Directed Reading A. Section: Bacteria CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA. bacteria? a. cocci b. spirilla c. flagella d. bacilli.
|
|
|
- Harold Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Bacteria 1 Which of the following is true of bacteria? a All bacteria are the same size b Most bacteria can be seen without a microscope c There are fewer bacteria on Earth than most other living things d There are more bacteria on Earth than any other living thing CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA 2 How many kingdoms of living things are there? a one c six b two d ten 3 What two kingdoms of living things do bacteria belong to? a Eubacteria and Archaebacteria b Fungi and Animalia c Archaebacteria and Fungi d Protista and Plantae 4 Eubacteria and Archaebacteria contain a all of the forms of life on Earth b the oldest forms of life on Earth c the youngest forms of life on Earth d none of the forms of life on Earth 5 All bacteria have a one cell b two cells c three cells d hundreds of cells 6 Which of the following is NOT one of the most common shapes of bacteria? a cocci b spirilla c flagella d bacilli 7 What determines a bacteria s shape? a its size b the kingdom it belongs to c its color d its cell wall Holt Science and Technology 1 Bacteria and Viruses
2 Match the correct description with the correct term Write the letter in the space 8 rod-shaped 9 long, spiral-shaped 10 spherical a cocci b bacilli c spirilla 11 Some bacteria use hairlike parts called to help them move around 12 Bacteria are organisms with one cell and no 13 An organism with no nucleus is a(n) 14 An organism with a nucleus is a(n) 15 What three things can a prokaryote do that allow it to function as an independent organism? 16 Bacteria reproduce by 17 Describe how bacteria reproduce through binary fission 18 What kind of places do most bacteria grow best in? 19 What kind of places do some bacteria not grow well in? 20 Genetic material covered by a thick, protective membrane is a(n) Holt Science and Technology 2 Bacteria and Viruses
3 21 How is it possible that a bacteria could begin to grow after 30 million years in a fossilized insect s stomach? KINGDOM EUBACTERIA 22 Most bacteria are a archaebacteria c fungi b protista d eubacteria 23 The kingdom that has the most organisms is a Fungi c Eubacteria b Archaebacteria d Protista 24 Eubacteria are classified by a their size c the way they get food b their shape d the way they reproduce 25 Most eubacteria are a consumers c decomposers b producers d food sources Match the correct description with the correct term Write the letter in the space 26 bacteria that get their food from dead organic matter 27 bacteria that eat other organism or live in or on the body of another a producers b decomposers c consumers 28 bacteria that make their own food 29 What do producer bacteria use to make food? 30 A bacterium that contains the green pigment chlorophyll is 31 Many cyanobacteria contain that give them different colored tints Holt Science and Technology 3 Bacteria and Viruses
4 32 How do flamingos get their pink color? KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA Match the correct definition with the correct term Write the letter in the space 33 bacteria that live in swamps and animal intestines 34 bacteria that live in ocean vents and hot springs a heat lovers b salt lovers c methane makers 35 bacteria that live in salty environments 36 One kind of organism that often lives where no other organism can is a(n) 37 What kind of environment do archaebacteria prefer? 38 What are three places where archaebacteria have been found? 39 How are archaebacteria different from eubacteria? Holt Science and Technology 4 Bacteria and Viruses
5 TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE Answer Key Directed Reading A SECTION: BACTERIA 1 D 8 B 2 C 9 C 3 A 10 A 4 B 11 flagella 5 A 12 nucleus 6 C 13 prokaryote 7 D 14 eukaryote 15 Answers will vary Sample answer: move; get energy; reproduce 16 binary fission 17 Answers will vary Sample answer: Bacteria reproduce by binary fission through three steps (1) The cell s DNA is copied and binds to the cell membrane (2) The DNA and its copy separate as the cell and membrane grow (3) When the cell is about double its original size, the membrane pinches inward A new cell wall forms and separates the two new cells 18 Answers will vary Sample answer: moist, warm places 19 Answers will vary Sample answer: dry or cold places 20 endospore 21 Answers will vary Sample answer: Bacteria can surround their own bodies with a thick, protective membrane called an endospore, which allows them to remain inactive until conditions are favorable for growth 22 D 23 C 24 C 25 A 26 B 27 C 28 A 29 energy in sunlight 30 cyanobacteria 31 pigments 32 Answers will vary Sample answer: by eating red cyanobacteria 33 C 34 A 35 B 36 archaebacteria 37 one with little or no oxygen 38 Answers will vary Sample answer: hot springs at Yellowstone National Park; below ice in Antarctica; far below the Earth s surface 39 Answers will vary Sample answer: Many archaebacteria do not have cell walls Archaebacteria with cell walls have a different kind than those eubacteria have Archaebacteria also often live where nothing else can live SECTION: BACTERIA S ROLE IN THE WORLD 1 Answers will vary Sample answer: Bacteria live in water, air, and the human body 2 D 3 B 4 C 5 Answers will vary Sample answer: It s in a form they can t use 6 Answers will vary Sample answer: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria take in nitrogen from the air and change its form 7 nitrogen fixation 8 Answers will vary Sample answer: Decomposer bacteria break down dead plants and animal matter 9 Answers will vary Sample answer: It makes nutrients available to other living things 10 bioremediation 11 Answers will vary Sample answer: Some bacteria change harmful chemicals into harmless ones 12 B 13 C 14 lactose 15 Answers will vary Sample answer: Bacteria break down the sugar in milk, or lactose, and change it into lactic acid 16 antibiotics 17 bacteria Holt Science and Technology 85 Bacteria and Viruses
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
2 Domains and Kingdoms
 CHAPTER 9 2 Domains and Kingdoms SECTION Classification BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are prokaryotes classified? How are eukaryotes classified?
CHAPTER 9 2 Domains and Kingdoms SECTION Classification BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are prokaryotes classified? How are eukaryotes classified?
There are 5 kingdoms: Animalia multicellular animals, heterotrophic (eat other things), evolved 700,000,000 years ago (1,000,000 2,000,000 species)
 Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Name Block Chapter 6, Section 3, Bacteria, pages Information taken from Prentice Hall Science Explorer, Life Science, 2004
 SOL LS.4 The student will investigate and understand how organisms can be classified. Key concepts include a) The distinguishing characteristics of domains of organisms b) The distinguishing characteristics
SOL LS.4 The student will investigate and understand how organisms can be classified. Key concepts include a) The distinguishing characteristics of domains of organisms b) The distinguishing characteristics
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
6 Kingdoms of Life. What is life? How are all living things organized?
 6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
The Microbial World. Microorganisms of the Sea
 The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
2 Domains and Kingdoms
 CHAPTER 11 2 s and Kingdoms SECTION Classification 7.1.a, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Which domains are
CHAPTER 11 2 s and Kingdoms SECTION Classification 7.1.a, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Which domains are
Domains and Kingdoms. Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria
 Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria
 Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Notes - Microbiology Monera
 Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING
 BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites. 8th grade
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
19-1 Notes Bacteria. Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope
 19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
BACTERIA. Bacteria - small one celled monerans Bacteria like a warm, dark, and moist environment They are found almost everywhere: -on most objects
 Kingdom Monera 1 BACTERIA Bacteria - small one celled monerans Bacteria like a warm, dark, and moist environment They are found almost everywhere: -water -soil -skin -on most objects -air -food -inside
Kingdom Monera 1 BACTERIA Bacteria - small one celled monerans Bacteria like a warm, dark, and moist environment They are found almost everywhere: -water -soil -skin -on most objects -air -food -inside
Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi
 KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
Directed Reading B. Section: Domains and Kingdoms
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Domains and Kingdoms 1. What categories did people think all organisms fit into before Euglena was discovered? a. plants or animals b. fish or birds c. plants
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Domains and Kingdoms 1. What categories did people think all organisms fit into before Euglena was discovered? a. plants or animals b. fish or birds c. plants
Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Bacteria and Viruses. 1 Bacteria CHAPTER 18. MAINIDEA Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
 CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
Directed Reading B. Section: The Cell Cycle
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Cell Cycle 1. When your body makes new cells, what is being replaced? a. water c. cells that have died b. energy d. heat 2. What does making new cells allow
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Cell Cycle 1. When your body makes new cells, what is being replaced? a. water c. cells that have died b. energy d. heat 2. What does making new cells allow
Organizing Life s Diversity
 17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 3 Domains and Kingdoms The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. What You ll Learn major characteristics of the
Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you
 45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
Biological Kingdoms. An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things
 Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria
 Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Define: Alleles. Define: Chromosome. In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways.
 Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
OBJECTIVE 3: CLASSIFY ORGANISMS USING AN ORDERLY PATTERN BASED UPON STRUCTURE
 OBJECTIVE 3: CLASSIFY ORGANISMS USING AN ORDERLY PATTERN BASED UPON STRUCTURE Taxonomic systems are based on similar characteristics. These systems attempt to model the natural order, thus helping research
OBJECTIVE 3: CLASSIFY ORGANISMS USING AN ORDERLY PATTERN BASED UPON STRUCTURE Taxonomic systems are based on similar characteristics. These systems attempt to model the natural order, thus helping research
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes
 Name Exam Date Class Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes What is Classification? is when we place organisms into based on their. Classification is also known as. Taxonomists are scientists that & organisms
Name Exam Date Class Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes What is Classification? is when we place organisms into based on their. Classification is also known as. Taxonomists are scientists that & organisms
CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms. Microorganisms covered in this chapter:
 Biology 2201 Name: CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms Microorganisms covered in this chapter: Kingdom Bacteria or Monera: Pg. 132-137 Bacteria are simple, prokaryotic organisms. They can be classified according
Biology 2201 Name: CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms Microorganisms covered in this chapter: Kingdom Bacteria or Monera: Pg. 132-137 Bacteria are simple, prokaryotic organisms. They can be classified according
Origins - Three Domain Classification PROKARYOTES
 Bacteria Origins - Three Domain Classification EU PROKARYOTES I. Origins of Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria A. Prokaryotes = 1. Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Prokaryote
Bacteria Origins - Three Domain Classification EU PROKARYOTES I. Origins of Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria A. Prokaryotes = 1. Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Prokaryote
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses. Name Class Date
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
copyright cmassengale Kingdoms and Classification
 1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi
 complete petri dishes Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Viruses Lesson 1 Objectives Name and describe the characteristics of viruses and how they multiply. Discuss both positive and negative
complete petri dishes Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Viruses Lesson 1 Objectives Name and describe the characteristics of viruses and how they multiply. Discuss both positive and negative
Domains and Kingdoms
 Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Protists. Bacteria. Archea
 Protists Bacteria Archea Archaeans include inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on the planet. Image of acid mine drain filled with Archaea. Archaea also thrive in mud and they are one
Protists Bacteria Archea Archaeans include inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on the planet. Image of acid mine drain filled with Archaea. Archaea also thrive in mud and they are one
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
Comparing Kingdoms Lab
 Comparing Kingdoms Lab Name: Introduction: Living things are all around us. In der to identify ganisms effectively, scientists have developed methods of classifying ganisms into six maj groups called Kingdoms.
Comparing Kingdoms Lab Name: Introduction: Living things are all around us. In der to identify ganisms effectively, scientists have developed methods of classifying ganisms into six maj groups called Kingdoms.
Kingdom Monera. These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class.
 Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms
 Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
What s In a Name? (Lexile 840L)
 6.12: lassification of Organisms What s In a Name? (Lexile 840L) 1 Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet. These
6.12: lassification of Organisms What s In a Name? (Lexile 840L) 1 Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet. These
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
Directed Reading A. Section: The Cell Cycle. you finish reading this sentence? THE LIFE OF A CELL. cell. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Cell Cycle 1. Why is it important for your body to produce millions of new cells by the time you finish reading this sentence? THE LIFE OF A CELL 2. When
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Cell Cycle 1. Why is it important for your body to produce millions of new cells by the time you finish reading this sentence? THE LIFE OF A CELL 2. When
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Unit 5. Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5. Bacteria: Unicellular R E A D P
 Unit 5 Bacteria: Unicellular Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5 R E A D P. 2 9 3-305 Bacterial Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Single cellular no membrane bound organelles primitive Parts of Bacteria 1. Cell membrane
Unit 5 Bacteria: Unicellular Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5 R E A D P. 2 9 3-305 Bacterial Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Single cellular no membrane bound organelles primitive Parts of Bacteria 1. Cell membrane
Chapter 17B. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains. Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
 Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Unicellular Marine Organisms. Chapter 4
 Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort
 Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
Biology Study Guide. VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards)
 NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
Building the Tree of Life
 18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
The two daughter cells are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.
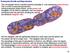 Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Some history. Now, we know that Robert Hooke was not looking at living cells, but the remains of dead cell walls.
 The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
Biology Test 2 The Cell. For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Life on Earth Topic Test
 Life on Earth Topic Test Multiple Choice Questions Select the best alternative and indicate your response on the answer sheet. (1 mark each) 1. The list below contains common substances that exist in Earth
Life on Earth Topic Test Multiple Choice Questions Select the best alternative and indicate your response on the answer sheet. (1 mark each) 1. The list below contains common substances that exist in Earth
Bacillus anthracis. Causes Anthrax Especially deadly when inhaled
 Eubacteria Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. An estimated 5 X 1030individuals. One bacterium can give rise to 10 million in 24 hours. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without
Eubacteria Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. An estimated 5 X 1030individuals. One bacterium can give rise to 10 million in 24 hours. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour
 MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
Bacteria. The Three Types of Important Heterotrophic Bacteria
 Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Name Class Date. 2. What does making new cells allow you to do? a. grow b. sleep c. eat d. make food
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Cell Cycle 1. Your body makes new cells to replace what? a. cells that are growing bigger b. cells that are multiplying c. cells that have died d. cells
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Cell Cycle 1. Your body makes new cells to replace what? a. cells that are growing bigger b. cells that are multiplying c. cells that have died d. cells
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago.
 Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING
 Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Kingdoms Powerpoint. Prokaryotes- unicellular organisms that have a true nucleus bound by a membrane Used to be one group=
 Name: Period: Kingdoms Powerpoint The Six Kingdoms: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia Three s: Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya The main factors that determine which kingdom an organism
Name: Period: Kingdoms Powerpoint The Six Kingdoms: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia Three s: Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya The main factors that determine which kingdom an organism
Biology Study Guide. VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards)
 NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
NAME: Biology Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW (+5 for making flashcards) asexual reproduction autotroph binary fission binomial nomenclature carnivore cell cilia classification conjugation decomposer
1B Review Questions (54)
 1) Taxing is the science of a) Finding animals b) Involving naming and categorizing species 1B Review Questions (54) c) Microorganisms d) Discovery on protists 2) What is the order of classification from
1) Taxing is the science of a) Finding animals b) Involving naming and categorizing species 1B Review Questions (54) c) Microorganisms d) Discovery on protists 2) What is the order of classification from
Reading Science! Name: Date: What s In A Name? Lexile 870L
 6.12: lassification of Organisms Name: ate: 1 2 3 What s In Name? Lexile 870L Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as
6.12: lassification of Organisms Name: ate: 1 2 3 What s In Name? Lexile 870L Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as
Classification Systems. Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room!
 Classification Systems Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room! A Vast Science Biology, the study of life, is no simple science.
Classification Systems Classification is just a fancy word for organization. So this chapter is equivalent to Biology cleaning its room! A Vast Science Biology, the study of life, is no simple science.
3) What are the names of the SIX kingdoms? Next to each one, write whether it is prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
 Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
Cell organelles. Cell Wall
 Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Station A: #3. If two organisms belong to the same order, they must also belong to the same
 Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
Name Date Hour Table Taxonomy Reading
 Taxonomy Reading As you have discovered, living things are put into groups according to their characteristics. This is called classification. The characteristics that are used to classify living things
Taxonomy Reading As you have discovered, living things are put into groups according to their characteristics. This is called classification. The characteristics that are used to classify living things
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Introduction to Bacteria
 Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
S T U D E N T G U I D E
 How do scientists organize organisms? Part IA: In what domain do I belong? Scientists sort life forms into categories based on their characteristics. First, scientists look at the types of cells an organism
How do scientists organize organisms? Part IA: In what domain do I belong? Scientists sort life forms into categories based on their characteristics. First, scientists look at the types of cells an organism
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
1. Which of the following is a virus? C D. 2. Which of the following is found in both cells and viruses?
 TEKS 4C compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza 1. Which of
TEKS 4C compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza 1. Which of
The Cell The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Cells are not the smallest structure that make up living organisms. They are merely the smallest functional units. Cells themselves contain smaller units called o Tiny
The Cell The building blocks of life Cells are not the smallest structure that make up living organisms. They are merely the smallest functional units. Cells themselves contain smaller units called o Tiny
Cells & Bacteria Notes
 Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista
 Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista Domain Eubacteria Domain Archae The Prokaryotes Cell type: Prokaryotes Found in: Domain Bacteria Domain Archae Cell type: Prokaryotes Two Domains: Bacteria and Archae Do
Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista Domain Eubacteria Domain Archae The Prokaryotes Cell type: Prokaryotes Found in: Domain Bacteria Domain Archae Cell type: Prokaryotes Two Domains: Bacteria and Archae Do
Unit 10: The simplest living beings
 Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Broughton High School. Name: Class: Date: / /
 1 Name: Class: Date: / / Chapter 19 Bacteria 1 Describe the classification of Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. Archaebacteria Eubacteria 2 Describe the differences between Photosynthetic & Chemosynthetic
1 Name: Class: Date: / / Chapter 19 Bacteria 1 Describe the classification of Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. Archaebacteria Eubacteria 2 Describe the differences between Photosynthetic & Chemosynthetic
Outline 10: Origin of Life. Better Living Through Chemistry
 Outline 10: Origin of Life Better Living Through Chemistry What is Life? Internal chemical activity providing growth, repair, and generation of energy. The ability to reproduce. The capacity to respond
Outline 10: Origin of Life Better Living Through Chemistry What is Life? Internal chemical activity providing growth, repair, and generation of energy. The ability to reproduce. The capacity to respond
Classification of Living Things
 Classification of Living Things What is classification? Classification: putting things into orderly groups based on similar characteristics. Ways we classify things Supermarket aisles Libraries Classes
Classification of Living Things What is classification? Classification: putting things into orderly groups based on similar characteristics. Ways we classify things Supermarket aisles Libraries Classes
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
What are Dichotomous Keys?
 Classification What are Dichotomous Keys? a method for determining the identity of something (like the name of a butterfly, a plant, a lichen, or a rock) by going through a series of choices that leads
Classification What are Dichotomous Keys? a method for determining the identity of something (like the name of a butterfly, a plant, a lichen, or a rock) by going through a series of choices that leads
Life at Its Many Levels
 Slide 1 THE SCOPE OF BIOLOGY Biology is the scientific study of life Slide 2 Life at Its Many Levels Biologists explore life at levels ranging from the biosphere to the molecules that make up cells Slide
Slide 1 THE SCOPE OF BIOLOGY Biology is the scientific study of life Slide 2 Life at Its Many Levels Biologists explore life at levels ranging from the biosphere to the molecules that make up cells Slide
