Course Information for Introductory Biology II: Biology at the Macroscopic Level
|
|
|
- Conrad Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course Information for COURSE NUMBER: COURSE TITLE: BL1021 Introductory Biology II: Biology at the Macroscopic Level COURSE DESCRIPTION: This is a Biology course designed for students who have successfully passed Introductory Biology I. Students will carry over their knowledge from Introductory Biology I to gain a thorough understanding of Biology at the macroscopic level. A combination of both Introductory Biology I and II will achieve better understanding of basic concepts that are required for success in various Biology courses in Health Sciences, Natural Resources and/or University programs. Students will be expected to complete assignments and labs to show their understanding of the concepts. PREREQUISITES: CO-REQUISITES: BL Introductory Biology I None CREDIT VALUE: Four (4) COURSE HOURS PER WEEK: Three (3) LAB HOURS PER WEEK: Two (2) SUGGESTED TEXT: Simon, E. J., Reece, J. B., & Dickey, J. L. (2010). Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (3 rd ed.). Toronto, ON: Pearson Education Canada. ISBN 10: ; ISBN 13: BL1021 Laboratory Manual and Workbook. College of the North Atlantic, Prince Philip Drive, St. John s, NL LEARNING RESOURCES: Pechenik, J. (2009). Short guide to writing about Biology (7 th ed.). New York, NY: Longman Publishing. ISBN 10: X; ISBN 13: MAJOR TOPICS: 1.0 Multicellular Structure 2.0 Plants 3.0 Animals College of the North Atlantic BL1021 Page 1 of 6
2 4.0 Animal Systems 5.0 Evolution and Populations 6.0 Ecology 7.0 Communities and Ecosystems LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1.0 Multicellular Structure 2.0 Plants 1.1 Define tissues, organs and organ systems in relation to division of labor 1.2 Describe and compare the four main protist groups. Explain how these different groups impact our lives 1.3 Describe the structure of multicellular protists, using examples, as organisms that do not display division of labor 1.4 Describe the structure of multicellular fungi, using examples, as organisms that do not display division of labor 1.5 Compare unicellular to multicellular life, and explain the advantages of each system 2.1 The Move Onto Land Describe the process by which algae likely evolved onto land Distinguish between algae and plants. Describe the functions of the following terrestrial adaptations: stomata, cuticle, lignin, vascular tissue, and gametangia Describe the four major periods of plant evolution Explain how mosses, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms differ 2.2 Plant Structure Describe a typical plant cell with organelles and structures that are specific to plant cells Describe the basic characteristics of plants and further describe plants as multicellular organisms with tissues, organs and organ systems Describe the four organs of a flowering plant; roots, stems, leaves and flowers Compare the structure of monocots and dicots Compare the structures and functions of root and shoot systems Define a taproot, runner, rhizome, tuber, and tendril Compare the structures and functions of the epidermis, vascular tissue system (xylem and phloem), and ground tissue system of roots and shoots Compare the structure of a leaf, root and stem as organs composed of various tissues: dermal,, ground and vascular tissue Relate the structure of the leaf to its function of photosynthesis and transpiration College of the North Atlantic BL1021 Page 2 of 6
3 2.3 Plant Life Cycles Describe the parts of a flower and their functions. Relate this structure to the life cycle of an angiosperm Compare the alternation of generations found in bryophytes and angiosperms, defining gametophyte, gametes, sporophyte, spores, zygote, fertilization, mitosis and meiosis Explain how a seed forms Describe the formation and functions of fruit 3.0 Animals 3.1 Evolution of Animals Describe a typical animal cell Describe the basic characterisitics of animals and further describe animals as multicellular organisms composed of tissues, organs and organ systems Distinguish among the nine major animal phyla (Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Mollusca, Annelida, Arthropoda, Ecinodermata, Chordata) according to the presence or type of tissues, body symmetry, and body cavities Define vertebrate versus invertebrate, giving examples of various vertebrates Describe the general structure of the invertebrate phyla Describe the four characteristics of phylum Chordata Describe the adaptations of fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds Distinguish among monotremes, marsupials, and eutherian mammals, and provide examples of each. Describe the characteristics common to all mammals 3.2 Animal Structure and Function Describe the hierarchical levels of organization in an animal Describe several examples of how form fits function in biological structure Define and compare anatomy and physiology Define a tissue. Describe the four main categories of animal tissues, noting examples of each. Describe the relationships among tissues, organs, and organ systems Explain how an animal's size and shape affect how it exchanges energy and materials with its surrounding environment Define homeostasis and illustrate with an example Define thermoregulation and compare the characteristics of endotherms and ectotherms Describe adaptations, in humans and other animals, that aid in thermoregulation 4.0 Animal Systems College of the North Atlantic BL1021 Page 3 of 6
4 4.1 Define and distinguish among herbivores, carnivores and omnivores 4.2 Describe the four stages of animal nutrition, i.e. ingestion, digestion, absorption and elimination 4.3 Describe the human digestive system and relate to function 4.4 Compare the human digestive tract to the digestive compartment found in other animals 4.5 Define and distinguish among malnutrition, undernutrition, and obesity 4.6 Describe the three main components of circulatory systems and explain why most animals require a circulatory system 4.7 Define open circulatory system and closed circulatory system 4.8 Describe the components and functions of the human cardiovascular system 4.9 Explain how the circulatory and respiratory systems cooperate to facilitate gas exchange 4.10 List four types of respiratory surfaces and give examples of animals that use them 4.11 Describe the human respiratory system and relate to function 4.12 Describe the body s nonspecific external and internal defense mechanisms 4.13 Describe the general structure and functions of the lymphatic system 4.14 Describe the human immune system as a specific defense system and describe the components that are part of the immune system 4.15 Describe the human endocrine system and relate to function 4.16 Describe the types of reproduction found in animals and distinguish between internal and external fertilization 4.17 Compare the structure and function of the female and male human reproductive system 4.18 Describe human development from fertilization to birth 4.19 Describe the structure and function of the human nervous system and compare to other animals 4.20 Describe the five general categories of sensory receptors found in animals. Note examples of each 4.21 Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons. Describe three types of joints and provide examples of each 4.22 Describe the components of animals motor systems including the relationship of muscle to skeleton 4.23 Define the process of osmoregulation. Distinguish between osmoconformers and osmoregulators 4.24 Describe the components and functions of the human excretory system and how it contributes to the process of osmoregulation 5.0 Evolution and Populations 5.1 Define evolution 5.2 Explain how each of the following provides evidence that evolution occurs: fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology and molecular biology 5.3 Describe natural selection and adaptive evolution, including Darwin s observations College of the North Atlantic BL1021 Page 4 of 6
5 5.4 Define a population, describe its properties, and explain why a population is the smallest unit of evolution 5.5 Discuss the mechanisms of microevolution and distinguish between the following set of terms: genetic drift versus gene flow; the founder effect versus bottleneck effect; and directional selection, diversifying selection, and stabilizing selection 5.6 Describe the processes included in the study of macroevolution and distinguish between nonbranching and branching evolution 5.7 Define the biological species concept and distinguish between different types of reproductive isolating mechanisms and speciation 6.0 Ecology 6.1 Define ecology, and distinguish between abiotic and biotic components of the environment 6.2 Define biosphere and the four levels of ecology 6.3 Distinguish between the science of ecology and the term environmentalism 6.4 Explain why the biosphere is patchy. List and describe the major abiotic factors affecting the distribution of life in the biosphere 6.5 Define population ecology and population density 6.6 Explain how the mark-recapture method can be used to estimate population size 6.7 Compare the circumstances that produce clumped, uniform, and random dispersion patterns 6.8 Compare the exponential growth model to the logistic growth model. Describe examples of each 6.9 Distinguish between density-dependent and density-independent factors 6.10 Compare and give examples of the three general types of survivorship curves 6.11 Compare the characteristics of species that show opportunistic or equilibrial life histories. Describe examples of each 7.0 Communities and Ecosystems 7.1 Define a community and describe the four key properties of a community 7.2 Discuss the interspecific interaction in communities including competition, predation, symbiotic relationships and community networks 7.3 Define the competitive exclusion principle and describe the process of resource partitioning 7.4 Explain how predation maintains species diversity 7.5 Describe ecological succession and distinguish between primary and secondary succession 7.6 Explain why stability and balance are not characteristic of most communities 7.7 Define ecosystems and give examples to show the interactions between communities and their environment 7.8 Define trophic levels as part of food chains and food webs within ecosystems 7.9 Define producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers 7.10 Discuss energy flow in ecosystems, including the energy pyramids and the laws of thermodynamics College of the North Atlantic BL1021 Page 5 of 6
6 7.11 Discuss the importance of the biogeochemical cycles in ecosystems including the carbon and nitrogen cycle 7.12 Define biomes, using examples, and discuss the influence climate has on biome distribution 7.13 Discuss various human impacts on biological communities and ecosystems LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR THE LABORATORY: The following laboratory objectives are incorporated throughout the biology course. 1. Investigate the multicellular structure of Protists and Fungi. 2. Investigate the various plant structures. 3. Dissect a fetal pig to observe structure and function of mammalian organ systems. This lab will require supervision. 4. Investigate population sampling methods in Biology. 5. Investigate the diversity of organisms at a community level. EVALUATION: Labs/Assignments: 15% Tests: 30% Midterm Exam: 15% Final Exam: 40% Pass Mark: 50% DATE DEVELOPED: December 2004 DATE REVIEWED: REVISION NUMBER: 4 DATE REVISED: July 2012 Effective PeopleSoft Date: Note to instructor: Check PIRS to ensure this outline is the most current version. College of the North Atlantic BL1021 Page 6 of 6
Bossier Parish Community Master Syllabus. Course and Prefix Number: BLGY 102 Credit Hours: 3
 Bossier Parish Community Master Syllabus Course and Prefix Number: BLGY 102 Credit Hours: 3 Course Title: General Biology II Course Prerequisites: BLGY 101 or equivalent Textbook: Mader, S. and M. Windelspecht;
Bossier Parish Community Master Syllabus Course and Prefix Number: BLGY 102 Credit Hours: 3 Course Title: General Biology II Course Prerequisites: BLGY 101 or equivalent Textbook: Mader, S. and M. Windelspecht;
Course Syllabus. Department: Science and Technology. Date: February 3, I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122. Course Name: General Biology II
 Department: Science and Technology Date: February 3, 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122 Course Name: General Biology II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 4 Credit hours and 5 Contact
Department: Science and Technology Date: February 3, 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122 Course Name: General Biology II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 4 Credit hours and 5 Contact
Successful completion of Algebra 1 provides the mathematical skills you ll need for Biology B.
 Syllabus Biology B Course Overview Biology is a science dedicated to studying all forms of life on Earth. You are probably familiar with a number of plants and animals, but do you know what makes them
Syllabus Biology B Course Overview Biology is a science dedicated to studying all forms of life on Earth. You are probably familiar with a number of plants and animals, but do you know what makes them
Course ID May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE. Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology)
 Degree Applicable Glendale Community College Course ID 005073 May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology) Catalog Statement BIOL 102 provides
Degree Applicable Glendale Community College Course ID 005073 May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology) Catalog Statement BIOL 102 provides
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Understands that kingdoms are subdivided into phylum etc.
 August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND. Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution
 CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
Bergen Community College Division of Math, Science, and Technology Department of Biology and Horticulture. Course Syllabus. BIO 101 General Biology I
 Bergen Community College Division of Math, Science, and Technology Department of Biology and Horticulture Semester and year: Course Number and Section: Meeting Times and Locations: Instructor: Office Location:
Bergen Community College Division of Math, Science, and Technology Department of Biology and Horticulture Semester and year: Course Number and Section: Meeting Times and Locations: Instructor: Office Location:
CABRILLO COLLEGE : Fall 2008
 Instructor: Nicole Crane Office #620 ph. 479-5094 e-mail: nicrane@cabrillo.edu www.cabrillo.edu/~ncrane CABRILLO COLLEGE : Fall 2008 BIOLOGY 1C: Plant Biology and Ecological Principles Textbooks: 1) Biology,
Instructor: Nicole Crane Office #620 ph. 479-5094 e-mail: nicrane@cabrillo.edu www.cabrillo.edu/~ncrane CABRILLO COLLEGE : Fall 2008 BIOLOGY 1C: Plant Biology and Ecological Principles Textbooks: 1) Biology,
Introduction to Biology with Lab
 Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
Introduction to Biology
 Introduction to Biology Course Description Introduction to Biology is an introductory course in the biological sciences. Topics included are biological macromolecules, cell biology and metabolism, DNA
Introduction to Biology Course Description Introduction to Biology is an introductory course in the biological sciences. Topics included are biological macromolecules, cell biology and metabolism, DNA
5TH-8TH GRADE SCIENCE TOPICS
 5TH-8TH GRADE SCIENCE TOPICS Chemistry 5 6 7 8 sort/classify objects mass/weight length, width, height, volume states of matter density physical/chemical properties and changes parts of the atom periodic
5TH-8TH GRADE SCIENCE TOPICS Chemistry 5 6 7 8 sort/classify objects mass/weight length, width, height, volume states of matter density physical/chemical properties and changes parts of the atom periodic
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
CABRILLO COLLEGE : Spring 2012
 CABRILLO COLLEGE : Spring 2012 BIOLOGY 1C: Plant Biology and Ecological Principles Instructor: Nicole Crane Office #620 Office hours: MW 2:40-4:00, Thursday 12:40-1:40 ph. 479-5094 e-mail: nicrane@cabrillo.edu
CABRILLO COLLEGE : Spring 2012 BIOLOGY 1C: Plant Biology and Ecological Principles Instructor: Nicole Crane Office #620 Office hours: MW 2:40-4:00, Thursday 12:40-1:40 ph. 479-5094 e-mail: nicrane@cabrillo.edu
Activity Activity Title. Chapter Title Chapter Description Lesson Title Lesson Description Introduction to Living Things
 Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
d. Abscisic Acid (ABA) e. Ethylene
 AP Bio Plant Unit Review Guide and FRQs Plant Diversity Ch 23 1. List characteristics that distinguish plants from other organisms in other kingdoms. 2. Distinguish between sporophyte or gametophyte, which
AP Bio Plant Unit Review Guide and FRQs Plant Diversity Ch 23 1. List characteristics that distinguish plants from other organisms in other kingdoms. 2. Distinguish between sporophyte or gametophyte, which
BIO 1124 Principles of Biology II
 BIO 1124 Principles of Biology II Course Number and Title: BIO 1124 Principles of Biology II Catalog Description: A combined lecture and laboratory course for non-science majors that emphasize the survey
BIO 1124 Principles of Biology II Course Number and Title: BIO 1124 Principles of Biology II Catalog Description: A combined lecture and laboratory course for non-science majors that emphasize the survey
10/4/ :31 PM Approved (Changed Course) BIO 10 Course Outline as of Summer 2017
 10/4/2018 12:31 PM Approved (Changed Course) BIO 10 Course Outline as of Summer 2017 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: BIO 10 Title: INTRO PRIN BIOLOGY Full Title: Introduction to Principles of Biology
10/4/2018 12:31 PM Approved (Changed Course) BIO 10 Course Outline as of Summer 2017 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: BIO 10 Title: INTRO PRIN BIOLOGY Full Title: Introduction to Principles of Biology
Life Science Curriculum Sixth Grade
 Life Science Curriculum Sixth Grade The Sixth Grade life science curriculum emphasizes a more complex understanding of cycles, patterns and relationships in the living world. Students build on basic principles
Life Science Curriculum Sixth Grade The Sixth Grade life science curriculum emphasizes a more complex understanding of cycles, patterns and relationships in the living world. Students build on basic principles
Biology B. There are no objectives for this lesson.
 Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
BIOLOGY Grades Summer Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d. General Description:
 Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Range of Competencies
 BIOLOGY Content Domain Range of Competencies l. Nature of Science 0001 0003 20% ll. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 0004 0005 13% lll. Genetics and Evolution 0006 0009 27% lv. Biological Unity and Diversity
BIOLOGY Content Domain Range of Competencies l. Nature of Science 0001 0003 20% ll. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 0004 0005 13% lll. Genetics and Evolution 0006 0009 27% lv. Biological Unity and Diversity
Kingdom Animalia. Special Features: Advanced nervous systems means cephalization (faces), brains, and efficient mobility (walk/run/swim/grab)
 Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Cell Number: Multicellular with extensive specialization Cell Type: Eukaryotic Animal Cells (no cell wall) Food: Heterotrophic Carnivore (meat), Herbivore (plants), Omnivore
Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Cell Number: Multicellular with extensive specialization Cell Type: Eukaryotic Animal Cells (no cell wall) Food: Heterotrophic Carnivore (meat), Herbivore (plants), Omnivore
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau
 Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
McDougal Littell Science, Cells and Heredity MAZER PDF. IL Essential Lesson. IL Extend Lesson. Program Planning Guide LP page.
 s7an-ppg-pc-il-002-012.indd 2 7/18/05 2:46:40 PM 2 McDougal Littell Science, Cells and Heredity Chapter 1: The Cell, pp. 6 37 1.1 The cell is the basic unit of living things. pp. 9 17 Explore: Activity
s7an-ppg-pc-il-002-012.indd 2 7/18/05 2:46:40 PM 2 McDougal Littell Science, Cells and Heredity Chapter 1: The Cell, pp. 6 37 1.1 The cell is the basic unit of living things. pp. 9 17 Explore: Activity
Pre-AP BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SPRING
 Terms to define: Classification Phylogeny Cladogram binomial nomenclature Taxonomy Natural Selection vestigial structures homologous structures analogous structures Genetic Drift Allele Frequency Homozygous
Terms to define: Classification Phylogeny Cladogram binomial nomenclature Taxonomy Natural Selection vestigial structures homologous structures analogous structures Genetic Drift Allele Frequency Homozygous
BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW. Concept/Question. How does energy flow in the ecosystem? How do cells maintain homeostasis of ph, salinity, temperature, etc?
 BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW Concept/Question Notes How does energy flow in the ecosystem? How do cells maintain homeostasis of ph, salinity, temperature, etc? Bonds- What are bonds? What are the different types
BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW Concept/Question Notes How does energy flow in the ecosystem? How do cells maintain homeostasis of ph, salinity, temperature, etc? Bonds- What are bonds? What are the different types
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things
 Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
THE STUDY OF BIOLOGY Biology is the study of life and the interactions between living things and their nonliving environment.
 BIOLOGY 1 COURSE SYLLABUS A General Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) is developed annually which defines the student s program for the year and includes goals, objectives and evaluation procedures
BIOLOGY 1 COURSE SYLLABUS A General Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) is developed annually which defines the student s program for the year and includes goals, objectives and evaluation procedures
Biology. Topics or Context: (how the students will do it and where will it be taught) Experiments. Analyze data. Lecture Concept mapping
 Intro & Metric Rev, Microscope, and Scientific Method Evaluate the data collected during an investigation, critique the data-collection procedures and results, and suggest ways to make any needed improvements
Intro & Metric Rev, Microscope, and Scientific Method Evaluate the data collected during an investigation, critique the data-collection procedures and results, and suggest ways to make any needed improvements
Introduction to Biology Web Course Informational and Test Schedule
 Introduction to Biology Web Course Informational and Test Schedule Spring 2011 Inquiry into Life by Sylvia Mader Introduction to Biological Science (BIO1100AAW1 & 2) Three Hours Credit Nancy Petersen Brian
Introduction to Biology Web Course Informational and Test Schedule Spring 2011 Inquiry into Life by Sylvia Mader Introduction to Biological Science (BIO1100AAW1 & 2) Three Hours Credit Nancy Petersen Brian
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education
 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System Jefferson State Community College Date Adopted: July 1, 1998 Date Reviewed: December 1, 1999 Date Revised:
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System Jefferson State Community College Date Adopted: July 1, 1998 Date Reviewed: December 1, 1999 Date Revised:
Science 7 Acceleration Study Guide
 Name: Science 7 Acceleration Study Guide These are the units/topics covered in the exam: Laboratory Safety The Scientific Method and Measurement Classification Ecology Evolution Genetics Cells/Microscope
Name: Science 7 Acceleration Study Guide These are the units/topics covered in the exam: Laboratory Safety The Scientific Method and Measurement Classification Ecology Evolution Genetics Cells/Microscope
Biology regimented study plan
 For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
REVIEW 7: PLANT ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY UNIT. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 7: PLANT ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Gas exchange a. structure: stomates b. function: diffusion, supports
Period Date REVIEW 7: PLANT ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Gas exchange a. structure: stomates b. function: diffusion, supports
A Planned Course Statement for. Biology I, CP. Course # 401 Grade(s) 9, 10. Length of Period (mins.) 40 Total Clock Hours: 140
 East Penn School District Secondary Curriculum A Planned Course Statement for Biology I, CP Course # 401 Grade(s) 9, 10 Department: Science ength of Period (mins.) 40 Total Clock Hours: 140 Periods per
East Penn School District Secondary Curriculum A Planned Course Statement for Biology I, CP Course # 401 Grade(s) 9, 10 Department: Science ength of Period (mins.) 40 Total Clock Hours: 140 Periods per
Unit 7: Plant Evolution, Structure and Function
 Time: 7 Days (some time spent working over breaks on this topic) and then an exam 16% of the AP Exam is on this material. Topics Covered: Reproduction, growth, and development Structural, physiological,
Time: 7 Days (some time spent working over breaks on this topic) and then an exam 16% of the AP Exam is on this material. Topics Covered: Reproduction, growth, and development Structural, physiological,
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE. Department: Science Grade(s): 11-12
 Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Advanced Placement Biology Course Number: 2222 Department: Science Grade(s): 11-12 Level(s): Advanced Placement Credit: 1½ Course Description
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Advanced Placement Biology Course Number: 2222 Department: Science Grade(s): 11-12 Level(s): Advanced Placement Credit: 1½ Course Description
Month Content Skills Next Generation and Louisville Standards
 August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
August Living Things - Develops an understanding of the organism. Classification Distinguishes between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Recognizes organisms are organized into tissues, organs,
Kingdom Plantae. A Brief Survey of Plants
 Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Ontario Science Curriculum Grade 9 Academic
 Grade 9 Academic Use this title as a reference tool. SCIENCE Reproduction describe cell division, including mitosis, as part of the cell cycle, including the roles of the nucleus, cell membrane, and organelles
Grade 9 Academic Use this title as a reference tool. SCIENCE Reproduction describe cell division, including mitosis, as part of the cell cycle, including the roles of the nucleus, cell membrane, and organelles
Contra Costa College Course Outline
 Contra Costa College Course Outline Department & Number: BIOSC 110 Course Title: Introduction to Biological Science Pre-requisite: None Corequisite: None Advisory: None Entry Skill: None Lecture Hours:
Contra Costa College Course Outline Department & Number: BIOSC 110 Course Title: Introduction to Biological Science Pre-requisite: None Corequisite: None Advisory: None Entry Skill: None Lecture Hours:
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF THE FRASER VALLEY COURSE INFORMATION. DISCIPLINE/DEPARTMENT: Biology IMPLEMENTATION DATE: May 1994
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF THE FRASER VALLEY COURSE INFORMATION DISCIPLINE/DEPARTMENT: Biology IMPLEMENTATION DATE: May 1994 Revised: Introductory Biology II 4 SUBJECT/NUMBER OF COURSE DESCRIPTIVE TITLE UCFV
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF THE FRASER VALLEY COURSE INFORMATION DISCIPLINE/DEPARTMENT: Biology IMPLEMENTATION DATE: May 1994 Revised: Introductory Biology II 4 SUBJECT/NUMBER OF COURSE DESCRIPTIVE TITLE UCFV
BIOLOGY I, PRE-AP. Section Description State Standard Addressed
 Grade Level: 9 Course #: 3024T Length: Full Year Credits: Two Diploma: Core 40, Academic Honors Prerequisite: None COURSE DESCRIPTION: BIOLOGY I, PRE-AP This course is designed to introduce the student
Grade Level: 9 Course #: 3024T Length: Full Year Credits: Two Diploma: Core 40, Academic Honors Prerequisite: None COURSE DESCRIPTION: BIOLOGY I, PRE-AP This course is designed to introduce the student
Days: 7% (14) Unit 1: Chemistry of Life Text: Chapter 2, 6
 Days: 7% (14) Unit 1: Chemistry of Life Text: Chapter 2, 6 Aug 9 Aug 26 Top 100 Topics Objectives Activities/ Assessments 1. Basics of Matter 2. Properties of Water 3. Functional Groups and Bonding 4.
Days: 7% (14) Unit 1: Chemistry of Life Text: Chapter 2, 6 Aug 9 Aug 26 Top 100 Topics Objectives Activities/ Assessments 1. Basics of Matter 2. Properties of Water 3. Functional Groups and Bonding 4.
Study Guide. Biology 2101B. Science. Biodiversity. Adult Basic Education. Biology 2101A. Prerequisite: Credit Value: 1
 Adult Basic Education Science Biodiversity Prerequisite: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003. Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A
Adult Basic Education Science Biodiversity Prerequisite: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003. Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A
Name: Date: ID: 3. What are some limitations to scientific models? - Most models include simplifications, approximations, and/or lack details
 Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
Name: Date: ID: 2 ND 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE Shared Answers Communication Skills 1. Define the term Scientific Model in your own terms. - A description of a system, theory, or phenomenon 2. List 5 things we
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003
 [LH4] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003 Date: Friday 15 January 2016 Time: 10.00 am
[LH4] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003 Date: Friday 15 January 2016 Time: 10.00 am
Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology
 Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology TEKS Comments Louisiana GLE (Bio.1) Scientific Processes. The
Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology TEKS Comments Louisiana GLE (Bio.1) Scientific Processes. The
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record BIO 101
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record BIO 101 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog BIO 101 Biological Principles 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record BIO 101 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog BIO 101 Biological Principles 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Anatomy and Physiology 4601
 Anatomy and Physiology 4601 Description Basic concepts of human anatomy and physiology will be explored in this health (life) sciencefocused course. Using a systems approach, students will learn about
Anatomy and Physiology 4601 Description Basic concepts of human anatomy and physiology will be explored in this health (life) sciencefocused course. Using a systems approach, students will learn about
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Name 5 reasons why we think plants are A OK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Plant Cells: Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular
Introduction to Plants Name 5 reasons why we think plants are A OK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Plant Cells: Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular
Kingdom Plantae. X. Responding to Environment (10B, 12B) What are plant hormones? (p.648) What are receptor proteins? (p.648)
 X. Responding to Environment (10B, 12B) What are plant hormones? (p.648) What are receptor proteins? (p.648) Kingdom Plantae What are auxins? (p.648) What are nastic responses? (p.651) What is a tropic
X. Responding to Environment (10B, 12B) What are plant hormones? (p.648) What are receptor proteins? (p.648) Kingdom Plantae What are auxins? (p.648) What are nastic responses? (p.651) What is a tropic
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review! Chapter 31!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Biology IA & IB Syllabus Mr. Johns/Room 2012/August,
 Biology IA & IB Syllabus Mr. Johns/Room 2012/August, 2017-2018 Description of Course: A study of the natural world centers on cellular structure and the processes of life. First semester topics include:
Biology IA & IB Syllabus Mr. Johns/Room 2012/August, 2017-2018 Description of Course: A study of the natural world centers on cellular structure and the processes of life. First semester topics include:
The move from water to land. The move from water to land. Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants. Green algae are the ancestors to all plants
 Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants From Protists to Plants Moving right along! Green algae are the ancestors to all plants Who, ME? Wow I feel so important! Charophyceans 475 million years ago, shallow seas
Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants From Protists to Plants Moving right along! Green algae are the ancestors to all plants Who, ME? Wow I feel so important! Charophyceans 475 million years ago, shallow seas
Due Friday, January 11, 2008
 Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL )
 Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) FIELD 13: BIOLOGY TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Multiple-Choice Range of Objectives Approximate Test Weighting I. Nature of Science 01 04 10% II. Chemistry
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) FIELD 13: BIOLOGY TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Multiple-Choice Range of Objectives Approximate Test Weighting I. Nature of Science 01 04 10% II. Chemistry
Adam Bernstein Advanced Biology Honors Science Department Curriculum Map
 Unit 1-September -Chemistry of Life (2-3 Weeks) What are the atoms found in living things? How does atomic structure determines the behavior of an element. How does a molecules shape relates to its function?
Unit 1-September -Chemistry of Life (2-3 Weeks) What are the atoms found in living things? How does atomic structure determines the behavior of an element. How does a molecules shape relates to its function?
The Case of the Museum Mix-Up Activity Sheet
 Webquest Activity Page 1 The Case of the Museum Mix-Up Activity Sheet Name Part A Use your knowledge about the major plant and animal phyla to help John label the specimens! Remember to use the web resources
Webquest Activity Page 1 The Case of the Museum Mix-Up Activity Sheet Name Part A Use your knowledge about the major plant and animal phyla to help John label the specimens! Remember to use the web resources
California Biology Handbook... CA1
 California Biology Handbook........................... CA1 The California Biology Handbook includes correlations of the Biology/Life Science standards to the content in Biology: The Dynamics of Life. Also
California Biology Handbook........................... CA1 The California Biology Handbook includes correlations of the Biology/Life Science standards to the content in Biology: The Dynamics of Life. Also
Cells and Genetics. Life Science. Cell parts. Cell parts cont. Cell processes. Cell Division 5/4/2015
 Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Manitoba Curriculum Framework of Outcomes Grades K-3
 Grades K-3 Reference Specific Learning Outcomes Wetlands Rainforest It is expected that students will: 100-4 observe and identify similarities and differences in the needs of living Organisms, Migration,
Grades K-3 Reference Specific Learning Outcomes Wetlands Rainforest It is expected that students will: 100-4 observe and identify similarities and differences in the needs of living Organisms, Migration,
Unit 2: PLANTS. The move to land. Chapter 16 P Chapter 28 P and P
 Unit 2: PLANTS The move to land Chapter 16 P. 315-327 Chapter 28 P. 604-613 and P. 616-620 Outcomes 2.1 The Move onto Land 2.2 Plant Structure 2.3 Plant Life Cycles 2.1 Move on to Land - What is a Plant?
Unit 2: PLANTS The move to land Chapter 16 P. 315-327 Chapter 28 P. 604-613 and P. 616-620 Outcomes 2.1 The Move onto Land 2.2 Plant Structure 2.3 Plant Life Cycles 2.1 Move on to Land - What is a Plant?
1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT
 Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
Exam Short Answer Assessment Rubric (assuming a 0-10 point scale)
 Biology 162 BIG LAB EXAM Thursday 28 April 2005 page 1 Exam Short Answer Assessment Rubric (assuming a 0-10 point scale) Criteria for a Grade of: 10 Your response consists of clear concise and insightful
Biology 162 BIG LAB EXAM Thursday 28 April 2005 page 1 Exam Short Answer Assessment Rubric (assuming a 0-10 point scale) Criteria for a Grade of: 10 Your response consists of clear concise and insightful
Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land
 Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
 EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) TEKS EXAMgen Biology 3rd Edition Outline 112.34 Biology *TEKS in red denote Readiness Standards ex: (B.4)(B)R *TEKS in green denote Supporting
EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) TEKS EXAMgen Biology 3rd Edition Outline 112.34 Biology *TEKS in red denote Readiness Standards ex: (B.4)(B)R *TEKS in green denote Supporting
Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure
 Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure Plant evolution Plant Evolution Chlorophytes Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophytes are a green
Botany: Part I Overview of Plants & Plant Structure Plant evolution Plant Evolution Chlorophytes Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Chlorophytes are a green
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review. Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6)
 Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Readings Lecture Topics Class Activities Labs Projects Chapter 1: Biology 6 th ed. Campbell and Reese Student Selected Magazine Article
 Unit Subtopics and Duration Unit 1: Principles of Science Themes in science Research and Lab techniques 6 days Readings Lecture Topics Class Activities Labs Projects Chapter 1: Biology 6 th ed. Campbell
Unit Subtopics and Duration Unit 1: Principles of Science Themes in science Research and Lab techniques 6 days Readings Lecture Topics Class Activities Labs Projects Chapter 1: Biology 6 th ed. Campbell
Kentucky Core Content for Science Assessment Correlations
 Kentucky Core Content for Science LIFE SCIENCE STANDARDS THE CELL 3.1.1: Cells have particular structures that underlie their function. Every cell is surrounded by a membrane that separates it from the
Kentucky Core Content for Science LIFE SCIENCE STANDARDS THE CELL 3.1.1: Cells have particular structures that underlie their function. Every cell is surrounded by a membrane that separates it from the
Classification: Evolution:
 Review for Final Exam Suggestions All material covered in the course is testable. The following are suggested topics to cover, but is not meant to be an exhaustive list. Topics that are not listed but
Review for Final Exam Suggestions All material covered in the course is testable. The following are suggested topics to cover, but is not meant to be an exhaustive list. Topics that are not listed but
Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
Have cell walls Made of
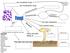 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
Some History: In the life cycle of the kelp Laminaria. One way to separate algae from protozoa is that. Rocks of Cambrian Age (ca.
 One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
Unit 8: Ecology Guided Reading Questions (60 pts total)
 AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 8: Ecology Guided Reading Questions (60 pts total) Chapter 51 Animal
AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 8: Ecology Guided Reading Questions (60 pts total) Chapter 51 Animal
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter in class follow along lecture notes
 Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Washtenaw Community College Comprehensive Report. BIO 101 Concepts of Biology Effective Term: Fall 2013
 Washtenaw Community College Comprehensive Report BIO 101 Concepts of Biology Effective Term: Fall 2013 Course Cover Division: Math, Science and Health Department: Life Sciences Discipline: Biology Course
Washtenaw Community College Comprehensive Report BIO 101 Concepts of Biology Effective Term: Fall 2013 Course Cover Division: Math, Science and Health Department: Life Sciences Discipline: Biology Course
Plants. SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes.
 Plants SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. 1. Students will explain how the structures of plant tissues and organs are directly
Plants SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. 1. Students will explain how the structures of plant tissues and organs are directly
Ch Plants.Biology.Landis
 Nom de plume Chapt2 Chapter 22 - Plant Diversity Section 22 1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551 555) This section explains what a plant is and describes what plants need to survive. It also explains how
Nom de plume Chapt2 Chapter 22 - Plant Diversity Section 22 1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551 555) This section explains what a plant is and describes what plants need to survive. It also explains how
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GENERAL BIOLOGY II BIO4135 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GENERAL BIOLOGY II BIO4135 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE. Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE)
 Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
Biology II : Embedded Inquiry
 Biology II : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
Biology II : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
BIOLOGY 144 MODULE OUTLINES AND STUDY OBJECTIVES
 BIOLOGY 144 MODULE OUTLINES AND STUDY OBJECTIVES (2017) The module is based on the prescribed text (Biology:The Dynamic Science, 3 rd edition, Russell, Hertz, McMillan). The numbers in brackets represent
BIOLOGY 144 MODULE OUTLINES AND STUDY OBJECTIVES (2017) The module is based on the prescribed text (Biology:The Dynamic Science, 3 rd edition, Russell, Hertz, McMillan). The numbers in brackets represent
Advanced Placement Biology
 Advanced Placement Biology 2014-2015 Course Description This course is designed to be equivalent to a two-semester college introductory biology course sequence. AP Biology covers topics regularly covered
Advanced Placement Biology 2014-2015 Course Description This course is designed to be equivalent to a two-semester college introductory biology course sequence. AP Biology covers topics regularly covered
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
GENERAL INFORMATION. Number of One credit (1)
 GENERAL INFORMATION Course 2000410 Number: Course Path: Section: Basic and Adult Education» Grade Group: Secondary Grades 9-12» Subject: Science» SubSubject: Biological Sciences» Course Title: Zoology
GENERAL INFORMATION Course 2000410 Number: Course Path: Section: Basic and Adult Education» Grade Group: Secondary Grades 9-12» Subject: Science» SubSubject: Biological Sciences» Course Title: Zoology
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, SHEME OF WORK - Biology SCHEME OF WORK.
 SCHEME OF WORK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Biology Year: first grade, 1.X School year:../ List of topics # Topics Time period 1. Introduction to Biology 09 2. Origin and History of life 10 3. Cell
SCHEME OF WORK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Biology Year: first grade, 1.X School year:../ List of topics # Topics Time period 1. Introduction to Biology 09 2. Origin and History of life 10 3. Cell
AP Biology. Evolution of Land Plants. Kingdom: Plants. Plant Diversity. Animal vs. Plant life cycle. Bryophytes: mosses & liverworts
 Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Montgomery County Community College BIO 122 General Biology II 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 122 General Biology II 4-3-3 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course emphasizes evolution as it applies to the development, adaptation and taxonomy of organisms. The five
Montgomery County Community College BIO 122 General Biology II 4-3-3 COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course emphasizes evolution as it applies to the development, adaptation and taxonomy of organisms. The five
Plants. and their classi.ication
 + Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
+ Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
Course Information for Introductory Biology I: Biology at the Microscopic Level
 Course Information for 2018-2019 COURSE NUMBER: COURSE TITLE: BL1020 Introductory Biology I: Biology at the Microscopic Level COURSE DESCRIPTION: This is a Biology course designed for students who have
Course Information for 2018-2019 COURSE NUMBER: COURSE TITLE: BL1020 Introductory Biology I: Biology at the Microscopic Level COURSE DESCRIPTION: This is a Biology course designed for students who have
Textbook Evert RF and SE Eichorn 2012 Raven Biology of Plants. Eighth Edition. WH Freeman. (Table of Contentsi). Lecture Topics
 Science/Biology 2010.04 Plant Biology 3 credits lecture (3 hours/week; 12 weeks); 1 credit laboratory (3 hours/week; 12 weeks) Current advances in plant biology research, highlighting plant structure,
Science/Biology 2010.04 Plant Biology 3 credits lecture (3 hours/week; 12 weeks); 1 credit laboratory (3 hours/week; 12 weeks) Current advances in plant biology research, highlighting plant structure,
