UC Riverside International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings ( )
|
|
|
- Emery Bailey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UC Riverside International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings ( ) Title A Viroid Different from Citrus Exocortis Viroid Found in Commercial Citrus in Sicily Permalink Journal International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings ( ), 10(10) ISSN Authors Albanese, G. La Rosa, R. Davino, M. et al. Publication Date 1988 Peer reviewed escholarship.org Powered by the California Digital Library University of California
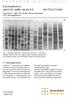
2 A Viroid Different from Citrus Exocortis Viroid Found in Commercial Citrus in Sicily Giuliana Albanese, Rosa La Rosa, M. Davino, Rosemarie W. Hammond, D. R. Smith and T. 0. Dienerz ABSTRACT. A low molecular weight RNA, named citrus "B" viroid (CBV), has been detected alone or associated with citrus exocortis viroid (CEV) in many commercial citrus species and varieties. The electrophoretic mobility of CBV on 5% polyacrylarnide gels under denaturing conditions is between those of CEV and the fast form of coconut cadang cadang viroid (CCCV) RNA1. CBV replicates in zucchini squash, a common host for CEV, but not in ten other herbaceous hosts of CEV. Citrus nucleic acid extracts containing CBV were reacted with full-length CEV-, potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV)-cDNA probes and with CEV-, PSTV-, tomato apical stunt viroid (TASV)- and tomato planta macho viroid (TPMV)-RNA probes. CBV did not hybridize with any of the probes. Inoculations of partially purified CBV onto different citrus indicator plants gave variable epinasty on Etrog citron, but no symptoms in other indicators. Index words. PAGE, molecular hybridization. Detection of citrus exocortis viroid (CEV) by polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic (PAGE) analysis of citrus nucleic acid extracts has been widely demonstrated (1, 3, 4). We routinely use this method of CEV diagnosis because it is suitable for detecting severe as well as mild isolates and requires only a small amount (1-3 g) of citrus tissue from the greenhouse or from the field (8). A new viroid, which we named citrus "B" viroid to distinguish it from CEV, has been detected recently in many Sicilian commercial citrus trees (2). Many citrus viroids other than CEV also have been found by different authors in other countries (6, 10). We report here studies to determine whether CBV is related to CEV or may be associated with other citrus diseases caused by unknown pathogenic agents. MATERIALS AND METHODS Inoculum source. Tissue samples taken from citrus trees located in different citrus areas were used. Source plants had been previously indexed for psorosis, cachexia (xyloporosis) and CEV by routine tests (2) "Research work supported by CNR, Italy. Special grant IPRA. Sub-project no. 1, paper no and were propagated on Volkamer lemon rootstock or graft inoculated onto Arizona 861-S-1 citron and grown in the greenhouse at C. A severe CEV isolate (PV-194) from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) was inoculated by stem-slashing into Arizona 861-S-1 citron and into Volkamer lemon as a control. Electrophoretic tests. Young bark of shoots collected in the field (during spring or autumn) or in the greenhouse was used to extract nucleic acids from citrus. These were obtained by a phenol-chloroform extraction and 2M LiC1-fractionation (1). Nucleic acids from herbaceous plants were extracted by the method of Macquaire, et al. (9). Extracts were electrophoresed in bidirectional 5% polyacrylamide gels with second direction electrophoresis under denaturing conditions (11). The fast form of coconut cadang cadang viroid (CCCV) RNAl was coelectrophoresed as a marker. Silver stain (Bio-rad, Richmond, California) protein protocol, was used to develop slabs (4). Biological tests. CEV and CBV RNAs were separately recovered from denaturing gels (dpage) by cutting out the bands corresponding to circular forms and grinding the gel in a mortar and pestle in 0.05 M
3 166 Tenth ZOCV Conference glycine, 0.03 M K2HP04 (ph 9.2) buffer. Viroids were stem-slash inoculated into Arizona 861-S-1 citron and Parson's Special mandarin. Nucleic acids extracted from CBV- and CEV-infected citrus trees were dissolved in 0.04 M K2HP04 (ph 8.0) buffer and inoculated by stemslashing into herbaceous hosts listed in table 2 and by rubbing onto carborundum-dusted young leaves of Gynura aurantiaca D. C. CEV (PV-194) was used as a control in every inoculation. Infection was checked weekly by observation of symptoms and monthly by electrophoretic analysis. Molecular hybridization. To prepare 32P-labeled DNA and RNA probes, double-stranded cdnas of CEVJ variant "d" (13), potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV) (5), tomato apical stunt viroid (TASV) (7), and tomato planta macho viroid (TPMV) (7) were separately inserted into appropriate restriction endonuclease sites (specific for each viroid) of vector psp65 and amplified in Escherichia coli strain JM83. High specific activity radioactive probes were prepared either by nick-translation using a commercial kit (Bethesda Research Laboratories) or by in vitro syr.thesis of an RNA probe using SP6 RNA polymerase and a linearized DNA template (Promega Biotec, Inc.). Nucleic acid extracts from citrus, which in PAGE analysis disclosed CEV, CEV + CBV, or CBV, and extracts from tomato which had been inoculated with PSTV or CEV + CBV were denatured with 4 M formaldehyde and were used undiluted or diluted three-, ten- and one-hundred fold with 7.5X SSC buffer (15 mm The prehybridization reaction was performed using 1 ml of buffer with 40% (vlv) formamide, 0.18 M NaC1, 10 mm sodium cacodylate, 1 mm EDTA, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and calf thymus DNA (300 kg1 ml) at ph 7.0 per 35 cm2 of membrane area at 55 C for 30 min to 1 h. Dextran sulfate was then added to 10% (wlv) and the membranes further incubated for 30 min to 1 h. Hybridization was NaC1, 1.5 mm sodium citrate). In dot blot tests, samples were Fig. 1. Second direction polyacrylamide pipetted (2 plldilution) Onto a treated gel (5%) electrophoresis (PAGE) (upwards membrane (I2). In migration under denaturating conditions and northern blot analysis, extracts were staining with silver), of nucleic acids extransferred onto membranes after tracted from: l-coconut cadang-cadang virelectrophoresis on 1.5% agarose. Nit- oid (CCCV) RNA I-fast-infected coconut; 2, 3, 4 and Witrus exocortis viroid (CEV)- rocellulose membranes with bound and 66B,, viroid (CBV)-infected citrus; extracts were then baked 2 h at 80 C WBV-infected citrus; TqEV-infected in vacuo. citrus.
4 performed for 18 h at 42 or 55 C in the presence of 10% dextran sulfate (14) and "'P-labeled probes (1-2 x 10"pmI ml for DNA probes and x 10" cprnlml for RNA probes). The membranes were then washed at 55 C with three changes (10 minlchange) of buffer (0.36 M NaC1, 0.02 M Tris, 0.1% SDS, ph 7.0) and then with three changes of 0.1X of the above buffer. An additional stringent wash at 65 C with 3 changes (20 mintchange) of 0.1X SSC with 0.1% SDS was made to the membranes hybridized with RNA-probes. Membranes hybridized with RNA-probes were then treated with RNase A (1 kglml) in 2X SSC buffer at room temperature for 15 min and then rinsed at 50 C for 30 min in 0.1X SSC with 0.1% SDS. Autoradiography was carried out overnight at -70 C with Kodak XAR- 5 film and intensifying screen. RESULTS Electrophoretic tests and comparison with bioassays of source plants. CBV electrophoretic mobility, between CEV and fast form of CCCV RNAl (fig. l), reveals a molecular size of about 308 nucleotides. Detection frequence of CBV and/or CEV in tested citrus plants by PAGE and by bioassay on Arizona 861-S-1 citron is reported in table 1. When PAGE revealed only CBV, the reaction of Arizona 861-S-1 citron was invariably mild, whereas when PAGE revealed CEV alone or CEV and CBV, symptoms on citron were always severe. Biological tests. Inoculations of viroid preparations eluted from dpage induced symptoms. CEV infection of Arizona 861-S-1 citron resulted in severe stunting, leaf curling, and veinal necrosis, whereas CBV infection resulted only in mild stunting and variable epinasty (fig. 2) 1 month after inoculation. PAGE analysis of these tissues disclosed the presence of a viroid RNA with the mobility of the RNA used for inoculation. Extracts from source trees were also inoculated on Parson's Special mandarin. One year after inoculation all test plants were negative for the browning reaction for cachexia (xyloporosis). TABLE 1 POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL (5%) ELECTROPHORETIC (PAGE) ANALYSIS AND BIOASSAY RESULTS ON CITRON FOR SOURCE PLANTS CONTAINING CITRUS EXOCORTIS VIROID (CEV) AND CITRUS "B" VIROID (CBV) No. of PAGE tests detecting CEV CBV CEV Pathogenicity + Total no. of on Arizona Source plants CBV PAGE tests 861-S-1 citron Citronz Severe Volkamer lemonz Severe Navelina 1 sweet orange Mild Navelina 8 sweet orange Severe Vaniglia sweet orange Mild Continella Fem. lemon Severe Avana mandarin Mild Murcott tangor Mild Comune 1 clementine Mild Comune 2 clementine Severe Comune 3 clementine Severe Star Ruby grapefruit Severe Fantastic0 bergamot Severe Volkamer lemon Mild "Inoculated with CEV isolate PV-194 ATCC.
5 Tenth ZOCV Conference Fig. 2. Arizona 861-S-1 citrons (from left to right) inoculated with citrus exocortis viroid (CEV), citrus "B" viroid (CBV) (gel band), and healthy.
6 Diseases Induced by Viroids and Viroidlike Pathogens 169 TABLE 2 BIOLOGICAL REACTION AND POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL (5%) ELECTROPHORETIC ANALYSIS OF HERBACEOUS HOSTS DAYS AFTER INOCULATION WITH NUCLEIC ACID EXTRACTS CONTAINING CITRUS EXOCORTIS VIROID (CEV) AND CITRUS "B" VIROID (CBV) Host Symptomsz CEV CBV Aster grandiflorus Capsicum annuum 'Yolo Wonder' Chrysanthemum morifolium 'White Spider' Cucurbita pep0 Italica Dahlia variabilis Gynura aurantiaca Lycopersicon esculentum 'Rutgers' Ocimum basilicum Petunia hybrida Solanum melongena 'Long Purple' Zinnia elegans "+ = presence or - = absence of symptoms or viroid band. Among herbaceous hosts inoculated with citrus nucleic acid extracts containing CEV and CBV, only Rutgers tomato, Gynura aurantiaca and zucchini squash showed epinasty and a mild stunting. CEV was recovered by PAGE analysis days after inoculation from all tested species, whereas CBV could be detected only in zucchini squash extracts (table 2). Molecular hybridization. A total of 63 citrus extracts classified into three groups (CEV, CEV + CBV, and CBV) according to PAGE analysis were tested by dot-blot hybridization with CEV-, PSTV-, TASV-, and TPMV-RNA probes. The number of hybridized extracts of the total spotted per group and their degree of hyb- ridization are reported in table 3. Almost all citrus extracts of CEV and CEV + CBV groups hybridized with every probe used. The lack of reaction of some samples may be attributable to handling errors. Of 26 CBV extracts tested with all of the probes, only one or two hybridized. These positive reactions may be CEV which was not detected by PAGE analysis in those few extracts. The observed differences in hybridization intensity are consistent with the degree of homology among the respective viroids. Results of northern blot hybridization carried out on some extracts with PSTV- and CEV-cDNA probes agree with those of dot blot assays (fig. 3) TABLE 3 HYBRIDIZATION WITH RNA PROBES OF CITRUS EXTRACTS SHOWING CITRUS EXOCORTIS VIROID (CEV), CEV PLUS CITRUS " B VIROID (CBV) OR CBV ONLY IN POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL (5%) ELECTROPHORETIC (PAGE) TESTS RNA probes Viroids CEV TAS + TPMVz PSTVz detected by PAGE ay by a b a b CEV 12/ / /15 + CEV + CBV / /23 + CBV 2/ / /26 + "TASV = tomato atypical stunt viroid; TPMV = tomato planta macho viroid; PSTV = potato spindle tuber viroid. Ya = no. positive of total samples tested; b = degree of hybridization: high; + + medium; + low.
7 Tenth ZOCV Conference Fig. 3. Autoradiographs of northern blots with nucleic acid extracts of! 1 and Lpotato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV)-inoculated tomato at decreasing dilutions; Ghealthy tomato; 7- citron inoculated with citrus exocortis viroid (CEV) (ATCC PV-194); 8-Navelina 8 sweet orange infected with CEV and citrus "B" viroid (CBV); 9-citron inoculated with Navelina 1 sweet orange infected with CBV; 10-gel eluted PSTV. Hybridization with cdna probes of PSTV and CEV. and verify the absence of any reactions between CBV and all of the probes utilized. Extracts of tomato plants inoculated with citrus extracts containing CEV + CBV hybridized with the PSTV probe better than with CEV probe (fig. 4). To eliminate spurious hybridization results with RNA probes, it was essential to treat membranes with RNase prior to autoradiography (fig. 5). DISCUSSION The electrophoretic mobility of CBV, its pathogenicity on Arizona 861-S-1 citron, and lack of replication on most herbaceous hosts of CEV suggest that it is a viroid physically and biologically distinct from CEV. Comparison between CBV and other new citrus viroids (6, 10) has been attempted. Mild stunting and variahle epinasty induced by CBV on Arizona 861-S-1 citron seems to be very similar to symptoms induced by citron variable viroid (CVaV) (10). Moreover, CBV electrophoretic mobility suggests a molecular size within the range (311 to 335 nucleotides) reported for RNAs I, I1 and I11 (6). However, electrophoretic conditions and comigrated markers in that work were different from ours and therefore results are not comparable. More experiments must be made to demonstrate whether any of the newly described citrus viroids are similar to CBV andlor if one of them is identical with CBV. The lack of hybridization of extracts containing CBV with any of the probes used indicates that this viroid is different from the PSTV group viroids. Extracts from citrus trees infected with CEV and CEV + CBV hybridized, as expected, more strongly with the CEV probe than with the PSTV probe (fig. 3, 4, 5), but extracts from tomatoes that had been inoculated with citrus nucleic
8 Diseases Induced by Viroids and Viroidlike Pathogens Fig. 4. Autoradiographs of nitrocellulose dot blots with nucleic acid extracted from: 1--citrus exocortis viroid (CEV)-infected citrus; 2, 5 and U E V and citrus "B" viroid (CBV)-infected citrus; 3 and 74BV-infected citrus; &healthy citrus; MEV+CBV and Spotato spindle tuber viroid (PSW)-inoculated tomato. Hybridization with PSTV- and CEV-cDNA probes. Fig. 5. Autoradiographs of nitrocellulose dot blots with nucleic acid extracted from: l-citrus exocortis viroid (CEV)-infected citrus; 2, 5 and GCEV and citrus "B" viroid (CBV)-infected citrus; 3, 7 and MBV-infected citrus; &healthy citrus; %potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVIinfected tomato. Hybridization with PSW- and CEV-RNA probes, before (above) and after (below) RNase treatment.
9 Tenth IOCV Conference acid extracts containing both CEV and CBV hybridized more strongly with the PSTV probe than the CEV probe (fig. 4). This unexpected finding remains to be explained. Studies are in progress to determine the CBV nucleotide sequence. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank Dr. R. H. Symons, Adelaide, Australia, for kindly providing the CEV clone. NOTE ADDED IN PROOF Nucleic acid hybridization experiments with a cdna probe to hop stunt viroid (kindly supplied by Dr. E. Shikata, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan) have shown that CBV is a strain of this viroid (manuscript in preparation). LITERATURE CITED 1. Albanese, G., R. La Rosa, and G. Polizzi Indexing of citrus for exocortis by bidirectional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis, p In Proc. of Meeting "Integrated pest control in citrus-groves," Acireale. 2. Albanese, G., R. La Rosa, and M. Davino Un nuovo viroide riscontrato in Sicilia in diverse specie e cultivar di agrumi. In Atti Incontro su "I1 recente contribute della ricerca a110 sviluppo dell 'agrumicoltura italiana", Cagliari (in press). 3. Baksh, N., R. F. Lee, and S. M. Garnsey Detection of citrus exocortis viroid by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, p In Proc. 9th Conf. IOCV. IOCV, Riverside. 4. Boccardo, G., R. La Rosa, and A. Catara Detection of citrus exocortis viroid by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of nucleic acid from glasshouse citrus, p In Proc. 9th Conf. IOCV. IOCV, Riverside. 5. Cress, D. E., M. C. Kiefer, and R. A. Owens Construction of infectious potato spindle tuber viroid cdna clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 11: Duran-Vila, N., R. Flores, and J. S. Semancik Characterization of viroid-like RNAs associated with the citrus exocortis syndrome. Virology 150: Kiefer, M. C., R. A. Owens, and T. 0. Diener Structural similarities between viroids and transposable genetic elements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A., 80: La Rosa, R., G. Albanese, A. Azzaro, F. Sesto, and F. Domina Suitability of nucleic acid analysis to diagnose viroid infections in citrus, p In Proc. 10th Conf. IOCV., IOCV, Riverside. 9. Macquaire, G., M. Monsion, J. C. Bachelier, C. Faydi, and J. Dunez The slab gel electrophoresis assay for detection and investigation of chrysanthemum chlorotic mottle viroid (CChMV) in infected plants. Agronomie 1: Schlemmer, A., C. N. Roistacher, and J. S. Semancik A unique, infectious RNA associated with citron showing symptoms typical of citrus exocortis disease. Phytopathology 75: Schumacher, J., J. W. Randles, and D. Riesner A two-dimensional electrophoretic technique for the detection of circular viroids and virusoids. Anal. Biochem. 135: Thomas, P. S Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 77: Visvader, J. E. and R. H. Symons Eleven new sequence variants of citrus exocortis viroid and the correlation of sequence with pathogenicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 13: Wahl, G. M., M. Tern, and G. R. Stark Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran-sulfate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A., 76:
Viroids are unique plant pathogens that are smaller than viruses and consist of a short single-stranded circular RNA without a protein coat (Diener,
 Citrus Viroids Viroids are unique plant pathogens that are smaller than viruses and consist of a short single-stranded circular RNA without a protein coat (Diener, 1971). These pathogens cause damage to
Citrus Viroids Viroids are unique plant pathogens that are smaller than viruses and consist of a short single-stranded circular RNA without a protein coat (Diener, 1971). These pathogens cause damage to
The Citrus Exocortis Disease: A Complex of Viroid-RNAs
 The Citrus Exocortis Disease: A Complex of Viroid-RNAs N. Duran-Vila, J. A. Pina, J. F. Ballester, J. Juarez, C. N. Roistacher, R. Rivera-Bustamante, and J. S. Semancik ABSTRACT. Citrons inoculated with
The Citrus Exocortis Disease: A Complex of Viroid-RNAs N. Duran-Vila, J. A. Pina, J. F. Ballester, J. Juarez, C. N. Roistacher, R. Rivera-Bustamante, and J. S. Semancik ABSTRACT. Citrons inoculated with
Citrus Cachexia Viroid, a New Viroid of Citrus: Relationship to Viroids of the Exocortis Disease Complex
 J. gen. Virol. (1988), 69, 3059-3068. Printed in Great Britain 3059 Key words: citrus cachexia viroid/exocortis disease/viroids Citrus Cachexia Viroid, a New Viroid of Citrus: Relationship to Viroids of
J. gen. Virol. (1988), 69, 3059-3068. Printed in Great Britain 3059 Key words: citrus cachexia viroid/exocortis disease/viroids Citrus Cachexia Viroid, a New Viroid of Citrus: Relationship to Viroids of
Viroids. NOMENCLATURE Replication Pathogenicity. Nabil Killiny
 Viroids NOMENCLATURE Replication Pathogenicity Nabil Killiny A VIROID is A VIR(virus) OID(like) particle. Viroids are sub-viruses composed exclusively of a single circular strand of nucleic acid (RNA)
Viroids NOMENCLATURE Replication Pathogenicity Nabil Killiny A VIROID is A VIR(virus) OID(like) particle. Viroids are sub-viruses composed exclusively of a single circular strand of nucleic acid (RNA)
ABSTRACT. RESULTS sucrose, 0.1% yeast extractand M MgSO 4 for 18-24
 Physiology and Biochemistry Accumulation of Viroid RNA in Tumor Cells After Double Infection by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Citrus Exocortis Viroid J. S. Semancik, L. K. Grill, and E. L. Civerolo Department
Physiology and Biochemistry Accumulation of Viroid RNA in Tumor Cells After Double Infection by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Citrus Exocortis Viroid J. S. Semancik, L. K. Grill, and E. L. Civerolo Department
UNIVERSITY OF ADELAIDE STRUCTURED PROGRAMME FOR PHD STUDENTS RESEARCH PROPOSAL: DARYL R.
 UNIVERSITY OF ADELAIDE STRUCTURED PROGRAMME FOR PHD STUDENTS http://www.acue.adelaide.edu.au/sp/webb.html RESEARCH PROPOSAL: DARYL R. WEBB Localization by in situ hybridization of members of viroid subgroups
UNIVERSITY OF ADELAIDE STRUCTURED PROGRAMME FOR PHD STUDENTS http://www.acue.adelaide.edu.au/sp/webb.html RESEARCH PROPOSAL: DARYL R. WEBB Localization by in situ hybridization of members of viroid subgroups
Detection of Viroid and Viroid-like RNAs from Grapevine
 J. gen. Virol. (1985), 66, 2095 2102. Printed in Great Britain 2095 Key words: viroid/viroid-like RNAs/grapevine Detection of Viroid and Viroid-like RNAs from Grapevine By RICARDO FLORES, 1. NURIA DURAN-VILA,
J. gen. Virol. (1985), 66, 2095 2102. Printed in Great Britain 2095 Key words: viroid/viroid-like RNAs/grapevine Detection of Viroid and Viroid-like RNAs from Grapevine By RICARDO FLORES, 1. NURIA DURAN-VILA,
Berkeley, California. Charlottesville, Virginia. THE VIRUSES: Catalogue, Characterization, and Classification Heinz Fraenkel-Conrat
 The Viroids THE VmUSES Series Editors HEINZ FRAENKEL-CONRAT, University of California Berkeley, California ROBERT R. WAGNER, University of Virginia School of Medicine Charlottesville, Virginia THE VIRUSES:
The Viroids THE VmUSES Series Editors HEINZ FRAENKEL-CONRAT, University of California Berkeley, California ROBERT R. WAGNER, University of Virginia School of Medicine Charlottesville, Virginia THE VIRUSES:
Determination of the Dominant Variants of Hop Stunt Viroid in Two Different Cachexia Isolates from North and South of Iran
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2016) Vol. 18: 1431-1440 Determination of the Dominant Variants of Hop Stunt Viroid in Two Different Cachexia Isolates from North and South of Iran S. N. Banihashemian 1, S. M. Bani
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2016) Vol. 18: 1431-1440 Determination of the Dominant Variants of Hop Stunt Viroid in Two Different Cachexia Isolates from North and South of Iran S. N. Banihashemian 1, S. M. Bani
UC Riverside International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings ( )
 UC Riverside International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings (1957-2010) Title Replication/Accumulation and Symptom Expression of Citrus Viroids on Some Species of Citrus and Related
UC Riverside International Organization of Citrus Virologists Conference Proceedings (1957-2010) Title Replication/Accumulation and Symptom Expression of Citrus Viroids on Some Species of Citrus and Related
A citrus exocortis viroid variant from broad bean (Vicia faba L.): infectivity and pathogenesis
 Journal of General Virology (1995), 76, 2271-2277. Printed in Great Britain 227l A citrus exocortis viroid variant from broad bean (Vicia faba L.): infectivity and pathogenesis C. Fagoaga, 1 J. S. Semancik
Journal of General Virology (1995), 76, 2271-2277. Printed in Great Britain 227l A citrus exocortis viroid variant from broad bean (Vicia faba L.): infectivity and pathogenesis C. Fagoaga, 1 J. S. Semancik
Isolation of Total RNA and mrna from Plant Tissues
 Promega Notes Magazine Number 54, 1995, p.02 Isolation of Total RNA and mrna from Plant Tissues By: Isabel Murillo, Dora Raventos, Estelle Jaeck, Blanca San Segundo* Centro de Investigacion y Desarrollo
Promega Notes Magazine Number 54, 1995, p.02 Isolation of Total RNA and mrna from Plant Tissues By: Isabel Murillo, Dora Raventos, Estelle Jaeck, Blanca San Segundo* Centro de Investigacion y Desarrollo
Tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid: an evolutionary link in the origin of pospiviroids
 Journal of General Virology (1999), 80, 2823 2828. Printed in Great Britain... Tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid: an evolutionary link in the origin of pospiviroids Rudra P. Singh, 1 Xianzhou Nie 1 and Mathuresh
Journal of General Virology (1999), 80, 2823 2828. Printed in Great Britain... Tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid: an evolutionary link in the origin of pospiviroids Rudra P. Singh, 1 Xianzhou Nie 1 and Mathuresh
A New Candidatus Liberibacter Species Associated with Solanaceous Plants
 A New Candidatus Liberibacter Species Associated with Solanaceous Plants Lia Liefting, Bevan Weir, Lisa Ward, Kerry Paice, Gerard Clover Plant Health and Environment Laboratory MAF Biosecurity New Zealand
A New Candidatus Liberibacter Species Associated with Solanaceous Plants Lia Liefting, Bevan Weir, Lisa Ward, Kerry Paice, Gerard Clover Plant Health and Environment Laboratory MAF Biosecurity New Zealand
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials
 Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Viruses in Camellias. Simon W. Scott. Clemson University
 Viruses in Camellias Simon W. Scott Clemson University 1 In plants all viruses are graft-transmissible agents but Not all graft-transmissible agents are viruses 2 As you are all well aware camellias are
Viruses in Camellias Simon W. Scott Clemson University 1 In plants all viruses are graft-transmissible agents but Not all graft-transmissible agents are viruses 2 As you are all well aware camellias are
Cocadviroid Coconut cadang-cadang viroid
 Cocadviroid Coconut cadang-cadang viroid Scientific Name Cocadviroid coconut cadang-cadang viroid Synonyms: None Common Name Cadang-cadang viroid, coconut cadang-cadang viroid, yellow mottling disease
Cocadviroid Coconut cadang-cadang viroid Scientific Name Cocadviroid coconut cadang-cadang viroid Synonyms: None Common Name Cadang-cadang viroid, coconut cadang-cadang viroid, yellow mottling disease
REVIEW Chrysanthemum Stunt Viroid
 JARQ 47 (3), 237 242 (2013) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp REVIEW Chrysanthemum Stunt Viroid Yosuke MATSUSHITA* NARO Institute of Floricultural Science (Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8519, Japan) Abstract The chrysanthemum
JARQ 47 (3), 237 242 (2013) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp REVIEW Chrysanthemum Stunt Viroid Yosuke MATSUSHITA* NARO Institute of Floricultural Science (Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8519, Japan) Abstract The chrysanthemum
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
Identification and molecular properties of a 306 nucleotide viroid associated with apple dimple fruit disease
 '/epf"al.ot'o 'ZtTff~./~ olq~'y (! 99%.77L283 C28.37...Y.r!nted!9..G.re~!..B[!!a!~... SHORT COMMUNICATION Identification and molecular properties of a 306 nucleotide viroid associated with apple dimple
'/epf"al.ot'o 'ZtTff~./~ olq~'y (! 99%.77L283 C28.37...Y.r!nted!9..G.re~!..B[!!a!~... SHORT COMMUNICATION Identification and molecular properties of a 306 nucleotide viroid associated with apple dimple
Eggplant Latent Viroid, the Candidate Type Species for a New Genus within the Family Avsunviroidae (Hammerhead Viroids)
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2003, p. 6528 6532 Vol. 77, No. 11 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.11.6528 6532.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Eggplant
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2003, p. 6528 6532 Vol. 77, No. 11 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.11.6528 6532.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Eggplant
RNA-Solv Reagent. R preps R preps R preps
 RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
RNA-Solv Reagent. R preps R preps R preps
 RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
RNA-Solv Reagent R6830-00 5 preps R6830-01 100 preps R6830-02 200 preps March 2013 RNA-Solv Reagent Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Before Beginning...4 Analysis
Direct Sequence Analysis of Viroid RNA. Purified TPMV. and TASV were partially cleaved with RNase T1, RNase U2, or
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 80, pp. 6234-6238, October 1983 Biochemistry Structural similarities between viroids and transposable genetic elements (tomato planta macho viroid/tomato apical stunt viroid/rna
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 80, pp. 6234-6238, October 1983 Biochemistry Structural similarities between viroids and transposable genetic elements (tomato planta macho viroid/tomato apical stunt viroid/rna
Citrus viroid V: Occurrence, Host Range, Diagnosis, and Identification of New Variants
 Virology Citrus viroid V: Occurrence, Host Range, Diagnosis, and Identification of New Variants P. Serra, M. Eiras, S. M. Bani-Hashemian, N. Murcia, E. W. Kitajima, J. A. Daròs, R. Flores, and N. Duran-Vila
Virology Citrus viroid V: Occurrence, Host Range, Diagnosis, and Identification of New Variants P. Serra, M. Eiras, S. M. Bani-Hashemian, N. Murcia, E. W. Kitajima, J. A. Daròs, R. Flores, and N. Duran-Vila
SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis):
 SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis): Aim: SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) is one of the common methods used in the molecular biology
SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis): Aim: SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) is one of the common methods used in the molecular biology
mrna Isolation Kit for Blood/Bone Marrow For isolation mrna from blood or bone marrow lysates Cat. No
 For isolation mrna from blood or bone marrow lysates Cat. No. 1 934 333 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Key advantages The purification of mrna requires two steps: 1. Cells
For isolation mrna from blood or bone marrow lysates Cat. No. 1 934 333 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Key advantages The purification of mrna requires two steps: 1. Cells
Qiong Wu & Mengji Cao & Huanan Su & Sagheer Atta & Fangyun Yang & Xuefeng Wang & Changyong Zhou
 DOI 10.1007/s10658-014-0380-2 Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of itrus viroid I-LSS variants from citrus in Pakistan and hina reveals their possible geographic origin Qiong Wu & Mengji
DOI 10.1007/s10658-014-0380-2 Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of itrus viroid I-LSS variants from citrus in Pakistan and hina reveals their possible geographic origin Qiong Wu & Mengji
E.Z.N.A. MicroElute Clean-up Kits Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. MicroElute Clean-up Kits Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Kit Contents... 3 Preparing Reagents/Storage and Stability... 4 Guideline for Vacuum Manifold... 5 MicroElute Cycle-Pure - Spin Protocol...
E.Z.N.A. MicroElute Clean-up Kits Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Kit Contents... 3 Preparing Reagents/Storage and Stability... 4 Guideline for Vacuum Manifold... 5 MicroElute Cycle-Pure - Spin Protocol...
Unit G: Pest Management. Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
Phenol-Chloroform reagents. Selection guide. OH ; MW : High quality reagents for use in nucleic acid purification.
 Phenol-Chloroform reagents Extraction with phenol and phenol/chloroform mixtures is a universal method for purification of DNA and RNA. Proteins and restriction enzymes are removed by phenol and chloroform
Phenol-Chloroform reagents Extraction with phenol and phenol/chloroform mixtures is a universal method for purification of DNA and RNA. Proteins and restriction enzymes are removed by phenol and chloroform
Rapid generation of genetic heterogeneity in progenies from individual cdna clones of peach latent mosaic viroid in its natural host
 Journal of General Virology (1999), 80, 2239 2252. Printed in Great Britain... Rapid generation of genetic heterogeneity in progenies from individual cdna clones of peach latent mosaic viroid in its natural
Journal of General Virology (1999), 80, 2239 2252. Printed in Great Britain... Rapid generation of genetic heterogeneity in progenies from individual cdna clones of peach latent mosaic viroid in its natural
Protocol for 2D-E. Protein Extraction
 Protocol for 2D-E Protein Extraction Reagent 1 inside the ReadyPrep TM Sequential Extraction kit (in powder form) 50ml of deionized water is used to dissolve all the Reagent 1. The solution is known as
Protocol for 2D-E Protein Extraction Reagent 1 inside the ReadyPrep TM Sequential Extraction kit (in powder form) 50ml of deionized water is used to dissolve all the Reagent 1. The solution is known as
RNA Transport. R preps R preps
 RNA Transport R0527-00 5 preps R0527-01 50 preps July 2014 RNA Transport Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Protocol...4 Storage Procedure...4 Recovery Procedure...5
RNA Transport R0527-00 5 preps R0527-01 50 preps July 2014 RNA Transport Table of Contents Introduction...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Protocol...4 Storage Procedure...4 Recovery Procedure...5
Data Sheet. Azide Cy5 RNA T7 Transcription Kit
 Cat. No. Size 1. Description PP-501-Cy5 10 reactions à 40 µl For in vitro use only Quality guaranteed for 12 months Store all components at -20 C. Avoid freeze and thaw cycles. DBCO-Sulfo-Cy5 must be stored
Cat. No. Size 1. Description PP-501-Cy5 10 reactions à 40 µl For in vitro use only Quality guaranteed for 12 months Store all components at -20 C. Avoid freeze and thaw cycles. DBCO-Sulfo-Cy5 must be stored
Detection of Tobacco mosaic virus in Petunia and Tobacco By Light Microscopy Using a Simplified Inclusion Body Staining Technique
 International Journal of Agricultural Technology 2017 Vol. 13(2): 163-168 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 2630-0192 (Online) Detection of Tobacco mosaic virus in Petunia and Tobacco By
International Journal of Agricultural Technology 2017 Vol. 13(2): 163-168 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 2630-0192 (Online) Detection of Tobacco mosaic virus in Petunia and Tobacco By
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard. Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard
 Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
Molecular Variability of Citrus Exocortis Viroid in a Single Naturally Infected Citrus Tree
 Molecular Variability of Citrus Exocortis Viroid in a Single Naturally Infected Citrus Tree A ELLEUCH 1, M MARRAKCHI 1, D LÉVESQUE 2, N BESSAIS 3, J P PERREAULT 2 and H FAKHFAKH 1 1 Laboratoire de Génétique
Molecular Variability of Citrus Exocortis Viroid in a Single Naturally Infected Citrus Tree A ELLEUCH 1, M MARRAKCHI 1, D LÉVESQUE 2, N BESSAIS 3, J P PERREAULT 2 and H FAKHFAKH 1 1 Laboratoire de Génétique
SEQUENCE VARIABILITY OF HOP STUNT VIROID ISOLATES FROM STONE FRUITS IN TURKEY
 Journal of Plant Pathology (2008), 90 (1), 23-28 Edizioni ETS Pisa, 2008 23 SEQUENCE VARIABILITY OF HOP STUNT VIROID ISOLATES FROM STONE FRUITS IN TURKEY M. Gazel 1, C. Ulubas Serce 1, K. Caglayan 1 and
Journal of Plant Pathology (2008), 90 (1), 23-28 Edizioni ETS Pisa, 2008 23 SEQUENCE VARIABILITY OF HOP STUNT VIROID ISOLATES FROM STONE FRUITS IN TURKEY M. Gazel 1, C. Ulubas Serce 1, K. Caglayan 1 and
Sero: p30 Crossover Electrophoresis for Semen
 Safety Principle Equipment and supplies SAFETY WARNING Electrophoretic procedures have electrical hazards associated with them. Therefore, at minimum, the presence of two analysts is required during these
Safety Principle Equipment and supplies SAFETY WARNING Electrophoretic procedures have electrical hazards associated with them. Therefore, at minimum, the presence of two analysts is required during these
DNA can be extracted from the following sample types using this procedure: Archived
 Sample types Principle Safety Equipment and supplies DNA can be extracted from the following sample types using this procedure: concentrated DNA samples (e.g., blood, saliva, non-contact samples) hair
Sample types Principle Safety Equipment and supplies DNA can be extracted from the following sample types using this procedure: concentrated DNA samples (e.g., blood, saliva, non-contact samples) hair
Viroids: New and Continuing Risks for Horticultural
 Page 1 of 13 MPMI Phytopathology Plant Disease Plant Health Progress Plant Disease Management Reports APS PRESS Phytopathology News WebCasts Common Names of Plant Diseases APSnet Features Image Resources
Page 1 of 13 MPMI Phytopathology Plant Disease Plant Health Progress Plant Disease Management Reports APS PRESS Phytopathology News WebCasts Common Names of Plant Diseases APSnet Features Image Resources
Has this proposal has been seen and agreed by the relevant study group(s)? Please select answer in the box on the right
 This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES
 PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES GABRIELA POPA', AURELIA BREZEANU~, C. PETRUTA CORNEA', J.P. BOE The effects of inoculation with wild type of Agrobacterium
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES GABRIELA POPA', AURELIA BREZEANU~, C. PETRUTA CORNEA', J.P. BOE The effects of inoculation with wild type of Agrobacterium
U.S. Patent No. 9,051,563 and other pending patents. Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Direct-zol 96 RNA Catalog Nos. R2054, R2055, R2056 & R2057 Highlights Quick, 96-well purification of high-quality (DNA-free) total RNA directly from TRIzol, TRI Reagent and all other
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Direct-zol 96 RNA Catalog Nos. R2054, R2055, R2056 & R2057 Highlights Quick, 96-well purification of high-quality (DNA-free) total RNA directly from TRIzol, TRI Reagent and all other
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
First report on Hop stunt viroid (HSVd) from some Mediterranean countries
 Phytopathol. Mediterr. (2000) 39, 271-276 First report on Hop stunt viroid (HSVd) from some Mediterranean countries KHALID AMARI 1, MARI CARMEN CAÑIZARES 1, ARBEN MYRTA 2, SEAD SABANADZOVIC 3, M BAREK
Phytopathol. Mediterr. (2000) 39, 271-276 First report on Hop stunt viroid (HSVd) from some Mediterranean countries KHALID AMARI 1, MARI CARMEN CAÑIZARES 1, ARBEN MYRTA 2, SEAD SABANADZOVIC 3, M BAREK
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE- DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY. STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE PROCEDURE NO: GLP 021 MOD: 1st Issue Page: 1 of 6
 Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
Page: 1 of 6 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this equipment. Therefore,
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH, D Weinheim, Supporting Information for Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z 18050
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH, D-69451 Weinheim, 2001. Supporting Information for Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z 18050 Protein Affinity Labeling Mediated by Genetically Encoded Peptide Tags Frank Amini, Thomas
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH, D-69451 Weinheim, 2001. Supporting Information for Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z 18050 Protein Affinity Labeling Mediated by Genetically Encoded Peptide Tags Frank Amini, Thomas
Maria V. Yamburenko, Yan O. Zubo, Radomíra Vanková, Victor V. Kusnetsov, Olga N. Kulaeva, Thomas Börner
 ABA represses the transcription of chloroplast genes Maria V. Yamburenko, Yan O. Zubo, Radomíra Vanková, Victor V. Kusnetsov, Olga N. Kulaeva, Thomas Börner Supplementary data Supplementary tables Table
ABA represses the transcription of chloroplast genes Maria V. Yamburenko, Yan O. Zubo, Radomíra Vanková, Victor V. Kusnetsov, Olga N. Kulaeva, Thomas Börner Supplementary data Supplementary tables Table
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha
 Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus. Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008
 Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008 Jude Grosser University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center,
Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008 Jude Grosser University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center,
Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Tomato Cells and Crown Gall Induction
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 1971, p. 634-639 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 106, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Tomato Cells and
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 1971, p. 634-639 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 106, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Tomato Cells and
NOVABEADS FOOD 1 DNA KIT
 NOVABEADS FOOD 1 DNA KIT NOVABEADS FOOD DNA KIT is the new generation tool in molecular biology techniques and allows DNA isolations from highly processed food products. The method is based on the use
NOVABEADS FOOD 1 DNA KIT NOVABEADS FOOD DNA KIT is the new generation tool in molecular biology techniques and allows DNA isolations from highly processed food products. The method is based on the use
Qubit RNA IQ Assay Kits
 USER GUIDE Qubit RNA IQ s Catalog No. Q33221, Q33222 Pub. No. MAN0017405 Rev. B.0 Product information The Qubit RNA IQ provides a fast, simple method to check whether an RNA sample has degraded using the
USER GUIDE Qubit RNA IQ s Catalog No. Q33221, Q33222 Pub. No. MAN0017405 Rev. B.0 Product information The Qubit RNA IQ provides a fast, simple method to check whether an RNA sample has degraded using the
TYansmission of grapevine viroids is not likely to occur mechanically by normal pruning
 Vitis 34 (2), 119-123 (1995) TYansmission of grapevine viroids is not likely to occur mechanically by normal pruning by U. STAUB, H. POLIVKA, J.V. HERRMANN~) and H.J. GROSS Bayerische Julius-Maximilians-Universitat,
Vitis 34 (2), 119-123 (1995) TYansmission of grapevine viroids is not likely to occur mechanically by normal pruning by U. STAUB, H. POLIVKA, J.V. HERRMANN~) and H.J. GROSS Bayerische Julius-Maximilians-Universitat,
Epidemiology of Grapevine leafroll associated virus-3 and regional management
 Epidemiology of Grapevine leafroll associated virus-3 and regional management Acknowledgements Funding sources: American Vineyard Foundation (AVF) California Grape Rootstock Improvement Commission California
Epidemiology of Grapevine leafroll associated virus-3 and regional management Acknowledgements Funding sources: American Vineyard Foundation (AVF) California Grape Rootstock Improvement Commission California
The Identification of Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid on Potato and Tomato Production in Libya
 The Identification of Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid on Potato and Tomato Production in Libya Haniyeha Mohammed Alghemoda, Jaber Abdullah Khalil, Taher Ahmed Abouhliqha and Khaled EL Dugdug Abstract This
The Identification of Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid on Potato and Tomato Production in Libya Haniyeha Mohammed Alghemoda, Jaber Abdullah Khalil, Taher Ahmed Abouhliqha and Khaled EL Dugdug Abstract This
Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc
 OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE
 EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE Ed Stover, Malendia Maccree, Malli Aradhya, Ali E. McClean, and Daniel A. Kluepfel INTRODUCTION Crown Gall disease of walnut is caused by the
EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE Ed Stover, Malendia Maccree, Malli Aradhya, Ali E. McClean, and Daniel A. Kluepfel INTRODUCTION Crown Gall disease of walnut is caused by the
THE IRON-CHLOROPHYLL RELATEONSHIP IN YOUNG HASS AVOCADO LEAVES
 Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 83:372-375. 1970. THE IRON-CHLOROPHYLL RELATEONSHIP IN YOUNG HASS AVOCADO LEAVES E. F. Wallihan and R. G. Sharpless University of California, Riverside ABSTRACT Young summer
Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 83:372-375. 1970. THE IRON-CHLOROPHYLL RELATEONSHIP IN YOUNG HASS AVOCADO LEAVES E. F. Wallihan and R. G. Sharpless University of California, Riverside ABSTRACT Young summer
Genetic variability/stability of micropropagated and standard propagated raspberry and blackberry plants
 THE SUSTAINABLE IMPROVEMENT OF EUROPEAN BERRY PRODUCTION, QUALITY AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE IN CHANGING ENVIRONMENT: STRAWBERRIES, CURRANTS, BLACKBERRIES, BLUEBERRIES AND RASPBERRIES (EUBERRY) SUBCONTARCT:
THE SUSTAINABLE IMPROVEMENT OF EUROPEAN BERRY PRODUCTION, QUALITY AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE IN CHANGING ENVIRONMENT: STRAWBERRIES, CURRANTS, BLACKBERRIES, BLUEBERRIES AND RASPBERRIES (EUBERRY) SUBCONTARCT:
RNA Labeling Kit. User Manual
 RNA Labeling Kit User Manual RNA Labeling Kit The RNA Labeling Kit contains reagents to perform 10 transcription reactions (50 µl each) and 12 independent labeling reactions. Introduction and product description:
RNA Labeling Kit User Manual RNA Labeling Kit The RNA Labeling Kit contains reagents to perform 10 transcription reactions (50 µl each) and 12 independent labeling reactions. Introduction and product description:
Day 1: Plant Material Collection
 Day 1: Plant Material Collection Each team will collect leaf material for DNA extraction and flower blooms (later) for RNA extraction. Once the leaves have been harvested the plants are put into a growth
Day 1: Plant Material Collection Each team will collect leaf material for DNA extraction and flower blooms (later) for RNA extraction. Once the leaves have been harvested the plants are put into a growth
Potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd)
 Plant Viruses 2007 Global Science Books Potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) Michael Schmitz Gerhard Steger * Institut für Physikalische Biologie, Geb. 26.12.U1, Universitätsstr. 1, Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Plant Viruses 2007 Global Science Books Potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) Michael Schmitz Gerhard Steger * Institut für Physikalische Biologie, Geb. 26.12.U1, Universitätsstr. 1, Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Virology. Trafficking of the Potato spindle tuber viroid between tomato and Orobanche ramosa
 Virology 399 (2010) 187 193 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro Trafficking of the Potato spindle tuber viroid between tomato and Orobanche
Virology 399 (2010) 187 193 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro Trafficking of the Potato spindle tuber viroid between tomato and Orobanche
High-throughput Isolation of Genomic DNA From Buccal Swab on the Eppendorf epmotion 5075 VAC
 APPLICATION NOTE No. 378 I August 2016 High-throughput Isolation of Genomic DNA From Buccal Swab on the Eppendorf epmotion 5075 VAC Hatim Boughanem, Manuel Macias-Gonzalez, BIOEASY SL, Spain Abstract The
APPLICATION NOTE No. 378 I August 2016 High-throughput Isolation of Genomic DNA From Buccal Swab on the Eppendorf epmotion 5075 VAC Hatim Boughanem, Manuel Macias-Gonzalez, BIOEASY SL, Spain Abstract The
FIRST REPORT OF AUSTRALIAN GRAPEVINE VIROID FROM THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION
 Journal of Plant Pathology (2003), 85 (1), 53-57 Edizioni ETS Pisa, 2003 53 FIRST REPORT OF AUSTRALIAN GRAPEVINE VIROID FROM THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION A. Elleuch 1, M. Marrakchi 1, J.P. Perreault 2 and
Journal of Plant Pathology (2003), 85 (1), 53-57 Edizioni ETS Pisa, 2003 53 FIRST REPORT OF AUSTRALIAN GRAPEVINE VIROID FROM THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION A. Elleuch 1, M. Marrakchi 1, J.P. Perreault 2 and
Product Name Quantity* Product No.
 Page 1 of 6 Lit.# ML002 Rev. 11/15/06 Label IT Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits Product Name Quantity* Product No. Label IT CX-Rhodamine Labeling Kit Full Size MIR 3100 Trial Size MIR 3125 Label IT Fluorescein
Page 1 of 6 Lit.# ML002 Rev. 11/15/06 Label IT Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits Product Name Quantity* Product No. Label IT CX-Rhodamine Labeling Kit Full Size MIR 3100 Trial Size MIR 3125 Label IT Fluorescein
Identification of culturable endophytes isolated from apple tissues with antagonism towards Neonectria ditissima
 Identification of culturable endophytes isolated from apple tissues with antagonism towards Neonectria ditissima Jing Liu, Hayley Ridgway & Eirian Jones Background Apple production in NZ widely cultivated
Identification of culturable endophytes isolated from apple tissues with antagonism towards Neonectria ditissima Jing Liu, Hayley Ridgway & Eirian Jones Background Apple production in NZ widely cultivated
All the media were prepared in Milli RO grade water and autoclaved at 15 pounds per square inch for. 10 g 5g 5g
 }lppend~ STANDARD MEDIA All the media were prepared in Milli RO grade water and autoclaved at 15 pounds per square inch for 15 min unless otherwise indicated. LB Broth (Luria Bertani Broth) Bacto-Tryptone
}lppend~ STANDARD MEDIA All the media were prepared in Milli RO grade water and autoclaved at 15 pounds per square inch for 15 min unless otherwise indicated. LB Broth (Luria Bertani Broth) Bacto-Tryptone
Ch 10. Classification of Microorganisms
 Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Chapter 19. Gene creatures, Part 1: viruses, viroids and plasmids. Prepared by Woojoo Choi
 Chapter 19. Gene creatures, Part 1: viruses, viroids and plasmids Prepared by Woojoo Choi Dead or alive? 1) In this chapter we will explore the twilight zone of biology and the gene creature who live there.
Chapter 19. Gene creatures, Part 1: viruses, viroids and plasmids Prepared by Woojoo Choi Dead or alive? 1) In this chapter we will explore the twilight zone of biology and the gene creature who live there.
Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics
 Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics The distance learning course Plant pathology and entomology consist of four online modules that treat with the main groups of plant
Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics The distance learning course Plant pathology and entomology consist of four online modules that treat with the main groups of plant
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Protease Inhibitor Cocktail A (1 tablet / 7 10 ml, Roche Cat# ) Protease inhibitor Cocktail B (0.5ml per 250ml, Calbiochem Cat# )
 Protocol for Western Blotting Tissue/Cell Sample Preparation Lysis Buffer 1 (ph8.0) o 50mM Tris-Cl o 150mM NaCl o 1% v/v NP40 o protease inhibitor cocktail A/B Lysis Buffer 2 (RIPA) (ph 8.0) o 50mM Tris-Cl
Protocol for Western Blotting Tissue/Cell Sample Preparation Lysis Buffer 1 (ph8.0) o 50mM Tris-Cl o 150mM NaCl o 1% v/v NP40 o protease inhibitor cocktail A/B Lysis Buffer 2 (RIPA) (ph 8.0) o 50mM Tris-Cl
Chapter 8. Summarizing Discussion
 Chapter 8 Summarizing Discussion Chapter 8 This thesis focuses on the ecology and pathogenicity of biovar 3 Dickeya sp. provisionally called D. solani, a blackleg and soft rot pathogen, recently introduced
Chapter 8 Summarizing Discussion Chapter 8 This thesis focuses on the ecology and pathogenicity of biovar 3 Dickeya sp. provisionally called D. solani, a blackleg and soft rot pathogen, recently introduced
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
 SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Protein Isolation and Purification Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells,
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Protein Isolation and Purification Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells,
Dr. Jennifer Weller WORKFLOW DURING THE B3 CAMP MAKING SOLUTIONS FROM STOCKS. B3 Summer Science Camp at Olympic High School
 Dr. Jennifer Weller WORKFLOW DURING THE B3 CAMP MAKING SOLUTIONS FROM STOCKS B3 Summer Science Camp at Olympic High School LAB WORKFLOW OVERVIEW Collect Samples (June 12 th ) Extract DNA from the samples
Dr. Jennifer Weller WORKFLOW DURING THE B3 CAMP MAKING SOLUTIONS FROM STOCKS B3 Summer Science Camp at Olympic High School LAB WORKFLOW OVERVIEW Collect Samples (June 12 th ) Extract DNA from the samples
Programmed ph-driven Reversible Association and Dissociation of Inter-Connected. Circular DNA Dimer Nanostructures
 Supporting information Programmed ph-driven Reversible Association and Dissociation of Inter-Connected Circular DNA Dimer Nanostructures Yuwei Hu, Jiangtao Ren, Chun-Hua Lu, and Itamar Willner* Institute
Supporting information Programmed ph-driven Reversible Association and Dissociation of Inter-Connected Circular DNA Dimer Nanostructures Yuwei Hu, Jiangtao Ren, Chun-Hua Lu, and Itamar Willner* Institute
E lectrophores is with S DS buffer kit ph 8.0 INS T R UC T IONS
 A M E R S H A M B I O S C I E N C E S E lectrophores is with S DS buffer kit ph 8.0 INS T R UC T IONS C leang elª with S DS B uffer K it for horizontal S DS electrophores is Ð Fig. 1. SD S electrophoresis
A M E R S H A M B I O S C I E N C E S E lectrophores is with S DS buffer kit ph 8.0 INS T R UC T IONS C leang elª with S DS B uffer K it for horizontal S DS electrophores is Ð Fig. 1. SD S electrophoresis
CELL REPLICATION. Fluorescent light microscopy showing mitosis, especially immunolabelled cytoskeleton and tubulin
 CELL REPLICATION Fluorescent light microscopy showing mitosis, especially immunolabelled cytoskeleton and tubulin Cell REPLICATION PROLIFERATION MUTIPLICATION DIVISION CELL REPLICATION Fluorescent light
CELL REPLICATION Fluorescent light microscopy showing mitosis, especially immunolabelled cytoskeleton and tubulin Cell REPLICATION PROLIFERATION MUTIPLICATION DIVISION CELL REPLICATION Fluorescent light
Plant Stress and Phytophthora ramorum Infection
 Plant Stress and Phytophthora ramorum Infection Dr. Rick Bostock Department of Plant Pathology University of California, Davis COMTF Annual Meeting June 8-11, 2010 Root stress predisposition to Phytophthora
Plant Stress and Phytophthora ramorum Infection Dr. Rick Bostock Department of Plant Pathology University of California, Davis COMTF Annual Meeting June 8-11, 2010 Root stress predisposition to Phytophthora
Research and Reviews: Journal of Botanical Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Botanical Sciences e-issn: 2320-0189 Illness Detection on Cotton Leaves by Gabor Wavelet. Afshin shaabany*, and Fatemeh Jamshidi Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Research and Reviews: Journal of Botanical Sciences e-issn: 2320-0189 Illness Detection on Cotton Leaves by Gabor Wavelet. Afshin shaabany*, and Fatemeh Jamshidi Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Welcome to BIOL 572: Recombinant DNA techniques
 Lecture 1: 1 Welcome to BIOL 572: Recombinant DNA techniques Agenda 1: Introduce yourselves Agenda 2: Course introduction Agenda 3: Some logistics for BIOL 572 Agenda 4: Q&A section Agenda 1: Introduce
Lecture 1: 1 Welcome to BIOL 572: Recombinant DNA techniques Agenda 1: Introduce yourselves Agenda 2: Course introduction Agenda 3: Some logistics for BIOL 572 Agenda 4: Q&A section Agenda 1: Introduce
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
ULYSIS Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits
 ULYSIS Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits Table 1. Contents and storage Material Amount Storage Stability ULS labeling reagent (Component A) Dimethylformamide (DMF, 50% solution in water) or Dimethylsulfoxide
ULYSIS Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits Table 1. Contents and storage Material Amount Storage Stability ULS labeling reagent (Component A) Dimethylformamide (DMF, 50% solution in water) or Dimethylsulfoxide
Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA
 Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Alkaline Phosphatase Labeling Kit-NH2
 Alkaline Phosphatase Labeling Kit-NH2 Catalog Number KA0001 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Alkaline Phosphatase Labeling Kit-NH2 Catalog Number KA0001 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
U.S. Patent No. 9,051,563 and other pending patents. Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Direct-zol RNA MiniPrep Catalog Nos. R050, R05, R05, & R053 Highlights Quick, spin column purification of high-quality (DNA-free) total RNA directly from TRIzol, TRI Reagent and other
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Direct-zol RNA MiniPrep Catalog Nos. R050, R05, R05, & R053 Highlights Quick, spin column purification of high-quality (DNA-free) total RNA directly from TRIzol, TRI Reagent and other
Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit. M preps M preps M preps
 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit M5635-00 5 preps M5635-01 50 preps M5635-02 200 preps January 2013 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit M5635-00 5 preps M5635-01 50 preps M5635-02 200 preps January 2013 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
Protein separation and characterization
 Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
Plus and minus RNAs of peach latent mosaic viroid self-cleave
 Proc. NatI. cad. Sci. S Vol. 89, pp. 3711-3715, May 1992 Biochemistry Plus and minus RNs of peach latent mosaic viroid self-cleave in vitro via hammerhead structures (viroids/viroid-like satellite RNs/self-cleavage)
Proc. NatI. cad. Sci. S Vol. 89, pp. 3711-3715, May 1992 Biochemistry Plus and minus RNs of peach latent mosaic viroid self-cleave in vitro via hammerhead structures (viroids/viroid-like satellite RNs/self-cleavage)
Basic Principles of Kinetics and Thermodynamics Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
 Basic Principles of Kinetics and Thermodynamics Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Review: Garrett and Grisham, Enzyme Kinetics (Chapt. 13), in Biochemistry, Third Edition,
Basic Principles of Kinetics and Thermodynamics Arthur L. Haas, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Review: Garrett and Grisham, Enzyme Kinetics (Chapt. 13), in Biochemistry, Third Edition,
North American Bramble Growers Research Foundation 2016 Report. Fire Blight: An Emerging Problem for Blackberry Growers in the Mid-South
 North American Bramble Growers Research Foundation 2016 Report Fire Blight: An Emerging Problem for Blackberry Growers in the Mid-South Principal Investigator: Burt Bluhm University of Arkansas Department
North American Bramble Growers Research Foundation 2016 Report Fire Blight: An Emerging Problem for Blackberry Growers in the Mid-South Principal Investigator: Burt Bluhm University of Arkansas Department
ON THE BACTERIOSTATIC ACTION OF SOME BASIC PROTEIN FRACTIONS OBTAINED FROM NEOPLASTIC TISSUES. TAKASHI SUGIMURA and TETSUO ONO
 [GANN, 48, 81-90; March, 1957] ON THE BACTERIOSTATIC ACTION OF SOME BASIC PROTEIN FRACTIONS OBTAINED FROM NEOPLASTIC TISSUES TAKASHI SUGIMURA and TETSUO ONO (Cancer Institute, Japanese Foundation for Cancer
[GANN, 48, 81-90; March, 1957] ON THE BACTERIOSTATIC ACTION OF SOME BASIC PROTEIN FRACTIONS OBTAINED FROM NEOPLASTIC TISSUES TAKASHI SUGIMURA and TETSUO ONO (Cancer Institute, Japanese Foundation for Cancer
Prealbumin (Mouse) ELISA KitI
 Prealbumin (Mouse) ELISA KitI Catalog Number KA2070 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Prealbumin (Mouse) ELISA KitI Catalog Number KA2070 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
