Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis
|
|
|
- Delilah Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis
2 Advanced - Station 1 1.What are the levels of organization in order from smallest to largest? 2. What is the pattern in the levels of organization? 2. The patterns in the levels of organization is.
3 Advanced - Station 2 1. What levels of organization make up an organelle? 1. An organelle is made up of. 2. Describe the different between a compound and molecules. 1. Compounds are.. While molecules.. 3. What is the relationship between cells and tissue? 1. The relationship between cells and tissue.
4 Station 3 1. What are the three postulates of the Cell Theory. 1. The three parts of the cell theory are What evidence supports the cell theory? 1. Evidence that supports the cell theory is.. 3. Can the information in the Cell Theory explain metal? Explain. 1. Information in the cell theory explain metal because.
5 Station 4 1. Define homeostasis. 1. Homeostasis is 2. How does an ecosystem maintain homeostasis? 1. An ecosystem maintains homeostasis by.. 3. A biotic factor is a worm or llama. An abiotic factor is the sun or rocks. Define biotic factor. Define abiotic factor. 1. A biotic factor is 2. An abiotic factor is..
6 Advanced - Station 5 1. How do the cells in a person s body help them in homeostasis? 1. A person s cells help maintain homeostasis by. 2. What organelles are involved in removing waste from the cell? 1. Organelles involved in removing waste are 3. Describe the different between exocytosis and autophagy.
7 Advanced - Station 6 1.Write and fill in the chart below Location - Organelle Process Purpose Mitochondria Photosynthesis
8 Advanced Station 7 1. What is the function of the Stoma? 2. Compare and contrast transpiration in plants to respiration in animals?
9 Station 8 1. Why is photosynthesis only found in plants? 2. How are the following terms related? Mitochondria, carbon dioxide, photosynthesis
10 Station 9 1. What process creates energy for the cell? 2. How could the cytoplasm and vacuoles be similar?
11 Station How are the ER, ribosomes, and Golgi apparatus related? 2. How are the cytoplasm and vacuoles similar? 3. If carnivorous plants consume insects why do they still need a chloroplast?
12 Answers
13 Advanced - Station 1 1. What are the levels of organization in order from smallest to largest? 1. Atoms, elements, molecules, compounds, cells, tissue, organ, organ system, organisms 2. What is the pattern in the levels of organization? 2. The patterns in the levels of organization is the smaller levels make up the larger levels.
14 Advanced - Station 2 1. What levels of organization make up an organelle? 1. An organelle is made up of atoms, elements, molecules, and compounds 2. Describe the different between a compound and molecules. 1. Compounds are made up of different elements (CO2) While molecules are made up of the same elements (O2) 3. What is the relationship between cells and tissue? 1. The relationship between cells and tissue are similar cells working together create tissue.
15 Station 3 1. What are the three postulates of the Cell Theory. 1. The three parts of the cell theory are 1. Cells make up all living things 2. Cells come from other cells 3. Cells are the basic (smallest) unit of life 2. What evidence supports the cell theory? 1. Evidence that supports the cell theory is looking at plants, animals, insects, bacteria, etc all have cells However, things that are not alive and never have been alive do not have cells. 3. Can the information in the Cell Theory explain metal? Explain. 1. Information in the cell theory can not explain metal because metal is not alive.
16 Station 4 1. Define homeostasis. 1. Homeostasis is keeping internal stable conditions. 2. How does an ecosystem maintain homeostasis? 1. An ecosystem maintains homeostasis by having enough food for the animals, enough water, shelter, not having too many predators, etc. 3. A biotic factor is a worm or llama. An abiotic factor is the sun or rocks. Define biotic factor. Define abiotic factor. 1. A biotic factor is living things 2. An abiotic factor is non-living things
17 Advanced - Station 5 1. How do the cells in a person s body help them in homeostasis? 1. person s cells help maintain homeostasis by 1. removing waste 2. reproducing and making more cells 3. breaking down glucose to make energy What organelles are involved in removing waste from the cell? 2. Organelles involved in removing waste are vacuoles, cytoplasm, cell membrane, lysosomes. 2. Describe the different between exocytosis and autophagy. 1. Exocytosis the waste is removed from the cell. Autophagy the waste or cell parts are recycled.
18 Advanced - Station 6 1.Write and fill in the chart below Location - Organelle Process Purpose Chlorplast Photosynthesis To make glucose or food for the plant Mitochondria Celluar Respiraiton To convert the glucose and oxygen into energy
19 Advanced Station 7 1. What is the function of the Stoma? 1. Stomas bring in CO2 and release Oxygen and water. 2. Compare and contrast transpiration in plants to respiration in animals? 1. Both transpiration and respiration is the release of gases and water. Transpiration is the intake of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen, while respiration is the intake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide.
20 Station 8 1. Why is photosynthesis only found in plants? 1. Plants have to make their food (sugar / glucose) to get energy and photosynthesis is the process that makes the food. 2. How are the following terms related? Mitochondria, carbon dioxide, photosynthesis Photosynthesis makes glucose, and oxygen which is used in the mitochondria to make energy for the cell and release CO2
21 Station 9 1. What process creates energy for the cell? 1. Cellular respiration 2. How could the cytoplasm and vacuoles be similar? 1. Both are used in exocytosis 2. The cytoplasm stores and holds things together in the cell, vacuoles stores things inside it self
22 Station How are the ER, ribosomes, and Golgi apparatus related? 1. The ribosomes read the DNA from the nucleus. The ER helps ribosomes make proteins. The Golgi apparatus receives and ships the proteins and other substances from the ER. 2. How are the cytoplasm and vacuoles similar? 3. If carnivorous plants consume insects why do they still need a chloroplast? 1. There is no guarantee that they will catch enough insects and get enough nutrients. By still having the chloroplast they can make food for themselves and get extra energy by breaking down insects.
Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis
 Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis Homeostasis - maintenance of internal stable conditions in a constantly changing environment that are necessary for life's functions Maintaining
Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis Homeostasis - maintenance of internal stable conditions in a constantly changing environment that are necessary for life's functions Maintaining
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Turns sunlight, water & carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into sugar & oxygen through photosynthesis
 CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
Structures and Functions of Plant and Animal Cells
 Structures and Functions of Plant and Animal Cells 7.L.1.2 - Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts,
Structures and Functions of Plant and Animal Cells 7.L.1.2 - Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts,
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Unit 2: Cells. Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions
 Unit 2: Cells Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions Vocabulary Cell Chloroplast Tissue Cell wall Organ Lysosome
Unit 2: Cells Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions Vocabulary Cell Chloroplast Tissue Cell wall Organ Lysosome
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Tuesday, February 9, 16
 Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Discovery of the Cell
 Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cellular Transportation & Respiration
 Cellular Transportation & Respiration Passive Transport A cell membrane is semiperamble, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. Passive transport is the movement of
Cellular Transportation & Respiration Passive Transport A cell membrane is semiperamble, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. Passive transport is the movement of
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
The Cell. The basic unit of all living things
 The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
Warm-Up. Answer the following questions in a complete sentence and explain why each answer is correct.
 Warm-Up Answer the following questions in a complete sentence and explain why each answer is correct. Unlike a eukaryotic cell, a prokaryotic does not have A. DNA. B. a cell membrane. C. cytoplasm. D.
Warm-Up Answer the following questions in a complete sentence and explain why each answer is correct. Unlike a eukaryotic cell, a prokaryotic does not have A. DNA. B. a cell membrane. C. cytoplasm. D.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification
 Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles
 BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
It helps scientists understand the workings of the human body and of other animals and plants
 Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
A D A E J (L) J(s) K L
 I A E A D G C B C F G E F H B J (L) H K L J(s) Animal Cells Less Support Needed Large, multicellular organisms made of animal cells often have support systems such as bones or exoskeletons Plant and Animal
I A E A D G C B C F G E F H B J (L) H K L J(s) Animal Cells Less Support Needed Large, multicellular organisms made of animal cells often have support systems such as bones or exoskeletons Plant and Animal
Topic 1.1 Characteristics of Living Things
 Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Topic 1.1 Characteristics of Living Things DIRECTIONS: In the textbook, read Unit 1 Topics 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. Once you are done, answer the questions below. To check your understanding
Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Topic 1.1 Characteristics of Living Things DIRECTIONS: In the textbook, read Unit 1 Topics 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. Once you are done, answer the questions below. To check your understanding
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
 BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
Name: Period: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ Cell Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover a.
Name: Period: _ Date: _ Cell Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover a.
Cell Structure and Function. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Honors Biology summer assignment. Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class
 Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Sunday, November 8, 15
 Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
The Cell Theory. Prokaryotic (Pre) ( Nucleus) Cells 10/28/2013. Types of Cells. All living things have cells. Always single- celled lacks organelles
 Types of Cells Cells 1. I can explain the cell theory The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced
Types of Cells Cells 1. I can explain the cell theory The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards
 Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
 Cell Dairy Farm 1. Pens and corrals The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnecting flattened tunnels which are attached to the outer membrane of the nucleus. The ER is the transport network
Cell Dairy Farm 1. Pens and corrals The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnecting flattened tunnels which are attached to the outer membrane of the nucleus. The ER is the transport network
Biology Semester One Final Exam Review
 Biology Semester One Final Exam Review PART ONE: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1) Define Biology. (Remember to break words down into the prefix and suffix to determine the meaning if needed.) The study of life
Biology Semester One Final Exam Review PART ONE: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1) Define Biology. (Remember to break words down into the prefix and suffix to determine the meaning if needed.) The study of life
Parts of the Cell book pgs
 Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS SIMILARITIES IN PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized
The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called. ecology.
 The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called ecology. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is
The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called ecology. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is
B05 comparison of plant and animal cells.notebook. November 22, 2012
 Worksheet:List of Cell Organelles and Functions Instructions: After watching the video, complete the following table http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o1gqycijata&feature=related Organelle Location Function
Worksheet:List of Cell Organelles and Functions Instructions: After watching the video, complete the following table http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o1gqycijata&feature=related Organelle Location Function
1. Why are keystone species good? 2. What kind of solution does water ALWAYS move towards? 3. Do plant cells have mitochondria? Why? 4.
 1. Why are keystone species good? 2. What kind of solution does water ALWAYS move towards? 3. Do plant cells have mitochondria? Why? 4. What happens to sugars produced during photosynthesis? 5. How does
1. Why are keystone species good? 2. What kind of solution does water ALWAYS move towards? 3. Do plant cells have mitochondria? Why? 4. What happens to sugars produced during photosynthesis? 5. How does
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Biology Test Review Science 8
 Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Focus on 5. Newton s Laws of Inertia
 Focus on 5 Newton s Laws of Inertia Newton s First Law Objects at rest do not move unless something moves it. Objects in motion do not stop unless something stops it. Newton s Second Law Force = mass times
Focus on 5 Newton s Laws of Inertia Newton s First Law Objects at rest do not move unless something moves it. Objects in motion do not stop unless something stops it. Newton s Second Law Force = mass times
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES Cell Theory 1. All living things 2. Cells are the. 3. Cells are produced All Living things have cells a. Unicellular b. Multicellular Types of Cells a. Prokaryote: i.
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES Cell Theory 1. All living things 2. Cells are the. 3. Cells are produced All Living things have cells a. Unicellular b. Multicellular Types of Cells a. Prokaryote: i.
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review
 Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Cells: 2 Star. 7. The diagram below represents a cell.
 ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com
 Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/12/2016 65A Warm-Up Tuesday A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student s average speed in
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/12/2016 65A Warm-Up Tuesday A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student s average speed in
CELL STRUCTURE. What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide?
 CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
Biology Semester 1 Study Guide
 Biology Semester 1 Study Guide Part 1: Scientific Investigations You are conducting an experiment to determine if increased UV radiation from the decrease in the ozone layer is killing off frog tadpoles.
Biology Semester 1 Study Guide Part 1: Scientific Investigations You are conducting an experiment to determine if increased UV radiation from the decrease in the ozone layer is killing off frog tadpoles.
7 Characteristics of Life
 7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Cell Theory. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century!
 Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Cell Structure: Organelles. Unit Seventh Grade
 Cell Structure: Organelles Unit 3 --- Seventh Grade Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing. Your body contains trillions of cells.
Cell Structure: Organelles Unit 3 --- Seventh Grade Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing. Your body contains trillions of cells.
1. Cell Theory Organelle containing the genetic information of the cell.
 GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
 All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
protein synthesis cell theory Centrioles specialization. unicellular ribosomes. mitochondria cell interdependence prokaryotes
 All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
2. What is Energy? A. The ability to do work B. The Sun C. The Earth D. Photosynthesis
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Pre/Post-Test Score /100 Standards Assessed: SC.6.L.14.3 Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes to maintain homeostasis, including
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Pre/Post-Test Score /100 Standards Assessed: SC.6.L.14.3 Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes to maintain homeostasis, including
Cell Structure and Function How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive?
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic. Record
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic. Record
SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1
 OBJECTIVE: INTRODUCE BIOLOGY AND REVIEW SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1 ON THE WHITEBOARDS! Brainstorm about what you remember about cells What you know about them (choose a colour) What you sort of remember
OBJECTIVE: INTRODUCE BIOLOGY AND REVIEW SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1 ON THE WHITEBOARDS! Brainstorm about what you remember about cells What you know about them (choose a colour) What you sort of remember
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words is the closest in meaning to the word structure? a. evidence c. duty b. shape d. location Complete each
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words is the closest in meaning to the word structure? a. evidence c. duty b. shape d. location Complete each
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
Biology Midterm Review
 Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Lapbook Pre-test. SC.912.L.18.7: Identify the reactants, products, and basic functions of photosynthesis.
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Lapbook Pre-test Covers Standards: SC.912.L.18.7: Identify the reactants, products, and basic functions of photosynthesis. SC.912.L.18.8: Identify the reactants,
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Lapbook Pre-test Covers Standards: SC.912.L.18.7: Identify the reactants, products, and basic functions of photosynthesis. SC.912.L.18.8: Identify the reactants,
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function
 BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different?
 Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Module 6 Note Taking Guide. Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life
 Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Cells. basic structure of life
 Cells basic structure of life Cells are the smallest unit of life Cells (the smallest unit of life)- make up all living things, including your own body. Cells can differ in shape and sizes. The different
Cells basic structure of life Cells are the smallest unit of life Cells (the smallest unit of life)- make up all living things, including your own body. Cells can differ in shape and sizes. The different
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 CELL THEORY & FUNCTION DISCOVERY OF THE CELL Can t see cells, so who knew they existed? Discovered after the microscope was invented. Mid 1600s when scientists began using microscopes Robert Hooke
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION DISCOVERY OF THE CELL Can t see cells, so who knew they existed? Discovered after the microscope was invented. Mid 1600s when scientists began using microscopes Robert Hooke
A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart
 CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
Identify the three factors that are required for there to be competition
 Semester Review Identify the cause of molecular movement Identify the three factors that are required for there to be competition Passive transport mechanisms always move molecules in what direction along
Semester Review Identify the cause of molecular movement Identify the three factors that are required for there to be competition Passive transport mechanisms always move molecules in what direction along
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration. mages/life/chap1_2/ph otosyn.swf://
 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration http://mrescience.com/i mages/life/chap1_2/ph otosyn.swf:// Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. Plants use light to make their own food. Where does
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration http://mrescience.com/i mages/life/chap1_2/ph otosyn.swf:// Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. Plants use light to make their own food. Where does
BIO 2 GO! 3217 The Cell- Respiration and Photosynthesis
 BIO 2 GO! The Cell- Respiration and Photosynthesis Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of green plants only. Respiration takes place in the mitochondria of all living organisms, plant or animal.
BIO 2 GO! The Cell- Respiration and Photosynthesis Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of green plants only. Respiration takes place in the mitochondria of all living organisms, plant or animal.
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Cell Theory. All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells
 Created by Mrs. Herman Sept. 2012 Cell Theory All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells Animal Cells Plant Cells The
Created by Mrs. Herman Sept. 2012 Cell Theory All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells Animal Cells Plant Cells The
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Unit 4: Cells. Biology 309/310. Name: Review Guide
 Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
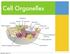 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 7-1 Life Is Cellular CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall The Discovery of the Cell 1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. Cork looked
7-1 Life Is Cellular CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall The Discovery of the Cell 1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. Cork looked
Cell Structure and Function Practice
 Cell Structure and Function Practice 1. The National Aeronautics and Space Agency (NASA) has a command center in Houston, Texas, that directs space missions. Which part of a cell functions like this command
Cell Structure and Function Practice 1. The National Aeronautics and Space Agency (NASA) has a command center in Houston, Texas, that directs space missions. Which part of a cell functions like this command
II. Eukaryotic Cell Structure A. Boundaries 1. plasma membrane a. serves as a boundary b/w the cell and its environment b. controls movement of
 I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals Fungi Bacteria. Loose DNA DNA Nucleus Membrane-Bound Organelles Humans
 UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
Relationships and Energy within the Ecosystem Study Guide
 Name Date Class AM PM Relationships and Energy within the Ecosystem Study Guide Your test is on Outcome 1: Evaluate the relationships within an ecosystem to show similarities and differences. Fill in the
Name Date Class AM PM Relationships and Energy within the Ecosystem Study Guide Your test is on Outcome 1: Evaluate the relationships within an ecosystem to show similarities and differences. Fill in the
The Cell System. The main job of a cell is to make proteins Proteins make up almost all of our body. Proteins do a lot of different things!
 Cell System The Cell System The main job of a cell is to make proteins Proteins make up almost all of our body. Proteins do a lot of different things! Structural (build bones, muscles, skin, etc.) Defensive
Cell System The Cell System The main job of a cell is to make proteins Proteins make up almost all of our body. Proteins do a lot of different things! Structural (build bones, muscles, skin, etc.) Defensive
Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions. AP Biology
 Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions AP Biology The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. New cells come from existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living
Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions AP Biology The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. New cells come from existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living
Test 2: Cell Structure and Function
 Name Test 2: Cell Structure and Function Date 1. Our bodies are made of, which are made up of many different parts and are the basic units of life. 1. a. cells b. organelles c. molecules d. proteins 2.
Name Test 2: Cell Structure and Function Date 1. Our bodies are made of, which are made up of many different parts and are the basic units of life. 1. a. cells b. organelles c. molecules d. proteins 2.
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
 Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems Introductory Questions What are the common structures that make up all living things? CELLS What do you think are the basic materials involved in the metabolism of all
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems Introductory Questions What are the common structures that make up all living things? CELLS What do you think are the basic materials involved in the metabolism of all
Midterm Study Guide Major Concepts
 Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Chapter 7 Cell Structure
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure Mr. C. Biology 1 07 Cell Structure Chapter 7 Cell Structure All living things are made of cells. Cells are made up of 3 main parts, Cell Membrane A skin that controls what enters
Chapter 7 Cell Structure Mr. C. Biology 1 07 Cell Structure Chapter 7 Cell Structure All living things are made of cells. Cells are made up of 3 main parts, Cell Membrane A skin that controls what enters
The Cell. What is a cell?
 The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
Cells The Units of Life
 Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. Write an A if you agree with the statement. Write a D if you disagree with the statement. Before You Read Bacteria are the smallest
Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. Write an A if you agree with the statement. Write a D if you disagree with the statement. Before You Read Bacteria are the smallest
