Unit 2 Biodiversity Ch. 4 Patterns of Life
|
|
|
- Loren Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 2 Biodiversity Ch. 4 Patterns of Life Name: 4.1 Characteristics of Life In order to be considered living, an organism must possess the following Six (6) characteristics: 1. Living things are organized systems made up of one or more cells. Ex: Tissues (A group of cells working together for a common function) Organelles small structures inside a cell that undergo functions. Organ systems groups of organs working together for a common function. 2. Living matter must maintain some type of homeostasis. Homeostasis The process of maintaining a stable internal environment. Homeostasis is accomplished using feedback mechanisms to regulate bodily function. Ex: Controlling temperature and chemical composition. 3. Living matter grows and develops This refers to an increase in the size and differentiation of cells. Differentiation changes in cells that make them suited for specific functions. 4. Living matter Reproduces and passes on genetic material as a blueprint for growth and subsequent reproduction. This is really biogenesis. Life has to reproduce in order to continue the species. 5. Living matter acquires matter and energy from the external environment and converts it into different forms. Refers to the ingestion or absorption of materials (feeding) and then metabolizing materials for the creation of energy etc to carry out bodily functions. 6. Living matter responds to stimuli from the environment and adapts. Organisms must adapt to their environment in order to survive. Ex: A fish will slow down its gill rate in cold water Ex: A plant will grow toward the light. 1
2 4.2 Naming and Classifying Organisms Classification: The grouping together of ideas, things etc. on the basis of similarity. Ex: Classifying trees as plants, classifying all horses as animals Taxonomy: The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living things. Taxonomist: A person who works at or studies taxonomy. Classification Systems (History): The goal of a classification system is a way to identify an organism and place it into the correct group of related organisms (similar characteristics). Aristotle (2000 years ago): Aristotle made the First attempt at classification. He divided ALL organisms into TWO large groups he called kingdoms. The two groups were called kingdom Animalia and kingdom Plantae Animals were classified on the basis of where they lived. (Land, water, air) Plants were classified on the basis of their structure. (herbs, shrubs, trees) Ernest Haeckel (1866): Proposed a THIRD kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista was a dumping ground to help deal with organisms that were neither animals nor plants. Ex: Euglena had characteristics of both plants and animals, so placed within Kingdom Protista. As biologists learned more about structure and function of different organisms, more kingdoms were added: Kingdom Fungi was the fourth kingdom proposed. Organisms from this kingdom were originally classified as plants, but fungi are not photosynthetic and are heterotrophic, so they became a separate kingdom. Kingdom Bacteria was the fifth kingdom proposed. Bacteria lack a nucleus and other organelles, and able to grow and obtain energy is a wide range of environments. Kingdom Archaea was the sixth kingdom proposed. These have unique structures and mechanisms where no other organisms can survive. Refer to page. 105 Figure 4.3 for the fan diagram of these kingdoms. 2
3 All six kingdoms are separated into the THREE DOMAINS of Life: A. Domain Bacteria Kingdom Bacteria or Monera B. Domain Archaea Kingdom Archaebacteria or Archaea C. Domain Eukarya Kingdoms Animalia, Plantae, Protista and Fungi Also note page. 107 in your textbook - take note of evolutionary origins. NOTE: Domain Eukarya originates from the word Eukaryotic meaning to have a nucleus. NOTE: Domains are the largest group of classification. Kingdoms are just below domains. Modern Taxonomy: This is the modern taxonomy done today - the sorting and grouping of organisms based upon similar characteristics. Modern taxonomy is based upon the work of Carolus Linnaeus. Carolus Linnaeus Based his grouping on Structural similarities in organisms. Provided the following major groupings or taxons in a hierarchy: See pg. 109 o Kingdom (broadest group) o Phylum o Class o Order o Family o Genus o Species (most specific) KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GOOD SUPPER! A GOOD WAY TO REMEMBER! Taxon A group of similar organisms based upon similar characteristics Ex: Kingdom = a taxon 3
4 NOTE: The more taxons two organisms have in common, the more closely related they are. Humans and Lynx have 3 taxons in common so they are more closely related. Binomial Nomenclature: A system of providing a Scientific Name for an organism. Invented by Linnaeus A Scientific Name Made up of the Genus and Species names of an organism. Genus name is ALWAYS Capitalized. Species name is never capitalized. Both names are italicized. Genus name can be abbreviated. Ex: Canis lupus Scientific name of the Wolf Ex: D. melanogaster Scientific name of Drosophilia fly Scientific Names versus Common Names: Common Name: Name commonly used for an organism. Ex: dog 4
5 Why are scientific names used rather than common names? Common names are NOT precise. Ex: The word cat can describe many kinds of cats not just the domestic cat. Common names can give misleading information. Ex: Using the name fish for an organism such as a starfish is not accurate. Starfish are not fish! Modern Techniques of Classification Today, scientists use the following techniques to help them classify and identify organisms. A. Evidence from the Fossil Record (Radioactive Dating) B. Evidence from Anatomy (Comparative Structural Anatomy) C. Evidence from Embryonic Development (Comparative Embryology) D. Evidence from Biochemistry (Amino Acids) E. Evidence from DNA (DNA sequencing) F. Metabolic Behaviour G. Phylogeny H. Cladistics Why do scientists use these techniques? Biologists use these techniques to classify organisms on the basis of their similarity and the existence of a common ancestor. A common ancestor would suggest that similar organisms are related A. Evidence from the Fossil Record Scientists use Carbon Dating (uses radioactive isotope > C-14) to find the ages of organisms. Carbon dating can tell the age of an organism up to yrs ago. Unstable isotopes are known as radioactive isotopes. Atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Radioactive isotopes decay at known rates so inferences can be made from the rocks and the fossils that are contained in the rock since they contain radioactive isotopes. The age of an organism can help tell if it was an ancestor of some species. Ex: Archaeopteryx is believed to be an ancestor of today s birds. 5
6 B. Evidence from Anatomy (Comparative Structural Anatomy) Structural anatomy is the comparison of bones found in certain animals to suggest a common ancestor. Looks at the Homologous (similar) structures of differing organisms that would indicate a similar evolutionary origin. Ex: Human arm, Bat wing, Horse s leg and whale flipper are all similar suggesting a common ancestor. Thus, these organisms may be related. Fig. 4.9 (Page. 114) C. Evidence from Embryonic Development (Comparative Embryology) Comparative embryology is the comparison of early embryos of organisms to suggest a common ancestor. Ex: Embryos of tunicates have structures similar to tadpole embryos. This would suggest that these organisms have a common ancestor. Fig (Page. 114) and see also Figure 4.10 (Page. 114) D. Evidence from Biochemistry Biochemical techniques that look at the arrangement of Amino Acids. Amino Acid: the basic building block of proteins. Remember Unit 1, the ribosome organelle is are the area at which you would see these! Similar Amino acid patterns/sequences would suggest the organisms are related or share a common ancestor. Ex: Human blood and baboon blood are very close in amino acid sequence. Therefore humans, for example, are more closely related to baboons than they are horses. Also other examples are found on Figures 4.12 and 4.23 (Page.115) E. Evidence from DNA DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid (the molecule that determines the genetic makeup of an organism). DNA analysis maps out the genetic sequencing of an organism. The closer the DNA sequences of two organisms, the more closely related they are. Remember from grade 9 AT and CG are base pairs. The more base pairs they have in common, the more closely related they will be. F. Evidence from Metabolic Behaviour The ability to digest certain substances or if an organism is a producer, consumer or decomposer can be used to classify organisms. G. Phylogeny Phylogeny - The evolutionary history of an organism. 6
7 Phylogeny is used to trace the history of an organism to help classify it. An organism is classified using a Phylogenic Tree. Pg. 116 Fig 4.14 Phylogenic tree (similar to family trees) - Shows the relationships among various organisms. It is a hypothesis about the evolutionary relationships among organisms. The root of the tree suggests a common ancestor. All organisms above the root share some part of the characteristics of the common ancestor. These are called Primitive Characteristics. Primitive Characteristics: Characteristics originally present in a common ancestor that have been passed on to other organisms. Branches in the tree suggest New Species that have evolved. Each species that has evolved would have new features called Derived Characteristics. Derived Characteristics: These are new characteristics that have evolved in an organism as the organism has adapted to its environment etc. H. Cladistics Cladistics: A classification system based upon phylogeny. Based upon the idea that there is a common ancestor and new species gain derived characteristics. Cladograms Branching diagrams used to trace the evolutionary history of organisms and to then classify them. Pg. 118 (Figures 4.16 and 4.17) Speciation Event: The separation of organisms into different groups or species. Internode: A common ancestor to any branches above it. Root: A common ancestor to all organisms above it. Sister Taxons: organisms that are very closely related. 7
8 4.3 Viruses Virus particulate that contains strands of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat (capsid) and that acts as a mobile gene that parasitizes cells. Most viruses contain RNA instead of DNA (70% contain RNA). RNA is still considered to be a genetic blueprint, however it is different from DNA since it is single stranded and the base pair T is replaced with U. Viruses have no cellular structure, therefore they are not considered organisms and are not classified in any kingdom of living things. Viruses are specific for different cells. Ex. T4 virus bacteria, HIV white blood cells. Viruses also have a variety of shapes. See Figure 4.20 Page Origin of Viruses Probably evolved after the first cells came into existence. They probably originated as fragments of nucleic acid that escaped original cells. They survived by being parasites of the same type of similar type of cells. Characteristics of Viruses No cellular structure No cytoplasm, organelles or membranes Not able to grow or reproduce independently Not able to exchange gases(respire) independently Act as parasites Rely on HOST cell for survival They are inert (no reproduction) outside of their host cell. Each virus has a specifically shaped attachment protein so it will only attach to certain cells. Viruses are able to reproduce by two different methods: 1. The Lytic Cycle (Ex: T4 Bacteriophage) PAGE 123 A short cycle about 30 minutes Produces up to 200 viruses a cycle Virus injects its DNA/RNA into a host cell. Genetic material of virus takes over machinery of cell and produces new viral cells. HOST CELL IS DESTROYED YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW THE LYTIC CYCLE IN MORE DETAIL THAN PROVIRUS. 8
9 The Five (5) stages of the Lytic Cycle: a. Attachment The virus attaches itself to the host s cell wall. b. Entry The virus injects its DNA/RNA into the host cell. c. Replication The host s cellular metabolism reproduces the viral DNA or RNA. d. Assembly New viral particles are made by the host cell s machinery (protein synthesis). e. Lysis or Release The host cell s plasma membrane and cell wall break open releasing new viruses. The host cell dies. 2. The Lysogenic or Provirus Cycle PAGE. 124 Viral DNA/RNA enters cell and becomes part of cell s DNA. (Called a provirus when this happens) Viral DNA is reproduced with cell DNA. Viral DNA can exist in this form for years without harm to host cell. When active, the provirus separates from host cell DNA and undergoes Lytic cycle. Host cell is NOT usually destroyed. EX: HIV, Herpes 9
Section 1 Lesson 1 Living Versus Nonliving
 Page 1 of 12 Section 1 Lesson 1 Living Versus Nonliving Characteristics of Living Things In order to be considered living, an organism must possess the following Six (6) characteristics. a. Living things
Page 1 of 12 Section 1 Lesson 1 Living Versus Nonliving Characteristics of Living Things In order to be considered living, an organism must possess the following Six (6) characteristics. a. Living things
Characteristics of Life
 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY Chapter 4- Patterns of Life Biology 2201 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1) living things are organized systems made up of one or more cells
UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY Chapter 4- Patterns of Life Biology 2201 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1) living things are organized systems made up of one or more cells
The Road to the Six Kingdoms
 Bio 2201 Unit 2 The Road to the Six Kingdoms A 2011study estimated there are about 8.6 million species on earth. Only 1.8 million species have been identified and named. *Chromista is a sub-kingdom group
Bio 2201 Unit 2 The Road to the Six Kingdoms A 2011study estimated there are about 8.6 million species on earth. Only 1.8 million species have been identified and named. *Chromista is a sub-kingdom group
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Zoology. Classification
 Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
Zoology Zoology involves studying all aspects of organisms belonging to the animal kingdom taxonomy, animal physiology, comparative anatomy, and ecology. Our study of Zoology will be focused on the different
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Classification. copyright cmassengale
 Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that ever lived!!!!! New organisms are still being found and identified 2 What is
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Biologists estimate that there are about 5 to 100 million species of organisms living on Earth today. Evidence from morphological, biochemical, and gene sequence
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Biologists estimate that there are about 5 to 100 million species of organisms living on Earth today. Evidence from morphological, biochemical, and gene sequence
CLASSIFICATION NOTES
 CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification Classification = arrangement of living things into groups according to their observed similarities. Important because it allows us to be able to study life easier Living
CLASSIFICATION NOTES Classification Classification = arrangement of living things into groups according to their observed similarities. Important because it allows us to be able to study life easier Living
Classification of Living Things. Unit II pp 98
 Classification of Living Things Unit II pp 98 Why There is a Need for Classifying There are over 2 million different types of organisms known. biologists can organize living things into groups. Taxonomy
Classification of Living Things Unit II pp 98 Why There is a Need for Classifying There are over 2 million different types of organisms known. biologists can organize living things into groups. Taxonomy
Unit Two: Biodiversity. Chapter 4
 Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms
 Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Taxonomy Taxonomy: field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms Why do we need it? problems with different languages common names can be confusing examples: woodchuck, groundhog crayfish,
Biology Unit 02 Biodiversity Section 01 Test Taxonomy/Classification
 Biology 2201(A) Unit 02 Biodiversity Page 1 of 12 Biology 2201 Unit 02 Biodiversity Section 01 Test Taxonomy/Classification Instructions for Students: 1. This test is composed of two parts. Part 1 consists
Biology 2201(A) Unit 02 Biodiversity Page 1 of 12 Biology 2201 Unit 02 Biodiversity Section 01 Test Taxonomy/Classification Instructions for Students: 1. This test is composed of two parts. Part 1 consists
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1. Taxonomy The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living organisms About 1.8 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1. Taxonomy The branch of biology that deals with the classification of living organisms About 1.8 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists
Classification and Viruses Practice Test
 Classification and Viruses Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part
Classification and Viruses Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part
Creating a Dichotomous Key
 Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
Dichotomous Keys A tool used that allows users to determine the identity of unknown species Keys consist of a series of choices, where the user selects from a series of connected pairs Each pair of choices
What is the purpose of the Classifying System? To allow the accurate identification of a particular organism
 What is the purpose of the Classifying System? To allow the accurate identification of a particular organism Taxonomy The practice of classifying organisms -Taxonomy was founded nearly 300 years ago by
What is the purpose of the Classifying System? To allow the accurate identification of a particular organism Taxonomy The practice of classifying organisms -Taxonomy was founded nearly 300 years ago by
3) What are the names of the SIX kingdoms? Next to each one, write whether it is prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
 Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
Topic #1: Taxonomy 1) What is taxonomy? system of naming and classifying organisms 2) Name the eight levels of taxonomic categories, starting with the most general and ending with the most specific. Domain,
The Living Environment Unit 4 History of Biological Diversity Unit 17: Organizing the Diversity of Life-class key.
 Name: Period: Chapter 17 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: The Tree of Life Objective: How may we organize so many different organisms? The Tree of Life o organize organisms by structure
Name: Period: Chapter 17 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: The Tree of Life Objective: How may we organize so many different organisms? The Tree of Life o organize organisms by structure
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
Outline. Classification of Living Things
 Outline Classification of Living Things Chapter 20 Mader: Biology 8th Ed. Taxonomy Binomial System Species Identification Classification Categories Phylogenetic Trees Tracing Phylogeny Cladistic Systematics
Outline Classification of Living Things Chapter 20 Mader: Biology 8th Ed. Taxonomy Binomial System Species Identification Classification Categories Phylogenetic Trees Tracing Phylogeny Cladistic Systematics
9/19/2012. Chapter 17 Organizing Life s Diversity. Early Systems of Classification
 Section 1: The History of Classification Section 2: Modern Classification Section 3: Domains and Kingdoms Click on a lesson name to select. Early Systems of Classification Biologists use a system of classification
Section 1: The History of Classification Section 2: Modern Classification Section 3: Domains and Kingdoms Click on a lesson name to select. Early Systems of Classification Biologists use a system of classification
Welcome to biology. Evolution, Homeostasis and Reproduction (the first lecture)
 Welcome to biology Evolution, Homeostasis and Reproduction (the first lecture) What is unique to life? Cell membrane contains protoplasm inside, is alive outside is dead (1) Complex - Cells have very complex
Welcome to biology Evolution, Homeostasis and Reproduction (the first lecture) What is unique to life? Cell membrane contains protoplasm inside, is alive outside is dead (1) Complex - Cells have very complex
CLASSIFICATION. Why Classify? 2/18/2013. History of Taxonomy Biodiversity: variety of organisms at all levels from populations to ecosystems.
 Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Classification. Essential Question Why is it important to place living things into categories?
 Classification Essential Question Why is it important to place living things into categories? Compare and contrast Taxonomy comparison 18.1 History of Taxonomy Objectives Describe Aristotle s classification
Classification Essential Question Why is it important to place living things into categories? Compare and contrast Taxonomy comparison 18.1 History of Taxonomy Objectives Describe Aristotle s classification
Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food.
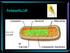 Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
A. Correct! Taxonomy is the science of classification. B. Incorrect! Taxonomy is the science of classification.
 DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity
 Name Class Date Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity (pages 447-450) Key Concepts How are living things organized for study? What is binomial nomenclature? What is Linnaeus s system of classification?
Name Class Date Section 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity (pages 447-450) Key Concepts How are living things organized for study? What is binomial nomenclature? What is Linnaeus s system of classification?
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Learning Outcome B1 13/10/2012. Student Achievement Indicators. Taxonomy: Scientific Classification. Student Achievement Indicators
 Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Chapter 17. Organizing Life's Diversity
 Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the six kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base classification
Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the six kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base classification
Classification Notes
 Name Living Environment Classification Notes Characteristics of Living Things All living things have a cellular organization, contain similar chemicals, use energy, grow and develop, respond to their surroundings,
Name Living Environment Classification Notes Characteristics of Living Things All living things have a cellular organization, contain similar chemicals, use energy, grow and develop, respond to their surroundings,
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Biology Classification Unit 11. CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics
 Biology Classification Unit 11 11:1 Classification and Taxonomy CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics TAXONOMY: the science of classifying living things
Biology Classification Unit 11 11:1 Classification and Taxonomy CLASSIFICATION: process of dividing organisms into groups with similar characteristics TAXONOMY: the science of classifying living things
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 6: Evolution & The Diversity of Life
 Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 6: Evolution & The Diversity of Life Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Darwin and Natural Selection Vocabulary Term Charles
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 6: Evolution & The Diversity of Life Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Darwin and Natural Selection Vocabulary Term Charles
Fig. 26.7a. Biodiversity. 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading. 2. Course Syllabus. Fig. 26.7b Table
 Fig. 26.7a Biodiversity 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading 2. Course Syllabus Fig. 26.7b Table 26.2-1 1 Table 26.2-2 Outline: Systematics and the Phylogenetic Revolution I. Naming and
Fig. 26.7a Biodiversity 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading 2. Course Syllabus Fig. 26.7b Table 26.2-1 1 Table 26.2-2 Outline: Systematics and the Phylogenetic Revolution I. Naming and
Phylogeny 9/8/2014. Evolutionary Relationships. Data Supporting Phylogeny. Chapter 26
 Phylogeny Chapter 26 Taxonomy Taxonomy: ordered division of organisms into categories based on a set of characteristics used to assess similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature,
Phylogeny Chapter 26 Taxonomy Taxonomy: ordered division of organisms into categories based on a set of characteristics used to assess similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature,
UNIT 4 TAXONOMY AND CLASSIFICATION
 UNIT 4 TAXONOMY AND CLASSIFICATION CHAPTER 13 IN TEXT READ P. 4.0 CLASSIFICATION AND TAXONOMY 4.1 Define taxonomy 4.2 Discuss the reasons for classifying organisms 4.3 Define species and binomial nomenclature
UNIT 4 TAXONOMY AND CLASSIFICATION CHAPTER 13 IN TEXT READ P. 4.0 CLASSIFICATION AND TAXONOMY 4.1 Define taxonomy 4.2 Discuss the reasons for classifying organisms 4.3 Define species and binomial nomenclature
Chapter 17. Organizing Life's Diversity
 Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the 3 domains and the 6 kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base
Chapter 17 Organizing Life's Diversity Key Concepts: Chapter 17 1. List the 3 domains and the 6 kingdoms. 2. Our current system of classification was originally based on structures; scientists now base
Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes
 Name Exam Date Class Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes What is Classification? is when we place organisms into based on their. Classification is also known as. Taxonomists are scientists that & organisms
Name Exam Date Class Unit 9: Taxonomy (Classification) Notes What is Classification? is when we place organisms into based on their. Classification is also known as. Taxonomists are scientists that & organisms
Objectives. Classification. Activity. Scientists classify millions of species
 Objectives Classification Notes 8.1 Summarize classification Describe the evidence used to classify organisms. List the seven levels of classification. Describe and list the six kingdoms of living organisms
Objectives Classification Notes 8.1 Summarize classification Describe the evidence used to classify organisms. List the seven levels of classification. Describe and list the six kingdoms of living organisms
Concept Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history.
 Concept 15.4 Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history. What is Taxonomy: identification, naming, and classification of species. Common Names: can cause confusion - May refer to several species (ex.
Concept 15.4 Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history. What is Taxonomy: identification, naming, and classification of species. Common Names: can cause confusion - May refer to several species (ex.
Chapter 17. Table of Contents. Objectives. Taxonomy. Classifying Organisms. Section 1 Biodiversity. Section 2 Systematics
 Classification Table of Contents Objectives Relatebiodiversity to biological classification. Explainwhy naturalists replaced Aristotle s classification system. Identifythe main criterion that Linnaeus
Classification Table of Contents Objectives Relatebiodiversity to biological classification. Explainwhy naturalists replaced Aristotle s classification system. Identifythe main criterion that Linnaeus
Classification Systems. - Taxonomy
 Classification Systems - Taxonomy Why Classify? 2.5 million kinds of organisms Not complete- 20 million organisms estimated Must divide into manageable groups To work with the diversity of life we need
Classification Systems - Taxonomy Why Classify? 2.5 million kinds of organisms Not complete- 20 million organisms estimated Must divide into manageable groups To work with the diversity of life we need
Origins of Life. Fundamental Properties of Life. Conditions on Early Earth. Evolution of Cells. The Tree of Life
 The Tree of Life Chapter 26 Origins of Life The Earth formed as a hot mass of molten rock about 4.5 billion years ago (BYA) -As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were formed from water condensation Life
The Tree of Life Chapter 26 Origins of Life The Earth formed as a hot mass of molten rock about 4.5 billion years ago (BYA) -As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were formed from water condensation Life
Classification. Species of Organisms. What is Classification?
 Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are known species of organisms This is organisms that ever lived!!!!! are still being found and identified 2 What is Classification? is the arrangement of organisms
Classification 1 Species of Organisms There are known species of organisms This is organisms that ever lived!!!!! are still being found and identified 2 What is Classification? is the arrangement of organisms
SECTION 17-1 REVIEW BIODIVERSITY. VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms.
 SECTION 17-1 REVIEW BIODIVERSITY VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. taxonomy, taxon 2. kingdom, species 3. phylum, division 4. species name, species
SECTION 17-1 REVIEW BIODIVERSITY VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. taxonomy, taxon 2. kingdom, species 3. phylum, division 4. species name, species
Taxonomy. The science of naming organisms.
 Taxonomy The science of naming organisms. Why Classify? Aristotle Did It Plant or animal? If an animal, does it Fly Swim Crawl Simple classifications Used common names Carolus Linnaeus did it better
Taxonomy The science of naming organisms. Why Classify? Aristotle Did It Plant or animal? If an animal, does it Fly Swim Crawl Simple classifications Used common names Carolus Linnaeus did it better
Vocabulary: Fill in the definition for each word. Use your book and/or class notes. You can put the words in your own words. Animalia: Archaea:
 Name: _ Due Date: _ Per: _ Unit 4.2 Study Guide Directions: Complete all sections to the best of your ability. On the day of the Quiz (the due date for this assignment) turn this in with all of your Unit
Name: _ Due Date: _ Per: _ Unit 4.2 Study Guide Directions: Complete all sections to the best of your ability. On the day of the Quiz (the due date for this assignment) turn this in with all of your Unit
First things first: What IS classification and WHY do we do it (or DO we)? How are living things classified? Classification Systems
 How are living things classified? Objective: Describe the system used today to classify organisms (including the seven levels of classification as well as scientific names) First things first: What IS
How are living things classified? Objective: Describe the system used today to classify organisms (including the seven levels of classification as well as scientific names) First things first: What IS
9.3 Classification. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Linnaean Classification
 9.3 Classification Lesson Objectives Outline the Linnaean classification, and define binomial nomenclature. Describe phylogenetic classification, and explain how it differs from Linnaean classification.
9.3 Classification Lesson Objectives Outline the Linnaean classification, and define binomial nomenclature. Describe phylogenetic classification, and explain how it differs from Linnaean classification.
LS CH 7 practice. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 LS CH 7 practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all living things share? a. a cellular
LS CH 7 practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all living things share? a. a cellular
Friday April 8 th 2016
 Friday April 8 th 2016 Warm-Up Select a highlighter. Get a bottle of glue. Update your Table of Contents (see whiteboard). Today In Science Classification Presentation and Notes How many different types
Friday April 8 th 2016 Warm-Up Select a highlighter. Get a bottle of glue. Update your Table of Contents (see whiteboard). Today In Science Classification Presentation and Notes How many different types
How are living things classified?
 Classification Systems How are living things classified?! Learning Goals 12, 13, 14, 15 & 16 on your rubric! TAXONOMY: The study of classification, or how living things are grouped! Aristotle classified
Classification Systems How are living things classified?! Learning Goals 12, 13, 14, 15 & 16 on your rubric! TAXONOMY: The study of classification, or how living things are grouped! Aristotle classified
Kingdoms in Eukarya: Protista, Fungi, Plantae, & Animalia Each Eukarya kingdom has distinguishing characteristics:
 NAME pg. 1 Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Eukarya Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo sapiens Mnemonic: DUMB KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GOOD SOUP Domain
NAME pg. 1 Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Eukarya Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo sapiens Mnemonic: DUMB KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GOOD SOUP Domain
Chapter 1. How Do Biologists Study Life?
 Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Classification Cladistics & The Three Domains of Life. Biology Mrs. Flannery
 Classification Cladistics & The Three Domains of Life Biology Mrs. Flannery Finding Order in Diversity Earth is over 4.5 billion years old. Life on Earth appeared approximately 3.5 billion years ago and
Classification Cladistics & The Three Domains of Life Biology Mrs. Flannery Finding Order in Diversity Earth is over 4.5 billion years old. Life on Earth appeared approximately 3.5 billion years ago and
NAME: DATE: PER: CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Powerpoint Notes
 NAME: DATE: PER: CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Powerpoint Notes 1. Species of Organisms a) There are known species of organisms b) This is only of all organisms that ever lived. c) are still being found and identified.
NAME: DATE: PER: CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Powerpoint Notes 1. Species of Organisms a) There are known species of organisms b) This is only of all organisms that ever lived. c) are still being found and identified.
The Tree of Life. Chapter 17
 The Tree of Life Chapter 17 1 17.1 Taxonomy The science of naming and classifying organisms 2000 years ago Aristotle Grouped plants and animals Based on structural similarities Greeks and Romans included
The Tree of Life Chapter 17 1 17.1 Taxonomy The science of naming and classifying organisms 2000 years ago Aristotle Grouped plants and animals Based on structural similarities Greeks and Romans included
CH. 18 Classification
 CH. 18 Classification Name:_ 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part because organisms a. are going extinct. b. are very numerous and diverse. c. are too much alike. d. share
CH. 18 Classification Name:_ 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part because organisms a. are going extinct. b. are very numerous and diverse. c. are too much alike. d. share
The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains.
 Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1
 CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
Chapter 18: Classification
 Chapter 18: Classification Dichotomous Key A way to identify unknown organisms Contains major characteristics of groups of organisms Pairs of CONTRASTING descriptions 4. After each description key either
Chapter 18: Classification Dichotomous Key A way to identify unknown organisms Contains major characteristics of groups of organisms Pairs of CONTRASTING descriptions 4. After each description key either
1. Which of the following is a virus? C D. 2. Which of the following is found in both cells and viruses?
 TEKS 4C compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza 1. Which of
TEKS 4C compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza 1. Which of
Taxonomy and Biodiversity
 Chapter 25/26 Taxonomy and Biodiversity Evolutionary biology The major goal of evolutionary biology is to reconstruct the history of life on earth Process: a- natural selection b- mechanisms that change
Chapter 25/26 Taxonomy and Biodiversity Evolutionary biology The major goal of evolutionary biology is to reconstruct the history of life on earth Process: a- natural selection b- mechanisms that change
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort
 Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
What are living things, and how can they be classified?
 Classifying Organisms What are living things, and how can they be classified? binomial nomenclature species genus dichotomous key cladogram Classifying Living Things Classification: organizing information
Classifying Organisms What are living things, and how can they be classified? binomial nomenclature species genus dichotomous key cladogram Classifying Living Things Classification: organizing information
Station A: #3. If two organisms belong to the same order, they must also belong to the same
 Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS. Chapter 18
 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Chapter 18 How many species are there? About 1.8 million species have been given scientific names Nearly 2/3 of which are insects 99% of all known animal species are smaller
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Chapter 18 How many species are there? About 1.8 million species have been given scientific names Nearly 2/3 of which are insects 99% of all known animal species are smaller
CLASSIFICATION. Similarities and Differences
 CLASSIFICATION Similarities and Differences TEKS 8A: Students will define taxonomy and recognize the importance of a standard system to the scientific community 8B: Students will categorize organisms using
CLASSIFICATION Similarities and Differences TEKS 8A: Students will define taxonomy and recognize the importance of a standard system to the scientific community 8B: Students will categorize organisms using
Biology Test Review: Classification/Taxonomy
 Name: Period: Biology Test Review: Classification/Taxonomy MAKE SURE YOUR BOOKLET IS COMPLETELY FINISHED! If you are missing information, it can be found on your teacher s webpage. I. Definitions Try to
Name: Period: Biology Test Review: Classification/Taxonomy MAKE SURE YOUR BOOKLET IS COMPLETELY FINISHED! If you are missing information, it can be found on your teacher s webpage. I. Definitions Try to
Unit 5: Taxonomy. KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. Linnaeus developed the scientific naming system still used today. Taxonomy is the science of naming and classifying organisms. White
KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. Linnaeus developed the scientific naming system still used today. Taxonomy is the science of naming and classifying organisms. White
Classification Practice Test
 Classification Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. An organism may have different
Classification Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. An organism may have different
Hierarchies can be represented as trees:
 Diversity of Life Classification - an organized scheme for grouping organisms - a tool for communication - Hierarchical - a series of successive and inclusive rankings Domain - the highest rank - contains
Diversity of Life Classification - an organized scheme for grouping organisms - a tool for communication - Hierarchical - a series of successive and inclusive rankings Domain - the highest rank - contains
What is Life? Characteristics of Living Things. Needs of Living Things. Experiments of Redi & Pasteur. Bacteria to Plants - Ch 1 Living Things
 What is Life? Bacteria to Plants - Ch 1 Living Things aka: organisms What are the six characteristics of living things? - briefly describe each What are the major chemicals found in cells? Do organisms
What is Life? Bacteria to Plants - Ch 1 Living Things aka: organisms What are the six characteristics of living things? - briefly describe each What are the major chemicals found in cells? Do organisms
Let s get started. So, what is science?
 Let s get started So, what is science? Well Science Science is the observation of phenomena and the theoretical explanation of it. Simply, it is the state of knowing. Biology Biology is the study of life.
Let s get started So, what is science? Well Science Science is the observation of phenomena and the theoretical explanation of it. Simply, it is the state of knowing. Biology Biology is the study of life.
Speciation and Classification
 Speciation and Classification Species- a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring Forming a new species Each population of a single species lives in a different place.
Speciation and Classification Species- a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring Forming a new species Each population of a single species lives in a different place.
Summary Finding Order in Diversity Modern Evolutionary Classification
 ( Is (.'I.isiifiuilimi Summary 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity There are millions of different species on Earth. To study this great diversity of organisms, biologists must give each organ ism a name.
( Is (.'I.isiifiuilimi Summary 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity There are millions of different species on Earth. To study this great diversity of organisms, biologists must give each organ ism a name.
PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY SPECIES
 CLASSIFICATION LEVELS KINGDOM PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES Classification of ME! Animalia Multicellular, mobile, eukaryotic, heterotroph Chordata Dorsal nerve chord, pharyngeal gill slits, bilateral
CLASSIFICATION LEVELS KINGDOM PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES Classification of ME! Animalia Multicellular, mobile, eukaryotic, heterotroph Chordata Dorsal nerve chord, pharyngeal gill slits, bilateral
Vocabulary Classification the process of arranging organisms into groups based on similarities Taxonomy the science of naming and classifying
 Classification.. Vocabulary Classification the process of arranging organisms into groups based on similarities Taxonomy the science of naming and classifying organisms trait a characteristic or behavior
Classification.. Vocabulary Classification the process of arranging organisms into groups based on similarities Taxonomy the science of naming and classifying organisms trait a characteristic or behavior
Binomial Nomenclature
 Binomial Nomenclature 1a A two-part scientific naming system using Latin words. Written in italics with Genus capitalized and species portion lower case. Ex. Quercus alba 1b Clade 2a A clade is a group
Binomial Nomenclature 1a A two-part scientific naming system using Latin words. Written in italics with Genus capitalized and species portion lower case. Ex. Quercus alba 1b Clade 2a A clade is a group
1.1 Characteristics of Life Block: Date:
 Biology 12 Name: 1.1 Characteristics of Life Block: Date: ization of Life (p. 3) Definition Cell Example Blood cell Tissue Muscle tissue Several tissues joined together to form a function system Circulatory
Biology 12 Name: 1.1 Characteristics of Life Block: Date: ization of Life (p. 3) Definition Cell Example Blood cell Tissue Muscle tissue Several tissues joined together to form a function system Circulatory
Biology 2.1 Taxonomy: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum. ICan2Ed.com
 Biology 2.1 Taxonomy: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum ICan2Ed.com Taxonomy is the scientific field that catalogs, describes, and names living organisms. The way to divide living organisms into groups based on
Biology 2.1 Taxonomy: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum ICan2Ed.com Taxonomy is the scientific field that catalogs, describes, and names living organisms. The way to divide living organisms into groups based on
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
Station 1. Explain how scientists use each item below to determine the evolutionary relationships among organisms. 1. Structural similarities:
 Station 1 Explain how scientists use each item below to determine the evolutionary relationships among organisms. 1. Structural similarities: 2. Breeding behavior: 3. Geographical distribution: 4. Chromosome
Station 1 Explain how scientists use each item below to determine the evolutionary relationships among organisms. 1. Structural similarities: 2. Breeding behavior: 3. Geographical distribution: 4. Chromosome
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
4. Which structure controls the amount of light that reaches the object being viewed?
 Biology 2201 Midterm Name: Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Transfer Answers to the answer sheet attached at the back. 1. Which supports the cell theory? abiogenesis biogenesis comparative DNA spontaneous
Biology 2201 Midterm Name: Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Transfer Answers to the answer sheet attached at the back. 1. Which supports the cell theory? abiogenesis biogenesis comparative DNA spontaneous
and just what is science? how about this biology stuff?
 Welcome to Life on Earth! Rob Lewis 512.775.6940 rlewis3@austincc.edu 1 The Science of Biology Themes and just what is science? how about this biology stuff? 2 1 The Process Of Science No absolute truths
Welcome to Life on Earth! Rob Lewis 512.775.6940 rlewis3@austincc.edu 1 The Science of Biology Themes and just what is science? how about this biology stuff? 2 1 The Process Of Science No absolute truths
Classification of Living Things Ch.11 Notes
 Classification of Living Things Ch.11 Notes Why do we classify things?! Supermarket aisles! Libraries! Classes! Teams/sports! Members of a family! Roads! Cities! Money What is classification?! Classification:
Classification of Living Things Ch.11 Notes Why do we classify things?! Supermarket aisles! Libraries! Classes! Teams/sports! Members of a family! Roads! Cities! Money What is classification?! Classification:
Module 6 Note Taking Guide. Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life
 Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Module 6 Note Taking Guide Lesson 6.01:Organization of Life Lesson Page: Organization of Living Things The smallest level of organization for living things. Example: Oxygen, Hydrogen - A group of atoms
Unit 8 Classification
 Unit 8 Classification Chapter 18: Classification www.pearsonrealize.com 18.1 Finding Order in Diversity (510) 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification (516) 18.3 Building the Tree of Life (523) Name: Teacher:
Unit 8 Classification Chapter 18: Classification www.pearsonrealize.com 18.1 Finding Order in Diversity (510) 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification (516) 18.3 Building the Tree of Life (523) Name: Teacher:
Evidence for Evolution
 Evidence for Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Paleontology Comparative Anatomy Embryology Comparative Biochemistry Geographical Distribution How old is everything? The History of Earth as a Clock Station 1: Paleontology
Evidence for Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Paleontology Comparative Anatomy Embryology Comparative Biochemistry Geographical Distribution How old is everything? The History of Earth as a Clock Station 1: Paleontology
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups. Mrs. Hilliard
 Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
Biology Unit 1 Warm Ups Mrs. Hilliard Communication in Science Choose one of the three topics to write a detailed procedure for. 1. How to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. 2. How to brush your
What makes things alive? CRITERIA FOR LIFE
 What makes things alive? CRITERIA FOR LIFE Learning Goals I can determine if something is alive based on the criteria for life. I can describe the history of life on Earth. I can describe how organisms
What makes things alive? CRITERIA FOR LIFE Learning Goals I can determine if something is alive based on the criteria for life. I can describe the history of life on Earth. I can describe how organisms
chapter 18 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 18 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. One goal of scientists is to assign every organism a universally accepted name according to
chapter 18 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. One goal of scientists is to assign every organism a universally accepted name according to
Name: Period: What is the term used to describe the shape of DNA? What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
 Name: Period: Station 1. Analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. a. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. b. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information.
Name: Period: Station 1. Analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. a. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. b. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information.
Biologists use a system of classification to organize information about the diversity of living things.
 Section 1: Biologists use a system of classification to organize information about the diversity of living things. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are
Section 1: Biologists use a system of classification to organize information about the diversity of living things. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are
Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY!
 Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY Chapter 1 KEY FIGURES: 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 VOCABULARY: Adaptation: a trait that increases the fitness Cells: a developed, system bound with a thin outer layer made of
Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY Chapter 1 KEY FIGURES: 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 VOCABULARY: Adaptation: a trait that increases the fitness Cells: a developed, system bound with a thin outer layer made of
Introduction to the Study of Life
 1 Introduction to the Study of Life Bio 103 Lecture GMU Dr. Largen 2 Outline Biology is the science of life The process of science Evolution, unity and diversity Core principles of biology 3 The Science
1 Introduction to the Study of Life Bio 103 Lecture GMU Dr. Largen 2 Outline Biology is the science of life The process of science Evolution, unity and diversity Core principles of biology 3 The Science
