3 Movement of substances in living organisms
|
|
|
- Georgiana Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then levels off (almost back to CO conc. in air) / eq () carbon dioxide rapidly enters bag from air in room / eq b) increase (in % humidity) transpiration / evaporation stomata open / eq water passes out of leaf / into bag collects in bag / eq c) i) both graphs labelled (A and B, or carbon dioxide and humidity) both graphs start from same positions as on first graph CO graph rises steadily and does not fall (student may need to extend vertical axis to show the rise) humidity graph rises steadily and does not fall no photosynthesis in dark / CO not taken up in dark / eq respiration continues and produces CO (collects in bag) / eq Total a) i) (left hand side) carbon dioxide + water (=/ arrow) (right hand side) (= / arrow) glucose / carbohydrate + oxygen (accept symbols for words even if equation is not balanced) (colour of indicator) shows carbon dioxide concentration / eq shows the concentration (of carbon dioxide) left in the tube after 60 minutes / eq if carbon dioxide concentration is high (after 60 minutes), the rate of photosynthesis is low / vice versa / eq one example of colour linked correctly to carbon dioxide concentration or ph (e.g. turns purple in low concentration of carbon dioxide / alkaline / high ph / eq) b) i) rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing light intensity / eq steep increase (in rate of photosynthesis) with increasing light at lower light intensities / eq moderate increase (in rate of photosynthesis) at middle light intensities / eq less increase (in rate of photosynthesis) at higher light intensities / levels off / eq relevant figures from graphs quoted to support any of the above (for mark) rate of photosynthesis increases then falls off / eq (if no reference to light intensity) high chlorophyll algal balls have higher rate of photosynthesis / or converse for low chlorophyll / eq high chlorophyll algal balls, rate of photosynthesis increases more rapidly at low light intensities / converse / eq relevant figures from graphs quoted to support any of the above Total 0 6
2 Movement of substances in living organisms a) i) people concerned about effects on health specific examples (e.g. link to cancer, heart disease) / eq education (about effects of smoking) / publicity (e.g. campaigns, advertising) / government advice / eq individuals cut down on number of cigarettes smoked (e.g. per day) / eq costs / too expensive / effects of taxation / eq world population increased (so overall increase in production even if individuals smoke fewer) / eq USA (shown in graph ) not typical of other countries / eq more people take up smoking (in other countries) / eq change in age pattern of smoking (e.g. more younger people smoke) / eq b) tar (in smoke) damage to cilia / tiny hairs on surface of bronchi / bronchioles less effective mechanism for moving mucus layer (out of lungs) / eq mucus builds up in passages in lungs / airways tend to get blocked / eq bacteria / dust / eq not removed, more chance of infection / eq c) carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin / oxyhaemoglobin less haemoglobin available to transport oxygen cells receive less oxygen (oxygen) needed for respiration person is breathless / lacks energy / eq d) alveoli provide the gas exchange surface (between lungs and blood) / eq (if less elastic) cannot expand / fill with air when air drawn into lungs / eq reduces surface area (for gas exchange) / eq less oxygen passes into blood shorter breaths (as in breathlessness) allow higher ventilation rate / eq Total Practical activities a) i) () appropriate number of rows and columns, depending on orientation of table () suitable headings for rows / columns, including units (seconds/ eq and %/ percent / eq) () time correctly inserted, including 0 or second for first reading () results for oxygen concentration correctly inserted (5) + (6) up to marks for calculation of percentage difference (all correct =, one error =, more errors = 0) 5 repeat the experiment several times and calculate the mean value / eq i the longer the breath is held, the smaller the amount / percentage of oxygen in exhaled air / the greater the amount of oxygen absorbed / eq the rate at which oxygen is absorbed decreases, as time breath is held increases / eq b) i) alveoli / air sacs (while air is in the lungs) oxygen diffuses / eq from alveoli / gas exchange surface, to blood / eq from high concentration to low concentration / down concentration gradient / eq the longer the breath is held, the more time there is for oxygen to diffuse into the blood / eq progressively less diffuses as student holds breath for longer / eq (because) smaller difference in concentration gradient between alveoli and blood / eq Total 7
3 Mark schemes Question Mark scheme Marks a) i) columns + headings (number of stomata in section + section) rows + for heading (+ can have one for totals) (can accept variation in table which are columns and which are rows but it must include the necessary information) lines drawn to show sections counts for sections (nearly) correct counts for other sections (nearly) correct (see diagram for one set of results [ ], though other people will get different results depending on where they drew their grid and their system for counting, hence the nearly correct) i b) i) c) system for checking / numbering stomata during counting / eq decide how to count those on boundaries (e.g. larger proportion allocated to that section) decide how to record those that are doubtful (probably closed stomata) eq mark is for adding up to give the total, then saying which is more, even if the wrong answer is given likely answer for green area (total = 0) see comment above about differences in doing the counts sample more areas on same leaf area / do more peels (and do counts) do peels from more leaves (and sample in similar way) ref reliability / repeat counts use counts done by different people to reduce individual error eq (no stomata) reduces loss of water / ref transpiration / helps conserve water / eq if no stomata (on upper surface), reduces loss of water from part of leaf in direct sunlight underside of leaf more humid / shaded / eq Total Note for part (a) (: This is probably more counting than you would get in an examination question, but given here to give you practice in how to do this and the decisions you need to take to get suitable results in a similar practical situation. Check with the diagram to see how closely you agree Total _MS_EIGCSE_CBPB_0-6.indd 8 8/05/ :7 PM
4 Movement of substances in living organisms a) set of tubes, each with different-sized balls replicate tubes ( or tubes of each size ball) (in each tube) same number of balls / same depth of balls in tube / same mass of balls / eq same volume of (hydrogencarbonate) indicator (in each tube) named other condition same (e.g. light / temperature) b) carbon dioxide produced by respiration (in algae) c) i) (yellow) to orange-red / to red / to purple photosynthesis occurs (in light) uses carbon dioxide match colours in indicator / tubes against colours on colour chart / eq choose colour to be end point for observation all tubes start from same colour (e.g. yellow) measure time for tubes to reach (agreed) end point repeat measurements (e.g. start to finish) / eq measure / record the diameter of algal balls i smaller balls, indicator changes colour more quickly / show faster use of carbon dioxide / faster rate of photosynthesis / eq ref larger surface area in relation to volume / carbon dioxide can escape more easily from inside of ball / eq larger balls (show faster use of carbon dioxide / rate of photosynthesis / indicator changes colour more quickly / eq) more chlorophyll in each ball / eq (depends on how the student counted or controlled number of balls when setting up) (allow reasonable supporting reason in relation to the suggestion) Total a) i) (using graph) eliminates variation / anomalies / dubious readings / gives better average over whole time / eq (if only final) might be error in that reading graph better as helps show pattern during the time (of investigation) (total) distance time (in minutes) same distance and time for each place gradient of (both) graphs i rate of transpiration is same as rate of water uptake (i.e. movement of meniscus along capillary tube) / eq b) i) test / vary one factor at a time (e.g. effect of difference in humidity, difference in temperature) keep all other factors the same (e.g. temperature, light, wind speed) use same plant each time / use different plants (same species) but approx. same area of leaf on the shoot / eq repeats / replicates of readings i allow time for plant to settle in each new condition / eq Total 0 9
5 Mark schemes Understanding structure, function and processes a) i) shape (circular + biconcave) (label) cell membrane / cytoplasm (if nucleus shown, nd mark = 0) (white blood cells) various shapes / irregular shape / not biconcave / eq (white blood cells) nucleus present (white blood cells) larger size / eq b) i) contain haemoglobin / eq (haemoglobin) combines with oxygen / eq no nucleus so more space for haemoglobin biconcave shape so large surface area to volume ratio (large SA to volume ratio) allows rapid diffusion of oxygen / gaseous exchange / eq small size / biconcave shape allows them to squeeze through small capillaries / eq pulmonary vein c) pathogens ingested / engulfed / eq, by phagocytes pathogens broken down by enzymes / digested / destroyed / eq antibodies made / released by lymphocytes antibodies, attach to pathogen / destroy pathogen / eq specific to antigen / eq (both points should relate to same type of white blood cell) Total 0 a) i) B / trachea keep trachea open / avoid being closed by food passing down oesophagus / eq b) i) F / ribs H / diaphragm (ribs) intercostal / muscles between ribs (contract) move ribcage / ribs up and out (diaphragm) pulled flat / not domed shape / eq increases volume of chest cavity / eq pressure lowered + air drawn in / eq c) i) E large surface area / eq thin (surface) moist (surface) close contact with many blood capillaries / eq Total 0
6 Movement of substances in living organisms a) i) root hair cells osmosis i long extension / eq provides large surface area / eq thin walls b) i) tubes with narrow diameter / eq no end walls continuous column water / no barriers / eq (column / water molecules) held together by cohesion (narrow tubes) capillarity lignified walls / eq c) i) transpiration / evaporation / eq stomata / stoma i guard cells (surround stoma / pore / gap) take in more water / become turgid lose water / become flaccid ref curved shape / eq allowing more gap / flaccid + closes pore / gap ref sunlight (open) / eq dark (closed) Total a) i) transpiration / evaporation transpiration pull / description, contributes to water uptake / eq transpiration rate / rate of evaporation faster on dry day (compared to humid day) / accept reverse / eq transpiration rate / rate of evaporation faster on windy day (compared to still day) / accept reverse / eq therefore more water uptake when rate of transpiration / eq faster b) (thick) waxy cuticle (reduces water loss through surface) lack of stomata on outside surface rolled leaf retains humid / moist air in region inside the curve / eq stomata present inside but reduced transpiration / evaporation into humid / eq region hairs trap moisture inside the curve / eq Total 9
7 Mark schemes 5 a) lungs b) i) left ventricle C has thicker walls than B / eq (C) pumps blood all round body / (B) pumps only to lungs needs high pressure / more muscle to contract / eq c) i) B most veins carry blood back to heart from cells / tissues / eq (cells) use oxygen in respiration / eq vessel E different as back to heart from lungs / collected oxygen / eq d) carries absorbed / digested food from small intestine to liver sugars from breakdown of carbohydrate / amino acids from breakdown of proteins / eq e) i) D (high pressure) needed to maintain circulation all round body / eq f) F = renal artery (higher urea), G = renal vein (lower urea) / blood vessels to and from kidney / eq kidney function removes urea / eq ref ultrafiltration / eq selective reabsorption of other materials / eq urea passes out in urine / eq g) i) (any vein) e.g. B, G, H, K prevent blood flowing backwards / eq Total 5 Applying principles a) i) plasma enzymes are specific for substrate / work only with correct / one substrate / eq active site on enzyme, glucose fits / eq b) respiration, uses / decreases (glucose) any vein out of tissue (e.g. from muscle / any cells) storage of glucose in liver as glycogen, decreases / removes (glucose) hepatic vein / change from level in hepatic artery release of glucose from stored glycogen in liver / muscles, increases / releases (glucose) hepatic vein / change from level in hepatic artery absorption of glucose from digested food (after a meal), increase hepatic portal vein eq + eq (process + increase or decrease = mark) (linked to correct blood vessel = mark) c) i) pancreas stimulates uptake of glucose by liver / muscles converted to glycogen (and stored) d) fungal culture grown in fermenter / eq (culture) provided with oxygen / nutrients / correct temperature / aseptic conditions / stirring / eq enzymes collected from growth medium / eq Total
8 Movement of substances in living organisms a) i) (rise caused by carbon dioxide from) respiration of students / people in the room in exhaled air no exchange of air / fresh air from outside room i (fall caused by) green plants use / take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis in light not enough carbon dioxide given off from respiration / eq carbon dioxide level rises plant no longer carries out photosynthesis / takes in carbon dioxide carbon dioxide from respiration causes rise in level / eq b) i) vertical axis labelled carbon dioxide concentration (but no units expected) horizontal axis labelled time in hours, show full range of hours (can be in blocks) curve to show fluctuation in relation to time of day / possible light and dark changes / sensible relationship showing high carbon dioxide at night, lower during day (detailed answers in but here mark for sensible fluctuations in curve) (reasons actual interpretations could be different as maize field could be in any time zone / latitude / time of year etc. but assume descriptions given as reasonable norm ) (midnight to hrs) carbon dioxide high, respiration but no photosynthesis, light too low (06.00 to noon) carbon dioxide high then begins to fall as light intensity increases because carbon dioxide taken up (by maize plants and used for photosynthesis) ( noon to 8.00 hrs) carbon dioxide low as light intensity continues to be high and photosynthesis continues to use carbon dioxide (8.00 hrs to midnight) carbon dioxide begins to rise as light becomes too low for photosynthesis and carbon dioxide continues to be produced from respiration Total 5 a) i) alveoli / alveolus / air sacs lower concentration of oxygen (in alveoli) less difference in the concentration gradient (between alveoli and blood in capillaries) / eq slower rate of diffusion (of oxygen into blood) i increased ventilation (into lungs) / brings more fresh air into lungs / eq increases available oxygen (to diffuse into blood) / eq b) i) haemoglobin carries oxygen to cells / oxyhaemoglobin / eq more haemoglobin so more oxygen available to release energy / eq by respiration helps to overcome shortage of oxygen in the air (at high altitude) / eq shows relevance of their study in wider science context / supports their own findings / eq c) more haemoglobin remains in the body, carries more oxygen to cells / eq more energy released by respiration so higher performance / eq Total 0
B4 Organising animals and plants. Student Book answers. B4.1 The blood. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2006 question paper 0610 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2006 question paper 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2006 question paper 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark
Topic 10: Transpiration, transport and support in plants
 Topic 10: Transpiration, transport and support in plants 1. Transpiration is A. the loss of water vapour from the surfaces of plants due to evaporation B. the gain of water vapour from the surfaces of
Topic 10: Transpiration, transport and support in plants 1. Transpiration is A. the loss of water vapour from the surfaces of plants due to evaporation B. the gain of water vapour from the surfaces of
Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy
 Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy AEROBIC RESPIRATION All cells in the body need energy - this energy is released in a process known as respiration Cells that are more active need more energy - e.g during
Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy AEROBIC RESPIRATION All cells in the body need energy - this energy is released in a process known as respiration Cells that are more active need more energy - e.g during
Organs and leaf structure
 Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Transport of substances in plants
 Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does not cross the
 Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Exchanging Materials in Plants
 Exchanging Materials in Plants 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 All living things need to exchange materials Plants need to obtain certain materials for
Exchanging Materials in Plants 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 All living things need to exchange materials Plants need to obtain certain materials for
INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and one C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY
 GHS EOT I S. 3 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) APRIL 2018 TIME: 2 HOURS NAME:.CLASS/NO.. INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and one C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A 1 7 13 19
GHS EOT I S. 3 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) APRIL 2018 TIME: 2 HOURS NAME:.CLASS/NO.. INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and one C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A 1 7 13 19
Transportation in Plants
 Transportation in Plants Bell Ringer - 5 Min Why do you need transportation in living organisms? Explain your answer with a suitable example. Water movement through plants How does water move through a
Transportation in Plants Bell Ringer - 5 Min Why do you need transportation in living organisms? Explain your answer with a suitable example. Water movement through plants How does water move through a
Paget High School. Preparing for A level Biology
 Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
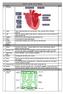 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 20 of 34
 Page 20 of 34 (i) The role of haemoglobin in transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide To include the reversible binding of oxygen molecules, carbonic anhydrase, haemoglobinic acid, HCO3- and the chloride
Page 20 of 34 (i) The role of haemoglobin in transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide To include the reversible binding of oxygen molecules, carbonic anhydrase, haemoglobinic acid, HCO3- and the chloride
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants
 Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Roots, Shoots & Leaves
 Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
Name: Photosynthesis. Class: Date: 76 minutes. Time: 76 marks. Marks: level 1, 2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Photosynthesis Name: Class: Date: Time: 76 minutes Marks: 76 marks Comments: level, 2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water energy glucose +
Photosynthesis Name: Class: Date: Time: 76 minutes Marks: 76 marks Comments: level, 2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water energy glucose +
Transport in Plant (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Plant (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Plants have transport systems to move food, water and minerals around. These systems use continuous tubes called xylem and phloem: - Xylem vessels
Transport in Plant (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Plants have transport systems to move food, water and minerals around. These systems use continuous tubes called xylem and phloem: - Xylem vessels
4-4 Bioenergetics Biology
 4-4 Bioenergetics Biology.0 Figure shows a plant cell. Figure. Draw one line from each part of the cell to its function. [3 marks] Part of the cell Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondria Function Where most
4-4 Bioenergetics Biology.0 Figure shows a plant cell. Figure. Draw one line from each part of the cell to its function. [3 marks] Part of the cell Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondria Function Where most
Jeddah Knowledge International School
 Jeddah Knowledge International School Biology Revision Pack Answer key 2016-2017 Quarter 3 Grade 9 Name: Section: ANSWER KEY- SCIENCE GRADE 9, QUARTER 3 1 Mark Scheme Multiple Choice Part A 1. Which gas
Jeddah Knowledge International School Biology Revision Pack Answer key 2016-2017 Quarter 3 Grade 9 Name: Section: ANSWER KEY- SCIENCE GRADE 9, QUARTER 3 1 Mark Scheme Multiple Choice Part A 1. Which gas
LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: UNIT 2.1: Osmosis and Plant transport
 NAME 0 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 2.1.1-2.1.9 UNIT 2.1: Osmosis and Plant transport LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Pupils should be able to: Good Average Requires Attention 1 Carry out
NAME 0 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 2.1.1-2.1.9 UNIT 2.1: Osmosis and Plant transport LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Pupils should be able to: Good Average Requires Attention 1 Carry out
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
Plants and Photosynthesis
 Plants and Photosynthesis Name: Look for more resources at www.burtbooks.com 1 Date: Let s revise the parts of the plant. Look at the names of the parts carefully. Then turn to the next page and fill in
Plants and Photosynthesis Name: Look for more resources at www.burtbooks.com 1 Date: Let s revise the parts of the plant. Look at the names of the parts carefully. Then turn to the next page and fill in
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
4 Bioenergetics higher (import)
 4 Bioenergetics higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 Plants are grown in glasshouses to protect them from the weather or extend the growing season. Plants
4 Bioenergetics higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 Plants are grown in glasshouses to protect them from the weather or extend the growing season. Plants
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 3.3: Transport in plants Notes Plants require a transport system to ensure that all the cells of a plant receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is achieved through
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 3.3: Transport in plants Notes Plants require a transport system to ensure that all the cells of a plant receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is achieved through
PLANT SCIENCE. 9.2 Transport in Angiospermophytes
 PLANT SCIENCE 9.2 Transport in Angiospermophytes Support of terrestrial plants Support of terrestrial plants comes through: Thickened cellulose in cell walls Turgor pressure of cells Lignified xylem Xylem
PLANT SCIENCE 9.2 Transport in Angiospermophytes Support of terrestrial plants Support of terrestrial plants comes through: Thickened cellulose in cell walls Turgor pressure of cells Lignified xylem Xylem
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
CHAPTER TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
in angiosperms 10/29/08 Roots take up water via roots Large surface area is needed Roots branch and have root hairs Cortex structure also helps uptake
 in angiosperms A. Root System Roots take up water via roots Large surface area is needed Roots branch and have root hairs Cortex structure also helps uptake 1 B. Minerals Nitrogen (NO 3-,NH 4+ ) Potassium
in angiosperms A. Root System Roots take up water via roots Large surface area is needed Roots branch and have root hairs Cortex structure also helps uptake 1 B. Minerals Nitrogen (NO 3-,NH 4+ ) Potassium
active transport active transport support
 1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2016 Science I & II Duration: 3 Hours Index No:- 1) The most essential organelle that should be present in a typical cell
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2016 Science I & II Duration: 3 Hours Index No:- 1) The most essential organelle that should be present in a typical cell
B2 Quick Revision Questions. B2 for AQA GCSE examination 2018 onwards
 B2 Quick Revision Questions Question 1 Which raw materials are used in photosynthesis and what are the products of the reaction? Answer 1 Carbon dioxide Water Glucose Oxygen Question 2 What type of reaction
B2 Quick Revision Questions Question 1 Which raw materials are used in photosynthesis and what are the products of the reaction? Answer 1 Carbon dioxide Water Glucose Oxygen Question 2 What type of reaction
Multicellular Organisms. Calderglen High School National 5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms
 Calderglen High School National 5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 Sub topic: Producing new cells Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell and carry coded instructions called genes from
Calderglen High School National 5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 Sub topic: Producing new cells Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell and carry coded instructions called genes from
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
 Question 1: What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion of
Question 1: What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion of
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
 D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level (91156)
 NCEA Level 2 Biology (91156) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level (91156) Assessment Criteria Achievement Achievement with
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91156) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level (91156) Assessment Criteria Achievement Achievement with
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Photosynthesis Revision 1
 Photosynthesis Revision 73 minutes 73 marks Page of 35 Q. This question is about photosynthesis. (a) Plants make glucose during photosynthesis. Some of the glucose is changed into insoluble starch. What
Photosynthesis Revision 73 minutes 73 marks Page of 35 Q. This question is about photosynthesis. (a) Plants make glucose during photosynthesis. Some of the glucose is changed into insoluble starch. What
untitled 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both
 Name: ate: 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both. are produced by nerve cells B. are highly specific in their actions. slow the rates of chemical reactions. are involved
Name: ate: 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both. are produced by nerve cells B. are highly specific in their actions. slow the rates of chemical reactions. are involved
ARIF ULLAH ITHS
 SUMMARY Feature of xylem and phloem and their role. Distribution of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles) in stem and root of dicotyledonous plants. Transport of water from the root to the atmosphere through
SUMMARY Feature of xylem and phloem and their role. Distribution of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles) in stem and root of dicotyledonous plants. Transport of water from the root to the atmosphere through
Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants
 Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms have specialized cells of many different types that allow them to grow to a larger size than single-celled organisms.
Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms have specialized cells of many different types that allow them to grow to a larger size than single-celled organisms.
Bio Factsheet. Transport in Plants. Number 342
 Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
7.1.3 Plant and Animal Cells
 7.1.3 Plant and Animal Cells 50 minutes 7s Page 1 of 17 Q1. The diagram shows a plant cell. Some parts of the cell are named. (a) Which two named parts are present in plant cells but not animal cells?
7.1.3 Plant and Animal Cells 50 minutes 7s Page 1 of 17 Q1. The diagram shows a plant cell. Some parts of the cell are named. (a) Which two named parts are present in plant cells but not animal cells?
The Science Department Academic Year Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview
 The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Transport in Vascular Plants
 Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Vascular tissue Transports nutrients throughout a plant; such
Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Vascular tissue Transports nutrients throughout a plant; such
Chapter 35 Regulation and Transport in Plants
 Chapter 35 Regulation and Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these needs? Interdependent
Chapter 35 Regulation and Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these needs? Interdependent
Cells Key Words. Task. Key words. Write a definition for each of the key words listed below. Microscope. Plant cell. Animal Cell.
 KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/43 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/43 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This
Photosynthesis Revision 4
 Photosynthesis Revision 4 85 minutes 85 marks Page of 3 Q. Low light intensity is one factor that limits the yield of a crop. In Britain, many tomato growers use artificial lights to increase the yield
Photosynthesis Revision 4 85 minutes 85 marks Page of 3 Q. Low light intensity is one factor that limits the yield of a crop. In Britain, many tomato growers use artificial lights to increase the yield
Biology 5094 O Level 2013 Answers Scheme
 Biology 5094 O Level 2013 Answers Scheme Paper 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 B C C D D A D C D C 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 C D A A D B C C B D 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 D B A C B B B A B B 31 32 33 34
Biology 5094 O Level 2013 Answers Scheme Paper 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 B C C D D A D C D C 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 C D A A D B C C B D 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 D B A C B B B A B B 31 32 33 34
NOTES: CH 36 - Transport in Plants
 NOTES: CH 36 - Transport in Plants Recall that transport across the cell membrane of plant cells occurs by: -diffusion -facilitated diffusion -osmosis (diffusion of water) -active transport (done by transport
NOTES: CH 36 - Transport in Plants Recall that transport across the cell membrane of plant cells occurs by: -diffusion -facilitated diffusion -osmosis (diffusion of water) -active transport (done by transport
Chapter 36~ Transport in Plants
 Chapter 36~ Transport in Plants Structural Features Used for Resource Acquistion Roots and stems to do transport of resources Diffusion, active transport, and bulk flow Work in vascular plants to transport
Chapter 36~ Transport in Plants Structural Features Used for Resource Acquistion Roots and stems to do transport of resources Diffusion, active transport, and bulk flow Work in vascular plants to transport
Water and Food Transportation
 Water and Food Transportation Sugars in a Plant Sugar Form Location in Plant Organ Function of Sugar form Glucose Leaf Energy (made in photosynthesis summer, used in cellular respiration for growth-spring)
Water and Food Transportation Sugars in a Plant Sugar Form Location in Plant Organ Function of Sugar form Glucose Leaf Energy (made in photosynthesis summer, used in cellular respiration for growth-spring)
UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms.
 UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. 1 Law
UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. 1 Law
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Biology
 Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Biology Duration: 2.30 Hours Part 1 Index No:- 1) Choose the correct answer and underline it 1) The diagram shows a high-power
Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Biology Duration: 2.30 Hours Part 1 Index No:- 1) Choose the correct answer and underline it 1) The diagram shows a high-power
1.1 Characteristics common to organisms
 Biology Form 3 Page 5 Ms. R. Buttigieg 1.1 Characteristics common to organisms see GCSE Biology pg. 292 Biology is the study of living things. We call living things organisms. Plants and animals are ALL
Biology Form 3 Page 5 Ms. R. Buttigieg 1.1 Characteristics common to organisms see GCSE Biology pg. 292 Biology is the study of living things. We call living things organisms. Plants and animals are ALL
1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [3] A excretion I gas exchange
![1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [3] A excretion I gas exchange 1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [3] A excretion I gas exchange](/thumbs/84/90652061.jpg) 1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [] A excretion I gas exchange (b) water enters by osmosis ; down a water potential gradient / high(er) to low(er) water potential
1 (a) carbon dioxide / CO 2 ; (aerobic) respiration ; (simple) diffusion ; [] A excretion I gas exchange (b) water enters by osmosis ; down a water potential gradient / high(er) to low(er) water potential
Hazel Grove High School Year 10 Homework Book Term 2 Spring Focus Biology topic 8, Chemistry topic 7 and Physics topics 12/13.
 Hazel Grove High School Year 10 Homework Book Term 2 Spring Focus Biology topic 8, Chemistry topic 7 and Physics topics 12/13 Homework Score on Quiz Introduction to Science Homework Science Homework will
Hazel Grove High School Year 10 Homework Book Term 2 Spring Focus Biology topic 8, Chemistry topic 7 and Physics topics 12/13 Homework Score on Quiz Introduction to Science Homework Science Homework will
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but
AP Biology Chapter 36
 Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Transpiration. Interesting Fact:
 Transpiration Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. Transpiration is thought to be a 'necessary cost or evil' to allow the plant to absorb water from
Transpiration Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. Transpiration is thought to be a 'necessary cost or evil' to allow the plant to absorb water from
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Transport in plants
 Transport in plants Question Paper 1 Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board OCR Topic Exchange and transport Sub-Topic Transport in plants Booklet Question Paper 1 Time Allowed: 75 minutes Score: / 62
Transport in plants Question Paper 1 Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board OCR Topic Exchange and transport Sub-Topic Transport in plants Booklet Question Paper 1 Time Allowed: 75 minutes Score: / 62
The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves.
 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes. For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
How to use this book. How the book is organised. Answering questions. Learning and using the terminology. Developing skills
 How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
M1. (a) light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark ignore solar / sunshine 1
 M. (a) light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark ignore solar / sunshine by chlorophyll / chloroplasts if no other marks awarded, allow mark for photosynthesis / equation for photosynthesis
M. (a) light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark ignore solar / sunshine by chlorophyll / chloroplasts if no other marks awarded, allow mark for photosynthesis / equation for photosynthesis
How many lessons is it?
 Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Study Guide Chapter
 Study Guide Chapter 4-10152015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. During the process of diffusion, a. cell surrounds and absorbs large particles.
Study Guide Chapter 4-10152015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. During the process of diffusion, a. cell surrounds and absorbs large particles.
Which farm is likely to have been using too much fertiliser on its land? farm C. farm B
 1 What is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast? lactic acid carbon dioxide 2 What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose + carbon
1 What is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast? lactic acid carbon dioxide 2 What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose + carbon
PHOTOSYNTHESIS GR 11 LIFE SCIENCES
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS GR 11 LIFE SCIENCES Definition: Photosynthesis is the process where the energy of the sunlight is used by green plants (and some animals) to bond molecules together to form carbohydrates
PHOTOSYNTHESIS GR 11 LIFE SCIENCES Definition: Photosynthesis is the process where the energy of the sunlight is used by green plants (and some animals) to bond molecules together to form carbohydrates
Recap. Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water. Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption.
 Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Foundation Cell Biology
 Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
2803/01 Transport January 2005 Mark Scheme
 2803/01 Transport January 2005 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all
2803/01 Transport January 2005 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
D leaf palisade cell (1) Answer Acceptable answers Mark. through (partially permeable) membrane (2) Answer Acceptable answers Mark
 1(a) D leaf palisade cell 1(b) An explanation linking two of the following: by osmosis Ignore references to diffusion reject active transport from an area of high water concentration to an area of low
1(a) D leaf palisade cell 1(b) An explanation linking two of the following: by osmosis Ignore references to diffusion reject active transport from an area of high water concentration to an area of low
1. Transpiration may be defined as the loss of water vapour by diffusion from a plant to its environment.
 1. Transpiration may be defined as the loss of water vapour by diffusion from a plant to its environment. The diagram below shows apparatus that can be used to estimate transpiration rates of a leafy shoot.
1. Transpiration may be defined as the loss of water vapour by diffusion from a plant to its environment. The diagram below shows apparatus that can be used to estimate transpiration rates of a leafy shoot.
Animal Cell Organelles. Plant Cell. Organelle. Cell Wall. Chloroplasts. Vacuole
 Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/21 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
Basic Biological Principles
 Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
8.L.5.1 Practice Questions
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
thebiotutor. AS Biology OCR. Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport. Module 2.3 Transport in Plants. Answers.
 thebiotutor AS Biology OCR Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport Module 2.3 Transport in Plants Answers Andy Todd 2013 1 1. (i) transports water (up plant); ACCEPT alternative wording for transport e.g.
thebiotutor AS Biology OCR Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport Module 2.3 Transport in Plants Answers Andy Todd 2013 1 1. (i) transports water (up plant); ACCEPT alternative wording for transport e.g.
Pre-AP Biology Unit II: Cell Structure and Function Quiz
 Pre-AP Biology Unit II: Cell Structure and Function Quiz Your kitchen is compartmentalized. Structures within the cell, called organelles, form compartments within the cell. 1. What is an example of an
Pre-AP Biology Unit II: Cell Structure and Function Quiz Your kitchen is compartmentalized. Structures within the cell, called organelles, form compartments within the cell. 1. What is an example of an
23 4 Leaves Slide 1 of 32
 23 4 Leaves 1 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. 2 of 32 Leaf Structure To collect sunlight, most leaves have thin, flattened
23 4 Leaves 1 of 32 Leaf Structure The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. 2 of 32 Leaf Structure To collect sunlight, most leaves have thin, flattened
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Page 1. Name: UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
7.1.2 Cell Functions. 104 minutes. 137 marks. Page 1 of 30
 7.1.2 Cell Functions 104 minutes 137 marks Page 1 of 30 ## Most pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another either by wind or by insects. Look at the drawings below which show pollen grains
7.1.2 Cell Functions 104 minutes 137 marks Page 1 of 30 ## Most pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another either by wind or by insects. Look at the drawings below which show pollen grains
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
screw clip air bubble Transpiration itself is not measured directly by a potometer....
 1. Transpiration is the loss of water from plants by evaporation. The diagram below shows a potometer, an apparatus used to estimate transpiration rates. water reservoir leafy shoot screw clip air bubble
1. Transpiration is the loss of water from plants by evaporation. The diagram below shows a potometer, an apparatus used to estimate transpiration rates. water reservoir leafy shoot screw clip air bubble
What are plants used for?
 1 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 What are plants used for? 3 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 How many different uses of plants can you spot? Using plants 4 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 How
1 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 What are plants used for? 3 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 How many different uses of plants can you spot? Using plants 4 of 48 Boardworks Ltd 2007 How
Fill in the gaps: You would write this as: we can use for living processes.
 AQA Trilogy Biology Unit 4.4: Bioenergetics Complete the word equation for + + Write the name of each chemical next to its formula. Which elements make up each chemical? How does the rate of photosynthesis
AQA Trilogy Biology Unit 4.4: Bioenergetics Complete the word equation for + + Write the name of each chemical next to its formula. Which elements make up each chemical? How does the rate of photosynthesis
Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process?
 1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
