5. Synthesis and characterization of lead metal nanoparticles from heavy metal hyperaccumulator plants
|
|
|
- Kelly Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER - V 5. Synthesis and characterization of lead metal nanoparticles from heavy metal hyperaccumulator plants 5.1 Introduction Microscopic particles whose size is measured in nanometers (10-9 m) are called nanoparticles. These particles have very special properties which are used for the production and applications in technological devices. In recent years, nanotechnology is emerging as a revolutionizing field of research with multiple disciplines of science like physics, chemistry, materials science and biology. The synthesis of nanomaterials by the use of green chemicals has vital importance in medicinal and technological aspects. Lead metal nanoparticles have a wide range of applications in the field of environmental pollution control, drug delivery system, material chemistry and so on (Longoria et al., 2014). In conventional, various chemical and physical methods are utilized for the synthesis of nanomaterials, but due to the fact of usage of a large amount of hazardous chemicals, it becomes mandate to find an alternative eco-friendly methodology. In search of green chemistry approach, the usage of plants and microbes were of the prime target, which were considered safe, simple, nontoxic, biocompatible and environment friendly. Accumulation of metal ions in plants is largely used in phytoremediation, which has been regarded as a low-cost, eco-friendly and efficient approach for the cleanup of the polluted site. Synthesis of metal nanoparticles assisted by biological agents provides advantages over chemical and physical methods due to the fact that it is costeffective, environmentally friendly and easily scalable for large-scale synthesis and obviates the need for high pressure, energy, temperature, and toxic chemicals. However, research on this field has been focused mainly on gold and silver and many applications of these metallic nanostructures have been sufficiently explored. In the case of heavy metals such as lead, traditional chemical and physical procedures are employed to synthesize nanoparticles. Nevertheless, available procedures to obtain lead (Pb) nanoparticles are not simple. It has been generally 99
2 understood that lead particles are readily oxidized even at room temperature and under high vacuum and usually various techniques are needed to prevent oxidation, such as embedding the Pb particles in amorphous silicon oxide matrices or employing inorganic templates (Stella et al., 1994). The interest of lead nanoparticles is currently increasing due to their lubricant properties and superconducting fluctuation diamagnetism phenomena that lead nanoparticles present (Zhao et al., 2004; Guin et al., 2010). Lead is a kind of conventional lubricant, so the application of Pb nanoparticles in lubricating additives is potentially interesting. It was reported recently that Pb nanostructures present excellent antiwear performance in a broad concentration range where it is issued as lubricating oil additive (Zhao et al., 2004). In the presence of an external magnetic field, superconducting metals in the nanometer regime exhibit superconducting fluctuation diamagnetism when the particle diameter is smaller than the superconducting coherence length of the material. In the case of lead the useful reported size is 87 nm. Thus Pb nanoparticles are presently used as a model to study the quantum size effect of the superconducting properties, as well as fluctuation diamagnetism. For this reason, there is an increasing interest to synthesize Pb nanoparticles with size under 87 nm (Zhao et al., 2004; Karna et al., 2011). Plants and plant extracts have been successfully used to produce metallic nanostructures. The traditional methods for disposal of hyperaccumulator plants, such as incineration (Stuchi and Jakob, 1997; Bennet and Shaw, 2000; Reijnders, 2005), landfill (Zhao et al., 2000; Sarret et al. 2001) and ashing (Sas-Nowosielska et al. 2004), cannot reuse the metals in them and may lead to the secondary pollution. Because of the high concentrations of heavy metals in these plants, B. juncea and other metal hyperaccumulators cannot be used as composting materials (high levels of toxic metals in leachate pose a serious threat to soils and underground water). These plants do not necessarily remain in the environment as much as there are not good disposal options for them currently. However, the metals in these plants are also a kind of resource, and the reuse of the metals in hyperaccumulators is feasible and significant. 100
3 Heavy metals in soil and eco system pose a serious threat to the ecosystem and human health and therefore the implementation of appropriate remedial measures is required (Vaxevanidou et al., 2008). Hyperaccumulators are plants that can accumulate exceptionally high quantities of heavy metals. In consideration of high metals concentrations in hyperaccumulator plants, the plants cannot be usually used as composting, agricultural forage and feed. The metals in plants must be removed, otherwise, they will return to and retain in soils. It is natural to come up with such imaginations using the Pb-hyperaccumulator plants as the material for synthesis of Pb metal nanoparticles. Sesbania grandiflora has been reported to be highly efficient to remove and accumulate heavy metals like mercury (Hg) and lead (Pb) in both leaf and root tissues. However, this is the first study examining the cellular level of the accumulation of lead in S. grandiflora. While the capacity of some plants to remove heavy metals is widely known, only a limited number of studies (Chen et al., 2009; Jiang et al., 2010) have explored their potential uses reducing agents for the production of heavy metal nanoparticles. The results presented here serve as the basis to further explore the development of an optimal protocol using S. grandiflora as a reducing agent to biosynthesize heavy metal nanoparticles. 5.2 Materials and methods Plant culture and growth conditions Sesbania grandiflora seeds were collected from Kovai Marketing, Salem, Tamil nadu, India and the seeds were germinated on trays containing a mixture of coir waste and sand in a 3:1 ratio. After germination, seedlings (10 day-old) were used for hydroponics study. The seedlings were grown in plastic containers with full-strength Hoagland s nutrient solution (Hoagland and Arnon, 1950) for 7 days grown in the green house at room temperature (37 C) and natural sunlight (13h/11h, day/night). The solutions were continuously aerated Heavy metal treatment and nanoparticle synthesis After 7 days in hydroponics culture, lead treatment was initiated. The seedlings were treated with Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (1000 mg L -1 ). Seedlings without lead 101
4 treatment served as a control. The treatment groups along with the control were arranged in a randomized design and each contained five or six seedlings. After ten days of growth, seedlings were harvested and thoroughly washed with tap water followed by distilled water and washed three times with 10 mm chelating EDTA for desorption of surface bound lead. Approximately 5 g fresh weight of each sample was dried for XRD, FTIR and SEM with EDX analysis Characterization of lead nanoparticles After nanoparticle synthesis, approximately 5 g fresh weight of each sample was dried for FTIR, XRD, and SEM with EDX analysis. The lead nanoparticles were characterized by the following three methods: Dry samples before and after bioreduction, were analyzed by XRD measurements. The synthesized lead nanoparticles solution was drop coated on to glass substrate and carried out on Shimadzu-MODEL XRD 6000 operated at a voltage of 40 Kv and a current of 30 Ma with Cu, K radiation in a θ-2θ configuration. Further, fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra of the samples were measured using Perkin-Elmer makesmodel spectrum RXI in the transmittable mode at the range of cm - 1 in KBr pellets to know the possible functional groups involved in the formation of nanoparticles. For the morphological analysis of the prepared nanostructured samples, scanning electron microscopy (JEOL JSM-5400 model) of the synthesized lead nanoparticles samples was performed. The average particle size of the prepared Pb nanoparticles was determined using the Sigma ScanPro Software. 5.3 Results Fourier Transform Infra Red Spectroscopy The FTIR spectroscopy measurements were carried out to identify the possible biomolecules present in the leaf extracts that bound specifically on the lead surface. The IR spectrum of lead nanoparticles obtained from this method showed the absorption peaks at 3278, 3186, 2921, 2857, 1655, 1527, 1426, 1363, 1243, 1102, 1067, 540 cm -1 for control leaf extracts; 3298, 3191, 2921, 2853, 1649, 1529, 1423, 1385, 1361, 1103, 1069, 893, 665, 618, 536 cm -1 for leaf synthesized lead nanoparticles; 3282, 2924, 2091, 1660, 1513, 1433, 1360, 1243, 1057, 605 cm -1 for 102
5 control root extracts; 3665, 2920, 2746, 1729, 1682, 1513, 1432, 1356, 1238, 1101, 1064, 805, 668, 618 cm -1 for root synthesized lead nanoparticles represents N- H stretch (1 per N-H bond) amines group, 3186 represents N-H stretch amides group, 2921 represents C-H stretch Alkenes group, 1655 represents C=O stretch amides group, 1527 represents N-H bend (1 ) amides group, 1426 denotes the O-H bend stretching carboxylic acids group, 1363 represents -NO 2 (aliphatic) nitro groups, 1243 represents C-O-C stretch dialkyl ethers group, 1102 represents C-C stretch ketones group, 1067 represents the C-N Stretch (alkyl) amines group, 540 cm -1 represents C-Cl stretch alkyl halides group represents N-H stretch (1 per N-H bond) amines group, 3191 represents N-H stretch amides group, 2921 represents C-H stretch Alkenes group, 1649 represents C=O stretch amides group, 1527 represents N-H bend (1 ) amides group, 1423 denotes the O-H bend stretching carboxylic acids group, 1361 represents -NO 2 (aliphatic) nitro groups, 1103 represents C-C stretch ketones group, 1069 represents the C-N Stretch (alkyl) amines group, 536 cm -1 represents C-Cl stretch alkyl halides group (Fig. 25). Therefore, this confirms that the IR band at 1385 cm 1 can be assigned to a C-O bond vibration associated with Pb moieties in a monodentate coordination mode. For roots, spectra show absorptions at 1377 cm 1 and 1322 cm 1 for material unexposed and exposed to lead solution. The intensity of the band for root exposed to Pb salts is increased and shifted; this could be related to metallic nitrates content in roots. These results together suggested that the synthesized lead nanoparticles were capped by the phytoconstituents, viz., flavonoids, alkaloids and tannins that were present in the aqueous extracts. The functional groups of many compounds proved to have potential to act as reducing agents in the synthesis of lead nanoparticles. Infrared spectroscopy (IR) results indicate that flavonoids, alkaloids and tannins are the major components that may be acting as the reducing agents for lead ions; these findings strongly suggest the potential use of this S. grandiflora to further explore the bioassisted synthesis of heavy metal nanostructures. 103
6 Fig. 25. FT-IR spectra recorded from dry leaves (A) and roots (B) of S. grandiflora seedlings grown for 10 days period in hydroponics medium supplemented with Pb(NO 3 ) 2 104
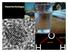
7 5.3.2 X-ray Diffraction analysis X-ray diffraction studies were performed to confirm the crystalline structure of the synthesized lead nanoparticles. The crystalline nature of PbNPs was confirmed by XRD analysis. A number of Bragg s reflection peaks at 2θ values of 21.61, 28.31, 46.05, 50.35, 58.53, and corresponding to the (200), (101), (202) and (220) planes for leaves, for root synthesized lead nanoparticles reflection peaks at 2θ values of 28.31, 46.05, 50.22, and corresponding to (101), (200), (202), (220) planes (Fig. 26). The synthesized nanoparticles were crystalline in nature. Furthermore, the diffraction peaks were few to be narrow, which showed the crystalline nature of lead metal nanoparticles. The presence of very short and broad peaks indicates that the synthesized lead metal nanoparticle was amorphous. The unindexed peaks of and was reported in the previous literature works related to the lead nanoparticles. Appearances of these peaks were due to the presence of phytochemical compounds in the leaf and root extracts SEM and EDX analysis SEM images were measured and topographical analysis was performed based on the surface study. The SEM studies provide the information on the morphology and size of the synthesized lead metal nanoparticles. According to the SEM micrograph, the morphology of the lead nanoparticles was observed as spherical in shape. The sizes of the lead nanoparticle were found to be in the ranges of nm for leaf and nm for root. Most of the nanoparticles aggregated and only a few of them were scattered, as observed under SEM image system (Fig. 27). The confirmation of metallic lead in the synthesized product was further confirmed by the EDAX analysis where a strong signal from the lead atoms in the nanoparticles and weaker signals from oxygen and other atoms were provenients from proteins/enzymes present in the leaf and root extracts. Metallic lead nanocrystals showed strong absorption spectra in the range 1-3 kev. The sharp signal peak of lead strongly confirmed the reduction of lead nitrate to lead nanoparticles. Strong signals from the Pb atoms in the nanoparticles were observed and signals from O, Si, C, Na, Mg and Cl atoms were also recorded. The EDX attachment present with the SEM is known to provide information on the biochemical analysis of the fields that are being investigated or the composition at specific locations (spot EDX). 105
8 Fig. 26. XRD spectra recorded from dry leaves (A) and roots (B) of S. grandiflora seedlings grown for 10 days period in hydroponics medium supplemented with Pb(NO 3 ) 2 106
9 Fig. 27. SEM with EDX spectra recorded from leaves (A) and roots (B) of S. grandiflora seedlings grown for 10 days period in hydroponics medium supplemented with Pb(NO 3 ) 2 107
10 5.4 Discussion S. grandiflora has been used in phytoremediation of pollutants because it can be easily grown and could produce high biomass in terrestrial environment. S. grandiflora and other metal hyperaccumulators cannot be used as composting materials (high levels of toxic metals in leachate pose a serious threat to soils and underground water). Thus, these plants remain in the natural food chain. The lead in S. grandiflora plants returns to the soil after the plants have died and decomposed, which poses a serious threat to the ecosystem and to human health. However, the metals in these plants are also a kind of resource, and the recycling of the metals in hyperaccumulators is feasible, significant and useful. The growth inhibition rate was varied according to the Pb concentration used. Growth reduction was positively correlated with Pb treatment and the maximum reduction of shoot growth noticed was 47%, while the root growth was decreased by 59% at 1000 mg L -1 Pb treatment (Table 7). Furthermore, several visual toxic symptoms such as chlorosis, withering and falling of leaves were also noticed in Pb treated seedlings while control plant did not show such toxicity symptoms. Accumulation of Pb content level was greater in roots than in shoots. The shoots accumulated mg g -1 dry weight, while roots accumulated mg g -1 dry weight. A 5.13 fold increase was noticed in roots compared to the shoots at 1000 mg L -1 Pb exposure. Plants were analyzed and all showed higher amounts of lead (weight %) in roots than in leaves. Also the concentration of glutathione (GSH), the activity of glutathione synthase (GS) and the expression levels of the SmGS gene are all higher in leaves than in roots, suggesting that GSH play an important role in protecting leaves from the detrimental effects of lead (Estrella-Gomez et al., 2009). In the present study, the S. grandiflora plant was exposed to a much higher concentration of lead in the medium; therefore it is not surprising that the roots also had high concentrations of this metal. It is well documented that S. grandiflora is able to accumulate high amounts of lead in its tissues, in fact it is considered to be a Pb-hyper-accumulator. However, in the present work it is revealed that lead accumulates in the form of nanostructured material. Accumulation 108
11 occurs mainly in the cell wall of leaves and roots and closer analysis revealed that PbNPs accumulate differently in the cell wall structures. In general, cell walls of plant consist of 3 types of layers, middle lamella, primary wall and secondary wall; the middle lamella is rich in pectin and free of cellulose, the primary wall is composed of polysaccharides (cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin) and proteins while the principal components of secondary walls are cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Although primary and secondary cell wall boundaries are not clearly distinguished in the micrographs we present, it is clear that the concentration of PbNPs is not the same in the entire cell wall of roots and leaves cells; they appear to be arranged in bands. The intensity of the band for root exposed to Pb salts is increased and shifted; this could be related to metallic nitrates content in roots. Similar results were also reported by McCluskey et al. (1990). These results together suggested that the synthesized lead nanoparticles were capped by the phytoconstituents, viz., flavonoids, alkaloids and tannins that were present in the aqueous extracts. The functional groups of many compounds proved to have potential to act as reducing agents in the synthesis of lead nanoparticles. Either free amine groups or cystein residues in the proteins which ultimately stabilizes the lead nanoparticles (Gole et al., 2001). Biological components are known to interact with metal salts via these functional groups and mediate their reduction to nanoparticles. Infrared spectroscopy (IR) results indicate that flavonoids, alkaloids and tannins are the major components that may be acting as the reducing agents for lead ions; these findings strongly suggest the potential use of this S. grandiflora to further explore the bioassisted synthesis of heavy metal nanostructures. The synthesized nanoparticles were crystalline in nature. Furthermore, the diffraction peaks were few to be narrow, which showed the crystalline nature of lead metal nanoparticles. The presence of very short and broad peaks indicates that the synthesized lead metal nanoparticle was amorphous. The unindexed peaks of and were reported in the previous literature works related to the lead nanoparticles. Appearances of these peaks were due to the presence of 109
12 phytochemical compounds in the leaf and root extracts. Similar results were also reported earlier by Longoria et al. (2014). The SEM studies provide the information on the morphology and size of the synthesized silver nanoparticles. According to the SEM micrograph, the morphology of the lead nanoparticles was observed as spherical in shape. The sizes of the lead nanoparticle were found to be in the ranges of nm for leaf and nm for root. Most of the nanoparticles aggregated and only a few of them were scattered, as observed under SEM. The sharp signal peak of silver strongly confirmed the reduction of lead ion to lead metal nanoparticles. Strong signals from the Pb atoms in the nanoparticles were observed and signals from S, O and Cl atoms were also recorded. The signals were likely due to X-ray emission from carbohydrates/proteins/enzymes present in the cell wall of the biomass (Mishra et al., 2010). Xu and Kall (2002) demonstrated that the shape of metal nanoparticles considerably changed their optical and electronic properties due to the presence of various bioactive molecules. The EDX attachment present with the SEM is known to provide information on the biochemical analysis of the fields that are being investigated or the composition at specific locations (spot EDX). In the presence study, the metallic lead nanocrystals showed strong absorption spectra in the range 1-3 kev. Recently, Longoria et al. (2014) obtained quasi-spherical shape of lead metal nanoparticles at 1-3 kev by using Salvinia minima fern. 5.5 Summary The concentration of lead in S. grandiflora shoots and roots were greater than 10,000 mg kg -1 (dry weight). The plant has a high tolerance for lead in soil, and S. grandiflora can be classified as a lead hyperaccumulator and used to remediate lead contaminated sites. Lead metal nanoparticles were synthesized from S. grandiflora seedling and characterized by FTIR, XRD and SEM with EDS. FTIR results confirmed the presence of various phytochemicals viz., Phosphines, Sulfonates, Amides and Alky halides in lead treated of S. grandiflora. The presence of various phytochemical constituents in lead treated seedlings had reduced the lead ion into metallic lead nanoparticles compared to untreated control seedlings. The XRD pattern and EDS spectrum clearly showed that crystalline substances of the 110
13 lead metal nanoparticles were synthesized. The sizes of the lead nanoparticle were found to be in the ranges of nm for leaf and nm for root. These results indicated that S. grandiflora plant possess the great potential for lead accumulation and nanoparticle synthesis and also shows promising results for further development of a green process for nanoparticle synthesis using this fast growing S. grandiflora plant. 111
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
6. CHARACTERIZATION OF AS (III) IONS BIOSORPTION BY THE LIVE, HEAT AND ALKALINE- TREATED FUNGAL BIOMASS ON THE BASICS OF SURFACE STUDIES
 6. CHARACTERIZATION OF AS (III) IONS BIOSORPTION BY THE LIVE, HEAT AND ALKALINE- TREATED FUNGAL BIOMASS ON THE BASICS OF SURFACE STUDIES 6. Introduction Infrared spectroscopy is a technique used to identify
6. CHARACTERIZATION OF AS (III) IONS BIOSORPTION BY THE LIVE, HEAT AND ALKALINE- TREATED FUNGAL BIOMASS ON THE BASICS OF SURFACE STUDIES 6. Introduction Infrared spectroscopy is a technique used to identify
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid-Assisted Synthesis of Nano Antimony Oxide by Microwave Method
 Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid-Assisted Synthesis of Nano Antimony Oxide by Microwave Method Azadeh Tadjarodi*, Mohammad karimpour Department of Chemistry, Iran University of Science and Technology, Narmak,
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid-Assisted Synthesis of Nano Antimony Oxide by Microwave Method Azadeh Tadjarodi*, Mohammad karimpour Department of Chemistry, Iran University of Science and Technology, Narmak,
A highly reactive chalcogenide precursor for the synthesis of metal chalcogenide quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic supplementary information A highly reactive chalcogenide precursor for the synthesis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic supplementary information A highly reactive chalcogenide precursor for the synthesis
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach
 Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Supporting Information. Self-assembled nanofibers from Leucine Derived Amphiphiles as Nanoreactors for Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information Self-assembled nanofibers from Leucine Derived Amphiphiles as Nanoreactors for Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles Karen T. Johnson, Theodore E. Gribb, Evan M. Smoak, and Ipsita A. Banerjee*
Supporting Information Self-assembled nanofibers from Leucine Derived Amphiphiles as Nanoreactors for Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles Karen T. Johnson, Theodore E. Gribb, Evan M. Smoak, and Ipsita A. Banerjee*
driving agent and study of photocatalytic activity Mohammad Salehi Department of Chemistry, Iran University of Science and Technology, Narmak, Tehran
 A simplified microwave-assisted synthesis of NiMoO 4 nanoparticles by using organic driving agent and study of photocatalytic activity Azadeh Tadjarodi *, Raheleh Pradehkhorram, Mina Imani, Samaneh Ebrahimi,
A simplified microwave-assisted synthesis of NiMoO 4 nanoparticles by using organic driving agent and study of photocatalytic activity Azadeh Tadjarodi *, Raheleh Pradehkhorram, Mina Imani, Samaneh Ebrahimi,
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols
 Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
The characterization of MnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method
 The characterization of MnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method LF Koao 1, F B Dejene 1* and HC Swart 2 1 Department of Physics, University of the Free State (Qwaqwa Campus),
The characterization of MnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method LF Koao 1, F B Dejene 1* and HC Swart 2 1 Department of Physics, University of the Free State (Qwaqwa Campus),
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis The samples were also characterized by scanning electron
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis The samples
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis The samples
Magnetic halloysite: an envirmental nanocatalyst for the synthesis of. benzoimidazole
 doi:10.3390/ecsoc-21-04726 Magnetic halloysite: an envirmental nanocatalyst for the synthesis of benzoimidazole Ali Maleki*, Zoleikha Hajizadeh Catalysts and Organic Synthesis Research Laboratory, Department
doi:10.3390/ecsoc-21-04726 Magnetic halloysite: an envirmental nanocatalyst for the synthesis of benzoimidazole Ali Maleki*, Zoleikha Hajizadeh Catalysts and Organic Synthesis Research Laboratory, Department
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide
 Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Infrared Spectroscopy
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Infrared Spectroscopy History and Application: Infrared (IR) radiation is simply one segment of the electromagnetic spectrum
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Infrared Spectroscopy History and Application: Infrared (IR) radiation is simply one segment of the electromagnetic spectrum
Synthesis and characterization of hybride polyaniline / polymethacrylic acid/ Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites
 Synthesis and characterization of hybride polyaniline / polymethacrylic acid/ Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites Mohammad Reza Saboktakin*, Abel Maharramov, Mohammad Ali Ramazanov Department of Chemistry, Baku State
Synthesis and characterization of hybride polyaniline / polymethacrylic acid/ Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites Mohammad Reza Saboktakin*, Abel Maharramov, Mohammad Ali Ramazanov Department of Chemistry, Baku State
Analysis of Cadmium (Cd) in Plastic Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy
 Analysis of Cadmium (Cd) in Plastic Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Hiroshi Onodera Application & Research Center, JEOL Ltd. Introduction um, PBB and PBDE) are subject to usage restrictions in Europe.
Analysis of Cadmium (Cd) in Plastic Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Hiroshi Onodera Application & Research Center, JEOL Ltd. Introduction um, PBB and PBDE) are subject to usage restrictions in Europe.
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
A novel one-step synthesis of PEG passivated multicolour fluorescent carbon dots for potential biolabeling application
 Supporting Information A novel one-step synthesis of PEG passivated multicolour fluorescent carbon dots for potential biolabeling application Abhay Sachdev, Ishita Matai, S. Uday Kumar, Bharat Bhushan,
Supporting Information A novel one-step synthesis of PEG passivated multicolour fluorescent carbon dots for potential biolabeling application Abhay Sachdev, Ishita Matai, S. Uday Kumar, Bharat Bhushan,
Uptake and localization of Lead in Eichhornia crassipes grown within a hydroponic system
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2012, 3 (1):51-59 Uptake and localization of Lead in Eichhornia crassipes grown within a hydroponic system Sangita
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2012, 3 (1):51-59 Uptake and localization of Lead in Eichhornia crassipes grown within a hydroponic system Sangita
Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation
 Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation Zhigang Xiong, Li Li Zhang, Jizhen Ma, X. S. Zhao* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation Zhigang Xiong, Li Li Zhang, Jizhen Ma, X. S. Zhao* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Low-Temperature Solid-Phase Method to Synthesize Highly Fluorescent Carbon Nitride Dots with Tunable Emission Juan Zhou, Yong Yang, and Chun-yang Zhang* Single-Molecule Detection
Supporting Information A Low-Temperature Solid-Phase Method to Synthesize Highly Fluorescent Carbon Nitride Dots with Tunable Emission Juan Zhou, Yong Yang, and Chun-yang Zhang* Single-Molecule Detection
Infrared Spectroscopy
 Infrared Spectroscopy IR Spectroscopy Used to identify organic compounds IR spectroscopy provides a 100% identification if the spectrum is matched. If not, IR at least provides information about the types
Infrared Spectroscopy IR Spectroscopy Used to identify organic compounds IR spectroscopy provides a 100% identification if the spectrum is matched. If not, IR at least provides information about the types
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: Vol.7, No.6, pp ,
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.6, pp 2620-2624, 2014-2015 Structural, Optical and Morphological Properties of Silver Nanoparticles using Green
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.6, pp 2620-2624, 2014-2015 Structural, Optical and Morphological Properties of Silver Nanoparticles using Green
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBON-COATED Ni 1 x Cu x FERROMAGNETIC NANOPARTICLES FOR SELF-REGULATING MAGNETIC HYPERTHERMIA
 Armenian Journal of Physics, 2013, vol. 6, issue 1, pp. 61-65 SYNTHESIS AND HARATERIZATION OF ARBON-OATED Ni 1 x u x FERROMAGNETI NANOPARTILES FOR SELF-REGULATING MAGNETI HYPERTHERMIA A. S. MANUKYAN 1*,
Armenian Journal of Physics, 2013, vol. 6, issue 1, pp. 61-65 SYNTHESIS AND HARATERIZATION OF ARBON-OATED Ni 1 x u x FERROMAGNETI NANOPARTILES FOR SELF-REGULATING MAGNETI HYPERTHERMIA A. S. MANUKYAN 1*,
Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell
 Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell D. Han, S. Y. Lim, B. J. Kim, L. Piao and T. D. Chung* Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. 2010, 46, 5587-558
Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell D. Han, S. Y. Lim, B. J. Kim, L. Piao and T. D. Chung* Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. 2010, 46, 5587-558
Polyaniline-SbO 2 Composites: Preparation, Characterization and a c conductivity Study
 RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 11 (December 2012), PP 09-13 www.researchinventy.com Polyaniline-SbO 2 Composites: Preparation,
RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 11 (December 2012), PP 09-13 www.researchinventy.com Polyaniline-SbO 2 Composites: Preparation,
ppm = parts per million
 Nano Silver Silver nanoparticles are rapidly becoming a part of our daily life in the form of cosmetics, food packaging, wound dressings, detergents, and antimicrobial coatings. Ultimately, the nanoparticles
Nano Silver Silver nanoparticles are rapidly becoming a part of our daily life in the form of cosmetics, food packaging, wound dressings, detergents, and antimicrobial coatings. Ultimately, the nanoparticles
LEAF EXTRACT MEDIATED GREEN SYNTHESIS OF COPPER OXIDE NANOPARTICLES USING OCIMUM TENUIFLORUM AND ITS CHARACTERISATION
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 435-440 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com LEAF EXTRACT MEDIATED GREEN SYNTHESIS OF COPPER OXIDE NANOPARTICLES USING OCIMUM TENUIFLORUM AND ITS CHARACTERISATION
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 435-440 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com LEAF EXTRACT MEDIATED GREEN SYNTHESIS OF COPPER OXIDE NANOPARTICLES USING OCIMUM TENUIFLORUM AND ITS CHARACTERISATION
Two-dimensional dendritic Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties
 Supporting Information for Two-dimensional dendritic Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties Yingpu Bi, *a Hongyan Hu, a Zhengbo Jiao, a Hongchao Yu, a Gongxuan Lu, a and Jinhua Ye
Supporting Information for Two-dimensional dendritic Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties Yingpu Bi, *a Hongyan Hu, a Zhengbo Jiao, a Hongchao Yu, a Gongxuan Lu, a and Jinhua Ye
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Time-dependent growth of zinc hydroxide nanostrands and their crystal structure Xinsheng Peng, ab Jian Jin, a Noriko Kobayashi, a Wolfgang Schmitt, c and Izumi Ichinose* a a Organic
Supplementary Information Time-dependent growth of zinc hydroxide nanostrands and their crystal structure Xinsheng Peng, ab Jian Jin, a Noriko Kobayashi, a Wolfgang Schmitt, c and Izumi Ichinose* a a Organic
Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage
 Electronic Supplementary Information Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage Bin Luo, a Yan Fang, a Bin Wang, a Jisheng Zhou, b Huaihe Song, b and Linjie
Electronic Supplementary Information Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage Bin Luo, a Yan Fang, a Bin Wang, a Jisheng Zhou, b Huaihe Song, b and Linjie
Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance. absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive ions from.
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
Chapter 6 Magnetic nanoparticles
 Chapter 6 Magnetic nanoparticles Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are a class of nanoparticle which can be manipulated using magnetic field gradients. Such particles commonly consist of magnetic elements
Chapter 6 Magnetic nanoparticles Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are a class of nanoparticle which can be manipulated using magnetic field gradients. Such particles commonly consist of magnetic elements
Sunlight- mediated synthesis of silver and gold. against wound infection causing bacteria
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 12, December 2016 142 Sunlight- mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Active Manuka Honey 20+ UMF R against
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 12, December 2016 142 Sunlight- mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Active Manuka Honey 20+ UMF R against
Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor
 Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
MORPHOLOGY STUDIES ON SILVER NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY GREEN METHOD USING TRIDAX PROCUMBENS AND OCIMUM TENUIFLORUM LEAF EXTRACTS
 MORPHOLOGY STUDIES ON SILVER NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY GREEN METHOD USING TRIDAX PROCUMBENS AND OCIMUM TENUIFLORUM LEAF EXTRACTS M. Sundarrajan*, A.Jeelani, S.Janarthanan Department of Physics, Sri
MORPHOLOGY STUDIES ON SILVER NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY GREEN METHOD USING TRIDAX PROCUMBENS AND OCIMUM TENUIFLORUM LEAF EXTRACTS M. Sundarrajan*, A.Jeelani, S.Janarthanan Department of Physics, Sri
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information High Electrocatalytic Activity of Self-standing Hollow NiCo 2 S 4 Single Crystalline Nanorod Arrays towards Sulfide Redox Shuttles in Quantum Dot-sensitized Solar Cells
Electronic Supplementary Information High Electrocatalytic Activity of Self-standing Hollow NiCo 2 S 4 Single Crystalline Nanorod Arrays towards Sulfide Redox Shuttles in Quantum Dot-sensitized Solar Cells
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
SYNTHESIS OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOSTRUCTURES BY NOVEL PRECURSOR
 Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties (NAP-2011). Vol. 1, Part I 107 SYNTHESIS OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOSTRUCTURES BY NOVEL PRECURSOR M. Salavati Niasari 1,2* 1 Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty
Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties (NAP-2011). Vol. 1, Part I 107 SYNTHESIS OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOSTRUCTURES BY NOVEL PRECURSOR M. Salavati Niasari 1,2* 1 Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty
Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification
 Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite
 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
Reproduction Chemical Reactions. 8J Light 8G Metals & Their Uses 8C Breathing & Respiration 8D Unicellular Organisms
 Science: Key Stage 3 Based on the Exploring Science Scheme of Learning Term 1 & 2 Term 3 & 4 Term 5 & 6 Year 7 Cells, Tissues & Organs Particles Forces & Motion Reproduction Chemical Reactions Chemical
Science: Key Stage 3 Based on the Exploring Science Scheme of Learning Term 1 & 2 Term 3 & 4 Term 5 & 6 Year 7 Cells, Tissues & Organs Particles Forces & Motion Reproduction Chemical Reactions Chemical
Gestão e Produção Sustentável. Durability Electromagnetic radiation. ENG K49 Materiais de origem vegetal aplicados na construção
 Gestão e Produção Sustentável Durability Electromagnetic radiation ENG K49 Materiais de origem vegetal aplicados na construção Ricardo Fernandes Carvalho Electromagnetic radiation spectral band Microwaves
Gestão e Produção Sustentável Durability Electromagnetic radiation ENG K49 Materiais de origem vegetal aplicados na construção Ricardo Fernandes Carvalho Electromagnetic radiation spectral band Microwaves
Supporting Information. Solution-Based Growth of Monodisperse Cube-Like BaTiO 3 Colloidal Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Solution-Based Growth of Monodisperse Cube-Like BaTiO 3 Colloidal Nanocrystals Shiva Adireddy, Baobao Cao, Cuikun Lin, Weilie Zhou and Gabriel Caruntu* Chemistry Department and the
Supporting Information Solution-Based Growth of Monodisperse Cube-Like BaTiO 3 Colloidal Nanocrystals Shiva Adireddy, Baobao Cao, Cuikun Lin, Weilie Zhou and Gabriel Caruntu* Chemistry Department and the
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic
 Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of halogenated carbon quantum dots as an important intermediate for surface modification Jin Zhou, Pei Lin, Juanjuan Ma, Xiaoyue Shan, Hui Feng, Congcong
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of halogenated carbon quantum dots as an important intermediate for surface modification Jin Zhou, Pei Lin, Juanjuan Ma, Xiaoyue Shan, Hui Feng, Congcong
Application of Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles in Heavy Metal Removal
 Application of Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles in Heavy Metal Removal 5.1 Introduction Different contaminants are released to water bodies due to the rapid industrialization of human society, including heavy metal
Application of Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles in Heavy Metal Removal 5.1 Introduction Different contaminants are released to water bodies due to the rapid industrialization of human society, including heavy metal
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF COMMON OPAL. Pimthong Thongnopkun, 1,* Sukanya Pramol 2
 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF COMMON OPAL Pimthong Thongnopkun, 1,* Sukanya Pramol 2 1,2 Gems and Jewelry Research Unit, Faculty of Gems, Burapha University, Chanthaburi 22170, Thailand. *e-mail: pimthong@buu.ac.th,
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF COMMON OPAL Pimthong Thongnopkun, 1,* Sukanya Pramol 2 1,2 Gems and Jewelry Research Unit, Faculty of Gems, Burapha University, Chanthaburi 22170, Thailand. *e-mail: pimthong@buu.ac.th,
Infrared Spectroscopy: Identification of Unknown Substances
 Infrared Spectroscopy: Identification of Unknown Substances Suppose a white powder is one of the four following molecules. How can they be differentiated? H N N H H H H Na H H H H H A technique that is
Infrared Spectroscopy: Identification of Unknown Substances Suppose a white powder is one of the four following molecules. How can they be differentiated? H N N H H H H Na H H H H H A technique that is
Paper ID: Biosynthesis Of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Camellia Sinensis Plant Powder
 Paper ID: 1810535 Biosynthesis Of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Camellia Sinensis Plant Powder Suriani Ibrahim 1, a *, Nurul Zariyah Jakaria@Zakaria 1,b, Shaifulazuar Rozali 1,c, Nik Nazri Nik Ghazali
Paper ID: 1810535 Biosynthesis Of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Camellia Sinensis Plant Powder Suriani Ibrahim 1, a *, Nurul Zariyah Jakaria@Zakaria 1,b, Shaifulazuar Rozali 1,c, Nik Nazri Nik Ghazali
Electrically pulsatile responsive drug delivery platform for treatment of Alzheimer s disease
 Electronic Supplementary Material Electrically pulsatile responsive drug delivery platform for treatment of Alzheimer s disease Li Wu 1,2, Jiasi Wang 1,2, Nan Gao 1, Jinsong Ren 1, Andong Zhao 1,2, and
Electronic Supplementary Material Electrically pulsatile responsive drug delivery platform for treatment of Alzheimer s disease Li Wu 1,2, Jiasi Wang 1,2, Nan Gao 1, Jinsong Ren 1, Andong Zhao 1,2, and
One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Facile tuning of plasmon bands in hollow silver nanoshells using mild reductant and mild stabilizer
 Facile tuning of plasmon bands in hollow silver nanoshells using mild reductant and mild stabilizer Satarupa Pattanayak a, Amiya Priyam a, * and Pradip Paik b,c Supplementary Information Optimization of
Facile tuning of plasmon bands in hollow silver nanoshells using mild reductant and mild stabilizer Satarupa Pattanayak a, Amiya Priyam a, * and Pradip Paik b,c Supplementary Information Optimization of
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of. Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Infra Red Spectroscopy
 CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit I Infra Red Spectroscopy M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit I Infra Red Spectroscopy M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Efficient vapor-assisted aging synthesis of functional and high
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Efficient vapor-assisted aging synthesis of functional and high
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBON NANOTUBES USING EGG ALBUMIN BY CHEMICAL METHOD
 International Journal of Metallurgical & Materials Science and Engineering (IJMMSE) ISSN 2278-2516 Vol. 3, Issue 2, Jun 2013, 13-20 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBON NANOTUBES USING
International Journal of Metallurgical & Materials Science and Engineering (IJMMSE) ISSN 2278-2516 Vol. 3, Issue 2, Jun 2013, 13-20 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBON NANOTUBES USING
A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On
 Supplementary Information A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On an Organic Solid Matrix in the Presence of Gold Single Crystals Khaleda Banu,,,*
Supplementary Information A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On an Organic Solid Matrix in the Presence of Gold Single Crystals Khaleda Banu,,,*
Chapter 10. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Application of IR Raman Spectroscopy
 Application of IR Raman Spectroscopy 3 IR regions Structure and Functional Group Absorption IR Reflection IR Photoacoustic IR IR Emission Micro 10-1 Mid-IR Mid-IR absorption Samples Placed in cell (salt)
Application of IR Raman Spectroscopy 3 IR regions Structure and Functional Group Absorption IR Reflection IR Photoacoustic IR IR Emission Micro 10-1 Mid-IR Mid-IR absorption Samples Placed in cell (salt)
Supporting information
 Supporting information Manipulating the Concavity of Rhodium Nanocubes Enclosed with High-index Facets via Site-selective Etching Yumin Chen, Qing-Song Chen, Si-Yan Peng, Zhi-Qiao Wang, Gang Lu, and Guo-Cong
Supporting information Manipulating the Concavity of Rhodium Nanocubes Enclosed with High-index Facets via Site-selective Etching Yumin Chen, Qing-Song Chen, Si-Yan Peng, Zhi-Qiao Wang, Gang Lu, and Guo-Cong
Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and its application as a highly selective and sensitive sensor for the detection
Electronic Supplementary Information for Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and its application as a highly selective and sensitive sensor for the detection
Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene oxide) templated nickel oxide nanofibers for dye degradation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Adsorption of Cd(II) ions by synthesize chitosan from fish shells
 British Journal of Science 33 Adsorption of Cd(II) ions by synthesize chitosan from fish shells Angham G. Hadi Babylon University, College of Science, Chemistry Department. Abstract One of the major applications
British Journal of Science 33 Adsorption of Cd(II) ions by synthesize chitosan from fish shells Angham G. Hadi Babylon University, College of Science, Chemistry Department. Abstract One of the major applications
Spectroscopy. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
 Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Learning objectives Learning outcomes After completing this course, the student will be able to: Recognize the concept and principle of FT-IR Spectroscopy
Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Learning objectives Learning outcomes After completing this course, the student will be able to: Recognize the concept and principle of FT-IR Spectroscopy
DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR ARTEMISININ
 DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR ARTEMISININ Timothy Dexter T. Tan, Anne Marianne Allison S. Tan, Drexel H. Camacho Chemistry Department, De La Salle University, 2401 Taft Avenue, Manila Abstract: Metal-organic
DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR ARTEMISININ Timothy Dexter T. Tan, Anne Marianne Allison S. Tan, Drexel H. Camacho Chemistry Department, De La Salle University, 2401 Taft Avenue, Manila Abstract: Metal-organic
Prof. Dr. Biljana Škrbić, Jelena Živančev
 5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) A thin-layered chromatography plate prepared from naphthalimide-based receptor immobilized SiO 2 nanoparticles as a portable chemosensor and adsorbent for Pb
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) A thin-layered chromatography plate prepared from naphthalimide-based receptor immobilized SiO 2 nanoparticles as a portable chemosensor and adsorbent for Pb
Infrared Spectroscopy An Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups
 Infrared Spectroscopy An Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Infrared Spectroscopy I. Physics Review Frequency, υ (nu), is the number of wave cycles that
Infrared Spectroscopy An Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Infrared Spectroscopy I. Physics Review Frequency, υ (nu), is the number of wave cycles that
NANOTECHNOLOGY SOLID WASTE IMPLICATIONS. Gurumurthy Ramachandran. University of Minnesota
 NANOTECHNOLOGY SOLID WASTE IMPLICATIONS Gurumurthy Ramachandran University of Minnesota Engineering at the Atomic Level: Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Manipulating atoms Writing with atoms. D.M. Eigler,
NANOTECHNOLOGY SOLID WASTE IMPLICATIONS Gurumurthy Ramachandran University of Minnesota Engineering at the Atomic Level: Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Manipulating atoms Writing with atoms. D.M. Eigler,
Nanotechnologies for drinking water purification
 Nanotechnologies for drinking water purification T. Pradeep pradeep@iitm.ac.in O 99.84 pm 104.45 O 2 nm H H Gas hydrates to ozone chemistry Water - prosperity, health, serenity, beauty, artistry, purity..
Nanotechnologies for drinking water purification T. Pradeep pradeep@iitm.ac.in O 99.84 pm 104.45 O 2 nm H H Gas hydrates to ozone chemistry Water - prosperity, health, serenity, beauty, artistry, purity..
Synthesis and Characterization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Water Purification Applications
 Synthesis and Characterization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Water Purification Applications Sukhman Kaur Gill, Gursharan Singh, Madhu Khatri * University Institute of Engineering and
Synthesis and Characterization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Water Purification Applications Sukhman Kaur Gill, Gursharan Singh, Madhu Khatri * University Institute of Engineering and
Bandgap engineering through nanocrystalline magnetic alloy grafting on. graphene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Bandgap engineering through nanocrystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Bandgap engineering through nanocrystalline
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticle: Synthesis, Characterization and Bio-imaging Application S.C. Ray (a),*, Arindam Saha, Nikhil R. Jana * and Rupa Sarkar Centre for Advanced Materials,
Supporting Information Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticle: Synthesis, Characterization and Bio-imaging Application S.C. Ray (a),*, Arindam Saha, Nikhil R. Jana * and Rupa Sarkar Centre for Advanced Materials,
Facile synthesis of yolk-shell structured Si-C nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion battery 1. Experimental 1.1 Chemicals
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Facile synthesis of yolk-shell structured Si-C nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion battery
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Facile synthesis of yolk-shell structured Si-C nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion battery
Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Composites Embeded with Silver Nanoparticles
 World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 2012, 2, 19-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2012.21004 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjnse) 19 Synthesis and Characterization
World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 2012, 2, 19-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2012.21004 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjnse) 19 Synthesis and Characterization
ROLE OF SURFACE COATING ON ACCUMULATION OF CADMIUM SULFIDE QUANTUM DOTS IN SOYBEAN PLANTS AND STRESS MECHANISMS SANGHAMITRA MAJUMDAR
 ROLE OF SURFACE COATING ON ACCUMULATION OF CADMIUM SULFIDE QUANTUM DOTS IN SOYBEAN PLANTS AND STRESS MECHANISMS SANGHAMITRA MAJUMDAR Jason C. WHITE (The Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station) Arturo
ROLE OF SURFACE COATING ON ACCUMULATION OF CADMIUM SULFIDE QUANTUM DOTS IN SOYBEAN PLANTS AND STRESS MECHANISMS SANGHAMITRA MAJUMDAR Jason C. WHITE (The Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station) Arturo
Advanced Pharmaceutical Analysis
 Lecture 2 Advanced Pharmaceutical Analysis IR spectroscopy Dr. Baraa Ramzi Infrared Spectroscopy It is a powerful tool for identifying pure organic and inorganic compounds. Every molecular compound has
Lecture 2 Advanced Pharmaceutical Analysis IR spectroscopy Dr. Baraa Ramzi Infrared Spectroscopy It is a powerful tool for identifying pure organic and inorganic compounds. Every molecular compound has
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Single-crystalline Pd square nanoplates enclosed by {100}
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Single-crystalline Pd square nanoplates enclosed by {100}
EXPT. 7 CHARACTERISATION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS USING IR SPECTROSCOPY
 EXPT. 7 CHARACTERISATION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS USING IR SPECTROSCOPY Structure 7.1 Introduction Objectives 7.2 Principle 7.3 Requirements 7.4 Strategy for the Interpretation of IR Spectra 7.5 Practice Problems
EXPT. 7 CHARACTERISATION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS USING IR SPECTROSCOPY Structure 7.1 Introduction Objectives 7.2 Principle 7.3 Requirements 7.4 Strategy for the Interpretation of IR Spectra 7.5 Practice Problems
PREPARATION OF NEW LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE, Co-V LDH
 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Preparation of new layered 10 (2005) double 59-63hydroxide, Co-V LDH 59 PREPARATION OF NEW LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE, Co-V LDH O. Saber 1 and H. Tagaya 2 1 Egyptian Petroleum Research
Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Preparation of new layered 10 (2005) double 59-63hydroxide, Co-V LDH 59 PREPARATION OF NEW LAYERED DOUBLE HYDROXIDE, Co-V LDH O. Saber 1 and H. Tagaya 2 1 Egyptian Petroleum Research
Chapter 12. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Copper nanoparticulates in guar-gum: a recyclable catalytic system for the Huisgen[3+2]-Cycloaddition of Azides and Alkynes without additives under ambient conditions Ajeet Kumar,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Copper nanoparticulates in guar-gum: a recyclable catalytic system for the Huisgen[3+2]-Cycloaddition of Azides and Alkynes without additives under ambient conditions Ajeet Kumar,
The CdS and CdMnS nanocrystals have been characterized using UV-visible spectroscopy, TEM, FTIR, Particle Size Measurement and Photoluminiscence.
 Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Hetero-crystals with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties and Stabilities
 Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Rhombic Dodecahedral AgX/Ag 3 PO 4 (X=Cl, Br, I) Hetero-crystals with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties and Stabilities Yingpu Bi, Shuxin Ouyang, Junyu Cao,
Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Rhombic Dodecahedral AgX/Ag 3 PO 4 (X=Cl, Br, I) Hetero-crystals with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties and Stabilities Yingpu Bi, Shuxin Ouyang, Junyu Cao,
CHAPTER 6. SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST
 135 CHAPTER 6 SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST 6.1 INTRODUCTION -Pinene is a terpenoid family of organic compound which is inexpensive, readily available and renewable
135 CHAPTER 6 SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST 6.1 INTRODUCTION -Pinene is a terpenoid family of organic compound which is inexpensive, readily available and renewable
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Precious metal recovery from nanowaste for sustainable nanotechnology: Current challenges and life cycle considerations
 Precious metal recovery from nanowaste for sustainable nanotechnology: Current challenges and life cycle considerations Dr. Peter Vikesland Dr. Sean McGinnis Paramjeet Pati pvikes@vt.edu smcginn@vt.edu
Precious metal recovery from nanowaste for sustainable nanotechnology: Current challenges and life cycle considerations Dr. Peter Vikesland Dr. Sean McGinnis Paramjeet Pati pvikes@vt.edu smcginn@vt.edu
Supplementary Information. Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro
 Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
(IJIRSE) International Journal of Innovative Research in Science & Engineering ISSN (Online)
 Synthesis, Size Characterization and Photocatalytic Activities of Zinc Ferrites and Cobalt Ferrites Nanoparticles Using Oxidative Degradations of Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet and Alizarin Red s in Aqueous
Synthesis, Size Characterization and Photocatalytic Activities of Zinc Ferrites and Cobalt Ferrites Nanoparticles Using Oxidative Degradations of Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet and Alizarin Red s in Aqueous
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Generic Method for Rational Scalable Synthesis of Monodisperse Metal Sulfide Nanocrystals Haitao Zhang, Byung-Ryool Hyun, Frank W. Wise, Richard D. Robinson * Department of Materials
Supporting Information A Generic Method for Rational Scalable Synthesis of Monodisperse Metal Sulfide Nanocrystals Haitao Zhang, Byung-Ryool Hyun, Frank W. Wise, Richard D. Robinson * Department of Materials
The Effect of Coal Fly Ash Treatment with NaOH on the Characters and Adsorption Mechanism toward Methyl Violet in The Solution
 2012 3rd International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering IPCBEE vol.38 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore The Effect of Coal Fly Ash Treatment with Na on the Characters and Adsorption
2012 3rd International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering IPCBEE vol.38 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore The Effect of Coal Fly Ash Treatment with Na on the Characters and Adsorption
Supporting Information. For. Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver
 Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF SiO 2 COATED Fe 2 NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY CHEMICAL VAPOR CONDENSATION PROCESS
 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Structure and magnetic 4 (2003) properties 55-59 of coated 55 STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF COATED NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY CHEMICAL VAPOR CONDENSATION PROCESS Ji-Hun Yu,
Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Structure and magnetic 4 (2003) properties 55-59 of coated 55 STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF COATED NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY CHEMICAL VAPOR CONDENSATION PROCESS Ji-Hun Yu,
