Chem 315/316 Reactions. Bromo organic compounds C1 & C2 carbon skeletons C3 carbon skeletons C4 carbon skeletons. Alcohols. Chem 316 / Beauchamp 1
|
|
|
- Isabel Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic 13 omo organic compounds 1 & 2 carbon skeletons 3 carbon skeletons 4 carbon skeletons 3 5 carbon skeletons 6 carbon skeletons ther patterns A few ways to make - (generic and specific) 2 hν free radical substitution weakest - = fastest rxn Me, 1 o = N 2 2 o, 3 o = N 1 also, P 3, 2 and 1. Tsl / py 2. Na Markovnikov addition 1. B / 3 anit-markovnikov addition 2 Fe 3 earrangements are possible with + intermediates. Alcohols 316 Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
2 hem 316 / Beauchamp 2 1 & 2 carbon skeletons 3 carbon skeletons 4 carbon skeletons 3 5 carbon skeletons 6 carbon skeletons ther patterns A few ways to make - Ns Me, 1 o = N 2 1 o 2 2 o, 3 o = N 1 possible rearrangement N 2 Ns acyl substitution Markovnikov addition (possible rearrangement) 1. B 3 1. gx 2 / / 2. NaB 4 1. Markovnikov addition ( rearrangement) anit-markovnikov addition 1 o o 3 o 1 o 2 o NaB 4 1. NaB 4 3 o 1 o 2 o 1. Al 4 1 o 3 = throw away 1. Al 4 1 o = throw away 1. Al 4 1 o 1. Al 4 There's even more ways, but this is eugh for w. earrangements are possible with + intermediates. Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
3 hem 316 / Beauchamp 3 Ethers 1 & 2 carbon skeletons 3 carbon skeletons 4 carbon skeletons 3 5 carbon skeletons 6 carbon skeletons ther patterns A few ways to make - Na 2 1. gx 2 / 2. NaB 4 Me, 1 o = N 2 2 o, 3 o = N 1 possible rearrangements Markovnikov addition (possible rearrangement) Markovnikov addition ( rearrangement) = a second carbon pattern Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
4 hem 316 / Beauchamp 4 Amines 1 & 2 carbon skeletons 3 carbon skeletons 4 carbon skeletons N N N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 5 carbon skeletons N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 6 carbon skeletons N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 ther patterns N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 us N 2 N 2 A few ways to make -N 2 (1 o, 2 o, 3 o amines) 1. phthalimidate (from phthalimide + Na) 2. Na 1. N 2 (p = 5) 2. Na 3 BN N 2 o amine 1 o amine N 1. NaN 2 3 N 2 2. Al N (p = 5) 2. Na 3 BN (or Pd/ 2 ) N 3 o amine 1. N 3 (p = 5) 2. Na 3 BN N 2 1 o amine 1 o amine 1 N 1. Al 4 2 N 2 1 1, 2 = = 1 o amine 1 =, 2 = = 2 o amine 1, 2 = = 3 o amine N 1. Al4 N 2 1 o amine Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
5 hem 316 / Beauchamp 5 Nitriles 1 & 2 carbon skeletons 3 carbon skeletons 4 carbon skeletons N N N N N N 3 N N 5 carbon skeletons N N N N N N N 6 carbon skeletons N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N ther patterns N N N N N us N N A way to make -N NaN Me, 1 o, 2 o = N 2 N N 3 1 o amine (a. Al 4 b. WK) 1 o amide (l/ 2 ) acid ( 2 4 / 2 / ) aldehyde (a. DIBA b. WK) ketone (a. Mg b. WK) N 2 1 o amides l 2 N good mechanism problem Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
6 hem 316 / Beauchamp 6 Alkynes 2 carbon skeleton 3 carbon skeleton 4 carbon skeletons 5 carbon skeletons 6 carbon skeletons ther patterns A way to make ( = ) 2 eqs. 2 hν 1. excess. NaN excess. NaN 2 elated s 1. NaN = 1 o 1. NaN o 1. NaN o 1. NaN NaN NaN o 2 o 3 o 3 + / 2 (g +2 ) B / / 2 (g +2 ) 2 Pd/ Pd/ 2 quiline Na / N 3 1. NaN excess. NaN 2 (zipper rxn) ontinue with any of the s above. 1. NaN excess. NaN 2 (zipper rxn) Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
7 hem 316 / Beauchamp 7 Thiols and ulfides 1 & 2 carbon skeletons 3 carbon skeletons 4 carbon skeletons () () 3 () () us () () () () 5 carbon skeletons () () () () () () () 6 carbon skeletons () () () () () us () () () () () () us () ther patterns () () () us () us () () () () () () () us () () A way to make - A way to make -- Ns Me, 1 o, 2 o = N 2 thiol Ns Me, 1 o, 2 o = N 2 sulfide Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
8 hem 316 / Beauchamp 8 Aldehydes ( 2 ) n n = any number ( 2 ) n n = any number A few ways to make 2 r 3 /py P 1. 2 B / 2 N 1. DIBA l 1. DIBA ' 1. DIBA 1. 3, -78 o Ketones ( 2 ) n n = any number ( 2 ) n n = any number ' A few ways to make ' 2 r 3 /py P 1. 1 r 3 / 2 Jones or 1 r 3 /py P g g +2 2 N eqs. 1 1 l 1. 1 u 1. 3, -78 o l All 3 Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
9 hem 316 / Beauchamp 9 arboxylic acids ( 2 ) n n = any number ( 2 ) n n = any number A few ways to make 2 2 r 3 / 2 Jones r 3 / 2 Jones 1. Mg N 2 l/ 2 1 o amide ' target ' throw away or throw away ' target 1. 3, -78 o / 2 x KMn 4 / (n -1) carbons l 2 (side rxn) ' N 2 1 o,2 o,3 o amides ' 2 N ' one is a keeper and one is a throw away Acid chlorides l l l l l l ( 2 ) n l n = any number l l l l l l l ( 2 ) n l n = any number A few ways to make l l 2 We use this one. l ll oxalyl chloride l anhydride ( 2 ) ester () 1 o amide (N 3 ) 2 o amide (N 2 ) 3 o amide ( 2 N) aldehyde ( 2 Al = DIBA) ketone ( 2 u + = cuprate) Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
10 hem 316 / Beauchamp 10 Esters ( 2 ) n n = any number ( 2 ) n n = any number A few ways to make 2 ' ' 1. Na 2. X (X = Me,1 o,2 o ) ' ' l -- 3 N ' ' Ts (- 2 ) ' Fischer ester synthesis 2 4 Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
11 hem 316 / Beauchamp 11 Products from s of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in our course: arbon electrophiles 3 methyl X orga reagents N (Mg) orga reagents N arbon and hydrogen nucleophiles Na Na N 2 u Al 4 Na B 4 acetylides cyanide cuprates (LA) alkynes nitriles 2 X coupling alkyls alkyls Al diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBA) N primary X N N alkynes nitriles 2 X coupling alkyls alkyls N secondary X N N E2 nitriles 2 X coupling alkyls alkyls N ethylene oxide 1 o 1 o 1 o 1 o alkynes nitriles 1 o 1 o 1 o N propylene oxide 2 o 2 o 2 o 2 o alkynes nitriles 2 o 2 o 2 o N isobutylene oxide 3 o 3 o 3 o 3 o alkynes nitriles 3 o 3 o 3 o N methanal 1 o 1 o 1 o cyahydrin alkynes N methal methal N simple aldehydes 2 o 2 o 2 o alkynes cyahydrin N 1 o 1 o N simple 3 o 3 o 3 o alkynes cyahydrin unless sterically hindered N 2 o 2 o N simple esters 3 o 3 o (Nu: twice) (Nu: twice) N N 1 o (Nu: twice) 1 o N aldehydes simple carboxylic acids (B: once Nu: once) acid/base net rxn acid/base net rxn N acid/base net rxn acid/base net rxn acid/base net rxn acid/base net rxn l simple acid chlorides 3 o (Nu: twice) 3 o (Nu: twice) N N 1 o 1 o N N simple nitriles N N N 1 o amines (also amines from amides) N aldehydes (also aldehydes from 3 o amides) carbon dioxide carboxylic acids carboxylic acids carboxylic acids N N N N N α,β-unsaturated 3 o 3 o N conjugate addition WK = rmal workup to neutralize the. For the basic s (like above) above this would require mild acid neutralization ( 3 + ). N = or productive result or emphasized N alcohols alcohols N Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
12 hem 316 / Beauchamp 12 ' ' (Mg) ' 2 u Na Al Na 4 B N Na 4 1 o 2 primary X alkyl coupling alkyne nitriles 1 o 2-1 o 2-2 o 2 secondary X epoxides (+2+) (+2+) alkyl coupling (+2+) E2 (+2+) nitriles (+2+) 2 o 2-2 o 2-2 methanal 1 o 1 o 1 o 1 o methal methal aldehydes 2 o 2 o 2 o 2 o 1 o 1 o 2 3 o 3 o 3 o 3 o 2 o 2 o carbon dioxide carboxylic acids carboxylic acids 2 ' esters 3 o (twice) 3 o (twice) 1 o 2 carboxylic acids acid/base x 1 nucleophile x 1 acid/base acid/base 1 o nitrils N N 2 3 o amides 1 o N 2 1 o,2 o,3 o N 2 l acid chlorides 3 o 3 o 1 o α,β-unsaturated carbonyls 1,2-addition 1,2-addition conjugate addition (1,4-addition) 1,2-addition conjugate addition (1,4-addition) WK = workup with electrophilic/acidic 3 + = applicable to our course (, productive or emphasized) 1,2-addition Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
13 hem 316 / Beauchamp 13 Use clues in the target molecule to determine what the last step could have been. nce you work back one step, use clues in that molecule to determine how you could work back one additional step. epeat this process until you get to the necessary starting ome points to remember: 1. can be oxidized to aldehydes (from 1 o ) or carboxylic acids (from 1 o, which can be made into esters or acid chlorides and more), or (from 2 o ). 2. can be made into a leaving group (l,, I, Ts), which can be made into amines, esters, nitriles, ethers, alkynes, thiols, thioethers, replaced with /D and much more. 3. can be eliminated in 2 4 /, but rearrangements could be a problem. can be eliminated with potassium t- butoxide, but regioselectivity can be a problem (requires anti β -/ α -X conformation). tarting tructures: 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 n-propyl n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl 3 3 isopropyl phenyl available until topic 13 TM = butan-1-ol (a few examples) 1. e e = epoxide strategy 2 3 ethyl c c = carbonyl strategy n-propyl 1. B / Na Pd/ 2 1. NaN 2 2. alkyne strategy Pd/ 2 1. NaN alkyne strategy TM = butan-2-ol (a few examples) c c = carbonyl strategy c 3 c = carbonyl strategy 2 e e = epoxide strategy or 1. gx 2 / 2 2. NaB 4 Pd/ 2 1. NaN 2 2. any of these s will work alkyne strategy Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
14 hem 316 / Beauchamp 14 Alkene s unsubstituted mosubstituted mosubstituted trans disubstituted cis disubstituted cis disubstituted gem disubstituted gem disubstituted trisubstituted tetrasubstituted alkyne patterns 2 4 / & & Ts / &,,, & & (l, I are similar) &,,, rearrangement & & &,,, E & Z Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
15 hem 316 / Beauchamp g(ac) 2 / 2 2. NaB 4 (avoids rearrangements) N rearrangement & & &,,, 1. g(ac) 2 / 2. NaB (avoids rearrangements) N rearrangement & & E & Z &,,, vniyl ether vniyl ether 1. (B 3 ) 2 diborane 1. 2 B dialkylborane anti-markovnikov addition / for s / for alkynes N rearrangement & &,,,,,, 1. (B 3 ) / 3 diborane for s 1. 2 B 2. 2 / 3 dialkylborane for alkynes anti-markovnikov addition N rearrangement & & E,,,,,, vniyl bromide vniyl bromide Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
16 hem 316 / Beauchamp 16 2 (l 2 is similar) anti-addition N rearrangement meso (achiral) (dl) or (±) (dl) or (±) & & 2 / 2 (l 2 / 2 is similar) anti-addition / Markovnikov addition an form epoxides with Na N rearrangement meso (achiral) (dl) or (±) (dl) or (±) Pd / 2 palladium & hydrogen syn-addition & & meso Pd / 2 palladium & hydrogen syn-addition Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
17 hem 316 / Beauchamp 17 Na / N 3 in ammonia anti-addition potassium permanganate syn-addition KMn 4 or s 4 osmium tetroxide & (dl) or (±) meso (achiral) meso (achiral) N rearrangement cis and trans to methyl meso (achiral) l meta chloroperbenzoic acid (mpba) syn-addition & & & & & cis and trans to methyl & 1. 3, -78 o cleaves double bone into two = groups (aldehydes or ) Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
18 hem 316 / Beauchamp , -78 o 2. NaB 4 cleaves double bone into two alcohol groups , -78 o cleaves double bone into two = groups (acids or ) , I 2 Zn / u immons mith reagent syn-addition & & & & & & cis and trans to methyl 2 I 2 Zn / u immons mith reagent syn-addition X = or l X X X X 2 X 2 2 X 2 & & & & & X X 2 X 2 X 2 & cis and trans to methyl Z:\classes\315\315 andouts\functional group yn Probs1.doc
Products from reactions of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in the 14 C Game and our course:
 synthesis strategies, hem / / Beauchamp roducts from reactions of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in the Game and our course: arbon electrophiles methyl primary organolithium reagents
synthesis strategies, hem / / Beauchamp roducts from reactions of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in the Game and our course: arbon electrophiles methyl primary organolithium reagents
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton)
 314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
Nucleophilic Substitution & Elimination Chemistry 1
 ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 What kind of mechanisms are possible? What is the major mechanism occuring? Write in ALL mechanism details (lone pairs, formal charge, curved arrows, etc.).
ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 What kind of mechanisms are possible? What is the major mechanism occuring? Write in ALL mechanism details (lone pairs, formal charge, curved arrows, etc.).
These same reaction schemes are available without the mechanistic details, so you can practice filling in those details.
 314/315 reactions and mechanisms through topic 11 and some of topic 12 1 These same reaction schemes are available without the mechanistic details, so you can practice filling in those details. Problems
314/315 reactions and mechanisms through topic 11 and some of topic 12 1 These same reaction schemes are available without the mechanistic details, so you can practice filling in those details. Problems
S N 2 and E2 Mechanisms (strong base/nucleophile competition reacting at a carbon or reacting at a proton)
 Electrophile (Lewis Acid) = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor (can also be an acidic proton = onsted acid) ucleophile (Lewis Base) = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair
Electrophile (Lewis Acid) = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor (can also be an acidic proton = onsted acid) ucleophile (Lewis Base) = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair
Alcohol Synthesis. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Four new mechanisms to learn: S N 2 vs E2 and S N 1 vs E1
 cleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Four new mechanisms to learn: vs E2 and 1 vs E1 = substitution = a leaving group () is lost from a carbon atom () and replaced by nucleophile (:) = nucleophilic
cleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Four new mechanisms to learn: vs E2 and 1 vs E1 = substitution = a leaving group () is lost from a carbon atom () and replaced by nucleophile (:) = nucleophilic
acetaldehyde (ethanal)
 hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CH Organic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- Fall 2013
 C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
When H and OH add to the alkyne, an enol is formed, which rearranges to form a carbonyl (C=O) group:
 Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Chem 263 Nov 7, elimination reaction. There are many reagents that can be used for this reaction. Only three are given in this course:
 hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Carbon-heteroatom single bonds basic C N C X. X= F, Cl, Br, I Alkyl Halide C O. epoxide Chapter 14 H. alcohols acidic H C S C. thiols.
 hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes
 Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Electrophilic Additions o Regio vs stereoselectivity Regio where do the pieces add? Markovnikov s rule hydrogen will go to the side of the double bond with most hydrogens.
Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Electrophilic Additions o Regio vs stereoselectivity Regio where do the pieces add? Markovnikov s rule hydrogen will go to the side of the double bond with most hydrogens.
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Nucleophilic Substitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry Beauchamp 1 Problem 1 - ow can you tell whether the 2 reaction occurs with front side attack, backside attack or front and backside attack? Use the two molecules
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry Beauchamp 1 Problem 1 - ow can you tell whether the 2 reaction occurs with front side attack, backside attack or front and backside attack? Use the two molecules
Chem 2100, Organic Chemistry I WS07, Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hem 2100, rganic hemistry I WS07, r. Rainer Glaser Exam #4 The Final Unsaturated ydrocarbons & xygen hemistry Friday, May 11, 2oo7, 10:30am-12:30pm Name: Answer Key Question 1. Elimination Reactions. 20
hem 2100, rganic hemistry I WS07, r. Rainer Glaser Exam #4 The Final Unsaturated ydrocarbons & xygen hemistry Friday, May 11, 2oo7, 10:30am-12:30pm Name: Answer Key Question 1. Elimination Reactions. 20
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Introduction
 hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
11.5 PREPARATION AND OXIDATIVE CLEAVAGE OF GLYCOLS
 11.5 PEPAATIN AND XIDATIVE EAVAGE F GY 50 These reactions also provide methods for the formation of carbon carbon bonds. eactions that form carbon carbon bonds are especially important in organic chemistry
11.5 PEPAATIN AND XIDATIVE EAVAGE F GY 50 These reactions also provide methods for the formation of carbon carbon bonds. eactions that form carbon carbon bonds are especially important in organic chemistry
Topic 6 Alkyl halide and carbonyl compounds Organic compounds containing a halogen
 Topic 6 Alkyl halide and carbonyl compounds rganic compounds containing a halogen ompounds are named in standard way, eg: 3 1 3 3 2 3 2-iodo-2-methylpropane (tertiary alkyl halide) l 3 4-chlorotoluene
Topic 6 Alkyl halide and carbonyl compounds rganic compounds containing a halogen ompounds are named in standard way, eg: 3 1 3 3 2 3 2-iodo-2-methylpropane (tertiary alkyl halide) l 3 4-chlorotoluene
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Topic 6 Alkyl halide and carbonyl compounds Organic compounds containing a halogen
 Topic 6 Alkyl halide and carbonyl compounds rganic compounds containing a halogen ompounds are named in standard way 3 1 3 3 2 3 2-iodo-2-methylpropane (tertiary alkyl halide) l 3 4-chlorotoluene (aryl
Topic 6 Alkyl halide and carbonyl compounds rganic compounds containing a halogen ompounds are named in standard way 3 1 3 3 2 3 2-iodo-2-methylpropane (tertiary alkyl halide) l 3 4-chlorotoluene (aryl
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles
 Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Aldehydes and Ketones
 Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
Chapter 8: Chemistry of Alkynes (C n H 2n-2 )
 hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
Chem Final Examination August 7, 2004
 Chem 281 2004-2 Final Examination August 7, 2004 Name: Student Number: Note: You are allowed to use models for this exam. Notes, textbooks and calculators are strictly prohibited. Write your final answers
Chem 281 2004-2 Final Examination August 7, 2004 Name: Student Number: Note: You are allowed to use models for this exam. Notes, textbooks and calculators are strictly prohibited. Write your final answers
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
+ HBr!H = OH CH CH 2. HgOAc
 radical substitution Cl hv + Cl 2 + Cl! = Energy radical addition RR + electrophilic addition + C3 C3! = Energy Energy + 2 acetone water + 2 2 +! =! = Energy Energy acid catalyzed hydration + 2 +! = Energy
radical substitution Cl hv + Cl 2 + Cl! = Energy radical addition RR + electrophilic addition + C3 C3! = Energy Energy + 2 acetone water + 2 2 +! =! = Energy Energy acid catalyzed hydration + 2 +! = Energy
10.1. Electrophilic Addition of to to give. Works with HCl HBr HI. Electrophilic Addition Mechanism. H Cl Cl. 3D picture of intermediate: Rxn Coord
 10.1 Electrophilic Addition of to to give Works with I F Electrophilic Addition Mechanism 3D picture of intermediate: E xn oord Thermodynamics: + Δ (kcal/mol) + + = Alkene ydration: Electrophilic Addition
10.1 Electrophilic Addition of to to give Works with I F Electrophilic Addition Mechanism 3D picture of intermediate: E xn oord Thermodynamics: + Δ (kcal/mol) + + = Alkene ydration: Electrophilic Addition
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
Double and Triple Bonds. The addition of an electrophile and a
 Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
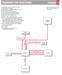 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
Four new mechanisms to learn: S N 2 vs E2 and S N 1 vs E1
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Four new mechanisms to learn: 2 vs E2 and 1 vs E1 = substitution = a leaving group () is lost from a carbon atom () and replaced by nucleophile (u:) = nucleophilic
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Four new mechanisms to learn: 2 vs E2 and 1 vs E1 = substitution = a leaving group () is lost from a carbon atom () and replaced by nucleophile (u:) = nucleophilic
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
 hapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols sp 3 alcohol phenol (aromatic alcohol) pka~ 16-18 pka~ 10 Alcohols contain an group connected to a saturated carbon (sp 3 ) Phenols contain an group connected to a carbon
hapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols sp 3 alcohol phenol (aromatic alcohol) pka~ 16-18 pka~ 10 Alcohols contain an group connected to a saturated carbon (sp 3 ) Phenols contain an group connected to a carbon
Electrophilic Addition
 . Reactivity of = Electrons in pi bond are loosely held. Electrophiles are attracted to the pi electrons. arbocation intermediate forms. Nucleophile adds to the carbocation. Net result is addition to the
. Reactivity of = Electrons in pi bond are loosely held. Electrophiles are attracted to the pi electrons. arbocation intermediate forms. Nucleophile adds to the carbocation. Net result is addition to the
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Synthesis of Amines Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction II. Reductive Amination
 Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Mechanism Summary for A-level AQA Chemistry
 Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols
 Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols [ Chapter 9 Sections: 9.10; Chapter 13 Sections: 13.1-13.3, 13.9-13.10] 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols simple alcohols C3 C3C2 Eddie Sachs 1927-1964 larger alcohols find the
Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols [ Chapter 9 Sections: 9.10; Chapter 13 Sections: 13.1-13.3, 13.9-13.10] 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols simple alcohols C3 C3C2 Eddie Sachs 1927-1964 larger alcohols find the
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE COUNTERPART OF ELIMINATIONS
 ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
Chem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp
 hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp Exams are designed so that no one question will make or break you. The best strategy is to work steadily, starting with those problems you understand best. Partial credit
hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp Exams are designed so that no one question will make or break you. The best strategy is to work steadily, starting with those problems you understand best. Partial credit
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
Nomenclature Question
 Topic 13: i-licker Slides Beauchamp 1 omenclature Question 2 2 a. 1,2-diamino-5,11-dioxo-6-isopropoxy-7-hydroxy-9-cyanoundec-3E-en-1-one b. 3-cyano-5-hydroxy-6-isopropoxy-7,11-dioxo-10,11-diaminoundec-8E-enal
Topic 13: i-licker Slides Beauchamp 1 omenclature Question 2 2 a. 1,2-diamino-5,11-dioxo-6-isopropoxy-7-hydroxy-9-cyanoundec-3E-en-1-one b. 3-cyano-5-hydroxy-6-isopropoxy-7,11-dioxo-10,11-diaminoundec-8E-enal
sp 2 geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear ΔH C-C ΔH C-H % s character pk a 464 KJ/mol 33% 44
 hapter 10: Alkynes 10.1 Introduction to Alkynes ~ 111 ~ 122 1.06 Å 180 1.1 Å ~ 116 1.08 Å 1.54 Å 1.34 Å 1.20 Å hybridization of sp 3 sp 2 sp geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear 368 KJ/mol 632 KJ/mol
hapter 10: Alkynes 10.1 Introduction to Alkynes ~ 111 ~ 122 1.06 Å 180 1.1 Å ~ 116 1.08 Å 1.54 Å 1.34 Å 1.20 Å hybridization of sp 3 sp 2 sp geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear 368 KJ/mol 632 KJ/mol
Chem 263 Nov 3, 2016
 hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
Hydrogen iodide is a strong acid and will drive the reverse reaction, meaning the forward reaction will not occur.
 EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
Loudon Chapter 14 Review: Reactions of Alkynes Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/16/2018
 An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Isomerism CH 4 C 2 H 6 C 3 H 8 C 4 H 10 C 5 H 12. Constitutional isomers...
 Isomerism 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 5 12 onstitutional isomers... 3 8 Positional isomers... Functional isomers... ow many constitutional isomers are there for the formula 4 8? arbon atoms are often classified as
Isomerism 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 5 12 onstitutional isomers... 3 8 Positional isomers... Functional isomers... ow many constitutional isomers are there for the formula 4 8? arbon atoms are often classified as
+ HBr ΔH = OH CH CH 2. HgOAc
 radical substitution l hv + l 2 + l Energy radical addition RR + electrophilic addition + 3 3 Energy Energy + 2 acetone water + 2 2 + Energy Energy acid catalyzed hydration + 2 + Energy + + 2 + + 2 = 2
radical substitution l hv + l 2 + l Energy radical addition RR + electrophilic addition + 3 3 Energy Energy + 2 acetone water + 2 2 + Energy Energy acid catalyzed hydration + 2 + Energy + + 2 + + 2 = 2
CHEMISTRY Topic #8: Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group In Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups In Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group O O - - O - O R Y R C+ Y R Y Nu -Ȳ R N u + Y=goodleavinggroup
Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group In Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups In Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group O O - - O - O R Y R C+ Y R Y Nu -Ȳ R N u + Y=goodleavinggroup
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
ALCOHOLS: Properties & Preparation
 ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: -, where is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol. 2.
ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: -, where is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol. 2.
Learning Guide for Chapter 14 - Alcohols (I)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 14 - Alcohols (I) I. Introduction to Alcohols and Thiols II. Acid/base Behavior of Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols III. Nomenclature of Alcohols IV. Synthesis of Alcohols Previous
Learning Guide for Chapter 14 - Alcohols (I) I. Introduction to Alcohols and Thiols II. Acid/base Behavior of Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols III. Nomenclature of Alcohols IV. Synthesis of Alcohols Previous
Reduction. Boron based reagents. NaBH 4 / NiCl 2. Uses: Zn(BH 4 ) 2. Preparation: Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model.
 Uses: Ar N 2 Ar N 2 Ar N Ar N 2 eduction Boron based reagents NaB 4 / NiCl 2 2 Ar C N Ar C N 2 Preparation: Zn(B 4 ) 2 ZnCl 2 (Ether) NaB 4 Zn(B 4 ) 2 Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model
Uses: Ar N 2 Ar N 2 Ar N Ar N 2 eduction Boron based reagents NaB 4 / NiCl 2 2 Ar C N Ar C N 2 Preparation: Zn(B 4 ) 2 ZnCl 2 (Ether) NaB 4 Zn(B 4 ) 2 Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model
2Dstructuredrawing Chem314 Beauchamp
 2Dstructuredrawing hem314 Beauchamp 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 2 (neutral) (cation) (anion) (free radical) use zig-zag drawing for sp 3 chains 1 o carbocation 1 o carbanion 1 o free radical 3 3 3 3 3 3 (cation)
2Dstructuredrawing hem314 Beauchamp 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 2 (neutral) (cation) (anion) (free radical) use zig-zag drawing for sp 3 chains 1 o carbocation 1 o carbanion 1 o free radical 3 3 3 3 3 3 (cation)
CHEM 203. Midterm Exam 1 October 31, 2008 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Alkenes. Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula C n H 2n. Nomenclature
 Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Química Orgânica I. Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1
 Química rgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB Q I 2007/08 1 alcohols Adaptado de rganic Chemistry, 6th Edition; Wade rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition; McMurry AFB Q I 2007/08 2 Typical
Química rgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB Q I 2007/08 1 alcohols Adaptado de rganic Chemistry, 6th Edition; Wade rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition; McMurry AFB Q I 2007/08 2 Typical
Chapter 1 Introduction, Formulas and Spectroscopy Overview
 hapter 1 Introduction, Formulas and Spectroscopy verview Problem 1 (p 1) - elpful equations: c = ( )( ) and = (1 / ) so c = ( ) / ( ) c =. x 1 8 m/sec =. x 1 1 cm/sec a. Which photon of electromagnetic
hapter 1 Introduction, Formulas and Spectroscopy verview Problem 1 (p 1) - elpful equations: c = ( )( ) and = (1 / ) so c = ( ) / ( ) c =. x 1 8 m/sec =. x 1 1 cm/sec a. Which photon of electromagnetic
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity Tutorial Six Question 1
 en Mills, University of istol, 4 March 2008 rganic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity Tutorial Six Question 1 ydrobromination of styrene hydrogen adds to the terminal carbon, so that the carbocation can
en Mills, University of istol, 4 March 2008 rganic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity Tutorial Six Question 1 ydrobromination of styrene hydrogen adds to the terminal carbon, so that the carbocation can
Lecture Notes Chemistry Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 36 Synthesis of Amines
 Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Loudon Chapter 10 Review: Alcohols & Thiols Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/26/2016
 Alcohols (R) and thiols (RS) have many reactions in common with alkyl halides, but they don t do everything exactly the same. The main difference between this and alkyl halide chemistry is that unlike
Alcohols (R) and thiols (RS) have many reactions in common with alkyl halides, but they don t do everything exactly the same. The main difference between this and alkyl halide chemistry is that unlike
