Diversity in Living Organisms
|
|
|
- Lionel Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter-7 Diversity in Living Organisms Biodiversity means the diversity of life forms. It is a word commonly used to refer to the variety of life forms found in a particular region. Classification helps us in exploring the diversity of life forms. The major characteristics considered for classifying all organisms into five major kingdoms are: (a) whether they are made of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells (b) whether the cells are living singly or organised into multicellular and thus complex organisms (c) whether the cells have a cell-wall and whether they prepare their own food. Biologists, such as Ernst Haeckel (1894), Robert Whittaker (1959) and Carl Woese (1977) have tried to classify all living organisms into broad categories, called kingdoms. The Hierarchy of Classification- Groups: All living organisms are divided on the above bases into five kingdoms, namely Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. These groups are formed on the basis of their cell structure, mode and source of nutrition and body organisation. While Monera is a prokaryotic kingdom, the rest are eukaryotic kingdoms. Woese further devided the Monera into Archaebacteria (or Archaea) and Eubacteria (or Bacteria). MONERA (i) These organisms do not have a defined nucleus or organelles, nor do any of them show multi-cellular body designs. (ii) Some of them have cell walls while some do not. (iii) The mode of nutrition of organisms in this group can be either by synthesising their own food (autotrophic) or getting it from the environment (heterotrophic). (iv) This group includes bacteria, blue-green algae or cyanobacteria, and mycoplasma. PROTISTA (eukaryotic organisms) (i) This group includes many kinds of unicellular eukaryotic organisms. (ii) Some of these organisms use appendages, such as hair-like cilia or whip-like flagella for moving around. (iii) Their mode of nutrition can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. (iv) Examples are unicellular algae, diatoms and protozoans. FUNGI (i) These are heterotrophic eukaryotic organisms. (ii) They use decaying organic material as food and are therefore called saprophytes. (iii) Many of them have the capacity to become multicellular organisms at certain stages in their lives. (iv) (v) They have cell-walls made of a tough complex sugar called chitin. Examples are yeast and mushrooms
2 2 PLANTAE (i) These are multicellular eukaryotes with cell walls. (ii) They are autotrophs and use chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Thus, all plants are included in this group. (iii) Examples: multicellular green plants, advanced algae ANIMALIA (i) These are organisms which are multicellular eukaryotes. (ii) Their cells do not have cell-walls. (iii) They are heterotrophs. (iv) Examples: Multicellular animals. Plantae and Animalia are further divided into subdivisions on the basis of increasing complexity of body organisation. Basis of classification among plants: First level: depends on whether the plant body has well differentiated, distinct components
3 3 Next level: based on whether the differentiated plant body has special tissues for the transport of water and other substances within it. Another level: ability to bear seeds and whether the seeds are enclosed within fruits. Classification among plants: THALLOPHYTA (i) They do not have well-differentiated body design (ii) These plants are predominantly aquatic. (iii) The plants in this group are commonly called algae. (iv) Examples: Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Cladophora and Chara BRYOPHYTA (i) These are called the amphibians of the plant kingdom. (ii) The plant body is commonly differentiated to form stem and leaf-like structures. (iii) There is no specialised tissue for the conduction of water and other substances from one part of the plant body to another. (iv) Examples are moss (Funaria) and Marchantia PTERIDOPHYTA (i) The plant body is differentiated into roots, stem and leaves (ii) has specialised tissue for the conduction of water and other substances from one part of the plant body to another. (iii) Some examples are Marsilea, ferns and horse-tails Please note that the thallophytes, the bryophytes and the pteridophytes have (i) naked embryos that are called spores. (ii) The reproductive organs of plants in all these three groups are very inconspicuous, and they are therefore called cryptogamae, or those with hidden reproductive organs. Please note that (i) plants with well differentiated reproductive tissues that ultimately make seeds are called phanerogams. (ii) Seeds are the result of the reproductive process. (iii) They consist of the embryo along with stored food, which serves for the initial growth of the embryo during germination. (iv) This group is further classified, based on whether the seeds are naked or enclosed in fruits, giving us two groups: gymnosperms and angiosperms.
4 4 GYMNOSPERMS (i) This term is made from two Greek words: gymno means naked and sperma means seed. (ii) The plants of this group bear naked seeds and are usually perennial, evergreen and woody. (iii) Examples are pines, such as deodar ANGIOSPERMS (i) This word is made from two Greek words: angio means covered and sperma means seed. (ii) These are also called flowering plants. (iii) The seeds develop inside an organ which is modified to become a fruit. (iv) Plant embryos in seeds have structures called cotyledons. Cotyledons are called seed leaves because in many instances they emerge and become green when the seed germinates. Thus, cotyledons represent a bit of pre-designed plant in the seed.
5 5 (v) (vi) The angiosperms are divided into two groups on the basis of the number of cotyledons present in the seed. Plants with seeds having a single cotyledon are called monocotyledonous or monocots. Plants with seeds having two cotyledons are called dicots Classification among Animalia: They are classified based on the extent and type of the body design differentiation found. 1. PORIFERA (i) The word means organisms with holes. There are holes or pores, all over the body. (ii) These are animals not capable of movement and are attached to some solid support. (iii) They have a canal system in the body that helps in circulating water throughout the body to bring in food and oxygen. (iv) These animals are covered with a hard outside layer or skeleton. (v) The body design involves very minimal differentiation. (vi) They are commonly called sponges, and are mainly found in marine habitats. (vii) Examples: Euplectelia, Sycon, Spongilla 2. COELENTERATA (i) These are animals living in water. (ii) They show more body design differentiation. (iii) There is a cavity in the body. (iv) The body is made of two layers of cells: one makes up cells on the outside of the body, and the other makes the inner lining of the body. (v) Some of these species live in colonies (corals), while others have a solitary like span (Hydra). Jellyfish and sea anemones are common examples 3. PLATYHELMINTHES (i) The body of these are far more complexly designed. The body is bilaterally symmetrical, meaning that the left and the right halves of the body have the same design. (ii) There are three layers of cells from which differentiated tissues can be made, so such animals are called triploblastic. (iii) There is some degree of tissue formation. However, there is no true internal body cavity, in which well developed organs can be accommodated. (iv) The body is flattened from top to bottom, so these animals are called flatworms. (v) They are either freeliving or parasitic. (vi) Some examples are freeliving animals like planarians, or parasitic animals like liverflukes. 4. NEMATODA (i) The nematode body is also bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. (ii) However, the body is cylindrical rather than flattened. (iii) There are tissues, but no real organs, although a sort of body cavity or a pseudocoelom, is present. (iv) These are very familiar as parasitic worms causing diseases, such as the worms causing elephantiasis (filarial worms) or the worms in the intestines (roundworm or pinworms).
6 6 5. ANNELIDA (i) Annelid animals are also bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic, but in addition they have a true body cavity. (ii) This allows true organs to be packaged in the body structure. There is, thus, extensive organ differentiation. (iii) This differentiation occurs in a segmental fashion, with the segments lined up one after the other from head to tail. (iv) These animals are found in a variety of habitats fresh water, marine water as well as land. Earthworms and leeches are familiar examples 6. ARTHROPODA (i) This is probably the largest group of animals. (ii) These animals are bilaterally symmetrical and segmented. (iii) There is an open circulatory system, and so the blood does not flow in welldefined blood vessels. (iv) The coelomic cavity is blood-filled. They have jointed legs (the word arthropod means jointed legs ). (v) Some familiar examples are prawns, butterflies, houseflies, spiders, scorpions and crabs 7. MOLLUSCA (i) In the animals of this group, there is bilateral symmetry. (ii) The coelomic cavity is reduced. (iii) There is little segmentation. (iv) They have an open circulatory system and kidney-like organs for excretion. (v) There is a foot that is used for moving around. (vi) Examples are snails and mussels. 8. ECHINODERMATA (i) In Greek, echinos means hedgehog, and derma means skin. Thus, these are spiny skinned organisms. (ii) These are exclusively free-living marine animals. (iii) They are triploblastic and have a coelomic cavity. (iv) They also have a peculiar water-driven tube system that they use for moving around. (v) They have hard calcium carbonate structures that they use as a skeleton. Examples are starfish and sea urchins. 9. PROTOCHORDATA (i) These animals are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and have a coelom(internal body cavity). (ii) In addition, they show a new feature of body design, namely a notochord at least at some stages during their lives. (The notochord is a long rod-like support structure (chord=string) that runs along the back of the animal separating the nervous tissue from the gut). (iii) Protochordates are marine animals. (iv) Examples are Balanoglossus, Herdemania and Amphioxus 10. VERTEBRATA (i) These animals have a true vertebral column and internal skeleton, allowing a completely different distribution of muscle attachment points to be used for movement.
7 7 (ii) (iii) (iv) Vertebrates are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomic and segmented, with complex differentiation of body tissues and organs. All chordates possess the following features: have a notochord have a dorsal nerve cord are triploblastic have paired gill pouches are coelomate. Vertebrates are grouped into five classes: Pisces, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammalia Pisces These are fish. They are water living animals. Their skin is covered with scales/plates. They obtain oxygen dissolved in water by using gills. They are cold-blooded They lay eggs Amphibia Respiration is through either gills or lungs. They lay eggs. These animals are found both in water and on land. Frogs, toads and salamanders are some examples 10.3 Reptilia These animals are cold-blooded, have scales and breathe through lungs. While most of them have a three-chambered heart, crocodiles have four heart chambers. They lay eggs with tough coverings. Snakes, turtles, lizards and crocodiles fall in this category 10.4 AVES These are warm-blooded animals and have a four-chambered heart. They lay eggs. There is an outside covering of feathers, and two forelimbs are modified for flight. They breathe through lungs. All birds fall in this category 10.5 Mammals Mammals are warm-blooded animals with four-chambered hearts. They have mammary glands for the production of milk to nourish their young. Their skin has hairs as well as sweat and oil glands. Most mammals familiar to us produce live young ones. However, a few of them, like the platypus and the echidna lay eggs, and some, like kangaroos give birth to very poorly developed young ones.!@#$%^&*()
8 8 Broad classification of Kingdom Animalia based on common fundamental features: The Hierarchy of Classification- Groups: Classification of kingdoms is done by naming the sub-groups at various levels as given in the scheme shown in the picture. Thus, by separating organisms on the basis of a hierarchy of characteristics into smaller and smaller groups, we arrive at the basic unit of classification, which is a species.
9 9 Classification of animals:
10 Salient Features of Different Phyla in the Animal Kingdom: 10 Phylum Level of Organisation Symmetry Coelom Segmentation Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Distinctive Features Porifera Cellular Various Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Body with pores and canals in walls. Coelenterata (Cnidaria) Tissue Radial Absent Absent Incomplete Absent Absent Cnidoblasts present. Platyhelminthes Organ-system Bilateral Absent Absent Incomplete Absent Absent Flat body, suckers. Nematoda Organ-system Bilateral Pseudo coelomate Absent Complete Absent Absent Often worm-shaped, elongated. Annelida Organ-system Bilateral Coelomate Present Complete Present Absent Body segmentation like rings. Arthropoda Organ-system Bilateral Coelomate Present Complete Present Present Exoskeleton of cuticle, jointed appendages. Mollusca Organ-system Bilateral Coelomate Absent Complete Present Present External skeleton of shell usually present. Echinodermata Organ-system Radial Coelomate Absent Complete Present Present Water vascular system, radial symmetry. Hemichordata (Protochordata) Chordata (Vertebrata) Organ-system Bilateral Coelomate Absent Complete Present Present Worm-like with proboscis, collar and trunk. Organ-system Bilateral Coelomate Present Complete Present Present Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, gill slits with limbs or fins.
ATHENA GLOBAL SCHOOL GRADE: IX
 ATHENA GLOBAL SCHOOL GRADE: IX SUB: SCIENCE CHAPTER-7-DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS The Hierarchy of classification: Five kingdom of classification: (i) Monera (ii)protista (iii)fungi (iv)plantae (v)animalia
ATHENA GLOBAL SCHOOL GRADE: IX SUB: SCIENCE CHAPTER-7-DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS The Hierarchy of classification: Five kingdom of classification: (i) Monera (ii)protista (iii)fungi (iv)plantae (v)animalia
Diversity in Living Organisms
 Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Class IX Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms Science
 Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
Diversity in Living Organism
 Diversity in Living Organism Why do we classify organisms? Answer:- There are millions of species on this earth. For anybody, it is impossible to study about each of them in his lifetime. Classification
Diversity in Living Organism Why do we classify organisms? Answer:- There are millions of species on this earth. For anybody, it is impossible to study about each of them in his lifetime. Classification
Downloaded from
 Science For Class IX Diversity in Living Organisms (Q.1) Classification according to habitat was done by: (A) Darwin (B) Aristotle (C) Linnaeus (D) Haeckel (Q.2) The Origin of Species was
Science For Class IX Diversity in Living Organisms (Q.1) Classification according to habitat was done by: (A) Darwin (B) Aristotle (C) Linnaeus (D) Haeckel (Q.2) The Origin of Species was
Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms Science
 Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms Science In Text Questions Page No: 80 1. Why do we classify organisms? : There are millions of organisms on this earth. So, it is harder to study them one by one.
Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms Science In Text Questions Page No: 80 1. Why do we classify organisms? : There are millions of organisms on this earth. So, it is harder to study them one by one.
Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 7 DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS Multiple Choice Questions 1. Find out incorrect sentence (a) Protista includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms (b) Whittaker considered cell structure, mode and
Chapter 7 DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS Multiple Choice Questions 1. Find out incorrect sentence (a) Protista includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms (b) Whittaker considered cell structure, mode and
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS
 KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
Protists. Simple Eukaryotes. Regents Biology Common ancestor. Domain Archaebacteria. Domain Eukaryotes. Domain Bacteria
 Protists Simple Eukaryotes Domain Bacteria Domain Archaebacteria Domain Eukaryotes Regents Biology 2006-2007 Common ancestor General characteristics Classification criteria eukaryotes not animal, plant
Protists Simple Eukaryotes Domain Bacteria Domain Archaebacteria Domain Eukaryotes Regents Biology 2006-2007 Common ancestor General characteristics Classification criteria eukaryotes not animal, plant
Classification. Grouping & Identifying Living Things
 Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Classifying Living Things We put livings things into three Domains Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Which are divided into 6 Kingdoms Plant Animal Fungi Protist
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Classifying Living Things We put livings things into three Domains Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Which are divided into 6 Kingdoms Plant Animal Fungi Protist
Kingdom Animalia. Special Features: Advanced nervous systems means cephalization (faces), brains, and efficient mobility (walk/run/swim/grab)
 Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Cell Number: Multicellular with extensive specialization Cell Type: Eukaryotic Animal Cells (no cell wall) Food: Heterotrophic Carnivore (meat), Herbivore (plants), Omnivore
Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Cell Number: Multicellular with extensive specialization Cell Type: Eukaryotic Animal Cells (no cell wall) Food: Heterotrophic Carnivore (meat), Herbivore (plants), Omnivore
The Case of the Museum Mix-Up Activity Sheet
 Webquest Activity Page 1 The Case of the Museum Mix-Up Activity Sheet Name Part A Use your knowledge about the major plant and animal phyla to help John label the specimens! Remember to use the web resources
Webquest Activity Page 1 The Case of the Museum Mix-Up Activity Sheet Name Part A Use your knowledge about the major plant and animal phyla to help John label the specimens! Remember to use the web resources
Class IX Biology Chapter 7 : Diversity In Living Organisms NCERT Solutions 1. Why do we classify organisms? Ans. By classification of organisms we
 Class IX Biology Chapter 7 : Diversity In Living Organisms NCERT Solutions 1. Why do we classify organisms? Ans. By classification of organisms we keep them in different class, order, family and genus
Class IX Biology Chapter 7 : Diversity In Living Organisms NCERT Solutions 1. Why do we classify organisms? Ans. By classification of organisms we keep them in different class, order, family and genus
GOYAL BROTHERS PRAKASHAN
 Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 7 Diversity in Living Organisms IMPORTANT NOTES 1. There are more than a million kinds of living things exhibiting an infinite variety in form, structure and living
Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 7 Diversity in Living Organisms IMPORTANT NOTES 1. There are more than a million kinds of living things exhibiting an infinite variety in form, structure and living
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
Diversity of Organisms and Classification
 Diversity of Organisms and Classification Essential Vocabulary DNA Prokaryotic: : a cell that lacks a nucleus. Eukaryotic: : a cell that has a nucleus and other complex structures Feeding Autotrophic:
Diversity of Organisms and Classification Essential Vocabulary DNA Prokaryotic: : a cell that lacks a nucleus. Eukaryotic: : a cell that has a nucleus and other complex structures Feeding Autotrophic:
Biology 11. The Kingdom Animalia
 Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Diversity in Living Organism
 Diversity in Living Organism 1 The lowest category of classification is (a) phylum (b) genus (c) species (d) family 2 Prokaryotic organism is found in kingdom. (a) protista (b) fungi, (c) monera (d) plantae
Diversity in Living Organism 1 The lowest category of classification is (a) phylum (b) genus (c) species (d) family 2 Prokaryotic organism is found in kingdom. (a) protista (b) fungi, (c) monera (d) plantae
copyright cmassengale Kingdoms and Classification
 1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
Kingdom. Phylum. Class. Order. Family. Genus. Species
 5.5 - Classification 5.5.1 - Outline the binomial system of nomenclature In this system, each species has two names - a noun and an adjective. The first is the genus, which starts with an upper case letter,
5.5 - Classification 5.5.1 - Outline the binomial system of nomenclature In this system, each species has two names - a noun and an adjective. The first is the genus, which starts with an upper case letter,
Classification of organisms. The grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy: branch of biology that classifies organisms
 Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
not to be republished NCERT C hapter DIVERSITY ORGANISMS Questions Activity What is the Basis of Classification?
 C hapter 7 DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS Have you ever thought of the multitude of life-forms that surround us? Each organism is different from all others to a lesser or greater extent. For instance, consider
C hapter 7 DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS Have you ever thought of the multitude of life-forms that surround us? Each organism is different from all others to a lesser or greater extent. For instance, consider
Kingdom: Animals. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Animals Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor 1 Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell
Kingdom: Animals Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor 1 Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell
Brief Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
 Brief Introduction to the Animal Kingdom Vocabulary Vertebrate Invertebrate Detritivore Asymmetry Bilateral symmetry Radial symmetry Cephalization Coelum Pseudocoelum Acoelomates Blastula Blastophore Protosome
Brief Introduction to the Animal Kingdom Vocabulary Vertebrate Invertebrate Detritivore Asymmetry Bilateral symmetry Radial symmetry Cephalization Coelum Pseudocoelum Acoelomates Blastula Blastophore Protosome
UNITY AND DIVERSITY. Why do we classify things? Organizing the world of organsims. The Tree of Life
 Classification Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! Organisms are classified
Classification Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! Organisms are classified
Today: Animal Body Plans. Animal Body Plans: The Gut. The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Animal Body Plans: Symmetry
 Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Kingdoms and Domains. Lisa Michalek
 Kingdoms and Domains Lisa Michalek The Kingdoms of Life Biologists have organized living things into large groups called Kingdoms. Biologists group organisms into six Kingdoms based on RNA and DNA sequencing
Kingdoms and Domains Lisa Michalek The Kingdoms of Life Biologists have organized living things into large groups called Kingdoms. Biologists group organisms into six Kingdoms based on RNA and DNA sequencing
Tuesday February 26, 2013 Invertebrate Animals Animals: Multicellular, no cell wall or chlorophyll, eukaryotic, heterotrophs
 Name: Class: Biology Weekly Packet February 25 th - March 1 st, 2013 Monday February 25, 2013 Catalyst Tuesday February 26, 2013 Invertebrate Animals Animals: Multicellular, no cell wall or chlorophyll,
Name: Class: Biology Weekly Packet February 25 th - March 1 st, 2013 Monday February 25, 2013 Catalyst Tuesday February 26, 2013 Invertebrate Animals Animals: Multicellular, no cell wall or chlorophyll,
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Biology B. There are no objectives for this lesson.
 Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Invertebrate Diversity
 CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
A. Why Classify? 1. organization makes it easier to understand and find information 2. taxonomy scientists classify organisms and assign each
 Classification A. Why Classify? 1. organization makes it easier to understand and find information 2. taxonomy scientists classify organisms and assign each organism a universally accepted name by using
Classification A. Why Classify? 1. organization makes it easier to understand and find information 2. taxonomy scientists classify organisms and assign each organism a universally accepted name by using
Characteristics of Animals
 Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE
 BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS There are two general types of cell - the animal cell and the plant cell. The animal cell is the most basic with the fewest parts. The plant
BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS There are two general types of cell - the animal cell and the plant cell. The animal cell is the most basic with the fewest parts. The plant
Are these organisms. animals or not?
 1 2 3 4 5 Are these organisms 6 7 8 animals or not? 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Typical Animal Characteristics Eukaryotic Multicellular Ability to move Reproduce Obtain food (heterotrophic)
1 2 3 4 5 Are these organisms 6 7 8 animals or not? 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Typical Animal Characteristics Eukaryotic Multicellular Ability to move Reproduce Obtain food (heterotrophic)
Biological Kingdoms. An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things
 Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport
 Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Sponges. What is the sponge s habitat. What level of organization do sponges have? Type of symmetry?
 Sponges What is the sponge s habitat Marine (few freshwater species) What level of organization do sponges have? Cell level Type of symmetry? None Type of digestive system (none, complete or incomplete)?
Sponges What is the sponge s habitat Marine (few freshwater species) What level of organization do sponges have? Cell level Type of symmetry? None Type of digestive system (none, complete or incomplete)?
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
What defines the zygote, the blastula, and the gastrula? Draw pictures.
 What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
Introduction to Animal Kingdom. Invertebrates and Vertebrates
 Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
WHAT AM I? Classification. Game
 WHAT AM I? Classification Game Slide will provide information your opponent might need in order to determine if you are correct or not, which might include the following: KINGDOM PLANTAE : Palm Tree Eukaryotic
WHAT AM I? Classification Game Slide will provide information your opponent might need in order to determine if you are correct or not, which might include the following: KINGDOM PLANTAE : Palm Tree Eukaryotic
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Characteristics of Living Organisms o Movement o Respiration o Sensitivity o Growth o Reproduction o Excretion o
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Characteristics of Living Organisms o Movement o Respiration o Sensitivity o Growth o Reproduction o Excretion o
23.1 Animal Characteristics EQ Although diverse, what common characteristics do all animal share?
 23.1 Animal Characteristics EQ Although diverse, what common characteristics do all animal share? Sea Slug 23.1 Animal Characteristics Animals are the most physically diverse kingdom of organisms and all
23.1 Animal Characteristics EQ Although diverse, what common characteristics do all animal share? Sea Slug 23.1 Animal Characteristics Animals are the most physically diverse kingdom of organisms and all
Monday, 03 February 2014
 Monday, 03 February 2014 Species diversity: the number of different species and the number of individuals of each species within any one community. Genetic diversity: the variety of genes possessed by
Monday, 03 February 2014 Species diversity: the number of different species and the number of individuals of each species within any one community. Genetic diversity: the variety of genes possessed by
Kingdom Animalia. Zoology the study of animals
 Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Animal Kingdom Characteristics
 ANIMAL KINGDOM Animal Kingdom Characteristics 1. No Cell Wall 2. Symmetry 3. Body Symmetry 4. Heterotrophic and Motility 5. Survival Behavior and Adaptations 6. Diploid Reproduction 7. Multicellular formation
ANIMAL KINGDOM Animal Kingdom Characteristics 1. No Cell Wall 2. Symmetry 3. Body Symmetry 4. Heterotrophic and Motility 5. Survival Behavior and Adaptations 6. Diploid Reproduction 7. Multicellular formation
WHAT AM I? Classification. Game
 WHAT AM I? Classification Game GAME INSTRUCTIONS 1. Get an ipad and scorecard 2. Pick your teams (2 against 2 OR 1 against 1) & choose who will play first 3. Pull up game slides on teacher website 4. The
WHAT AM I? Classification Game GAME INSTRUCTIONS 1. Get an ipad and scorecard 2. Pick your teams (2 against 2 OR 1 against 1) & choose who will play first 3. Pull up game slides on teacher website 4. The
Chapter 33: Invertebrates
 Name Period Chapters 31, 32, and 33 should be considered as a single unit, and you should try to put all of them together in a single conceptual framework. Due to the scope of our course, you are likely
Name Period Chapters 31, 32, and 33 should be considered as a single unit, and you should try to put all of them together in a single conceptual framework. Due to the scope of our course, you are likely
GENERAL TOPIC SPECIFIC TOPIC
 SUBJECT: TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: DURATION: GENERAL TOPIC: SPECIFIC TOPIC: Integrated Science Mr. S. Campbell 7 2 wks Grouping Grouping- Plants And Animals Grouping- Plants And Animals Students will be able
SUBJECT: TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: DURATION: GENERAL TOPIC: SPECIFIC TOPIC: Integrated Science Mr. S. Campbell 7 2 wks Grouping Grouping- Plants And Animals Grouping- Plants And Animals Students will be able
Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Understands that kingdoms are subdivided into phylum etc.
 August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
Classification Chapter 18
 Classification Chapter 18 The domain system Prokaryotic domains Bacteria and Archaea Eukaryotes Are in the domain Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Earliest organisms Prokaryotes Eukoryotes Figure 15.10B
Classification Chapter 18 The domain system Prokaryotic domains Bacteria and Archaea Eukaryotes Are in the domain Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Earliest organisms Prokaryotes Eukoryotes Figure 15.10B
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things
 Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
Month Content Skills Next Generation and Louisville Standards
 August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
Eukaryote Phylogeny. Glycogen. Kingdom Animalia. Amoebozoa Animalia. Plantae. Chromalveolata Rhizaria. Fungi. Excavata
 Eukaryote Phylogeny most protozoans, brown algae, & water molds Excavata Chromalveolata Rhizaria Plantae Amoebozoa Animalia Fungi cpsts. w/ 2 memb. chitin, hyphae glycogen eukaryotic cells (nucleus, etc.)
Eukaryote Phylogeny most protozoans, brown algae, & water molds Excavata Chromalveolata Rhizaria Plantae Amoebozoa Animalia Fungi cpsts. w/ 2 memb. chitin, hyphae glycogen eukaryotic cells (nucleus, etc.)
Lab 6: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Bio 10 Lab #6 1 Animal Kingdom Major characteristics: Lab 6: An Introduction to Animal Diversity Most people, when they think of animals, think of those similar to ourselves: dogs, cats, horses, apes,
Bio 10 Lab #6 1 Animal Kingdom Major characteristics: Lab 6: An Introduction to Animal Diversity Most people, when they think of animals, think of those similar to ourselves: dogs, cats, horses, apes,
What Is an Animal? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. About 98 percent of all animals are invertebrates. The Kingdom Animalia
 What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
Classification. copyright cmassengale
 Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Classification. The three-domains. The six-kingdom system. The traditional five-kingdom system. Bacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Classification The three-domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya The six-kingdom system Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia The traditional five-kingdom system Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
Classification The three-domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya The six-kingdom system Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia The traditional five-kingdom system Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch Animals Invertebrates
 Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch 10-11 Animals Invertebrates Write the correct word in the blanks to show directions on an animal body: ** Word Bank (Posterior, Ventral, Dorsal, Anterior) top surface front
Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch 10-11 Animals Invertebrates Write the correct word in the blanks to show directions on an animal body: ** Word Bank (Posterior, Ventral, Dorsal, Anterior) top surface front
PSI Biology Classification Classification
 Classification Classification & Naming Classwork 1. What is the correct order of the current classification hierarchy, from most general to most specific? 2. Are two organisms in domain more or less closely
Classification Classification & Naming Classwork 1. What is the correct order of the current classification hierarchy, from most general to most specific? 2. Are two organisms in domain more or less closely
Biology. Slide 1 / 47. Slide 2 / 47. Slide 3 / 47. Classification
 Slide 1 / 47 Slide 2 / 47 Biology lassification 2015-10-28 www.njctl.org 1 Which of the following accurately lists the levels of classification in our current taxonomic system? Slide 3 / 47 A Phylum, kingdom,
Slide 1 / 47 Slide 2 / 47 Biology lassification 2015-10-28 www.njctl.org 1 Which of the following accurately lists the levels of classification in our current taxonomic system? Slide 3 / 47 A Phylum, kingdom,
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY
 INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
The BIOTIC Component
 The BIOTIC Component Ecology = the study of organisms and their interaction with their environment Environment includes abiotic components and processes: light rainfall temperature humidity topography
The BIOTIC Component Ecology = the study of organisms and their interaction with their environment Environment includes abiotic components and processes: light rainfall temperature humidity topography
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Moving Forward Quizlet Each section we cover, 1 group will go to our class on Quizlet and create 20 flash cards on the topic (/5mks) If I warn you about talking while I m talking,
Introduction to Animals Moving Forward Quizlet Each section we cover, 1 group will go to our class on Quizlet and create 20 flash cards on the topic (/5mks) If I warn you about talking while I m talking,
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
California Biology Handbook... CA1
 California Biology Handbook........................... CA1 The California Biology Handbook includes correlations of the Biology/Life Science standards to the content in Biology: The Dynamics of Life. Also
California Biology Handbook........................... CA1 The California Biology Handbook includes correlations of the Biology/Life Science standards to the content in Biology: The Dynamics of Life. Also
Chps : Animals. Characteristics of kingdom Animalia: Multicellular Heterotrophic Most are motile Possess sense organs
 Chps 23-26: Animals Chps. 23-27: Animals Characteristics of kingdom Animalia: Multicellular Heterotrophic Most are motile Possess sense organs Animal Characteristics Forms of symmetry: Radial Bilateral
Chps 23-26: Animals Chps. 23-27: Animals Characteristics of kingdom Animalia: Multicellular Heterotrophic Most are motile Possess sense organs Animal Characteristics Forms of symmetry: Radial Bilateral
Name: Date: ID: 3. What are some limitations to scientific models? - Most models include simplifications, approximations, and/or lack details
 Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
Pre-AP BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SPRING
 Terms to define: Classification Phylogeny Cladogram binomial nomenclature Taxonomy Natural Selection vestigial structures homologous structures analogous structures Genetic Drift Allele Frequency Homozygous
Terms to define: Classification Phylogeny Cladogram binomial nomenclature Taxonomy Natural Selection vestigial structures homologous structures analogous structures Genetic Drift Allele Frequency Homozygous
Introduction to Animal Diversity. Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
1.1 Characteristics of Life Block: Date:
 Biology 12 Name: 1.1 Characteristics of Life Block: Date: ization of Life (p. 3) Definition Cell Example Blood cell Tissue Muscle tissue Several tissues joined together to form a function system Circulatory
Biology 12 Name: 1.1 Characteristics of Life Block: Date: ization of Life (p. 3) Definition Cell Example Blood cell Tissue Muscle tissue Several tissues joined together to form a function system Circulatory
A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1
 Name A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1 AP WINTER BREAK ASSIGNMENT (CH 25-34). Complete the questions using the chapters of your textbook Campbell s Biology (8 th edition). CHAPTER 25: The History of
Name A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1 AP WINTER BREAK ASSIGNMENT (CH 25-34). Complete the questions using the chapters of your textbook Campbell s Biology (8 th edition). CHAPTER 25: The History of
Domains and Kingdoms
 Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES SAMPLE. Biology. Secondary Science 7B. Years 7 9. Written by Valerie Marett. CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 542
 AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Biology Secondary Science 7B Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 542 Science for Secondary Students 7B Biology Contents Living and Non-Living
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Biology Secondary Science 7B Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 542 Science for Secondary Students 7B Biology Contents Living and Non-Living
Features of the Animal
 Features of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Even though members of the animal kingdom are incredibly diverse, animals share common features that distinguish them from organisms in other kingdoms.
Features of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Even though members of the animal kingdom are incredibly diverse, animals share common features that distinguish them from organisms in other kingdoms.
Topic 5 (Student) 5.3 Classification of biodiversity
 Topic 5 (Student) 5.3 Classification of biodiversity 5.3 Nature of science: Cooperation and collaboration between groups of scientists scientists use the binomial system to identify a species rather than
Topic 5 (Student) 5.3 Classification of biodiversity 5.3 Nature of science: Cooperation and collaboration between groups of scientists scientists use the binomial system to identify a species rather than
Have cell walls Made of
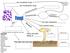 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
LIFE ON EARTH I CHARACTERISTICS OF THE LIVING
 1 LIFE ON EARTH I CHARACTERISTICS OF THE LIVING I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Which one is not a unicellular organism? (a) Bacteria (b) Mushroom (c) Yeast (d) Amoeba 2.
1 LIFE ON EARTH I CHARACTERISTICS OF THE LIVING I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Which one is not a unicellular organism? (a) Bacteria (b) Mushroom (c) Yeast (d) Amoeba 2.
BIOLOGY. Classification & Phylogeny. Slide 1 / 92. Slide 2 / 92. Slide 3 / 92. Vocabulary Click on each word below to go to the definition.
 Slide 1 / 92 Slide 2 / 92 BIOLOGY Classification & Phylogeny April 2013 www.njctl.org Vocabulary Click on each word below to go to the definition. Slide 3 / 92 acoelomate angiosperm bilateral symmetry
Slide 1 / 92 Slide 2 / 92 BIOLOGY Classification & Phylogeny April 2013 www.njctl.org Vocabulary Click on each word below to go to the definition. Slide 3 / 92 acoelomate angiosperm bilateral symmetry
Intro to Animals. Chapter 32
 Intro to Animals Chapter 32 1) Multicellular Organization (Different cells have different functions) Specialization: adaptation of a cell for a particular function Remember: cells tissues organs organ
Intro to Animals Chapter 32 1) Multicellular Organization (Different cells have different functions) Specialization: adaptation of a cell for a particular function Remember: cells tissues organs organ
Final Exam Study Guide. Evolution
 Name: Biology I A Final Exam Study Guide Date: Mr. Tiesler Evolution An adaptation is a physical or behavioral change that improves a population s ability to survive. Evolution is the process by which
Name: Biology I A Final Exam Study Guide Date: Mr. Tiesler Evolution An adaptation is a physical or behavioral change that improves a population s ability to survive. Evolution is the process by which
Unit 10: Animals Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity 1. Define the following
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity 1. Define the following
A. Carranza Physiology Study Guide Bio 10
 Plants Types (gradual adaptations to land) Byrophytes: Mosses, hornwart, liverwarts Development of cuticle to conserve water Ferns, lycophytes and horsetails Cuticle plus rudimentary vascular and root
Plants Types (gradual adaptations to land) Byrophytes: Mosses, hornwart, liverwarts Development of cuticle to conserve water Ferns, lycophytes and horsetails Cuticle plus rudimentary vascular and root
Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet Chapter 33 Introduction to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia: 1. Approximately how many different animal species are alive on Earth currently. How many those species have
Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet Chapter 33 Introduction to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia: 1. Approximately how many different animal species are alive on Earth currently. How many those species have
Zoology. Classification
 Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER
 SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER 1-2018 NAME: GRADE: 5 ( ) DATE: 1 QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: Air sacs, arthropods, Cytoplasm,
SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER 1-2018 NAME: GRADE: 5 ( ) DATE: 1 QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: Air sacs, arthropods, Cytoplasm,
The Evolution of Animal Diversity. Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University
 The Evolution of Animal Diversity Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University Create your own animal? Start with a basic plant. Make the plant into a simple animal such as a worm. Consider:
The Evolution of Animal Diversity Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University Create your own animal? Start with a basic plant. Make the plant into a simple animal such as a worm. Consider:
Due Friday, January 11, 2008
 Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics. I. Characteristics of Animals. Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen
 What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM. Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna
 KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
Organizing Life s Diversity
 17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups. Mrs. Hilliard
 Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Marks -40 Theory Classes Section- First Botany Systematic and binomial system of nomenclature - meaning of the terms taxonomy, systematics,
 Sr..No. 1. 1.1 Agril. Polytechnic Syllabus First Year Subject :- (C) Biology I (Theory) Reference Book :- Biology Std XI Publisher :- Secretary, Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary
Sr..No. 1. 1.1 Agril. Polytechnic Syllabus First Year Subject :- (C) Biology I (Theory) Reference Book :- Biology Std XI Publisher :- Secretary, Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary
BIOS1101 Lab Notes. Contents ANIMALS. Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates. Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates
 Contents ANIMALS Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates Lab 3: Animal Structure 1 Gross morphology Lab 4: Animal Structure 2 Histology Lab 5: The Nervous System & Sensory
Contents ANIMALS Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates Lab 3: Animal Structure 1 Gross morphology Lab 4: Animal Structure 2 Histology Lab 5: The Nervous System & Sensory
Classifying Animals. Teacher s Guide Middle School. Visual Learning Company Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome
 eacher s Guide Middle School Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Graphics: Dean Ladago red hodal Visual Learning Company 1-800-453-8481 www.visuallearningco.com
eacher s Guide Middle School Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Graphics: Dean Ladago red hodal Visual Learning Company 1-800-453-8481 www.visuallearningco.com
