Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
|
|
|
- Christal Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe thunderstorms o Mesoscale convective systems (MCS) Squall line Bow echo Mesoscale convective complexes o Supercell thunderstorms Thunderstorm formation o Key altitudes o Humidity o Instability o Triggering vs convective inhibition o Wind shear Distribution of thunderstorms Thunderstorm outlooks, watches, and warnings Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
2 Thunderstorm Appearance A thunderstorm is a convective storm with large vertical extent, often extending from the boundary layer to the tropopause. What are the main parts of an ordinary thunderstorm? - updraft tower - anvil - rain and downdraft - gust front What causes the flat anvil top of a thunderstorm to form? Gust front: The boundary that separates cold downdraft air from surrounding warmer air at the surface. What causes the downdraft and gust front to form?
3 Thunderstorm Cells and Evolution The basic element of a thunderstorm is a thunderstorm cell. A thunderstorm cell is often as deep (~10 km) as it is wide. What are the three stages of a thunderstorm cell s life cycle? What three conditions are needed for the development of a thunderstorm cell? Why does the air parcel rise during the towering cumulus stage of thunderstorm development? During the mature stage the thunderstorm is at its most intense. What cloud particle and precipitation types are present in the thunderstorm cell during the mature stage? Rain (and sometimes small hail) and lightning occur during this stage.
4 What causes the storm to enter the dissipating stage? The entire life cycle of an ordinary thunderstorm cell usually lasts less than 1 hour. How can new storms form after the original thunderstorm cell dissipates? Thunderstorm Types and Organization Single cell thunderstorm Single cell thunderstorms (also called air mass thunderstorms) develop in a manner similar to the ordinary thunderstorm cell described above. In what environment are single cell thunderstorms likely to form? An air mass thunderstorm that produces short duration severe weather is called a pulse storm. Multicell Thunderstorms Most thunderstorms in North America are multicell storms. Multiple cells (evident on radar) are embedded in the single cloud mass of a multicell storm. What allows multiple cells to form and co-exist in this type of thunderstorm?
5 Steering-level winds: Average winds in the lowest ~6 km of the atmosphere? Orographic Thunderstorms What is the direction of movement of individual cells within a multicell thunderstorm relative to the steering-level winds? What is the direction of movement of the entire multicell thunderstorm relative to the steering-level winds? What causes this difference in movement? Orographic thunderstorm: Single or multicell storm triggered by mountains What conditions lead to orographic thunderstorms remaining stationary? What type of hazardous weather can occur under these conditions? How do orographic thunderstorms triggered over the Rocky Mountains impact weather over the Great Plains? Severe Thunderstorms Severe thunderstorm: A thunderstorm that produces at least one of the following: hail with a diameter of at least 1 inch, wind gusts of at least 50 kts, or a tornado.
6 Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCS) Mesoscale convective system: A type of multicell storm often organized as a narrow line of thunderstorms with heavy precipitation at its leading edge and a trailing region of lighter precipitation. How do the environmental conditions that favor MCS development differ from those found for single or other multicell thunderstorms? What can trigger an MCS? How does the cold air pool behind the leading edge of an MCS form? Meso-high: A mesoscale sized area of high pressure that forms at the surface as a result of the cold air pool. What causes low pressure to form at mid-levels in an MCS? The rear inflow jet (RIJ) forms as a result of the pressure gradient created by the mid-level area of low pressure. How does precipitation falling from the rear of the MCS impact the RIJ? What impact does this have on severe weather occurring at the surface?
7 Squall line A squall line is a type of MCS that is triggered by a linear feature such as a cold front, dry line, or gust front. Squall lines can be hundreds of km long but tens to a few hundred km wide and persist for several hours to several days. Bow Echo A bow echo is a type of MCS that will form when a strong updraft and moderate to strong wind shear in the lowest 2 to 3 km of the environment is present. What impact does the strong wind shear have on the bow echo? Derecho: A sequence of bow echoes that cause wind damage along a path >400 km for at least 3 h with wind speeds 26 m s -1 and gusts 33 m s -1. Mesoscale Convective Complex (MCC) Mesoscale convective complex (MCC): A long-lived large MCS with a cloud shield diameter 350 km, cloud top temperature -33ºC and cloud top temperature -53ºC in a region with a diameter 250 km. MCCs are often triggered by warm fronts or weak mid-tropospheric waves and are often associated with low level jets.
8 Supercell Thunderstorms Supercell thunderstorm: A violent thunderstorm that has a rotating updraft. What features are present in a supercell thunderstorm that are not seen in an ordinary thunderstorm? - mesocyclone (rotating updraft with striations) - overshooting top (dome) - forward flank downdraft (FFD) - rear flank downdraft (RFD) - flanking line Additional cloud features seen with supercell thunderstorms include: - beaver tail - cumulus along the flanking line - pileus cloud over dome - mammatus (can also be seen in ordinary thunderstorms) - wall cloud - tail cloud - scud - funnel cloud or tornado How will the anvil seen with a supercell differ from that in an ordinary thunderstorm? What conditions favor the formation of supercell thunderstorms?
9 A supercell thunderstorm can last for several hours with new thunderstorms (the flanking line) triggered along the supercell RFD outflow. The rotating mesocyclone in a supercell has a diameter of 3 to 10 km and extends through the entire depth of the supercell. What types of weather are associated with supercell thunderstorms? Supercells are responsible for creating most of the violent (EF3 to EF5) tornadoes. How does the formation of the FFD and RFD differ? How is precipitation distributed across a supercell? Weak echo region (WER): An area of weak or no radar echo near the updraft. This is also known as an echo-free vault. What causes most of the precipitation to fall ahead of the updraft? Why is hail and heavy rain observed adjacent to the updraft while lighter precipitation is observed further from the updraft? There are three general types of supercell thunderstorms - classic (CL), low-precipitation (LP), and high-precipitation (HP) supercells
10 LP supercell HP supercell How do the three types of supercells differ? Thunderstorm Formation What three conditions are needed to allow a thunderstorm to develop? What additional condition is needed for stronger thunderstorms to form?
11 Key Altitudes Thermodynamic diagrams can be used to illustrate the thermodynamic features associated with thunderstorms and their environments. From an environmental sounding the mixed layer, capping inversion, and tropopause can be identified. As discussed in chapter 6 the change in air parcel thermodynamic state can be illustrated on a thermodynamic diagram. The air parcel represents the thermodynamic state of a thunderstorm and allows this state to be compared to the thunderstorm s environment. Lifting condensation level (LCL): The level where a rising air parcel first becomes saturated. Level of free convection (LFC): The level where a rising air parcel first becomes warmer than its environment. Equilibrium level (EL): The level above the LFC where a rising air parcel becomes cooler than its environment. This is also called the limit of convection (LOC).
12 An overshooting top (overshooting dome) can form above the EL when the momentum of a strong updraft carries the rising air parcel above its EL. Example: Use the data below to plot the environmental sounding and the air parcel temperature as it rises from 1000 mb to 200 mb on the thermodynamic diagram below m g/kg m m m m Pressure (mb) m 5574 m m m 766 m 111 m Temperature (deg C) An air parcel at the surface (1000 mb) has a temperature of 30 deg C and a dew point temperature of 20 deg C. The following environmental temperatures were observed by a radiosonde: 100 mb -30 deg C 200 mb -40 deg C 300 mb -40 deg C 500 mb -10 deg C 700 mb 5 deg C 800 mb 10 deg C 1000 mb 30 deg C
13 What is the air parcel lifting condensation level (LCL)? How does the rate at which the air parcel temperature decreases with height change above the LCL? What causes this change? To what level must the surface air parcel be lifted in order for a thunderstorm to develop? What is the name of this level in the atmosphere? At what pressure will the air parcel cease to rise? What is the name given to this level in the atmosphere? High Humidity in the ABL Thunderstorms often draw air from the ABL. As this air rises in the thunderstorm water vapor condenses and releases latent heat, which is the main energy source for thunderstorms. The warmer and moister the ABL the stronger a thunderstorm will become. What variables can be used to assess the amount of moisture in the ABL? Instability, CAPE, and Updrafts What conditions define a conditionally unstable atmosphere? Thunderstorms form when the atmosphere is conditionally unstable. Convective available potential energy (CAPE): A measure of the energy available to create an updraft in a rising air parcel CAPE is proportional to the area on a thermodynamic diagram between an air parcel s temperature and the temperature of its environment between the LFC and the EL.
14 Example: Illustrate the CAPE on the thermodynamic diagram for the example thunderstorm above. CAPE increases as the parcel temperature becomes increasingly warmer than the environmental temperature. The amount of CAPE can be used to estimate potential thunderstorm intensity. As the CAPE increases the maximum updraft speed (w max ) in a thunderstorm will increase. w max = 2 CAPE Due to the effects of frictional drag the likely maximum updraft speed is: w max likely = w max / 2
15 Triggering vs Convective Inhibition Often air in the ABL will rise to the top of the ABL but cannot rise up to its LFC due to a capping inversion. An external mechanism is needed to lift the air parcel to its LFC and trigger the development of a thunderstorm. The negative area, on a thermodynamic diagram, between the air parcel temperature and the environmental temperature before the air parcel reaches its LFC is proportional to the convective inhibition (CIN). This CIN must be overcome before a thunderstorm can form. The amount of CIN can be used to determine if a thunderstorm will develop. How does CIN determine how warm and humid the ABL can become, and thus how strong of a thunderstorm could form?
16 What external processes can serve as a trigger for thunderstorm development? Boundaries between air masses Orographic lifting Gravity waves Localized intense heating
17 Wind Shear Wind shear: The change of horizontal wind speed and/or direction with height. One measure of wind shear is the change of the wind components over some layer of the atmosphere: ΔM = ( ΔU) 2 + ( ΔV ) 2 Meteorologists use a hodograph to illustrate wind shear. Weak wind shear is associated with single cell (ordinary) thunderstorms. Moderate to strong wind shear is needed to allow multicell or supercell thunderstorms to form. Why is moderate to strong wind shear needed for the formation of long lived thunderstorms?
18 What role does wind shear play in generating the rotation in a supercell thunderstorm? The bulk Richardson number (BRN) is a measure of instability and wind shear. BRN = CAPE 0.5 ΔM ( ) 2 The BRN can be used to forecast the type of thunderstorm that may form.
19 Distribution of Thunderstorms Average number of days per year when thunderstorms occur Thunderstorm Outlooks, Watches, and Warnings The National Weather Service (NWS) issues severe weather outlooks, watches, and warnings to advise the public of severe weather risks. Thunderstorm outlook: A general statement about the level of risk for severe weather occurring in the next 6 to 72 h Watch: A statement issued by the National Weather Service to indicate that conditions are favorable for severe weather in the next 0.5 to 6 h Warning: Issued to indicate that severe weather is occurring or is imminent.
Advanced Spotter Training Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms
 Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms From Last Time We discussed the different ways to make air rise. We discussed convection, convergence, and the different kinds of fronts.
Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms From Last Time We discussed the different ways to make air rise. We discussed convection, convergence, and the different kinds of fronts.
Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning
 Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds
Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms. Spring 2018
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2018 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2018 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning
 Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning Thunderstorms are responsible for most of what we refer to as severe weather,
Thunderstorm: a cumulonimbus cloud or collection of cumulonimbus clouds featuring vigorous updrafts, precipitation and lightning Thunderstorms are responsible for most of what we refer to as severe weather,
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting. Primer on organized convection
 Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Practical Use of the Skew-T, log-p diagram for weather forecasting Primer on organized convection Outline Rationale and format of the skew-t, log-p diagram Some basic derived diagnostic measures Characterizing
Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology. Thunderstorms
 1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
1 of 7 Thunderstorm Notes by Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology Thunderstorms There are three types of thunderstorms: single-cell (or air mass) multicell (cluster or squall line) supercell Although
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #11 Severe Weather 54 points
 ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #11 Severe Weather 54 points Question 1 (10 points): Thunderstorm development a) Sketch and describe the stages of development of a single cell thunderstorm. About how long does
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #11 Severe Weather 54 points Question 1 (10 points): Thunderstorm development a) Sketch and describe the stages of development of a single cell thunderstorm. About how long does
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part VI. Supercell Storms. Supercell Photos
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part VI. Supercell Storms Photographs Todd Lindley (This part contains materials taken from UCAR MCS training module) Supercell Photos 1 Introduction A supercel storm is defined
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part VI. Supercell Storms Photographs Todd Lindley (This part contains materials taken from UCAR MCS training module) Supercell Photos 1 Introduction A supercel storm is defined
TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst
 THUNDERSTORMS TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst What are Thunderstorms? A storm produced by a cumulonimbus cloud that contains lightning and thunder
THUNDERSTORMS TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst What are Thunderstorms? A storm produced by a cumulonimbus cloud that contains lightning and thunder
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis. Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus
 Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients. Ted Funk
 Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients Ted Funk NWS Louisville, KY Spring 2002 Environmental Parameters Supercells occur within environments exhibiting several wellknown characteristics
Tornadogenesis in Supercells: The Three Main Ingredients Ted Funk NWS Louisville, KY Spring 2002 Environmental Parameters Supercells occur within environments exhibiting several wellknown characteristics
Thunderstorms. Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms. Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms. Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms 5/2/11
 A storm containing lightning and thunder; convective storms Chapter 14 Severe thunderstorms: At least one: large hail wind gusts greater than or equal to 50 kt Tornado 1 2 Ordinary Cell Ordinary Cell AKA
A storm containing lightning and thunder; convective storms Chapter 14 Severe thunderstorms: At least one: large hail wind gusts greater than or equal to 50 kt Tornado 1 2 Ordinary Cell Ordinary Cell AKA
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters
 Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis. Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus
 Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Warm season forecasting! Some material adapted from Material Produced at COMET for their Residence Course in Hydrometeorology
 Warm season forecasting! Some material adapted from Material Produced at COMET for their Residence Course in Hydrometeorology 1 Outline! Types of stability and application to forecasting! Dry and moist
Warm season forecasting! Some material adapted from Material Produced at COMET for their Residence Course in Hydrometeorology 1 Outline! Types of stability and application to forecasting! Dry and moist
Meteorology. Chapter 10 Worksheet 2
 Chapter 10 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Downdrafts totally dominate the in the development of a thunderstorm. a) dissipating stage b) mature
Chapter 10 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Downdrafts totally dominate the in the development of a thunderstorm. a) dissipating stage b) mature
10/21/2012. Chapter 10 Thunderstorms. Part II. Growth and Development of ordinary Cell Thunderstorms Thunderstorm Electrification.
 Chapter 10 Thunderstorms Part I Growth and Development of ordinary Cell Thunderstorms Thunderstorm Electrification Tornadoes Part II Simplified model depicting the life cycle of an ordinary thunderstorm
Chapter 10 Thunderstorms Part I Growth and Development of ordinary Cell Thunderstorms Thunderstorm Electrification Tornadoes Part II Simplified model depicting the life cycle of an ordinary thunderstorm
contact with ground for 1 hour plus, starting 1500 MDT moved N., covered about 37 km width varied m
 Goal for today: Finish Ch. 11 Lightning, Thunder & Tornadoes 16 Nov., 2011 Edmonton tornado 31 July 1987 contact with ground for 1 hour plus, starting 1500 MDT moved N., covered about 37 km width varied
Goal for today: Finish Ch. 11 Lightning, Thunder & Tornadoes 16 Nov., 2011 Edmonton tornado 31 July 1987 contact with ground for 1 hour plus, starting 1500 MDT moved N., covered about 37 km width varied
CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A thunderstorm is considered to be a weather system. a. synoptic-scale b. micro-scale c. meso-scale 2. By convention, the mature stage
CHAPTER 11 THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A thunderstorm is considered to be a weather system. a. synoptic-scale b. micro-scale c. meso-scale 2. By convention, the mature stage
HAZARDOUS WEATHER 1. Dr. Julie Laity Geography 266
 HAZARDOUS WEATHER 1 Dr. Julie Laity Geography 266 Violent Weather Thunderstorms Atmospheric turbulence Lightning and thunder Hail Derechos Tornadoes Tornado measurement and science Tropical Cyclones Hurricanes
HAZARDOUS WEATHER 1 Dr. Julie Laity Geography 266 Violent Weather Thunderstorms Atmospheric turbulence Lightning and thunder Hail Derechos Tornadoes Tornado measurement and science Tropical Cyclones Hurricanes
Department of Geosciences San Francisco State University Spring Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points)
 Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
NOAA S National Weather Service
 NOAA S National Weather Service Elite Concepts of Severe Storm Spotting 2011 Rusty Kapela Milwaukee/Sullivan www.weather.gov/mkx Elite Spotter Outline Review Types of T storms Tornadic Supercell Classic,
NOAA S National Weather Service Elite Concepts of Severe Storm Spotting 2011 Rusty Kapela Milwaukee/Sullivan www.weather.gov/mkx Elite Spotter Outline Review Types of T storms Tornadic Supercell Classic,
Review of Basic Severe Thunderstorm & Tornado Spotting Concepts. Jim Allsopp National Weather Service Chicago/Romeoville, IL
 Review of Basic Severe Thunderstorm & Tornado Spotting Concepts Jim Allsopp National Weather Service Chicago/Romeoville, IL Why Do We Need Spotters? Radar has limitations, only spotters can provide view
Review of Basic Severe Thunderstorm & Tornado Spotting Concepts Jim Allsopp National Weather Service Chicago/Romeoville, IL Why Do We Need Spotters? Radar has limitations, only spotters can provide view
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Mesoscale Convective Systems. The COMET Program March 2002
 Mesoscale Convective Systems The COMET Program March 2002 Overview! Introduction to MCSs! Squall Lines! Bow Echoes! Mesoscale Convective Complexes Introduction Definition! Mesoscale convective systems
Mesoscale Convective Systems The COMET Program March 2002 Overview! Introduction to MCSs! Squall Lines! Bow Echoes! Mesoscale Convective Complexes Introduction Definition! Mesoscale convective systems
NOAA S National Weather Service
 NOAA S National Weather Service Night Spotting Advanced Concepts of Severe Storm Spotting 2012 Rusty Kapela Milwaukee/Sullivan Weather.gov/milwaukee Problems Spotters Encounter Spotters can only see a
NOAA S National Weather Service Night Spotting Advanced Concepts of Severe Storm Spotting 2012 Rusty Kapela Milwaukee/Sullivan Weather.gov/milwaukee Problems Spotters Encounter Spotters can only see a
Reading. What meteorological conditions precede a thunderstorm? Thunderstorms: ordinary or single cell storms, multicell storms, supercell storms
 Thunderstorms: ordinary or single cell storms, multicell storms, supercell storms Reading Ahrens, Chapter 14: Thunderstorms and Tornadoes This lecture + next (Lightning, tornadoes) will cover the topic.
Thunderstorms: ordinary or single cell storms, multicell storms, supercell storms Reading Ahrens, Chapter 14: Thunderstorms and Tornadoes This lecture + next (Lightning, tornadoes) will cover the topic.
THUNDERSTORMS Brett Ewing October, 2003
 THUNDERSTORMS Brett Ewing October, 2003 A natural hazard that occurs often on a daily basis in the lower and mid-latitudes is thunderstorms. Thunderstorms is a weather system that can produce lightning,tornadoes,
THUNDERSTORMS Brett Ewing October, 2003 A natural hazard that occurs often on a daily basis in the lower and mid-latitudes is thunderstorms. Thunderstorms is a weather system that can produce lightning,tornadoes,
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall ERTH FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES NAME SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Fall 2016 Part 1. Weather Map Interpretation ERTH 365.02 FINAL EXAMINATION KEY 200 pts Questions 1 through 9 refer to Figure 1,
Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting and Climatology in Arizona. Ken Drozd Warning Coordination Meteorologist NOAA/NWS Tucson, AZ
 Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting and Climatology in Arizona Ken Drozd Warning Coordination Meteorologist NOAA/NWS Tucson, AZ THUNDERSTORM FORMATION All thunderstorms result from the same necessary conditions
Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting and Climatology in Arizona Ken Drozd Warning Coordination Meteorologist NOAA/NWS Tucson, AZ THUNDERSTORM FORMATION All thunderstorms result from the same necessary conditions
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011
 Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011 Instructions: Write your name (last name and first name) on your bubble sheet. Write your student identification number on the bubble sheet, and carefully and completely
Test Form: A Key Final Exam: Spring 2011 Instructions: Write your name (last name and first name) on your bubble sheet. Write your student identification number on the bubble sheet, and carefully and completely
CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Chapter 14. Contents. Copyright 2011, 2015 by Roland Stull. Meteorology for Scientists and Engineers, 3rd Ed.
 Chapter 14 Copyright 2011, 2015 by Roland Stull. Meteorology for Scientists and Engineers, 3rd Ed. Thunderstorms Contents Thunderstorm Characteristics 481 Appearance 482 Clouds Associated with Thunderstorms
Chapter 14 Copyright 2011, 2015 by Roland Stull. Meteorology for Scientists and Engineers, 3rd Ed. Thunderstorms Contents Thunderstorm Characteristics 481 Appearance 482 Clouds Associated with Thunderstorms
Advanced Spotter Training: Anticipating Severe Weather Threats. Professor Paul Sirvatka College of DuPage Meteorology
 Advanced Spotter Training: Anticipating Severe Weather Threats College of DuPage Meteorology Preparing for Severe Weather Preparedness involves understanding the probable and potential threats. Understanding
Advanced Spotter Training: Anticipating Severe Weather Threats College of DuPage Meteorology Preparing for Severe Weather Preparedness involves understanding the probable and potential threats. Understanding
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 6 Content: Severe Weather Notes
 Severe weather can pose a risk to you and your property. Meteorologists monitor extreme weather to inform the public about dangerous atmospheric conditions. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes are
Severe weather can pose a risk to you and your property. Meteorologists monitor extreme weather to inform the public about dangerous atmospheric conditions. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes are
Meteorology Lecture 18
 Meteorology Lecture 18 Robert Fovell rfovell@albany.edu 1 Important notes These slides show some figures and videos prepared by Robert G. Fovell (RGF) for his Meteorology course, published by The Great
Meteorology Lecture 18 Robert Fovell rfovell@albany.edu 1 Important notes These slides show some figures and videos prepared by Robert G. Fovell (RGF) for his Meteorology course, published by The Great
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment. Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS)
 Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Weather Systems. The air around high-pressure weather systems tends to swirl in a clockwise direction, and usually brings clear skies.
 Weather Systems A weather system is a set of temperature, wind, pressure, and moisture conditions for a certain region that moves as a unit for a period of several days. Low-pressure weather systems form
Weather Systems A weather system is a set of temperature, wind, pressure, and moisture conditions for a certain region that moves as a unit for a period of several days. Low-pressure weather systems form
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Photographs Todd Lindley 3.2 Ordinary or "air-mass storm 3.2.1. Main Characteristics Consists of a single cell (updraft/downdraft pair) Forms in environment characterized
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Photographs Todd Lindley 3.2 Ordinary or "air-mass storm 3.2.1. Main Characteristics Consists of a single cell (updraft/downdraft pair) Forms in environment characterized
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes Photographs Todd Lindley Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system 1 Bright
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes Photographs Todd Lindley Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system 1 Bright
14 THUNDERSTORM FUNDAMENTALS
 Copyright 7 by Roland Stull. Practical Meteorology: An Algebra-based Survey of Atmospheric Science v. 4 THUNDERSTORM FUNDAMENTALS Contents 4.. Thunderstorm Characteristics 48 4... Appearance 48 4... Clouds
Copyright 7 by Roland Stull. Practical Meteorology: An Algebra-based Survey of Atmospheric Science v. 4 THUNDERSTORM FUNDAMENTALS Contents 4.. Thunderstorm Characteristics 48 4... Appearance 48 4... Clouds
Convective Dynamics. Jeremy A. Gibbs. March 3, University of Oklahoma
 Convective Dynamics Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu March 3, 2015 1 / 70 Overview Administrative Homework 2 Exam 1 Convective Dynamics Introduction to Thunderstorms/Moist Atm. Convection
Convective Dynamics Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu March 3, 2015 1 / 70 Overview Administrative Homework 2 Exam 1 Convective Dynamics Introduction to Thunderstorms/Moist Atm. Convection
The Earth System - Atmosphere III Convection
 The Earth System - Atmosphere III Convection Thunderstorms 1. A thunderstorm is a storm that produces lightning (and therefore thunder) 2. Thunderstorms frequently produce gusty winds, heavy rain, and
The Earth System - Atmosphere III Convection Thunderstorms 1. A thunderstorm is a storm that produces lightning (and therefore thunder) 2. Thunderstorms frequently produce gusty winds, heavy rain, and
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox
 Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Anthony A. Rockwood Robert A. Maddox An unusually intense MCS produced large hail and wind damage in northeast Kansas and northern Missouri during the predawn hours of June 7 th, 1982. Takes a look at
Section 13-1: Thunderstorms
 Section 13-1: Thunderstorms Chapter 13 Main Idea: The intensity and duration of thunderstorms depend on the local conditions that create them. Air-mass thunderstorm Mountain thunderstorm Sea-breeze thunderstorm
Section 13-1: Thunderstorms Chapter 13 Main Idea: The intensity and duration of thunderstorms depend on the local conditions that create them. Air-mass thunderstorm Mountain thunderstorm Sea-breeze thunderstorm
Tornado Occurrences. Tornadoes. Tornado Life Cycle 4/12/17
 Chapter 19 Tornadoes Tornado Violently rotating column of air that extends from the base of a thunderstorm to the ground Tornado Statistics Over (100, 1000, 10000) tornadoes reported in the U.S. every
Chapter 19 Tornadoes Tornado Violently rotating column of air that extends from the base of a thunderstorm to the ground Tornado Statistics Over (100, 1000, 10000) tornadoes reported in the U.S. every
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Instabilities and Basic Convection
 Instabilities and Basic Convection Buoyant Instability (gravity is restoring force) Assume a stationary incompressible fluid (like water), so that ρ = ρ 0 + ρ/ z z and also it is in hydrostatic equilibrium
Instabilities and Basic Convection Buoyant Instability (gravity is restoring force) Assume a stationary incompressible fluid (like water), so that ρ = ρ 0 + ρ/ z z and also it is in hydrostatic equilibrium
Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Spring 2016 Meteorology 260
 Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Spring 2016 Meteorology 260 Name Laboratory #9 Key: Joplin Tornado Day Subsynoptic, Thermodynamic, and Wind Shear Setting Part A: 1600 UTC Surface Chart Subsynoptic
Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Spring 2016 Meteorology 260 Name Laboratory #9 Key: Joplin Tornado Day Subsynoptic, Thermodynamic, and Wind Shear Setting Part A: 1600 UTC Surface Chart Subsynoptic
Final Exam Clicker Questions ATOC 1050 Spring 2011 Chapter 16: Mountain Snowstorms
 Final Exam Clicker Questions ATOC 1050 Spring 2011 Chapter 16: Mountain Snowstorms True or false: Mean annual snowfall in the western United States always increases from south to north. Total precipitation
Final Exam Clicker Questions ATOC 1050 Spring 2011 Chapter 16: Mountain Snowstorms True or false: Mean annual snowfall in the western United States always increases from south to north. Total precipitation
Marine Weather Primer
 1 of 73 Marine Weather Primer Mark A. Thornton LakeErieWX: Marine Weather Education and Forecasting Resources Mark@LakeErieWX.com 2 of 73 3 of 73 Marine Weather Seminars & Workshops Learn a little meteorology
1 of 73 Marine Weather Primer Mark A. Thornton LakeErieWX: Marine Weather Education and Forecasting Resources Mark@LakeErieWX.com 2 of 73 3 of 73 Marine Weather Seminars & Workshops Learn a little meteorology
Chapter Introduction. Weather. Patterns. Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part V ñ Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and MCCs. Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part V ñ Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and MCCs Photographs Todd Lindley (This part contains materials taken from UCAR MCS training module) Bright band associated with stratiform
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics Part V ñ Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and MCCs Photographs Todd Lindley (This part contains materials taken from UCAR MCS training module) Bright band associated with stratiform
Tornadoes. tornado: a violently rotating column of air
 Tornadoes tornado: a violently rotating column of air Tornadoes What is the typical size of a tornado? What are typical wind speeds for a tornado? Five-stage life cycle of a tornado Dust Swirl Stage Tornado
Tornadoes tornado: a violently rotating column of air Tornadoes What is the typical size of a tornado? What are typical wind speeds for a tornado? Five-stage life cycle of a tornado Dust Swirl Stage Tornado
Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Spring 2016 Meteorology 260
 Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Spring 2016 Meteorology 260 Name Laboratory #9: Joplin Tornado Day Subsynoptic, Thermodynamic, and Wind Shear Setting Part A: 1600 UTC Surface Chart Subsynoptic Analyses
Department of Earth & Climate Sciences Spring 2016 Meteorology 260 Name Laboratory #9: Joplin Tornado Day Subsynoptic, Thermodynamic, and Wind Shear Setting Part A: 1600 UTC Surface Chart Subsynoptic Analyses
MET Lecture 26 Tornadoes I
 MET 4300 Lecture 26 Tornadoes I A Large Tornado approaches Lyndon, Kansas, on May 8, 2003 Outline Definition, life cycle Tornado formation within supercells Tornado formation within nonsupercell thunderstorms
MET 4300 Lecture 26 Tornadoes I A Large Tornado approaches Lyndon, Kansas, on May 8, 2003 Outline Definition, life cycle Tornado formation within supercells Tornado formation within nonsupercell thunderstorms
Thunderstorms and Severe Weather. (Chapt 15)
 Thunderstorms and Severe Weather (Chapt 15) The Big Picture We ve emphasized horizontal transport of energy to balance the planetary energy budget: Hadley Cell Subtropical divergence Midlatitude cyclones
Thunderstorms and Severe Weather (Chapt 15) The Big Picture We ve emphasized horizontal transport of energy to balance the planetary energy budget: Hadley Cell Subtropical divergence Midlatitude cyclones
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Severe Thunderstorms
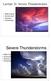 Lecture 26 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 1 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 2 Severe Thunderstorms: NWS Criteria NWS Criteria: to
Lecture 26 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 1 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 2 Severe Thunderstorms: NWS Criteria NWS Criteria: to
Air Mass. 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types
 Air Mass 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types A. Continental-relatively dry air masses that form over land. B. Maritime: relatively humid air masses
Air Mass 1. Air Mass : Large body of Air with similar temperature and humidity (or moisture) ; 4 types A. Continental-relatively dry air masses that form over land. B. Maritime: relatively humid air masses
Thunderstorm. Thunderstorms result from the rapid upward movement of warm, moist air.
 Severe Weather Thunderstorm A thunderstorm (aka an electrical storm, a lightning storm, or a thundershower) is a type of storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect, thunder.
Severe Weather Thunderstorm A thunderstorm (aka an electrical storm, a lightning storm, or a thundershower) is a type of storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect, thunder.
Thunderstorm Basics. Thunderstorm Climatology
 Thunderstorm Basics Part of the fascination many people have with thunderstorms is the mystery that surrounds them. Leading researchers are still learning about many of the phenomena associated with thunderstorms.
Thunderstorm Basics Part of the fascination many people have with thunderstorms is the mystery that surrounds them. Leading researchers are still learning about many of the phenomena associated with thunderstorms.
Weather Patterns and Severe Storms
 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given
Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given
Weather Pattern Notes
 Weather Pattern Notes Please copy notes into you notebooks on pgs 72,74, and 76. Include 3 Questions that your notes answer on EACH of the pages you have notes on for full credit. Lesson 2-1 Pressure Systems
Weather Pattern Notes Please copy notes into you notebooks on pgs 72,74, and 76. Include 3 Questions that your notes answer on EACH of the pages you have notes on for full credit. Lesson 2-1 Pressure Systems
Physics 137 Exam 3 Review
 Physics 137 Exam 3 Review Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones 1. Air Mass: body of air with very little horizontal variation in temperature or humidity at any given altitude 2.
Physics 137 Exam 3 Review Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones 1. Air Mass: body of air with very little horizontal variation in temperature or humidity at any given altitude 2.
A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines
 A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines Note: Lecture notes presented here based on course Daily Weather Laboratory
A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines Note: Lecture notes presented here based on course Daily Weather Laboratory
777 GROUNDSCHOOL Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms
 777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER
 SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
Meteorology Lecture 19
 Meteorology Lecture 19 Robert Fovell rfovell@albany.edu 1 Important notes These slides show some figures and videos prepared by Robert G. Fovell (RGF) for his Meteorology course, published by The Great
Meteorology Lecture 19 Robert Fovell rfovell@albany.edu 1 Important notes These slides show some figures and videos prepared by Robert G. Fovell (RGF) for his Meteorology course, published by The Great
Convective Dynamics. Jeremy A. Gibbs. March 10, University of Oklahoma
 Convective Dynamics Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu March 10, 2015 1 / 66 Overview Multicellular Storms Intro Lifecycle Thunderstorm Outflow as a Density Current Cell Regeneration 2
Convective Dynamics Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu March 10, 2015 1 / 66 Overview Multicellular Storms Intro Lifecycle Thunderstorm Outflow as a Density Current Cell Regeneration 2
Chapter 21. Weather Patterns and Severe Storms
 Chapter 21 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture
Chapter 21 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1 Air Masses Air Masses and Weather Air Masses An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS
 9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
Thunderstorms and Tornadoes. Chapter 14
 Thunderstorms and Tornadoes Chapter 14 Thunderstorms A storm containing lightning and thunder convective storms Severe thunderstorms (NWS def) one of following: large hail - ¾ in dia Surface wind gusts
Thunderstorms and Tornadoes Chapter 14 Thunderstorms A storm containing lightning and thunder convective storms Severe thunderstorms (NWS def) one of following: large hail - ¾ in dia Surface wind gusts
Air Mass Thunderstorms. Air Mass Thunderstorms. Air Mass Thunderstorms. Lecture 26 Air Mass Thunderstorms and Lightning
 Lecture 26 and Lightning Life Cycle Environment Climatology Lightning 1 2 Short-lived, isolated thunderstorms that are not severe are often called air-mass thunderstorms. There are three stages describing
Lecture 26 and Lightning Life Cycle Environment Climatology Lightning 1 2 Short-lived, isolated thunderstorms that are not severe are often called air-mass thunderstorms. There are three stages describing
Tuesday, September 13, 16
 Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT
 Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT Standard 1: Air Masses Air Mass An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude When an air mass
Unit 5 Part 2 Test PPT Standard 1: Air Masses Air Mass An air mass is an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude When an air mass
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points
 ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain
Feel free to ask me if you are confused about the meaning of any question. Good luck, and have a great spring break!
 Name: _ MEA 214 Midterm Exam, Spring 2011 Feel free to ask me if you are confused about the meaning of any question. Good luck, and have a great spring break! 1.) For each of the characteristics listed
Name: _ MEA 214 Midterm Exam, Spring 2011 Feel free to ask me if you are confused about the meaning of any question. Good luck, and have a great spring break! 1.) For each of the characteristics listed
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere
 Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
Part. I Introduction. Part II Scale Characteristics and Climatology of MCSs
 Talking points for MCS teletraining session Part. I Introduction Slide 1 Slides 2-3 Title Objectives Part II Scale Characteristics and Climatology of MCSs Slides 4-5 Climatology of mesoscale convective
Talking points for MCS teletraining session Part. I Introduction Slide 1 Slides 2-3 Title Objectives Part II Scale Characteristics and Climatology of MCSs Slides 4-5 Climatology of mesoscale convective
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries
 11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
11A.2 Forecasting Short Term Convective Mode And Evolution For Severe Storms Initiated Along Synoptic Boundaries Greg L. Dial and Jonathan P. Racy Storm Prediction Center, Norman, Oklahoma 1. Introduction
Lightning. lightning: an electrical discharge in the atmosphere. Electricity. Lightning, Thunder and Tornados PHYS 189. Electricity.
 , lightning: an electrical discharge in the atmosphere (), week 12 1 / 40 , lightning: an electrical discharge in the atmosphere cloud-to-cloud (80%) cloud-to-ground (20%) (), week 12 1 / 40 Fundamentals
, lightning: an electrical discharge in the atmosphere (), week 12 1 / 40 , lightning: an electrical discharge in the atmosphere cloud-to-cloud (80%) cloud-to-ground (20%) (), week 12 1 / 40 Fundamentals
Lightning AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Multicell Thunderstorms
 Lightning AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Thunderstorms Lightning Initiation Lightning Detection Upward lightning Lecture 22 Nov 14, 2017 1
Lightning AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Thunderstorms Lightning Initiation Lightning Detection Upward lightning Lecture 22 Nov 14, 2017 1
Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Air Masses Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. high pressure poles low pressure equator wind
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Air Masses Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. high pressure poles low pressure equator wind
Chapter 6 Clouds. Cloud Development
 Chapter 6 Clouds Chapter overview Processes causing saturation o Cooling, moisturizing, mixing Cloud identification and classification Cloud Observations Fog Why do we care about clouds in the atmosphere?
Chapter 6 Clouds Chapter overview Processes causing saturation o Cooling, moisturizing, mixing Cloud identification and classification Cloud Observations Fog Why do we care about clouds in the atmosphere?
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014
 Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Severe Weather Event of 13 July 2014 By Richard H. Grumm and Elyse M. Colbert National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Severe weather affected the eastern United States (Fig. 1) from northwestern
Clouds and turbulent moist convection
 Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY
 P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY 2009 Stephen S. Parker* National Weather Service, Boise, ID 1. INTRODUCTION During the early afternoon hours of 3 May
P8.14 CLASSIC AND HP MINI-SUPERCELLS IN SOUTHEAST OREGON AND SOUTHWEST IDAHO ON 3 MAY 2009 Stephen S. Parker* National Weather Service, Boise, ID 1. INTRODUCTION During the early afternoon hours of 3 May
Chap 14: Thunderstorms & Tornadoes
 Chap 14: Thunderstorms & Tornadoes Ordinary thunderstorms Severe thunderstorms Microburst Mesoscale convective systems Squall line Mesoscale convective complex Multicell thunderstorms move to right of
Chap 14: Thunderstorms & Tornadoes Ordinary thunderstorms Severe thunderstorms Microburst Mesoscale convective systems Squall line Mesoscale convective complex Multicell thunderstorms move to right of
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points
 ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) The equation to
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x10 8 m/s) The equation to
I. Air Masses A. Defined: large body of air, 1600 km or more across, with similar temperature and moisture at similar altitudes 1.
 I. Air Masses A. Defined: large body of air, 1600 km or more across, with similar temperature and moisture at similar altitudes 1. Brings these characteristics with it as it moves to different areas 2.
I. Air Masses A. Defined: large body of air, 1600 km or more across, with similar temperature and moisture at similar altitudes 1. Brings these characteristics with it as it moves to different areas 2.
Meteorology. Review Extreme Weather a. cold front. b. warm front. What type of weather is associated with a:
 Meteorology 5.08 Extreme Weather References: FTGU pages 132, 144, 145, 148-155 Air Command Weather Manual Chapters 9 and 15 Review What type of weather is associated with a: a. cold front b. warm front
Meteorology 5.08 Extreme Weather References: FTGU pages 132, 144, 145, 148-155 Air Command Weather Manual Chapters 9 and 15 Review What type of weather is associated with a: a. cold front b. warm front
Air Masses and Fronts II
 Air Masses and Fronts II Brief review An air mass is a large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are fairly similar in any horizontal direction Source regions for air masses tend to
Air Masses and Fronts II Brief review An air mass is a large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are fairly similar in any horizontal direction Source regions for air masses tend to
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Weather Service (NWS) Severe Thunderstorm Observing and Radar Monitoring
 The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Presents National Weather Service (NWS) Severe Thunderstorm Observing and Radar Monitoring Severe Weather Spotter Line 1-888-668-3344 Spotter
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Presents National Weather Service (NWS) Severe Thunderstorm Observing and Radar Monitoring Severe Weather Spotter Line 1-888-668-3344 Spotter
1 August 2006 An Investigation of a Bow Echo along the Wasatch Front. Randy Graham and Chris Gibson 6 April 2007
 1 August 2006 An Investigation of a Bow Echo along the Wasatch Front Randy Graham and Chris Gibson 6 April 2007 Overview Environment review Review of terrain-induced discrete propagation Bow Echo interactions
1 August 2006 An Investigation of a Bow Echo along the Wasatch Front Randy Graham and Chris Gibson 6 April 2007 Overview Environment review Review of terrain-induced discrete propagation Bow Echo interactions
