Evolutionary Developmental Biology
|
|
|
- Daniella Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evolutionary Developmental Biology It all started with the Swiss professor Louis Agassiz ( ), who emigrated to the US and became a Harvard prof... EVO a.k.a. EVO-DEVO DEVO Hence, the embryos of different animals resemble each other more strongly in proportion as we examine them at an earlier period.... during almost the whole period of embryonic life, the young fish and the young frog differ scarcely at all: so it is with the young snake compared with the embryo bird. Principles of Zoology (1848) Agassiz had shown that embryonic fish go from a stage with an asymmetrical, heterocercal tail (top), to a stage with a symmetrical homocercal tail (bottom). Heterocercal-tailed fish also appear earlier in the fossil record than homocercal-tailed fish... Cheirolepis 380 million years old Caturus 180 million years old 1
2 This also seemed to parallel the ladder of complexity : less complex fish, like the sturgeon (top), had heterocercal tails, while more complex fish, like bass (bottom), had homocercal tails... Agassiz certainly thought it was important! I have devoted my whole life to the study of Nature, and yet a single sentence may express all that I have done. I have shown that there is a correspondence between the succession of Fishes in geological times and the different stages of their growth in the egg, that is all. It chanced to be a result that was found to apply to other groups and has led to other conclusions of a like nature. Lecture, 1869 This threefold parallelism seemed of crucial importance... but what did it mean? But Agassiz, the last of the scientific creationists, refused to consider that this threefold pattern might have an evolutionary explanation... In one word, all these facts in their natural connection proclaim aloud the One God, whom man may know, adore, and love; and Natural History must in good time become the analysis of the thoughts of the Creator of the Universe. Essay on Classification (1859) 2
3 Darwin, however, thought that it could only make sense if you assumed some kind of evolutionary link among organisms! Agassiz insists that ancient animals resemble to a certain extent the embryos of recent animals of the same classes; or that the geological succession of extinct forms is in some degree parallel to the embryological development of recent forms. I must follow Pictet and Huxley in thinking that the truth of this doctrine is very far from proved. Yet I fully expect to see it hereafter confirmed... For this doctrine of Agassiz accords well with the theory of natural selection. Origin of Species, chapter 10 Haeckel was also a great invertebrate zoologist he worked a lot on protists, sponges and jellyfish and a gifted illustrator, even influencing the applied arts and design motifs of his time. Darwin s Apostle to Germany, Ernst Haeckel ( ) popularized Darwinian ideas in his native country. He s the one who drew up elaborate tree diagrams of how evolution had progressed (with man at the top, of course)... Here s another picture of his work this illustrates the microscopic silica skeletons of some marine protists called Radiolaria which I put in here for no other reason than that they look really cool... 3
4 He was also a student of embryology, or ontogeny. He s often quoted as saying Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny, but what he actually said was: The rapid and brief ontogeny is a condensed synopsis of the long and slow history of the stem (phylogeny)... Haeckel reasoned thus: Evolution would add changes to the adult stages of the life cycle This makes the most sense if you re a Lamarckian and Haeckel did accept Lamarckian evolution! Previous adult stages would be pushed backwards in developmental time Embryonic development was a record (often condensed and abridged and compressed) of an organism s past evolutionary history Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny Haeckel s Biogenetic Law The truth turned out to be much more interesting... Haeckel s Biogenetic Law doesn t work organisms do not literally repeat their ancestral stages in any real sense Von Baer s Law, proposed by Haeckel s rival Karl von Baer, is more accurate: Generalized features, common to all members of a taxon, appear in development before the features of subgroups do.... but evolution can and does modify any stage of an organism s life cycle, sometimes almost beyond recognition BUT... learning how evolution and development are interrelated has become a very fruitful area of research. 4
5 Vertebrate embryos do go through a stage known as the pharyngula at which they most closely resemble each other. Haeckel has been accused of faking his drawings, but the similarities at the pharyngula stage are real. The ways that different vertebrates get to the pharyngula, however, vary a great deal the early stages of chicken development (top) don t look anything like the early stages of frog, fish, or amphioxus development (bottom), largely because of the very different amounts of yolk in different eggs affecting the cells ability to divide. Development across the vertebrates may be diagrammed as an hourglass very different early stages and adults, but a common phylotypic stage, the pharyngula, in between. Other phyla, such as arthropods, show a similar pattern. We now know that embryos at the phylotypic stage are most similar, not only in shape, but in patterns of gene expression. Notice that at the phylotypic stage, a set of genes called HOX is transcribed and translated more later on what they do! 5
6 Haeckel s Law isn t accepted today, but in some cases he was dead-on... Embryos may show features that the adults have lost this is another source of information for classification and phylogenetic studies.... this history of the embryo (ontogeny) must be completed by a second, equally valuable, and closely connected branch of thought the history of race (phylogeny). Both of these branches of evolutionary science, are, in my opinion, in the closest causal connection; this arises from the reciprocal action of the laws of heredity and adaptation... These barnacles were once classified as molluscs until their larvae were discovered to be very much like the larvae of crustaceans which is what barnacles really are. Even rhizocephalans weird fungus-like parasites on decapod crustaceans such as crabs have turned out to be crustaceans very close to the true barnacles, based on their larvae. 6
7 Another nifty example (which von Baer himself never believed): "Sea squirts", or tunicates, have blobby adult bodies, but larvae with chordate features. "tadpole larva" of the tunicate Botryllus schlosseri adult colony of the tunicate Botryllus schlosseri Heterochrony Different timing evolutionary change in the timing of a developmental event May be global (affecting whole organism) or local (restricted to one part or organ) Heterochronic effects may be grouped into two broad classes: Paedomorphosis: descendant is less developed / less mature than ancestor Peramorphosis: descendant is more developed / more mature than ancestor Modes of Heterochrony Paedomorphosis can be the result of: progenesis (finishing early) neoteny (slower growth rate) postdisplacement (starting late) Peramorphosis can result from: hypermorphosis (finishing late). acceleration (greater growth rate) predisplacement (starting early) These terms may apply to whole organisms (global heterochrony) or to parts of them (local heterochrony) Case study: Axolotls The axolotl was first described as a bizarre aquatic salamander with external gills. Gills are a feature of larval salamanders. Yet axolotls reached sexual maturity, and bred. Iodine added to the water suddenly transformed axolotls into adult tiger salamanders (Ambystoma tigrinum) Some populations of axolotls don t transform, or transform only rarely, when iodine is added... 7
8 Top: adult tiger salamander. Bottom: axolotl (paedomorphic tiger salamander) Paedomorphosis is common among salamanders. Note how this hellbender (top) and mudpuppy (bottom) both have gills, paddle tails, and weaker limbs... And then this aquatic salamander, Siren, is probably the champion paedomorphic salamander of all time! What s more, these can t be induced to metamorphose. 8
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
 Evolutionary Developmental Biology a.k.a. EVO-DEVO Paedomorphosis is common among salamanders. Note how this hellbender (top) and mudpuppy (bottom) both have gills, paddle tails, and weaker limbs... Top:
Evolutionary Developmental Biology a.k.a. EVO-DEVO Paedomorphosis is common among salamanders. Note how this hellbender (top) and mudpuppy (bottom) both have gills, paddle tails, and weaker limbs... Top:
Phylogenetics - IB 200B 17 Feb Heterochrony & Phylogenetics
 Heterochrony & Phylogenetics All members of a monophyletic taxon share a common ancestor whose developmental pathway was modified to produce descendant morphologies. Haeckel, E. 1899 - originally a physician
Heterochrony & Phylogenetics All members of a monophyletic taxon share a common ancestor whose developmental pathway was modified to produce descendant morphologies. Haeckel, E. 1899 - originally a physician
Phylogenetics - IB 200B 8 Feb Heterochrony & Phylogenetics
 Heterochrony & Phylogenetics All members of a monophyletic taxon share a common ancestor whose developmental pathway was modified to produce descendant morphologies. Haeckel, E. 1899 - originally a physician
Heterochrony & Phylogenetics All members of a monophyletic taxon share a common ancestor whose developmental pathway was modified to produce descendant morphologies. Haeckel, E. 1899 - originally a physician
Evolution and Development Evo-Devo
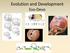 Evolution and Development Evo-Devo Darwin wrote a book on barnacles. Plate 1 (Lepas), from A monograph on the sub-class Cirripedia, by Charles Darwin. Comparative embryology There is an obvious similarity
Evolution and Development Evo-Devo Darwin wrote a book on barnacles. Plate 1 (Lepas), from A monograph on the sub-class Cirripedia, by Charles Darwin. Comparative embryology There is an obvious similarity
Patterns of Evolution
 Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings within a phylogeny Groupings can be categorized
Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings within a phylogeny Groupings can be categorized
Classifications can be based on groupings g within a phylogeny
 Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings g within a phylogeny y Groupings can be categorized
Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings g within a phylogeny y Groupings can be categorized
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION. Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology
 SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley
 Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley B.D. Mishler Feb. 7, 2012. Morphological data IV -- ontogeny & structure of plants The last frontier
Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley B.D. Mishler Feb. 7, 2012. Morphological data IV -- ontogeny & structure of plants The last frontier
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #6 -- Tempo and Mode in Macroevolution -- Nov.
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #6 -- Tempo and Mode in Macroevolution -- Nov.
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Outline. v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: v Animal Phylogeny
 BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
15.3 Darwin Presents his Case. Biology Mr. Hines
 15.3 Darwin Presents his Case Biology Mr. Hines Darwin returned to England with a wealth of new data. He brought many specimens from the Galapagos to further his studies and to present his data to others.
15.3 Darwin Presents his Case Biology Mr. Hines Darwin returned to England with a wealth of new data. He brought many specimens from the Galapagos to further his studies and to present his data to others.
v Scientists have identified 1.3 million living species of animals v The definition of an animal
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
(http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/evidence-for-evolution.topicarticleid-8741,articleid-8636.html)
 Teacher Wrap-up Background Information Darwin noted the striking similarity among embryos of complex animals such as humans, chickens, frogs, reptiles, and fish. He wrote that the uniformity is evidence
Teacher Wrap-up Background Information Darwin noted the striking similarity among embryos of complex animals such as humans, chickens, frogs, reptiles, and fish. He wrote that the uniformity is evidence
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
A. Incorrect! Form is a characteristic used in the morphological species concept.
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 23: Evolutionary Processes No. 1 of 10 The biological-species concept is based on. (A) Form. (B) Similar size. (C) Similar appearance to all other individuals in the population.
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 23: Evolutionary Processes No. 1 of 10 The biological-species concept is based on. (A) Form. (B) Similar size. (C) Similar appearance to all other individuals in the population.
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis
 18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Patterns of evolution
 To branch or not to branch Patterns of evolution Chapter 3 Cladogenesis lineages branch into two or more lines Anagenesis evolutionary change in a lineage without branching Anagenesis and Cladogenesis
To branch or not to branch Patterns of evolution Chapter 3 Cladogenesis lineages branch into two or more lines Anagenesis evolutionary change in a lineage without branching Anagenesis and Cladogenesis
8/23/2014. Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
UNITY AND DIVERSITY. Why do we classify things? Organizing the world of organsims. The Tree of Life
 Classification Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! Organisms are classified
Classification Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! Organisms are classified
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Biological Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
The Environment and Change Over Time Biological Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
Piecing It Together. 1) The envelope contains puzzle pieces for 5 vertebrate embryos in 3 different stages of
 Piecing It Together 1) The envelope contains puzzle pieces for 5 vertebrate embryos in 3 different stages of development. Lay out the pieces so that you have matched up each animal name card with its 3
Piecing It Together 1) The envelope contains puzzle pieces for 5 vertebrate embryos in 3 different stages of development. Lay out the pieces so that you have matched up each animal name card with its 3
Homework. Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17
 Homework Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17 Create a Species Project Learning Targets I can explain how comparing organisms can provide evidence that they have common ancestors. What is the evidence
Homework Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17 Create a Species Project Learning Targets I can explain how comparing organisms can provide evidence that they have common ancestors. What is the evidence
ORIGIN OF EVOLUTIONARY NOVELTIES
 ORIGIN OF EVOLUTIONARY NOVELTIES What are the origins of novel phenotypes? Can small quantitative changes lead to large qualitative phenotypic alterations? CHANGES IN RELATIVE GROWTH RATES CAN RESULT IN
ORIGIN OF EVOLUTIONARY NOVELTIES What are the origins of novel phenotypes? Can small quantitative changes lead to large qualitative phenotypic alterations? CHANGES IN RELATIVE GROWTH RATES CAN RESULT IN
Tree thinking pretest
 Page 1 Tree thinking pretest This quiz is in three sections. Questions 1-10 assess your basic understanding of phylogenetic trees. Questions 11-15 assess whether you are equipped to accurately extract
Page 1 Tree thinking pretest This quiz is in three sections. Questions 1-10 assess your basic understanding of phylogenetic trees. Questions 11-15 assess whether you are equipped to accurately extract
The Road to the Six Kingdoms
 Bio 2201 Unit 2 The Road to the Six Kingdoms A 2011study estimated there are about 8.6 million species on earth. Only 1.8 million species have been identified and named. *Chromista is a sub-kingdom group
Bio 2201 Unit 2 The Road to the Six Kingdoms A 2011study estimated there are about 8.6 million species on earth. Only 1.8 million species have been identified and named. *Chromista is a sub-kingdom group
Evidences of Evolution (Clues)
 Evidences of Evolution (Clues) Darwin stated that all organisms descended from a common ancestor Darwin based his theory of Natural Selection on observations of: Traits, geographical distribution, selective
Evidences of Evolution (Clues) Darwin stated that all organisms descended from a common ancestor Darwin based his theory of Natural Selection on observations of: Traits, geographical distribution, selective
Where Do Bat Wings Come From?
 Where o at Wings ome From? 1 ats are the only mammals that have evolved the power of flight. They can avoid obstacles and slip through tight spaces. Many species are nocturnal and use echolocation to guide
Where o at Wings ome From? 1 ats are the only mammals that have evolved the power of flight. They can avoid obstacles and slip through tight spaces. Many species are nocturnal and use echolocation to guide
November 25, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 25 Development and evolution. - let s finish off Monday s lecture. The end-permian extinction
 November 25, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 25 Development and evolution - let s finish off Monday s lecture The end-permian extinction - some consider the end-permian extinction to one of the four most
November 25, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 25 Development and evolution - let s finish off Monday s lecture The end-permian extinction - some consider the end-permian extinction to one of the four most
Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab
 Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
2/17/17. B. Four scientists important in development of evolution theory
 UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process of biological change by which descendants
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process of biological change by which descendants
Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution
 Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution Descent with modification by means of natural selection All life has descended from a common ancestor The mechanism of modification is natural selection Concept
Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution Descent with modification by means of natural selection All life has descended from a common ancestor The mechanism of modification is natural selection Concept
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution. I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution
 UNIT IV Chapter 10 Principles of Evolution UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process
UNIT IV Chapter 10 Principles of Evolution UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process
Vestigial Structures. Structure Possible Function(s) Why it is considered vestigial Appendix
 Vestigial Structures A vestigial structure is a structure or organ that through the course of evolution has either diminished in size or usefulness. It is believed that the human appendix, wisdom teeth
Vestigial Structures A vestigial structure is a structure or organ that through the course of evolution has either diminished in size or usefulness. It is believed that the human appendix, wisdom teeth
Classification of organisms. The grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy: branch of biology that classifies organisms
 Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Biology 20 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Evidence for Evolution. Today s species that exist have evolved from ancestral ones.
 Biology 20 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Evidence for Evolution Today s species that exist have evolved from ancestral ones. This theory of evolution is supported by many different types of evidence collected by
Biology 20 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Evidence for Evolution Today s species that exist have evolved from ancestral ones. This theory of evolution is supported by many different types of evidence collected by
Station 1 Fossil Record
 The very first horses evolved on the North American continent over 55 million years ago. The horse fossil record is very rich in transitional species. This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of
The very first horses evolved on the North American continent over 55 million years ago. The horse fossil record is very rich in transitional species. This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of
Biology. Slide 1 of 25. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 25 2 of 25 Macroevolution Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary patterns and processes that occur over long periods of time. 3 of 25 Macroevolution What are six important patterns
Biology 1 of 25 2 of 25 Macroevolution Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary patterns and processes that occur over long periods of time. 3 of 25 Macroevolution What are six important patterns
15 Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection 15-1 The Puzzle of Life's Diversity
 15-1 The Puzzle of Life's Diversity Study the photo of leaves... What else do you see? How did the Leaf Mantis come to look like decaying leaves? Define evolution in its simplest meaning? Review the meaning
15-1 The Puzzle of Life's Diversity Study the photo of leaves... What else do you see? How did the Leaf Mantis come to look like decaying leaves? Define evolution in its simplest meaning? Review the meaning
Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution.
 Section 2: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How do fossils provide evidence of evolution? How does
Section 2: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How do fossils provide evidence of evolution? How does
Chapter 16: Evolutionary Theory
 Chapter 16: Evolutionary Theory Section 1: Developing a Theory Evolution: Artificial Selection: Evolution: I. A Theory to Explain Change Over Time B. Charles Darwin C. Theory: D. Modern evolutionary theory
Chapter 16: Evolutionary Theory Section 1: Developing a Theory Evolution: Artificial Selection: Evolution: I. A Theory to Explain Change Over Time B. Charles Darwin C. Theory: D. Modern evolutionary theory
Systematics - BIO 615
 A Knyght ther was, and that a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and he was a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and that a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and he was a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and he wasn
A Knyght ther was, and that a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and he was a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and that a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and he was a worthy man, A Knyght ther was, and he wasn
A. camouflage B. hibernation C. migration D. communication. 8. Beetles, grasshoppers, bees, and ants are all.
 1. A flounder is a type of fish. The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings. If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom. This is known as. 2 Which
1. A flounder is a type of fish. The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings. If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom. This is known as. 2 Which
Q1. The diagram shows how the number of species in different vertebrate groups changed between 400 million years ago and 5 million years ago.
 Q. The diagram shows how the number of species in different vertebrate groups changed between 400 million years ago and 5 million years ago. The wider a block is, the more species there are. (a) Which
Q. The diagram shows how the number of species in different vertebrate groups changed between 400 million years ago and 5 million years ago. The wider a block is, the more species there are. (a) Which
Evolution Common Assessment 1
 Evolution Common Assessment 1 1. The field of biology that includes the study of the origin of new species through time is known as 5. A. biochemistry B. evolution C. ecology D. embryology 2. Evidence
Evolution Common Assessment 1 1. The field of biology that includes the study of the origin of new species through time is known as 5. A. biochemistry B. evolution C. ecology D. embryology 2. Evidence
A Summary of the Theory of Evolution
 A Summary of the Theory of Evolution Raúl Esperante Geoscience Research Institute Loma Linda, California What is Evolution? What does the term evolution mean? The word has three meanings that are relevant
A Summary of the Theory of Evolution Raúl Esperante Geoscience Research Institute Loma Linda, California What is Evolution? What does the term evolution mean? The word has three meanings that are relevant
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
Science in Motion Ursinus College
 Science in Motion Ursinus College NAME EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION LAB INTRODUCTION: Evolution is not just a historical process; it is occurring at this moment. Populations constantly adapt in response to changes
Science in Motion Ursinus College NAME EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION LAB INTRODUCTION: Evolution is not just a historical process; it is occurring at this moment. Populations constantly adapt in response to changes
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
III. The principle of natural selection and how this can lead to speciation
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution Lecture #3 -- Darwin -- Nov. 7, 2008 (ch. 22: 450-467)
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution Lecture #3 -- Darwin -- Nov. 7, 2008 (ch. 22: 450-467)
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
"PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200B Spring 2011
 "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200B Spring 2011 Evolution and development ("evo-devo") The last frontier in our understanding of biological forms is an understanding
"PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200B Spring 2011 Evolution and development ("evo-devo") The last frontier in our understanding of biological forms is an understanding
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
The Classification of Organisms
 Biology Chapter 8 The Classification of Organisms 8A - The Necessity of Classifying People group things together for convenience. (spices, pans, tools, instruments in orchestra) Taxonomy (or systematics)
Biology Chapter 8 The Classification of Organisms 8A - The Necessity of Classifying People group things together for convenience. (spices, pans, tools, instruments in orchestra) Taxonomy (or systematics)
A) Pre-Darwin History:
 Darwin Notes A) Pre-Darwin History: Ancient Greek philosophers such as and believed species were permanent and did not evolve. These ideas prevailed for 2,000 years. In 1859 Charles Darwin published. This
Darwin Notes A) Pre-Darwin History: Ancient Greek philosophers such as and believed species were permanent and did not evolve. These ideas prevailed for 2,000 years. In 1859 Charles Darwin published. This
Thursday, January 14. Teaching Point: SWBAT. assess their knowledge to prepare for the Evolution Summative Assessment. (TOMORROW) Agenda:
 Thursday, January 14 Teaching Point: SWBAT. assess their knowledge to prepare for the Evolution Summative Assessment. (TOMORROW) Agenda: 1. Show Hinsz your completed Review WS 2. Discuss answers to Review
Thursday, January 14 Teaching Point: SWBAT. assess their knowledge to prepare for the Evolution Summative Assessment. (TOMORROW) Agenda: 1. Show Hinsz your completed Review WS 2. Discuss answers to Review
16.4 Evidence of Evolution
 16.4 Evidence of Evolution Lesson Objectives Explain how geologic distribution of species relates to their evolutionary history. Explain how fossils and the fossil record document the descent of modern
16.4 Evidence of Evolution Lesson Objectives Explain how geologic distribution of species relates to their evolutionary history. Explain how fossils and the fossil record document the descent of modern
7. Where do most crustaceans live? A. in the air B. in water C. on the land D. underground. 10. Which of the following is true about all mammals?
 1 A flounder is a type of fish The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom This is known as 2 Which
1 A flounder is a type of fish The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom This is known as 2 Which
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny
 Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Chapter 7. Evolution and the Fossil Record
 Chapter 7 Evolution and the Fossil Record 1 Guiding Questions What lines of evidence convinced Charles Darwin that organic evolution produced the species of the modern world? What are the two components
Chapter 7 Evolution and the Fossil Record 1 Guiding Questions What lines of evidence convinced Charles Darwin that organic evolution produced the species of the modern world? What are the two components
Phylogeny 9/8/2014. Evolutionary Relationships. Data Supporting Phylogeny. Chapter 26
 Phylogeny Chapter 26 Taxonomy Taxonomy: ordered division of organisms into categories based on a set of characteristics used to assess similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature,
Phylogeny Chapter 26 Taxonomy Taxonomy: ordered division of organisms into categories based on a set of characteristics used to assess similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature,
Early History. Principles of Evolution. The History of Evolutionary Thought. The History of Evolutionary Thought. The History of Evolutionary Thought
 Principles of Evolution Has become a unifying principle in Biology For >150 years, stimulated controversy mostly nonscientists Initial theory sparked controversy within science and biology Early History
Principles of Evolution Has become a unifying principle in Biology For >150 years, stimulated controversy mostly nonscientists Initial theory sparked controversy within science and biology Early History
Chapter 16: Reconstructing and Using Phylogenies
 Chapter Review 1. Use the phylogenetic tree shown at the right to complete the following. a. Explain how many clades are indicated: Three: (1) chimpanzee/human, (2) chimpanzee/ human/gorilla, and (3)chimpanzee/human/
Chapter Review 1. Use the phylogenetic tree shown at the right to complete the following. a. Explain how many clades are indicated: Three: (1) chimpanzee/human, (2) chimpanzee/ human/gorilla, and (3)chimpanzee/human/
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology
 Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Modern Evolutionary Classification. Section 18-2 pgs
 Modern Evolutionary Classification Section 18-2 pgs 451-455 Modern Evolutionary Classification In a sense, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will mate. Taxonomic
Modern Evolutionary Classification Section 18-2 pgs 451-455 Modern Evolutionary Classification In a sense, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will mate. Taxonomic
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Quazi accurate photo history
 Quazi accurate photo history Evolution- change over time Fossils preserved remains Geologic Time earth s history The evidence shows changes in environment changes in species The Theory of Evolution supported
Quazi accurate photo history Evolution- change over time Fossils preserved remains Geologic Time earth s history The evidence shows changes in environment changes in species The Theory of Evolution supported
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 8 Reproduction and Development 1.Asexual reproduction: a. Is the primary form
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 8 Reproduction and Development 1.Asexual reproduction: a. Is the primary form
Homeotic Genes and Body Patterns
 Homeotic Genes and Body Patterns Every organism has a unique body pattern. Although specialized body structures, such as arms and legs, may be similar in makeup (both are made of muscle and bone), their
Homeotic Genes and Body Patterns Every organism has a unique body pattern. Although specialized body structures, such as arms and legs, may be similar in makeup (both are made of muscle and bone), their
Classification Flow Chart
 Classification Flow Chart THINGS To classify plants, see page warm 8 cold 6 9 7 air 0 water dry skin, eggs on land moist skin, eggs in water = the five classes of vertebrates eggs pouch placenta classification
Classification Flow Chart THINGS To classify plants, see page warm 8 cold 6 9 7 air 0 water dry skin, eggs on land moist skin, eggs in water = the five classes of vertebrates eggs pouch placenta classification
EVOLUTION. Charles Darwin
 EVOLUTION Charles Darwin Question for Thought Earth has millions of other kinds of organisms of every imaginable shape, size, and habitat. This variety of living things is called biological diversity.
EVOLUTION Charles Darwin Question for Thought Earth has millions of other kinds of organisms of every imaginable shape, size, and habitat. This variety of living things is called biological diversity.
Animal Diversity. Features shared by all animals. Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers
 Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011
 Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Chapter 10 Study Guide SECTION 1: Early Ideas about Evolution
 NAME Chapter 10 Study Guide SECTION 1: Early Ideas about Evolution BIOLOGY PREAP/GT Match each scientist with the statement that best reflects his ideas about evolutionary theory. 1. Linnaeus a. Species
NAME Chapter 10 Study Guide SECTION 1: Early Ideas about Evolution BIOLOGY PREAP/GT Match each scientist with the statement that best reflects his ideas about evolutionary theory. 1. Linnaeus a. Species
5/31/2012. Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter
 Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter Objectives: - Review meiosis -Species -Repro. Isolating mechanisms - Speciation -Is evolution always slow -Extinction How Are Populations, Genes, And Evolution Related?
Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter Objectives: - Review meiosis -Species -Repro. Isolating mechanisms - Speciation -Is evolution always slow -Extinction How Are Populations, Genes, And Evolution Related?
Evidence of Evolution. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution
 Lesson Overview Lesson Overview 16.4 THINK ABOUT IT Scientists in some fields, including geology, physics, paleontology, chemistry, and embryology, did not have the technology or understanding to test
Lesson Overview Lesson Overview 16.4 THINK ABOUT IT Scientists in some fields, including geology, physics, paleontology, chemistry, and embryology, did not have the technology or understanding to test
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Regents Biology
 Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Objective: Determine the different types of evidence for proving evolution Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Comparative Anatomy
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Objective: Determine the different types of evidence for proving evolution Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Comparative Anatomy
In a way, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will! MODERN EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION 18-2 MATE
 MODERN EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION 18-2 In a way, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will! MATE Taxonomic groups are invented by scientists to group organisms with
MODERN EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION 18-2 In a way, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will! MATE Taxonomic groups are invented by scientists to group organisms with
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity. Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom extends far beyond humans and other animals we may encounter 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom extends far beyond humans and other animals we may encounter 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified
The Evolutionary Biology Of Plants By Karl J. Niklas READ ONLINE
 The Evolutionary Biology Of Plants By Karl J. Niklas READ ONLINE The Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Brown University shares a common interest in how including plants, insects and spiders,
The Evolutionary Biology Of Plants By Karl J. Niklas READ ONLINE The Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Brown University shares a common interest in how including plants, insects and spiders,
Diversity in Living Organisms
 Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years ago. The
Evolution 8 th Grade Science Mr. Banks
 Evolution 8 th Grade Science Mr. Banks Evolution is a scientific theory Lets discuss for a moment what a scientific theory is. Hypothesis vs theory vs law Hypothesis - a proposed explanation for a natural
Evolution 8 th Grade Science Mr. Banks Evolution is a scientific theory Lets discuss for a moment what a scientific theory is. Hypothesis vs theory vs law Hypothesis - a proposed explanation for a natural
Class IX Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms Science
 Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
Question 1: Why do we classify organisms? There are a wide range of life forms (about 10 million 13 million species) around us. These life forms have existed and evolved on the Earth over millions of years
PHYLOGENY WHAT IS EVOLUTION? 1/22/2018. Change must occur in a population via allele
 PHYLOGENY EXERCISE 1 AND 2 WHAT IS EVOLUTION? The theory that all living organisms on earth are related and have a common ancestor. These organism have changed over time and are continuing to change. Changes
PHYLOGENY EXERCISE 1 AND 2 WHAT IS EVOLUTION? The theory that all living organisms on earth are related and have a common ancestor. These organism have changed over time and are continuing to change. Changes
Companion to Cells, Heredity & Classification Student Resources
 Companion to Cells, Heredity & Classification Student Resources The 21st Century Center for Research and Development in Cognition and Science Instruction The CaSEbook Companion: Student Resource Book
Companion to Cells, Heredity & Classification Student Resources The 21st Century Center for Research and Development in Cognition and Science Instruction The CaSEbook Companion: Student Resource Book
Evolution and Darwin
 Evolution and Darwin Evolution The processes that have transformed life on earth from it s earliest forms to the vast diversity that characterizes it today - Darwin Old Theories of Evolution Jean Baptiste
Evolution and Darwin Evolution The processes that have transformed life on earth from it s earliest forms to the vast diversity that characterizes it today - Darwin Old Theories of Evolution Jean Baptiste
Bio 175 FALL 2004 EVOLUTION FINAL EXAMINATION Monday December 6, 2004
 1 Bio 175 FALL 2004 EVOLUTION FINAL EXAMINATION Monday December 6, 2004 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your NAME ON EVERY PAGE and ANSWER ONLY IN THE SPACE PROVIDED. 2. Please read the question carefully
1 Bio 175 FALL 2004 EVOLUTION FINAL EXAMINATION Monday December 6, 2004 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your NAME ON EVERY PAGE and ANSWER ONLY IN THE SPACE PROVIDED. 2. Please read the question carefully
BIOLOGY. Chapter 27 Introduction to Animal Diversity
 BIOLOGY Chapter 27 Introduction to Animal Diversity Fig. 32-1 An Overview of Animal Diversity Multicellular Nutrition mode: Heterotrophic (ingestion) Cell structure & specialization Tissues develop from
BIOLOGY Chapter 27 Introduction to Animal Diversity Fig. 32-1 An Overview of Animal Diversity Multicellular Nutrition mode: Heterotrophic (ingestion) Cell structure & specialization Tissues develop from
Theory of Evolution. Chapter 15
 Theory of Evolution Chapter 15 The History of Evolutionary Thought Evolution The development of new types of organisms from preexisting types of organisms over time. Also could be described as a heritable
Theory of Evolution Chapter 15 The History of Evolutionary Thought Evolution The development of new types of organisms from preexisting types of organisms over time. Also could be described as a heritable
Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food.
 Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus
 The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus 1 st COMPREHENSIVE WORKSHEET SEPTEMBER 2015 SCIENCE CLASS 7 Teacher Name: Ms.Seema Adil Class: 7 Date:5 th November 2016 Name: Section: Date: CHAPTER: CLASSIFYING
The City School North Nazimabad Boys Campus 1 st COMPREHENSIVE WORKSHEET SEPTEMBER 2015 SCIENCE CLASS 7 Teacher Name: Ms.Seema Adil Class: 7 Date:5 th November 2016 Name: Section: Date: CHAPTER: CLASSIFYING
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
7.1 What is the Theory of Evolution?
 Evolution 7.1 What is the Theory of Evolution? SCIENTIFIC THEORY: a well-tested scientific explanation that no evidence contradicts Theories explain the basic ideas of science. If scientists find new evidence
Evolution 7.1 What is the Theory of Evolution? SCIENTIFIC THEORY: a well-tested scientific explanation that no evidence contradicts Theories explain the basic ideas of science. If scientists find new evidence
Patterns in Evolution - Novelty
 Patterns in Evolution - Novelty Uses of Phylogenetic Analysis Allows mapping order of character state changes Documents evolutionary trends in development Reveals that Homoplasy is common Can attempt to
Patterns in Evolution - Novelty Uses of Phylogenetic Analysis Allows mapping order of character state changes Documents evolutionary trends in development Reveals that Homoplasy is common Can attempt to
Patterns in Evolution - Novelty. Uses of Phylogenetic Analysis. Allows mapping order of character state changes
 Patterns in Evolution - Novelty Uses of Phylogenetic Analysis Allows mapping order of character state changes Documents evolutionary trends in development Reveals that Homoplasy is common Can attempt to
Patterns in Evolution - Novelty Uses of Phylogenetic Analysis Allows mapping order of character state changes Documents evolutionary trends in development Reveals that Homoplasy is common Can attempt to
MS-LS3-1 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits
 MS-LS3-1 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits MS-LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result
MS-LS3-1 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits MS-LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result
1/30/2012. Review. Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter
 Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter Objectives: - Review meiosis -Species -Repro. Isolating mechanisms - Speciation -Is evolution always slow -Extinction Review Meiosis: division of cells that results
Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter Objectives: - Review meiosis -Species -Repro. Isolating mechanisms - Speciation -Is evolution always slow -Extinction Review Meiosis: division of cells that results
