Micro-porous layer with composite carbon black for PEM fuel cells
|
|
|
- Linda Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) Micro-porous layer with composite carbon black for PEM fuel cells X.L. Wang a,b, H.M. Zhang a,, J.L. Zhang c, H.F. Xu a,b, Z.Q. Tian a,b, J. Chen a,b, H.X. Zhong a,b, Y.M. Liang a,b, B.L. Yi a,b a Fuel Cell R&D Center, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, CAS, Dalian , China b Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, CAS, Beijing , China c Institute for Fuel Cell Innovation, National Research Council Canada, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T 1W5 Received 11 November 2005; received in revised form 17 January 2006; accepted 17 January 2006 Available online 28 February 2006 Abstract Effects of carbon black in micro-porous layer (MPL) on the performance of H 2 /air proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) were studied and characterized extensively. Physical properties of gas diffusion layers (GDLs) involving surface morphology, gas permeability, hydrophilic/hydrophobic porosity and electron conductivity were examined. To construct an effective bi-functional pore structure, a novel MPL using composite carbon black consisting of Acetylene Black and Black Pearls 2000 carbon was presented for the first time. An optimal cell performance with the maximum power density of 0.91 W cm 2 was obtained by the MPL containing 10 wt.% Black Pearls 2000 in composite carbon black Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: PEMFC; Gas diffusion layer; Micro-porous layer; Composite carbon black; Hydrophilic/hydrophobic porosity 1. Introduction Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are promising alternative power sources for stationary and mobile applications. The porous gas diffusion layer (GDL), as a component of membrane electrode assembly (MEA), plays an important role in the PEMFC by affecting the diffusion of reactants and water, and the conduction of electrons. The gas diffusion layer is typically a carbon-based porous substrate as shown in Fig. 1. The most common macro-porous gas diffusion backing (GDB) used in GDL is either carbon paper or carbon cloth, which serves as a current collector and a physical support for the catalyst layer. Micro-porous layer (MPL) consisting of carbon black powder and hydrophobic agent is applied on one side or two sides of the GDB. The function of MPL is to provide proper pore structure and hydrophobicity to allow a better gas transport and water removal from the catalyst layer, and also minimize electric contact resistance with the adjacent catalyst layer. Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: zhanghm@dicp.ac.cn (H.M. Zhang). For the critical role in achieving high performance of PEMFC, MPL has been paid to extensive attention. Studies on the effects of the PTFE and carbon loadings in MPL were carried out [1 7]. Many other carbon blacks besides the typically used Vulcan XC-72(R) were employed to fabricate MPL [2,3,8 11]. Acetylene Black was found to be superior to others mainly because of its special characteristics involving lower surface area and pore volume. Moreover, it was found [10] that the fluro-polymer was distributed more uniformly in MPL when using Acetylene Black and held the carbon powder particles together in a tight hydrophobic arrangement. Antolini et al. [9] suggested that employing cathode containing Vulcan XC-72 in the catalyst side and Shawinigan Acetylene Black in the gas side in MPL could optimize the cell performance at high operation pressure. In most of the papers conducted on MPL morphology, catalyst ink was applied on GDL with painting, brushing or spraying method [2,3,8,9,11]. It is known that GDL is a porous substrate and thus the pore structure of GDL could be changed by the leaked catalyst ink. As a result, the essential features of different GDLs may be concealed to some extent. To minimize the impact of the catalyst layer, catalyst-coated-membrane (CCM) is employed in this work, in which catalyst layer is fabricated directly onto the proton exchange membrane /$ see front matter 2006 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.electacta
2 4910 X.L. Wang et al. / Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) Fig. 1. Schematic of a dual-layer gas diffusion layer. The present work aims to reveal the effects of gas and water transportation on cell performance by applying MPLs with different features. With the measurements of surface morphology, electron conductivity, gas permeability and hydrophobic/hydrophilic porosity, the key properties of different GDLs are compared. By employing cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance, more information related to electrochemical reaction and mass transport with various GDLs are investigated. A novel MPL made with composite carbon powders of Acetylene Black carbon and Black Pearls 2000 carbon is described firstly. It appears to form a bi-functional pore structure permitting the good transportation for both reactant gases and liquid water. 2. Experimental 2.1. Preparation of membrane electrode assembly Cathode gas diffusion layers were prepared using wetproofed carbon papers (TGPH-030, Toray) as GDBs. An alcohol suspension of carbon powder and 10 wt.% PTFE emulsion stirred thoroughly by ultrasonic machine was spread onto the both sides of GDB to form a precursor of MPL, then the precursor was baked at 240 C for 30 min, and finally it was sintered at 350 C for 40 min. The carbon loading in each side of MPL was 0.5 mg cm 2. PTFE content in MPL was 30 wt.% and the detail parameters of different GDLs are listed in Table 1. GDLs using Acetylene Black, Black Pearls 2000 and composite carbon black in MPL were designated as AB, BP and CC, respectively. The wet-proofed bare TGPH-030 carbon paper was denoted as CP. The anode GDLs used in the experiments were the same, with SGL carbon papers as GDBs and Vulcan XC-72 as MPL carbon powder. To prepare a catalyst-coated-membrane (CCM), a homogeneous mixture of Pt/C catalyst (46.1 wt.%, Tanaka), Nafion solution (5 wt.%, DuPont) and isopropanol was sprayed directly onto each side of a Nafion 1035 membrane. Nafion content in the catalyst layer was 25 wt.% and Pt loading was 0.25 mg cm 2 for both cathode and anode. To stabilize the catalyst layer and enhance the contact between catalyst layer and membrane, the as-prepared CCM was firstly treated at 160 C under a pressure of 1.0 MPa for 5 min, and then sandwiched between two gas diffusion layers followed by a hot-press procedure at 160 C and 10.0 MPa for 1 min to form membrane electrode assembly (MEA). The effective area of MEA was 5cm Electrochemical measurements of single cells MEAs were evaluated in single cells at 80 C under 0.2 MPa. The reactant gases, hydrogen and air, were externally humidified before entering the single cells by bubbling through the water at 90 and 85 C, respectively. Constant reactant utilization of 40% for oxygen in air and 80% for hydrogen were used. The cell voltages versus current densities curves were obtained with a homemade electrical load. The electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) were recorded at 0.5 V in the frequency range of 100 mhz to 10 khz with an amplitude of sinusoidal signal of 10 mv rms. A frequency response detector (EG&G Model 1025) and a potentiostat/galvanostat (EG&G Model 273A) were employed. All measurements reported in this paper were made in two-electrode Table 1 Parameters of different gas diffusion layers GDLs Type of carbon powder Total carbon loading (mg cm 2 ) Thickness (nm) In-plane conductivity (m cm) Bulk porosity (%) Permeability coefficient ( m 2 ) AB Acetylene Black carbon BP Black Pearls 2000 carbon CC Composite carbon black CP
3 X.L. Wang et al. / Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) arrangement, with the anode serving as both counter and reference electrode and the cathode used as working electrode. The cyclic voltammetry (CV) was performed on the electrodes using a potentiostat/galvanostat (EG&G Model 273A) at a scan rate of 50 mv s 1. In the measurement of CV curves, humidified nitrogen was passed through the cathode which was served as working electrode and hydrogen were fed into the anode which was used as both counter and reference electrode Physical characteristics BET surface areas, pore volumes of the different carbon powders were determined by ASAP-2010 (Micromeritics) physisorption system using N 2 as adsorbate at 77 K. The morphological characteristics of the micro-porous surface layer were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEM- 1200EX, JEOL Co.). In-plane conductivity of GDL was measured using a four-point method. The contact angles on the surface layers of desired carbon powders were tested with a sessile drop method [12] Gas permeability Permeability was measured by flowing nitrogen through GDL and then relating the flow rate to the applied pressure drop by means of a differential manometer. The size of each sample was 5.0 cm 5.0 cm. Before the samples were examined, they were pressed as what had done to MEA to ensure the real pore structure at cell testing. The permeability coefficient was calculated based on Darcy s law: κ = vµ X P where k is the permeability coefficient of a porous substrate (m 2 ); v is the superficial velocity, calculated from nitrogen flow rate divided by the area of sample (m 2 s 1 ); µ is the fluid viscosity, Pa s for nitrogen at 23 C; X is the thickness of a substrate (m); P is the pressure drop across a substrate (Pa) Porosity Bulk porosity Bulk porosity of each sample was determined from an analog Archimedes measurement. In this technique, the sample was hanged and immersed in decane, which could fill both hydrophilic and hydrophobic pores [13]. The solid volume of GDL was calculated from the principle of buoyancy. Bulk porosity of GDL is defined as its total pore volume divided by the summation of its total pore volume and its solid volume Hydrophilic/hydrophobic porosity The measurement of the hydrophilic porosity of the GDL was carried out with a homemade special apparatus. The sample was placed horizontally in the apparatus at room temperature. Water vapour carried by the air flowed through the sample. In this process, capillary condensation occurred in the hydrophilic pores inside of the GDL and the liquid water accumulated with time. By weighing the sample before and after measurement, hydrophilic porosity could be calculated. Hydrophobic porosity was decided by subtracting the hydrophilic porosity from bulk porosity. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Physical properties of carbon powder The physical properties of carbon powders chosen for investigation are summarized in Table 2. The surface area varies greatly from 62.0 m 2 g 1 for Acetylene Black to m 2 g 1 for Black Pearls This can be explained by the tremendous difference in pore volume and pore size distribution. The Black Pearls 2000 reveals smaller particle size and larger pore volume as compared to Acetylene Black, from which we can deduce that the MPL made of Black Pearls 2000 involves more micro-pores than that of Acetylene Black. Note that the definition of pore range is different with the general criteria. As reported by Jordan et al. [3] and Yu et al. [14], the pores in GDL are mainly in three size: macro-pores in the range of m, meso-pores in the range of m, and micro-pores below 0.1 m. Composite carbon black with 80 wt.% Acetylene Black and 20 wt.% Black Pearls 2000 shows moderate characteristics between the original materials with surface area of m 2 g 1. Images of water droplets on the surface of different carbon layer are shown in Fig. 2. By fitting a tangent to three-phase point where liquid surface touches the solid surface the contact angle is measured. Because there is no hydrophobic agent added, the contact angles on the surface of carbon layer imply surface characteristics of the desired carbon powders. It is obvious that the surface layer using Black Pearls 2000 with contact angle of 53 is more hydrophilic and the surface using Acetylene Black with contact angle of 153 shows stronger hydrophobicity. One reason for the phenomenon might be the more pores for Black Pearls 2000 which is in possession of high surface area and capability to adsorb water [15] relative to Acetylene Black. Another possibility is that more hydrophilic functional groups on Black Pearls 2000 resulting in the hydrophilic property. While on the interface of composite carbon black layer, contact angle of 146 is measured, which is slightly lower than that on the surface of Acetylene Black because of the adding of Black Pearls Table 2 Physical parameters of different carbon powders Type of carbon black Source Surface area (m 2 g 1 ) Particle size (nm) Pore volume (cm 3 g 1 ) Acetylene Black Acetylene Black Pearls 2000 Oil furnace Composite carbon
4 4912 X.L. Wang et al. / Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) Fig. 2. Contact angles on the surface layer of: (a) Black Pearls 2000; (b) Acetylene Black; (c) composite carbon black Effects of different carbon powder on MPL Single cell performance of MEAs with various GDLs was compared as shown in Fig. 3. At potential of 0.15 V, electrode with AB shows current density of 1800 ma cm 2 which is obviously higher than that of BP with 1000 ma cm 2. The difference arises mainly from the mass transport through each GDL because all the related factors are identical including CCMs, anodes, cell assembling pressures and operating conditions. And also there is little difference in conductivity of each GDL as listed in Table 1. SEM images of MPLs with different carbon powders at 500 magnifications are displayed in Fig. 4. MPL with Acetylene Fig. 3. Cell performance of electrodes with different MPLs for H 2 /air with cell temperature 80 C, anode humidifier temperature 90 C, cathode humidifier temperature 85 C, pressure of 0.2 MPa. Black shows a homogeneous surface with rich pores formed by the small aggregates of carbon powders and PTFE. In contrast, MPL using Black Pearls 2000 presents a stronger compactness of carbon and a few larger cracks due to its smaller pore size. Based on the analysis of the properties of original carbon powders and the SEM images, we believe that there are many more hydrophobic macro- and meso-pores in AB, which is beneficial to the gas diffusion and reduces the mass transport limitation. On the other hand, the micro-pores provided by AB should be less and the liquid water removal by capillary-driven force would be hindered. This would be a potential factor to restrict cell performance especially at high current density region. On the contrary, BP shows more hydrophilic micro-pores serving as water flow paths, but most of them adsorb water internal leading to serious water flooding. The deductions will be further verified in the consequent sections. To maintain the requirements of the well transportation of gases and liquid water, a novel GDL fabricated with composite carbon black (80 wt.% Acetylene Black and 20 wt.% Black Pearls 2000) is suggested by combination the advantages of AB and BP. The SEM photograph of CC is shown in Fig. 4(c). Clearly, the pore structure appears to be more uniform and has finer pores with proper size. As expected, electrode using CC presents the best performance with current density of 2000 ma cm 2 at potential of 0.15 V. It can be attributed to the more functional pores formed, which facilitate the efficient mass transportation. The electrochemical active surface (EAS) of Pt was detected by CV measurements to investigate the influence of GDL on CCM. The calculated hydrogen desorption charges are 104, 100 and 91 mc for electrodes with AB, BP and CC, respectively. For the identical CCM applied, there is little difference in EAS of
5 X.L. Wang et al. / Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) Fig. 4. Scanning electron micrographs (500 ) of: (a) AB; (b) BP; (c) CC. Pt in various electrodes, suggesting that the degree of contact between GDL and CCM has a negligible influence to the cell performance. Electrochemical impedance spectra at 0.5 V for each electrode are shown in Fig. 5. To date, more and more researches of EIS on fuel cell indicated that the impedance loop appeared at the higher frequency was due to the double layer charging through the charge transfer resistance and the arc at lower frequency was caused by the gas-phase transport limitation [4,6,16 18].As can be seen from Fig. 5, the impedance spectra observed for all electrodes appears two distinguishable arcs at cell potential of 0.5 V. Electrode with BP shows obviously larger oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) charge transfer resistance arc and mass trans- port impedance arc than that of AB and CC. On the contrary, the impedance of CC demonstrates the smallest transport-related loop. The difference between polarization curves of various GDLs can be reasonably explained by the EIS results Gas permeability measurement of different GDLs Gas permeability is expected to correlate with the through holes which serve as mass transport paths when cell working. Comparison of permeability coefficients of GDLs and wetproofed bare carbon paper is demonstrated in Fig. 6. It is evident that an addition of micro-porous layers to the macro-porous CP decreases the through-plane permeability significantly. BP Fig. 5. Impedance spectra for electrodes with different MPLs at 0.5 V. Fig. 6. Gas permeability of different GDLs.
6 4914 X.L. Wang et al. / Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) Fig. 8. Curves of water incremental ratio vs. experiment time of BP. Fig. 7. Porosity of different GDLs. shows a quiet smaller value than AB and CC. AB exhibits highest capability of reactants passage due to the larger pore size. CC, with composite carbon powder, presents a slight lower permeability value than AB attributing to the adding of Black Pearls 2000 with small particle size. Williams et al. revealed that a GDL with higher gas permeability had higher limiting current because higher gas permeability might increase the effective diffusion coefficient as well as enhance more convection [19]. The gained conclusion was based on the special operation conditions of lower humidity and higher temperature, where the gas transport was focused on and the influence of liquid water was eliminated to a substantial extent. In our work, over saturated system is employed to study the two-phase flow occurred in most cells. So the higher limiting current but the lower permeability of CC than those of AB could be explained by the proper pore size distribution and reasonable hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity Porosity measurement of different GDLs Bulk porosity and hydrophobic/hydrophilic porosity of each GDLs and wet-proofed bare carbon paper are displayed in Fig. 7. The bulk porosity of TGPH-030 bare carbon paper without PTFE is 80.0% reported by Toray Industries, Inc. While because of the occupancy of PTFE, bulk porosity of wet-proofed bare carbon paper is decreased to 76.5%, which is coincident with the calculated value of 75.4%. It indicates that the testing method is creditable. The accession of MPLs reduces the bulk porosity dramatically from 80% to 70%. But it seems that there is no obvious difference in various GDLs in bulk porosity. Fig. 8 shows the curves of water incremental ratio versus experiment time for hydrophilic porosity measurement of BP. At the beginning, the curves rise up for the water vapour condenses in the hydrophilic pores and the liquid water accumulates until such pores are completely filled. About 10 h later, no incremental water is observed, so incremental ratio keeps constantly with time going on. Repeating experiment indicates that the difference is only 1.5%. The same testing method is carried out on the other GDLs and the values for comparison are selected in the smoothing region at about 15 h. BP exhibits the highest ratio of hydrophilic pores about 20.23%, which means more pores are easy to be occupied by liquid water and relative fewer pores are left for gas transport, so the electrode with BP is intended to be flooding. AB shows lowest fraction of hydrophilic pores about 10.70% and more hydrophobic pores correspondingly ensures the gas transport. CC demonstrates an appropriate distribution of 11.16% hydrophilic pores and 58.74% hydrophobic pores. The flow of liquid water is improved tremendously by the little appending of hydrophilic pores compared with AB. The results suggest that the combination of two distinctive carbon powders can form a bi-functional pore structure permitting the well transportation of both reactant gases and liquid water Optimization of MPL with composite carbon black Fig. 9 shows the effect of Black Pearls 2000 content in composite carbon black on the cell performance. The optimum Fig. 9. Polarization curves for electrodes using MPLs for H 2 /air with 5, 10, 20 and 30 wt.% Black Pearls 2000 in composite carbon black, cell temperature 80 C, anode humidifier temperature 90 C, cathode humidifier temperature 85 C, pressure of 0.2 MPa.
7 X.L. Wang et al. / Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) content of 10 wt.% is obtained with the maximum power density of 0.91 W cm 2. MPL with 5 wt.% Black Pearls 2000 in composite carbon black shows inferior performance to that of 10 wt.% Black Pearls 2000 content. But with the increasing content of Black Pearls 2000 up to 20 wt.% or 30 wt.%, the electrode performance is decreased because MPL with more Black Pearls 2000 is intended to be more hydrophilic and easier to be flooding. 4. Conclusions Effects of carbon powders in MPL on the performance of H 2 /air PEM fuel cell are studied and characterized extensively. GDL with Black Pearls 2000 shows the lowest gas permeability and highest hydrophilic porosity of 20.32%, which leads to the serious mass polarization losses. On the contrary, GDL using Acetylene Black exhibits the highest permeability and lowest hydrophilic porosity of 10.70%, which is suitable to gas transport but not sufficient for the removal of liquid water. To form an effective bi-functional pore structure, composite carbon black consisting of Acetylene Black and Black Pearls 2000 carbon is used to fabricate MPL. An enhanced cell performance with peak power density of 0.91 W cm 2 is obtained by the MPL with 10 wt.% Black Pearls 2000 in composite carbon black. Acknowledgement This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No ). References [1] Z.G. Qi, A. Kaufman, J. Power Sources 109 (2002) 38. [2] L.R. Jordan, A.K. Shukla, T. Behrsing, N.R. Avery, B.C. Muddle, M. Forsyth, J. Power Sources 86 (2000) 250. [3] L.R. Jordan, A.K. Shukla, T. Behrsing, N.R. Avery, B.C. Muddle, M. Forsyth, J. Appl. Electrochem. 30 (2000) 641. [4] J.M. Song, S.Y. Cha, W.M. Lee, J. Power Sources 94 (2001) 78. [5] E. Antolini, R.R. Passos, E.A. Ticianelli, J. Appl. Electrochem. 32 (2002) 383. [6] L. Giorgi, E. Antolini, A. Pozio, E. Passalacqua, Electrochim. Acta 43 (1998) [7] J. Moreira, A.L. Ocampo, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 28 (2003) 625. [8] E. Passalacqua, G. squadrito, F. Lufrano, A. Patti, L. Giorgi, J. Appl. Electrochem. 31 (2001) 449. [9] E. Antolini, R.R. Passos, E.A. Ticianelli, J. Power Sources 109 (2002) 477. [10] M. Maja, C. Orecchia, M. Strano, P. Tosco, M. Vanni, Electrochim. Acta 46 (2000) 423. [11] M. Neergat, A.K. Shukla, J. Power Sources 104 (2002) 289. [12] M. Mathias, J. Roth, J. Fleming, W. Lehnert, Handbook of Fuel Cells: Fundamentals, Technology and Applications, 6th ed., vol. 3, Wiley, England, 2003 [Chapter 46]. [13] M.V. Williams, E. Begg, L. Bonville, H.R. Kunz, J.M. Fenton, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151 (2004) A1173. [14] J.R. Yu, Y. Yoshiskawa, T. Matsuura, M.N. Islam, M. Hori, Electrochem. Solid-state Lett. 8 (2005) A152. [15] X. Wang, I.M. Hsing, P.L. Yue, J. Power Sources 96 (2001) 282. [16] V.A. Paganin, C.L.F. Oliveira, E.A. Ticianelli, T.E. Springer, E.R. Gonzalez, Electrochim. Acta 43 (1998) [17] M. Ciureanu, R. Roderge, J. Phys. Chem. B 105 (2001) [18] Z. Xie, S. Holdcroft, J. Electroanal. Chem. 568 (2004) 247. [19] M.V. Williams, H.R. Kunz, J.M. Fenton, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151 (2004) A1617.
A bi-functional micro-porous layer with composite carbon black for PEM fuel cells
 Journal of Power Sources 162 (2006) 474 479 Short communication A bi-functional micro-porous layer with composite carbon black for PEM fuel cells Xiaoli Wang a,b, Huamin Zhang a,, Jianlu Zhang c, Haifeng
Journal of Power Sources 162 (2006) 474 479 Short communication A bi-functional micro-porous layer with composite carbon black for PEM fuel cells Xiaoli Wang a,b, Huamin Zhang a,, Jianlu Zhang c, Haifeng
Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells
 Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Cross Section of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
 PEMFC Electrodes 1 Cross Section of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Anode Cathode 2 Typical PEMFC Electrodes: - Anode Hydrogen Oxidation - Pt Ru / C - Cathode Oxygen reduction - Pt / C Pt is alloyed
PEMFC Electrodes 1 Cross Section of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Anode Cathode 2 Typical PEMFC Electrodes: - Anode Hydrogen Oxidation - Pt Ru / C - Cathode Oxygen reduction - Pt / C Pt is alloyed
Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications. Pfaffenwaldring 6, Stuttgart, Germany
 Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications S. Altmann a,b, T. Kaz b, K. A. Friedrich a,b a Institute of Thermodynamics and Thermal Engineering, University Stuttgart,
Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications S. Altmann a,b, T. Kaz b, K. A. Friedrich a,b a Institute of Thermodynamics and Thermal Engineering, University Stuttgart,
General Energy PEM Membrane Tests
 General Energy PEM Membrane Tests Date 11/03/2016 Author Annette Mosdale, R&D PaxiTech Client Ms. Sophia Hu General Energy Room 404, 321 Talent Building, No. 1009 East Tianyuan Road Nanjing 210000 PR China
General Energy PEM Membrane Tests Date 11/03/2016 Author Annette Mosdale, R&D PaxiTech Client Ms. Sophia Hu General Energy Room 404, 321 Talent Building, No. 1009 East Tianyuan Road Nanjing 210000 PR China
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 196 (2011) 3172 3177 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Study of sulfur dioxide crossover in
Journal of Power Sources 196 (2011) 3172 3177 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Study of sulfur dioxide crossover in
F-Doped Carbon Blacks: Highly Efficient Metal-free Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
 Supporting Information F-Doped Carbon Blacks: Highly Efficient Metal-free Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Xiujuan Sun, 1, 2, 3 Yuwei Zhang, 1, 2 Ping Song, 1, 2 Jing Pan, 4 Lin Zhuang, 4
Supporting Information F-Doped Carbon Blacks: Highly Efficient Metal-free Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Xiujuan Sun, 1, 2, 3 Yuwei Zhang, 1, 2 Ping Song, 1, 2 Jing Pan, 4 Lin Zhuang, 4
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A honeycomb-like porous carbon derived from pomelo peel for use in high-performance
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A honeycomb-like porous carbon derived from pomelo peel for use in high-performance
Polyoxometalate Coupled Graphene Oxide-Nafion Composite. Membrane for Fuel Cell Operating at Low Relative Humidity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Polyoxometalate Coupled Graphene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Polyoxometalate Coupled Graphene
An analytical solution for transport of oxygen in cathode gas diffusion layer of PEMFC
 Journal of Power Sources 160 (006) 50 56 An analytical solution for transport of oxygen in cathode gas diffusion layer of PEMFC C.R. Tsai a, Falin Chen a, A.C. Ruo a, Min-Hsing Chang b,, Hsin-Sen Chu c,
Journal of Power Sources 160 (006) 50 56 An analytical solution for transport of oxygen in cathode gas diffusion layer of PEMFC C.R. Tsai a, Falin Chen a, A.C. Ruo a, Min-Hsing Chang b,, Hsin-Sen Chu c,
Analysis of the Catalyst Layer of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells
 33 Research Report Analysis of the Catalyst Layer of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Takahisa Suzuki Hajime Murata Tatsuya Hatanaka Yu Morimoto Comprehensive techniques for diagnosing the catalyst layer
33 Research Report Analysis of the Catalyst Layer of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Takahisa Suzuki Hajime Murata Tatsuya Hatanaka Yu Morimoto Comprehensive techniques for diagnosing the catalyst layer
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 191 (2009) 304 311 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Effects of anode microporous layers made
Journal of Power Sources 191 (2009) 304 311 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Effects of anode microporous layers made
Conservation, Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources Republic Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 7 (2012) 525-533 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effects of the Addition of Flourinated Polymers and Carbon Nanotubes in Microporous Layer
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 7 (2012) 525-533 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effects of the Addition of Flourinated Polymers and Carbon Nanotubes in Microporous Layer
Modeling of Liquid Water Distribution at Cathode Gas Flow Channels in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell - PEMFC
 Modeling of Liquid Water Distribution at Cathode Gas Flow Channels in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell - PEMFC Sandro Skoda 1*, Eric Robalinho 2, André L. R. Paulino 1, Edgar F. Cunha 1, Marcelo Linardi
Modeling of Liquid Water Distribution at Cathode Gas Flow Channels in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell - PEMFC Sandro Skoda 1*, Eric Robalinho 2, André L. R. Paulino 1, Edgar F. Cunha 1, Marcelo Linardi
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells
 January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells Fuel Cells Instructor James M. Fenton, Professor, Chemical Engineering University of Connecticut Teaching Assistants: 1.
January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells Fuel Cells Instructor James M. Fenton, Professor, Chemical Engineering University of Connecticut Teaching Assistants: 1.
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Lakshminarayanan V 1, Karthikeyan P 2, D. S. Kiran Kumar 1 and SMK Dhilip Kumar 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, KGiSL Institute
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Lakshminarayanan V 1, Karthikeyan P 2, D. S. Kiran Kumar 1 and SMK Dhilip Kumar 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, KGiSL Institute
The impact of anode design on fuel crossover of direct ethanol fuel cell
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 1, February 2016, pp. 273 278. c Indian Academy of Sciences. The impact of anode design on fuel crossover of direct ethanol fuel cell SETHU SUNDAR PETHAIAH 1,, JAYAKUMAR
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 1, February 2016, pp. 273 278. c Indian Academy of Sciences. The impact of anode design on fuel crossover of direct ethanol fuel cell SETHU SUNDAR PETHAIAH 1,, JAYAKUMAR
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 194 (2009) 847 853 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Study of the cell reversal process of large
Journal of Power Sources 194 (2009) 847 853 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Study of the cell reversal process of large
Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA, 16802
 Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells using Fluent Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park,
Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells using Fluent Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park,
RESEARCH ON BENZENE VAPOR DETECTION USING POROUS SILICON
 Section Micro and Nano Technologies RESEARCH ON BENZENE VAPOR DETECTION USING POROUS SILICON Assoc. Prof. Ersin Kayahan 1,2,3 1 Kocaeli University, Electro-optic and Sys. Eng. Umuttepe, 41380, Kocaeli-Turkey
Section Micro and Nano Technologies RESEARCH ON BENZENE VAPOR DETECTION USING POROUS SILICON Assoc. Prof. Ersin Kayahan 1,2,3 1 Kocaeli University, Electro-optic and Sys. Eng. Umuttepe, 41380, Kocaeli-Turkey
Two-phase transport and the role of micro-porous layer in polymer electrolyte fuel cells
 Electrochimica Acta 49 (2004) 4359 4369 Two-phase transport and the role of micro-porous layer in polymer electrolyte fuel cells Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering,
Electrochimica Acta 49 (2004) 4359 4369 Two-phase transport and the role of micro-porous layer in polymer electrolyte fuel cells Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering,
Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts
 Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts Raja Swaidan The Cooper Union Advisor: Dr. Branko N. Popov Electrochemical Engineering 26 July 2007 Overview of Research Studied
Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts Raja Swaidan The Cooper Union Advisor: Dr. Branko N. Popov Electrochemical Engineering 26 July 2007 Overview of Research Studied
Electrochemical Modification of Pt/C Catalyst by Silicomolybdic Acid
 ACTA PHYSICO-CHIMICA SINICA Volume 22, Issue 4, April 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2006, 22(4), 419 423. RESEARCH PAPER Electrochemical
ACTA PHYSICO-CHIMICA SINICA Volume 22, Issue 4, April 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2006, 22(4), 419 423. RESEARCH PAPER Electrochemical
Nanostructured Ti 0.7 Mo 0.3 O 2 Support Enhances Electron Transfer to Pt : High-Performance Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
 Nanostructured Ti 0.7 Mo 0.3 O 2 Support Enhances Electron Transfer to Pt : High-Performance Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Seonbaek Ha Professor : Carlo U. Segre 12. 06. 2013 Department of Chemical
Nanostructured Ti 0.7 Mo 0.3 O 2 Support Enhances Electron Transfer to Pt : High-Performance Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Seonbaek Ha Professor : Carlo U. Segre 12. 06. 2013 Department of Chemical
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performance for Oxygen Reduction via Active Interfaces of Layer-By-Layered Titanium Nitride / Titanium Carbonitride Structures Zhaoyu Jin, 1 Panpan Li,
Supporting Information Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performance for Oxygen Reduction via Active Interfaces of Layer-By-Layered Titanium Nitride / Titanium Carbonitride Structures Zhaoyu Jin, 1 Panpan Li,
V.A.11 Development of Ultra-Low Platinum Alloy Cathode Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
 V.A.11 Development of Ultra-Low Platinum Alloy Cathode Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Branko N. Popov University of South Carolina (USC) 301 Main Street Columbia, SC 29208 Phone:
V.A.11 Development of Ultra-Low Platinum Alloy Cathode Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Branko N. Popov University of South Carolina (USC) 301 Main Street Columbia, SC 29208 Phone:
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
produce water. Figure 1. Basic Diagram of a PEMFC. [1]
![produce water. Figure 1. Basic Diagram of a PEMFC. [1] produce water. Figure 1. Basic Diagram of a PEMFC. [1]](/thumbs/72/67618243.jpg) Effects of Graphene Oxide on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Henry Ho, Jesse Matsuda, Mailun Yang, Likun Wang, Miriam Rafailovich Materials Science and Chemical Engineering Department, Stony Brook,
Effects of Graphene Oxide on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Henry Ho, Jesse Matsuda, Mailun Yang, Likun Wang, Miriam Rafailovich Materials Science and Chemical Engineering Department, Stony Brook,
Optimization of platinum nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells using pulse electrochemical deposition
 Optimization of platinum nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells using pulse electrochemical deposition Ryan Lindeborg, AJ Swoboda Harvard College 16, Princeton College 15 Jonathan Burk,
Optimization of platinum nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells using pulse electrochemical deposition Ryan Lindeborg, AJ Swoboda Harvard College 16, Princeton College 15 Jonathan Burk,
Investigations on the Electrode Process of Concentrated V(IV)/V(V) Species in a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
 ACTA PHYSICO-CHIMICA SINICA Volume 22, Issue 4, April 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2006, 22(4), 403 408. RESEARCH PAPER Investigations
ACTA PHYSICO-CHIMICA SINICA Volume 22, Issue 4, April 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2006, 22(4), 403 408. RESEARCH PAPER Investigations
Title. Author(s)Tabe, Yutaka; Kikuta, Kazushige; Chikahisa, Takemi; CitationJournal of Power Sources, 193(2): Issue Date
 Title Basic evaluation of separator type specific phenomen of water condensation characteristics and current de Author(s)Tabe, Yutaka; Kikuta, Kazushige; Chikahisa, Takemi; CitationJournal of Power Sources,
Title Basic evaluation of separator type specific phenomen of water condensation characteristics and current de Author(s)Tabe, Yutaka; Kikuta, Kazushige; Chikahisa, Takemi; CitationJournal of Power Sources,
Current and Temperature Distributions in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
 Current and Temperature Distributions in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by Ibrahim Alaefour A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
Current and Temperature Distributions in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by Ibrahim Alaefour A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
A novel self-healing electrochromic film based on triphyelamine. cross-linked polymer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 217 Supporting Information A novel self-healing electrochromic film based on triphyelamine
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 217 Supporting Information A novel self-healing electrochromic film based on triphyelamine
Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage
 Electronic Supplementary Information Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage Bin Luo, a Yan Fang, a Bin Wang, a Jisheng Zhou, b Huaihe Song, b and Linjie
Electronic Supplementary Information Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage Bin Luo, a Yan Fang, a Bin Wang, a Jisheng Zhou, b Huaihe Song, b and Linjie
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 190 (2009) 223 229 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Effect of polymer binders in anode catalyst
Journal of Power Sources 190 (2009) 223 229 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Effect of polymer binders in anode catalyst
Facile Surface Functionalization of Carbon/Nafion for Enhancement of Methanol Electro-Oxidation. Hsin-Chu 30010, Taiwan
 10.1149/1.3484693 The Electrochemical Society Facile Surface Functionalization of Carbon/Nafion for Enhancement of Methanol Electro-Oxidation Yu-Chi Hsieh, a Li-Chung Chang, b Pu-Wei Wu, a, * Jyh-Fu Lee,
10.1149/1.3484693 The Electrochemical Society Facile Surface Functionalization of Carbon/Nafion for Enhancement of Methanol Electro-Oxidation Yu-Chi Hsieh, a Li-Chung Chang, b Pu-Wei Wu, a, * Jyh-Fu Lee,
Effect of Dispersion Solvent in Catalyst Ink on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 2551-2565 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Dispersion Solvent in Catalyst Ink on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 2551-2565 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Dispersion Solvent in Catalyst Ink on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
Joint Sino-German Project GZ 205 (101/5) New composite DMFC anode with PEDOT as mixed conductor and catalyst support. Report
 Joint Sino-German Project GZ 25 (11/5) New composite DMFC anode with PEDOT as mixed conductor and catalyst support Report 15. 4. 24 14. 4. 26 K. Jüttner, R. Dittmeyer, L. Li, J.-F. Drillet DECHEMA e.v.,
Joint Sino-German Project GZ 25 (11/5) New composite DMFC anode with PEDOT as mixed conductor and catalyst support Report 15. 4. 24 14. 4. 26 K. Jüttner, R. Dittmeyer, L. Li, J.-F. Drillet DECHEMA e.v.,
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING OF A HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL
 CONDENSED MATTER FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING OF A HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL V. IONESCU 1 1 Department of Physics and Electronics, Ovidius University, Constanta, 900527, Romania, E-mail: ionescu.vio@gmail.com
CONDENSED MATTER FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING OF A HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL V. IONESCU 1 1 Department of Physics and Electronics, Ovidius University, Constanta, 900527, Romania, E-mail: ionescu.vio@gmail.com
Supporting information:
 Supporting information: The Role of Anisotropic Structure and Its Aspect Ratio: High-Loading Carbon Nanospheres Supported Pt Nanowires and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Electrooxidation Feng-Zhan
Supporting information: The Role of Anisotropic Structure and Its Aspect Ratio: High-Loading Carbon Nanospheres Supported Pt Nanowires and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Electrooxidation Feng-Zhan
Effect of Hydrophobic Particles in a Gas Diffusion Electrode on Cell Performance in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 10 (2015) 9131-9141 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Hydrophobic Particles in a Gas Diffusion Electrode on Cell Performance in
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 10 (2015) 9131-9141 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Hydrophobic Particles in a Gas Diffusion Electrode on Cell Performance in
CFD Analysis of PEM Fuel Cell
 CFD Analysis of PEM Fuel Cell Group Seminar Munir Khan Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University Outline 1 Geometry 2 Mathematical Model 3 Results 4 Conclusions I 5 Pore Scale
CFD Analysis of PEM Fuel Cell Group Seminar Munir Khan Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University Outline 1 Geometry 2 Mathematical Model 3 Results 4 Conclusions I 5 Pore Scale
An Ideal Electrode Material, 3D Surface-Microporous Graphene for Supercapacitors with Ultrahigh Areal Capacitance
 Supporting Information An Ideal Electrode Material, 3D Surface-Microporous Graphene for Supercapacitors with Ultrahigh Areal Capacitance Liang Chang, 1 Dario J. Stacchiola 2 and Yun Hang Hu 1, * 1. Department
Supporting Information An Ideal Electrode Material, 3D Surface-Microporous Graphene for Supercapacitors with Ultrahigh Areal Capacitance Liang Chang, 1 Dario J. Stacchiola 2 and Yun Hang Hu 1, * 1. Department
Electrocatalytic activity of silver decorated cerium dioxide. toward oxygen reduction reaction and its application for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Electrocatalytic activity of silver decorated cerium dioxide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Electrocatalytic activity of silver decorated cerium dioxide
Highly Durable MEA for PEMFC Under High Temperature and Low Humidity Conditions. Eiji Endoh a. Yokohama, JAPAN
 10.1149/1.2356118, copyright The Electrochemical Society Highly Durable MEA for PEMFC Under High Temperature and Low Humidity Conditions Eiji Endoh a a Research Center, Asahi Glass Co., Ltd. 1150 Hazawacho,
10.1149/1.2356118, copyright The Electrochemical Society Highly Durable MEA for PEMFC Under High Temperature and Low Humidity Conditions Eiji Endoh a a Research Center, Asahi Glass Co., Ltd. 1150 Hazawacho,
Supporting Information Towards N-doped graphene via solvothermal synthesis
 Supporting Information Towards N-doped graphene via solvothermal synthesis Dehui Deng1, Xiulian Pan1*, Liang Yu1, Yi Cui1, Yeping Jiang2, Jing Qi3, Wei-Xue Li1, Qiang Fu1, Xucun Ma2, Qikun Xue2, Gongquan
Supporting Information Towards N-doped graphene via solvothermal synthesis Dehui Deng1, Xiulian Pan1*, Liang Yu1, Yi Cui1, Yeping Jiang2, Jing Qi3, Wei-Xue Li1, Qiang Fu1, Xucun Ma2, Qikun Xue2, Gongquan
Synthesis of Oxidized Graphene Anchored Porous. Manganese Sulfide Nanocrystal via the Nanoscale Kirkendall Effect. for supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Synthesis of Oxidized Graphene Anchored Porous Manganese Sulfide Nanocrystal
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Synthesis of Oxidized Graphene Anchored Porous Manganese Sulfide Nanocrystal
Performance Enhancement by Adaptation of Long Term Chronoamperometry in Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cell using Palladium Anode Catalyst
 Performance Enhancement by Adaptation of Long Term Chronoamperometry Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, Vol. 33, No. 8 2539 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2012.33.8.2539 Performance Enhancement by Adaptation
Performance Enhancement by Adaptation of Long Term Chronoamperometry Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, Vol. 33, No. 8 2539 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2012.33.8.2539 Performance Enhancement by Adaptation
Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous carbon derived from human hair as. highly efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Connected nanoparticle catalysts possessing a porous,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Connected nanoparticle catalysts possessing a porous,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Towards Neat Methanol Operation of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: A Novel Self-Assembled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Towards Neat Methanol Operation of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: A Novel Self-Assembled
Bulk graphdiyne powder applied for highly efficient lithium storage
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Bulk graphdiyne powder applied for highly efficient lithium storage Shengliang Zhang, ab Huibiao
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Bulk graphdiyne powder applied for highly efficient lithium storage Shengliang Zhang, ab Huibiao
Supporting Information
 Platinum-Gold Nanoparticles: A Highly Active Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Rechargeable Lithium-Air Batteries Yi-Chun Lu, Zhichuan Xu, Hubert A. Gasteiger, Shuo Chen, Kimberly Hamad- Schifferli and
Platinum-Gold Nanoparticles: A Highly Active Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Rechargeable Lithium-Air Batteries Yi-Chun Lu, Zhichuan Xu, Hubert A. Gasteiger, Shuo Chen, Kimberly Hamad- Schifferli and
for water oxidation through advancing the micro/meso-pore
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Nanoporous IrO 2 catalyst with enhanced activity and durability
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Nanoporous IrO 2 catalyst with enhanced activity and durability
High Salt Removal Capacity of Metal-Organic Gel Derived. Porous Carbon for Capacitive Deionization
 Supporting Information High Salt Removal Capacity of Metal-Organic Gel Derived Porous Carbon for Capacitive Deionization Zhuo Wang, Tingting Yan, Guorong Chen, Liyi Shi and Dengsong Zhang* Research Center
Supporting Information High Salt Removal Capacity of Metal-Organic Gel Derived Porous Carbon for Capacitive Deionization Zhuo Wang, Tingting Yan, Guorong Chen, Liyi Shi and Dengsong Zhang* Research Center
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany Hierarchical Nanosheet-Based MoS 2 Nanotubes Fabricated by an Anion-Exchange Reaction of MoO 3 Amine Hybrid Nanowires** Sifei Zhuo, You Xu,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany Hierarchical Nanosheet-Based MoS 2 Nanotubes Fabricated by an Anion-Exchange Reaction of MoO 3 Amine Hybrid Nanowires** Sifei Zhuo, You Xu,
Cyclic Voltametric Studies on the Interaction of Adrenaline With Formic Acid and Acetic Acid
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 6662-6669 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Cyclic Voltametric Studies on the Interaction of Adrenaline With Formic Acid and Acetic
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 6662-6669 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Cyclic Voltametric Studies on the Interaction of Adrenaline With Formic Acid and Acetic
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells
 Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
Optimization of the Microporous Layer for a Polybenzimidazole-based High Temperature PEMFC. Effect of carbon content
 Optimization of the Microporous Layer for a Polybenzimidazole-based High Temperature PEMFC. Effect of carbon content Justo Lobato, Pablo Cañizares, Manuel A Rodrigo, Diego Ubeda, Francisco J Pinar, Jose
Optimization of the Microporous Layer for a Polybenzimidazole-based High Temperature PEMFC. Effect of carbon content Justo Lobato, Pablo Cañizares, Manuel A Rodrigo, Diego Ubeda, Francisco J Pinar, Jose
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 184 (2008) 212 219 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Analysis of flooding as a stochastic process
Journal of Power Sources 184 (2008) 212 219 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Analysis of flooding as a stochastic process
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 008, 8, 1475-1487 Full Research Paper sensors ISSN 144-80 008 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Three-Dimensional Transport Modeling for Proton Exchange Membrane(PEM) Fuel Cell with Micro Parallel Flow
Sensors 008, 8, 1475-1487 Full Research Paper sensors ISSN 144-80 008 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Three-Dimensional Transport Modeling for Proton Exchange Membrane(PEM) Fuel Cell with Micro Parallel Flow
Supporting Information. Phenolic/resin assisted MOFs derived hierarchical Co/N-doping carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Modeling the Behaviour of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane within a Fuel Cell Using COMSOL
 Modeling the Behaviour of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane within a Fuel Cell Using COMSOL S. Beharry 1 1 University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago Abstract: In recent years, scientists
Modeling the Behaviour of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane within a Fuel Cell Using COMSOL S. Beharry 1 1 University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago Abstract: In recent years, scientists
Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid
 Electronic Supplementary Information Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Wen Lu, * Adam Goering, Liangti Qu, and Liming Dai * 1. Synthesis of
Electronic Supplementary Information Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Wen Lu, * Adam Goering, Liangti Qu, and Liming Dai * 1. Synthesis of
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary material (ESI) for Nanoscale Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials by Using Metal-Cyanide Coordination Polymers and Their Lithium Storage
Electronic Supplementary material (ESI) for Nanoscale Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials by Using Metal-Cyanide Coordination Polymers and Their Lithium Storage
3-D Modelling of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with Anisotropic Material Properties. Abstract
 3-D Modelling of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with Anisotropic Material Properties P.C. Sui 1, Sanjiv Kumar 2, Ned Djilali 1 1 Institute for Integrated Energy Systems,University of Victoria, Victoria,
3-D Modelling of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with Anisotropic Material Properties P.C. Sui 1, Sanjiv Kumar 2, Ned Djilali 1 1 Institute for Integrated Energy Systems,University of Victoria, Victoria,
Optimizing the Performance of a Single PEM Fuel Cell
 Zhuqian Zhang School of Mechanical Electronic and Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, P.R.C. Xia Wang 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Oakland University, Rochester, MI e-mail:
Zhuqian Zhang School of Mechanical Electronic and Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, P.R.C. Xia Wang 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Oakland University, Rochester, MI e-mail:
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 187 (2009) 32 38 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Potential dependence of sulfur dioxide poisoning
Journal of Power Sources 187 (2009) 32 38 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour Potential dependence of sulfur dioxide poisoning
Facile Synthesis of Hybrid Graphene and Carbon Nanotube as. Metal-Free Electrocatalyst with Active Dual Interfaces for
 Facile Synthesis of Hybrid Graphene and Carbon Nanotube as Metal-Free Electrocatalyst with Active Dual Interfaces for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction Jang-Soo Lee, a Kiyoung Jo, b Taemin Lee, a Taeyeong
Facile Synthesis of Hybrid Graphene and Carbon Nanotube as Metal-Free Electrocatalyst with Active Dual Interfaces for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction Jang-Soo Lee, a Kiyoung Jo, b Taemin Lee, a Taeyeong
High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by
 Supporting Information for: High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by Engineering Graphene Assemblies Min Zhou,, Xianglong Li, *, Bin Wang, Yunbo Zhang, Jing Ning, Zhichang Xiao, Xinghao Zhang,
Supporting Information for: High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by Engineering Graphene Assemblies Min Zhou,, Xianglong Li, *, Bin Wang, Yunbo Zhang, Jing Ning, Zhichang Xiao, Xinghao Zhang,
Nanomaterials and Chemistry Key Laboratory, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, (P. R. China).
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Synergistically enhanced activity of graphene quantum dot/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites as metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Synergistically enhanced activity of graphene quantum dot/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites as metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of 1T-MoSe 2 ultrathin
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of 1T-MoSe 2 ultrathin
Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction activity of nitrogen-doped carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Macroporous bubble graphene film via template-directed ordered-assembly for high rate supercapacitors
 Electronic Supporting Information for Macroporous bubble graphene film via template-directed ordered-assembly for high rate supercapacitors Cheng-Meng Chen* a, Qiang Zhang b, Chun-Hsien Huang c, Xiao-Chen
Electronic Supporting Information for Macroporous bubble graphene film via template-directed ordered-assembly for high rate supercapacitors Cheng-Meng Chen* a, Qiang Zhang b, Chun-Hsien Huang c, Xiao-Chen
Self-Supported Three-Dimensional Mesoporous Semimetallic WP 2. Nanowire Arrays on Carbon Cloth as a Flexible Cathode for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic supplementary information Self-Supported Three-Dimensional Mesoporous Semimetallic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic supplementary information Self-Supported Three-Dimensional Mesoporous Semimetallic
Effect of Electro-Oxidation Current Density on Performance of Graphite Felt Electrode for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 8 (2013) 4700-4711 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Electro-Oxidation Current Density on Performance of Graphite Felt Electrode
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 8 (2013) 4700-4711 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Effect of Electro-Oxidation Current Density on Performance of Graphite Felt Electrode
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bamboo-Like Carbon Nanotube/Fe 3 C Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Highly Efficient Catalysis for Oxygen Reduction Wenxiu Yang a,b, Xiangjian Liu a,b, Xiaoyu Yue a,b, Jianbo Jia,
Supporting Information Bamboo-Like Carbon Nanotube/Fe 3 C Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Highly Efficient Catalysis for Oxygen Reduction Wenxiu Yang a,b, Xiangjian Liu a,b, Xiaoyu Yue a,b, Jianbo Jia,
DISCLAIMER. Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. Images are produced from the best available original document.
 ; i i : L4 0 t DSCLAMER Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. mages are produced from the best available original document. EVALUATON OF THE HUMDFCATON REQTJREMENTS OF
; i i : L4 0 t DSCLAMER Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. mages are produced from the best available original document. EVALUATON OF THE HUMDFCATON REQTJREMENTS OF
Nitrogen-doped Activated Carbon for High Energy Hybridtype Supercapacitor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Nitrogen-doped Activated Carbon for High Energy Hybridtype
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Nitrogen-doped Activated Carbon for High Energy Hybridtype
Huan Pang, Jiawei Deng, Shaomei Wang, Sujuan Li, Jing Chen and Jiangshan Zhang
 1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Facile synthesis of porous nickel manganite materials and their morphologies effect on electrochemical properties Huan Pang, Jiawei Deng, Shaomei Wang, Sujuan
1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Facile synthesis of porous nickel manganite materials and their morphologies effect on electrochemical properties Huan Pang, Jiawei Deng, Shaomei Wang, Sujuan
Macroporous bubble graphene film via template-directed ordered-assembly for high rate supercapacitors
 Electronic Supporting Information for Macroporous bubble graphene film via template-directed ordered-assembly for high rate supercapacitors Cheng-Meng Chen* a, Qiang Zhang b, Chun-Hsien Huang c, Xiao-Chen
Electronic Supporting Information for Macroporous bubble graphene film via template-directed ordered-assembly for high rate supercapacitors Cheng-Meng Chen* a, Qiang Zhang b, Chun-Hsien Huang c, Xiao-Chen
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Facet-Selective Deposition of FeO x on α-moo 3 Nanobelts for Lithium Storage Yao Yao, 1 Nuo Xu, 2 Doudou Guan, 1 Jiantao Li, 1 Zechao Zhuang, 1 Liang Zhou,*,1 Changwei Shi 1, Xue
Supporting Information Facet-Selective Deposition of FeO x on α-moo 3 Nanobelts for Lithium Storage Yao Yao, 1 Nuo Xu, 2 Doudou Guan, 1 Jiantao Li, 1 Zechao Zhuang, 1 Liang Zhou,*,1 Changwei Shi 1, Xue
Performance Analysis of a Two phase Non-isothermal PEM Fuel Cell
 Performance Analysis of a Two phase Non-isothermal PEM Fuel Cell A. H. Sadoughi 1 and A. Asnaghi 2 and M. J. Kermani 3 1, 2 Ms Student of Mechanical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology Tehran,
Performance Analysis of a Two phase Non-isothermal PEM Fuel Cell A. H. Sadoughi 1 and A. Asnaghi 2 and M. J. Kermani 3 1, 2 Ms Student of Mechanical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology Tehran,
Supplementary Information. For. A Universal Method for Preparing Functional ITO Electrodes with Ultrahigh Stability
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information For A Universal Method for Preparing Functional ITO Electrodes with Ultrahigh
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information For A Universal Method for Preparing Functional ITO Electrodes with Ultrahigh
Determination of Electron Transfer Number for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: from Theory to Experiment
 Supporting Information Determination of Electron Transfer Number for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: from Theory to Experiment Ruifeng Zhou 1, 2, Yao Zheng 1, Mietek Jaroniec 3 and Shi-Zhang Qiao 1, * 1 School
Supporting Information Determination of Electron Transfer Number for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: from Theory to Experiment Ruifeng Zhou 1, 2, Yao Zheng 1, Mietek Jaroniec 3 and Shi-Zhang Qiao 1, * 1 School
Easy synthesis of hollow core, bimodal mesoporous shell carbon nanospheres and their. application in supercapacitor
 Electronic Electronic Supplementary Information Easy synthesis of hollow core, bimodal mesoporous shell carbon nanospheres and their application in supercapacitor Bo You, Jun Yang,* Yingqiang Sun and Qingde
Electronic Electronic Supplementary Information Easy synthesis of hollow core, bimodal mesoporous shell carbon nanospheres and their application in supercapacitor Bo You, Jun Yang,* Yingqiang Sun and Qingde
Performance Simulation of Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 50-334 Volume 8, Number 1 (018), pp. 05-1 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Performance Simulation of Passive Direct
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 50-334 Volume 8, Number 1 (018), pp. 05-1 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Performance Simulation of Passive Direct
Fabrication Method for Laboratory-Scale High Performance Membrane Electrode Assemblies for Fuel Cells
 Fabrication Method for Laboratory-Scale High Performance Membrane Electrode Assemblies for Fuel Cells Megan B. Sassin,,a* Yannick Garsany,,b Benjamin D. Gould, a and Karen E. Swider-Lyons a a U.S Naval
Fabrication Method for Laboratory-Scale High Performance Membrane Electrode Assemblies for Fuel Cells Megan B. Sassin,,a* Yannick Garsany,,b Benjamin D. Gould, a and Karen E. Swider-Lyons a a U.S Naval
Science and Technology, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian , P. R. China b
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Fabrication of Superior-Performance SnO 2 @C Composites for Lithium-Ion Anodes Using Tubular Mesoporous Carbons with Thin Carbon Wall and High Pore Volume Fei Han,
Electronic Supplementary Information for Fabrication of Superior-Performance SnO 2 @C Composites for Lithium-Ion Anodes Using Tubular Mesoporous Carbons with Thin Carbon Wall and High Pore Volume Fei Han,
Supporting Information for. Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen. reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with.
 Supporting Information for Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with silica Sakae Takenaka 1 *, Naoto Susuki 1, Hiroaki Miyamoto 1, Eishi
Supporting Information for Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with silica Sakae Takenaka 1 *, Naoto Susuki 1, Hiroaki Miyamoto 1, Eishi
Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example)
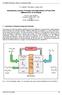 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
ARC-ASSISTED CO-CONVERSION OF COAL-BASED CARBON AND ACETYLENE
 ARC-ASSISTED CO-CONVERSION OF COAL-BASED CARBON AND ACETYLENE Jieshan Qiu*, Yongfeng Li, Yunpeng Wang Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School of Chemical Engineering,
ARC-ASSISTED CO-CONVERSION OF COAL-BASED CARBON AND ACETYLENE Jieshan Qiu*, Yongfeng Li, Yunpeng Wang Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School of Chemical Engineering,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Adding refractory 5d transition metal W into PtCo
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Adding refractory 5d transition metal W into PtCo
Carbon Quantum Dots/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide. Composite as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water
 Supplementary Information Carbon Quantum Dots/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Composite as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation Di Tang, Juan Liu, Xuanyu Wu, Ruihua Liu, Xiao Han, Yuzhi Han,
Supplementary Information Carbon Quantum Dots/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Composite as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation Di Tang, Juan Liu, Xuanyu Wu, Ruihua Liu, Xiao Han, Yuzhi Han,
Computational Analysis of Heat Transfer in Air-cooled Fuel Cells
 Proceedings of ASME 2011, 5th International Conference on Energy Sustainability & 9th Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology Conference, ESFuelCell2011 August 7-10, 2011, Washington, DC, USA ESFuelCell2011-54794
Proceedings of ASME 2011, 5th International Conference on Energy Sustainability & 9th Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology Conference, ESFuelCell2011 August 7-10, 2011, Washington, DC, USA ESFuelCell2011-54794
Journal of Power Sources
 Journal of Power Sources 195 (2010) 5875 5881 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour H 2 /air alkaline membrane fuel cell
Journal of Power Sources 195 (2010) 5875 5881 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Power Sources journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jpowsour H 2 /air alkaline membrane fuel cell
Simultaneous oxygen-reduction and methanol-oxidation reactions at the cathode of a DMFC: A model-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study
 Journal of Power Sources 167 (2007) 265 271 Simultaneous oxygen-reduction and methanol-oxidation reactions at the cathode of a DMFC: A model-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study C.Y. Du,
Journal of Power Sources 167 (2007) 265 271 Simultaneous oxygen-reduction and methanol-oxidation reactions at the cathode of a DMFC: A model-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study C.Y. Du,
Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: HYD Lecture 08. Composite Membranes
 Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells HYD7007 01 Lecture 08. Composite Membranes Dept. of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Spring, 2011 Prof. David
Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells HYD7007 01 Lecture 08. Composite Membranes Dept. of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Spring, 2011 Prof. David
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Ultrasmall Sn Nanodots Embedded inside N-Doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Ultrasmall Sn Nanodots Embedded inside N-Doped
