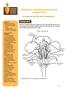
Lecture 14 Red gram ( Cajanus cajan ) (2n = 22) Family Fabaceae Adaptations for self pollination
|
|
|
- Madeline O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 14 Red gram (Cajanus cajan) (2n = 22) Family Fabaceae Self pollination is the rule in Red gram and natural crossing extents up to 65 per cent. Therefore it is also known as often cross pollinated crop. Adaptations for self pollination 1. Bisexual 2. Close proximity of anthers and stigma 3. Simultaneous maturity of anthers and stigma., emasculation and pollination techniques in Red gram Mature flower buds are to be covered with paper bags for one or two days. Hand emasculation followed by artifical cross pollination is essential. Emasculation should be done in the previous day evening and the emasculated buds are protected by covers. Early morning on the next day, pollination is done using pollen collected from the protected flowers of the selected male parents. Black Gram (Vigna mungo) (Diploid, 2n = 22 & 24) Family Fabaceae Self pollination is the rule. Here pollination occurs before floer opening (cleistogamous) in night. Anthesis time 1 am 4 am. The flower opens in the morning at 7 am. The interval between pollination and opening of flower is 4 hours. This ensures self fertilization., emasculation and pollination techniques in Black gram As in red gram, bagging is done to avoid insect contact. Young unopened bud is kept between thumb and fore fingers of the left hand. The point of dissecting needle is inserted just under the standard petal in an oblique position along the top of the bud. The left side of the standard and wing petal are pushed outward and held with thumb and left hand. The left side of the keel petal is removed with the forceps. The pistil and stigma are then exposed and the anthers are removed with the forceps. Evening emasculation followed by morning pollination gives best results. Pollination is done by gently rubbing anther of male,
2 inserting the staminal column and closing it with standard and wing petal. Since flower shedding is common, putting better paper bag is avoided. The emasculated flowers are identified with thread wound round. The crossed pod will be smaller in size with two or three seeds only. Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), Family Fabaceae (Diploid 2n = 22 and 24) Pollination Highly self pollinated because of Cleistogamy, Close proximity of the anthers and stigma and Simultaneous maturity of anthers and stigma Keeping the plants in insect proof cages will lead to selfing. Covering of individual flower buds will lead to poor pod setting. Select young buds, in an inflorescence and remove all immature buds. Split open the keel petals and remove the stamens one by one holding the filaments. Bring corolla back to position and cover the bud with a folded leaflet. Protection is given by keeping the plants in insect proof cages. Pollination is done on the next day morning by exposing the stigma from the keel petal and brushing it with the pollen collected from the male parent. and crossing are the essential procedures in crop improvement process. The exact procedures used to ensure self or cross-pollination of specific plants will depend on the floral structure and normal manner of pollination. Generally effecting cross-pollination in a strictly self-pollinating species is more difficult than vice-versa because for instance preventing selfpollination occurring inside the unopened flowers is cumbersome. Bengal Gram Cicer arietinum (2n = 14, 16), (Channa, Chick Pea), Family Fabaceae Chickpea is a self pollinated species with normal out crossing limited to 1.58%. self pollination takes place one or two days before opening up of the flower. The flower open in the morning and close in the afternoon and each flower opens on tow or three successive days. Time of anthesis is 3 AM to 9 AM. For hybridization crossing work should be started when the first pod on the selected plant is already formed. In Northern India, emasculation is done a day prior
3 to pollination. The pollination is done in the morning hours give better setting. In south India, pollination immediately after emasculation give higher seed setting. Soybean Glycine max (2n = 40), Family Fabaceae Flower open early in the morning. The pollen is shed normally shortly before or after the flower opens. But pollen shedding may occur sometimes with in the bud itself. Normally cross pollination does not exceed 1 percent. Emasculation and crossing Hand emasculation is the method followed for crop breeding which is tedious since the floral parts are so small and seed set is also less. Emasculation is done in the evening and pollination is done in the morning hours. Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) (2n = 40), Family Fabaceae Self pollination is the rule in groundnut. Anthesis commences at 6 am and continues upto 8 am. Anther dehisces two hours prior to opening of the flower. Twenty four hours before anthesis, the buds are very small. During the day, elongation of calyx, proceeds slowly but process gets accelerated during night. Since cleistogamous condition prevails in groundnut, selfing is most easy in this crop. Usually covering is unnecessary and difficult. Keeping the plants in insect proof cages will ensure self pollination. Mature flower buds which are ready to open in the next day are selected and emasculated in the evening. They can be easily identified by the size and length of calyx tube. The flower bud of groundnut is of crescent shape, being bulged on one side and slightly depressed on the other. The keel petal is located on the bulged side and the standard is present on the depressed side. For emasculation, hold the bud between the thumb and the index finger of the left hand and with the help of a razor blade in the right hand; make a cut on the depressed side at two-thirds the length below the tip so as to cut the standard and a portion of the wing petals. Then gently pull the calyx and corolla by holding at the tip of the flower bud. By doing this, the sepals and the petals except the keel would be removed, with the help of the fine forceps gently liberate the bundle of stamens and the pistil from the keel and nip off the anthers.
4 With a hand lens, examine the tips of filaments so as to ensure complete removal of the anthers. Take a piece of straw tube (used for sipping cool drinks), 4 to 5 cm long and close one side opening by bending the tip. Cover the emasculated flower bud with the straw tube by slowly inserting calyx tube into it. This would ensure perfect protection to the stigma from any natural cross pollination. The next morning take out the straw tube, dust the stigma with the desired pollen and reinsert the tube. Pollination between 7 and 8 am was found to give more success. If the stigma is found dry, pollinate after smearing it with 2 per cent sucrose solution. Next day early morning between 7 am and 11 am pollen is collected from mature yellow anthers of the selected male parent and dusted on the receptive stigma. For cross pollination, the selected male flower is held between thumb and the middle finger after the standard and wing petals are removed. The flower with keel protruding is taken to the stigma of the emasculated flower. A gentle push on gently keel by the finger forces lumps of pollen grains of the cover the entire stigmatic surface. Five to seven days after pollination successful crosses will produce gynophores (pegs) with the dried flowers at their tips. These are then introduced into small wire rings of 4 mm diameter which are marked for respective crosses. Sesame (Sesamum indicum) (2n = 26), Family Pedaliaceae Gingelly is a self pollinated (Autogamous) crop. In some varieties cross pollination also takes place to a limited extend of 5-6 per cent. Very high cross pollination between 14 and 65 per cent has been recorded in a few varieties in India. Hence, the crop can be classified as often cross pollinated. Cross pollination may occur due to wind and bee activities. On a bright clear day, the flowers open between 5 and 7 am. In the mature flower bud, just before the flower opens, the four unripe anthers are much below the stigma which at this stage is not receptive. The anthers begin to burst longitudinally after 4am in the next day and commence to liberate their pollen. At this time, the stigma becomes receptive. The plant comes to flowering 4 weeks after sowing. 1. Tieing with thread: can be effected by tieing the corolla of the unopened flower which is selected in the previous day evening itself. 2. Smearing of semi-solid clay: can be done by smearing a speck of semi-solid clay, on the upper portion of tubular petals of unopened flowers. The clay while on drying does not allow the tubular petals to open and hence self pollination is the rule.
5 This method is cheap and less time consuming one. This method is noat effective during rainy days. During rainy days, fevicol may be applied on young flower bud to ensure selfing. Soda- straw method The emasculation technique in sesame is easy for crossing due to epipetalous nature of the stamens. The flower bud which is expected to open in the next day morning is selected in the previous day evening between 3 P.M. and 6 P.M. and emasculated by just removing the corolla tube in which the stamens are attached. Then, the emasculated flower buds are covered with a piece of soda-straw tube, bent at the top in order to avoid contamination from foreign pollens. During the next day morning, between 7 A.M. and 9.A.M., pollen from the desired male parents were dusted gently on the surface of the stigmas of the emasculated flower buds after removing the soda-straw and again covered. The unemasculated flowers are removed in the female parent. Individual crossed flowers are tagged with coloured thread for the identification of crossed capsules. Different coloured threads are used for different type of crosses. Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) (2n = 20), Family - Astraceae Sunflower in highly cross pollinated crop mainly through insects (Entomophily) and to a limited extent by wind (Anemophily). The flower opening starts from outerside of the head and proceeds towards centre. The head takes 5-10 days for complete blooming depend on size of head and season. Anthesis occurs between 5 to 8 A.M. Pollen viable for 12 hours. Stigma is receptive for 2-3 days. The staminal filaments elongate rapidly and the anthers appear above the top of the corolla. Anthers dehisce early than maturity of stigma. (Protoandry). In this crop, the cross pollination occurs due to protandry, limited area of stigmatic surfaces for receptivity, ray floret colour attracts insects and abundance of sweet secretions in the disc florets. The flower head is protected with a suitable cover before the commencement of anthesis in any of the florets and the cover is retained till fertilization is over in all the florets. Artificial self pollination with pollen collected from the same flower or another flower of the same plant using a soft brush will enhance seed settings.
6 i. Hand Emasculation Emasculation is done in the early morning by removing the anthers of the disc florets in 2 to 3 whorls with forceps and the other florets in the head are removed. About 9-10 am the pollens from desired male parent are collected and dusted on the emasculated head. This process is continued for 2 to 3 days. ii. Without emasculation In sunflower, head emasculation is difficult. Considering this difficulty, the heads are pollinated without emasculation. On the basis of hybrid vigour, plants are distinguished from the selfed plants. The presence of marker genes for identifying hybrids is also utilised effectively. iii. Chemical induction of male sterility. This is achieved by spraying of 100ppm GA (Gametocide) during bud-initiation stage consecutively for three days in the morning. Pollination is carried out by collecting pollen from heads which are already bagged prior to flowering. Pollen may be collected from flowering heads into paper bags. Pollination is done in the morning by applying the freshly collected pollen by a small piece of cotton, a hair brush or through fine cloth bag. After each cross, care must be taken to avoid contamination by wiping the hands with alcohol. Castor (Ricinus communis) (2n = 20), Family Euphorbiaceae Cross pollination is the rule in this crop. It is mainly wind pollinated. But insect activity is also seen to some extend since the young leaves just below the inflorescence exude copious nectar at the time of flower opening cause insect pollination. Unisexual flowers, protogynous, elevated position of female flower in the inflorescence, mechanisms to promote wind pollination and nectar glands to attract insect promotes cross pollination. Here male flowers open first (protoandry). After one or two days of male flowers opening, female flowers open. However, protogyny is also reported. The opening is between 4.30 and 5.00 A.M. Pollen grains are viable for a 2 days and stigma is receptive for 3 days. Each candle takes days to complete flowering.
7 The whole inflorescence is protected with not yet opened are selected. From the selected inflorescence all the male flowers are removed and the female flowers protected with a suitable cover. Artificial cross pollination is done when the stigmas of the retained female flowers become receptive by rubbing the anthers of male flowers collected from the selected male parent. During the rain day old bags are to be replaced with new bags to avoid fungal attack, and free air movement. 1. Emasculation: It can be achieved by removing or rubbing off the staminate flowers by finger and thumb. 2. : Pollen grains are collected from the desired male parent and are dusted on the stigma of the female parent. Again the inflorescence is covered.
INEA HYBRIDISATION PROTOCOLS 2011
 INEA HYBRIDISATION PROTOCOLS 2011 Anton Ivancic Hybridisation of taro (Colocasia esculenta) Floral characteristics of taro Colocasia esculenta is an allogamous, protogynous species, for which the main
INEA HYBRIDISATION PROTOCOLS 2011 Anton Ivancic Hybridisation of taro (Colocasia esculenta) Floral characteristics of taro Colocasia esculenta is an allogamous, protogynous species, for which the main
Maximizing productivity of wheat and barley under dry-land systems HYBRIDIZATION. Faddel Ismail NCARE June,
 Maximizing productivity of wheat and barley under dry-land systems HYBRIDIZATION Faddel Ismail NCARE June, 8-10 2015 Hybridization Hybridization is the process of crossing two genetically different individuals
Maximizing productivity of wheat and barley under dry-land systems HYBRIDIZATION Faddel Ismail NCARE June, 8-10 2015 Hybridization Hybridization is the process of crossing two genetically different individuals
Parts of a Flower. A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program
 Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Chapter III- The Flower
 Worksheet Class 8-Flower, Pollination and Fertilization, Ecosystem. Chapter III- The Flower 1.Name the following. a.a flower in which both male and female reproductive organs are lacking. b.the groups
Worksheet Class 8-Flower, Pollination and Fertilization, Ecosystem. Chapter III- The Flower 1.Name the following. a.a flower in which both male and female reproductive organs are lacking. b.the groups
8 Reproduction in flowering plants
 Self-assessment questions 8.01 8 Reproduction in flowering plants 1 Which is the most accurate statement? The principal role of a flower in the life cycle of a plant is: (a) attracting insects (b) producing
Self-assessment questions 8.01 8 Reproduction in flowering plants 1 Which is the most accurate statement? The principal role of a flower in the life cycle of a plant is: (a) attracting insects (b) producing
Anatomy of Flowering Plants
 Dry Lab BIOLOGY Anatomy of Flowering Plants Investigation Manual ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS Table of Contents 2 Overview 2 Outcomes 2 Time Requirements 3 Background 6 Safety 6 Materials 7 Activity 1 10
Dry Lab BIOLOGY Anatomy of Flowering Plants Investigation Manual ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS Table of Contents 2 Overview 2 Outcomes 2 Time Requirements 3 Background 6 Safety 6 Materials 7 Activity 1 10
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION. This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination.
 FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
Name Section Lab 4 Flowers, Pollination and Fruit
 Name Section Lab 4 Flowers, Pollination and Fruit Flowers are designed on plants for sexual reproduction. They contain organs that produce gametes (sex cells), which, after fertilization, lead to the formation
Name Section Lab 4 Flowers, Pollination and Fruit Flowers are designed on plants for sexual reproduction. They contain organs that produce gametes (sex cells), which, after fertilization, lead to the formation
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit
 BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit Script to Narrate the PowerPoint, 06PowerPointFlowers and Fruit.ppt It is not permitted to export
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit Script to Narrate the PowerPoint, 06PowerPointFlowers and Fruit.ppt It is not permitted to export
STUDIES ON FLOWER BIOLOGY AND POLLINATION IN MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.)
 STUDIES ON FLOWER BIOLOGY AND POLLINATION IN MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) Manju Devi, Harish Kumar Sharma, Kiran Rana and Divender Kumar Mehta* Department of Entomology *Department of Vegetable Science
STUDIES ON FLOWER BIOLOGY AND POLLINATION IN MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) Manju Devi, Harish Kumar Sharma, Kiran Rana and Divender Kumar Mehta* Department of Entomology *Department of Vegetable Science
Plants can be either herbaceous or woody.
 Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Basal angiosperms, and plant breeding systems Today s lecture
 Basal angiosperms, and plant breeding systems Today s lecture Nymphaeaceae Magnoliaceae Ranunculaceae Video Breeding systems Class exercise Angiosperm phylogeny Soltis et al., 2011 Ranunculaceae' Monocots'
Basal angiosperms, and plant breeding systems Today s lecture Nymphaeaceae Magnoliaceae Ranunculaceae Video Breeding systems Class exercise Angiosperm phylogeny Soltis et al., 2011 Ranunculaceae' Monocots'
Use of gametocide for emasculation in Soybean (Glycine max (L) Merr.).
 Use of gametocide for emasculation in Soybean (Glycine max (L) Merr.). S K Lal *, C Devkumar 1, R L Sapra, and K P Singh. Genetics Division, IARI, New Delhi, India 1 Division of Agriculture Chemicals,
Use of gametocide for emasculation in Soybean (Glycine max (L) Merr.). S K Lal *, C Devkumar 1, R L Sapra, and K P Singh. Genetics Division, IARI, New Delhi, India 1 Division of Agriculture Chemicals,
Plant Growth and Development Part I. Levels of Organization
 Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules 1
Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules 1
UNIT 3. PLANTS. PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
1 Evolution of Plants
 1 Evolution of Plants Plant Evolutionary Tree 1 How Did Plant Life Begin? BIBLICAL WORLDVIEW EVOLUTIONARY WORLDVIEW The Biblical worldview is that plants began on the third day of creation, created by
1 Evolution of Plants Plant Evolutionary Tree 1 How Did Plant Life Begin? BIBLICAL WORLDVIEW EVOLUTIONARY WORLDVIEW The Biblical worldview is that plants began on the third day of creation, created by
Levels of Organization
 Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Plant
Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Plant
Kingdom Plantae. Plants or metaphytes are, autotrophic multicellular eukaryotes, with tissues.
 Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Objectives. To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants.
 1 Objectives To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants. 2 Main Menu Plant Cell Biology Plant Structures Roots
1 Objectives To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants. 2 Main Menu Plant Cell Biology Plant Structures Roots
Pollination and Seed Yield in Grass Seed Crops. Thomas G Chastain Oregon State University
 Pollination and Seed Yield in Grass Seed Crops Thomas G Chastain Oregon State University Seed Yield Potential vs. Actual Yield An example for perennial ryegrass Florets not pollinated, fertilized, or aborted
Pollination and Seed Yield in Grass Seed Crops Thomas G Chastain Oregon State University Seed Yield Potential vs. Actual Yield An example for perennial ryegrass Florets not pollinated, fertilized, or aborted
Name Date Block. Plant Structures
 Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People
 Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
1 Rice Growth and Development
 1 Rice Growth and Development Karen Moldenhauer and Nathan Slaton Rice is an annual grass (Figure 1-1) with round, hollow, jointed culms; narrow, flat, sessile leaf blades joined to the leaf sheaths with
1 Rice Growth and Development Karen Moldenhauer and Nathan Slaton Rice is an annual grass (Figure 1-1) with round, hollow, jointed culms; narrow, flat, sessile leaf blades joined to the leaf sheaths with
Chapter 15 PLANT STRUCTURES AND TAXONOMY
 Chapter 15 PLANT STRUCTURES AND TAXONOMY Chapter 15: Parts of a plant Manufactures food by photosynthesis Attracts insects for pollination Contains seeds Supports branches and transports food and water
Chapter 15 PLANT STRUCTURES AND TAXONOMY Chapter 15: Parts of a plant Manufactures food by photosynthesis Attracts insects for pollination Contains seeds Supports branches and transports food and water
Laboratory Exercise on the Segregation of Flower Color and Related Genes Using Velvet Flower (Salpiglossis sinuata Ruiz et Pavon)
 Laboratory Exercise on the Segregation of Flower Color and Related Genes Using Velvet Flower (Salpiglossis sinuata Ruiz et Pavon) Chiwon W. Lee ADDITIONAL INDEX WORDS. flower color inheritance, cleistogamy,
Laboratory Exercise on the Segregation of Flower Color and Related Genes Using Velvet Flower (Salpiglossis sinuata Ruiz et Pavon) Chiwon W. Lee ADDITIONAL INDEX WORDS. flower color inheritance, cleistogamy,
Ch. 4- Plants. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy
 Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
Basic Principles of Plant Science EXAMINING PLANT STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS
 Basic Principles of Plant Science EXAMINING PLANT STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Cellular Structure of Plants Cells are the structural basis of all living organisms. A cell is a tiny structure that forms the
Basic Principles of Plant Science EXAMINING PLANT STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Cellular Structure of Plants Cells are the structural basis of all living organisms. A cell is a tiny structure that forms the
Shoot System. Root System. below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue. Ground Tissue. Vascular Tissue. above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers)
 Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 8.2 - Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction in Plants In a plant, the flower is the sexual organ, and it has both male and females parts.
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 8.2 - Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction in Plants In a plant, the flower is the sexual organ, and it has both male and females parts.
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
2a. General: Describe 3 specialised uses for plants. Plants can be used as: i. raw materials ii. foods iii. medicines
 1a. General: Give examples of advantages of there being a wide variety of plants. Greater number of characteristics for breeding. Bigger choice for use as raw materials, foods and medicines. Provide different
1a. General: Give examples of advantages of there being a wide variety of plants. Greater number of characteristics for breeding. Bigger choice for use as raw materials, foods and medicines. Provide different
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to the life cycle of flowering plants (90928)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90928) 2017 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to the life cycle of flowering plants (90928) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90928) 2017 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to the life cycle of flowering plants (90928) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Root cross-section (Ranunculus)
 Plant Lab Review Root cross-section (Ranunculus) Epidermis Cortex Vascular Cylinder Phloem Endodermis Xylem Ranunculus Root Cross section Give three functions of the root Anchor plant Absorb water and
Plant Lab Review Root cross-section (Ranunculus) Epidermis Cortex Vascular Cylinder Phloem Endodermis Xylem Ranunculus Root Cross section Give three functions of the root Anchor plant Absorb water and
EFFECT OF POLLINATION TIME AND CROSSING RATIO ON SEED YIELD AND QUALITY OF BRINJAL HYBRID UNDER DHARWAD REGION OF KARNATAKA
 Indian J. Agric. Res., 42 (1) : 7-12, 2008 EFFECT OF POLLINATION TIME AND CROSSING RATIO ON SEED YIELD AND QUALITY OF BRINJAL HYBRID UNDER DHARWAD REGION OF KARNATAKA Shivashankaragouda B. Patil, M.N.
Indian J. Agric. Res., 42 (1) : 7-12, 2008 EFFECT OF POLLINATION TIME AND CROSSING RATIO ON SEED YIELD AND QUALITY OF BRINJAL HYBRID UNDER DHARWAD REGION OF KARNATAKA Shivashankaragouda B. Patil, M.N.
GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST
 GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST SUPPLEMENTAL SAMPLE OPEN-RESPONSE ITEM WITH SAMPLE RESPONSES AND ANALYSES NOTE: This sample open-response item is provided as a supplement to the Test Information
GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST SUPPLEMENTAL SAMPLE OPEN-RESPONSE ITEM WITH SAMPLE RESPONSES AND ANALYSES NOTE: This sample open-response item is provided as a supplement to the Test Information
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
The Birds and Bees of Wildflowers! Pollination Strategies of Plants All text and photos by Kris H. Light 2005
 The Birds and Bees of Wildflowers! Pollination Strategies of Plants All text and photos by Kris H. Light 2005 The Parts of Flowers Petals Stamens Sepals Pistils Strawberry Hedgehog Cactus Boy parts and
The Birds and Bees of Wildflowers! Pollination Strategies of Plants All text and photos by Kris H. Light 2005 The Parts of Flowers Petals Stamens Sepals Pistils Strawberry Hedgehog Cactus Boy parts and
Asexual & Plant Reproduction
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ sexual & Plant Reproduction Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ sexual & Plant Reproduction Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
*Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats.
 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. Reproduction In Plants Plant reproduction is the production of new
Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. Reproduction In Plants Plant reproduction is the production of new
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
 DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS BIO - Notes - Topic: Reproduction in Plants P a g e 1 27 1. Asexual Reproduction Is a form of reproduction resulting in the production of genetically identical
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS BIO - Notes - Topic: Reproduction in Plants P a g e 1 27 1. Asexual Reproduction Is a form of reproduction resulting in the production of genetically identical
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden
 U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden Why are Pollinators Important? Pollinators are nearly as important as sunlight, soil and water to the reproductive success of over 75%
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden Why are Pollinators Important? Pollinators are nearly as important as sunlight, soil and water to the reproductive success of over 75%
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution
 Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer to your text book to answer
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer to your text book to answer
Deterioration of Crop Varieties Causes and Maintenance
 Deterioration of Crop Varieties Causes and Maintenance Deterioration of Genetic Purity The genetic purity of a variety or trueness to its type deteriorates due to several factors during the production
Deterioration of Crop Varieties Causes and Maintenance Deterioration of Genetic Purity The genetic purity of a variety or trueness to its type deteriorates due to several factors during the production
Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1
 Unit 3. Plants Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1 WORKSHEET 3.1 1. Read and circle the words that are part of a plant. Draw the plant. This plant has six roots. It
Unit 3. Plants Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1 WORKSHEET 3.1 1. Read and circle the words that are part of a plant. Draw the plant. This plant has six roots. It
TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS
 TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS INTRO https://media1.britannica.com/eb-media/41/62941-004-e3f5377b.jpg IB BIO 9.4 2 Flowers are reproductive structures found in flowering plants. Their function is to
TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS INTRO https://media1.britannica.com/eb-media/41/62941-004-e3f5377b.jpg IB BIO 9.4 2 Flowers are reproductive structures found in flowering plants. Their function is to
Basal angiosperms, and plant breeding systems. Angiosperm phylogeny
 Basal angiosperms, and plant breeding systems Angiosperm phylogeny Soltis et al., 2011 Ranunculaceae' Monocots' Magnoliids' ANITA'grade' Basal angiosperms Angiosperm phylogeny A N A ANITA grade Amborella
Basal angiosperms, and plant breeding systems Angiosperm phylogeny Soltis et al., 2011 Ranunculaceae' Monocots' Magnoliids' ANITA'grade' Basal angiosperms Angiosperm phylogeny A N A ANITA grade Amborella
Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam -- Printed in The Netherlands
 Scientia Horticulturae, 14 (1981) 27--33 Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam -- Printed in The Netherlands 27 FLOWERING AND FRUIT-SET RESPONSE TO TEMPERATURE IN THE AVOCADO CULTIVAR 'HASS'
Scientia Horticulturae, 14 (1981) 27--33 Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam -- Printed in The Netherlands 27 FLOWERING AND FRUIT-SET RESPONSE TO TEMPERATURE IN THE AVOCADO CULTIVAR 'HASS'
SAMPLE PAGE. Flowers Express Lapbook. Any Age. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
HYBRID SEED PRODUCTION IN MAIZE. Crossing technique : Manual emasculation by detasseling
 HYBRID SEED PRODUCTION IN MAIZE Crossing technique : Manual emasculation by detasseling Detasseling : Removal of male inflorescence from the monoecious crop Time for detasseling : The time taken for shedding
HYBRID SEED PRODUCTION IN MAIZE Crossing technique : Manual emasculation by detasseling Detasseling : Removal of male inflorescence from the monoecious crop Time for detasseling : The time taken for shedding
Lab sect. (TA/time): Botany 113 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/21/00
 Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Botany 113 Spring 2000 First Hourly Exam 4/21/00 1) (15 pts) Match the letter of the characteristics for a plant given on the right with the family on the left. Not all of the
Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Botany 113 Spring 2000 First Hourly Exam 4/21/00 1) (15 pts) Match the letter of the characteristics for a plant given on the right with the family on the left. Not all of the
Hand Pollination Effects in the Cheyrimoya (Annona cherimola)
 California Avocado Society 1941 Yearbook 26: 94-98 Hand Pollination Effects in the Cheyrimoya (Annona cherimola) C. A. Schroeder University of California, Los Angeles Although the cherimoya was introduced
California Avocado Society 1941 Yearbook 26: 94-98 Hand Pollination Effects in the Cheyrimoya (Annona cherimola) C. A. Schroeder University of California, Los Angeles Although the cherimoya was introduced
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life
 Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Angiosperms: Phylum Anthophyta, the flowering plants
 Angiosperms: Phylum Anthophyta, the flowering plants 1. Overview of seed plant evolution Figure 29.7 Land plant evolution. 2. Traits of flowering plants a) Flowers b) Pollination syndromes c) Avoiding
Angiosperms: Phylum Anthophyta, the flowering plants 1. Overview of seed plant evolution Figure 29.7 Land plant evolution. 2. Traits of flowering plants a) Flowers b) Pollination syndromes c) Avoiding
Diseases of Sesame. Dr. S. Parthasarathy, M.Sc. (Ag)., Ph.D., FBSS.
 Diseases of Sesame Dr. S. Parthasarathy, M.Sc. (Ag)., Ph.D., FBSS. Assistant Professor (Plant Pathology), Dept. of Plant Pathology, College of Agricultural Technology, Theni Diseases of Sesame Charcoal
Diseases of Sesame Dr. S. Parthasarathy, M.Sc. (Ag)., Ph.D., FBSS. Assistant Professor (Plant Pathology), Dept. of Plant Pathology, College of Agricultural Technology, Theni Diseases of Sesame Charcoal
Plant parts and their functions
 UNIT 8 Plant parts and their functions In unit 2, we learnt about the classification and basic parts of plants. Here, we will learn in greater details about the different functions carried out by the plant
UNIT 8 Plant parts and their functions In unit 2, we learnt about the classification and basic parts of plants. Here, we will learn in greater details about the different functions carried out by the plant
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 6 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity 7.2.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? Who was
CHAPTER 6 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity 7.2.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? Who was
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce SPECIFIC TOPIC: Living Things and How They
 SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce SPECIFIC TOPIC: Living Things and How They Reproduce Living Things and How They Reproduce Students
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce SPECIFIC TOPIC: Living Things and How They Reproduce Living Things and How They Reproduce Students
Anatomy of Plants Student Notes
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Anatomy of Plants Student Notes Plant Cell Biology Segment 1. Plants Plants are organisms are incapable of movement produce food through 2. Animals Animals are multicellular
Directions: Fill in the blanks. Anatomy of Plants Student Notes Plant Cell Biology Segment 1. Plants Plants are organisms are incapable of movement produce food through 2. Animals Animals are multicellular
Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination
 * Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
* Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
Florida Native Landscaping
 Florida Native Landscaping ORH 3815/5815C Lecture 1 How to Identify Plants Lecture Outline I. The Plant Kingdom II. III. IV. Binomial Nomenclature Floral formula technique Flower terminology V. Leaf terminology
Florida Native Landscaping ORH 3815/5815C Lecture 1 How to Identify Plants Lecture Outline I. The Plant Kingdom II. III. IV. Binomial Nomenclature Floral formula technique Flower terminology V. Leaf terminology
Timed Readings Plus in Science, Book 10 (Fry level 13) Jamestown Education, Glencoe McGraw-Hill (scanned from published book)
 Timed Readings Plus in Science, Book 10 (Fry level 13) Jamestown Education, Glencoe McGraw-Hill (scanned from published book) 25-A Flower and Plant Reproduction Flowers, the harbingers of spring and the
Timed Readings Plus in Science, Book 10 (Fry level 13) Jamestown Education, Glencoe McGraw-Hill (scanned from published book) 25-A Flower and Plant Reproduction Flowers, the harbingers of spring and the
Pollination Biology of Sopubia delphinifolia G. Don
 Pollination Biology of Sopubia delphinifolia G. Don Kavitha GR, Thriveni MC *, Vijay CR, Shivamurthy GR Department of Studies in Botany, Manasagangotri, Mysore-570 006 thrivenimc@gmail.com Abstract: The
Pollination Biology of Sopubia delphinifolia G. Don Kavitha GR, Thriveni MC *, Vijay CR, Shivamurthy GR Department of Studies in Botany, Manasagangotri, Mysore-570 006 thrivenimc@gmail.com Abstract: The
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those
 1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
Session Seven Flowering, fruit set and yield
 Session Seven Flowering, fruit set and yield New Zealand and Australia Avocado Grower s s Conference 05 20-22 22 September 2005 Tauranga,, New Zealand Reproductive Biology of Avocado Gad Ish-Am Agricultural
Session Seven Flowering, fruit set and yield New Zealand and Australia Avocado Grower s s Conference 05 20-22 22 September 2005 Tauranga,, New Zealand Reproductive Biology of Avocado Gad Ish-Am Agricultural
CRUCIFER AND OTHER OIL OR FIBRE SPECIES. -- Cruciferae --
 CRUCIFER AND OTHER OIL OR FIBRE SPECIES -- Cruciferae -- BROWN MUSTARD (Brassica juncea L. Czernj. et Cosson) number # Vegetative - seed cotyledons: length - seed cotyledons: width - leaf: colour - leaf:
CRUCIFER AND OTHER OIL OR FIBRE SPECIES -- Cruciferae -- BROWN MUSTARD (Brassica juncea L. Czernj. et Cosson) number # Vegetative - seed cotyledons: length - seed cotyledons: width - leaf: colour - leaf:
Unit 2B- The Plants. Plants can be classified according to the presence or absence of vascular tissue.
 Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Phylum Bryophyta : (Page 169)
 Kingdom Plantae : Plants... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic organisms - rigid cell walls built of cellulose - life cycles show alternation of generations...two distinct phases called
Kingdom Plantae : Plants... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic organisms - rigid cell walls built of cellulose - life cycles show alternation of generations...two distinct phases called
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles
 Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/20/12
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2012 First Hourly Exam 4/20/12 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2012 First Hourly Exam 4/20/12 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
BUBBLEGUM. T.H.Seeds CANNABIS BOTANY EXTREME CLOSE-UP PHOTOGRAPHY
 BUBBLEGUM TM T.H.Seeds CANNABIS BOTANY EXTREME CLOSE-UP PHOTOGRAPHY T.H.Seeds CANNABIS BOTANY TM Here at T.H.Seeds TM we are continuously fascinated by what could be nature s greatest miracle, the Cannabis
BUBBLEGUM TM T.H.Seeds CANNABIS BOTANY EXTREME CLOSE-UP PHOTOGRAPHY T.H.Seeds CANNABIS BOTANY TM Here at T.H.Seeds TM we are continuously fascinated by what could be nature s greatest miracle, the Cannabis
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia
 Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Life Science Chapter 11 SEED PLANTS PART 2
 Life Science Chapter 11 SEED PLANTS PART 2 Advanced Seed Producing Advanced Seed Producing Vascular Plants Class: Gymnospermae Class: Angiospermae» Subclass: Monocotyledoneae» Subclass: Dicotyledoneae
Life Science Chapter 11 SEED PLANTS PART 2 Advanced Seed Producing Advanced Seed Producing Vascular Plants Class: Gymnospermae Class: Angiospermae» Subclass: Monocotyledoneae» Subclass: Dicotyledoneae
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 3 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
CHAPTER 3 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
Myrmecophily on Leucas chinensis (Lamiaceae)
 IOSR Journal Of Environmental Science, Toxicology And Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: 9-,p- ISSN: 9-99. Volume, Issue (Jul. - Aug. ), PP - www.iosrjournals.org Myrmecophily on Leucas chinensis (Lamiaceae)
IOSR Journal Of Environmental Science, Toxicology And Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: 9-,p- ISSN: 9-99. Volume, Issue (Jul. - Aug. ), PP - www.iosrjournals.org Myrmecophily on Leucas chinensis (Lamiaceae)
Plant hormones: a. produced in many parts of the plant b. have many functions
 Plant hormones: a. produced in many parts of the plant b. have many functions Illustrated with 4 plant hormones: Gibberellins Auxin Cytokinins Ethylene Gibberellins Gibberellins illustrate how plant hormones
Plant hormones: a. produced in many parts of the plant b. have many functions Illustrated with 4 plant hormones: Gibberellins Auxin Cytokinins Ethylene Gibberellins Gibberellins illustrate how plant hormones
BIO10 Plant Lecture Notes ch. 17. Plant Kingdom
 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Large Roses By Kathy Moore
 Skill Level 3 (of 4) A single large rose makes a stunning decoration for a cake top or as a combination with lilies, stephanotis freesia and bear grass. The variety of colour and size allows the cake decorator
Skill Level 3 (of 4) A single large rose makes a stunning decoration for a cake top or as a combination with lilies, stephanotis freesia and bear grass. The variety of colour and size allows the cake decorator
KINGDOM PLANTAE I. General II. Responses A. Tropisms - plant to a stimulus 1. - grows the stimulus 2. - grows the stimulus 3.
 KINGDOM PLANTAE I. General - - - - II. Responses A. Tropisms - plant to a stimulus 1. - grows the stimulus 2. - grows the stimulus 3. - growth response 4. - growth response 5. - growth response 6. / -
KINGDOM PLANTAE I. General - - - - II. Responses A. Tropisms - plant to a stimulus 1. - grows the stimulus 2. - grows the stimulus 3. - growth response 4. - growth response 5. - growth response 6. / -
Collecting Nectar and Pollen Samples: Methods and Cautions
 Collecting Nectar and Pollen Samples: Methods and Cautions Jessica Louque Larry Brewer Knowledge of residues in pollen and nectar resulting from applications of crop protection products can facilitate
Collecting Nectar and Pollen Samples: Methods and Cautions Jessica Louque Larry Brewer Knowledge of residues in pollen and nectar resulting from applications of crop protection products can facilitate
Directed Reading A. Section: Structures of Seed Plants. is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. is called ROOTS. size.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
SRGC Bulb Log Diary ISSN Pictures and text Ian Young. BULB LOG th August 2018
 SRGC ----- Bulb Log Diary ----- ISSN 2514-6114 Pictures and text Ian Young BULB LOG 32...8 th August 2018 I do not remember seeing so many hoverflies in the garden in previous years - it is one of the
SRGC ----- Bulb Log Diary ----- ISSN 2514-6114 Pictures and text Ian Young BULB LOG 32...8 th August 2018 I do not remember seeing so many hoverflies in the garden in previous years - it is one of the
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
THE STUDY OF POLLEN BIOLOGY OF Bauhinia variegata L. AT AGRA (U.P.)
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 5(1) : 83-87, 2014 THE STUDY OF POLLEN BIOLOGY OF Bauhinia variegata L. AT AGRA (U.P.) a b1 ANIL KUMAR AND PRABODH SRIVASTAVA ab Department of Botany, Dharm Samaj College, Aligarh, U.P.,
Indian J.Sci.Res. 5(1) : 83-87, 2014 THE STUDY OF POLLEN BIOLOGY OF Bauhinia variegata L. AT AGRA (U.P.) a b1 ANIL KUMAR AND PRABODH SRIVASTAVA ab Department of Botany, Dharm Samaj College, Aligarh, U.P.,
Scientific Identification & Classification
 Scientific Identification & Classification Plant Parts Leaves Stems Roots Flowers Leaves-External Petiole-leaf stalk or part that connects the leaf to the stem Blade-the large, flat part of the leaf Midrib-the
Scientific Identification & Classification Plant Parts Leaves Stems Roots Flowers Leaves-External Petiole-leaf stalk or part that connects the leaf to the stem Blade-the large, flat part of the leaf Midrib-the
The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants.
 INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
Lesson: Why a Butterfly Garden? Seeking Pollinator Certification for a Butterfly Garden
 Lesson: Why a Butterfly Garden? Seeking Pollinator Certification for a Butterfly Garden What is the primary threat to most endangered species? Why is our butterfly and pollinator population declining?
Lesson: Why a Butterfly Garden? Seeking Pollinator Certification for a Butterfly Garden What is the primary threat to most endangered species? Why is our butterfly and pollinator population declining?
YOM KAKIZAKI SAITAMAGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION, URAWA, SAITANA
 A THE FLOWERING HABIT AND NATURAL CROSSING IN THE EGG-PLANT YOM KAKIZAKI SAITAMAGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION, URAWA, SAITANA In regard to the frequency of natural crossing in the egg-plant,. Solauum
A THE FLOWERING HABIT AND NATURAL CROSSING IN THE EGG-PLANT YOM KAKIZAKI SAITAMAGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION, URAWA, SAITANA In regard to the frequency of natural crossing in the egg-plant,. Solauum
Mendel and the Gene Idea. Biology Exploring Life Section Modern Biology Section 9-1
 Mendel and the Gene Idea Biology Exploring Life Section 10.0-10.2 Modern Biology Section 9-1 Objectives Summarize the Blending Hypothesis and the problems associated with it. Describe the methods used
Mendel and the Gene Idea Biology Exploring Life Section 10.0-10.2 Modern Biology Section 9-1 Objectives Summarize the Blending Hypothesis and the problems associated with it. Describe the methods used
Level 2 Part II. MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist. Pages Montana Master Gardener Handbook
 Plant Growth and Development Level 2 Part II Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist Pages 24-48 Montana Master Gardener Handbook Vegetative parts of a plant Definitions Apical bud or
Plant Growth and Development Level 2 Part II Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist Pages 24-48 Montana Master Gardener Handbook Vegetative parts of a plant Definitions Apical bud or
Plant Vocabulary. Define
 Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
Plant Systematics and Plant/Pollinator Interactions. Jacob Landis
 Plant Systematics and Plant/Pollinator Interactions Jacob Landis Why study plants Important for food Clothing Drugs Bryophytes Lycophytes,Monilophytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts
Plant Systematics and Plant/Pollinator Interactions Jacob Landis Why study plants Important for food Clothing Drugs Bryophytes Lycophytes,Monilophytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts
Plants Notes. Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light
 Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Pollination of Avocado - Some New Insights with Special Reference to the 'Hass' Variety
 California Avocado Society 1986 Yearbook 70: 91-98 Pollination of Avocado - Some New Insights with Special Reference to the 'Hass' Variety Ron Bekey Farm Advisor, Ventura and Santa Barbara County The avocado
California Avocado Society 1986 Yearbook 70: 91-98 Pollination of Avocado - Some New Insights with Special Reference to the 'Hass' Variety Ron Bekey Farm Advisor, Ventura and Santa Barbara County The avocado
Cell parts. nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane. cell wall vacuole chloroplast
 7Ab/12 Cell parts nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane cell wall vacuole chloroplast found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in animal and plant cells found
7Ab/12 Cell parts nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane cell wall vacuole chloroplast found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in animal and plant cells found
In seed crop of onion (Allium cepa L.), the
 Research Paper : Studies on the influence of bee attractants on bee visition of Apis dorsata and Trigona sp. on onion (Allium cepa L.) J.S. PATIL, R.B. MOKAT, G.S. KAMATE AND R.V. MUPADE International
Research Paper : Studies on the influence of bee attractants on bee visition of Apis dorsata and Trigona sp. on onion (Allium cepa L.) J.S. PATIL, R.B. MOKAT, G.S. KAMATE AND R.V. MUPADE International
WATER REQUIREMENTS: Teacher Demonstration
 WATER REQUIREMENTS: Teacher Demonstration Objective Students will be able to describe the role of water in seed germination. : two cups of lima beans milk carton (one pint) water. Questions for the Students
WATER REQUIREMENTS: Teacher Demonstration Objective Students will be able to describe the role of water in seed germination. : two cups of lima beans milk carton (one pint) water. Questions for the Students
