Biology I: Macaw Book Unit IV: Microbiology
|
|
|
- Adela Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology I: Macaw Book Unit IV: Microbiology Chapter 21 Fungus Fungus Lab Name: Date: Hour: Fungus Lab Pre-Lab Discussion Fungi are heterotrophic eukaryotes with cell walls that contain chitin. Most people think only of mushrooms as fungi, but in fact mushrooms are just the fruiting body, reproductive structures, of a much larger organism. Most of the fungal organism is found underground in a mass of branching hyphae called mycelium below the soil. Mushrooms are not the only type of fungi. More than 100,000 species of fungi are known and the organisms are separated from one another in how they reproduce. All fungi can reproduce asexually by cell division of the mycelium, but fungi sexually reproduce differently in each phylum. In this lab investigation, you will observe fungus specimens from different phyla. You will be able to compare the similarities and differences between the fungi and their reproductive structures, and be able to describe their role in the environment. Problem What are the differences in reproduction and form between the fungus phyla? Materials (per pair) Microscope Prepared slides of: Rhizopus sp. Rhizopus sp. conjugation Peziza sp. Yeast Penicillium sp. Aspergillus sp. Lichen Safety Always handle the microscope with extreme care. You are responsible for its proper care and use. Always use caution when handling glass slides as they can break easily and cut you. Always use special caution when working with laboratory organisms. Be cautious of the mushrooms, yeast and blue cheese if you may be allergic. -1-
2 Procedure Part I: Zygomycota A. Obtain a common bread mold slide. In the first circle, draw Rhizopus. Obtain a slide of Rhizopus conjugation. In the second circle, draw a gametangia. In the third circle, draw a zygospore. Label the diagrams as indicated Rhizopus Gametangia Zygospore Label: Sporangiophore Sporangium Spores Label: + Stolon - Stolon Gametangia Label: + Stolon - Stolon Zygospore 1. What type of reproduction includes a sporangium? 2. What type of reproduction includes gametangia and zygospores? 3. If you collected a large mass of Rhizopus and transferred it to an orange and then collected a large mass of Aspergillus from an orange and transferred it to a slice of bread, both of the fungi would die. Explain why this happens. -2-
3 Part II: Ascomycota A. Draw Yeast and Peziza sp. from a slide. Label as indicated. Yeast Label: Cell wall Cytoplasm Bud Peziza sp. Label: Cell wall Cytoplasm Ascospore Ascus 4. What type of reproduction did you observe in the yeast? 5. What type of reproduction did you observe in the Peziza sp.? 6. Yeast cells are very versatile they are facultative anaerobes. Humans have been using yeast cells for centuries. List 2 different uses for yeast. a. b. -3-
4 Part III: Basidiomycota A. Use the live specimen and the diagram in the book to draw a Mushroom. Label as indicated. Label: Cap Gills Stipe (stalk) 7. Where are basidiospores produced on the mushroom? 8. What is the reproductive structure of a basidiomycota that grows from the mycelium? 9. Assume that it is mid-summer and you just mowed the lawn. That night a heavy rain falls and the next morning you notice mushrooms all over the yard! Cell divisions can take place rapidly in fungi, but not that fast! Explain this explosion of fungi in your yard. HINT: Read in your book about fungi in section
5 Part IV: Deuteromycota A. Draw Penicillium sp. and Aspergillus sp. from the slides. Label as indicated. Penicillium sp. Aspergillus sp. Label: Conidia Conidiophore Label: Conidia Conidiophore 10. In 1928, Alexander Fleming discovered something special. He notices one of his petri dishes of Staphylococcus (a bacteria) was contaminated with fungal growth. At first he thought that his experiment was ruined, but then realized that in the area near the fungi, all the bacteria were dead! HINT: Use the index of your textbook for help! a. What was Fleming s conclusion from this last observation? b. Name the fungus Fleming found in his petri dish. c. What does this fungus produce that affected bacteria. -5-
6 Part V: Lichens A. Draw a cross section (c.s.) of a Lichen from a slide. Label as indicated. Label: Algal cells Dense fungal hyphae Loose fungal hyphae 11. Many organisms form symbiotic relationships. There are several types of symbiotic relations. Sometimes one organism is harmed and the second organism benefits. With lichens, both organisms benefit. What is the name of a symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit? 12. What is the function of the fungus in this mutualistic relationship of the lichen? 13. What is the function of the algae in this mutualistic relationship of the lichen? -6-
21-2 Classification of Fungi Slide 2 of 44
 2 of 44 Fungi are classified according to their structure and method of reproduction. The four main groups of fungi are: Common molds (Zygomycota) Sac fungi (Ascomycota) Club fungi (Basidiomycota) Imperfect
2 of 44 Fungi are classified according to their structure and method of reproduction. The four main groups of fungi are: Common molds (Zygomycota) Sac fungi (Ascomycota) Club fungi (Basidiomycota) Imperfect
Kingdom Fungi. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Activity1: Zygomycota. Revised Fall 2017
 Kingdom Fungi Revised Fall 2017 ** You will require your text book Biological Science during this lab ** Learning Objectives Building on the learning objectives from your lab syllabus, you will be expected
Kingdom Fungi Revised Fall 2017 ** You will require your text book Biological Science during this lab ** Learning Objectives Building on the learning objectives from your lab syllabus, you will be expected
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: FUNGI
 Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: FUNGI Fungi are eukaryotic heterotrophs that have cell walls. They are part of the nature s recycling system. They break down organic compounds. Fungi are used in wine, beer, cheese,
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: FUNGI Fungi are eukaryotic heterotrophs that have cell walls. They are part of the nature s recycling system. They break down organic compounds. Fungi are used in wine, beer, cheese,
1. Access the page Reading: Fungi. 2. Zygomycota (bread mold): View the prepared slides of the zygospores and sporangia.
 Fungi Lab Learning Objectives State the kingdom of mushrooms, yeast, and bread molds State the phylum of the bread mold State the phylum of the mushroom (club fungi) State the phylum of the yeast (sac
Fungi Lab Learning Objectives State the kingdom of mushrooms, yeast, and bread molds State the phylum of the bread mold State the phylum of the mushroom (club fungi) State the phylum of the yeast (sac
UNIT XI. Kingdom Fungi
 UNIT XI Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Fungi The Study of Fungi is called Mycology What is probably the largest living organism on earth has been discovered in the Malheur National Forest in eastern Oregon. A fungus
UNIT XI Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Fungi The Study of Fungi is called Mycology What is probably the largest living organism on earth has been discovered in the Malheur National Forest in eastern Oregon. A fungus
Kingdom Fungi. 1. Student will be able to describe the characteristic features in the kingdom Fungi.
 Kingdom Fungi Molds, Sac Fungi, Mushrooms, and Lichens Essential Question(s): What makes fungi have their own kingdom? Objectives: 1. Student will be able to describe the characteristic features in the
Kingdom Fungi Molds, Sac Fungi, Mushrooms, and Lichens Essential Question(s): What makes fungi have their own kingdom? Objectives: 1. Student will be able to describe the characteristic features in the
Fungi What are they? Diverse group of eukaryotic organisms 100,000 to 1,000,000 species
 Kingdom Fungi Fungi What are they? Diverse group of eukaryotic organisms 100,000 to 1,000,000 species Fungi Characteristics Kingdom includes Molds, mushrooms & yeasts Characteristically: Most are multicellular
Kingdom Fungi Fungi What are they? Diverse group of eukaryotic organisms 100,000 to 1,000,000 species Fungi Characteristics Kingdom includes Molds, mushrooms & yeasts Characteristically: Most are multicellular
Fungi Coloring Worksheet
 Fungi Coloring Worksheet The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube formed
Fungi Coloring Worksheet The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube formed
Name: Block: FUNGI WORKSHEET
 FUNGI WORKSHEET Name: Block: The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube
FUNGI WORKSHEET Name: Block: The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube
INTRODUCTION budding, binary fission hyphae mycelium Figure 1.
 INTRODUCTION Although most of our work in this lab is done on bacteria, fungi are nonetheless an important aspect in microbiology. Besides being important food providers, fungi play central roles in recycling
INTRODUCTION Although most of our work in this lab is done on bacteria, fungi are nonetheless an important aspect in microbiology. Besides being important food providers, fungi play central roles in recycling
General Fungus Anatomy: Yeast: single cell fungi that reproduces by fission or budding
 Make-Up Assignment: Using the notes below as a guide, look up the organisms you are required to draw on the internet or in a book. Draw the organism in the circles provided and write a description of the
Make-Up Assignment: Using the notes below as a guide, look up the organisms you are required to draw on the internet or in a book. Draw the organism in the circles provided and write a description of the
Topic 18. Fungi. Web
 Topic 18. Fungi Historically fungi were considered to be plants. Molecular evidence, however, indicates that they are actually more closely allied with the animals. Fungi are all heterotrophic, and live
Topic 18. Fungi Historically fungi were considered to be plants. Molecular evidence, however, indicates that they are actually more closely allied with the animals. Fungi are all heterotrophic, and live
Eukaryotes Most are saprobes (live on dead organisms) Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi
 KINGDOM FUNGI 1 Characteristics 2 THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Eukaryotes Most are saprobes (live on dead organisms) Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi 3 THE CHARACTERISTICS
KINGDOM FUNGI 1 Characteristics 2 THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Eukaryotes Most are saprobes (live on dead organisms) Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi 3 THE CHARACTERISTICS
Fungal Characteristics 1)Cell wall made of Chitin 2)Heterotrophs and major Decomposers 3)Body is made of Long filaments of hyphae which form a
 Fungal Characteristics 1)Cell wall made of Chitin 2)Heterotrophs and major Decomposers 3)Body is made of Long filaments of hyphae which form a mycelium 4)Reproduce sexually and asexually Asexually by spores
Fungal Characteristics 1)Cell wall made of Chitin 2)Heterotrophs and major Decomposers 3)Body is made of Long filaments of hyphae which form a mycelium 4)Reproduce sexually and asexually Asexually by spores
Chapter 31: Fungi. Student:
 Chapter 31: Fungi Student: 1. Specialized symbiotic associations between the roots of plants and fungi are called A) lichens. B) hyphal associations. C) heterokaryotic junctions. D) mycorrhizae. E) a mycelium
Chapter 31: Fungi Student: 1. Specialized symbiotic associations between the roots of plants and fungi are called A) lichens. B) hyphal associations. C) heterokaryotic junctions. D) mycorrhizae. E) a mycelium
Kingdom Fungi. The Rotten World We Live In
 Kingdom Fungi The Rotten World We Live In 1 Fungi Characteristics General Information Eukaryotic Some are unicellular (yeast). Most are multicellular. Heterotrophic Secretes digestive enzymes onto food
Kingdom Fungi The Rotten World We Live In 1 Fungi Characteristics General Information Eukaryotic Some are unicellular (yeast). Most are multicellular. Heterotrophic Secretes digestive enzymes onto food
NUTRITION: A) Saprophytes = break down material extracellularly with secreted enzymes : eg) mushrooms, molds
 KINGDOM FUNGI (MYCOPHYTA) Mycology = the study of fungi fossil record dates to 900 million years ago at one time classified in the Plantae Kingdom Recent molecular evidence suggests that fungi are probably
KINGDOM FUNGI (MYCOPHYTA) Mycology = the study of fungi fossil record dates to 900 million years ago at one time classified in the Plantae Kingdom Recent molecular evidence suggests that fungi are probably
Fungi. Objectives: Introduction:
 Fungi Objectives: Be able to explain how fungi acquire their nutrients. Be able to explain the structural role that chitin (a substance also found in the exoskeletons of arthropods!) plays in fungi. Gain
Fungi Objectives: Be able to explain how fungi acquire their nutrients. Be able to explain the structural role that chitin (a substance also found in the exoskeletons of arthropods!) plays in fungi. Gain
Workshop on Kingdom Fungi
 Workshop on Kingdom Fungi by Dana Krempels Introduction Kingdom Fungi is an ostensibly monophyletic assemblage of ecologically important organisms that not only perform the vital function of decomposition,
Workshop on Kingdom Fungi by Dana Krempels Introduction Kingdom Fungi is an ostensibly monophyletic assemblage of ecologically important organisms that not only perform the vital function of decomposition,
Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes
 Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes OBJECTIVES 1. To observe representatives of major types of microbes. 2. To cultivate select representatives of major types of microbes. 3. Understand key
Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes OBJECTIVES 1. To observe representatives of major types of microbes. 2. To cultivate select representatives of major types of microbes. 3. Understand key
General Characteristics
 Fungi General Characteristics Primarily terrestrial Filamentous Hyphae Coenocytic (aseptate) septate mycelium Haustoria specialized parasitic hyphae Fungal Hyphae General Characteristics Heterotrophic
Fungi General Characteristics Primarily terrestrial Filamentous Hyphae Coenocytic (aseptate) septate mycelium Haustoria specialized parasitic hyphae Fungal Hyphae General Characteristics Heterotrophic
Have cell walls made of chitin (same material is found in the skeletons of arthropods)
 Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
KINGDOM FUNGI. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3a Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted
 KINGDOM FUNGI Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3a Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Fungi Mycology (mykes =mushroom; logia = study) Major decomposers of dead organic matter Ecosystem:
KINGDOM FUNGI Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3a Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Fungi Mycology (mykes =mushroom; logia = study) Major decomposers of dead organic matter Ecosystem:
Back Lesson Print Directed Reading A Section: Fungi CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Fungi CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI 1. What are fungi? 2. How do fungi get nutrients? 3. Many fungi are, which feed on dead plant or animal matter, while other fungi
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Fungi CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI 1. What are fungi? 2. How do fungi get nutrients? 3. Many fungi are, which feed on dead plant or animal matter, while other fungi
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 6: Fungi Read before starting!
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 6: Fungi Read before starting! This will be a take-home lab. We recommend that you complete this handout in the order presented work through
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 6: Fungi Read before starting! This will be a take-home lab. We recommend that you complete this handout in the order presented work through
How we study diversity: phylogenetic tree. Fungi vs. Animals. Fungi vs. Plants 3/8/18
 Ya Yang yangya@umn.edu How we study diversity: phylogenetic tree Office Hours: Monday 10-12 AM 714 Biological Sciences Center Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that are more closely related to animals than
Ya Yang yangya@umn.edu How we study diversity: phylogenetic tree Office Hours: Monday 10-12 AM 714 Biological Sciences Center Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that are more closely related to animals than
3/22/2011. Review. Review. Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell
 Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Study Guide B. Answer Key. Protists and Fungi
 Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Kingdom Fungi. Announcements
 Kingdom Fungi Announcements Friday lab: Fungi & Lichen Bring a Lichen to ID! Do prelab Quiz #4 Friday Study Prokaryotes & Protists Mushroom Fest extra credit due Fri Email me or bring to lab Endosymbiosis
Kingdom Fungi Announcements Friday lab: Fungi & Lichen Bring a Lichen to ID! Do prelab Quiz #4 Friday Study Prokaryotes & Protists Mushroom Fest extra credit due Fri Email me or bring to lab Endosymbiosis
Fungi. Kingdoms Fungi & Plantae. Fungi and Plants. Fungi and Plants. Phytophthora, Plasmopara. Rusts. Lecture 16
 Lecture 16 Kingdoms Fungi & Plantae Plantae Fungi Animalia Fungi and Plants Three lines of evolution from Protista based on mode of nutrition: Animals: Ingestion Fungi: Absorption Plants: Photosynthesis
Lecture 16 Kingdoms Fungi & Plantae Plantae Fungi Animalia Fungi and Plants Three lines of evolution from Protista based on mode of nutrition: Animals: Ingestion Fungi: Absorption Plants: Photosynthesis
What are fungi? Lesson 2. Reading Guide. Key Concepts. Vocabulary
 792 iscience Grade 7, Davis County Edition Lesson 2 Reading Guide Key Concepts ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the different types of fungi and how do they compare? Why are fungi important? What are lichens?
792 iscience Grade 7, Davis County Edition Lesson 2 Reading Guide Key Concepts ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the different types of fungi and how do they compare? Why are fungi important? What are lichens?
Fungi BIOLOGY. Visual Learning Company. Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome. Graphics: Fred Thodal Dean Ladago
 Instructor s Manual Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Lyndsey Canfield Heidi Berry Graphics: Fred Thodal Dean Ladago BIOLOGY Visual Learning Company
Instructor s Manual Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Lyndsey Canfield Heidi Berry Graphics: Fred Thodal Dean Ladago BIOLOGY Visual Learning Company
Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi)
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A protist is any organism
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A protist is any organism
Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike.
 SECTION 19.1 DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. VOCABULARY protist Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. 1. Are protists
SECTION 19.1 DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. VOCABULARY protist Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. 1. Are protists
CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms. Microorganisms covered in this chapter:
 Biology 2201 Name: CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms Microorganisms covered in this chapter: Kingdom Bacteria or Monera: Pg. 132-137 Bacteria are simple, prokaryotic organisms. They can be classified according
Biology 2201 Name: CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms Microorganisms covered in this chapter: Kingdom Bacteria or Monera: Pg. 132-137 Bacteria are simple, prokaryotic organisms. They can be classified according
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. FUNGI
 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. FUNGI FUNGI Fungi are absorptive heterotrophic eukaryotes that digest their food externally and absorb the nutrients Most fungi consist of a mass of threadlike hyphae
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. FUNGI FUNGI Fungi are absorptive heterotrophic eukaryotes that digest their food externally and absorb the nutrients Most fungi consist of a mass of threadlike hyphae
FUNGI are very successful and widespread
 because fungi have cell walls, and show a superficial resemblance, Fungi were long allied with PLANTS in fact they differ greatly from plants and are now considered to be more closely related to ANIMALS
because fungi have cell walls, and show a superficial resemblance, Fungi were long allied with PLANTS in fact they differ greatly from plants and are now considered to be more closely related to ANIMALS
A) Parasitic B) Mutualistic C) Decomposer D) The first and second responses are both correct. E) All of the listed responses are correct.
 Chapter 31, 10 th edition Q1.Fungi are organisms. ( Concept 31.1) A) mixotrophic B) chemoautotrophic C) photoheterotrophic D) photoautotrophic E) chemoheterotrophic Q2. fungi absorb nutrients from living
Chapter 31, 10 th edition Q1.Fungi are organisms. ( Concept 31.1) A) mixotrophic B) chemoautotrophic C) photoheterotrophic D) photoautotrophic E) chemoheterotrophic Q2. fungi absorb nutrients from living
Chapter 12. Eukaryotes. Characterizing and Classifying. 8/3/2014 MDufilho 1
 Chapter 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes 8/3/2014 MDufilho 1 General Characteristics of Eukaryotic Organisms Five major groups Protozoa Fungi Algae Water molds Slime molds Include both human
Chapter 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes 8/3/2014 MDufilho 1 General Characteristics of Eukaryotic Organisms Five major groups Protozoa Fungi Algae Water molds Slime molds Include both human
Fungi are absorptive heterotrophs that secrete digestive enzymes and are major decomposers of dead organic material
 Fungi 1 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc The scarlet hood (Hygrocybe coccinea) Fungi are absorptive heterotrophs that secrete digestive enzymes and are major decomposers of dead organic material 2 Animals 3 Myxozoa
Fungi 1 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc The scarlet hood (Hygrocybe coccinea) Fungi are absorptive heterotrophs that secrete digestive enzymes and are major decomposers of dead organic material 2 Animals 3 Myxozoa
CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI
 CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI Name Day M T W Th F Weekly Lifeline Period B_ Check Question What is a parasite? KICK-OFF LEARNING LOG KICK-OFF Response (1) A parasite is an organism that feeds off of another
CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI Name Day M T W Th F Weekly Lifeline Period B_ Check Question What is a parasite? KICK-OFF LEARNING LOG KICK-OFF Response (1) A parasite is an organism that feeds off of another
Kingdom Fungi. The characteristics of fungi The evolution of the fungi Fungal classification
 Kingdom Fungi The characteristics of fungi The evolution of the fungi Fungal classification The Characteristics of Fungi Body form * unicellular * filamentous (tube-like strands called hypha (singular)
Kingdom Fungi The characteristics of fungi The evolution of the fungi Fungal classification The Characteristics of Fungi Body form * unicellular * filamentous (tube-like strands called hypha (singular)
Protists & Fungi. Words to Know: Chapters 19 & 20. Label the paramecium diagram above. (pg. 548)
 Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter24
 1 UNIT 1: FUNGI th Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter24 OBJECTIVES In doing this unit you will look at representatives from several groups of the fungi and learn about the
1 UNIT 1: FUNGI th Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter24 OBJECTIVES In doing this unit you will look at representatives from several groups of the fungi and learn about the
INDEPENDENT STUDY: KINGDOM FUNGI
 INDEPENDENT STUDY: KINGDOM FUNGI Please complete the questions using your textbook as a reference. As you will see, this is not as detailed as your usual Guided Readings and you will have to focus on some
INDEPENDENT STUDY: KINGDOM FUNGI Please complete the questions using your textbook as a reference. As you will see, this is not as detailed as your usual Guided Readings and you will have to focus on some
The Fungi. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
 The Fungi Instructor: George Wong Office: St. John, 612B Phone: X63940 Email: gwong@hawaii hawaii.edu Office Hour: Wednesdays,3:30 Introduction Once upon a time fungi, algae and bacteria were classified
The Fungi Instructor: George Wong Office: St. John, 612B Phone: X63940 Email: gwong@hawaii hawaii.edu Office Hour: Wednesdays,3:30 Introduction Once upon a time fungi, algae and bacteria were classified
Fungi are diverse and widespread They are essential for the well-being of most terrestrial ecosystems because they break down organic material and
 Chapter 31 Fungi Fungi are diverse and widespread They are essential for the well-being of most terrestrial ecosystems because they break down organic material and recycle vital nutrients About 100,000
Chapter 31 Fungi Fungi are diverse and widespread They are essential for the well-being of most terrestrial ecosystems because they break down organic material and recycle vital nutrients About 100,000
A word of caution about a little knowing Lab organisms limit the view of the world of microbiology
 Diversity The world of living things (Figure from Madigan et al. 2002) Microbes in all three domains Two of the domains are exclusively prokaryotic and microbial The third contains both unicellular and
Diversity The world of living things (Figure from Madigan et al. 2002) Microbes in all three domains Two of the domains are exclusively prokaryotic and microbial The third contains both unicellular and
Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus.
 7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
Name: Date: Period: Forms a spore producing structure called an ascus Morals Truffles Yeast
 Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Mid-Year Exam Review
 Biology 504 Mid-Year Exam Review Name: Spontaneous Generation Ch. 2 Heath Biology 1. What is meant by spontaneous generation? Give 3 examples of the appearance of living things that people believed were
Biology 504 Mid-Year Exam Review Name: Spontaneous Generation Ch. 2 Heath Biology 1. What is meant by spontaneous generation? Give 3 examples of the appearance of living things that people believed were
Protists. Plant Like Animal Like Fungus Like. What are the three main groups of protists?*
 Protists & Fungi Protists Single celled or multi-celled organisms that live in moist areas Eukaryotic organisms Characteristics of plants, animals and fungi Grouped in to three main groups* Plant Like
Protists & Fungi Protists Single celled or multi-celled organisms that live in moist areas Eukaryotic organisms Characteristics of plants, animals and fungi Grouped in to three main groups* Plant Like
2/12/2013. Fungi. Figure 37.13
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Fungi Diverse and widespread Break down organic material and recycle vital nutrients About 100,000 species It is estimated there are actually 1.5 million species of fungi Fungi are heterotrophs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Fungi Diverse and widespread Break down organic material and recycle vital nutrients About 100,000 species It is estimated there are actually 1.5 million species of fungi Fungi are heterotrophs
Bell Work. identify the phylum that each character belongs to. Tuesday, February 19, 13
 Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera
Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera Bell Work identify the phylum that each character belongs to Porifera
Chapter 12: EUKARYOTIC MICROBES
 Chapter 12: EUKARYOTIC MICROBES 1. Protista: Algae & Protozoa 2. Fungi 3. Helminths 1. Protista: Algae & Protozoa Chapter Reading pp. 355-363, 374-378, 660-663, 665-666 Overview of the Algae Characteristics
Chapter 12: EUKARYOTIC MICROBES 1. Protista: Algae & Protozoa 2. Fungi 3. Helminths 1. Protista: Algae & Protozoa Chapter Reading pp. 355-363, 374-378, 660-663, 665-666 Overview of the Algae Characteristics
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes. Fungi. Chemoheterotrophic. Have cell walls typically composed of chitin. Do not perform photosynthesis
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
12/28/11. Introduction to Microbiology. Eukaryote microorganisms: The Fungi. Dr A. Fleming
 Lecture Preview: The Fungi What you will learn: 1. Fungi are eukaryotes 2. Usually filamantous (hyphae) 3. Spore bearing Introduction to Microbiology Eukaryote microorganisms: The Fungi 4. Can be pathogenic
Lecture Preview: The Fungi What you will learn: 1. Fungi are eukaryotes 2. Usually filamantous (hyphae) 3. Spore bearing Introduction to Microbiology Eukaryote microorganisms: The Fungi 4. Can be pathogenic
Fungi are heterotrophs and absorb nutrients from outside of their body
 Chapter 31 Fungi Nutrition and Ecology Fungi are heterotrophs and absorb nutrients from outside of their body Fungi use enzymes to break down a large variety of complex molecules into smaller organic compounds
Chapter 31 Fungi Nutrition and Ecology Fungi are heterotrophs and absorb nutrients from outside of their body Fungi use enzymes to break down a large variety of complex molecules into smaller organic compounds
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Protista and Fungi. Fungi. Protista
 Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists:
 VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
STRUCTURE, CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF FUNGI I
 STRUCTURE, CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF FUNGI I Charles Okolie, PhD Room 311 (on level 4), First College Building, Landmark University, Omu-Aran, Kwara State, Nigeria. Internal Tel. extension: 4048
STRUCTURE, CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF FUNGI I Charles Okolie, PhD Room 311 (on level 4), First College Building, Landmark University, Omu-Aran, Kwara State, Nigeria. Internal Tel. extension: 4048
19.1 Diversity of Protists. KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms.
 19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes. Fungi. Chemoheterotrophic. Have cell walls typically composed of chitin. Do not perform photosynthesis
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites. 8th grade
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
2.15 Fungi BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 2.15 Fungi BACKGROUND INFORMATION More than 100 000 species of fungi exist. Fungi are usually classified in four divisions: the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), Zygomycota (bread moulds), Ascomycota (yeasts
2.15 Fungi BACKGROUND INFORMATION More than 100 000 species of fungi exist. Fungi are usually classified in four divisions: the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), Zygomycota (bread moulds), Ascomycota (yeasts
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Rhodophyta. Grateloupia. Dasya. Spyridia. Cryptarachne. Porphyra
 Phaeophyta The brown algae are almost exclusively marine and are very common in the coastal waters of Florida. Many are very large in size, as the kelps of the Pacific coast. Brown algae have walls containing
Phaeophyta The brown algae are almost exclusively marine and are very common in the coastal waters of Florida. Many are very large in size, as the kelps of the Pacific coast. Brown algae have walls containing
Introduction to Fungi True or False
 Introduction to Fungi True or False 1. Fungi are a kingdom in the domain Prokarya. 2. Mushrooms are fungi. 3. Yeasts are fungi. 4. Amoeba are fungi. 5. Fungi have cell walls made of cellulose, just like
Introduction to Fungi True or False 1. Fungi are a kingdom in the domain Prokarya. 2. Mushrooms are fungi. 3. Yeasts are fungi. 4. Amoeba are fungi. 5. Fungi have cell walls made of cellulose, just like
Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus. Early Classification. Living Things
 Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Early Classification Living Things Plants Animals Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Aristotle's Classification Animals Air Dwellers Land Dwellers
Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Early Classification Living Things Plants Animals Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Aristotle's Classification Animals Air Dwellers Land Dwellers
CHAPTER 7 VIRUSES BACTERIA PROTISTS FUNGI
 CHAPTER 7 VIRUSES BACTERIA PROTISTS FUNGI 1 Chapter 7 Objectives: Section 1: 1. List characteristics of viruses and start reasons why viruses are considered to be nonliving 2. Describe the components of
CHAPTER 7 VIRUSES BACTERIA PROTISTS FUNGI 1 Chapter 7 Objectives: Section 1: 1. List characteristics of viruses and start reasons why viruses are considered to be nonliving 2. Describe the components of
Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over
 Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Biology Study Guide. VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards)
 NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Biology Grade 10A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Biology Grade 10A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true
LABORATORY EXERCISES # 15 and #16 WHAT LAND PLANT ADAPTATIONS FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION ARE DERIVED FROM ALGAE AND FUNGI?
 LABORATORY EXERCISES # 15 and #16 WHAT LAND PLANT ADAPTATIONS FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION ARE DERIVED FROM ALGAE AND FUNGI? INTRODUCTION For years, Taxonomists have argued about the number of Kingdoms
LABORATORY EXERCISES # 15 and #16 WHAT LAND PLANT ADAPTATIONS FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION ARE DERIVED FROM ALGAE AND FUNGI? INTRODUCTION For years, Taxonomists have argued about the number of Kingdoms
Groups of Fungi. Section 2
 Groups of Fungi Section 2 Chytrid Fungi Key Idea: The chytrids are a group of aquatic fungi that provide clues about the evolution of fungi. Chytrid Fungi Chytrids were once classified with protists because
Groups of Fungi Section 2 Chytrid Fungi Key Idea: The chytrids are a group of aquatic fungi that provide clues about the evolution of fungi. Chytrid Fungi Chytrids were once classified with protists because
Biology Study Guide. VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards)
 NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
BIO102: Plant Diversity DIVERSITY OF FUNGI
 DIVERSITY OF FUNGI www.bupoyesiku.net ~ 1 ~ Department of Plant Science Contents Topic: Diversity of Fungi...3 Objectives...3 Reading Assignment...3 Lecture...3 Introduction...4 Main Content...4 Background
DIVERSITY OF FUNGI www.bupoyesiku.net ~ 1 ~ Department of Plant Science Contents Topic: Diversity of Fungi...3 Objectives...3 Reading Assignment...3 Lecture...3 Introduction...4 Main Content...4 Background
Unit 4 Protists and Fungi
 Unit 4 Protists and Fungi Objectives Topic 1: Protists Protists are eukaryotes that are not members of the kingdoms, Plantae, Animalia, or Fungi Identify the defining characteristics of animal-like, plant-like
Unit 4 Protists and Fungi Objectives Topic 1: Protists Protists are eukaryotes that are not members of the kingdoms, Plantae, Animalia, or Fungi Identify the defining characteristics of animal-like, plant-like
Laboratory Fungi. 1. Differentiate between common members of the four taxa. 3. Recognize and name some common members of the taxa.
 Laboratory Fungi Fungi are generally classified as absorptive heterotrophs. Approximately 100,000 species have been placed into the basic taxa: chytridiomycota, zygomycota, ascomycota, and basidiomycota.
Laboratory Fungi Fungi are generally classified as absorptive heterotrophs. Approximately 100,000 species have been placed into the basic taxa: chytridiomycota, zygomycota, ascomycota, and basidiomycota.
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P AND CHAPTER 16 P
 BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review! Chapter 31!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Biology 1030 Winter 2009
 Microorganisms Chapter 17 (556-560, 564-565) Chapter 31 (608-623) Chapter 28 (549-569) Microorganisms Bacteria Cyanobacteria Fungi Protists Bacteria Are Wee 1 mm = 1000000 Largest prokaryote is 100000
Microorganisms Chapter 17 (556-560, 564-565) Chapter 31 (608-623) Chapter 28 (549-569) Microorganisms Bacteria Cyanobacteria Fungi Protists Bacteria Are Wee 1 mm = 1000000 Largest prokaryote is 100000
are defined as traits which enhance survival/reproduction. binomial nomenclature discovered penicillin father of paleontology
 Review Questions for Exam 1 are defined as traits which enhance survival/reproduction. is the primary unifying concept in biology. Describe evolution with just three words (like Darwin did). Match the
Review Questions for Exam 1 are defined as traits which enhance survival/reproduction. is the primary unifying concept in biology. Describe evolution with just three words (like Darwin did). Match the
3.1 The Fungi. Why Fungi Are Important. Classification and Phylogeny
 3.1 The Fungi Fungi (singular: fungus) are some of the most common but least visible organisms on Earth. Fungi often grow out of sight underground or within other organisms that may be either dead or alive.
3.1 The Fungi Fungi (singular: fungus) are some of the most common but least visible organisms on Earth. Fungi often grow out of sight underground or within other organisms that may be either dead or alive.
Lecture 3. The fungal cell - II
 Lecture 3 The fungal cell - II Asexual reproduction - formation of conidiospores (mitotic spores) Typical of Ascomycota Induction / suppression of conidiogenesis is controlled by both genetic and environmental
Lecture 3 The fungal cell - II Asexual reproduction - formation of conidiospores (mitotic spores) Typical of Ascomycota Induction / suppression of conidiogenesis is controlled by both genetic and environmental
04/08/52. Some are unicellular. Many reproduce. Hypha wall. Typically haploid Achlorophyllous Chemoheterotrophic. Sugar alcohols
 Eukaryotic Filamentous Some are unicellular Hypha wall Many reproduce Nuvee Prapasarakul Department of Vet Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Microbiology, Chulalongkorn University Mitoch ondria Nuclei
Eukaryotic Filamentous Some are unicellular Hypha wall Many reproduce Nuvee Prapasarakul Department of Vet Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Microbiology, Chulalongkorn University Mitoch ondria Nuclei
Chapter 23 Fungi. Cengage Learning 2016
 Chapter 23 Fungi Fungal Traits and Classification Fungi structure and function Walled cells Spend their lives fixed in place Produce haploid spores by meiosis Heterotrophs that store excess sugar as glycogen
Chapter 23 Fungi Fungal Traits and Classification Fungi structure and function Walled cells Spend their lives fixed in place Produce haploid spores by meiosis Heterotrophs that store excess sugar as glycogen
Biology. Slide 1of 34. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Mushrooms, morels, and truffles, delights of the gourmet,
 26 Kingdom Fungi Fungal spores. The rounded earthstar (Geastrum saccatum) releases a puff of microscopic spores after the sac, which is about 1.3 cm (0.5 in) wide, is hit by a raindrop. This fungus is
26 Kingdom Fungi Fungal spores. The rounded earthstar (Geastrum saccatum) releases a puff of microscopic spores after the sac, which is about 1.3 cm (0.5 in) wide, is hit by a raindrop. This fungus is
Phylum Mucoromycota Subphylum Mucoromycotina
 Phylum Mucoromycota Subphylum Mucoromycotina Mucorales part 1 Terrestrial fungi Fig. 1 RAxML phylogenetic tree of Kingdom Fungi based on the concatenated alignment of 192 conserved orthologous proteins.
Phylum Mucoromycota Subphylum Mucoromycotina Mucorales part 1 Terrestrial fungi Fig. 1 RAxML phylogenetic tree of Kingdom Fungi based on the concatenated alignment of 192 conserved orthologous proteins.
Introduction. Ecosystems would be in trouble without fungi to decompose dead organisms, fallen leaves, feces, and other organic materials.
 Introduction Ecosystems would be in trouble without fungi to decompose dead organisms, fallen leaves, feces, and other organic materials. This decomposition recycles vital chemical elements back to the
Introduction Ecosystems would be in trouble without fungi to decompose dead organisms, fallen leaves, feces, and other organic materials. This decomposition recycles vital chemical elements back to the
Have cell walls Made of
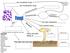 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
Welcome to the World of Fungi
 Welcome to the World of Fungi In the beginning Can you believe that fungi have been around on earth longer than humans? Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Humans have been on earth for about
Welcome to the World of Fungi In the beginning Can you believe that fungi have been around on earth longer than humans? Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Humans have been on earth for about
Lecture XXI Fungi Dr. Kopeny
 Lecture XXI Fungi Dr. Kopeny Delivered 2/18 Lecture outline Fungi -Origins and diversity -Organismal Biology; Vegetative and Reproductive bodies -Ecological Roles and Relationships Freeman (2002) Shelf
Lecture XXI Fungi Dr. Kopeny Delivered 2/18 Lecture outline Fungi -Origins and diversity -Organismal Biology; Vegetative and Reproductive bodies -Ecological Roles and Relationships Freeman (2002) Shelf
Welcome to the World of Fungi
 Welcome to the World of Fungi In the beginning Can you believe that fungi have been around on earth longer than humans? Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Humans have been on earth for about
Welcome to the World of Fungi In the beginning Can you believe that fungi have been around on earth longer than humans? Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Humans have been on earth for about
Chapter 8 THE KINGDOM FUNGI
 Chapter 8 THE KINGDOM FUNGI The words fungus and mold may evoke some unpleasant images. Fungi rot timbers, attack plants, spoil food and afflict humans with athlete s foot and worse maladies. However,
Chapter 8 THE KINGDOM FUNGI The words fungus and mold may evoke some unpleasant images. Fungi rot timbers, attack plants, spoil food and afflict humans with athlete s foot and worse maladies. However,
Chapter 21: Protists
 Chapter 21: Protists Section 1: Characteristics of Protists Gamete: a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another gamete to form a zygote Zygote: the cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 21: Protists Section 1: Characteristics of Protists Gamete: a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another gamete to form a zygote Zygote: the cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Bacteria. The Three Types of Important Heterotrophic Bacteria
 Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
