SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Patient Group Hem. Lesion Description Etiology FRONTAL LOBE GROUP 1 FL-LAT right SFG (pos), SFS, Central sulcus
|
|
|
- Steven Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1: Lesion locations of the Frontal Lobe (FL), Basal Ganglia (BG) and Parietal-temporal (PTL) clinical groups. Lesion site was determined by (T1 and T2 weighted) anatomical MRI datasets from a 3.0T system (Brucker 30/100 Medspec) and evaluated by the chief neurologist and an experienced neuroanatomist. Abbreviations: ant anterior, CA cerebral angiopathy, CG cingulate gyrus, e externa, EI embolic infarction, FL-LAT frontolateral group, FL-POL frontopolar, GP Globus pallidus, Intracerebral bleeding, IFG inferior frontal gyrus, ITG inferior temporal gyrus, i interna, Ischemic Infarction, IPS intraparietal sulcus, MTG middle temporal gyrus, OM olfactory meningioma, Other other regions containing small lesions or lacuna, pos posterior, SFG superior frontal gyrus, SFS superior frontal sulcus, SR surgically removed, T tumor, Traumatic brain injury Patient Group Hem. Lesion Description Etiology FRONTAL LOBE GROUP 1 FL-LAT right SFG (pos), SFS, Central sulcus 2 FL-LAT right IFG, MFG Other: insula (ant), left cerebellum 3 FL-LAT right MFG (ant) 4 FL-LAT left IFG (pars triangularis) Other: insula (ant) 5 FL-LAT left IFG, MFG (pos) Other: insula (ant), temporal pole 6 FL-LAT left Precentral sulcus Other: IPS (ant) 7 FL-LAT left IFG (pars orbitalis) Other: insula (ant) 8 FL-LAT left IFG (pos), MFG (pos) Other: insula (ant), putamen, right thalamus 9 FL-LAT left MFG (pos), Precentral gyrus, Other: thalamus 10 FL-POL left Frontal pole T-SR 11 FL-POL left Frontal pole, Orbital gyri Other: striatum, corpus callosum 12 FL-POL bilateral Orbital Gyri (R >> L) 13 FL-POL bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri Other: temporal pole, ITG (ant) 14 FL-POL bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri (R >> L) 15 FL-POL bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri (R >> L) Other: temporal pole, ITG (ant) 16 FL-POL bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri Other: temporal pole 17 FL-POL bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri OM-SR 18 FL-POL bilateral (L > R) Frontal pole, Orbital gyri
2 2 19 FL-POL right Frontal pole, Orbital gyri OM-SR 20 FL-POL bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri (L > R) Other: ITG, MTG, fusiform gyrus 21 FL-EXT right IFG, Orbital Gyrus Other: insula (ant) 22 FL-EXT bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital Gyrus, Frontomedian wall Other: striatum, temporal pole 23 FL-EXT left Frontal pole, Orbital Gyrus, Frontomedian wall Other: corpus callosum 24 FL-EXT left Frontal pole, Orbital Gyrus OM-SR Other: corpus callosum, striatum 25 FL-EXT right IFG, MFG, SFG Other: insula, postcentral gyrus, temporal pole, STG 26 FL-EXT left CG, Frontal pole, Orbital Gyrus, Frontomedian wall Other: corpus callosum, striatum, temporal pole, parietomedian wall 27 FL-EXT bilateral Frontal pole, Orbital gyri, Frontomedian wall (R >> L) 28 FL-EXT bilateral Frontal pole, Frontomedian wall CA, T-SR Other: corpus callosum 29 FL-EXT bilateral SFG, SFS, MFG T-SR BASAL GANGLIA GROUP 1 BG bilateral Putamen (pos), Internal Capsule, CA (R >> L) 2 BG left GPe, Internal Capsule, Caudate Nucleus (body) EI Other : thalamus (ant) 3 BG left Putamen (pos),gp, Internal Capsule, CA Other: thalamus (pos), claustrum 4 BG left Caudate Nucleus, Putamen, GP, Internal Capsule EI Other: claustrum 5 BG left Caudate Nucleus, Putamen 6 BG left Putamen (pos) 7 BG left Putamen (pos), GP, Internal capsule 8 BG left Putamen (pos), Caudate Nucleus, Internal capsule 9 BG right Putamen (pos), GPe, Internal capsule 10 BG right Putamen (pos), Caudate Nucleus 11 BG right Putamen, Caudate Nucleus (head) 12 BG right Caudate Nucleus (head) 13 BG right Putamen, Caudate Nucleus, Internal & External Capsule. Other: thalamus, postcentral gyrus 14 BG right Caudate Nucleus (head), Putamen (ant), GP, Substantia
3 3 Nigra 15 BG right Caudate Nucleus (body), Putamen (ant), Internal Capsule. 16 BG right Putamen (pos), Caudate Nucleus (body), Other: claustrum, insula PARIETAL-TEMPORAL GROUP 1 PTL bilateral STG, ITG, Angular Gyrus (R > L) Other: fusiform gyrus, lingual gyrus 2 PTL bilateral STG, MTG, Angular Gyrus, Supramarginal Gyrus Other: temporal pole, orbital gyrus 3 PTL bilateral STG, MTG, Supramarginal Gyrus (R > L) Other: temporal pole, frontal pole 4 PTL left STG, ITS, Supramarginal Gyrus, Postcentral Gyrus Other: insula, striatum, IFG 5 PTL left STG, STS Other: insula 6 PTL left STG, STS 7 PTL left STG, MTG, Temporal pole Other: striatum 8 PTL left STG, ITG, Angular gyrus Other: striatum 9 PTL left STG, Supramarginal Gyrus, Angular gyrus, IPS Other: posterior insula 10 PTL left STG, MTG, Supramarginal Gyrus, Angular gyrus, IPS Other: posterior insula 11 PTL right STG, Supramarginal Gyrus, CA
4 4 Table S2: Results of the FL versus FL-CT hierarchical regression analyses. The two values of especial interest are the Effect size (Cohen s f 2 ) attributable to the addition of Group variable to the Model as well as the associated Significance Level. R 2 Effect size (f 2 ) Beta Significance Alternate Uses Model 1: IQ P =.013 Originality.150 P = Model 2: Group.435 P <.001 Alternate Uses Fluency Conceptual Expansion Constraints of Examples ORIG RELE Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.464 P <.001 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.954 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.011 P =.941 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.223 P =.124 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.462 P =.001 RAT: Total Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.131 P =.372 RAT: Nonstandard Insight PS: Candle Task Incremental PS: Hanoi Task Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.086 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.187 P =.203 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.119 P =.416
5 Table S3: Results of the BG versus BG-CT hierarchical regression analyses. The two values of especial interest are the Effect size (Cohen s f 2 ) attributable to the addition of Group variable to the Model as well as the associated Significance Level. R 2 Effect size (f 2 ) Beta Significance Alternate Uses Model 1: IQ P =.002 Originality.309 P = Model 2: Group.366 P = Alternate Uses Fluency Conceptual Expansion Constraints of Examples ORIG RELE Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.292 P =.119 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.801 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.413 P =.066 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.160 P =.440 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.347 P =.101 RAT: Total Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.153 P =.472 RAT: Nonstandard Insight PS: Candle Task Incremental PS: Hanoi Task Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.739 P =.466 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.793 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.470 P =.037
6 Table S4: Results of the PTL versus PTL-CT hierarchical regression analyses. The two values of especial interest are the Effect size (Cohen s f 2 ) attributable to the addition of Group variable to the Model as well as the associated Significance Level. R 2 Effect size (f 2 ) Beta Significance Alternate Uses Model 1: IQ P =.060 Originality.365 P = Model 2: Group.171 P = Alternate Uses Fluency Conceptual Expansion Constraints of Examples ORIG RELE Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.397 P =.065 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.160 P =.502 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.041 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.072 P =.763 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.477 P =.015 RAT: Total Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.339 P =.103 RAT: Nonstandard Insight PS: Candle Task Incremental PS: Hanoi Task Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.728 P =.475 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.300 P =.192 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.245 P =.291
7 Table S5: Results of the FL-EXT versus FL-EXT-CT hierarchical regression analyses. The two values of especial interest are the Effect size (Cohen s f 2 ) attributable to the addition of Group variable to the Model as well as the associated Significance Level. R 2 Effect size (f 2 ) Beta Significance Alternate Uses Model 1: IQ P =.073 Originality.284 P = Model 2: Group.331 P = Alternate Uses Fluency Conceptual Expansion Constraints of Examples ORIG RELE Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.666 P =.004 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.473 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.705 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.126 P =.630 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.512 P =.050 RAT: Total Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.816 RAT: Nonstandard Insight PS: Candle Task Incremental PS: Hanoi Task Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.151 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.155 P =.577 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.846
8 Table S6: Results of the FL-LAT versus FL-LAT-CT hierarchical regression analyses. The two values of especial interest are the Effect size (Cohen s f 2 ) attributable to the addition of Group variable to the Model as well as the associated Significance Level. R 2 Effect size (f 2 ) Beta Significance Alternate Uses Model 1: IQ P =.845 Originality -.05 P = Model 2: Group.559 P = Alternate Uses Fluency Conceptual Expansion Constraints of Examples ORIG RELE Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.701 P =.001 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.122 P =.625 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.276 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.414 P =.092 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.500 P =.042 RAT: Total Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.268 P =.307 RAT: Nonstandard Insight PS: Candle Task Incremental PS: Hanoi Task Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.373 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.184 P =.480 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.058 P =.820
9 Table S7: Results of the FL-POL versus FL-POL-CT hierarchical regression analyses. The two values of especial interest are the Effect size (Cohen s f 2 ) attributable to the addition of Group variable to the Model as well as the associated Significance Level. R 2 Effect size (f 2 ) Beta Significance Alternate Uses Model 1: IQ P =.015 Originality.355 P = Model 2: Group.298 P = Alternate Uses Fluency Conceptual Expansion Constraints of Examples ORIG RELE Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.103 P =.687 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.988 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.458 P =.081 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.729 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.282 P =.295 RAT: Total Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.109 P =.671 RAT: Nonstandard Insight PS: Candle Task Incremental PS: Hanoi Task Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group P =.557 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.121 P =.656 Model 1: IQ P = P = Model 2: Group.211 P =.424
10 Figure S1: Degree of conceptual expansion (Mean and Standard Error) across all clinical and healthy control groups. The significance level is indicate by the number of arrows (***: p <.01, **: p.05, *: p.1). Significant results were also accompanied by medium to large effect sizes. 10
11 Figure S2: Number of solved/unsolved performances during insight problem solving (candle task) across all clinical and healthy control groups. The significance level is indicate by the number of arrows (***: p <.01, **: p.05, *: p.1). Significant results were also accompanied by medium to large effect sizes. 11
12 Figure S3: Number of solved/unsolved performances during incremental problem solving (tower of Hanoi task) across all clinical and healthy control groups. The significance level is indicate by the number of arrows (***: p <.01, **: p.05, *: p.1). Significant results were also accompanied by medium to large effect sizes. 12
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Supplementary Tables 2. Supplementary Figures 1/12 Supplementary tables TABLE S1 Response to Expected Value: Anatomical locations of regions correlating with the expected value
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Supplementary Tables 2. Supplementary Figures 1/12 Supplementary tables TABLE S1 Response to Expected Value: Anatomical locations of regions correlating with the expected value
Supplementary Information. Brain networks involved in tactile speed classification of moving dot patterns: the. effects of speed and dot periodicity
 Supplementary Information Brain networks involved in tactile speed classification of moving dot patterns: the effects of speed and dot periodicity Jiajia Yang, Ryo Kitada *, Takanori Kochiyama, Yinghua
Supplementary Information Brain networks involved in tactile speed classification of moving dot patterns: the effects of speed and dot periodicity Jiajia Yang, Ryo Kitada *, Takanori Kochiyama, Yinghua
Tracking whole-brain connectivity dynamics in the resting-state
 Tracking whole-brain connectivity dynamics in the resting-state Supplementary Table. Peak Coordinates of ICNs ICN regions BA t max Peak (mm) (continued) BA t max Peak (mm) X Y Z X Y Z Subcortical networks
Tracking whole-brain connectivity dynamics in the resting-state Supplementary Table. Peak Coordinates of ICNs ICN regions BA t max Peak (mm) (continued) BA t max Peak (mm) X Y Z X Y Z Subcortical networks
- Supplementary information -
 Influence of FKBP5 polymorphism and DNA methylation on structural changes of the brain in major depressive disorder - Supplementary information - Kyu-Man Han MD a*, Eunsoo Won, MD, PhD a*, Youngbo Sim,
Influence of FKBP5 polymorphism and DNA methylation on structural changes of the brain in major depressive disorder - Supplementary information - Kyu-Man Han MD a*, Eunsoo Won, MD, PhD a*, Youngbo Sim,
One patient and one control were unable to complete the TOMM. An additional HC had abnormally low scores
 Ling et al. 2013-1 Supplemental Methods Participants One patient and one control were unable to complete the TOMM. An additional HC had abnormally low scores on the TOMM only (T-score < 0), and was not
Ling et al. 2013-1 Supplemental Methods Participants One patient and one control were unable to complete the TOMM. An additional HC had abnormally low scores on the TOMM only (T-score < 0), and was not
Supplementary Material & Data. Younger vs. Older Subjects. For further analysis, subjects were split into a younger adult or older adult group.
 1 1 Supplementary Material & Data 2 Supplemental Methods 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Younger vs. Older Subjects For further analysis, subjects were split into a younger adult
1 1 Supplementary Material & Data 2 Supplemental Methods 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Younger vs. Older Subjects For further analysis, subjects were split into a younger adult
Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience 2e
 Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience 2e Thomas Trappenberg March 21, 2009 Chapter 9: Modular networks, motor control, and reinforcement learning Mixture of experts Expert 1 Input Expert 2 Integration
Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience 2e Thomas Trappenberg March 21, 2009 Chapter 9: Modular networks, motor control, and reinforcement learning Mixture of experts Expert 1 Input Expert 2 Integration
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of responses
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of responses a. For each subject, we classified neural activity using an electrode s response to a localizer task (see Experimental Procedures). Auditory (green), indicates
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of responses a. For each subject, we classified neural activity using an electrode s response to a localizer task (see Experimental Procedures). Auditory (green), indicates
Morphometrics with SPM12
 Morphometrics with SPM12 John Ashburner Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK. What kind of differences are we looking for? Usually, we try to localise regions of difference.
Morphometrics with SPM12 John Ashburner Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK. What kind of differences are we looking for? Usually, we try to localise regions of difference.
Basal Ganglia. Input: Cortex Output: Thalamus motor and sensory gajng. Striatum Caudate Nucleus Putamen Globus Pallidus
 An Interac*ve Channel Model of the Basal Ganglia: Bifurca*on Analysis Under Healthy and Parkinsonian Condi*ons Robert Merrison- Hort, Nada Yousif, Felix Njap, Ulrich G. Hofmann, Oleksandr Burylko, Roman
An Interac*ve Channel Model of the Basal Ganglia: Bifurca*on Analysis Under Healthy and Parkinsonian Condi*ons Robert Merrison- Hort, Nada Yousif, Felix Njap, Ulrich G. Hofmann, Oleksandr Burylko, Roman
Use Case. Interoperating between ontology and rules for identifying brain anatomical structures
 W3C Workshop Rule Interoperability Use Case Interoperating between ontology and rules for identifying brain anatomical structures Christine Golbreich 1, Olivier Bierlaire 1 2, Olivier Dameron 3 2, Bernard
W3C Workshop Rule Interoperability Use Case Interoperating between ontology and rules for identifying brain anatomical structures Christine Golbreich 1, Olivier Bierlaire 1 2, Olivier Dameron 3 2, Bernard
Diffusion Weighted MRI. Zanqi Liang & Hendrik Poernama
 Diffusion Weighted MRI Zanqi Liang & Hendrik Poernama 1 Outline MRI Quick Review What is Diffusion MRI? Detecting Diffusion Stroke and Tumor Detection Presenting Diffusion Anisotropy and Diffusion Tensor
Diffusion Weighted MRI Zanqi Liang & Hendrik Poernama 1 Outline MRI Quick Review What is Diffusion MRI? Detecting Diffusion Stroke and Tumor Detection Presenting Diffusion Anisotropy and Diffusion Tensor
Integrative Methods for Functional and Structural Connectivity
 Integrative Methods for Functional and Structural Connectivity F. DuBois Bowman Department of Biostatistics Columbia University SAMSI Challenges in Functional Connectivity Modeling and Analysis Research
Integrative Methods for Functional and Structural Connectivity F. DuBois Bowman Department of Biostatistics Columbia University SAMSI Challenges in Functional Connectivity Modeling and Analysis Research
3D Moment Invariant Based Morphometry
 3D Moment Invariant Based Morphometry J.-F. Mangin, F. Poupon, D. Rivière, A. Cachia, D. L. Collins, A. C. Evans, and J. Régis Service Hospitalier Frédéric Joliot, CEA, 91401 Orsay, France mangin@shfj.cea.fr,
3D Moment Invariant Based Morphometry J.-F. Mangin, F. Poupon, D. Rivière, A. Cachia, D. L. Collins, A. C. Evans, and J. Régis Service Hospitalier Frédéric Joliot, CEA, 91401 Orsay, France mangin@shfj.cea.fr,
ROI analysis of pharmafmri data: an adaptive approach for global testing
 ROI analysis of pharmafmri data: an adaptive approach for global testing Giorgos Minas, John A.D. Aston, Thomas E. Nichols and Nigel Stallard Abstract Pharmacological fmri (pharmafmri) is a new highly
ROI analysis of pharmafmri data: an adaptive approach for global testing Giorgos Minas, John A.D. Aston, Thomas E. Nichols and Nigel Stallard Abstract Pharmacological fmri (pharmafmri) is a new highly
NeuroImage. Diffeomorphic registration using geodesic shooting and Gauss Newton optimisation. John Ashburner, Karl J. Friston.
 NeuroImage 55 (2011) 954 967 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Technical Note Diffeomorphic registration using geodesic shooting and Gauss
NeuroImage 55 (2011) 954 967 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Technical Note Diffeomorphic registration using geodesic shooting and Gauss
Modelling Time- varying effec3ve Brain Connec3vity using Mul3regression Dynamic Models. Thomas Nichols University of Warwick
 Modelling Time- varying effec3ve Brain Connec3vity using Mul3regression Dynamic Models Thomas Nichols University of Warwick Dynamic Linear Model Bayesian 3me series model Predictors {X 1,,X p } Exogenous
Modelling Time- varying effec3ve Brain Connec3vity using Mul3regression Dynamic Models Thomas Nichols University of Warwick Dynamic Linear Model Bayesian 3me series model Predictors {X 1,,X p } Exogenous
Longitudinal growth analysis of early childhood brain using deformation based morphometry
 Longitudinal growth analysis of early childhood brain using deformation based morphometry Junki Lee 1, Yasser Ad-Dab'bagh 2, Vladimir Fonov 1, Alan C. Evans 1 and the Brain Development Cooperative Group
Longitudinal growth analysis of early childhood brain using deformation based morphometry Junki Lee 1, Yasser Ad-Dab'bagh 2, Vladimir Fonov 1, Alan C. Evans 1 and the Brain Development Cooperative Group
REVEALING THE INFLUENCE OF DEFINITE BRAIN REGIONS UPON THE EMERGENCE OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL PATTERNS IN THE RESTING-STATE BRAIN ACTIVITY
 REVEALING THE INFLUENCE OF DEFINITE BRAIN REGIONS UPON THE EMERGENCE OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL PATTERNS IN THE RESTING-STATE BRAIN ACTIVITY By Sergei D. Verzilin THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of
REVEALING THE INFLUENCE OF DEFINITE BRAIN REGIONS UPON THE EMERGENCE OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL PATTERNS IN THE RESTING-STATE BRAIN ACTIVITY By Sergei D. Verzilin THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of
From Pixels to Brain Networks: Modeling Brain Connectivity and Its Changes in Disease. Polina Golland
 From Pixels to Brain Networks: Modeling Brain Connectivity and Its Changes in Disease Polina Golland MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Joint work with Archana Venkataraman C.-F.
From Pixels to Brain Networks: Modeling Brain Connectivity and Its Changes in Disease Polina Golland MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Joint work with Archana Venkataraman C.-F.
Protracted brain development in a rodent model of extreme longevity
 Protracted brain development in a rodent model of extreme longevity Running title: Delayed brain development of the naked mole rat Orsolya K. Penz 1, *, Janos Fuzik 1,2, *, Aleksandra B. Kurek 2, Roman
Protracted brain development in a rodent model of extreme longevity Running title: Delayed brain development of the naked mole rat Orsolya K. Penz 1, *, Janos Fuzik 1,2, *, Aleksandra B. Kurek 2, Roman
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Automatic segmentation of the striatum and globus pallidus using MIST: Multimodal Image Segmentation Tool Visser, E.; Keuken, M.C.; Douaud, G.; Gaura, V.; Bachoud-Levi,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Automatic segmentation of the striatum and globus pallidus using MIST: Multimodal Image Segmentation Tool Visser, E.; Keuken, M.C.; Douaud, G.; Gaura, V.; Bachoud-Levi,
A Study of Brain Networks Associated with Swallowing Using Graph-Theoretical Approaches
 A Study of Brain Networks Associated with Swallowing Using Graph-Theoretical Approaches Bo Luan 1, Peter Sörös 2, Ervin Sejdić 1 * 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Swanson School of
A Study of Brain Networks Associated with Swallowing Using Graph-Theoretical Approaches Bo Luan 1, Peter Sörös 2, Ervin Sejdić 1 * 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Swanson School of
INSTITUTE FOR INTEGRATIVE SCIENCE & HEALTH
 INSTITUTE FOR INTEGRATIVE SCIENCE & HEALTH www.integrativescience.ca Major pedagogical emphasis in MSIT 101-103 was placed on helping students "how to learn" rather than just "what to learn". A pattern
INSTITUTE FOR INTEGRATIVE SCIENCE & HEALTH www.integrativescience.ca Major pedagogical emphasis in MSIT 101-103 was placed on helping students "how to learn" rather than just "what to learn". A pattern
Supplementary Figure 1. Structural MRIs.
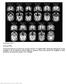 Supplementary Figure 1 Structural MRIs. Coronal and transverse sections of pre-electrode insertion T1 weighted MRIs, illustrating radiologically normal amygdala in the 10 patients for which ierps are presented.
Supplementary Figure 1 Structural MRIs. Coronal and transverse sections of pre-electrode insertion T1 weighted MRIs, illustrating radiologically normal amygdala in the 10 patients for which ierps are presented.
Improving White Matter Tractography by Resolving the Challenges of Edema
 Improving White Matter Tractography by Resolving the Challenges of Edema Jérémy Lecoeur, Emmanuel Caruyer, Luke Macyszyn, Ragini Verma To cite this version: Jérémy Lecoeur, Emmanuel Caruyer, Luke Macyszyn,
Improving White Matter Tractography by Resolving the Challenges of Edema Jérémy Lecoeur, Emmanuel Caruyer, Luke Macyszyn, Ragini Verma To cite this version: Jérémy Lecoeur, Emmanuel Caruyer, Luke Macyszyn,
Hierarchical Clustering Identifies Hub Nodes in a Model of Resting-State Brain Activity
 WCCI 22 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence June, -5, 22 - Brisbane, Australia IJCNN Hierarchical Clustering Identifies Hub Nodes in a Model of Resting-State Brain Activity Mark Wildie and
WCCI 22 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence June, -5, 22 - Brisbane, Australia IJCNN Hierarchical Clustering Identifies Hub Nodes in a Model of Resting-State Brain Activity Mark Wildie and
ROLE OF ROTATIONAL ACCELERATION AND DECELERATION PULSES ON BRAIN STRAINS IN LATERAL IMPACT
 ROLE OF ROTATIONAL ACCELERATION AND DECELERATION PULSES ON BRAIN STRAINS IN LATERAL IMPACT ABSTRACT Jianrong Li, Jiangyue Zhang, Narayan Yoganandan, Frank A. Pintar, Thomas A. Gennarelli Department of
ROLE OF ROTATIONAL ACCELERATION AND DECELERATION PULSES ON BRAIN STRAINS IN LATERAL IMPACT ABSTRACT Jianrong Li, Jiangyue Zhang, Narayan Yoganandan, Frank A. Pintar, Thomas A. Gennarelli Department of
Unravelling the Intrinsic Functional Organization of the Human Lateral Frontal Cortex: A Parcellation Scheme Based on Resting State fmri
 10238 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 25, 2012 32(30):10238 10252 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Unravelling the Intrinsic Functional Organization of the Human Lateral Frontal Cortex: A Parcellation Scheme
10238 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 25, 2012 32(30):10238 10252 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Unravelling the Intrinsic Functional Organization of the Human Lateral Frontal Cortex: A Parcellation Scheme
Quantitative Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Orientation: Theoretical Framework
 Quantitative Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Orientation: Theoretical Framework Yu-Chien Wu, 1,2 Aaron S. Field, 3 Moo K. Chung, 2,4,5 Benham Badie, 6 and Andrew L. Alexander 1,2,7 * Magnetic Resonance in
Quantitative Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Orientation: Theoretical Framework Yu-Chien Wu, 1,2 Aaron S. Field, 3 Moo K. Chung, 2,4,5 Benham Badie, 6 and Andrew L. Alexander 1,2,7 * Magnetic Resonance in
Multiple Orderings of Events in Disease Progression
 Multiple Orderings of Events in Disease Progression Alexandra L Young 1, Neil P Oxtoby 1, Jonathan Huang 2, Razvan V Marinescu 1, Pankaj Daga 1, David M Cash 1,3, Nick C Fox 3, Sebastien Ourselin 1,3,
Multiple Orderings of Events in Disease Progression Alexandra L Young 1, Neil P Oxtoby 1, Jonathan Huang 2, Razvan V Marinescu 1, Pankaj Daga 1, David M Cash 1,3, Nick C Fox 3, Sebastien Ourselin 1,3,
DYNAMIC FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY USING HEAT KERNEL
 DYNAMIC FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY USING HEAT KERNEL Shih-Gu Huang Moo K. Chung Ian C. Carroll H. Hill Goldsmith Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA
DYNAMIC FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY USING HEAT KERNEL Shih-Gu Huang Moo K. Chung Ian C. Carroll H. Hill Goldsmith Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA
Will Penny. 21st April The Macroscopic Brain. Will Penny. Cortical Unit. Spectral Responses. Macroscopic Models. Steady-State Responses
 The The 21st April 2011 Jansen and Rit (1995), building on the work of Lopes Da Sliva and others, developed a biologically inspired model of EEG activity. It was originally developed to explain alpha activity
The The 21st April 2011 Jansen and Rit (1995), building on the work of Lopes Da Sliva and others, developed a biologically inspired model of EEG activity. It was originally developed to explain alpha activity
Medical Image Analysis
 Medical Image Analysis Instructor: Moo K. Chung mchung@stat.wisc.edu Lecture 3. Deformation-based Morphometry (DBM) January 30, 2007 Deformation based Morphometry (DBM) It uses deformation fields obtained
Medical Image Analysis Instructor: Moo K. Chung mchung@stat.wisc.edu Lecture 3. Deformation-based Morphometry (DBM) January 30, 2007 Deformation based Morphometry (DBM) It uses deformation fields obtained
Measuring Brain Variability by Extrapolating Sparse Tensor Fields Measured on Sulcal Lines
 Measuring Brain Variability by Extrapolating Sparse Tensor Fields Measured on Sulcal Lines Pierre Fillard 1, Vincent Arsigny 1, Xavier Pennec 1, Kiralee M. Hayashi 2, Paul M. Thompson 2, and Nicholas Ayache
Measuring Brain Variability by Extrapolating Sparse Tensor Fields Measured on Sulcal Lines Pierre Fillard 1, Vincent Arsigny 1, Xavier Pennec 1, Kiralee M. Hayashi 2, Paul M. Thompson 2, and Nicholas Ayache
A framework for systematic promoter motif discovery and expression profiling from high dimensional brain transcriptome data. Jeremy A.
 A framework for systematic promoter motif discovery and expression profiling from high dimensional brain transcriptome data Jeremy A. Lieberman Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
A framework for systematic promoter motif discovery and expression profiling from high dimensional brain transcriptome data Jeremy A. Lieberman Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
Development of image processing tools and procedures for analyzing multi-site longitudinal diffusion-weighted imaging studies
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2014 Development of image processing tools and procedures for analyzing multi-site longitudinal diffusion-weighted imaging studies Joy Tamiko
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2014 Development of image processing tools and procedures for analyzing multi-site longitudinal diffusion-weighted imaging studies Joy Tamiko
Advances in Ultra-High Field MRI at 9.4T and Hybrid 3T MR-PET
 Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Advances in Ultra-High Field MRI at 9.4T and Hybrid 3T MR-PET N. Jon Shah Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine 4 Research Centre Juelich 52425 Juelich GERMANY Mitglied
Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Advances in Ultra-High Field MRI at 9.4T and Hybrid 3T MR-PET N. Jon Shah Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine 4 Research Centre Juelich 52425 Juelich GERMANY Mitglied
Electroencephalogram Based Causality Graph Analysis in Behavior Tasks of Parkinson s Disease Patients
 University of Denver Digital Commons @ DU Electronic Theses and Dissertations Graduate Studies 1-1-2015 Electroencephalogram Based Causality Graph Analysis in Behavior Tasks of Parkinson s Disease Patients
University of Denver Digital Commons @ DU Electronic Theses and Dissertations Graduate Studies 1-1-2015 Electroencephalogram Based Causality Graph Analysis in Behavior Tasks of Parkinson s Disease Patients
Influence of Stroke Infarct Location on Functional Outcome Measured by the Modified Rankin Scale
 Influence of Stroke Infarct Location on Functional Outcome Measured by the Modified Rankin Scale Bastian Cheng, MD; Nils Daniel Forkert, PhD; Melissa Zavaglia, PhD; Claus C. Hilgetag, PhD; Amir Golsari,
Influence of Stroke Infarct Location on Functional Outcome Measured by the Modified Rankin Scale Bastian Cheng, MD; Nils Daniel Forkert, PhD; Melissa Zavaglia, PhD; Claus C. Hilgetag, PhD; Amir Golsari,
Figure 1-figure supplement 1
 Figure 1-figure supplement 1 a 1 Stroop Task b 1 Reading Task 8 8 Percent Correct 6 4 2 Percent Correct 6 4 2 c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 Subject Number d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 Subject
Figure 1-figure supplement 1 a 1 Stroop Task b 1 Reading Task 8 8 Percent Correct 6 4 2 Percent Correct 6 4 2 c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 Subject Number d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 Subject
Jan 16: The Visual System
 Geometry of Neuroscience Matilde Marcolli & Doris Tsao Jan 16: The Visual System References for this lecture 1977 Hubel, D. H., Wiesel, T. N., Ferrier lecture 2010 Freiwald, W., Tsao, DY. Functional compartmentalization
Geometry of Neuroscience Matilde Marcolli & Doris Tsao Jan 16: The Visual System References for this lecture 1977 Hubel, D. H., Wiesel, T. N., Ferrier lecture 2010 Freiwald, W., Tsao, DY. Functional compartmentalization
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Humans: Practical Implications for Neuroanatomy
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Humans: Practical Implications for Neuroanatomy Collaborators Center for Morphometric Analysis: Nikos Makris Andy Worth Verne S. Caviness George Papadimitriou MGH-NMR Center
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Humans: Practical Implications for Neuroanatomy Collaborators Center for Morphometric Analysis: Nikos Makris Andy Worth Verne S. Caviness George Papadimitriou MGH-NMR Center
THE MYELOARCHITECTONICS OF THE DORSOMEDIAL THALAMIC NUCLEUS OF THE DOG
 Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1970. 30: 145-156 THE MYELOARCHITECTONICS OF THE DORSOMEDIAL THALAMIC NUCLEUS OF THE DOG BARBARA SYCHOWA Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Warsaw,
Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1970. 30: 145-156 THE MYELOARCHITECTONICS OF THE DORSOMEDIAL THALAMIC NUCLEUS OF THE DOG BARBARA SYCHOWA Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Warsaw,
Part I: SEM & Introduction to Time Series Models A brief introduction to SEM with an eating disorder example A fmri time series study + AR and MV
 Structural Equation Modeling with New Development for Mixed Designs Plus Introductions to Time Series Modeling, Bootstrap Resampling, & Partial Correlation Network Analysis (PCNA) Outline Part I: SEM &
Structural Equation Modeling with New Development for Mixed Designs Plus Introductions to Time Series Modeling, Bootstrap Resampling, & Partial Correlation Network Analysis (PCNA) Outline Part I: SEM &
腦網路連結分析 A Course of MRI
 本週課程內容 腦網路連結 (connectivity & network) 結構性與功能性連結關係 (structural/functional connectivity) 腦網路連結分析 A Course of MRI 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學物理治療暨輔助科技學系 alvin01@ym.edu.tw 複雜網路 : 圖學理論 (graph theory) Brain networks Larger
本週課程內容 腦網路連結 (connectivity & network) 結構性與功能性連結關係 (structural/functional connectivity) 腦網路連結分析 A Course of MRI 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學物理治療暨輔助科技學系 alvin01@ym.edu.tw 複雜網路 : 圖學理論 (graph theory) Brain networks Larger
Neural Network. Eung Je Woo Department of Biomedical Engineering Impedance Imaging Research Center (IIRC) Kyung Hee University Korea
 Neural Network Eung Je Woo Department of Biomedical Engineering Impedance Imaging Research Center (IIRC) Kyung Hee University Korea ejwoo@khu.ac.kr Neuron and Nervous System 2 Neuron (Excitable Cell) and
Neural Network Eung Je Woo Department of Biomedical Engineering Impedance Imaging Research Center (IIRC) Kyung Hee University Korea ejwoo@khu.ac.kr Neuron and Nervous System 2 Neuron (Excitable Cell) and
Diffusion-Tensor MR Imaging of Gray and White Matter Development during Normal Human Brain Maturation
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1445 1456, October 2002 Diffusion-Tensor MR Imaging of Gray and White Matter Development during Normal Human Brain Maturation Pratik Mukherjee, Jeffrey H. Miller, Joshua S. Shimony,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1445 1456, October 2002 Diffusion-Tensor MR Imaging of Gray and White Matter Development during Normal Human Brain Maturation Pratik Mukherjee, Jeffrey H. Miller, Joshua S. Shimony,
Large brain effective network from EEG/MEG data and dmr information
 Large brain effective network from EEG/MEG data and dmr information Brahim Belaoucha, Théodore Papadopoulo To cite this version: Brahim Belaoucha, Théodore Papadopoulo Large brain effective network from
Large brain effective network from EEG/MEG data and dmr information Brahim Belaoucha, Théodore Papadopoulo To cite this version: Brahim Belaoucha, Théodore Papadopoulo Large brain effective network from
Q-ball imaging of macaque white matter architecture
 36, 869 879 doi:1.198/rstb.25.1651 Published online 29 May 25 Q-ball imaging of macaque white matter architecture David S. Tuch 1,2, *, Jonathan J. Wisco 1, Mark H. Khachaturian 1,3, Leeland B. Ekstrom
36, 869 879 doi:1.198/rstb.25.1651 Published online 29 May 25 Q-ball imaging of macaque white matter architecture David S. Tuch 1,2, *, Jonathan J. Wisco 1, Mark H. Khachaturian 1,3, Leeland B. Ekstrom
Clicker Question. Discussion Question
 Connectomics Networks and Graph Theory A network is a set of nodes connected by edges The field of graph theory has developed a number of measures to analyze networks Mean shortest path length: the average
Connectomics Networks and Graph Theory A network is a set of nodes connected by edges The field of graph theory has developed a number of measures to analyze networks Mean shortest path length: the average
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes
 Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 1. Basic facts about the brain and its analysis.
 Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 1. Basic facts about the brain and its analysis. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń,
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 1. Basic facts about the brain and its analysis. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń,
Neuroimage Processing
 Neuroimage Processing Instructor: Moo K. Chung mkchung@wisc.edu Lecture 10-11. Deformation-based morphometry (DBM) Tensor-based morphometry (TBM) November 13, 2009 Image Registration Process of transforming
Neuroimage Processing Instructor: Moo K. Chung mkchung@wisc.edu Lecture 10-11. Deformation-based morphometry (DBM) Tensor-based morphometry (TBM) November 13, 2009 Image Registration Process of transforming
Modelling cortical folding pattern formation of the brain with a Turing system
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Modelling cortical folding pattern formation of the brain with a Turing system Hurdal, M.K. 1 and D.A.
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Modelling cortical folding pattern formation of the brain with a Turing system Hurdal, M.K. 1 and D.A.
Undirected graphs of frequency-dependent functional connectivity in whole brain networks
 36, 937 946 doi:198/rstb.25.1645 Published online 29 May 25 Undirected graphs of frequency-dependent functional connectivity in whole brain networks Raymond Salvador 1, John Suckling 1, Christian Schwarzbauer
36, 937 946 doi:198/rstb.25.1645 Published online 29 May 25 Undirected graphs of frequency-dependent functional connectivity in whole brain networks Raymond Salvador 1, John Suckling 1, Christian Schwarzbauer
Conscious Experience and the Theory of Everything
 Conscious Experience and the Theory of Everything Abstract A theory of everything is a single all-encompassing coherent theoretical framework of physics that fully explains and links together all physical
Conscious Experience and the Theory of Everything Abstract A theory of everything is a single all-encompassing coherent theoretical framework of physics that fully explains and links together all physical
Mapping of Cortical Motor Reorganization in Spinal Cord Injury
 University of Tennessee Health Science Center UTHSC Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations (ETD) College of Graduate Health Sciences -00 Mapping of Cortical Motor Reorganization in Spinal Cord Injury
University of Tennessee Health Science Center UTHSC Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations (ETD) College of Graduate Health Sciences -00 Mapping of Cortical Motor Reorganization in Spinal Cord Injury
COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING OF THE HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM
 COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING OF THE HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM Nonlinear Enhancement of the Adaptive Model Theory through Simulation and Experiment A thesis submitted in partial fulftlment of the requirements
COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING OF THE HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL SYSTEM Nonlinear Enhancement of the Adaptive Model Theory through Simulation and Experiment A thesis submitted in partial fulftlment of the requirements
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Saurabh Bhaskar Shaw Dwip Shah
 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy By Saurabh Bhaskar Shaw Dwip Shah What is Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy? [1] Non invasive method to look at concentration of metabolites invivo. 2 Basics of MRS Physics
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy By Saurabh Bhaskar Shaw Dwip Shah What is Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy? [1] Non invasive method to look at concentration of metabolites invivo. 2 Basics of MRS Physics
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI
 Magnetic resonance imaging MRI Introduction What is MRI MRI is an imaging technique used primarily in medical settings that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce very clear and detailed
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI Introduction What is MRI MRI is an imaging technique used primarily in medical settings that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce very clear and detailed
LOW RESOLUTION SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING IN THE ES- TIMATION OF IRON CONTENT IN DEEP GREY MATTER OF BRAIN AT 3 TESLA ABSTRACT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LOW RESOLUTION SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING IN THE ES- TIMATION OF IRON CONTENT IN DEEP GREY MATTER OF BRAIN AT 3 TESLA 1,2 Department of Physics, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur. Pakistan.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE LOW RESOLUTION SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING IN THE ES- TIMATION OF IRON CONTENT IN DEEP GREY MATTER OF BRAIN AT 3 TESLA 1,2 Department of Physics, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur. Pakistan.
Induced Magnetic Force in Human Heads Exposed to 4 T MRI
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 31:815 820 (2010) Original Research Induced Magnetic Force in Human Heads Exposed to 4 T MRI Ruiliang Wang, PhD, 1 * Gene-Jack Wang, MD, 1 Rita Z. Goldstein, PhD,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 31:815 820 (2010) Original Research Induced Magnetic Force in Human Heads Exposed to 4 T MRI Ruiliang Wang, PhD, 1 * Gene-Jack Wang, MD, 1 Rita Z. Goldstein, PhD,
Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. October 7, Efficiency: If size(w) = 100B, each prediction is expensive:
 Simple Variable Selection LASSO: Sparse Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 7, 2013 1 Sparsity Vector w is sparse, if many entries are zero: Very useful
Simple Variable Selection LASSO: Sparse Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 7, 2013 1 Sparsity Vector w is sparse, if many entries are zero: Very useful
Outlines: (June 11, 1996) Instructor:
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (June 11, 1996) Instructor: Tai-huang Huang Institute of Biomedical Sciences Academia Sinica Tel. (02) 2652-3036; Fax. (02) 2788-7641 E. mail: bmthh@ibms.sinica.edu.tw Reference:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (June 11, 1996) Instructor: Tai-huang Huang Institute of Biomedical Sciences Academia Sinica Tel. (02) 2652-3036; Fax. (02) 2788-7641 E. mail: bmthh@ibms.sinica.edu.tw Reference:
IMA Preprint Series # 2298
 RELATING FIBER CROSSING IN HARDI TO INTELLECTUAL FUNCTION By Iman Aganj, Neda Jahanshad, Christophe Lenglet, Arthur W. Toga, Katie L. McMahon, Greig I. de Zubicaray, Margaret J. Wright, Nicholas G. Martin,
RELATING FIBER CROSSING IN HARDI TO INTELLECTUAL FUNCTION By Iman Aganj, Neda Jahanshad, Christophe Lenglet, Arthur W. Toga, Katie L. McMahon, Greig I. de Zubicaray, Margaret J. Wright, Nicholas G. Martin,
Internally generated preactivation of single neurons in human medial frontal cortex predicts volition
 Internally generated preactivation of single neurons in human medial frontal cortex predicts volition Itzhak Fried, Roy Mukamel, Gabriel Kreiman List of supplementary material Supplementary Tables (2)
Internally generated preactivation of single neurons in human medial frontal cortex predicts volition Itzhak Fried, Roy Mukamel, Gabriel Kreiman List of supplementary material Supplementary Tables (2)
Development of Magnetic Resonance-Based Susceptibility Imaging Applications
 Development of Magnetic Resonance-Based Susceptibility Imaging Applications Sung-Min Gho The Graduate School Yonsei University Development of Magnetic Resonance-Based Susceptibility Imaging Applications
Development of Magnetic Resonance-Based Susceptibility Imaging Applications Sung-Min Gho The Graduate School Yonsei University Development of Magnetic Resonance-Based Susceptibility Imaging Applications
Neuroimage Processing
 Neuroimage Processing Instructor: Moo K. Chung mkchung@wisc.edu Lecture 2. General Linear Models (GLM) Multivariate General Linear Models (MGLM) September 11, 2009 Research Projects If you have your own
Neuroimage Processing Instructor: Moo K. Chung mkchung@wisc.edu Lecture 2. General Linear Models (GLM) Multivariate General Linear Models (MGLM) September 11, 2009 Research Projects If you have your own
The History of the Basal Ganglia: The Contribution of Karl Friedrich Burdach
 Neuroscience & Medicine, 2012, 3, 374-379 doi:10.4236/nm.2012.34046 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/nm) The History of the Basal Ganglia: The Contribution of Karl Friedrich
Neuroscience & Medicine, 2012, 3, 374-379 doi:10.4236/nm.2012.34046 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/nm) The History of the Basal Ganglia: The Contribution of Karl Friedrich
Quantitative Metrics for White Matter Integrity Based on Diffusion Tensor MRI Data. Stephanie Lee
 Quantitative Metrics for White Matter Integrity Based on Diffusion Tensor MRI Data Stephanie Lee May 5, 2005 Quantitative Metrics for White Matter Integrity Based on Diffusion Tensor MRI Data ABSTRACT
Quantitative Metrics for White Matter Integrity Based on Diffusion Tensor MRI Data Stephanie Lee May 5, 2005 Quantitative Metrics for White Matter Integrity Based on Diffusion Tensor MRI Data ABSTRACT
Journal of Neuroscience Methods
 Journal of Neuroscience Methods 199 (2011) 108 118 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Neuroscience Methods j o ur nal homep age: www.elsevier.com/locate/jneumeth Detecting overlapped
Journal of Neuroscience Methods 199 (2011) 108 118 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Neuroscience Methods j o ur nal homep age: www.elsevier.com/locate/jneumeth Detecting overlapped
Lateral Prefrontal Cortex is Organized into Parallel Dorsal and Ventral Streams Along the Rostro-Caudal Axis
 Cerebral Cortex October 2013;23:2457 2466 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs223 Advance Access publication August 9, 2012 Lateral Prefrontal Cortex is Organized into Parallel Dorsal and Ventral Streams Along the Rostro-Caudal
Cerebral Cortex October 2013;23:2457 2466 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs223 Advance Access publication August 9, 2012 Lateral Prefrontal Cortex is Organized into Parallel Dorsal and Ventral Streams Along the Rostro-Caudal
 1999 10 33 10 Chin J Radiol October 1999 Vol 33 No. 10 655 (MCAO) MR ; (DWI) 45 MR DWI T 1 WI T 2 WI (01536 ) (TTC) 8 MCAO 30 DWI 4912 % 3 (4715 %) 18 T 2 WI 2 (214 015) DWI T 2 WI DWI DWI TTC ( t t =
1999 10 33 10 Chin J Radiol October 1999 Vol 33 No. 10 655 (MCAO) MR ; (DWI) 45 MR DWI T 1 WI T 2 WI (01536 ) (TTC) 8 MCAO 30 DWI 4912 % 3 (4715 %) 18 T 2 WI 2 (214 015) DWI T 2 WI DWI DWI TTC ( t t =
Neuropsychologia 51 (2013) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Neuropsychologia
 Neuropsychologia 51 (2013) 67 78 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Distinct subdivisions of the cingulum bundle
Neuropsychologia 51 (2013) 67 78 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Distinct subdivisions of the cingulum bundle
COMPUTATIONAL ROLE OF DISINHIBITION IN BRAIN FUNCTION. A Dissertation YINGWEI YU
 COMPUTATIONAL ROLE OF DISINHIBITION IN BRAIN FUNCTION A Dissertation by YINGWEI YU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
COMPUTATIONAL ROLE OF DISINHIBITION IN BRAIN FUNCTION A Dissertation by YINGWEI YU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
The Nottingham eprints service makes this work by researchers of the University of Nottingham available open access under the following conditions.
 Wharton, Samuel and Bowtell, Richard W. (2015) Effects of white matter microstructure on phase and susceptibility maps. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 173 (3). pp. 1258-1269. ISSN 1522-2594 Access from
Wharton, Samuel and Bowtell, Richard W. (2015) Effects of white matter microstructure on phase and susceptibility maps. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 173 (3). pp. 1258-1269. ISSN 1522-2594 Access from
Tract-Specific Analysis for DTI of Brain White Matter
 Tract-Specific Analysis for DTI of Brain White Matter Paul Yushkevich, Hui Zhang, James Gee Penn Image Computing & Science Lab Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania IPAM Summer School July
Tract-Specific Analysis for DTI of Brain White Matter Paul Yushkevich, Hui Zhang, James Gee Penn Image Computing & Science Lab Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania IPAM Summer School July
False Discovery Rate Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies via Markov Random Fields
 1 False Discovery Rate Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies via Markov Random Fields Hien D. Nguyen* Geoffrey J. McLachlan Nicolas Cherbuin and Andrew L. Janke Abstract Magnetic resonance imaging
1 False Discovery Rate Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies via Markov Random Fields Hien D. Nguyen* Geoffrey J. McLachlan Nicolas Cherbuin and Andrew L. Janke Abstract Magnetic resonance imaging
Learning Structural Equation Models for fmri
 Learning Structural Equation Models for fmri Amos J. Storkey School of Informatics Enrico Simonotto Division of Psychiatry Heather Whalley Division of Psychiatry Stephen Lawrie Division of Psychiatry Lawrence
Learning Structural Equation Models for fmri Amos J. Storkey School of Informatics Enrico Simonotto Division of Psychiatry Heather Whalley Division of Psychiatry Stephen Lawrie Division of Psychiatry Lawrence
Biology EOC Review. Scientific Method. 1. List the steps of the scientific method: Define the following: Hypothesis: Theory: Law:
 Scientific Method 1. List the steps of the scientific method: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 2. Define the following: Hypothesis: Theory: Law: Biology EOC Review 3. Three redwood trees are kept at different humidity
Scientific Method 1. List the steps of the scientific method: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 2. Define the following: Hypothesis: Theory: Law: Biology EOC Review 3. Three redwood trees are kept at different humidity
Area, Age and Gender Dependence of the Nucleoside System in the Brain: a Review of Current Literature
 1012 Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 2011, 11, 1012-1033 Area, Age and Gender Dependence of the Nucleoside System in the Brain: a Review of Current Literature Zsolt Kovács 1,*, Gábor Juhász 2, Miklós
1012 Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 2011, 11, 1012-1033 Area, Age and Gender Dependence of the Nucleoside System in the Brain: a Review of Current Literature Zsolt Kovács 1,*, Gábor Juhász 2, Miklós
Testing Stationarity of Brain Functional Connectivity Using Change-Point Detection in fmri Data
 Testing Stationarity of Brain Functional Connectivity Using Change-Point Detection in fmri Data Mengyu Dai 1, Zhengwu Zhang 2 and Anuj Srivastava 1 1 Department of Statistics, Florida State University,
Testing Stationarity of Brain Functional Connectivity Using Change-Point Detection in fmri Data Mengyu Dai 1, Zhengwu Zhang 2 and Anuj Srivastava 1 1 Department of Statistics, Florida State University,
ALZHEIMER S disease (AD) is the most common type of
 576 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 61, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2014 Integration of Network Topological and Connectivity Properties for Neuroimaging Classification Biao Jie, Daoqiang Zhang, Wei
576 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 61, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2014 Integration of Network Topological and Connectivity Properties for Neuroimaging Classification Biao Jie, Daoqiang Zhang, Wei
Connectomics analysis and parcellation of the brain based on diffusion-weighted fiber tractography
 Connectomics analysis and parcellation of the brain based on diffusion-weighted fiber tractography Alfred Anwander Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences Leipzig, Germany What is the
Connectomics analysis and parcellation of the brain based on diffusion-weighted fiber tractography Alfred Anwander Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences Leipzig, Germany What is the
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING ELECTRODES AND SIMULATIONS FOR COMPARISON BETWEEN DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION. Fabiola Alonso Orozco
 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING AND SIMULATIONS FOR COMPARISON BETWEEN DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION ELECTRODES Fabiola Alonso Orozco 2012-04-10 LiTH-IMT/MASTER-EX-- 12/012-- SE Department of Biomedical Engineering
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING AND SIMULATIONS FOR COMPARISON BETWEEN DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION ELECTRODES Fabiola Alonso Orozco 2012-04-10 LiTH-IMT/MASTER-EX-- 12/012-- SE Department of Biomedical Engineering
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Research Article Thalamus Segmentation from Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Biomedical Imaging Volume 2007, Article ID 90216, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2007/90216 Research Article Thalamus Segmentation from Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ye Duan, Xiaoling Li, and Yongjian
Biomedical Imaging Volume 2007, Article ID 90216, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2007/90216 Research Article Thalamus Segmentation from Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ye Duan, Xiaoling Li, and Yongjian
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering TOWARDS CLOSED-LOOP OPTOGENETIC CONTROL OF PARKINSON S DISEASE
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering TOWARDS CLOSED-LOOP OPTOGENETIC CONTROL OF PARKINSON S DISEASE A Thesis in Mechanical Engineering by Kyle M. Reigh 215 Kyle
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering TOWARDS CLOSED-LOOP OPTOGENETIC CONTROL OF PARKINSON S DISEASE A Thesis in Mechanical Engineering by Kyle M. Reigh 215 Kyle
RS-fMRI analysis in healthy subjects confirms gender based differences
 RS-fMRI analysis in healthy subjects confirms gender based differences Alberto A. Vergani (aavergani@uninsubria.it) PhD student in Computer Science and Computational Mathematics University of Insubria
RS-fMRI analysis in healthy subjects confirms gender based differences Alberto A. Vergani (aavergani@uninsubria.it) PhD student in Computer Science and Computational Mathematics University of Insubria
Visualization and Labeling
 Visualization and Labeling Tools for Visualization and Labeling SPM MRIcron MRIcroGL xjview MARINA FreeSurfer Talairach Daemon SPM Anatomy Toolbox WFU Pickatlas SPM Visualization Gesture imitation with
Visualization and Labeling Tools for Visualization and Labeling SPM MRIcron MRIcroGL xjview MARINA FreeSurfer Talairach Daemon SPM Anatomy Toolbox WFU Pickatlas SPM Visualization Gesture imitation with
Next: Before we talk about topographic organization, we will review some species differences, and take a look at lamination in the midbrain tectum.
 Next: Before we talk about topographic organization, we will review some species differences, and take a look at lamination in the midbrain tectum. 1 Midbrain: Species comparisons An exercise in topology:
Next: Before we talk about topographic organization, we will review some species differences, and take a look at lamination in the midbrain tectum. 1 Midbrain: Species comparisons An exercise in topology:
Intro and Homeostasis
 Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
From Generic Knowledge to Specific Reasoning for Medical Image Interpretation using Graph based Representations
 From Generic Knowledge to Specific Reasoning for Medical Image Interpretation using Graph based Representations Jamal Atif, Céline Hudelot, Geoffroy Fouquier, Isabelle Bloch, Elsa Angelini GET - Ecole
From Generic Knowledge to Specific Reasoning for Medical Image Interpretation using Graph based Representations Jamal Atif, Céline Hudelot, Geoffroy Fouquier, Isabelle Bloch, Elsa Angelini GET - Ecole
stone age institute publication series
 stone age institute publication series Series Editors Kathy Schick and Nicholas Toth Stone Age Institute Gosport, Indiana and Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana Number 1. THE OLDOWAN: Case Studies
stone age institute publication series Series Editors Kathy Schick and Nicholas Toth Stone Age Institute Gosport, Indiana and Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana Number 1. THE OLDOWAN: Case Studies
Collective Dynamics in Human and Monkey Sensorimotor Cortex: Predicting Single Neuron Spikes
 Collective Dynamics in Human and Monkey Sensorimotor Cortex: Predicting Single Neuron Spikes Supplementary Information Wilson Truccolo 1,2,5, Leigh R. Hochberg 2-6 and John P. Donoghue 4,1,2 1 Department
Collective Dynamics in Human and Monkey Sensorimotor Cortex: Predicting Single Neuron Spikes Supplementary Information Wilson Truccolo 1,2,5, Leigh R. Hochberg 2-6 and John P. Donoghue 4,1,2 1 Department
NEUROSCIENCES MODULE. Semester: Three Year: Second Year MBBS Region/s: Neurosciences
 NEUROSCIENCES MODULE Semester: Three Year: Second Year MBBS Region/s: Neurosciences Course Duration: Six weeks l. Credit Hours: 6.0 Theory, 3.00 Practical and Demonstration Introduction: T h e N e u r
NEUROSCIENCES MODULE Semester: Three Year: Second Year MBBS Region/s: Neurosciences Course Duration: Six weeks l. Credit Hours: 6.0 Theory, 3.00 Practical and Demonstration Introduction: T h e N e u r
醫用磁振學 MRM 擴散張量影像 擴散張量影像原理. 本週課程內容 MR Diffusion 擴散張量造影原理 擴散張量造影應用 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 擴散張量造影原理 擴散張量造影應用 醫用磁振學 MRM 擴散張量影像 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI The Basics (3rd edition) Chapter 22: Echo Planar Imaging MRI in Practice, (4th edition)
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 擴散張量造影原理 擴散張量造影應用 醫用磁振學 MRM 擴散張量影像 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI The Basics (3rd edition) Chapter 22: Echo Planar Imaging MRI in Practice, (4th edition)
Group Study of Simulated Driving fmri Data by Multiset Canonical Correlation Analysis
 DOI 0.007/s265-00-0572-8 Group Study of Simulated Driving fmri Data by Multiset Canonical Correlation Analysis Yi-Ou Li Tom Eichele Vince D. Calhoun Tulay Adali Received: 8 August 200 / Revised: 5 November
DOI 0.007/s265-00-0572-8 Group Study of Simulated Driving fmri Data by Multiset Canonical Correlation Analysis Yi-Ou Li Tom Eichele Vince D. Calhoun Tulay Adali Received: 8 August 200 / Revised: 5 November
