Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department
|
|
|
- Cody Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Timeline (Weeks) Big Idea Essential Questions Concept(s) Skills/ Competenceis Standards/ Eligible Content Assessments Vocabulary Educational Resources Differentiation Eligible Content covered all year- S7.A.3.1.1,2; S7.B.1.1.1,2,3; S8.A.3.2.3; S8.A.2.1.2,3,4,5; S8.A.2.2.1,2,3; Common Core (CC) Standards covered all year A, B, C, D, G, H, I, J; A, B, C, H, J, I These assessments are done with every unit all year: exit slips, bell ringers, journal entries, tests, quizzes, lab reports Vocabulary that is used all year- Focus Scientific method, hypothesises, experiment, variable, conclusion, periodic table, element, atom, compound Curriculum is used throughout the year as a base text with supplemental materials added each unit. Graphic organizers, cloze notes, sentence stems, guided practice, chunking of assignments, adapted quizzes/tests will be used throughout the year.
2 Weeks 1-18 The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things. What are the common characteristics that all organisms share? There are structural and functional similarities and differences that characterize diverse living things. Describe the flow of energy from the sun, throughout the earth system, living and nonliving, from the cellular scale to the global scale, and describe the transformations of that energy as it moves through the system. Identify examples of the relationship(s) between structure and function in the living world. Standards A4; A2,4; Eligible Content- S8.A.1.1.1,2,3,4; S8.B.1.1; CC Standard C Carbohydrate, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, cellular respiration, growth and development, response to stimuli, photosynthesis, reproduction, organelles, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nuclear membrane, mitochondria, gogli body, ribosomes, chloroplast, endoplasmic reticulum, cell wall, lysosome, mitosis, interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, cell transport, SAS Resource- Cell Respiration: Releasing Energy
3 Vocabulary Continued, unicellular, multicellular, virus, bacteria, bacteriophage, moreran, parasite, saprophyte, fission, DNA, flagellum, cocci, bacilli, spirilla, colony, enoculate, taxonomy, genus, species, eukaryotic, prokaryotic, autotrophic, heterotrophic, pseudopods, cilia, Protists, algae, asexual reproduction, budding, spores, fermentation, fungi, vertebrate, invertebrate, regeneration, tissue, organ, organ system, phylum,
4 Vocab Continued: symmetry, endoskeleton, exoskeleton, chordate, endothermic, ectothermic, metomorphosis, adaptation, migration, hibernation, chlorophyll, vascular tissue, diffusion, osmosis, tropism, germination, dispersal, embryo,
5 The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things. How can one cell function as an organism? There are structural and functional similarities and differences that characterize diverse living things. Describe the flow of energy from the sun, throughout the earth system, living and nonliving, from the cellular scale to the global scale, and describe the transformations of that energy as it moves through the system. Identify examples of the relationship(s) between structure and function in the living world. Standard A1,4,5,6,8,9 ; A1, 5, 6,7,9; A9; Eligible Content- S6.B.3.1.1,2,3; S7.B.1.1.1,2,3; S7.B.1.2.1,2,3; S7.B.1.2.1,2,3; S8.B.1.1.1,2,3,4; S8.C.2.1.3; S8.C.2.2.1; S8.B.1.1.1; S8.B.1.1.3; S8.B.1.1.4; CC Standard A, B, C, D All living things are made up of smaller units called cells Same as above Cells carry out the many functions needed to sustain life. Same as above
6 Cells take in nutrients that they use to provide energy to carry out their life functions. Same as above Cells grow and divide thereby producing more cells Same as above There are defining structures of cells for both plants and animals. Same as above Some organisms are made up of only one cell. Same as above Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multicellular organisms. Same as above Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells Same as above
7 There is a relationship between structure and function at all biological levels of organization. Same as above All multicellular organisms have systems that interact with one another to perform specific functions and enable the organism to function as a whole. Same as above Disease affects the structures and/or functions of an organism. Same as above Every organism has a set of genetic instructions that determines its inherited traits Same as above
8 The gene is the basic unit of inheritance. Same as above Weeks Populations of organisms evolve by natural selection. What allows some populations of organisms to change and survive while others cannot? Individual organisms with certain traits are more likely than others to survive and have offspring. Identify examples of the relationship(s) between structure and function in the living world. Provide examples of when it is correct to use the terms scientific theory as opposed to an opinion. Standards B1,2,4,5; C1; C1,2,3; C A8; Eligible Content- S6.B.2.1.1,2; S6.B.3.1.1; S6.B.2.1.1,2; Research project S7.B.2.1.1,2,3; S7.B.2.2.1,2,3,4; S7.D.1.1.2; S7.D.1.2.1,2,3; S8.B.1.1.1; S8.B.1.1.3; S8.B.1.1.4; S8.B.2.1.1,2,3,4,5 ; S8.B.2.2.1,2 Gamete, adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, phosphate, Meiosis, dominant, recessive, heterozygous, homozygous, pure, hybrid, probability, monohybrid, dihybrid, alleles, biotechnology, genetic engineering, cloning, evolution, fossil, geologic time, mutation, variation, adaptation, natural selection,
9 Every organism has a set of instructions for specifying its traits. Identify examples of the relationship(s) between structure and function in the living world. Provide examples of when it is correct to use the terms scientific theory as opposed to an opinion. Hereditary information (set of instructions) is contained in genes, located on chromosomes in cells Same as above Organisms reproduce and pass their genes to the next generation (their offspring). Same as above
10 Genes can randomly change or mutate, Same as above causing changes in certain traits of the offspring. Changes in environmental conditions can affect the survival of populations and entire species. Same as above Inherited traits can increase their frequency in successive generations so that descendents are very different from their ancestors Same as above
11 Extinction of a species occurs when the environment changes and the Same as above adaptive characteristics of a species are insufficient to allow its survival. Weeks Living things depend on their habitat to meet their basic needs. When investigating different systems, how does a habitat meet the needs of a species? Air, soil, water, Recognize that the and indoor quality of human health pollution affect in our society is affected human health in a by air, water, soil, and variety of ways. indoor pollution. Standards A2; 3.1.7,A8; 4.1.7A,B,C; B; Eligibile Content- S7.C.2.1.1,2,3; S7.D.1.2.1,2,3; S7.D.1.1.2; S8.A.3.1.4; S8.A.3.2.1,3; S8.B.3.1.1,2,3; S8.B.3.2.1,2,3; S11.A.1.3, S8.B.3.3.1; S8.B.1.1.1,4; S8.D.1.3.1,2,3,4; S11.B.3.1, S11.B.3.3, S11.D.1.2; S8.C.2.2.1; S8.D.1.3.1,2,3,4; Stream Study, Biome Research Project biogeochemical cycles, biotic, abiotic, ecology, ecosystem, population, habitat, niche, producer, consumer, decomposer, symbiosis, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, niche, velocity, ph, acidity, alkalinity, macroinvertebrate, limiting factor, succession, biome, pollutants
12 Wetlands play an important part in pollution control, water quality and human health issues. Same as above The misuse of natural resources can negatively affect the sustainability of society. Same as above Diverse biomes exist in Pennsylvania. Describe in detail how the living and non-living components of an ecosystem interrelate and directly impact food chains and energy flow. The biotic and abiotic components within an ecosystem interact. Organisms have specific roles in ecosystems. Same as above Intentionally Blank
13 Specific habitat management practices influence the success or failure of species. Intentionally Blank Scientists use specific criteria to categorize organisms as threatened, endangered or extinct. Intentionally Blank How do changes within living and non-living components of aquatic, terrestrial and human systems affect the balance within and between them? Scientists use a variety of physical, chemical and biological parameters to determine water quality. Compare and contrast how adaptations allow a species to fulfill a role in their environment. 1.Analyze the water quality of a particular body of water and infer possible causes for those results based upon land use in the surrounding watershed.
14 Land use within a particular watershed will influence water quality. Compare and contrast how adaptations allow a species to fulfill a role in their environment. 1.Analyze the water quality of a particular body of water and infer possible causes for those results based upon land use in the surrounding watershed. A wide variety of wetland types exist within Pennsylvania. Describe the importance of wetlands for humans, plants, and animals. Wetlands serve a number of beneficial functions for humans, plants, animals, and the environment as a whole. Describe the importance of wetlands for humans, plants, and animals.
15 Watershed boundaries can include a variety of habitats, ecosystems, and human influences. Analyze the effect of natural and human events, topography, and geographic location on wetlands, watersheds, aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Biotic and abiotic components within a habitat change, or differ, based on their location and topography. Analyze the effect of natural and human events, topography, and geographic location on wetlands, watersheds, aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Natural and Analyze the effect of human events natural and human can affect events, topography, and aquatic, geographic location on terrestrial, and wetlands, watersheds, wetland aquatic and terrestrial environments in ecosystems. a variety of ways.
16 Organisms within an ecosystem interact with other biotic components, abiotic components and within populations. Explain in detail the complex interactions that occur among biotic and abiotic components within an ecosystem. Abiotic components are critically important for maintaining an ecosystem s homeostasis. Explain in detail the complex interactions that occur among biotic and abiotic components within an ecosystem. Limiting factors affect the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Explain in detail the complex interactions that occur among biotic and abiotic components within an ecosystem. Ecosystems and their components change over time. Explain in detail the complex interactions that occur among biotic and abiotic components within an ecosystem.
17 A variety of cycles exist within an ecosystem and each helps maintain balance within the ecosystem. Explain in detail the complex interactions that occur among biotic and abiotic components within an ecosystem. Every living organism is uniquely suited to fulfill a role within its ecosystem. Explain how adaptations, degree of specialization, and behavior of organisms affect the niche they fill within their ecosystem. Biological diversity directly impacts the stability of an ecosystem. Explain how adaptations, degree of specialization, and behavior of organisms affect the niche they fill within their ecosystem.
18 Weeks The survival of living things is dependent upon their adaptations and ability to respond to natural changes in and human influences on the environment. How is the survival of species and their ability to adapt affected by natural and human induced environmental changes? Species must be able to adapt to changes within their ecosystem in order to survive. Explain how specialization and generalization influence a species survival. Standards D,E; Eligible Content- S11.A.1.3, S11.B.1.1, S11.B.2.1, S11.B.3.1, S11.B.3.2 The degree of specialization of a species can cause it to become threatened, endangered, or extinct. Explain how specialization and generalization influence a species survival. Animal species can be classified as generalists or specialists in their eating habits. Explain how specialization and generalization influence a species survival.
19 Habitat destruction can lead to species loss or termination. Explain how specialization and generalization influence a species survival. The intervention of humans has influenced the survival of species through management practices. Analyze how human attempts at species management have influenced the species success or failure. Human endeavors and changes in natural cycles have caused species to become threatened, endangered, or extinct. Describe how a species adaptability determines its ability to survive rapid environmental changes due to human activities. Weeks The health of all living things is directly related to the quality of the environment. How does the quality of the environment affect the health of all living things within it? Remediation of pollutants can improve environmental quality for organisms within an ecosystem. Identify sources of pollution and explain how they affect the health of the organisms within the ecosystem. Standards C; A,C; Eligibile Content- S11.A.1.,2,3, S11.B.3.1, S11.B.3.2, S11.C.2.2 S11.D.1.2,3
20
21
Use evidence of characteristics of life to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Scranton School District Scranton, PA 7 th Grade Life Science Prerequisite: Completion of 6 th Grade Science Life Science establishes the study of living things and how they interact
7 th Grade Life Science Scranton School District Scranton, PA 7 th Grade Life Science Prerequisite: Completion of 6 th Grade Science Life Science establishes the study of living things and how they interact
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW:
 THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department. Standard(s )
 Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department Course Name: Biology Grade Level: 10 Timelin e Big Ideas Essential Questions Content/ Concepts Skills/ Competencies Standard(s ) Eligible Content
Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department Course Name: Biology Grade Level: 10 Timelin e Big Ideas Essential Questions Content/ Concepts Skills/ Competencies Standard(s ) Eligible Content
Grade 7 Science Learning Standards
 Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide
 Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
SIXTH GRADE CHALLENGE
 SIXTH GRADE CHALLENGE I. CORE CONCEPTUAL OBJECTIVE: The students will utilize scientific process skills and problem solving strategies to solve meaningful problems. A. CONTENT AND SKILLS: By the end of
SIXTH GRADE CHALLENGE I. CORE CONCEPTUAL OBJECTIVE: The students will utilize scientific process skills and problem solving strategies to solve meaningful problems. A. CONTENT AND SKILLS: By the end of
Biology Curriculum Map. Assessments. Labs. Formative Assessments. Quizzes. Summative Assessments. Projects
 Timeframe Marking Periods 1 & 2 Unit/Topic Biological principles, biochemistry Study of life Unifying Themes Biology tools & technology atoms, ions & molecules properties of water & carbon bonding & chemical
Timeframe Marking Periods 1 & 2 Unit/Topic Biological principles, biochemistry Study of life Unifying Themes Biology tools & technology atoms, ions & molecules properties of water & carbon bonding & chemical
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
6 th Grade Life Science Strand 3: Characteristics and Interactions of Living Organisms
 Middle School Life Science Standards There are 15 standards that encompass the proposed middle school life science standards. The new standards are listed 4 times to match the four times life science is
Middle School Life Science Standards There are 15 standards that encompass the proposed middle school life science standards. The new standards are listed 4 times to match the four times life science is
Miller & Levine Biology 2014
 A Correlation of Miller & Levine Biology To the Essential Standards for Biology High School Introduction This document demonstrates how meets the North Carolina Essential Standards for Biology, grades
A Correlation of Miller & Levine Biology To the Essential Standards for Biology High School Introduction This document demonstrates how meets the North Carolina Essential Standards for Biology, grades
Text of objective. Investigate and describe the structure and functions of cells including: Cell organelles
 This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
7 th Grade Life Science Teaching & Learning Framework
 7 th Grade Science 7 th Grade Life Science Teaching & Learning Framework Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Unit 1 9 weeks Structure and Function of Cells S7L2. Obtain, evaluate, and describe how
7 th Grade Science 7 th Grade Life Science Teaching & Learning Framework Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Unit 1 9 weeks Structure and Function of Cells S7L2. Obtain, evaluate, and describe how
Compare and contrast the cellular structures and degrees of complexity of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
 Subject Area - 3: Science and Technology and Engineering Education Standard Area - 3.1: Biological Sciences Organizing Category - 3.1.A: Organisms and Cells Course - 3.1.B.A: BIOLOGY Standard - 3.1.B.A1:
Subject Area - 3: Science and Technology and Engineering Education Standard Area - 3.1: Biological Sciences Organizing Category - 3.1.A: Organisms and Cells Course - 3.1.B.A: BIOLOGY Standard - 3.1.B.A1:
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Define: Alleles. Define: Chromosome. In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways.
 Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
CELLULAR ORGANIZATION UNICELLULAR & MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
 7.2 CELL STRUCTURE The student will investigate and understand that all living things are composed of cells. Key concepts include a. cell structure and organelles b. similarities and differences between
7.2 CELL STRUCTURE The student will investigate and understand that all living things are composed of cells. Key concepts include a. cell structure and organelles b. similarities and differences between
End of Course Review. Review sheet
 Review Tips: Review ALL vocabulary, notes, assignments and worksheets Holt Biology CP: Review Science Skills on pages 1050 1063 and Lab safety on pages xxiv xxvii Modern Biology H: Review Lab safety &
Review Tips: Review ALL vocabulary, notes, assignments and worksheets Holt Biology CP: Review Science Skills on pages 1050 1063 and Lab safety on pages xxiv xxvii Modern Biology H: Review Lab safety &
Biology EOCT Review. Milton High School
 Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Activity Activity Title. Chapter Title Chapter Description Lesson Title Lesson Description Introduction to Living Things
 Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
Introduction to Living Things Students will explore the characteristics of living things, life cycles, stimuli and behavior, and how organisms maintain homeostasis. Characteristics of Living Things differentiate
Curriculum Mapping, Alignment, and Analysis Glen Lake Community Schools
 Curriculum Mapping, Alignment, and Analysis Glen Lake Community Schools Grade:9 Content Area: Science Course: Biology Revised 8/27/03 Month Essential Questions What are the fundamental, enduring questions
Curriculum Mapping, Alignment, and Analysis Glen Lake Community Schools Grade:9 Content Area: Science Course: Biology Revised 8/27/03 Month Essential Questions What are the fundamental, enduring questions
Franklin Special School District Grade 7 Science
 08-09 SEVENTH GRADE: OVERVIEW The academic standards for seventh grade establish the content knowledge and skills for Tennessee students necessary to prepare them for the rigorous levels of higher education
08-09 SEVENTH GRADE: OVERVIEW The academic standards for seventh grade establish the content knowledge and skills for Tennessee students necessary to prepare them for the rigorous levels of higher education
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator!
 Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Basic Biology. Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology
 Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Biology Pacing Guide
 Unit Dates Glencoe Chapters 0 8/10 N/A Biology Intro 8/12 1 Cells 8/15 9/30 6.4 6.2 7.1 18.2 7.3 6.3 7.2 7.4 Topic GPS Classroom Procedures, Introduction to Biology SCSh 1-7 Macromolecules (6 days) Monomer/
Unit Dates Glencoe Chapters 0 8/10 N/A Biology Intro 8/12 1 Cells 8/15 9/30 6.4 6.2 7.1 18.2 7.3 6.3 7.2 7.4 Topic GPS Classroom Procedures, Introduction to Biology SCSh 1-7 Macromolecules (6 days) Monomer/
GREENCASTLE ANTRIM SCHOOL DISTRICT Planned Course Board Approved February 16, 2012 Course Title: Biology Grade Level(s) 10 11th
 GREENCASTLE ANTRIM SCHOOL DISTRICT Planned Course Board Approved February 16, 2012 Course Title: Biology Grade Level(s) 10 11th Course Materials: Primary Source(s) Supplemental Source(s) Course Materials:
GREENCASTLE ANTRIM SCHOOL DISTRICT Planned Course Board Approved February 16, 2012 Course Title: Biology Grade Level(s) 10 11th Course Materials: Primary Source(s) Supplemental Source(s) Course Materials:
Final Study Guide. Science Skills. Directions: Make a study set in Quizlet called Final Study Guide. Research the answers to each bullet.
 Final Study Guide Directions: Make a study set in Quizlet called Final Study Guide. Research the answers to each bullet. Make a one or more Quizlet cards (or actual index cards) for each bullet. Remember
Final Study Guide Directions: Make a study set in Quizlet called Final Study Guide. Research the answers to each bullet. Make a one or more Quizlet cards (or actual index cards) for each bullet. Remember
Miller & Levine Biology 2010
 A Correlation of 2010 to the Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors Grades 9-12 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how 2010 meets the Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors, grades 9-12. Correlation page references
A Correlation of 2010 to the Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors Grades 9-12 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how 2010 meets the Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors, grades 9-12. Correlation page references
Biology 1 EOC Study Guide
 Name: Biology 1 EOC Study Guide Date: Standard 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles 1. What are three tenets of the cell theory?
Name: Biology 1 EOC Study Guide Date: Standard 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles 1. What are three tenets of the cell theory?
FAIRBANKS NORTH STAR BOROUGH SCHOOL DISTRICT - SCIENCE CURRICULUM. Prentice Hall Biology (Miller/Levine) 2010 MASTERY CORE OBJECTIVES HIGH SCHOOL
 MASTERY CORE OBJECTIVES HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCE Overview: Life Science is a one-year course for students who learn best with extra time to approach the subject. The academic focus is to develop student
MASTERY CORE OBJECTIVES HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCE Overview: Life Science is a one-year course for students who learn best with extra time to approach the subject. The academic focus is to develop student
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW
 Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Biology Science Crosswalk
 SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including
SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including
Purpose of cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Cell membrane. Purpose of cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Contains organelles and site of many chemical reactions
 Cell membrane Purpose of cell membrane Cell membrane Cytoplasm Purpose of cytoplasm Contains organelles and site of many chemical reactions Plant cell wall Purpose of cell wall Provides support (plants
Cell membrane Purpose of cell membrane Cell membrane Cytoplasm Purpose of cytoplasm Contains organelles and site of many chemical reactions Plant cell wall Purpose of cell wall Provides support (plants
EOC Study Guide. CELLS SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells.
 EOC Study Guide CELLS SB. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Unit. What are the characteristics that all living things share?. What
EOC Study Guide CELLS SB. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Unit. What are the characteristics that all living things share?. What
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions
 NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
Standards: A, C, E; A; A, B; B; B; C; A; B; A
 Unit: Tools, Techniques, Themes of Biology Standards: 3.1.10 A, C, E; 3.2.10 A; 3.3.10 A, B; 3.7.10 B; 3.8.10 B; 4.3.10 C; 4.6.10 A; 4.7.10 B; 4.8.10 A Unit Essential Question(s): 1. What is the study
Unit: Tools, Techniques, Themes of Biology Standards: 3.1.10 A, C, E; 3.2.10 A; 3.3.10 A, B; 3.7.10 B; 3.8.10 B; 4.3.10 C; 4.6.10 A; 4.7.10 B; 4.8.10 A Unit Essential Question(s): 1. What is the study
table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment
 table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment Chapter 1: Characteristics of Living Things 1 A. Biology and the Living Environment 1 B. What is Science 1 C. Scientific Inquiry
table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment Chapter 1: Characteristics of Living Things 1 A. Biology and the Living Environment 1 B. What is Science 1 C. Scientific Inquiry
Course #: SC-49 Grade Level: Prerequisites: None # of Credits: 1
 Course #: SC-49 Grade Level: 9-12 Course Name: Biology Level of Difficulty: Medium Prerequisites: None # of Credits: 1 Strand 1: Inquiry Process s 1: 2: 3: 4: Science as inquiry is basic to science education
Course #: SC-49 Grade Level: 9-12 Course Name: Biology Level of Difficulty: Medium Prerequisites: None # of Credits: 1 Strand 1: Inquiry Process s 1: 2: 3: 4: Science as inquiry is basic to science education
Cells and Genetics. Life Science. Cell parts. Cell parts cont. Cell processes. Cell Division 5/4/2015
 Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Observe and explore a given system or concept to deepen scientific understanding. Analyze data to seek out patterns and/or make predictions
 Unit Title & UFDs Time Frame Description of What Students will Focus on Transfer Goals Subject Area TEKS Academic Vocabulary Unit 1: Living Systems 22-24 days 1 st 9 Weeks The students can identify levels
Unit Title & UFDs Time Frame Description of What Students will Focus on Transfer Goals Subject Area TEKS Academic Vocabulary Unit 1: Living Systems 22-24 days 1 st 9 Weeks The students can identify levels
Parts of an experiment. CP Biology EOC Quick Review The Study of Life 1/6/2012
 CP Biology EOC Quick Review The Study of Life Parts of an experiment Independent variable the factor that is being tested. The factor that causes change. Dependent variable the measurable factor that changes
CP Biology EOC Quick Review The Study of Life Parts of an experiment Independent variable the factor that is being tested. The factor that causes change. Dependent variable the measurable factor that changes
Keystone Exams: Biology Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content. Pennsylvania Department of Education
 Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION General Introduction to the Keystone Exam Assessment Anchors Introduction
Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION General Introduction to the Keystone Exam Assessment Anchors Introduction
Characteristics of Life
 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2,
 Test Review (12/7) 1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2, 20 2. 5. What structure is responsible
Test Review (12/7) 1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2, 20 2. 5. What structure is responsible
Name: Date: Period: Biology End of Course Vocabulary 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and
 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
GRADE 7. Units of Study: Cell Structure and Function Energy and Life Cell Reproduction and Genetics Environmental Changes Through Time Classification
 GRADE 7 Course Overview: In seventh grade, students are actively engaged in the inquiry process as they collaborate with others to understand complex scientific concepts. Students identify a question,
GRADE 7 Course Overview: In seventh grade, students are actively engaged in the inquiry process as they collaborate with others to understand complex scientific concepts. Students identify a question,
Area of Focus: Biology. Learning Objective 1: Describe the structure and function of organs. Pre-Learning Evaluation: Teaching Methods and Process:
 Area of Focus: Biology Learning Objective 1: Describe the structure and function of organs. Pre- Diagram and label the structure of the primary components of representative organs in plants and animals
Area of Focus: Biology Learning Objective 1: Describe the structure and function of organs. Pre- Diagram and label the structure of the primary components of representative organs in plants and animals
Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments
 Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments June 2014 Content Domain Range of Competencies Approximate Percentage of Test Score I. Science and Engineering Practices 0001 0003 21% II. Biochemistry and Cell Biology
Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments June 2014 Content Domain Range of Competencies Approximate Percentage of Test Score I. Science and Engineering Practices 0001 0003 21% II. Biochemistry and Cell Biology
EOC MILESTONE REVIEW
 Introduction 1. What does the term biology mean? EOC MILESTONE REVIEW 2. What is homeostasis and why is it important to living things? Content Domain: Cells (SB1) 1. Define eukaryote: List 3 examples of
Introduction 1. What does the term biology mean? EOC MILESTONE REVIEW 2. What is homeostasis and why is it important to living things? Content Domain: Cells (SB1) 1. Define eukaryote: List 3 examples of
Biology regimented study plan
 For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
POCONO MOUNTAIN SCHOOL DISTRICT
 COURSE: Life Science GRADE(S): 8 UNIT 1: Basic Science Principles PA ACADEMIC and PSSA STANDARDS S8.A.1 1 Explain, interpret, and apply scientific, environmental, or technological knowledge presented in
COURSE: Life Science GRADE(S): 8 UNIT 1: Basic Science Principles PA ACADEMIC and PSSA STANDARDS S8.A.1 1 Explain, interpret, and apply scientific, environmental, or technological knowledge presented in
Name: Date: Period: BIOLOGY Final Exam Study Guide. 3. List the 4 major macromolecules (biomolecules), their monomers AND their functions. a.
 Name: Date: Period: Water and Cells BIOLOGY Final Exam Study Guide 1. Define homeostasis: 2. Match the property of water with its correct description: a. High specific heat b. High heat of vaporization
Name: Date: Period: Water and Cells BIOLOGY Final Exam Study Guide 1. Define homeostasis: 2. Match the property of water with its correct description: a. High specific heat b. High heat of vaporization
Biology Final Review Ch pg Biology is the study of
 Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Biology II : Embedded Inquiry
 Biology II : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
Biology II : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
 7 th Grade Life Science Essential Questions: 1. How do the structures of organisms contribute to life s functions? 2. How do matter and energy move through individual organisms and ecosystems? 3. How does
7 th Grade Life Science Essential Questions: 1. How do the structures of organisms contribute to life s functions? 2. How do matter and energy move through individual organisms and ecosystems? 3. How does
Life Science Strand Grades K-8
 Life Science Strand Grades K-8 KINDERGARTEN K.L.1: Compare characteristics of animals that make them alike and different from other animals and nonliving things. K.L.1.1: Compare different types of the
Life Science Strand Grades K-8 KINDERGARTEN K.L.1: Compare characteristics of animals that make them alike and different from other animals and nonliving things. K.L.1.1: Compare different types of the
FINAL VERSION_ Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea
 Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
PRESCOTT UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT District Instructional Guide
 PRESCOTT UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT District Instructional Guide Grade Level: High School Subject: Biology Quarter/Semester 1/1 Core Text: Biology, Miller & Levine, 2006 Time Block Unit Content Skills Standards
PRESCOTT UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT District Instructional Guide Grade Level: High School Subject: Biology Quarter/Semester 1/1 Core Text: Biology, Miller & Levine, 2006 Time Block Unit Content Skills Standards
Biol 1409: Study Guide for Exam I. Introduction to Diversity
 Biol 1409: Study Guide for Exam I Introduction to Diversity 1. Define Biosphere and describe where it is found 2. Describe why our planet is so hospitable to life 3. Name and briefly describe the major
Biol 1409: Study Guide for Exam I Introduction to Diversity 1. Define Biosphere and describe where it is found 2. Describe why our planet is so hospitable to life 3. Name and briefly describe the major
10 th Grade Biology K
 10 th Grade Biology K Scranton School District Scranton, PA 10 th Grade Biology K Prerequisite: Successful completion of General Science This course is designed to prepare students for proficient and advanced
10 th Grade Biology K Scranton School District Scranton, PA 10 th Grade Biology K Prerequisite: Successful completion of General Science This course is designed to prepare students for proficient and advanced
7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet
 7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet Ms. Shirreffs Name: Introduction and Characteristics of Life 1. This year we studied life science, another word for life science is 2. Which term describes an organism
7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet Ms. Shirreffs Name: Introduction and Characteristics of Life 1. This year we studied life science, another word for life science is 2. Which term describes an organism
Describe the structure and composition of the cell membrane. (make a sketch) What does the Theory of Endosymbiosis state?
 Station 1. Analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell
Station 1. Analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM - BIOLOGY I
 WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM - BIOLOGY I COURSE NAME: Biology I UNIT: Basic Biological Principles NO. OF DAYS: 9 KEY LEARNING(S): UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: biologists identify and study living
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM - BIOLOGY I COURSE NAME: Biology I UNIT: Basic Biological Principles NO. OF DAYS: 9 KEY LEARNING(S): UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: biologists identify and study living
Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide 1 st 9 Weeks SOL Objectives Vocabulary 7 Days 14 Days BIO.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic,
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide 1 st 9 Weeks SOL Objectives Vocabulary 7 Days 14 Days BIO.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic,
Have cell walls Made of
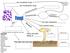 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
1. CHEMISTRY OF LIFE. Tutorial Outline
 Tutorial Outline North Carolina Tutorials are designed specifically for the Common Core State Standards for English language arts, the North Carolina Standard Course of Study for Math, and the North Carolina
Tutorial Outline North Carolina Tutorials are designed specifically for the Common Core State Standards for English language arts, the North Carolina Standard Course of Study for Math, and the North Carolina
Inquiry Process. Books GLCEs Vocabulary Pacing. Life Science 7
 Inquiry Process Life 7 Explorer Environmental Standard S.IP: Develop an understanding that scientific inquiry and reasoning involves observing, questioning, investigating, recording, and developing solutions
Inquiry Process Life 7 Explorer Environmental Standard S.IP: Develop an understanding that scientific inquiry and reasoning involves observing, questioning, investigating, recording, and developing solutions
Curriculum Overview 7 th Grade Science
 1 st Nine Weeks Unit 1: Lab Safety, Measurement, and Scientific Investigation 7.1AB, 7.2AB, 7.3A Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Control Demonstrate safe practices during laboratory
1 st Nine Weeks Unit 1: Lab Safety, Measurement, and Scientific Investigation 7.1AB, 7.2AB, 7.3A Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Control Demonstrate safe practices during laboratory
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
Biology Teaching & Learning Framework (Block) Unit 4. Unit 1 1 week. Evolution SB5
 Biology Biology Standards The Cobb Teaching and Learning Standards of Excellence for Science are designed to provide foundational knowledge and skills for all students to develop proficiency in science.
Biology Biology Standards The Cobb Teaching and Learning Standards of Excellence for Science are designed to provide foundational knowledge and skills for all students to develop proficiency in science.
Science 7 Acceleration Study Guide
 Name: Science 7 Acceleration Study Guide These are the units/topics covered in the exam: Laboratory Safety The Scientific Method and Measurement Classification Ecology Evolution Genetics Cells/Microscope
Name: Science 7 Acceleration Study Guide These are the units/topics covered in the exam: Laboratory Safety The Scientific Method and Measurement Classification Ecology Evolution Genetics Cells/Microscope
Killingly Public Schools. Grade 10 Draft: March 2004
 Killingly Public Schools Grade 10 Draft: March 2004 BIOLOGY Grade 10 Safety CONTENT STANDARD 10 B 1: The student will understand the critical role of safety in the science classroom setting. The student
Killingly Public Schools Grade 10 Draft: March 2004 BIOLOGY Grade 10 Safety CONTENT STANDARD 10 B 1: The student will understand the critical role of safety in the science classroom setting. The student
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Unit 1 The Science of Biology (5 days) Biology I Units and s Biology I A s 1. I can design a scientific experiment that includes a control group, experimental group, constants,
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Unit 1 The Science of Biology (5 days) Biology I Units and s Biology I A s 1. I can design a scientific experiment that includes a control group, experimental group, constants,
Biology Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
Seventh Grade Review. Life Science
 Seventh Grade Review Life Science Living organisms require food, water, shelter, energy, and space to survive Cells are the smallest units that carry out activities of life The three components of the
Seventh Grade Review Life Science Living organisms require food, water, shelter, energy, and space to survive Cells are the smallest units that carry out activities of life The three components of the
Biology Scope and Sequence
 Cell Structure and Function & Biological Processes and Systems First Grading Period (24 days) Readiness: B4.B The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Cell Structure and Function & Biological Processes and Systems First Grading Period (24 days) Readiness: B4.B The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Unit # - Title Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry
 Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry What is Biology? What is Science? What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? How do the rules
Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry What is Biology? What is Science? What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? How do the rules
California Subject Examinations for Teachers
 California Subject Examinations for Teachers TEST GUIDE SCIENCE SUBTEST II: LIFE SCIENCES Subtest Description This document contains the Life Sciences subject matter requirements arranged according to
California Subject Examinations for Teachers TEST GUIDE SCIENCE SUBTEST II: LIFE SCIENCES Subtest Description This document contains the Life Sciences subject matter requirements arranged according to
Miller Levine Biology
 A Correlation of To the 2018 Mississippi College and Career-Readiness Standards for Biology A Correlation of to the Biology BIO.1 Cells as a System Conceptual Understanding: Biologists have determined
A Correlation of To the 2018 Mississippi College and Career-Readiness Standards for Biology A Correlation of to the Biology BIO.1 Cells as a System Conceptual Understanding: Biologists have determined
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Biology Concepts at a Glance. - Identify Endergonic vs Exergonic - Activation Energy (graphs of endergonic vs exergonic reactions)
 Biology Concepts at a Glance Unit 1 Inquiry Scientific Method: - Problem - Hypothesis - Experiment - collect data - analyze data - conclusion Dependent vs. Independent Variables Controlled Variables Control
Biology Concepts at a Glance Unit 1 Inquiry Scientific Method: - Problem - Hypothesis - Experiment - collect data - analyze data - conclusion Dependent vs. Independent Variables Controlled Variables Control
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 2 nd SEMESTER FINAL EXAM:
 TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 2 nd SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 3 and 4 Will assess your
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 2 nd SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 3 and 4 Will assess your
Biology Pacing Guide
 Biology should investigate the chemistry and role of cells in life processes, genetics, evolution and the diversity of life. Students should learn about the world through the study of behavioral relationships,
Biology should investigate the chemistry and role of cells in life processes, genetics, evolution and the diversity of life. Students should learn about the world through the study of behavioral relationships,
Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin.
 Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin. Click here for Final Jeopardy Classify This For Cell Gene Gene the Dancin Machine Cycles & Changes Feed
Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin. Click here for Final Jeopardy Classify This For Cell Gene Gene the Dancin Machine Cycles & Changes Feed
Life Science FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES
 FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
Compare cellular structure and their functions in prokaryote and eukaryote cells.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards DNA molecules contain genetic information that is found in all cells. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins,
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards DNA molecules contain genetic information that is found in all cells. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins,
Characteristics of Living Things
 Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Mid-Term Study Guide. What is Science. 1. Compare hypothesis-driven and discovery science. 2. Compare theories, laws, and hypothesis
 What is Science Mid-Term Study Guide 1. Compare hypothesis-driven and discovery science 2. Compare theories, laws, and hypothesis What is Biology 3. List the 8 characteristics of living things 4. List
What is Science Mid-Term Study Guide 1. Compare hypothesis-driven and discovery science 2. Compare theories, laws, and hypothesis What is Biology 3. List the 8 characteristics of living things 4. List
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
Biology study. Basic Principles of Biology Chapter One. Chapters
 1 April 27, 2010 Chapters Chapter One 1 Biology study Chapter Two 2 Chapter Three 3 Chapter Four 4 Chapter Five 5 Chapter Six/ Seven 6/7 Chapter Eight 8 Chapters continued.. Chapter Nine 9 Chapter Ten
1 April 27, 2010 Chapters Chapter One 1 Biology study Chapter Two 2 Chapter Three 3 Chapter Four 4 Chapter Five 5 Chapter Six/ Seven 6/7 Chapter Eight 8 Chapters continued.. Chapter Nine 9 Chapter Ten
STAAR Biology Assessment
 STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
Name Date Block. Biology EOCT Review
 Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Name Date Period Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life?
 Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Use observations to describe what animals need to survive. (K-LS1-1) Use observations to describe what plants need to survive.
 (NGSS in Parentheses) Kindergarten Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards SAS Standards Assessment Anchor Eligible Content K Animals need food (plants and other
(NGSS in Parentheses) Kindergarten Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards SAS Standards Assessment Anchor Eligible Content K Animals need food (plants and other
7 th Grade Science Curriculum
 (1 st 9 Weeks- 1 st 4.5 9 Weeks) Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. NM & 1 Scientific Thinking and Practice Understand the
(1 st 9 Weeks- 1 st 4.5 9 Weeks) Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. NM & 1 Scientific Thinking and Practice Understand the
Teacher: Cheely/ Harbuck Course: Biology Period(s): All Day Week of: 1/12/15 EOCEP Lesson Plan/5E s
 EOCEP Lesson Plan/5E s Day of the Week Monday Curriculum 2005 SDE Support Doc Standard:: B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular basis of heredity. Indicator: B-4.5 Goals (Objectives
EOCEP Lesson Plan/5E s Day of the Week Monday Curriculum 2005 SDE Support Doc Standard:: B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular basis of heredity. Indicator: B-4.5 Goals (Objectives
