Biology Quarter 2 Credit Recovery. Overview. Reference textbook: Glencoe Biology 2007, ISBN
|
|
|
- Emily Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology Quarter 2 Credit Recovery Overview Reference textbook: Glencoe Biology 2007, ISBN Pre-Assessment 3 English versions 1 Spanish version Module 15 Assignments 2 Labs 1 Answer Key document that includes all assignments and labs Final Assessment 3 English versions Answer keys Materials List For lab work most materials are re-useable, but there are a few consumable items that will need replacing. 2 coins, masking tape, scissors coffee filter, scissors, real leaf, metric ruler, dime, rubbing alcohol, plastic cup Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 1
2 Name Assignment #1 Section 7-1: Cell Discovery and Theory In your textbook, read about the history of the cell theory and microscope technology. Respond to each statement. 1. Name the invention that helped scientists discover the cell. 2. Tell why Hooke called the structures he saw in the cork cellulae ("small rooms"). 3. Name the type of microscope that uses a series of magnifying lenses. Write the term or phrase that best completes each statement. Use these choices: cell theory cells daughter cells genetic material organisms The (4) includes the following three principles: All living organisms are composed of one or more (5). Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization of all living (6). Cells arise only from previously existing cells, with cells passing copies of their (7) on to their (8). Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 2
3 In your textbook, read about basic cell types. Complete the table by checking the correct column(s) for each description. Description Prokaryotes Eukaryotes 9. Organisms that break down molecules to generate energy 10. Organisms that have cells lacking internal membrane-bound organelles 11. Organisms whose cells do not have nuclei 12. Organisms that are either unicellular or multicellular 13. Organisms that are generally unicellular 14. Organisms that have cells containing organelles 15. Organisms that have plasma membranes Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 3
4 Name Assignment #2 Section 7-2: The Plasma (Cell) Membrane In your textbook, read about the function of the plasma (cell) membrane. Complete the table by checking the correct column(s) for each description. Description Selective Permeability Homeostasis Plasma (Cell) Membrane 1. The process of maintaining balance inside a cell 2. A boundary between a cell and its environment 3. The feature of the plasma (cell) membrane that keeps some substances out 4. Separates prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells from the watery environment in which they exist 5. The quality of a plasma (cell) membrane that allows oxygen and glucose to move in 6. Maintained by the plasma (cell) membrane In your textbook, read about the structure of the plasma (cell) membrane. Label the diagram of the plasma (cell) membrane. Use these choices: carbohydrate chain nonpolar tails polar head transport protein Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 4
5 Match the definition or description in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A 11. make up most of the molecules in the plasma (cell) membrane 12. a molecule that has a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate-containing compound 13. move substances through the plasma (cell) membrane 14. two layers of phospholipids arranged tail-to-tail 15. the phospholipid "sea" in which embedded substances float Column B A. transport proteins B. lipids C. phospholipid D. fluid mosaic model E. phospholipid bilayer Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 5
6 Name Assignment #3 Section 7-3: Structures and Organelles In your textbook, read about structures and organelles. Label the diagram of a typical animal cell. Use these choices: cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus microtubules mitochondrion nucleolus nucleus Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 6
7 If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, replace the italicized word or phrase to make it true. 8. Microtubules are long, hollow protein cylinders that form a rigid skeleton for the cell. 9. The Golgi apparatus contains most of the cell's DNA. 10. The nucleolus is the structure that produces sugars. 11. The endoplasmic reticulum is a stack of membranes that packages proteins into sacs called vesicles. 12. The cytoplasm is the semi-fluid internal environment of the cell. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 7
8 Name Assignment #4 Section 7-4: Cellular Transport Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A 1. moves small molecules across the plasma (cell) membrane using transport proteins 2. involves water moving across the plasma (cell) membrane to the side with the greater solute concentration 3. occurs when substances move against the concentration gradient; requires energy and the aid of carrier proteins 4. occurs when the plasma (cell) membrane surrounds a large substance inside the cell and moves it outside the cell 5. the condition that results when diffusion continues until the concentrations are the same in all areas Column B A. osmosis B. exocytosis C. facilitated diffusion D. dynamic equilibrium E. active transport F. endocytosis 6. occurs when the plasma (cell) membrane surrounds a large substance outside the cell and moves it inside the cell Complete the table by checking the correct column(s) for each description. Description 7. A solution that has the same osmotic concentration as a cell's cytoplasm 8. A solution that causes a cell to shrivel 9. A solution that causes a cell to swell 10. A solution that neither shrinks nor swells a cell 11. A solution in which there is more water outside the cell than inside the cell 12. A solution that causes water to move out of a cell Isotonic Solution Hypotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 8
9 Name Assignment #5 Chapter 7 Review: Cellular Structure and Function Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which defines a cell? A. microscopic organisms in water B. protein molecules in animals C. the basic unit of living things D. the smallest type of animal 2. Which is a structure common to all cells? A. mitochondria B. nucleus C. endoplasmic reticulum D. plasma membrane 3. Which is a protein fiber that forms the cell's supporting network? A. cytoskeleton B. cell wall C. endoplasmic reticulum D. plasma (cell) membrane Part B: Matching Matching Set 1 Place a check in the correct box to identify the type of cell described by each statement. Statement Eukaryote Prokaryote 4. A unicellular organism such as bacteria 5. A cell with a nucleus 6. A cell with organelles that do specific tasks 7. The first type of cell to evolve Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 9
10 Matching Set 2 Write the letter of the correct cell structure on the line next to the structure's description. Answers may be used only once. 8. creates energy for the cell 9. produces proteins 10. unwanted substances would build up in the cell without this organelle 11. contains the cell's DNA A. lysosome B. mitochondria C. nucleus D. ribosome Part C: Interpreting Drawings Write your response to each statement in the space provided. 12. Study the drawing of a plasma (cell) membrane. Identify the substances that belong with the arrows labeled A to E. Use the substances carbon dioxide, glucose, oxygen, wastes, and water for your labels. A. B. C. D. E. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 10
11 13. Study the drawings of the three solutions below. Identify the hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions. A. B. C. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 11
12 Name Assignment #6 Chapter 8 Concept Mapping: Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs cycle, mitochondria, releases. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 12
13 Name Assignment #7 Section 8-1: How Organisms Obtain Energy In your textbook, read about autotrophs and heterotrophs. Refer to the illustrations. Use each of the terms below only once to complete the passage. The assignment starts with #11. autotrophs Chemo-autotrophs Group A Group B heterotrophs The group that makes their own food is (1). The organisms in this group are called (2). The group that must eat other organisms for food is (3). The organisms in this group are called (4). Some organisms get their energy from inorganic substances, such as hydrogen sulfide. These organisms are called (5). Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 13
14 Name Assignment #8 Section 8-2: Photosynthesis In your textbook, read about light reactions. Number the following steps of light reactions in the order in which they occur. 1. The energy lost by electrons as they pass through the electron transport chain is used to make ATP. 2. The electrons pass from the chlorophyll to an electron transport chain. 3. Sunlight strikes the chlorophyll molecules in the thylakoid membranes. 4. NADP + molecules change to NADPH as they carry the electrons to the stroma of the chloroplast. 5. Light energy is transferred to the chlorophyll's electrons. 6. The electrons are passed down a second electron transport chain. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 14
15 Name Assignment #9 Section 8-3: Cellular Respiration In your textbook, read about cellular respiration. Use each of the terms below only once to complete the passage. aerobic glucose anaerobic glycolysis ATP mitochondria cellular respiration NADH cytoplasm oxygen energy Organisms obtain energy in a process called (1). This process harvests electrons from carbon compounds, such as (2), and uses that energy to make (3). ATP is used to provide (4) for cells to do work. In (5), glucose is broken down into pyruvate. Glycolysis is a(n) (6) process because it does not require oxygen. Glycolysis takes place in the (7). Two molecules of ATP and two molecules of (8) are formed for every glucose molecule that is broken down. (9) respiration takes place in the (10). It is aerobic because the process requires (11). Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 15
16 Name Assignment #10 Chapter 9 Concept Mapping: The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. Chromosomes arrive at poles. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 16
17 Name Assignment #11 Section 9-1: Cellular Growth In your textbook, read about cell size limitations. List two alternative futures for cells when they reach their size limitations In your textbook, read about the cell cycle. Draw the cell cycle in the space below. Include the following labels: cytokinesis, G 1, G 2, interphase, mitosis, S. 3. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 17
18 Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A 4. stage in which the cell divides into two daughter cells with identical nuclei 5. substage of interphase immediately after a cell divides 6. substage of interphase in which the cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division 7. stage in which the cell's nuclear material divides and separates 8. main stage in which the cell grows, carries out normal functions, and duplicates its DNA 9. substage in which the cell prepares for nuclear division and a protein that makes microtubles for cell division is synthesized Column B A. S phase B. cytokinesis C. G 1 D. G 2 E. interphase F. mitosis Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 18
19 Name Assignment #12 Section 9-2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis In your textbook, read about the stages of mitosis. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The nuclear membrane disintegrates during prophase. 2. Microtubules move chromatids to the poles of the cell during anaphase. 3. Chromosomes reach the poles of the cell during metaphase. 4. The cell's chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase. 5. The nuclear envelope re-forms during anaphase. 6. Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up along the equator of the cell during metaphase. 7. The nucleus reappears during prophase. 8. Centrioles migrate to the poles of the cell during telophase. 9. Chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 10. The first stage of mitosis is telophase. 11. The chromosomes decondense or unwind during telophase. 12. The shortest stage of mitosis is metaphase. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 19
20 Label the diagram of the stages of mitosis using lines Use these choices: anaphase metaphase prophase telophase Label the diagrams above using lines Use these choices: centrioles centromere sister chromatids spindle fibers Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 20
21 Name Assignment #13 Meiosis I and Meiosis II Complete the events chains about meiosis I and meiosis II. These terms may be used more than once: chromosomes, condense, cytokinesis, equator, line up, nuclei, pair up, separate, sister chromatids, spindle apparatus. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 21
22 Name: Assignment #14 Section 10-1: Meiosis In your textbook, read about meiosis I and meiosis II. Label the diagrams below. Use these choices: anaphase I anaphase II interphase metaphase I metaphase II prophase I prophase II telophase I telophase II Complete the table by checking the correct column(s) for each description. Description Mitosis Meiosis 10. Involved in the production of gametes 11. Involved in growth and repair 12. Promotes genetic variation in organisms 13. Consists of one nuclear division 14. Produces daughter cells that are genetically identical 15. Involves two sets of nuclear divisions 16. Produces daughter cells that are not identical 17. Involves the synapsis of homologous chromosomes 18. Occurs during asexual reproduction 19. Results in four haploid gametes 20. Also called reduction division Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 22
23 Name Assignment #15 Section 10-2: Mendelian Genetics In your textbook, read about how genetics began and the inheritance of traits. Write the term or phrase that best completes each statement. Use these choices: cross-pollination dominant gametes inherited recessive self-fertilization trait 1. Mendel was the first person to succeed in predicting how traits are from generation to generation. 2. In peas, both male and female sex cells, which are called, are in the same flower. 3. occurs when a male gamete fuses with a female gamete in the same flower. 4. Mendel used the technique called to breed one plant with another. 5. Mendel studied only one at a time and analyzed his data mathematically. 6. In individuals with a heterozygous genotype, the allele of a trait is hidden by the expression of the other phenotype. 7. In individuals with a heterozygous genotype, the allele of a trait is visible in the phenotype. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 23
24 In your textbook, read about Punnett squares. Complete the Punnett square by filling in the missing information. A student crossed true-breeding pea plants that had purple flowers (P) with truebreeding pea plants that had white flowers (p). All of the offspring had purple flowers. Then the student crossed two plants from the F 1 generation. The student's Punnett square is shown at right. What information should the student put in each blank? Remember, the dominant allele is always written first. For numbers 8-12, fill in the blanks in the Punnett square. In your textbook, read about the inheritance of traits and Punnett squares. Use each of the terms below only once to complete the passage. dihybrid gene genotypes monohybrid phenotypic ratio A cross between plants that involves one characteristic is called a (13) cross. Mendel also performed (14) crosses, which involve two (15) pairs, with pea plants. When he crossed two pea plants that were heterozygous for both seed shape (Rr) and for seed color (Yy), he observed a 9:3:3:1 (16) among the seeds of the offspring. A Punnett square shows the possible phenotypes and (17) of the offspring. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 24
25 Complete the Punnett square by filling in the missing information for numbers In your textbook, read about probability. Refer to the Punnett square above. Respond to the following statement. 31. Find the probability that a wrinkled, green seed will result. Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 25
26 Name Lab #1: Coin Crosses Class Time: 15 minutes Materials 2 coins, masking tape, scissors Procedure Here s how you can use coins to model Mendel s cross between two Tt pea plants. 1. Place a small piece of masking tape on each side of two coins. 2. Write a T (for tall) on one side of each coin and a t (for short) on the other. 3. Toss both coins together 20 times. Record the letter combinations that you obtain from each toss. Toss Results (TT, Tt, or tt) Toss Results (TT, Tt, or tt) Interpreting Data. 1. How many of the offspring would be tall plants? (Hint: What different letter combinations would result in a tall plant?) 2. How many would be short? 3. Convert your results in questions 1 and 2 to percentages. 4. Compare your results to Mendel s. Are the results that you came up with similar to Mendel s or not? Why or why not? Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 26
27 Name Lab #2: Looking at Pigments Class Time: 20 minutes Materials coffee filter, scissors, leaf, metric ruler, dime, rubbing alcohol, plastic cup Procedure CAUTION: Do not use plants that may cause allergic reactions. Advise students not to taste or inhale the alcohol. Make sure no open flames are present. A geranium works well. In a leaf you see the green, but there are other pigments! You can observe the pigments in a leaf by extracting them in a process called chromatography. 1. Cut a strip 5 cm by 20 cm out of a paper coffee filter. 2. Place a leaf on top of the paper strip, about 2 cm from the bottom. 3. Roll the edge of a dime over the leaf, which will press the leaf into the paper and leave behind a stripe of color on the paper strip. 4. Pour a tiny bit of rubbing alcohol into a plastic cup to a depth of 1 cm. Stand the paper strip in the cup so the color band is about 1 cm above the alcohol (do NOT let the green stripe actually touch the puddle of rubbing alcohol). Hook the other end of the strip over the top of the cup. 5. After 10 minutes, remove the paper strip and let it dry. Observe the strip. 6. Wash your hands. Analyze 1. What does the paper strip s appearance reveal about leaf pigments? 2. In the fall, when chlorophyll decreases in some plants, why do leaves change color? Biology Q2 Module-Glencoe, adapted with permission 3/12 27
Name Date Class. Meiosis I and Meiosis II
 Concept Mapping Meiosis I and Meiosis II Complete the events chains about meiosis I and meiosis II. These terms may be used more than once: chromosomes, condense, cytokinesis, equator, line up, nuclei,
Concept Mapping Meiosis I and Meiosis II Complete the events chains about meiosis I and meiosis II. These terms may be used more than once: chromosomes, condense, cytokinesis, equator, line up, nuclei,
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Name Date Class CHAPTER 10. Section 1: Meiosis
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 10 Section 1: Meiosis In your textbook, read about meiosis I and meiosis II. Label the diagrams below. Use these choices: anaphase I anaphase II interphase metaphase
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 10 Section 1: Meiosis In your textbook, read about meiosis I and meiosis II. Label the diagrams below. Use these choices: anaphase I anaphase II interphase metaphase
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. p
 Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Biology Unit 3 Exam DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
To help you complete this review activity and to help you study for your test, you should read SC State Standards B
 Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Biology 1 Semester Review
 Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
5. The cells in the liver that detoxify poison substances contain lots of a. smooth ER b. rough ER c. Golgi apparatus d. lysosomes e.
 Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
Essential Questions. Meiosis. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Life Science Review Packet. Cell Structure and Function: What Defines Life:
 Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle
 Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Chapter 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Section 1: Meiosis Section 2: Mendelian Genetics Section 3: Gene Linkage and Polyploidy Click on a lesson name to select. Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Section 1: Meiosis Section 2: Mendelian Genetics Section 3: Gene Linkage and Polyploidy Click on a lesson name to select. Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body
Anaphase. Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell
 Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Cell Theory Essential Questions
 Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
MIDTERM EXAM Figure 7-1
 No. MIDTERM EXAM 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark your response on your answer sheet. (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is
No. MIDTERM EXAM 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark your response on your answer sheet. (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is
Chapter Outline. The Living Cell. The Cell Theory. The Nature and Variety of Cells. Cell theory. Observing Cells: The Microscope
 Chapter Outline The Living Cell Chapter 21 The Nature and Variety of Cells How Does a Cell Work? Metabolism: Energy and Life Cell Division Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place
Chapter Outline The Living Cell Chapter 21 The Nature and Variety of Cells How Does a Cell Work? Metabolism: Energy and Life Cell Division Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions
 NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
Biology Semester Review
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things are made of what?
 All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Review Quizzes Chapters 6-10
 Review Quizzes Chapters 6-10 1. The product(s) of the light reactions of photosynthesis is/are a. pyruvate b. glucose c. ATP and NADPH d. CO 2 and H 2 O e. ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 1. The product(s)
Review Quizzes Chapters 6-10 1. The product(s) of the light reactions of photosynthesis is/are a. pyruvate b. glucose c. ATP and NADPH d. CO 2 and H 2 O e. ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 1. The product(s)
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions
 Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Name: Date: Period: Biology End of Course Vocabulary 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and
 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
Biology Review Second Quarter Mr. Pagani. 2 nd 9 Weeks. Review of major concepts of Biology. Plant structure & Function
 2 nd 9 Weeks Review of major concepts of Biology Plant structure & Function 1. Label each part of the plant diagram above. 2. What is the function of each part? (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) 3. What is a plant?)
2 nd 9 Weeks Review of major concepts of Biology Plant structure & Function 1. Label each part of the plant diagram above. 2. What is the function of each part? (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) 3. What is a plant?)
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Academic Biology: Midterm Review
 Academic Biology: Midterm Review Quarter #1 Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Biology the study of the living world Scientific Method Step 1: Observation Step 2: Forming a Question Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
Academic Biology: Midterm Review Quarter #1 Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Biology the study of the living world Scientific Method Step 1: Observation Step 2: Forming a Question Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES Cell Theory 1. All living things 2. Cells are the. 3. Cells are produced All Living things have cells a. Unicellular b. Multicellular Types of Cells a. Prokaryote: i.
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES Cell Theory 1. All living things 2. Cells are the. 3. Cells are produced All Living things have cells a. Unicellular b. Multicellular Types of Cells a. Prokaryote: i.
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
A.P. Biology Summer Assignment Mr. Moses
 A.P. Biology Summer Assignment 2018 - Mr. Moses Below, you will find items that you must cover during the summer. The review packet is designed to give students an understanding of the commitment necessary
A.P. Biology Summer Assignment 2018 - Mr. Moses Below, you will find items that you must cover during the summer. The review packet is designed to give students an understanding of the commitment necessary
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Cell Theory and Structure. Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles
 Cell Theory and Structure Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles Discoveries In 1665 Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork from an oak tree What he saw reminded him of
Cell Theory and Structure Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles Discoveries In 1665 Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork from an oak tree What he saw reminded him of
Review: Each molecule of glucose yields up to 38 molecules of ATP
 Review: Each molecule of glucose yields up to 38 molecules of ATP Electron shuttle across membrane Mitochondrion Cytoplasm 2 NADH 2 NADH (or 2 FADH 2 ) 2 NADH 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 GLYCOLYSIS Glucose 2 Pyruvate
Review: Each molecule of glucose yields up to 38 molecules of ATP Electron shuttle across membrane Mitochondrion Cytoplasm 2 NADH 2 NADH (or 2 FADH 2 ) 2 NADH 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 GLYCOLYSIS Glucose 2 Pyruvate
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Chapter 7. Cell Structure & Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review
 Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
PLEASE KEEP EACH EOC CHECK POINTS PAGE!! These will help you review for chapter tests as well as prepare for your EOC Exam!
 EOC Check Points Nature of Science 1. State the independent variable for the graph. 2. On which axis (X, Y) is the independent variable located? 3. State the dependent variable for the graph. 4. On which
EOC Check Points Nature of Science 1. State the independent variable for the graph. 2. On which axis (X, Y) is the independent variable located? 3. State the dependent variable for the graph. 4. On which
Cells. Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have ~ 100 TRILLION cells each!
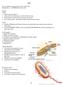 Cells Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have ~ 100 TRILLION cells each! History 1660 s Microscopes developed Allowed for the observation of cells for the first time Robert Hooke
Cells Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have ~ 100 TRILLION cells each! History 1660 s Microscopes developed Allowed for the observation of cells for the first time Robert Hooke
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Meiosis and Mendel. Chapter 6
 Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function
 Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Turns sunlight, water & carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into sugar & oxygen through photosynthesis
 CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
d. If the plants in pot 3 grew the fastest over a 3 week period, what would your conclusion be about the fertilizers?
 First Semester Exam Review 50 total questions Nature of Science: 5 questions Students will be able to: develop a testable question, form a hypothesis, identify the independent and dependent variables and
First Semester Exam Review 50 total questions Nature of Science: 5 questions Students will be able to: develop a testable question, form a hypothesis, identify the independent and dependent variables and
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
Know how to read a balance, graduated cylinder, ruler. Know the SI unit of each measurement.
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Hypothesis. Levels of organization. Theory. Controlled experiment. Homeostasis. ph scale. Characteristics of living things
 Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Biology Final Study for Multiple Choice Questions USE YOUR STUDY GUIDES & NOTES!!! Be able to explain, de<ine, & give examples for appropriate terms.
 Biology Final Study for Multiple Choice Questions USE YOUR STUDY GUIDES & NOTES!!! Be able to explain, de
Biology Final Study for Multiple Choice Questions USE YOUR STUDY GUIDES & NOTES!!! Be able to explain, de
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There are two
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There are two
Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide
 Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide These questions are designed to get you thinking about all the concepts we have discussed from Chapters 1-11. However, you will be responsible for knowing ALL the information
Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide These questions are designed to get you thinking about all the concepts we have discussed from Chapters 1-11. However, you will be responsible for knowing ALL the information
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
-Genetics- Guided Notes
 -Genetics- Guided Notes Chromosome Number The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance genes are located in specific on chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes chromosomes come in, one from the male parent and one
-Genetics- Guided Notes Chromosome Number The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance genes are located in specific on chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes chromosomes come in, one from the male parent and one
Biology 1 Notebook. Review Answers Pages 17 -?
 Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Cell Division. Genetic info must be copied. Each cell gets a complete copy of that info. It occurs in two main stages:
 10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cells. The basic units of a living system or organism
 Cells The basic units of a living system or organism Cell Theory developed by 3 German scientists: Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow These scientists discoveries led to the cell theory
Cells The basic units of a living system or organism Cell Theory developed by 3 German scientists: Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow These scientists discoveries led to the cell theory
Name Date Class. Photosynthesis and Respiration
 Concept Mapping Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs
Concept Mapping Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
The Cell. What is a cell?
 The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
Cell Types. Prokaryotes
 Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
B-2 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles.
 B-2 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles. B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one
B-2 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles. B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Passive. mechanisms. Active. mechanisms. Cell diffusion. Movement. Movement. Movement. Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as:
 Passive mechanisms Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active mechanisms Mechanisms that do require cellular energy such as: Active
Passive mechanisms Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active mechanisms Mechanisms that do require cellular energy such as: Active
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
Chapter Life Is Cellular
 Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Biology 2018 Final Review. Miller and Levine
 Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
8. Use the following terms: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, chromosome, spindle fibers, centrioles.
 Midterm Exam Study Guide: 2nd Quarter Concepts Cell Division 1. The cell spends the majority of its life in INTERPHASE. This phase is divided up into the G 1, S, and G 2 phases. During this stage, the
Midterm Exam Study Guide: 2nd Quarter Concepts Cell Division 1. The cell spends the majority of its life in INTERPHASE. This phase is divided up into the G 1, S, and G 2 phases. During this stage, the
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño
 Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key
 Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key 1. Which of the following is true of Interphase? a. It is part of Meiosis b. It occurs before Meiosis c. The cell does normal cell activities during interphase
Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key 1. Which of the following is true of Interphase? a. It is part of Meiosis b. It occurs before Meiosis c. The cell does normal cell activities during interphase
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
7 th Grade Science Unit 2NCFE Review
 7 th Grade Science Unit 2NCFE Review Cells The basic units of a living system or organism 2 Types of Cells: Prokaryotic - Cells that don t have a membrane-covered nucleus for example: bacteria Eukaryotic
7 th Grade Science Unit 2NCFE Review Cells The basic units of a living system or organism 2 Types of Cells: Prokaryotic - Cells that don t have a membrane-covered nucleus for example: bacteria Eukaryotic
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Name Date Block. Biology EOCT Review
 Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Biology Honors Mid-Term Review
 Biology Honors Mid-Term Review Please be on time to class. Avoid scheduling appointments or leaving class early. Exam Date: December 15 th and 16 th This study guide packet is due the day of the mid-term
Biology Honors Mid-Term Review Please be on time to class. Avoid scheduling appointments or leaving class early. Exam Date: December 15 th and 16 th This study guide packet is due the day of the mid-term
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function
 Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
