1.2. How our bodies defend themselves against infectious diseases
|
|
|
- Jeffery Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIGHER LEVEL SCIENCE BIOLOGY SYLLABUS 1. Keeping Healthy A combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise is needed to help keep the body healthy Diet and exercise a) A healthy diet contains the right balance of the different foods you need and the right amount of energy. b) The amount of energy expended by the body. c) Metabolic rate may be affected by inherited factors. Inherited factors also affect our health; for example cholesterol level How our bodies defend themselves against infectious diseases a) Microorganisms that cause infectious disease are called pathogens. b) Bacteria and viruses may reproduce rapidly inside the body and may produce poisons (toxins) that make us feel ill. Viruses damage the cells in which they reproduce. c) The body has different ways of protecting itself against pathogens. d) White blood cells help to defend against pathogens by: Ingesting pathogens; producing antibodies, which destroy particular bacteria or viruses; producing antitoxins, which counteract the toxins released by the pathogens. e) Some medicines, including painkillers, help to relieve the symptoms of infectious disease, but do not kill the pathogens. f) Antibiotics, including penicillin, are medicines that help to cure bacterial disease by killing infectious bacteria inside the body. g) Antibiotics kill individual pathogens of the non-resistant strain. Individual resistant pathogens survive and reproduce, so the population of the resistant strain increases. h) People can be immunised against a disease by introducing small quantities of dead or in active forms of the pathogen into the body. Vaccination 2. Nerves and Hormones The nervous system and hormones enable us to respond to external changes The nervous system: Receptors, reflex action, impulse across synapse 2.2. Control in the human body a) Internal conditions that are controlled include: The water content of the body The ion content of the body Temperature Blood sugar levels. b) Many processes within the body are coordinated by chemical substances called hormones. c) Several hormones are involves in the menstrual cycle of a woman: LH FSH Oestrogen d) The uses of hormones in controlling fertility include: Giving oral contraceptives that contain hormones to inhibit FSH production so that no eggs mature Giving FSH and LH in a fertility drug to a woman whose own level of FSH is too low to stimulate eggs to mature, for example in In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) treatment.
2 2.3. Control in plants a) Plants are sensitive to light, moisture and gravity. b) Plants produce hormones to coordinate and control growth. Auxin controls phototropism and gravitropism (geotropism). c) Plant growth hormones are used in agriculture and horticulture as weed killers and as rooting hormones. 3. The use and abuse of drugs 3.1. Drugs a) When new medical drugs are devised, they have to be extensively tested and trialled before being used. In the laboratory, using cells, tissues and live animals In clinical trials involving healthy volunteers and patients. b) Use of statins in lowering the risk of heart circulatory diseases. c) Thalidomide is a drug that was developed as a sleeping pill. It was also found to be effective in relieving morning sickness in pregnant women. d) Misuse of alcohol and nicotine. e) Drugs that an athlete can use to enhance performance. 4. Interdependence and Adaptation Organisms are well adapted to survive in their normal environment. Population size depends on a variety of factors including competition, predation, disease and human influences. Changes in the environment may affect the distribution and behaviour of organisms Adaptations a) Organisms, including microorganisms have features (Adaptations) that enable them to survive in the conditions in which they normally live. b) Some organisms live in environments that are very extreme. Extremophiles may be tolerant to high levels of salt, high temperatures or high pressures. (c) Animals and plants may be adapted for survival in the conditions where they normally live, e.g. deserts, the Arctic Environmental change a) Changes in the environment affect the distribution of living organisms. b) Living organisms can be used as indicators of pollution: Lichens Invertebrate Organisms and their environment Living organisms form communities and we need to understand the relationships within and between these communities. These relationships are affected by external influences. a) Physical factors that may affect organisms are: Temperature Availability of nutrients Amount of light Availability of water Availability of oxygen and carbon dioxide. b) Quantitative data on the distribution of organisms can be obtained by: Random sampling with quadrats Sampling along a transect.
3 4.4. Energy and biomass in food chains 4.5. Waste materials from plants and animals a) Decay processes b) The carbon cycle 5. Genetic variation, its control and Evolution 5.1. Genetic variation and its control a) Why organisms are different b) Reproduction: Sexual, Asexual c) Modern cloning techniques: Tissue culture, Embryo transplants, adult cell cloning. d) Genetic engineering. 5.2 Evolution Darwin s theory of evolution by natural selection Other theories, including that of Lamarck. 5.3 Speciation Changes in the environment of plants and animals may cause them to die out. The fossil record shows that new organisms arise, flourish, and after time become extinct. The record also shows changes that lead to the formation of new species Old and new species a) Evidence for early forms of life comes from fossils. b) Extinction may be caused by: Changes to the environment over geological time New predators New diseases New, more successful competitors A single catastrophic even, eg massive volcanic eruptions or collisions with asteroids Through the cyclic nature of speciation. c) New species arise as a result of: Isolation Genetic variation Natural selection Speciation 6. Cells and simple cell transport All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. To get into or out of cells, dissolved substances have to cross the cell membranes. 6.1 Cells and cell structure a) Human and animal cells: A nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Mitochondria Ribosomes b) Plant and algal cells also have a cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell. Plant cells often have: Chloroplasts A permanent vacuole.
4 c) Bacterial cell consists of cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall; the genes are not in a distinct nucleus. d) Yeast is a single-celled organism. Yeast cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function. 6.2 Diffusion Dissolved substances can move into and out of cells by diffusion. 6.3 Tissues, organs and organ systems: a) A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function. Examples of tissues include: Muscular tissue, which can contract to bring about movement Glandular tissue, which can produce substances such as enzymes and hormones Epithelial tissue, which covers some parts of the body. b) Organs are made of tissues. One organ may contain several tissues. The stomach is an organ that contains: Muscular tissue, to churn the contents Glandular tissue, to produce digestive juices Epithelial tissue, to cover the outside and the inside of the stomach. c) Organ systems are groups of organs that perform a particular function. d) Plant organs include stems, roots and leaves. Examples of plant tissues include: Epidermal tissues, which cover the plant Mesophyll, which carries out photosynthesis Xylem and phloem, which transport substances around the plant Photosynthesis Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions in which plants are grown can be changed to promote growth. a) Equation for photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen b) The rate of photosynthesis may be limited by: Shortage of light Low temperature Shortage of carbon dioxide. 7. Proteins their functions and uses Proteins have many functions, both inside and outside the cells of living organisms. Proteins, as enzymes, are now used widely in the home and in industry. 7.1 Proteins a) Protein molecules are made up of long chains of amino acids and form: Structural components of tissues such as muscles Hormones Antibodies Catalysts b) Enzymes: The shape of an enzyme is vital for the enzyme s function. High temperatures change the shape. Different enzymes work best at different ph values.
5 8. Cell division and inheritance Characteristics are passed on from one generation to the next in both plants and animals. 8.1 Interpret genetic diagrams, including family trees 8.2 Construct genetic diagrams of monohybrid crosses and predict the outcomes of monohybrid crosses and be able to use the terms homozygous, heterozygous, phenotype and genotype. 8.3 Cell division a) In body cells the chromosomes are normally found in pairs. Body cells divide by mitosis. b) The chromosomes contain the genetic information. c) When a body cell divides by mitosis: Copies of the genetic material are made. Then the cell divides once to form two genetically identical body cells. d) Meiosis: Cells in reproductive organs testes and ovaries in humans divide to form gametes. e) Cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow, called stem cells, can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells, eg nerve cells. 8.4 Genetic variation a) Sexual reproduction gives rise to variation b) In human females the sex chromosomes are the same (XX); in males the sex chromosomes are different (XY) c) Some characteristics are controlled by a single gene: Dominant allele, Recessive allele d) Chromosomes are made up of large molecules of DNA (Deoxyribo nucleic acid) which has a double helix structure. A gene is a small section of DNA. e) Each person (apart from identical twins) has unique DNA. This can be used to identify individuals in a process known as DNA fingerprinting. 8.5 Genetic disorders a) Some disorders are inherited. Polydactyly Cystic fibrosis 9. Gaseous exchange Aerobic and anaerobic respiration Respiration in cells can take place aerobically of anaerobically. The energy released is used in a variety of ways. The human body needs to react to the increased demand for energy during exercise. 9.1 Aerobic respiration: Oxygen + Glucose = Carbon dioxide + Water a) The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. b) During aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) chemical reactions occur that: Use glucose (a sugar) and oxygen Release energy. c) During exercise a number of changes take place: The heart rate increases
6 . The rate and depth of breathing increases. These changes increase the blood flow to the muscles and so increase the supply of sugar and oxygen and increase the rate of removal of carbon dioxide. d) Muscles store glucose as glycogen, which can then be converted back to glucose for use during exercise. 9.2 Anaerobic respiration a) During exercise, if insufficient oxygen is reaching the muscles they use anaerobic respiration to obtain energy. b) Anaerobic respiration is the incomplete breakdown of glucose and produces lactic acid. c) Oxygen debt 10. Transport systems in plants and animals 10.1 The blood system Heart structure and function The blood components Blood vessels: arteries, veins and capillaries 10.2 Transport systems in plants Flowering plants have separate transport systems: Xylem tissue transports water and mineral ions from the roots to the stem and leaves Phloem tissue carries dissolved sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant, including the growing regions and the storage organs. Factors affecting transpiration 11. Homeostasis Removal of waste and water control Waste products that have to be removed from the body Function of a healthy kidney Treatment by dialysis Disadvantages of dialysis Kidney transplants Temperature control Sugar control 12. Humans and their environment 12.1 Waste from human activity Water pollution Air pollution Indicators of air pollution Land pollution 12.2 Deforestation and the destruction of areas of peat Loss of biodiversity
7 Greenhouse gases Global warming 12.3 Biofuels Biogas 12.4 Food production Mycoprotein
What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of the cell wall. membrane?
 Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions. 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is -
 B2.1 Cells and Simple Cell Transport GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is - a) Animal cell b) Plant
B2.1 Cells and Simple Cell Transport GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is - a) Animal cell b) Plant
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE)
 Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Y9 3Y Combined BIOLOGY POS
 Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 4... 4... 4... 4... Animal and Plant Cells - Eukaryotes Structure Organelle function Bacterial cells - Prokaryotes Structure Organelle function Term (7w) 4... Cell
Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 4... 4... 4... 4... Animal and Plant Cells - Eukaryotes Structure Organelle function Bacterial cells - Prokaryotes Structure Organelle function Term (7w) 4... Cell
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY
 B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
AQA Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Biology Paper 2
 AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis is and why it is important stating specific examples from the human body 4.5.1 Homeostasis
AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis is and why it is important stating specific examples from the human body 4.5.1 Homeostasis
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Foundation Year Programme
 Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY SPECIFICATION Standard ATS sample material 2 3 Biology 1. Living organisms 1.1. Characteristics of living organisms a. List and define the main characteristics
Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY SPECIFICATION Standard ATS sample material 2 3 Biology 1. Living organisms 1.1. Characteristics of living organisms a. List and define the main characteristics
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 Keeping Healthy
 B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 Keeping Healthy Diet & Exercise What does metabolic rate mean? What is the proportion of fruit and vegetables that should be in a balanced diet? Weight Problems What health problems
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 Keeping Healthy Diet & Exercise What does metabolic rate mean? What is the proportion of fruit and vegetables that should be in a balanced diet? Weight Problems What health problems
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus. Q8 (Biology) (4.6)
 Q1 (4.6) What is variation? Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus Q3 (4.6) What are genes? Q4 (4.6) What sort of reproduction produces genetically
Q1 (4.6) What is variation? Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus Q3 (4.6) What are genes? Q4 (4.6) What sort of reproduction produces genetically
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Personalised Learning Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.1 Cell biology (Bio Paper 1) 4.1.1 Cell structure 4.1.2 Cell division Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.1 Cell biology (Bio Paper 1) 4.1.1 Cell structure 4.1.2 Cell division Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe
What do plants compete for? What do animals compete for? What is a gamete and what do they carry? What is a gene?
 How are these animals adapted to their surroundings: - a) Polar bear b) Camel c) Cactus What do plants compete for? What do animals compete for? What is a gamete and what do they carry? What is a gene?
How are these animals adapted to their surroundings: - a) Polar bear b) Camel c) Cactus What do plants compete for? What do animals compete for? What is a gamete and what do they carry? What is a gene?
AQA Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL
 Subject ASTINGS IG SCOOL YEAR 11 EXAMINATION GUIDE 2017-19 COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY- BIOLOGY Course code AQA GCSE BIOLOGY 8464 Website address Provisional examination dates http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/combined-science-trilogy-
Subject ASTINGS IG SCOOL YEAR 11 EXAMINATION GUIDE 2017-19 COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY- BIOLOGY Course code AQA GCSE BIOLOGY 8464 Website address Provisional examination dates http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/combined-science-trilogy-
Inheritance part 1 AnswerIT
 Inheritance part 1 AnswerIT 1. What is a gamete? A cell with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. 2. Name the male and female gametes in a) a human b) a daisy plant a) Male = sperm Female
Inheritance part 1 AnswerIT 1. What is a gamete? A cell with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. 2. Name the male and female gametes in a) a human b) a daisy plant a) Male = sperm Female
The topics in this unit are:
 The topics in this unit are: 1 Cells 2 Inside the cell 3 Mitosis 4 Meiosis 5 DNA and growth 6 mrna 7 Stem cells 8 Uses of stem cells 9 Therapeutic cloning 10 - Growth in plants 11 Meristems 12 Cuttings
The topics in this unit are: 1 Cells 2 Inside the cell 3 Mitosis 4 Meiosis 5 DNA and growth 6 mrna 7 Stem cells 8 Uses of stem cells 9 Therapeutic cloning 10 - Growth in plants 11 Meristems 12 Cuttings
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
How many lessons is it?
 Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
4) The diagram below represents the organization of genetic information within a cell nucleus.
 Name: 3987-1 - Page 1 1) Every single-celled organism is able to survive because it carries out A) sexual reproduction B) heterotrophic nutrition C) autotrophic nutrition D) metabolic activities 2) Which
Name: 3987-1 - Page 1 1) Every single-celled organism is able to survive because it carries out A) sexual reproduction B) heterotrophic nutrition C) autotrophic nutrition D) metabolic activities 2) Which
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks
 Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Science Unit Learning Summary
 Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions
 Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe features
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe features
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
Life Science FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES
 FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Record your answers to Part A and Part B 1 on this answer sheet. Part A. Part A Score
 Tear Here The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 20, 2007 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only ANSWER SHEET Female Student........................................
Tear Here The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION LIVING ENVIRONMENT Wednesday, June 20, 2007 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only ANSWER SHEET Female Student........................................
Activity Activity Title. Chapter Title Chapter Description Lesson Title Lesson Description Introduction to Living Things
 Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
 Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
Cell Biology. AQA Biology topic 1
 Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. (12 marks)
 Essays Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. 2. Compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 3. Describe the correct procedures
Essays Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. 2. Compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 3. Describe the correct procedures
Foundation Cell Biology
 Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Animal Cell Organelles. Plant Cell. Organelle. Cell Wall. Chloroplasts. Vacuole
 Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Paget High School. Preparing for A level Biology
 Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Unit 5: Living beings
 Unit 5: Living beings 1. Characteristics of living beings 2. Composition of living beings 3. The cell 4. The vital functions 5. Levels of organisation Think and answer? a. What living beings can you see
Unit 5: Living beings 1. Characteristics of living beings 2. Composition of living beings 3. The cell 4. The vital functions 5. Levels of organisation Think and answer? a. What living beings can you see
Biology Pacing Guide
 Unit Dates Glencoe Chapters 0 8/10 N/A Biology Intro 8/12 1 Cells 8/15 9/30 6.4 6.2 7.1 18.2 7.3 6.3 7.2 7.4 Topic GPS Classroom Procedures, Introduction to Biology SCSh 1-7 Macromolecules (6 days) Monomer/
Unit Dates Glencoe Chapters 0 8/10 N/A Biology Intro 8/12 1 Cells 8/15 9/30 6.4 6.2 7.1 18.2 7.3 6.3 7.2 7.4 Topic GPS Classroom Procedures, Introduction to Biology SCSh 1-7 Macromolecules (6 days) Monomer/
Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary 3 Biology Teaching Schedule ( )
 Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary Biology Teaching Schedule (009-010) Subject Teachers: KSit (Form coordinator), WChiang, SLee /10-day Cycle: Cycles 1 (1/9 11/9) Teaching Topics/Content Ch. 1 Introducing
Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary Biology Teaching Schedule (009-010) Subject Teachers: KSit (Form coordinator), WChiang, SLee /10-day Cycle: Cycles 1 (1/9 11/9) Teaching Topics/Content Ch. 1 Introducing
B I O. 1. B I O A N A L Y Z E T H E C E L L A S A L I V I N G S Y S T E M.
 Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Living Things. perform a specific job in the body. Skin and lining of organs. Blood, bones, cartilage, fat. Brain and nerves
 Living Things Structure & Function BIG IDEA : All living things are made of cells A. Unicellular Organisms 1. Made of only one cell. 2. Examples paramecia, amoebas, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms
Living Things Structure & Function BIG IDEA : All living things are made of cells A. Unicellular Organisms 1. Made of only one cell. 2. Examples paramecia, amoebas, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms
Biology EOC Review Study Questions
 Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
04/05/2017. Cell Biology. AQA 2016 Syllabus
 Cell Biology AQA 2016 Syllabus 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Cell Biology AQA 2016 Syllabus 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
How to use this book. How the book is organised. Answering questions. Learning and using the terminology. Developing skills
 How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
6 th Grade Life Science Strand 3: Characteristics and Interactions of Living Organisms
 Middle School Life Science Standards There are 15 standards that encompass the proposed middle school life science standards. The new standards are listed 4 times to match the four times life science is
Middle School Life Science Standards There are 15 standards that encompass the proposed middle school life science standards. The new standards are listed 4 times to match the four times life science is
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
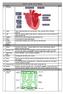 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
1.Study the statement above. Which cell organelle manages the process by which proteins are sorted and packaged to be sent where they are needed?
 Cell organelles carry out specific metabolic processes. 1.Study the statement above. Which cell organelle manages the process by which proteins are sorted and packaged to be sent where they are needed?
Cell organelles carry out specific metabolic processes. 1.Study the statement above. Which cell organelle manages the process by which proteins are sorted and packaged to be sent where they are needed?
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Application Questions Combined Science
 Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Application Questions Combined Science AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Application Questions Combined Science AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
What do scientists call Changes in the environment that we sense, eg light and sound. What do we call cells that detect stimuli?
 What do scientists call Changes in the environment that we sense, eg light and sound What do we call cells that detect stimuli? Give examples What is meant by the term Effector. State two examples What
What do scientists call Changes in the environment that we sense, eg light and sound What do we call cells that detect stimuli? Give examples What is meant by the term Effector. State two examples What
What is the structure of DNA?
 NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
Edexcel Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Key Concepts in biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Topic 1. Key Concepts in biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Curriculum Overview 7 th Grade Science
 1 st Nine Weeks Unit 1: Lab Safety, Measurement, and Scientific Investigation 7.1AB, 7.2AB, 7.3A Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Control Demonstrate safe practices during laboratory
1 st Nine Weeks Unit 1: Lab Safety, Measurement, and Scientific Investigation 7.1AB, 7.2AB, 7.3A Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Control Demonstrate safe practices during laboratory
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Science. synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis Using physics to make things work 3 Magnetic fields to keep things moving Energy calculations 4 Energy
 Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
SCIENCE OF THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT
 SCIENCE OF THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT A. Terms: 1. Observation: What is or. 2. Inference: A conclusion based on or evidence. 3. Hypothesis: An untested. A good hypothesis states both cause and effect 4. Theory:
SCIENCE OF THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT A. Terms: 1. Observation: What is or. 2. Inference: A conclusion based on or evidence. 3. Hypothesis: An untested. A good hypothesis states both cause and effect 4. Theory:
Text of objective. Investigate and describe the structure and functions of cells including: Cell organelles
 This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
VCE BIOLOGY Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the Study Design and the Study Design
 VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
1. The picture below shows a paramecium. 2. Anya is observing an organism in the laboratory. The table below shows her observations.
 Name: Period: Date: Life Science MCAS Review Packet Directions: Answer each of the following questions under the standards. The question may be multiple choice or open response, if needed please use a
Name: Period: Date: Life Science MCAS Review Packet Directions: Answer each of the following questions under the standards. The question may be multiple choice or open response, if needed please use a
1 st Semester Vocabulary
 1 st Semester Vocabulary 1. Qualitative Observation Observation that involves descriptions and characteristics. Example: Color and appearance The cat looks scared. The cat has green eyes. The cat has long
1 st Semester Vocabulary 1. Qualitative Observation Observation that involves descriptions and characteristics. Example: Color and appearance The cat looks scared. The cat has green eyes. The cat has long
The Science Department Academic Year Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview
 The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
What Is Biology? Biologists Study? The study of living things. Characteristics Classifications Interactions between organisms Health & Disease
 What Is Biology? The study of living things. Biologists Study? Characteristics Classifications Interactions between organisms Health & Disease Goal of Science To investigate To understand To explain To
What Is Biology? The study of living things. Biologists Study? Characteristics Classifications Interactions between organisms Health & Disease Goal of Science To investigate To understand To explain To
Bangor School Department Grade 7 Science
 Bangor School Department Grade 7 Science Teacher: School: NOTE: This record of assessments must be submitted to the Assistant Superintendent s Office by end of the school year. Date: 4 = Exceeds 3 = Meets
Bangor School Department Grade 7 Science Teacher: School: NOTE: This record of assessments must be submitted to the Assistant Superintendent s Office by end of the school year. Date: 4 = Exceeds 3 = Meets
Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms
 Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-10LW describes how structural features and other adaptations of living things help them to survive in their environment Check Date
Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-10LW describes how structural features and other adaptations of living things help them to survive in their environment Check Date
Biology Final Review Ch pg Biology is the study of
 Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Characteristics of Life
 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
B4 Organising animals and plants. Student Book answers. B4.1 The blood. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis
 Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis Homeostasis - maintenance of internal stable conditions in a constantly changing environment that are necessary for life's functions Maintaining
Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis Homeostasis - maintenance of internal stable conditions in a constantly changing environment that are necessary for life's functions Maintaining
Bio/Life: Cell Biology
 Bio/Life: Cell Biology 1a The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding
Bio/Life: Cell Biology 1a The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding
GCSE Combined Science
 AQA GCSE Combined Science Grades 9-1 Chace Community School Combined Science Grade 9-1 GCSE This course will give you two GCSE Science qualifications. You will cover Biology, Chemistry and Physics. During
AQA GCSE Combined Science Grades 9-1 Chace Community School Combined Science Grade 9-1 GCSE This course will give you two GCSE Science qualifications. You will cover Biology, Chemistry and Physics. During
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Curriculum Map. Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1)
 1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
Ms. Stacey-Ann Joseph HSB TEST 1
 SECTION A: LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Circle the most appropriate answer for each question. 1. Which are not organisms? A. Bacteria B. Cars C. Trees D. Wolves 2. Which is defined by the power
SECTION A: LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Circle the most appropriate answer for each question. 1. Which are not organisms? A. Bacteria B. Cars C. Trees D. Wolves 2. Which is defined by the power
OCR 21st Century Science: Biology B GCSE specification
 OCR 21st Century Science: Biology B GCSE specification For GCSE exams 2018 onwards Revision Guide page reference ISBN 9781407176864 Exam Practice Book page reference ISBN 9781407176871 Revision Guide and
OCR 21st Century Science: Biology B GCSE specification For GCSE exams 2018 onwards Revision Guide page reference ISBN 9781407176864 Exam Practice Book page reference ISBN 9781407176871 Revision Guide and
Name: Date: Answer: Answer:
 Name: Date: 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 50 Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: Standard(s):..0.F,...F,..0.D,...D,..0.C,...C,..0.E,...E,.5.0.F,.5..F
Name: Date: 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 50 Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: Standard(s):..0.F,...F,..0.D,...D,..0.C,...C,..0.E,...E,.5.0.F,.5..F
Which row in the chart correctly identifies the functions of structures A, B, and C? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
Biology EOCT Review. Milton High School
 Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Cell Theory. All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells
 Created by Mrs. Herman Sept. 2012 Cell Theory All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells Animal Cells Plant Cells The
Created by Mrs. Herman Sept. 2012 Cell Theory All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells Animal Cells Plant Cells The
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined. Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours
 Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Do NOT write on this test. Thank you!
 Organization and Development of Living Organisms (SC.6.L.14.1,2,3,4 and 5) 1. The diagram below represents a plant cell. Letter X represents a structure in the cell. Which structure is represented by X?
Organization and Development of Living Organisms (SC.6.L.14.1,2,3,4 and 5) 1. The diagram below represents a plant cell. Letter X represents a structure in the cell. Which structure is represented by X?
4.6.1 Reproduction Sexual and asexual reproduction Meiosis. Key opportunities for. development. skills development
 4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution In this section we will discover how the number of chromosomes are halved during meiosis and then combined with new genes from the sexual partner to produce unique
4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution In this section we will discover how the number of chromosomes are halved during meiosis and then combined with new genes from the sexual partner to produce unique
Biology. Revisiting Booklet. 6. Inheritance, Variation and Evolution. Name:
 Biology 6. Inheritance, Variation and Evolution Revisiting Booklet Name: Reproduction Name the process by which body cells divide:... What kind of cells are produced this way? Name the process by which
Biology 6. Inheritance, Variation and Evolution Revisiting Booklet Name: Reproduction Name the process by which body cells divide:... What kind of cells are produced this way? Name the process by which
SUBJECT: Science Grade Level: 8. Unit: Technology & Engineering (1 week)
 Grade 8 Science Curriculum Map - Norwell Middle School SUBJECT: Science Grade Level: 8 Unit: Technology & Engineering (1 week) Standard 2: Engineering Design 2.1- Identify and explain the steps of the
Grade 8 Science Curriculum Map - Norwell Middle School SUBJECT: Science Grade Level: 8 Unit: Technology & Engineering (1 week) Standard 2: Engineering Design 2.1- Identify and explain the steps of the
3.4a Hypotheses are valuable, even if they turn out not to be true, because they may lead to further investigation.
 September Science and Biology Chemistry of Life 1.1.1a-b, 1.1.3 a-b, 1.1.4a;4.2.1de4.3.1a;4.5.1a;1.3.1a1.2.3a-b, 1.3.4a-5a; 4.2.1i, 4.5.1a, 4.5.1c, 4.5.1f, 4.5.1g 1.1a-b Scientific explanations are built
September Science and Biology Chemistry of Life 1.1.1a-b, 1.1.3 a-b, 1.1.4a;4.2.1de4.3.1a;4.5.1a;1.3.1a1.2.3a-b, 1.3.4a-5a; 4.2.1i, 4.5.1a, 4.5.1c, 4.5.1f, 4.5.1g 1.1a-b Scientific explanations are built
Exploring Life Content Assessment 1
 Exploring Life Content Assessment 1 INSTRUCTIONS: Below you will find 42 questions that explore your understanding of science. Each question is numbered in the left-hand column and has only one correct
Exploring Life Content Assessment 1 INSTRUCTIONS: Below you will find 42 questions that explore your understanding of science. Each question is numbered in the left-hand column and has only one correct
Science Years 9 to 10
 Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Final Exam Review Questions
 Final Exam Review Questions 1. Bumblebees show some ability to control their own body temperature. During cold weather, bumblebees have been observed warming their flight muscles by shivering. The bees
Final Exam Review Questions 1. Bumblebees show some ability to control their own body temperature. During cold weather, bumblebees have been observed warming their flight muscles by shivering. The bees
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
 D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Standard Grade Biology Revision Notes
 Standard Grade Biology Revision Notes The Biosphere Habitat where an animal lives Community all the plants and animals in an area Ecosystem living and non living parts (habitat + community) Population
Standard Grade Biology Revision Notes The Biosphere Habitat where an animal lives Community all the plants and animals in an area Ecosystem living and non living parts (habitat + community) Population
The Common Ground Curriculum. Science: Biology
 The Common Ground Curriculum Science: Biology CGC Science : Biology Defining Biology: Biology is the study of living things in their environment. This is not a static, snapshot of the living world but
The Common Ground Curriculum Science: Biology CGC Science : Biology Defining Biology: Biology is the study of living things in their environment. This is not a static, snapshot of the living world but
Hypothesis. Levels of organization. Theory. Controlled experiment. Homeostasis. ph scale. Characteristics of living things
 Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
FINAL VERSION_ Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea
 Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
2. Draw two water molecules. Using a dotted line, show a hydrogen bond that could form between them.
 Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator!
 Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
