Practice Exam #3. Part 1: The Circumpolar Constellations
|
|
|
- Aldous Milo May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Practice Exam # Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Some Comments on the Real Exam This exam covers all material related to astronomy. Specifically, this exam covers: All of Part C of your course packet Planetarium Lab #1 (p. A 65 through A 68) The real exam will consist of 10 multiple-choice questions (worth 40 points), 5 to 7 essay questions and a few short-answer questions (the essay and short-answer questions are worth 60 points). As usual, you will be allowed to bring in one 8.5 x 11 inch cheat sheet with anything you want on it, both sides. As usual, you will take the multiple-choice part of the exam twice, once on your own and once with your group. You will receive 2 points for each right answer on the individual exam and 2 points for each right answer on the group exam. Be sure to bring the following items to the exam: cardboard solar motion model Star and Planet locator Materials Model Celestial Sphere Part 1: The Circumpolar Constellations Questions 1. Circle and name the five circumpolar constellations illustrated below. Identify and label the North Star. 2. Describe and illustrate how you can use the North Star to determine your latitude. * Supported by NSF Grant # Permission is granted to reproduce this material for classroom use. C 61
2 C 62 Practice Exam #3 3. Explain why the North Star stands still. Part 2: Celestial Hemispheres Useful Information On the equinoxes (March 21 and September 21), the angle of the noonday sun is 90 (your latitude). On the summer solstice, the angle of the noonday sun is 90 (your latitude) On the winter solstice, the angle of the noonday sun is 90 (your latitude) In any 24-hour period, the sun always appears to travel parallel to the Celestial Equator. Materials Cardboard solar motion models Clear plastic hemisphere Pens designed for overhead projectors Introduction: Activity/Questions Imagine yourself in the middle of a very large flat treeless plain, looking up at the sky. The sky above you looks like a giant inverted bowl. You are inside the bowl, in the exact center. The sun, moon, planets and stars seem to move on the surface of this huge bowl. We will now scale down this image. Imagine that you are the size of a pinhead. The lab table is the large flat plain and the small clear plastic hemisphere is the bowl that represents the sky. On the clear plastic hemisphere (representing the sky above you), draw the path of the sun across the sky in Chico (latitude 40 N) for each of the following dates: a. Vernal Equinox (around March 22) b. Autumnal Equinox (around September 22). c. Summer Solstice (around June 22) d. Winter Solstice (around December 22) Be sure to label North on the sphere. Be sure to draw the paths at the correct compass directions and at the correct angles from the horizon (as close as you can get them). Describe how you figured out the paths, showing all the steps of any mathematical calculations you did.
3 Practice Exam #3 C 63 Part 3: The Path of the Moon Across the Sky Background Information Most people know their astrological sun sign, but many people don't know that they also have a moon sign, (and a Venus sign, a Mars sign, etc.). Each of your signs is designated by the position of that celestial object in the sky, relative to the constellations of the Zodiac, at the time you were born. We will not ask you to comment on the significance (or insignificance) of your various signs with regard to your personality and future--those issues fall within the spiritual realm, not within the realm of science. But, we will ask you to explain why and over what period of time the moon travels through the various constellations of the Zodiac. The plane of Earth's orbit around the sun is tilted at a 23.5 angle to the Earth's equator. By contrast, the plane of the moon's orbit around the Earth is tilted at a 5 angle to the plane of the Earth's orbit around the sun. As a result, the apparent path of the moon across the sky is a little different from the apparent path of the sun across the sky. But, for the purposes of this activity, these differences don't matter and we will use the model on the Model Celestial Sphere to represent the moon. Materials: Model Celestial Sphere Activity: Turn the white knob on the outside of the Celestial Sphere to model the revolution of the moon around Earth. Note the path of the moon relative to the constellations of the Zodiac. Questions: 1. How long does it take the moon to complete one cycle through the constellations of the Zodiac? Explain. 2. Explain why the moon travels through the constellations of the Zodiac. 3. The chronological order of the signs is Capricorn Aquarius Pisces Aries Taurus Gemini Cancer Leo Virgo Libra Scorpio Sagittarius Do the moon signs go in the same order or do they go backwards? Explain. 4. How many days (approximately) does the moon take to travel through each sign of the zodiac?
4 C 64 Practice Exam #3 Part 4: The Moon Materials: White polystyrene ball on a pencil (to represent the moon) Glowing light bulb (to represent the sun) Activity: Use the ball on the stick and the light bulb to model the moon in its various phases. 1. Complete the table below, inserting the names of the moon phases, drawings of the moon and/or drawings of the positions of the moon, sun and Earth as appropriate. In your drawings of the moon, please leave the lit portion of the moon white and shade in the dark portion of the moon. Moon Phase Drawing of what the moon looks like from Earth (northern hemisphere) Drawing of Positions of moon, sun and Earth (looking down on Earth's North Pole) Waxing Gibbous 1 st Quarter Moon Earth
5 Practice Exam #3 C Questions about the photograph on the front cover of the course packet. Photographers: Crew of the Apollo 8 NASA mission to the moon Date of photograph: December 22, 1968 Title of photograph: View of rising Earth about five degrees above the Lunar horizon Explanation: The rising Earth is about five degrees above the lunar horizon in this telephoto view taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft near 110 east longitude. The horizon, about 570 kilometers (250 statute miles) from the spacecraft, is near the eastern limb of the Moon as viewed from the Earth. On the earth, the sunset terminator crosses Africa. The south pole is in the white area near the left end of the terminator. North and South America are under the clouds. The lunar surface probably has less pronounced color than indicated by this print. Questions a. Why did the Earth look like a lop-sided football instead of a full circle? b. What were the relative positions of the sun, Earth and moon on December 22, 1968? c. On that same day (December 22, 1968), what did the moon look like from Earth (i.e. what was the phase of the moon?) d. Why is the South Pole up? e. From any one place on the moon, does Earth ever really rise or set? Part 5: Multiple Choice 1. Why is it hotter at the equator than at the poles? a. Because the equator is closer to the sun. b. Because the sun's rays travel through more atmosphere at the equator. c. Because the sun's energy is more spread out at the equator. d. Because the sun's rays hit the earth's surface at a higher angle at the equator. e. Because the sun is always directly overhead at the equator. 2. If the Earth's axis only had a 5 tilt, how would the seasons in Chico be different from how they are now? a. The seasons would be shorter. b. The transitions between seasons would be more abrupt. c. The contrast in temperature between summer and winter wouldn't be as great. d. Summer days would be longer than they are now and winter days would be shorter than they are now. e. All of the above. 3. In Chico, the highest the sun ever gets at noon is above the horizon and the lowest the sun ever gets at noon is above the horizon. a. 90 ; 40 b ; 26.5 c ; 40 d. 47, 23.5 e. 40 ; 16.5
6 C 66 Practice Exam #3 4. You have been kidnapped and taken, blindfolded, to a remote site. You manage to peek outside one night and see the little dipper setting below the horizon. What is the approximate latitude of your location? a. 0 (Equator) b. 40 North c. 40 South d. 90 North (North Pole) e. 90 South (South Pole) 5. We can see Orion in November but not in May because in November whereas in May. a. Orion is directly above North America; Orion is directly above Europe. b. Earth tilts toward Orion; Earth tilts away from Orion. c. Polaris is high in the sky; Polaris is below the horizon. d. The sun is in Orion; the sun is opposite Orion. e. Earth is between the sun and Orion; the sun is between Earth and Orion. 6. Each star seems to rise a little later each day. True or false? Why? a. True, because the stars revolve very slowly around Earth in the same direction that Earth rotates on its axis. b. True, because the sun moves through the constellations of the Zodiac from west to east. c. False. Actually, each star seems to rise a little earlier each day because the earth rotates a little farther than 360 every 24 hours. d. False. Actually, each star rises at the same time every day because the position of each star is fixed on the Celestial Sphere. 7. The diagram below shows one possible configuration of the Earth and Moon. The white sides of the circles represent the sides that are lit up by the sun, which is too far away to show. The black sides are in shadow. Moon Earth Note: The relative sizes of the Earth and Moon are correctly shown on this diagram but the distance between them is not to scale (to make the diagram to scale, the Earth and Moon would have to be shown 10x as far apart). What would the moon look like from Earth? a. b. c. d. e.
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson
 Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
drinking straw, protractor, string, and rock. observer on Earth. Sun across the sky on March 21 as seen by an
 1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
1. The diagram below represents some constellations and one position of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. These constellations are visible to an observer on Earth at different times of the year. When
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses
 Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses
 Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Lab Activity on the Moon's Phases and Eclipses 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Earth is rotating on its own axis
 Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
3. a. In the figure below, indicate the direction of the Sun with an arrow.
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
b. Assuming that the sundial is set up correctly, explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
b. So at 12:00 p.m., are the shadows pointing in the direction you predicted? If they are not, you must explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Homework Assignment #7: The Moon
 Name Homework Assignment #7: The Moon 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Chapter 21 Origins of Modern Astronomy Motions of the
Name Homework Assignment #7: The Moon 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Chapter 21 Origins of Modern Astronomy Motions of the
2.2 The Reason for Seasons
 2.2 The Reason for Seasons Our goals for learning: What causes the seasons? How does the orientation of Earth's axis change with time? Thought Question TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer
2.2 The Reason for Seasons Our goals for learning: What causes the seasons? How does the orientation of Earth's axis change with time? Thought Question TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses. Chapters 2 and S1
 The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses Chapters 2 and S1 The celestial sphere and the coordinates system Chapter S1 How to find our way in the sky? Let s
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses Chapters 2 and S1 The celestial sphere and the coordinates system Chapter S1 How to find our way in the sky? Let s
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Astronomy 101 Exam 1 Form A
 Astronomy 101 Exam 1 Form A Name: Lab section number: (In the format M0**. See back page; if you get this wrong you may not get your exam back!) Exam time: one hour and twenty minutes Please put bags under
Astronomy 101 Exam 1 Form A Name: Lab section number: (In the format M0**. See back page; if you get this wrong you may not get your exam back!) Exam time: one hour and twenty minutes Please put bags under
Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018
 1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Day, Night & the Seasons. Lecture 2 1/21/2014
 Day, Night & the Seasons Lecture 2 1/21/2014 Logistics The following students see me after class: A. Gonzalez, Chen Anyone who was not here on first day see me after class Pin Numbers - if you have not
Day, Night & the Seasons Lecture 2 1/21/2014 Logistics The following students see me after class: A. Gonzalez, Chen Anyone who was not here on first day see me after class Pin Numbers - if you have not
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself. What does the universe look like from Earth? Constellations. 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky
 Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Altitude of the Moon and # of Hours it is Up
 Altitude of the and # of Hours it is Up 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Puzzle to Solve: On some days, the moon stays close
Altitude of the and # of Hours it is Up 2008 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Puzzle to Solve: On some days, the moon stays close
Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth
 Name Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico
Name Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico
Motions of the Earth
 Motions of the Earth Our goals for learning: What are the main motions of the Earth in space? How do we see these motions on the ground? How does it affect our lives? How does the orientation of Earth's
Motions of the Earth Our goals for learning: What are the main motions of the Earth in space? How do we see these motions on the ground? How does it affect our lives? How does the orientation of Earth's
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations we
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 1 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 1 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? Why do the constellations
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
Name: Date: 5. The bright stars Vega, Deneb, and Altair form A) the summer triangle. B) the winter triangle. C) the Big Dipper. D) Orion, the Hunter.
 Name: Date: 1. If there are about 6000 stars in the entire sky that can be seen by the unaided human eye, about how many stars would be seen at a particular instant on a given dark night from a single
Name: Date: 1. If there are about 6000 stars in the entire sky that can be seen by the unaided human eye, about how many stars would be seen at a particular instant on a given dark night from a single
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
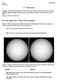 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Exam 1, 9/30/05
 Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Multiple Choice: Select the choice that best answers each question. Write your choice in the blank next to each number. (2 points each) 1. At the North Pole in mid-november, the sun rises at a. North of
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Seasons. What causes the seasons?
 Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
Unit 2. Cycles of the Sky
 Unit 2 Cycles of the Sky The Celestial Sphere Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Unit 2 Cycles of the Sky The Celestial Sphere Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
C) D) 2. The model below shows the apparent path of the Sun as seen by an observer in New York State on the first day of one of the four seasons.
 1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
1. Which diagram best represents the regions of Earth in sunlight on June 21 and December 21? [NP indicates the North Pole and the shading represents Earth's night side. Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
REVIEW CH #0. 1) Right ascension in the sky is very similar to latitude on the Earth. 1)
 REVIEW CH #0 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Right ascension in the sky is very similar to latitude on the Earth. 1) 2) Latitude and right ascension
REVIEW CH #0 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Right ascension in the sky is very similar to latitude on the Earth. 1) 2) Latitude and right ascension
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
The Celestial Sphere. Chapter 1. Constellations. Models and Science. Constellations. Diurnal vs. Annular Motion 9/16/2010
 The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Chapter 1 Image Slides. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 1 Image Slides Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH. 1: CYCLES OF THE SKY CO a 1.1 The Celestial Sphere CO b The nearest star to us is about
Chapter 1 Image Slides Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH. 1: CYCLES OF THE SKY CO a 1.1 The Celestial Sphere CO b The nearest star to us is about
Name: Partner(s): Day/Time: Version: plan
 Precession of the equinoxes https://dept.astro.lsa.umich.edu/ugactivities/labs/precession/precession.html 1 of 3 7/27/2016 10:14 PM Name: Partner(s): Day/Time: Version: plan Precession - Planetarium Activity
Precession of the equinoxes https://dept.astro.lsa.umich.edu/ugactivities/labs/precession/precession.html 1 of 3 7/27/2016 10:14 PM Name: Partner(s): Day/Time: Version: plan Precession - Planetarium Activity
Midterm Review #2-2018
 1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
1. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high tides, and the lowest low tides on Earth? (Diagrams are not drawn to scale.) A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions
Motion of the Sun. motion relative to the horizon. rises in the east, sets in the west on a daily basis. Basis for the unit of time, the DAY
 Motion of the Sun motion relative to the horizon rises in the east, sets in the west on a daily basis Basis for the unit of time, the DAY noon: highest point of Sun in sky relative to the horizon 1 altitude:
Motion of the Sun motion relative to the horizon rises in the east, sets in the west on a daily basis Basis for the unit of time, the DAY noon: highest point of Sun in sky relative to the horizon 1 altitude:
Astronomy 115 Section 4 Week 2. Adam Fries SF State
 Astronomy 115 Section 4 Week 2 Adam Fries SF State afries@sfsu.edu Important Notes: Homework #1 is Due at the beginning of class next time. Attendance Sheet is going around one last time! Homework Questions?
Astronomy 115 Section 4 Week 2 Adam Fries SF State afries@sfsu.edu Important Notes: Homework #1 is Due at the beginning of class next time. Attendance Sheet is going around one last time! Homework Questions?
Observing the Universe for Yourself
 Observing the Universe for Yourself Figure 6-20 Solar-System Formation What does the universe look like from Earth? With the naked eye, we can see more than 2,000 stars as well as the Milky Way. A constellation
Observing the Universe for Yourself Figure 6-20 Solar-System Formation What does the universe look like from Earth? With the naked eye, we can see more than 2,000 stars as well as the Milky Way. A constellation
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
Local Coordinates. These are centered upon you, the observer.
 Astronomy 30, Observing #3 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Materials: This lab, with the star chart completed from the pre-lab. Some sheets of paper for sketches. A pencil with eraser. A small flashlight, ideally
Astronomy 30, Observing #3 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Materials: This lab, with the star chart completed from the pre-lab. Some sheets of paper for sketches. A pencil with eraser. A small flashlight, ideally
C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increase.
 1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
1. Which event is a direct result of Earth's revolution? A) the apparent deflection of winds B) the changing of the Moon phases C) the seasonal changes in constellations viewed in the night sky D) the
Happy Lunar New Year!
 Happy Lunar New Year! (optional) To keep track of time, humans have created calendars based on the Sun (solar) the Moon (lunar) or both! Today is a New Moon Some Asian countries start the year on the second
Happy Lunar New Year! (optional) To keep track of time, humans have created calendars based on the Sun (solar) the Moon (lunar) or both! Today is a New Moon Some Asian countries start the year on the second
Daily & Annual Motions
 Daily & Annual Motions Key Ideas: Daily Motions Reflection of the Earth's Daily Rotation Circumpolar Stars Annual Motions Reflection of the Earth's Orbital Motion Ecliptic: The Path of the Sun Zodiacal
Daily & Annual Motions Key Ideas: Daily Motions Reflection of the Earth's Daily Rotation Circumpolar Stars Annual Motions Reflection of the Earth's Orbital Motion Ecliptic: The Path of the Sun Zodiacal
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS
 UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
A. the spinning of Earth on its axis B. the path of the Sun around Earth
 stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
Introduction to the sky
 Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
3 - Celestial Sphere
 3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
What causes the seasons? 2/11/09
 2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
2/11/09 We can recognize solstices and equinoxes by Sun s path across sky: Summer solstice: Highest path, rise and set at most extreme north of due east. Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
The Moon Project: Descriptions of Topics
 The Moon Project: Descriptions of Topics 2003 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Questions to Answer: Topic #1: Moon Rise and Set
The Moon Project: Descriptions of Topics 2003 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Questions to Answer: Topic #1: Moon Rise and Set
Syllabus, Semester Project, Scales/Scale Models. Questions? One comment
 Syllabus, Semester Project, Scales/Scale Models Questions? One comment Patterns in the Sky: Traxoline Cardinal Directions (N, S, E, W) Positions in the Sky ( high, low ) Meridian, Zenith, Horizon Noon
Syllabus, Semester Project, Scales/Scale Models Questions? One comment Patterns in the Sky: Traxoline Cardinal Directions (N, S, E, W) Positions in the Sky ( high, low ) Meridian, Zenith, Horizon Noon
MATERIALS TO SUPPORT KINESTHETIC ASTRONOMY LESSONS
 MATERIALS TO SUPPORT KINESTHETIC ASTRONOMY LESSONS Dear Educator, The materials here support the Kinesthetic Astronomy lesson that can be downloaded from the Space Science Institute web site [click on
MATERIALS TO SUPPORT KINESTHETIC ASTRONOMY LESSONS Dear Educator, The materials here support the Kinesthetic Astronomy lesson that can be downloaded from the Space Science Institute web site [click on
Astronomy is the oldest science! Eclipses. In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Bad Omens? Comets
 Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Before you Sit. Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium
 Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why?
 (1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements
 ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017
 Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon.
 Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon https://www.lpi.usra.edu/features/012419/oldest-rock/ Study Points Predict the approximate time of day/night you should look for first quarter
Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon https://www.lpi.usra.edu/features/012419/oldest-rock/ Study Points Predict the approximate time of day/night you should look for first quarter
LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season?
 Name: Date: LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season? The relationship between the Sun and Earth have been used since antiquity to measure time. The day is measured by the passage of the Sun
Name: Date: LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season? The relationship between the Sun and Earth have been used since antiquity to measure time. The day is measured by the passage of the Sun
Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about the cause of the seasons. In this lab, you will use globes to study the relative positions of Earth and the Sun during
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about the cause of the seasons. In this lab, you will use globes to study the relative positions of Earth and the Sun during
Define umbra and penumbra. Then label the umbra and the penumbra on the diagram below. Umbra: Penumbra: Light source
 Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.9, SC.8.N.1.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will learn from the lesson. Discuss
Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.9, SC.8.N.1.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will learn from the lesson. Discuss
SPACE REVIEW. 1. The time it takes for the Earth to around the sun is one year. a. rotate b. revolve
 SPACE REVIEW 1. The time it takes for the Earth to around the sun is one year. a. rotate b. revolve 2. Which planet is known as the "Red Planet"? a. Earth b. Mars c. Uranus d. Venus 3. One complete revolution
SPACE REVIEW 1. The time it takes for the Earth to around the sun is one year. a. rotate b. revolve 2. Which planet is known as the "Red Planet"? a. Earth b. Mars c. Uranus d. Venus 3. One complete revolution
Introduction To Astronomy Lesson 1
 Introduction To Astronomy Lesson 1 Topics for this Lesson Earth Based Coordinates The Celestial Sphere and Sky Coordinates The North Star Measuring Distances on the Sky The Motion of Objects in the Sky
Introduction To Astronomy Lesson 1 Topics for this Lesson Earth Based Coordinates The Celestial Sphere and Sky Coordinates The North Star Measuring Distances on the Sky The Motion of Objects in the Sky
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2018 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 29 September 2018 Time limit: 50 min
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2018 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 29 September 2018 Time limit: 50 min
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
November 20, NOTES ES Rotation, Rev, Tilt.notebook. vertically. night. night. counterclockwise. counterclockwise. East. Foucault.
 NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky ABSTRACT Today we will be calibrating your hand as an angular measuring device, and then heading down to the planetarium to see the night sky in motion.
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #2: Observing the Night Sky ABSTRACT Today we will be calibrating your hand as an angular measuring device, and then heading down to the planetarium to see the night sky in motion.
Physics Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3
 Physics 10293 Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3 Introduction In this lab, we will continue using Starry Night to explore some of the most important concepts we will cover in lecture. Continue with
Physics 10293 Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3 Introduction In this lab, we will continue using Starry Night to explore some of the most important concepts we will cover in lecture. Continue with
1-2. What is the name given to the path of the Sun as seen from Earth? a.) Equinox b.) Celestial equator c.) Solstice d.) Ecliptic
 Chapter 1 1-1. How long does it take the Earth to orbit the Sun? a.) one sidereal day b.) one month c.) one year d.) one hour 1-2. What is the name given to the path of the Sun as seen from Earth? a.)
Chapter 1 1-1. How long does it take the Earth to orbit the Sun? a.) one sidereal day b.) one month c.) one year d.) one hour 1-2. What is the name given to the path of the Sun as seen from Earth? a.)
12.1. The Night Sky. Earth s Motions
 12.1 The Night Sky LEARNING TIP Skim Section 12.1. Consider information gathered from the title, headings, figures, and words in bold. What do you expect to learn in this section? Astronomy is the branch
12.1 The Night Sky LEARNING TIP Skim Section 12.1. Consider information gathered from the title, headings, figures, and words in bold. What do you expect to learn in this section? Astronomy is the branch
Yr1 Lesson 1. The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession,
 Yr1 Lesson 1 The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession, Cosmic Intelligence Agency 2015 Astro Lesson 1! Signs, Symbols, Glyphs and Charts! The Celestial Sphere Great Circles of Astrology -
Yr1 Lesson 1 The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession, Cosmic Intelligence Agency 2015 Astro Lesson 1! Signs, Symbols, Glyphs and Charts! The Celestial Sphere Great Circles of Astrology -
Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4)
 Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Daily Motions. Daily Motions. Solar and Sidereal Days. Annual Motions of the Sun. Coordinate system on Earth. Annual Motion of the Stars.
 Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Earth rotates on a tilted axis and orbits the Sun.
 Page of 7 KY CONCPT arth rotates on a tilted axis and orbits the Sun. BFOR, you learned Stars seem to rise, cross the sky, and set because arth turns The Sun is very large and far from arth arth orbits
Page of 7 KY CONCPT arth rotates on a tilted axis and orbits the Sun. BFOR, you learned Stars seem to rise, cross the sky, and set because arth turns The Sun is very large and far from arth arth orbits
Earth Moon Motions A B1
 Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
Earth Moon Motions A B1 1. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that Earth (1) rotates on its axis (2) revolves around the Sun (3) undergoes cyclic tidal changes (4) has a slightly eccentric orbit 9.
ì<(sk$m)=cdfdhh< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Standards Preview Earth Sciences Standard Set 4. Earth Sciences 4. Objects in the sky move in regular and predictable patterns. As a basis for understanding this concept: 4.a. Students know the patterns
Standards Preview Earth Sciences Standard Set 4. Earth Sciences 4. Objects in the sky move in regular and predictable patterns. As a basis for understanding this concept: 4.a. Students know the patterns
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY
 CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
Full Moon. Phases of the Moon
 Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER)
 L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
L.O: EARTH'S 23.5 DEGREE TILT ON ITS AXIS GIVES EARTH ITS SEASONS March 21 (SPRING), June 21(SUMMER), Sept 22 (AUTUMN) & Dec 21(WINTER) 1. The apparent daily path of the Sun changes with the seasons because
Day, Night, Year, and Seasons
 Welcome Astronomers to the Sun, Moon, and Earth! The relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is very important to the existence of life on Earth. Our quest is to find out how their relationships
Welcome Astronomers to the Sun, Moon, and Earth! The relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth is very important to the existence of life on Earth. Our quest is to find out how their relationships
Earth, Sun, and Stars
 Earth, Sun, and Stars Daily Patterns Earth Spins Earth is always moving, even though you don t feel it. One way Earth moves is by spinning around an imaginary line. One end of the line would come out of
Earth, Sun, and Stars Daily Patterns Earth Spins Earth is always moving, even though you don t feel it. One way Earth moves is by spinning around an imaginary line. One end of the line would come out of
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Cosmic Rhythms & Planting Calendar. Working with Rhythms is a major area where BD improves on other streams of organic practices
 Cosmic Rhythms & Planting Calendar Working with Rhythms is a major area where BD improves on other streams of organic practices Introduction Conscious incorporation of rhythms into our agricultural activities
Cosmic Rhythms & Planting Calendar Working with Rhythms is a major area where BD improves on other streams of organic practices Introduction Conscious incorporation of rhythms into our agricultural activities
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Brock University. Test 1, October 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of Students: 470 Date of Examination: October 3, 2017
 Brock University Test 1, October 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of Students: 470 Date of Examination: October 3, 2017 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 17:00 17:50
Brock University Test 1, October 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of Students: 470 Date of Examination: October 3, 2017 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 17:00 17:50
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
10/17/2012. Observing the Sky. Lecture 8. Chapter 2 Opener
 Observing the Sky Lecture 8 Chapter 2 Opener 1 Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 2 Figure 2.6 Figure 2.4 Annotated 3 The Celestial Sphere The celestial sphere is the vast hollow sphere on which the stars appear fixed.
Observing the Sky Lecture 8 Chapter 2 Opener 1 Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 2 Figure 2.6 Figure 2.4 Annotated 3 The Celestial Sphere The celestial sphere is the vast hollow sphere on which the stars appear fixed.
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
