The Pod. Curriculum Information
|
|
|
- Gordon Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Curriculum Information The Pod The original Centre of the Cell experience! Visit our 16-cell-embryo-shaped Pod, suspended over the laboratories of the Blizard Institute. Once inside, you will learn about the amazing world of cells, the human body and the latest medical research. You can try your hand at virtual experiments, heal extensive virtual burns and have your cells counted. You also get to see real body parts and diagnose cancer using high-power microscopes. Running time: 90 minutes Maximum group size: 40 (including accompanying adults) Suitable for key stages 2 5 Running order 1. Introduction: What are cells? (Film) 2. Cell interactive games 3. Why do scientists study cells? (Film) 4. Medical Research interactive games 5. End: Careers in science and healthcare (Film) Please find the curriculum links listed below. Please note that some of these topics are covered in more depth than others during the one hour in the Pod itself. Students are free to ask questions about any topic at any time.
2 Key stage 2 Science curriculum links Working scientifically Year 5 and 6 identifying scientific evidence that has been used to support or refute ideas or arguments Animals, including humans Year 3 identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot make their own food; they get nutrition from what they eat identify that humans and some other animals have skeletons and muscles for support, protection and movement Year 4 describe the simple functions of the basic parts of the digestive system in humans identify the different types of teeth in humans and their simple functions Year 5 describe the changes as humans develop to old age Year 6 identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system, and describe the functions of the heart, blood vessels and blood recognise the impact of diet, exercise, drugs and lifestyle on the way their bodies function describe the ways in which nutrients and water are transported within animals, including humans
3 Living things and their habitats: Year 4 recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways Year 6 describe how living things are classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on similarities and differences, including microorganisms, plants and animals Evolution and inheritance Year 6 recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents
4 Key stage 3 Science curriculum links Working scientifically understand that scientific methods and theories develop as earlier explanations are modified to take account of new evidence and ideas Structure and function of living organisms Cells and organisation cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe, interpret and record cell structure using a light microscope the functions of the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria the hierarchical organisation of multicellular organisms: from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Nutrition and digestion content of a healthy human diet (from February 2016) the tissues and organs of the human digestive system the importance of bacteria in the human digestive system (from February 2016) Reproduction reproduction in humans (as an example of a mammal), including gametes, fertilisation, gestation and birth Genetics and evolution Inheritance, chromosomes, DNA and genes heredity as the process by which genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next the variation between species and between individuals of the same species means some organisms compete more successfully (from February 2016)
5 Key stage 4 Science curriculum links Working scientifically the ways in which scientific methods and theories develop over time appreciating the power and limitations of science and considering ethical issues which may arise explaining everyday and technological applications of science; evaluating associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and making decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments evaluating risks both in practical science and the wider societal context, including perception of risk Cell biology cells as the basic structural unit of all organisms; adaptations of cells related to their functions; the main sub-cellular structures of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells stem cells in animals Health, disease and the development of medicines the relationship between health and disease communicable diseases humans non-communicable diseases bacteria, viruses and fungi as pathogens in animals body defences against pathogens and the role of the immune system against disease reducing and preventing the spread of infectious diseases in animals the process of discovery and development of new medicines the impact of lifestyle factors on the incidence of non-communicable diseases
6 Evolution, inheritance and variation the genome as the entire genetic material of an organism (from February 2016) how the genome, and its interaction with the environment, influence the development of the phenotype of an organism (from February 2016) the potential impact of genomics on medicine most phenotypic features being the result of multiple, rather than single, genes (from February 2016) single gene inheritance and single gene crosses with dominant and recessive phenotypes genetic variation in populations of a species (from February 2016) the uses of modern biotechnology including gene technology; some of the practical and ethical considerations of modern biotechnology
7 Key stage 5 Science curriculum links AQA AS / A level Biology 3.2 Cells Structure of eukaryotic cells The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: cell-surface membrane nucleus (containing chromosomes, consisting of protein-bound, linear DNA, and one or more nucleoli) mitochondria Golgi apparatus and Golgi vesicles lysosomes (a type of Golgi vesicle that releases lysozymes) ribosomes rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum In complex multicellular organisms, eukaryotic cells become specialised for specific functions. Specialised cells are organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into systems All cells arise from other cells Within multicellular organisms, not all cells retain the ability to divide. Eukaryotic cells that do retain the ability to divide show a cell cycle. DNA replication occurs during the interphase of the cell cycle. Mitosis is the part of the cell cycle in which a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two daughter cells, each with the identical copies of DNA produced by the parent cell during DNA replication. The behaviour of chromosomes during interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase of mitosis. The role of spindle fibres attached to centromeres in the separation of chromatids. Division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis) usually occurs, producing two new cells. Mitosis is a controlled process. Uncontrolled cell division can lead to the formation of tumours and of cancers. Many cancer treatments are directed at controlling the rate of cell division.
8 3.6 Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environments Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment Homeostasis in mammals involves physiological control systems that maintain the internal environment within restricted limits. The importance of maintaining a stable core temperature and stable blood ph in relation to enzyme activity. The importance of maintaining a stable blood glucose concentration in terms of availability of respiratory substrate and of the water potential of blood. 3.7 Genetics, populations, evolution and ecosystems Inheritance The genotype is the genetic constitution of an organism. The phenotype is the expression of this genetic constitution and its interaction with the environment. There may be many alleles of a single gene Using genome projects (from February 2016) Sequencing projects have read the genomes of a wide range of organisms, including humans. This may have many applications, including the identification of potential antigens for use in vaccine production.
9 Edexcel AS / A level Biology Unit 1: Lifestyle, Transport, Genes and Health 1.3 Topic 1: Lifestyle, health and risk Explain why many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms) Describe the factors that increase the risk of CVD (genetic, diet, age, gender, high blood pressure, smoking and inactivity) Discuss how people use scientific knowledge about the effects of diet (including obesity indicators), exercise and smoking to reduce their risk of coronary heart disease 1.4 Topic 2: Genes and health (from February 2016) Describe a gene as being a sequence of bases on a DNA molecule coding for a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain (from February 2016) Explain how errors in DNA replication can give rise to mutations (from February 2016) Explain the uses of genetic screening: identification of carriers, preimplantation genetic diagnosis and prenatal testing (amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling) and discuss the implications of prenatal genetic screening Identify and discuss the social and ethical issues related to genetic screening from a range of ethical viewpoints Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment 2.3 Topic 3: The voice of the genome Describe the ultrastructure of an animal (eukaryotic) cell (nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, centrioles, lysosomes, and Golgi apparatus) and recognise these organelles from EM images. Explain the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rer) and the Golgi apparatus in protein transport within cells and including its role in formation of extracellular enzymes. Describe how the cells of multicellular organisms can be organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into systems. Explain the role of mitosis and the cell cycle for growth and asexual reproduction. Describe the stages of mitosis Explain how mammalian gametes are specialised for their functions
10 Unit 4: The Natural Environment and Species Survival 3.4 Topic 6: Infection, immunity and forensics Describe the major routes pathogens may take when entering the body and explain the role of barriers in protecting the body from infection, including the roles of skin, stomach acid, gut and skin flora Unit 5: Energy, Exercise and Coordination 4.3 Topic 7: Run for your life Explain how medical technology, including the use of keyhole surgery and prostheses, is enabling those with injuries and disabilities to participate in sports, eg cruciate ligaments repair using keyhole surgery and knee joint replacement using prosthetics 4.4 Topic 8: Grey matter Discuss the moral and ethical issues relating to the use of animals in medical research from two ethical standpoints
11 OCR AS / A level Biology A Module 2: Foundations in biology 2.1 Foundations in biology Cell structure The ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells and the functions of the different cellular components Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation The cell cycle The main stages of mitosis How cells of multicellular organisms are specialised for particular functions The organisation of cells into tissues, organs and organ systems The features and differentiation of stem cells The potential uses of stem cells in research and medicine Module 4: Biodiversity, evolution and disease 4.1 Communicable diseases, disease prevention and the immune system Communicable diseases, disease prevention and the immune system The different types of pathogen that can cause communicable diseases in plants and animals The principles of vaccination and the role of vaccination programmes in the prevention of epidemics The benefits and risks of using antibiotics to manage bacterial infection Module 5: Communication, homeostasis and energy 5.1 Communication and homeostasis Communication and homeostasis The need for communication systems in multicellular organisms
12 5.2 Energy for biological processes Respiration The need for cellular respiration The structure of the mitochondrion Module 6: Genetics, evolution and ecosystems 6.1 Genetics and evolution Patterns of inheritance The contribution of both environmental and genetic factors to phenotypic variation The principles of artificial selection and its uses The ethical considerations surrounding the use of artificial selection Manipulating genomes How gene sequencing has allowed for genome-wide comparisons between individuals and between species (from February 2016) 6.2 Cloning and biotechnology Cloning and biotechnology How artificial clones in animals can be produced by artificial embryo twinning or by enucleation and somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) The arguments for and against artificial cloning in animals
13 OCR AS / A level Biology B Module 2: Cells, chemicals for life, transport and gas exchange 2.1 Cells and chemicals for life Cells and microscopy The importance of microscopy in the development of the cell theory as a unifying concept in biology and the investigation of cell structure Module 3: Cell division, development and disease control 3.1 Cell division and development The developing cell: cell division and cell differentiation The cell cycle The changes that take place in the nuclei and cells of animals and plants during mitosis The microscopic appearance of cells undergoing mitosis Current applications and uses of stem cells 3.2 Pathogens, immunity and disease control Pathogenic microorganisms How pathogens (including bacteria, viruses and fungi) cause communicable disease The causes, means of transmission, symptoms and the principal treatment of tuberculosis (TB) The social, ethical, economic and biological factors involved in the attempts to control and prevent diseases in the context of TB Controlling communicable diseases The use of antibiotics in the treatment of communicable disease How the misuse of antibiotics can lead to the evolution of resistant strains of bacteria
14 3.3 Non-communicable diseases The cellular basis of cancer and treatment The factors that may increase the risk of developing non-communicable diseases The cellular basis of cancer The methods used to detect cancers The methods used to treat patients with cancer
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
How many lessons is it?
 Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Topic 2: Cells (12 hours)
 Topic : Cells ( hours). Cell theory hours.. Outline the cell theory. Include the following. Living organisms are composed of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Cells come from pre-existing cells...
Topic : Cells ( hours). Cell theory hours.. Outline the cell theory. Include the following. Living organisms are composed of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Cells come from pre-existing cells...
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
GRADE LEVEL: SEVENTH SUBJECT: SCIENCE DATE:
 CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION GRADE LEVEL: SEVENTH SUBJECT: SCIENCE DATE: 2016-2017 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 AND 2 UNIT 1 MASTER COPY 11-15-16 CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT
CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION GRADE LEVEL: SEVENTH SUBJECT: SCIENCE DATE: 2016-2017 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 AND 2 UNIT 1 MASTER COPY 11-15-16 CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
VCE BIOLOGY Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the Study Design and the Study Design
 VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Curriculum Links. AQA GCE Biology. AS level
 Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2,
 Test Review (12/7) 1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2, 20 2. 5. What structure is responsible
Test Review (12/7) 1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2, 20 2. 5. What structure is responsible
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE)
 Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology
 Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology TEKS Comments Louisiana GLE (Bio.1) Scientific Processes. The
Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology TEKS Comments Louisiana GLE (Bio.1) Scientific Processes. The
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Combined Science Biology Academic Overview
 Combined Science Biology Academic Overview 2018-19 Science Term 1.1 Term 1.2 Term 2.1 Term 2.2 Term 3.1 Term 3.1 Year 9 Key Concepts in Biology Key Concepts in Biology cont. Cells & Control Cells & Control
Combined Science Biology Academic Overview 2018-19 Science Term 1.1 Term 1.2 Term 2.1 Term 2.2 Term 3.1 Term 3.1 Year 9 Key Concepts in Biology Key Concepts in Biology cont. Cells & Control Cells & Control
Text of objective. Investigate and describe the structure and functions of cells including: Cell organelles
 This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
Anaphase. Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell
 Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Basic Biology. Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology
 Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Edexcel (A) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (A) Biology A-level Topic 3: Voice of the Genome Notes Cell Structure All living organisms are made of cells and share some common features. In multicellular organisms, cells are organised into
Edexcel (A) Biology A-level Topic 3: Voice of the Genome Notes Cell Structure All living organisms are made of cells and share some common features. In multicellular organisms, cells are organised into
Grade 7 Science Learning Standards
 Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Cellular Reproduction
 Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Include metabolism, response, homeostasis, growth, reproduction and nutrition.
 Topic 2: Cells Topic 2: Cells 2.1 Cell theory Assessment statement IBO Notes Include the following. Living organisms are composed of cells. 2.1.1 Outline the cell theory. Cells are the smallest unit of
Topic 2: Cells Topic 2: Cells 2.1 Cell theory Assessment statement IBO Notes Include the following. Living organisms are composed of cells. 2.1.1 Outline the cell theory. Cells are the smallest unit of
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Activity Activity Title. Chapter Title Chapter Description Lesson Title Lesson Description Introduction to Living Things
 Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
Cell Theory. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century!
 Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Biology 2018 Final Review. Miller and Levine
 Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
To help you complete this review activity and to help you study for your test, you should read SC State Standards B
 Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
AQA Biology Year 1 - Topic 2 - Cells
 Section Topic Description You should be able to: 3.2.1.1 Structure of Label the organelles present in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic Cells State the function and structure of the organelles in eukaryotic
Section Topic Description You should be able to: 3.2.1.1 Structure of Label the organelles present in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic Cells State the function and structure of the organelles in eukaryotic
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
The Importance of Cell Division Cell division
 Cell Division The Importance of Cell Division Cell division allows organisms to carry out three necessary functions: REPRODUCE GROW REPAIR DAMAGE FERTILIZATION: You started life as a single cell, but today
Cell Division The Importance of Cell Division Cell division allows organisms to carry out three necessary functions: REPRODUCE GROW REPAIR DAMAGE FERTILIZATION: You started life as a single cell, but today
Biology (age 11-14) Subject map
 Biology Biology (age 11-14) Subject map Big ideas and key concepts The Best Evidence Science Teaching resources can be used with your existing scheme of work, if desired. However, we have used research
Biology Biology (age 11-14) Subject map Big ideas and key concepts The Best Evidence Science Teaching resources can be used with your existing scheme of work, if desired. However, we have used research
Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Life Science FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES
 FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test
 Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Biology Semester Review
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Franklin Special School District Grade 7 Science
 08-09 SEVENTH GRADE: OVERVIEW The academic standards for seventh grade establish the content knowledge and skills for Tennessee students necessary to prepare them for the rigorous levels of higher education
08-09 SEVENTH GRADE: OVERVIEW The academic standards for seventh grade establish the content knowledge and skills for Tennessee students necessary to prepare them for the rigorous levels of higher education
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Biology Test 2 The Cell. For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name: Life Science Review Packet. Cell Structure and Function: What Defines Life:
 Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
 BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time?
 Chapter 5 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Think about this Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time? EQ: Why is cell division necessary for the growth & development of living organisms? Section
Chapter 5 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Think about this Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time? EQ: Why is cell division necessary for the growth & development of living organisms? Section
Highland Park Science Curriculum
 08/08/20115:20 PM 1 Biology I Semester I Unit IV Highland Park Science Curriculum Components Biology I Biology I Pre AP Extensions Biology I Pre AP TAG Extensions Unit Overview Cells and Cellular Mechanisms
08/08/20115:20 PM 1 Biology I Semester I Unit IV Highland Park Science Curriculum Components Biology I Biology I Pre AP Extensions Biology I Pre AP TAG Extensions Unit Overview Cells and Cellular Mechanisms
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division. SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6.
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions. Copyright 2013 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Overview Key Terms active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic organelle
Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Overview Key Terms active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic organelle
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Name: Period: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ Cell Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover a.
Name: Period: _ Date: _ Cell Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover a.
Biology 1 Semester Review
 Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
Science Unit Learning Summary
 Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Genetics word list. the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral)
 Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
Biology 1 Notebook. Review Answers Pages 17 -?
 Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Cellular Growth & Reproduction. Biology 1B Ms. Morris
 Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Structure and Cell Cycle
 E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell. Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components.
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
LS_C2-quizzes, Version: 1 1
 Name: Select the term that best completes the statement. A. cell division B. chromosomes C. cells D. divides E. centromere F. DNA G. chromatids H. nucleus Date: 1. is the chemical code that contains information
Name: Select the term that best completes the statement. A. cell division B. chromosomes C. cells D. divides E. centromere F. DNA G. chromatids H. nucleus Date: 1. is the chemical code that contains information
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division. Chapter 2 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division Cells The basic functional units of all living things Human cells vary widely but all have similar basic structure Cells vary widely in morphology Neuron Hair cell http://umech.mit.edu/hearing/intro/big/hccomp.000.gif
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division Cells The basic functional units of all living things Human cells vary widely but all have similar basic structure Cells vary widely in morphology Neuron Hair cell http://umech.mit.edu/hearing/intro/big/hccomp.000.gif
The Biology End-Of Course Exam will require students to apply scientific knowledge attained and described below in the NGSSS from middle grades
 The Biology End-Of Course Exam will require students to apply scientific knowledge attained and described below in the NGSSS from middle grades SC.912.N.1.1 Define a problem based on a specific body of
The Biology End-Of Course Exam will require students to apply scientific knowledge attained and described below in the NGSSS from middle grades SC.912.N.1.1 Define a problem based on a specific body of
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Name: Date: Hour: Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis. Monomer Polymer Example Drawing Function in a cell DNA
 Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction B1 B1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the events that occur during 3 stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. 2. Compare and
Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction B1 B1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the events that occur during 3 stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. 2. Compare and
Science 9 Biology. Cell Division and Reproduction Booklet 1 M. Roberts RC Palmer
 Science 9 Biology Cell Division and Reproduction Booklet 1 M. Roberts RC Palmer How do all living organisms reproduce and grow? Goal 1: Cell Review Recall and become reacquainted with the structures found
Science 9 Biology Cell Division and Reproduction Booklet 1 M. Roberts RC Palmer How do all living organisms reproduce and grow? Goal 1: Cell Review Recall and become reacquainted with the structures found
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions
 Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe features
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe features
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
B I O. 1. B I O A N A L Y Z E T H E C E L L A S A L I V I N G S Y S T E M.
 Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Cell Review. 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things.
 Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body
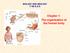 BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There are two
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There are two
Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 25: Mitosis
 Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 25: Mitosis Objective: Students will be able to explain the phases of Mitosis. Date Essential Questions: 1. What are the phases of the eukaryotic cell
Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 25: Mitosis Objective: Students will be able to explain the phases of Mitosis. Date Essential Questions: 1. What are the phases of the eukaryotic cell
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
