Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli
|
|
|
- Laureen Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli Lauren Nakonechny, Katherine Smith, Michael Volk, Robert Wallace Mentor: J. Ruby Abrams
2 Agenda Motivation Intro to multistability Purpose of paper Biological background Methods Modeling the lac system Measuring network parameters Phase diagrams Future work Implementation plan Sources Source: BioCote
3 Motivation Recreate and verify mathematical results from Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli by Ozbudak et al. Interest in applying mathematics to biology Intersectional knowledge Generate artificial data that mimics real-time data Apply mathematical model to other systems Solid/liquid/gas phase diagrams Compare - similarities and differences
4 Multistability of (general) systems Multiple internal states in response to single set of external outputs Biological switches Essential for variety of processes Positive feedback loops responsible for multistability of systems Loops do not guarantee multistability Phase diagrams Internal states as external parameters vary Determine requirements for switch within a system Bifurcation diagram Varying parameters
5 Purpose Present phase diagram of lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli BISTABLE Quantitatively investigate processes using phase diagram and mathematical model of network Sugar uptake Transcriptional regulation Show that hysteretic response of wild-type system can be converted to ultrasensitive graded response
6 Some biological background lac operon Three metabolic genes: lacz, lacy, laca Genes required for uptake and metabolism of lactose Two transcriptional regulators Repressor (LacI) turns off lactose metabolism Inducers (TMG) inhibit repression Activator (cyclic AMP receptor protein, CRP) triggers lactose metabolism Source: Nature Education
7 More on the lac operon... Glucose present: Low camp Repressor binds to operator and blocks RNA polymerase Repressor coded by LacI gene Less transcription of lac operon No glucose present: High camp camp binds to CAP (an activator of transcription) Allolactose binds to repressor to remove from operator Lots of transcription of the lac operon to break down lactose Source: Khan Academy
8 SO WHAT? Presence of TMG inhibits repression by LacI TMG and glucose affect the inhibitor and activator of lac expression independently **camp levels unaffected by TMG uptake, but affected by levels of glucose** Uptake of TMG induces synthesis of lactose permease (LacY, coded by LacY), which promotes further TMG uptake and facilitates uptake of lactose POSITIVE FEEDBACK LOOP potential for bistability Require cells with well-defined initial states (not induced or fully induced) - response of the bistable system depends on its history (hysteresis!)
9 Methods Vary 2 external inputs: extracellular concentrations of glucose and TMG Measure the levels of 2 fluorescent reporter proteins: Note: GFP - found at the lac promoter HcRed - found at the gat promoter; direct measure of CRP-cAMP levels TMG inhibits the inhibitor of GFP, therefore activating GFP Glucose inhibits the production of GFP & HcRed Figure: (Ozbudak et al.) Red arrow - activation Red blunt end - inhibition Black arrow - protein creation Dotted arrows - uptake across cell membrane
10 Modeling the lac system Equation S1 (Ozbudak et al.) - Active fraction of LacI: x: intracellular TMG concentration R T : total concentration of LacI tetramers R: concentration of active Lacl x 0 : half-saturation concentration n: Hill coefficient, extensive experimental evidence shows it is approximately 2 R/R T is a decreasing sigmoidal function of x Binding of TMG disrupts LacI activity; higher TMG occupancies cause further impairment
11 Modeling the lac system Equation S2 (Ozbudak et al.) - Rate of generation of LacY: y: concentration of LacY (lactose permease) in green fluorescence units y : time constant : lac expression level that would be obtained if every repressor molecule were inactive R: concentration of active Lacl R 0 : half-saturation concentration Repression factor is defined as ρ = 1 + R/R 0 Repression factor describes how tightly LacI may regulate lac expression Decreasing hyperbolic function of R with maximal value
12 Modeling the lac system Equation S3 (Ozbudak et al.)- Rate of entry of TMG concentration into cell: x: intracellular TMG concentration y: concentration of LacY (lactose permease) in green fluorescence units x : time constant : The transport rate; it gives the TMG uptake rate per LacY molecule TMG enters the cell at a rate proportional to y, and is similarly depleted in a first order reaction with time constant x Note: In the cell, TMG inactivates LacI and completes the feedback loop
13 Modeling the lac system Three equations (Ozbudak et al.):
14 Modeling the lac system Combine the three equations to obtain steady state result (Equation S4-(Ozbudak et al.)): ρ, α, and β are arbitrary functions of the external inputs, glucose (G) and TMG (T) levels As we vary these parameters, the system generates either one or two stable fixed points, with saddle node bifurcations separating these two behaviors
15 Modeling the lac system Rewrite Equation S4 as a cubic equation: Theoretically, a generic cubic function with two identical roots has the form: Note: θ = dimensionless ratio of roots (Ozbudak et al.)
16 Modeling the lac system Compare coefficients and find: (Ozbudak et al.) These parametric equations describe the boundary of the bistable region (see figure to the right) Switching boundaries Figure: (Ozbudak et al.)
17 Measuring network parameters α - lac expression level obtained if every repressor molecule were inactive (maximum induction) ρ (repression factor) - ratio of maximal to basal (read: every repressor molecule is active) activity β (transport rate) - TMG uptake rate per LacY molecule **measured in vivo** Figures: (Ozbudak et al.)
18 Measuring network parameters Apply saddle node condition at each switching threshold (on boundary of bistable region) CAVEATS: Done separately at ON and OFF regions Determine complete functional dependence on G and T (glucose and TMG levels, respectively) α 15% higher at OFF threshold Large error in calculation of rho at OFF threshold due to low fluorescence values; estimate α and ρ at ON threshold alone Decompose net TMG uptake rate as: (Ozbudak et al.)
19 Measuring network parameters Caveats cont d Assume power law for β T and use least-squares fitting routine to extract functions β T and β G We find: [G]=[T]=վM Equations: (Ozbudak et al.)
20 Phase diagrams: hysteresis vs. graded response Wild-type network phase diagram: Theoretical phase diagram: Figure: (Ozbudak et al.) Figure: (Ozbudak et al.)
21 Phase diagrams: hysteresis vs. graded response Wild-type network phase diagram: Maps out compete range of glucose and TMG levels over which system is bistable lac induction always takes place hysteretically Cells increase expression levels discontinuously as switching threshold is reached Theoretical phase diagram: System response (moving from uninduced to induced) can occur in a graded fashion (white sections) or hysteretically (grey section) Expression levels of individual cells move continuously between low and high values Predicted to occur when degree of operon repression (rho) is decreased BELOW wild-type levels Repression factor (and region of bistability) decreases to critical point at factor of 9 Graded behavior occurs beyond cusp
22 Current Progress Exploration of the parametric equations that describe the boundary of the bistable region Currently verifying plots based off of dynamic equations Developing general Matlab framework Figure: (Ozbudak et al.)
23 Current Progress Red Dot - Inflection point Blue Line: Trajectory as μ is changed
24 Future work Generate data and model trajectories with differential equations Arrows indicate initial conditions Red : TMG > 30 μm to turn on initially uninduced cells Blue : TMG < 3 μm to turn off initially induced cells Proves hysteresis Grey Region - Bistable Figure: (Ozbudak et al.)
25 Future Work Discretize the model and implement them in MATLAB Recreate the phase diagrams using numerical analysis Potential Ideas The discontinuous transition from low to high induction is analogous to a first order phase transition such as evaporation in a liquid gas system, with chemical noise instead of thermal noise driving stochastic transitions between these states We can attempt to validate this claim and show the similarities between the two systems
26 Implementation Plan Roles: Lauren - Mathematical analysis and biological interpretation Katie - Mathematical analysis and biological interpretation Michael - Numerical Modeling (MatLab) Rob - Team Coordinator, Numerical Modeling (MatLab)
27 Sources Ozbudak, Ertugrul M., Thattai, Mukund, Lim, Han N., Shraiman, Boris I., & van Oudenaarden, Alexander. Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli. Nature. 427, (2004). Hansen, L. H., Knudsen, S. & Sorenson, S. J. The effect of the lacy gene on the induction of IPTG inducible promoters, studied in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Curr. Microbiol. 36, (1998). Yagil, G. & Yagil, E. On the relation between effector concentration and the rate of induced enzyme synthesis. Biophys. J. 11, (1971). SOS Math - Bifurcations Khan Academy - lac operon Nature Education - lac operon
Multistability in the lactose utilization network of E. coli. Lauren Nakonechny, Katherine Smith, Michael Volk, Robert Wallace Mentor: J.
 Multistability in the lactose utilization network of E. coli Lauren Nakonechny, Katherine Smith, Michael Volk, Robert Wallace Mentor: J. Ruby Abrams Motivation Understanding biological switches in the
Multistability in the lactose utilization network of E. coli Lauren Nakonechny, Katherine Smith, Michael Volk, Robert Wallace Mentor: J. Ruby Abrams Motivation Understanding biological switches in the
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Stochastic simulations
 Stochastic simulations Application to molecular networks Literature overview Noise in genetic networks Origins How to measure and distinguish between the two types of noise (intrinsic vs extrinsic)? What
Stochastic simulations Application to molecular networks Literature overview Noise in genetic networks Origins How to measure and distinguish between the two types of noise (intrinsic vs extrinsic)? What
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION. Bacterial Genetics Lac and Trp Operon
 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Bacterial Genetics Lac and Trp Operon Levels of Metabolic Control The amount of cellular products can be controlled by regulating: Enzyme activity: alters protein function
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Bacterial Genetics Lac and Trp Operon Levels of Metabolic Control The amount of cellular products can be controlled by regulating: Enzyme activity: alters protein function
Topic 4 - #14 The Lactose Operon
 Topic 4 - #14 The Lactose Operon The Lactose Operon The lactose operon is an operon which is responsible for the transport and metabolism of the sugar lactose in E. coli. - Lactose is one of many organic
Topic 4 - #14 The Lactose Operon The Lactose Operon The lactose operon is an operon which is responsible for the transport and metabolism of the sugar lactose in E. coli. - Lactose is one of many organic
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Why? Control of Expression in Prokaryotes How do prokaryotes use operons to control gene expression? Houses usually have a light source in every room, but it would be a waste of energy to leave every light
Why? Control of Expression in Prokaryotes How do prokaryotes use operons to control gene expression? Houses usually have a light source in every room, but it would be a waste of energy to leave every light
REVIEW SESSION. Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E
 REVIEW SESSION Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E Gene Regulation Gene Regulation Gene expression can be turned on, turned off, turned up or turned down! For example, as test time approaches,
REVIEW SESSION Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E Gene Regulation Gene Regulation Gene expression can be turned on, turned off, turned up or turned down! For example, as test time approaches,
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
Name Period The Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Notes
 Bacterial DNA contains genes that encode for many different proteins (enzymes) so that many processes have the ability to occur -not all processes are carried out at any one time -what allows expression
Bacterial DNA contains genes that encode for many different proteins (enzymes) so that many processes have the ability to occur -not all processes are carried out at any one time -what allows expression
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05
 32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05 Review the operon concept Repressible operons (e.g. trp) Inducible operons (e.g. lac) Positive regulation of lac () Practice applying the operon concept
32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05 Review the operon concept Repressible operons (e.g. trp) Inducible operons (e.g. lac) Positive regulation of lac () Practice applying the operon concept
Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm February 25, 2005
 Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm February 25, 2005 Principles of gene regulation (cellular versus molecular level) Extracellular signals Chemical (e.g. hormones, growth factors) Environmental
Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm February 25, 2005 Principles of gene regulation (cellular versus molecular level) Extracellular signals Chemical (e.g. hormones, growth factors) Environmental
THE EDIBLE OPERON David O. Freier Lynchburg College [BIOL 220W Cellular Diversity]
![THE EDIBLE OPERON David O. Freier Lynchburg College [BIOL 220W Cellular Diversity] THE EDIBLE OPERON David O. Freier Lynchburg College [BIOL 220W Cellular Diversity]](/thumbs/90/102203867.jpg) THE EDIBLE OPERON David O. Freier Lynchburg College [BIOL 220W Cellular Diversity] You have the following resources available to you: Short bread cookies = DNA / genetic elements Fudge Mint cookies = RNA
THE EDIBLE OPERON David O. Freier Lynchburg College [BIOL 220W Cellular Diversity] You have the following resources available to you: Short bread cookies = DNA / genetic elements Fudge Mint cookies = RNA
Chapter 16 Lecture. Concepts Of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Chapter 16 Lecture Concepts Of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Chapter Contents 16.1 Prokaryotes Regulate Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Conditions 16.2
Chapter 16 Lecture Concepts Of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Chapter Contents 16.1 Prokaryotes Regulate Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Conditions 16.2
Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Their Viruses
 11 Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Their Viruses WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. Compare the structure of IPTG shown in Figure 11-7 with the structure of galactose shown in Figure 11-5. Why is
11 Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Their Viruses WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. Compare the structure of IPTG shown in Figure 11-7 with the structure of galactose shown in Figure 11-5. Why is
The Effect of Stochasticity on the Lac Operon: An Evolutionary Perspective
 The Effect of Stochasticity on the Lac Operon: An Evolutionary Perspective Milan van Hoek *, Paulien Hogeweg Theoretical Biology/Bioinformatics Group, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands The role
The Effect of Stochasticity on the Lac Operon: An Evolutionary Perspective Milan van Hoek *, Paulien Hogeweg Theoretical Biology/Bioinformatics Group, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands The role
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 8
 56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 8 Course organization Two complementary approaches to modeling and understanding biological networks Constraint-based modeling (Palsson) System-wide Metabolism Steady-state
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 8 Course organization Two complementary approaches to modeling and understanding biological networks Constraint-based modeling (Palsson) System-wide Metabolism Steady-state
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells:connecting the head and tail
 Initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells:connecting the head and tail GCCRCCAUGG 1: Multiple initiation factors with distinct biochemical roles (linking, tethering, recruiting, and scanning) 2: 5
Initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells:connecting the head and tail GCCRCCAUGG 1: Multiple initiation factors with distinct biochemical roles (linking, tethering, recruiting, and scanning) 2: 5
Warm-Up. Explain how a secondary messenger is activated, and how this affects gene expression. (LO 3.22)
 Warm-Up Explain how a secondary messenger is activated, and how this affects gene expression. (LO 3.22) Yesterday s Picture The first cell on Earth (approx. 3.5 billion years ago) was simple and prokaryotic,
Warm-Up Explain how a secondary messenger is activated, and how this affects gene expression. (LO 3.22) Yesterday s Picture The first cell on Earth (approx. 3.5 billion years ago) was simple and prokaryotic,
Villa et al. (2005) Structural dynamics of the lac repressor-dna complex revealed by a multiscale simulation. PNAS 102:
 Villa et al. (2005) Structural dynamics of the lac repressor-dna complex revealed by a multiscale simulation. PNAS 102: 6783-6788. Background: The lac operon is a cluster of genes in the E. coli genome
Villa et al. (2005) Structural dynamics of the lac repressor-dna complex revealed by a multiscale simulation. PNAS 102: 6783-6788. Background: The lac operon is a cluster of genes in the E. coli genome
Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts
 Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts - Activators and repressors - Input functions; Logic input functions; Multidimensional input functions - Dynamics and response time 2.1 Introduction The
Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts - Activators and repressors - Input functions; Logic input functions; Multidimensional input functions - Dynamics and response time 2.1 Introduction The
Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription
 Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples are mostly bacterial) Diarmaid Hughes ICM/Microbiology VT2009 Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples
Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples are mostly bacterial) Diarmaid Hughes ICM/Microbiology VT2009 Regulation of Gene Expression at the level of Transcription (examples
CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON
 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
Welcome to Class 21!
 Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Slide 1 / 7. Free Response
 Slide 1 / 7 Free Response Slide 2 / 7 Slide 3 / 7 1 The above diagrams illustrate the experiments carried out by Griffith and Hershey and Chaserespectively. Describe the hypothesis or conclusion that each
Slide 1 / 7 Free Response Slide 2 / 7 Slide 3 / 7 1 The above diagrams illustrate the experiments carried out by Griffith and Hershey and Chaserespectively. Describe the hypothesis or conclusion that each
Chapter 18: Control of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18: Control of Gene Expression 海洋生物研究所 曾令銘 海事大樓 426 室分機 : 5326 Differential Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions
Chapter 18: Control of Gene Expression 海洋生物研究所 曾令銘 海事大樓 426 室分機 : 5326 Differential Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Tuesday, December 27, 16
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Molecular Biology, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology Operons ???
 1 Description of Module Subject Name?? Paper Name Module Name/Title XV- 04: 2 OPERONS OBJECTIVES To understand how gene is expressed and regulated in prokaryotic cell To understand the regulation of Lactose
1 Description of Module Subject Name?? Paper Name Module Name/Title XV- 04: 2 OPERONS OBJECTIVES To understand how gene is expressed and regulated in prokaryotic cell To understand the regulation of Lactose
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Development Team. Regulation of gene expression in Prokaryotes: Lac Operon. Molecular Cell Biology. Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper Module : 15 : 23 Development Team Principal Investigator : Prof. Neeta Sehgal Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Co-Principal Investigator : Prof. D.K. Singh Department of Zoology, University
Paper Module : 15 : 23 Development Team Principal Investigator : Prof. Neeta Sehgal Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Co-Principal Investigator : Prof. D.K. Singh Department of Zoology, University
Week 10! !
 Week 10! 10-24-2013! Annotated Bibliography! Sources of papers! 3 papers! Peer-reviewed scientific literature (no review articles)! No more than 2 from:! the same author! the same journal! 2 of the 3 must
Week 10! 10-24-2013! Annotated Bibliography! Sources of papers! 3 papers! Peer-reviewed scientific literature (no review articles)! No more than 2 from:! the same author! the same journal! 2 of the 3 must
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 9
 56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 9 The Feed-Forward Loop Network Motif Subgraphs in random networks We have discussed the simplest network motif, self-regulation, a pattern with one node We now consider
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 9 The Feed-Forward Loop Network Motif Subgraphs in random networks We have discussed the simplest network motif, self-regulation, a pattern with one node We now consider
Analysis of the Lactose metabolism in E. coli using sum-of-squares decomposition
 Analysis of the Lactose metabolism in E. coli using sum-of-squares decomposition Ali Ahmadzadeh, Adam Halasz, Stephen Prajna Ali Jadbabaie and Vijay Kumar Abstract We provide a system-theoretic analysis
Analysis of the Lactose metabolism in E. coli using sum-of-squares decomposition Ali Ahmadzadeh, Adam Halasz, Stephen Prajna Ali Jadbabaie and Vijay Kumar Abstract We provide a system-theoretic analysis
Prokaryo'c Operon Model Ac'vity
 Prokaryo'c Operon Model Ac'vity Differen'al Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental condi6ons In mul6cellular eukaryotes, gene expression
Prokaryo'c Operon Model Ac'vity Differen'al Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental condi6ons In mul6cellular eukaryotes, gene expression
Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Gene Expression. AP Biology
 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Gene Expression Figure 18.1 How can this fish s eyes see equally well in both air and water? Aka. Quatro ojas Regulation of Gene Expression: Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Gene Expression Figure 18.1 How can this fish s eyes see equally well in both air and water? Aka. Quatro ojas Regulation of Gene Expression: Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Boolean models of gene regulatory networks. Matthew Macauley Math 4500: Mathematical Modeling Clemson University Spring 2016
 Boolean models of gene regulatory networks Matthew Macauley Math 4500: Mathematical Modeling Clemson University Spring 2016 Gene expression Gene expression is a process that takes gene info and creates
Boolean models of gene regulatory networks Matthew Macauley Math 4500: Mathematical Modeling Clemson University Spring 2016 Gene expression Gene expression is a process that takes gene info and creates
On the Use of the Hill Functions in Mathematical Models of Gene Regulatory Networks
 Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. Vol. 3, No. 2, 2008, pp. 85-97 On the Use of the Hill Functions in Mathematical Models of Gene Regulatory Networks M. Santillán 1 Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados
Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. Vol. 3, No. 2, 2008, pp. 85-97 On the Use of the Hill Functions in Mathematical Models of Gene Regulatory Networks M. Santillán 1 Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados
Lecture 6: The feed-forward loop (FFL) network motif
 Lecture 6: The feed-forward loop (FFL) network motif Chapter 4 of Alon x 4. Introduction x z y z y Feed-forward loop (FFL) a= 3-node feedback loop (3Loop) a=3 Fig 4.a The feed-forward loop (FFL) and the
Lecture 6: The feed-forward loop (FFL) network motif Chapter 4 of Alon x 4. Introduction x z y z y Feed-forward loop (FFL) a= 3-node feedback loop (3Loop) a=3 Fig 4.a The feed-forward loop (FFL) and the
A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators
 A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators Michael B. Elowitz & Stanislas Leibler, Nature, 403, 2000 igem Team Heidelberg 2008 Journal Club Andreas Kühne Introduction Networks of interacting
A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators Michael B. Elowitz & Stanislas Leibler, Nature, 403, 2000 igem Team Heidelberg 2008 Journal Club Andreas Kühne Introduction Networks of interacting
Bistable Behavior in a Model of the lac Operon in Escherichia coli with Variable Growth Rate
 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 March 2008 2065 2081 2065 Bistable Behavior in a Model of the lac Operon in Escherichia coli with Variable Growth ate M. Santillán Unidad Monterrey, Centro de Investigación
Biophysical Journal Volume 94 March 2008 2065 2081 2065 Bistable Behavior in a Model of the lac Operon in Escherichia coli with Variable Growth ate M. Santillán Unidad Monterrey, Centro de Investigación
APGRU6L2. Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes
 APGRU6L2 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP u if they have enough of a product, need to stop production
APGRU6L2 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP u if they have enough of a product, need to stop production
16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION
 16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION Chapter Outline 16.1 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES The operon is the unit of transcription in prokaryotes The lac operon for lactose metabolism is transcribed
16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION Chapter Outline 16.1 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES The operon is the unit of transcription in prokaryotes The lac operon for lactose metabolism is transcribed
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
UNIT 6 PART 3 *REGULATION USING OPERONS* Hillis Textbook, CH 11
 UNIT 6 PART 3 *REGULATION USING OPERONS* Hillis Textbook, CH 11 REVIEW: Signals that Start and Stop Transcription and Translation BUT, HOW DO CELLS CONTROL WHICH GENES ARE EXPRESSED AND WHEN? First of
UNIT 6 PART 3 *REGULATION USING OPERONS* Hillis Textbook, CH 11 REVIEW: Signals that Start and Stop Transcription and Translation BUT, HOW DO CELLS CONTROL WHICH GENES ARE EXPRESSED AND WHEN? First of
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Genetic networks and gene expression data
 GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Genetic networks and gene expression data 1 Gene Networks Definition: A gene network is a set of molecular components, such as genes and proteins, and interactions between
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Genetic networks and gene expression data 1 Gene Networks Definition: A gene network is a set of molecular components, such as genes and proteins, and interactions between
Co-ordination occurs in multiple layers Intracellular regulation: self-regulation Intercellular regulation: coordinated cell signalling e.g.
 Gene Expression- Overview Differentiating cells Achieved through changes in gene expression All cells contain the same whole genome A typical differentiated cell only expresses ~50% of its total gene Overview
Gene Expression- Overview Differentiating cells Achieved through changes in gene expression All cells contain the same whole genome A typical differentiated cell only expresses ~50% of its total gene Overview
the noisy gene Biology of the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB)
 Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam
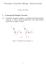 Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam October 28, 2010 1 Conceptual Simple Circuits 1.1 Consider the plots in figure 1. Identify all critical points with an x. Put a circle around the x for each
Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam October 28, 2010 1 Conceptual Simple Circuits 1.1 Consider the plots in figure 1. Identify all critical points with an x. Put a circle around the x for each
Regulation of gene expression. Premedical - Biology
 Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
GENE REGULATION AND PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT
 GENE REGULATION AND PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT By Surinder Kaur DIET Ropar Surinder_1998@ yahoo.in Mob No 9988530775 GENE REGULATION Gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a unit of function (polypeptide,
GENE REGULATION AND PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT By Surinder Kaur DIET Ropar Surinder_1998@ yahoo.in Mob No 9988530775 GENE REGULATION Gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a unit of function (polypeptide,
URL: <
 Citation: ngelova, Maia and en Halim, sma () Dynamic model of gene regulation for the lac operon. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 86 (). ISSN 7-696 Published by: IOP Publishing URL: http://dx.doi.org/.88/7-696/86//7
Citation: ngelova, Maia and en Halim, sma () Dynamic model of gene regulation for the lac operon. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 86 (). ISSN 7-696 Published by: IOP Publishing URL: http://dx.doi.org/.88/7-696/86//7
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 26. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday
 Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Hybrid Model of gene regulatory networks, the case of the lac-operon
 Hybrid Model of gene regulatory networks, the case of the lac-operon Laurent Tournier and Etienne Farcot LMC-IMAG, 51 rue des Mathématiques, 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9, France Laurent.Tournier@imag.fr, Etienne.Farcot@imag.fr
Hybrid Model of gene regulatory networks, the case of the lac-operon Laurent Tournier and Etienne Farcot LMC-IMAG, 51 rue des Mathématiques, 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9, France Laurent.Tournier@imag.fr, Etienne.Farcot@imag.fr
Unit 3: Control and regulation Higher Biology
 Unit 3: Control and regulation Higher Biology To study the roles that genes play in the control of growth and development of organisms To be able to Give some examples of features which are controlled
Unit 3: Control and regulation Higher Biology To study the roles that genes play in the control of growth and development of organisms To be able to Give some examples of features which are controlled
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Modeling network dynamics: the lac operon, a case study
 Modeling network dynamics: the lac operon, a case study José M. G. Vilar 1, C lin C. Guet 1,2, and Stanislas Leibler 1 1 The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA 2 Dept. of
Modeling network dynamics: the lac operon, a case study José M. G. Vilar 1, C lin C. Guet 1,2, and Stanislas Leibler 1 1 The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA 2 Dept. of
Gene regulation II Biochemistry 302. February 27, 2006
 Gene regulation II Biochemistry 302 February 27, 2006 Molecular basis of inhibition of RNAP by Lac repressor 35 promoter site 10 promoter site CRP/DNA complex 60 Lewis, M. et al. (1996) Science 271:1247
Gene regulation II Biochemistry 302 February 27, 2006 Molecular basis of inhibition of RNAP by Lac repressor 35 promoter site 10 promoter site CRP/DNA complex 60 Lewis, M. et al. (1996) Science 271:1247
Controlling Gene Expression
 Controlling Gene Expression Control Mechanisms Gene regulation involves turning on or off specific genes as required by the cell Determine when to make more proteins and when to stop making more Housekeeping
Controlling Gene Expression Control Mechanisms Gene regulation involves turning on or off specific genes as required by the cell Determine when to make more proteins and when to stop making more Housekeeping
Analysis of the Lactose metabolism in E. coli using sum-of-squares decomposition
 Analysis of the Lactose metabolism in E. coli using sum-of-squares decomposition Ali Ahmadzadeh, Adam Halasz, Stephen Prajna Ali Jadbabaie and Vijay Kumar Abstract We provide a system-theoretic analysis
Analysis of the Lactose metabolism in E. coli using sum-of-squares decomposition Ali Ahmadzadeh, Adam Halasz, Stephen Prajna Ali Jadbabaie and Vijay Kumar Abstract We provide a system-theoretic analysis
Name: SBI 4U. Gene Expression Quiz. Overall Expectation:
 Gene Expression Quiz Overall Expectation: - Demonstrate an understanding of concepts related to molecular genetics, and how genetic modification is applied in industry and agriculture Specific Expectation(s):
Gene Expression Quiz Overall Expectation: - Demonstrate an understanding of concepts related to molecular genetics, and how genetic modification is applied in industry and agriculture Specific Expectation(s):
Bi 8 Lecture 11. Quantitative aspects of transcription factor binding and gene regulatory circuit design. Ellen Rothenberg 9 February 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 11 Quantitative aspects of transcription factor binding and gene regulatory circuit design Ellen Rothenberg 9 February 2016 Major take-home messages from λ phage system that apply to many
Bi 8 Lecture 11 Quantitative aspects of transcription factor binding and gene regulatory circuit design Ellen Rothenberg 9 February 2016 Major take-home messages from λ phage system that apply to many
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES.
 GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES!! www.clutchprep.com GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES COCEPT: LAC OPERO An operon is a group of genes with similar functions that are
GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES!! www.clutchprep.com GEETICS - CLUTCH CH.12 GEE REGULATIO I PROKARYOTES COCEPT: LAC OPERO An operon is a group of genes with similar functions that are
Computational Cell Biology Lecture 4
 Computational Cell Biology Lecture 4 Case Study: Basic Modeling in Gene Expression Yang Cao Department of Computer Science DNA Structure and Base Pair Gene Expression Gene is just a small part of DNA.
Computational Cell Biology Lecture 4 Case Study: Basic Modeling in Gene Expression Yang Cao Department of Computer Science DNA Structure and Base Pair Gene Expression Gene is just a small part of DNA.
Gene regulation II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm February 28, 2005
 Gene regulation II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm February 28, 2005 Catabolic operons: Regulation by multiple signals targeting different TFs Catabolite repression: Activity of lac operon is restricted when
Gene regulation II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm February 28, 2005 Catabolic operons: Regulation by multiple signals targeting different TFs Catabolite repression: Activity of lac operon is restricted when
Gene Switches Teacher Information
 STO-143 Gene Switches Teacher Information Summary Kit contains How do bacteria turn on and turn off genes? Students model the action of the lac operon that regulates the expression of genes essential for
STO-143 Gene Switches Teacher Information Summary Kit contains How do bacteria turn on and turn off genes? Students model the action of the lac operon that regulates the expression of genes essential for
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.mn] 9 Feb 2008
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.mn] 9 Feb 2008 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.mn] 9 Feb 2008](/thumbs/84/90623045.jpg) The diffusive influx and carrier efflux have a strong effect on the bistability of the lac operon in Escherichia coli arxiv:0802.1287v1 [q-bio.mn] 9 Feb 2008 Jason T. Noel Department of Chemical Engineering,
The diffusive influx and carrier efflux have a strong effect on the bistability of the lac operon in Escherichia coli arxiv:0802.1287v1 [q-bio.mn] 9 Feb 2008 Jason T. Noel Department of Chemical Engineering,
Gene Regulation and Expression
 THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium that contains more than 4000 genes.
THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium that contains more than 4000 genes.
Prokaryotic Regulation
 Prokaryotic Regulation Control of transcription initiation can be: Positive control increases transcription when activators bind DNA Negative control reduces transcription when repressors bind to DNA regulatory
Prokaryotic Regulation Control of transcription initiation can be: Positive control increases transcription when activators bind DNA Negative control reduces transcription when repressors bind to DNA regulatory
12-5 Gene Regulation
 12-5 Gene Regulation Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 1 of 26 12-5 Gene Regulation Gene Regulation: An Example Gene
12-5 Gene Regulation Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 1 of 26 12-5 Gene Regulation Gene Regulation: An Example Gene
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Networks in systems biology
 Networks in systems biology Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson) Networks in systems
Networks in systems biology Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson) Networks in systems
Stochastic simulations!
 Stochastic simulations! Application to biomolecular networks! Literature overview Noise in genetic networks! Origins! How to measure the noise and distinguish between the two sources of noise (intrinsic
Stochastic simulations! Application to biomolecular networks! Literature overview Noise in genetic networks! Origins! How to measure the noise and distinguish between the two sources of noise (intrinsic
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 20072008 Bacterial metabolism n Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment u if they have enough of a product, need to stop production n why?
Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 20072008 Bacterial metabolism n Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment u if they have enough of a product, need to stop production n why?
JCB. Modeling network dynamics: the lac operon, a case study. The Journal of Cell Biology. Mini-Review
 JCB Mini-Review Modeling network dynamics: the lac operon, a case study José M.G. Vilar, 1 Călin C. Guet, 1,2 and Stanislas Leibler 1 1 The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10021 2 Department of Molecular
JCB Mini-Review Modeling network dynamics: the lac operon, a case study José M.G. Vilar, 1 Călin C. Guet, 1,2 and Stanislas Leibler 1 1 The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10021 2 Department of Molecular
Bistability and non-monotonic induction of the lac operon in the natural lactose uptake system. D. Zander, D. Samaga, R. Straube, K.
 Bistability and non-monotonic induction of the lac operon in the natural lactose uptake system D. Zander, D. Samaga, R. Straube, K. Bettenbrock 1 Abstract The E. coli lac operon is regulated by a positive
Bistability and non-monotonic induction of the lac operon in the natural lactose uptake system D. Zander, D. Samaga, R. Straube, K. Bettenbrock 1 Abstract The E. coli lac operon is regulated by a positive
Comparison of Deterministic and Stochastic Models of the lac Operon Genetic Network
 Biophysical Journal Volume 96 February 2009 887 906 887 Comparison of Deterministic and Stochastic Models of the lac Operon Genetic Network Michail Stamatakis* and Nikos V. Mantzaris Department of Chemical
Biophysical Journal Volume 96 February 2009 887 906 887 Comparison of Deterministic and Stochastic Models of the lac Operon Genetic Network Michail Stamatakis* and Nikos V. Mantzaris Department of Chemical
Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus:
 m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
Bistability in ODE and Boolean network models
 Bistability in ODE and Boolean network models Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson)
Bistability in ODE and Boolean network models Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson)
Bistability and a differential equation model of the lac operon
 Bistability and a differential equation model of the lac operon Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Fall 2016 M. Macauley
Bistability and a differential equation model of the lac operon Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Fall 2016 M. Macauley
Genetic transcription and regulation
 Genetic transcription and regulation Central dogma of biology DNA codes for DNA DNA codes for RNA RNA codes for proteins not surprisingly, many points for regulation of the process https://www.youtube.com/
Genetic transcription and regulation Central dogma of biology DNA codes for DNA DNA codes for RNA RNA codes for proteins not surprisingly, many points for regulation of the process https://www.youtube.com/
Translation - Prokaryotes
 1 Translation - Prokaryotes Shine-Dalgarno (SD) Sequence rrna 3 -GAUACCAUCCUCCUUA-5 mrna...ggagg..(5-7bp)...aug Influences: Secondary structure!! SD and AUG in unstructured region Start AUG 91% GUG 8 UUG
1 Translation - Prokaryotes Shine-Dalgarno (SD) Sequence rrna 3 -GAUACCAUCCUCCUUA-5 mrna...ggagg..(5-7bp)...aug Influences: Secondary structure!! SD and AUG in unstructured region Start AUG 91% GUG 8 UUG
Modelling gene expression control using P systems: The Lac Operon, a case study
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com BioSystems 91 (2008) 438 457 Short communication Modelling gene expression control using P systems: The Lac Operon, a case study Francisco José Romero-Campero,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com BioSystems 91 (2008) 438 457 Short communication Modelling gene expression control using P systems: The Lac Operon, a case study Francisco José Romero-Campero,
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration
 Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Controllo dell espressione genica: procarioti
 Controllo dell espressione genica: procarioti 1. Operon Regolazione dell espressione nei procarioti 2. Regulation mostly on the transcriptional level. POSITIVE: energy saving, regulation of only one mrna
Controllo dell espressione genica: procarioti 1. Operon Regolazione dell espressione nei procarioti 2. Regulation mostly on the transcriptional level. POSITIVE: energy saving, regulation of only one mrna
4. Why not make all enzymes all the time (even if not needed)? Enzyme synthesis uses a lot of energy.
 1 C2005/F2401 '10-- Lecture 15 -- Last Edited: 11/02/10 01:58 PM Copyright 2010 Deborah Mowshowitz and Lawrence Chasin Department of Biological Sciences Columbia University New York, NY. Handouts: 15A
1 C2005/F2401 '10-- Lecture 15 -- Last Edited: 11/02/10 01:58 PM Copyright 2010 Deborah Mowshowitz and Lawrence Chasin Department of Biological Sciences Columbia University New York, NY. Handouts: 15A
Controlling biological systems: the lactose regulation system of Escherichia coli
 Proceedings of the 7 American Control Conference Marriott Marquis Hotel at Times Square New York City, USA, July -3, 7 WeB8. Controlling biological systems: the lactose regulation system of Escherichia
Proceedings of the 7 American Control Conference Marriott Marquis Hotel at Times Square New York City, USA, July -3, 7 WeB8. Controlling biological systems: the lactose regulation system of Escherichia
Biological Pathways Representation by Petri Nets and extension
 Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
RNA Synthesis and Processing
 RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
Ch. 18 Regula'on of Gene Expression BIOL 222
 Ch. 18 Regula'on of Gene Expression BIOL 222 Overview: Conduc'ng the Gene'c Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In mul@cellular eukaryotes
Ch. 18 Regula'on of Gene Expression BIOL 222 Overview: Conduc'ng the Gene'c Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In mul@cellular eukaryotes
Random Boolean Networks
 Random Boolean Networks Boolean network definition The first Boolean networks were proposed by Stuart A. Kauffman in 1969, as random models of genetic regulatory networks (Kauffman 1969, 1993). A Random
Random Boolean Networks Boolean network definition The first Boolean networks were proposed by Stuart A. Kauffman in 1969, as random models of genetic regulatory networks (Kauffman 1969, 1993). A Random
The Gene The gene; Genes Genes Allele;
 Gene, genetic code and regulation of the gene expression, Regulating the Metabolism, The Lac- Operon system,catabolic repression, The Trp Operon system: regulating the biosynthesis of the tryptophan. Mitesh
Gene, genetic code and regulation of the gene expression, Regulating the Metabolism, The Lac- Operon system,catabolic repression, The Trp Operon system: regulating the biosynthesis of the tryptophan. Mitesh
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression
 13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression Lesson Objectives Describe gene regulation in prokaryotes. Explain how most eukaryotic genes are regulated. Relate gene regulation to development in multicellular organisms.
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression Lesson Objectives Describe gene regulation in prokaryotes. Explain how most eukaryotic genes are regulated. Relate gene regulation to development in multicellular organisms.
A Synthetic Oscillatory Network of Transcriptional Regulators
 A Synthetic Oscillatory Network of Transcriptional Regulators Michael Elowitz & Stanislas Leibler Nature, 2000 Presented by Khaled A. Rahman Background Genetic Networks Gene X Operator Operator Gene Y
A Synthetic Oscillatory Network of Transcriptional Regulators Michael Elowitz & Stanislas Leibler Nature, 2000 Presented by Khaled A. Rahman Background Genetic Networks Gene X Operator Operator Gene Y
IET Syst. Biol., 2008, Vol. 2, No. 5, pp doi: /iet-syb: & The Institution of Engineering and Technology 2008
 Published in IET Systems Biology Received on 17th January 2008 Revised on 3rd June 2008 Special Issue Selected papers from the First q-bio Conference on Cellular Information Processing ISSN 1751-8849 Determinants
Published in IET Systems Biology Received on 17th January 2008 Revised on 3rd June 2008 Special Issue Selected papers from the First q-bio Conference on Cellular Information Processing ISSN 1751-8849 Determinants
Biomolecular Feedback Systems
 Biomolecular Feedback Systems Domitilla Del Vecchio MIT Richard M. Murray Caltech Classroom Copy v0.6c, July 11, 2012 c California Institute of Technology All rights reserved. This manuscript is for review
Biomolecular Feedback Systems Domitilla Del Vecchio MIT Richard M. Murray Caltech Classroom Copy v0.6c, July 11, 2012 c California Institute of Technology All rights reserved. This manuscript is for review
Chapter 12. Genes: Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 12 Genes: Expression and Regulation 1 DNA Transcription or RNA Synthesis produces three types of RNA trna carries amino acids during protein synthesis rrna component of ribosomes mrna directs protein
Chapter 12 Genes: Expression and Regulation 1 DNA Transcription or RNA Synthesis produces three types of RNA trna carries amino acids during protein synthesis rrna component of ribosomes mrna directs protein
