electron Model Useful for explaining the structure of molecules especially
Localized Electron Model Models for Chemical Bonding Localized electron model (Valence bond model) Molecular orbital model Localized Electron Model Useful for explaining the structure of molecules especially
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Covalent Bonding. Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
- As for the liquids, the properties of different solids often differ considerably. Compare a sample of candle wax to a sample of quartz.
 32 SOLIDS * Molecules are usually packed closer together in the solid phase than in the gas or liquid phases. * Molecules are not free to move around each other as in the liquid phase. Molecular/atomic
32 SOLIDS * Molecules are usually packed closer together in the solid phase than in the gas or liquid phases. * Molecules are not free to move around each other as in the liquid phase. Molecular/atomic
Localized Electron Model
 Localized Electron Model Models for Chemical Bonding Localized electron model (Valence bond model) Molecular orbital model Localized Electron Model Useful for explaining the structure of molecules especially
Localized Electron Model Models for Chemical Bonding Localized electron model (Valence bond model) Molecular orbital model Localized Electron Model Useful for explaining the structure of molecules especially
Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms
 Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity =
Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity =
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Determine the number
Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Determine the number
Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals Molecules Bonding and 2 Molecular Structure Questions How are molecules held together? Why is O 2 paramagnetic? And how is this property connected
Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals Molecules Bonding and 2 Molecular Structure Questions How are molecules held together? Why is O 2 paramagnetic? And how is this property connected
8.3 Bonding Theories > Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding. 8.3 Bonding Theories. 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
 Chemical Bonding Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical bond! is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together Why are most
Chemical Bonding Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical bond! is a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together Why are most
Chapter 10. Structure Determines Properties! Molecular Geometry. Chemical Bonding II
 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Structure Determines Properties! Properties of molecular substances depend on the structure of the molecule The structure includes many factors, including: the skeletal arrangement
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Structure Determines Properties! Properties of molecular substances depend on the structure of the molecule The structure includes many factors, including: the skeletal arrangement
Covalent Bonding. Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
4 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
 CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
CHM Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) Charles Taylor 1/9
 CHM 111 - Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) - 2015 Charles Taylor 1/9 Introduction In CHM 110, we used kinetic theory to explain the behavior of gases. Now, we will discuss solids and liquids. While
CHM 111 - Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) - 2015 Charles Taylor 1/9 Introduction In CHM 110, we used kinetic theory to explain the behavior of gases. Now, we will discuss solids and liquids. While
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.0 Introduction A. Lewis structures do not show one of the most important aspects of molecules- their overall shapes B. The shape and size of molecules-
Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.0 Introduction A. Lewis structures do not show one of the most important aspects of molecules- their overall shapes B. The shape and size of molecules-
Molecular Geometries. Molecular Geometries. Remember that covalent bonds are formed when electrons in atomic orbitals are shared between two nuclei.
 Molecular Geometries Lewis dot structures are very useful in determining the types of bonds in a molecule, but they may not provide the best insight into the spatial geometry of a molecule, i.e., how the
Molecular Geometries Lewis dot structures are very useful in determining the types of bonds in a molecule, but they may not provide the best insight into the spatial geometry of a molecule, i.e., how the
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Molecular Compounds Compounds that are bonded covalently (like in water, or carbon dioxide) are called molecular compounds
 Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding Section 1: Molecular Compounds Bonds are Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Two types: Ionic bonds transfer of electrons (gained or
Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding Section 1: Molecular Compounds Bonds are Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Two types: Ionic bonds transfer of electrons (gained or
1051-3rd Chem Exam_ (A)
 1051-3rd Chem Exam_1060111(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The molecular-orbital model for Ge shows it to be A) a conductor,
1051-3rd Chem Exam_1060111(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The molecular-orbital model for Ge shows it to be A) a conductor,
1051-3rd Chem Exam_ (B)
 1051-3rd Chem Exam_1060111(B) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are. A) strong enough
1051-3rd Chem Exam_1060111(B) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are. A) strong enough
1051-3rd Chem Exam_ (C)
 1051-3rd Chem Exam_1060111(C) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The hybridizations of iodine in IF3 and IF5 are and, respectively.
1051-3rd Chem Exam_1060111(C) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The hybridizations of iodine in IF3 and IF5 are and, respectively.
Name Date Class MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS. Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides
 8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
Chapter 4. Molecular Structure and Orbitals
 Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization
 Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
1s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital (with node) 2px orbital 2py orbital 2pz orbital
 Atomic Orbitals 1s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital (with node) 2px orbital 2py orbital 2pz orbital Valence Bond Theory and ybridized Atomic Orbitals Bonding in 2 1s 1s Atomic Orbital
Atomic Orbitals 1s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital (with node) 2px orbital 2py orbital 2pz orbital Valence Bond Theory and ybridized Atomic Orbitals Bonding in 2 1s 1s Atomic Orbital
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review
 Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Chapter 10 Shapes of Molecules. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 10 Shapes of Molecules Dr. Sapna Gupta Shapes of Molecules - Importance All molecules have a 3D orientations; even the diatomic ones because atoms have a volume. In case of tri atomic or polyatomic
Chapter 10 Shapes of Molecules Dr. Sapna Gupta Shapes of Molecules - Importance All molecules have a 3D orientations; even the diatomic ones because atoms have a volume. In case of tri atomic or polyatomic
Chapter Molecules are 3D. Shapes and Bonds. Chapter 9 1. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Chapters and 7.4 plus 8.1 and 8.3-5: Bonding, Solids, VSEPR, and Polarity
 Chapters 7.1-2 and 7.4 plus 8.1 and 8.3-5: Bonding, Solids, VSEPR, and Polarity Chemical Bonds and energy bond formation is always exothermic As bonds form, chemical potential energy is released as other
Chapters 7.1-2 and 7.4 plus 8.1 and 8.3-5: Bonding, Solids, VSEPR, and Polarity Chemical Bonds and energy bond formation is always exothermic As bonds form, chemical potential energy is released as other
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Chemical Bonding. 5. _c Atoms with a strong attraction for electrons they share with another atom exhibit
 CHAPTER 6 REVIEW Chemical Bonding SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. a A chemical bond between atoms results from the attraction between the valence electrons and of
CHAPTER 6 REVIEW Chemical Bonding SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. a A chemical bond between atoms results from the attraction between the valence electrons and of
Bonding. Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6
 Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents 9.1 Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model 9.2 The Molecular Orbital Model 9.3 Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules 9.4 Bonding
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents 9.1 Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model 9.2 The Molecular Orbital Model 9.3 Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules 9.4 Bonding
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Covalent Bonding. Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
 Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Covalent Bonding Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Section 8.2 Naming Molecules Section 8.3 Molecular Structures Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes Section 8.5 Electronegativity and Polarity Click a hyperlink or
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals. Copyright 2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents (9.1) (9.2) (9.3) (9.4) (9.5) (9.6) Hybridization and the localized electron model The molecular orbital model Bonding in homonuclear diatomic
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents (9.1) (9.2) (9.3) (9.4) (9.5) (9.6) Hybridization and the localized electron model The molecular orbital model Bonding in homonuclear diatomic
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Chapter 7. Ionic & Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
 General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
Chapter 8 : Covalent Bonding. Section 8.1: Molecular Compounds
 Chapter 8 : Covalent Bonding Section 8.1: Molecular Compounds What is a molecule? A molecular compound? A molecule is a neutral group of atoms joined together by covalent bonds A molecular compound is
Chapter 8 : Covalent Bonding Section 8.1: Molecular Compounds What is a molecule? A molecular compound? A molecule is a neutral group of atoms joined together by covalent bonds A molecular compound is
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules
 Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change. Chapter 12: States of Matter
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
Big Idea #5: The laws of thermodynamics describe the essential role of energy and explain and predict the direction of changes in matter.
 KUDs for Unit 6: Chemical Bonding Textbook Reading: Chapters 8 & 9 Big Idea #2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ion, or molecules
KUDs for Unit 6: Chemical Bonding Textbook Reading: Chapters 8 & 9 Big Idea #2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ion, or molecules
Chapter 13: Phenomena
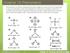 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Downloaded from
 I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #4 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Chemical Bonding I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. The energy required to break a chemical bond to
I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #4 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Chemical Bonding I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. The energy required to break a chemical bond to
SHAPES OF MOLECULES (VSEPR MODEL)
 1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids
 Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Why? Why is water usually a liquid and not a gas? Why does liquid water boil at such a high temperature
Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Why? Why is water usually a liquid and not a gas? Why does liquid water boil at such a high temperature
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 9. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Localized electron model A bond is made when a half-filled orbital of one atom overlaps with a half-filled orbital of another.! Bond: orbitals overlap straight on p
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Localized electron model A bond is made when a half-filled orbital of one atom overlaps with a half-filled orbital of another.! Bond: orbitals overlap straight on p
Shapes of Molecules VSEPR
 Shapes of Molecules In this section we will use Lewis structures as an introduction to the shapes of molecules. The key concepts are: Electron pairs repel each other. Electron pairs assume orientations
Shapes of Molecules In this section we will use Lewis structures as an introduction to the shapes of molecules. The key concepts are: Electron pairs repel each other. Electron pairs assume orientations
Bonding. Polar Vs. Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. Ionic or Covalent? Identifying Bond Types. Solutions + -
 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Bonding onors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Bonding onors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Bonding and IMF practice test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name Bonding and IMF practice test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol
Exam Name Bonding and IMF practice test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol
