Calculus with Applications Good Problems. Justin M. Ryan. Mathematics Department Butler Community College Andover, Kansas USA
|
|
|
- Gwen Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DGS GPBC Calculus with Applications Good Problems Justin M. Ryan Mathematics Department Butler Community College Andover, Kansas USA DRAFT 13 March 2017 These notes consist of a collection of in-class labs created for my Calc with Apps classes. The problems are good for different reasons, depending on the topic of interest. Υ
2
3 Preface Write Preface here. Philosophy of the problems, book used in class, etc. iii
4
5 Instructions Complete all exercises. You may work in groups or independently, depending on your personal learning taste. Attempt each problem without using a calculator, and only refer to your calculator (physical or online) if instructed by the problem, or if absolutely necessary. If you get stuck on a problem, discuss it with your group and/or neighboring groups. If the group is still stuck, then your entire group may ask me for a hint. Students are expected to be present and working on these Good Problems in class, during the time allotted by the instructor. Any problems that are not completed during class time are expected to be completed outside of class, before the next class meeting. This paper will not be collected, but you will need to submit your answers to selected problems on Canvas. v
6
7 Contents Preface Instructions iii v 1 Limits 1 2 The Derivative 7 3 Derivative Rules 13 4 Derivative Tests, and Review 17 5 Some Applied Examples 27 6 Related Rates Applications 31 7 Linear Approximations and Differentials 37 vii
8
9 1. Limits These Good Problems cover material from section 2.2 of our book. These good problems consist of a mix of computational and conceptual exercises. The goal is to cement the ideas of this week s lecture, with an eye looking forward to next week s lecture. 1. Consider the function f(x) = x2 + 3x + 3. Compute the following x 2 limits, if they exist. a.) lim x 1 f(x) b.) lim x 2 f(x) 2. Consider the function f(x) = 2x2 x 1. x 1 a.) What is the domain of f? b.) Calculate lim x 1 f(x).
10 2 Chapter 1. Limits 3. Consider the function f(x) = a.) Compute lim x 7 f(x) x + 7 x 2 + 9x b.) Compute lim x 2 f(x) Use a graphing utility to graph the function y = f(x). Explain in terms of the graph of y = f(x) why the limits lim f(x) and lim f(x) x 7 x 2 are fundamentally different.
11 3 4. Consider the function f(x) = x 2. a.) What is f(2)? f(x) f(2) b.) Compute lim. x 2 x 2 5. Consider the function f(x) = x 6. f(x + h) f(x) a.) Compute the difference quotient of f, DQ =, h h 0. [Hint: Use Pascal s Triangle (Binomial Theorem) to compute f(x + h).] f(x + h) f(x) b.) Compute lim. h 0 h
12 4 Chapter 1. Limits 6. Consider the following graph. Compute the following, i.) f(1) = v.) f(2) = ii.) lim x 1 f(x) = iii.) f(3) = iv.) lim x 3 f(x) = vi.) lim x 2 f(x) = vii.) lim x 2 + f(x) = viii.) lim x 2 f(x) = ix.) At what x-values is the function discontinuous? 7. Consider the following graph. Compute the following, i.) f(2) = v.) f(3) = ii.) lim x 2 f(x) = iii.) f(4) = iv.) lim x 4 f(x) = vi.) lim x 3 f(x) = vii.) lim x 3 + f(x) = viii.) lim x 3 f(x) = ix.) At what x-values is the function discontinuous?
13 5 8. Consider the following graph of a function y = f(x). Here a is a point in the domain of f and h is a nonzero constant. a.) Sketch the secant line passing through the points (a, f(a)) and (a + h, f(a + h)). b.) Write an expression that represents the slope of this secant line? c.) Suppose you take the limit as h 0. Describe what happens to the secant line that you drew in part a. d.) Describe what the limit of the slope in part b represents geometrically.
14 6 Chapter 1. Limits 9. Compute lim h 0 f(x + h) f(x) h for the function f(x) = x. 10. Compute lim h 0 f(x + h) f(x) h for the function f(x) = 1 x.
15 2. The Derivative These Good Problems cover section 2.3 of our book. We begin by reviewing the main conceptual ideas and definitions of the section. The concepts of these first three questions are the most important ideas of the first half of this course. 1. State the limit definition of derivative at a point. Write the limit in both forms. 2. State in words the geometric and physical interpretations of the derivative. 3. Suppose that f is differentiable at x = a. Write the general equation of the tangent line to the curve y = f(x) at x = a.
16 8 Chapter 2. The Derivative 4. Consider the function f(x) = x 3. a.) Compute the derivative of f at x = 1. b.) Write an equation of the tangent line to y = f(x) at the point ( 1, 1). 5. Compute the derivative of f(x) = 2x 1 at the point (5, 9).
17 9 6. Consider the function f(x) = x. a.) What is the domain of f? b.) Compute the derivative of f. c.) What is the domain of f? Explain in terms of the graph why this is different than your answer to part a. 7. Compute the derivative of f(x) = 3 x.
18 10 Chapter 2. The Derivative 8. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = 3x 2 x at the point (2, 10). 9. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = (x 1) 3 at the point ( 1, 8).
19 Find all points on the graph of y = x 4 2x 2 where the tangent line is horizontal. Hint: Compute the derivative y, set it equal to 0 (why 0?), then solve for x. 11. Let s = s(t) be a function that represents the position of a particle moving along a straight line. The velocity of the particle is defined to be the derivative v(t) = s (t). Find the velocity of a particle whose position function is s(t) = 2t 2 t.
20
21 3. Derivative Rules These Good Problems cover section 2.5 of our book. 1. Compute the derivatives of the functions. 1.) y = 3x 3 9x 2 + ln(x) 2.) f(x) = x 7 (x + 1) 5 3.) f(t) = te t 4.) y = x5 ln x 5.) h(t) = 4 t 5 4t 6.) q(s) = log(s) 7.) F (x) = ln(x 2 e x )
22 14 Chapter 3. Derivative Rules 2. Compute the derivatives of the functions. 1.) f(x) = (2x 2 x) 9 2.) V (x) = e 3x2 +5x 3.) g(x) = 1 (x 2 4) 2 3. Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve y = e 1 x2 at the point (1, 1). 4. Find all points on the curve y = x ln x where the tangent line is horizontal.
23 15 A manufacturer has determined that an employee with x days of production experience will be able to produce approximately P (x) = (1 e 0.2x ) items per day. Use a graphing utility to graph the function. 5. Approximately how many items will a beginning employee be able to produce each day? 6. How many items will an experienced employee (who has worked at the company for years) be able to produce? 7. What is the marginal production rate of an employee with 5 days experience? What are the units and what does this answer mean?
24 16 Chapter 3. Derivative Rules 8. An arrow shot straight up from ground level with an initial velocity of 128 feet per second will be at a height h(t) = 16t t feet after t seconds. Determine a.) At what time will the arrow reach its highest point (Hint: the arrow s velocity will be 0 at this point); and b.) How long will the arrow be aloft? 9. Consider a cubic function of the form f(x) = x 3 + Ax 2 + Bx + C. Find conditions on the constants A, B, and C to guarantee that the graph of y = f(x) has two distinct turning points.
25 4. Derivative Tests, and Review These Good Problems study the concepts presented in sections 2.6 and 2.7 of our text, then review material from the entire semester thus far as preparation for the first midterm exam. 1. Find the intervals of concavity of the function f(x) = 4x 4 8x Determine the concavity of the function y = x ln(x) at x = 1 e.
26 18 Chapter 4. Derivative Tests, and Review 3. Determine which points on the graph are local extrema, and which are inflection points. A C B D E 4. Determine the absolute (global) maximum and/or minimum values of the function f(x) = 1, if they exist. x 2 + 1
27 19 5. Find all critical points and local extreme points of the function f(x) = ln(x 2 6x + 11), and determine whether the extreme points are maxima or minima. 6. let f be a non-negative function on the interval [0, 10] such that f(0) = f(10) = 0. Define A(x) to be the area bounded between the x-axis, the graph of y = f(t), and the vertical line at x. At what value of x is A(x) a maximum? At what value of x is A(x) a minimum? 7. Let f be a positive function on the interval [2, 10] with graph shown below. Define S(x) to be the slope of the line through the points (0, 0 and (x, f(x)). At what value of x is S(x) a maximum? At what value of x is S(x) a minimum?
28 20 Chapter 4. Derivative Tests, and Review The remaining questions are intended to be review for the first midterm exam. 8. Compute the limits. Be sure to show enough work and use proper notation. a.) lim x 4 3x 2 9x + 4 b.) lim t 0 t 2 t 2t c.) lim x a x a x a d.) x lim x 2 x + 2 e.) lim u 0 + ln u
29 21 9. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute dy dx for y = x2 + 2x. You must use the limit definition and show enough work to receive any credit. 10. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute dy dx for y = x6. You must use the limit definition and show enough work to receive any credit.
30 22 Chapter 4. Derivative Tests, and Review 11. Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve y = ln(x) when x = Find all points on the curve y = e 6x3 9x 2 at which the tangent line is horizontal.
31 Consider the graph of the function y = f(x) given below. Explain why the limit as x approaches 0 does not exist. 14. Use the graph below to describe how the derivative of a function is defined at a point in terms of the secant lines through the point. 15. Find an equation of the normal line to the graph of y = x 3 at the point ( 2, 8). (The normal line is perpendicular to the tangent line.)
32 24 Chapter 4. Derivative Tests, and Review 16. Compute the derivatives. You can use the shortcut rules, but be sure to show enough work. a.) f(x) = 2 x (x 2 5x) b.) y = te t2 c.) x(t) = ln(t 2 1) d.) g(x) = ln x x 2 1 e.) q(s) = (s 3 9) 4 f.) p(x) = 6x x4 + 10x 3 15x x 3000
33 State the (limit) definition of continuity. 18. Determine whether the function is continuous. If it is discontinuous, state where. x 2 x 2, f(x) = 6 x 2 < x < 6, 2x 17 x Determine whether the function is continuous. If it is discontinuous, state where. 12 g(x) = 5x 3 5x
34 26 Chapter 4. Derivative Tests, and Review Some Comments This review is not meant the be comprehensive. You should also study past Good Problems and Recommended Exercises. The exam will be structured as follows. There will be 5 True/False questions and 5 Fill in the Blank questions, each worth 1 point each. Then there will be 18 Multiple Choice questions and 2 Short Answer questions, each worth 5 points each. The Multiple Choice questions are all or nothing (no partial credit), but partial credit will be possible on the Short Answer questions. You will not be allowed to use a calculator or any other electronic device on the exam. You will be allowed to use a single 3 5 in 2 note card of your own hand-written notes. If the note card is too big, or if the notes are not written by hand, then you will not be allowed to use the note card on the exam. You ll also need to know... Definitions! I won t ask you to state any definitions word-for-word, but I will expect you to know them. Definitions are the most important part of this course. Our goal is to eventually use Calculus to help us solve real world problems. But we cannot use Calculus for anything if we don t know what the terms mean.
35 5. Some Applied Examples These Good Problems closely follow Section 2.9 of our book. We will apply the tools of Calculus that we have added to our toolbox up to this point in the semester. 1. The manager of a garden store wants to build a 600 square foot rectangular enclosure on the store s parking lot in order to display some equipment. Three sides of the enclosure will be built with redwood fencing at a cost of $7 per running foot. The fourth side will be built of cement blocks at a cost of $14 per running foot. Find the dimensions that minimize the cost of the enclosure. 27
36 28 Chapter 5. Some Applied Examples 2. A concert promoter has found that if s/he sells tickets for $50 each then s/he can sell 1200 tickets, but for for every $5 rise in price 50 less tickets will be sold. What price should the tickets be sold at to maximize revenue? 3. Thought Exercise. The profit function is obtained by subtracting the cost function from the revenue function, P (x) = R(x) C(x). Determine criteria on the marginal revenue and marginal cost functions in order for the profit function to have a (local) maximum.
37 29 4. A company sells q ribbon winders per year at $p per winder. The demand function for ribbon winders is given by p = q. The ribbon winders cost $30 each to manufacture, plus there are fixed costs of $9000 per year. How many winders should be produced to maximize the profit? [Reminder: Revenue = q p.] 5. The cost in dollars to produce x gift baskets is given by C(x) = x+0.1x 2. How many baskets should be produced in order to minimize average cost? [Reminder: Average Cost = C(x) x.]
38 30 Chapter 5. Some Applied Examples 6. You have a 10 inch by 10 inch piece of cardboard which you plan to cut and fold as shown to form a box with a top. Find the dimensions of the box that has the largest volume. 7. You wish to open a coffee shop. In planning you estimate that if there is enough seating for between 40 and 80 people, the daily profit will be $50 per seat. However, if the seating capacity is more than 80 seats then the daily profit per seat will be decreased by $1 per seat over 80. What should the seating capacity be in order to maximize your shop s profit?
39 6. Related Rates Applications In these Good Problems we will apply the idea of related rates to solve some real world problems. For each of these problems, you should begin by drawing a picture (if appropriate), write down any equations that are not given, then do the calculus. 1. A right cylindrical tank is filled with water. The tank stands 2 meters tall and has a radius of 20 cm. How fast does the height of water in the tank drop when the water is being drained at a rate of 25 cm3? sec Find the exact rate that the height is decreasing when the height of the water is 1 meter high. [Volume of a cylinder: V = πr 2 h.] 31
40 32 Chapter 6. Related Rates Applications 2. A storage bin is in the shape of a right circular cone. The bin stands 10 feet tall and the top rim of the bin has a radius of 4 feet. If a grain is being pumped into the bin at a rate of 2 cubic feet per minute, what is the rate of change of the depth of the grain when the depth is 5 feet? [Volume of a cone: V = 1 3 πr2 h.]
41 33 3. A company that manufactures pet toys calculates that its cost and revenue can be modeled by the functions C(x) = x R(x) = 300x 0.2x 2 where x represents the number of toys produced in a week. If production in one particular week is increasing at a rate of 300 toys per week, find: a.) the rate at which the cost is changing, b.) the rate at which the revenue is changing, c.) the rate at which the profit is changing.
42 34 Chapter 6. Related Rates Applications 4. A company s profit is increasing at a rate of $6000 per week. The demand and cost functions are given by p(x) = x, C(x) = 3000x Find the rate of change of sales ( dx dt ) when the weekly sales are x = 50 units.
43 35 5. A young woman and her boyfriend plan to elope, but she must first rescue him from his mother who has locked him in his room. The woman has placed a 20 foot long ladder against his house and is knocking on his window when his mother begins pulling the bottom of the ladder away from the house at a rate of 3 feet per second. How fast is the top of the ladder (including the young couple!) falling when the bottom of the ladder is a.) 12 feet from the base of the wall? b.) 16 feet from the base of the wall? c.) 19 feet from the base of the wall?
44 36 Chapter 6. Related Rates Applications 6. Two resistors are connected in parallel with resistances R 1 and R 2 measured in Ohms (Ω). The total resistance, R, is given implicitly by 1 R = 1 R R 2. Suppose that R 1 is increasing at a rate of 0.4 Ω and R min 2 is decreasing at a rate of 0.7 Ω. At what rate is R changing when R min 1 = 80 Ω and R 2 = 105 Ω?
45 7. Linear Approximations and Differentials This week s Good Problems cover the linearizations of smooth functions. This topic is not in our book, but you can find my notes online at 1. Find the differential of each function. a.) y = x 2 e x b.) y = x 1 + 2x c.) y = 4 + 5x d.) y = x
46 38 Chapter 7. Linear Approximations and Differentials 2. Find the linearization y = L a f(x) of the given function at the given value of a. a.) f(x) = x 4 + 3x 2, a = 1 b.) f(x) = x, a = 0 c.) f(x) = x 3/4, a = 16
47 39 3. Use a linear approximation or differentials to approximate (2.001) Use a linear approximation or differentials to approximate
48 40 Chapter 7. Linear Approximations and Differentials 5. Verify that the linearization of f(x) = 3 1 x at a = 0 is given by L 0 f(x) = x. For what values of x is L 0 f accurate to within 0.1? 6. Consider the function y = x. Compare the values of dy and y when x = 1 and dx = x = 1. Sketch a diagram of two triangles with segment lengths dx, dy, and y.
49 41 7. The edge of a cube is measured to be 30 cm, with a possible error of 0.1 cm. Use differentials to estimate the maximum possible error and relative error in computing the surface area of the cube. 8. The circumference of a sphere was measured to be 84 cm with a possible error of 0.5 cm. Use differentials to estimate the maximum error in the calculated volume. What is the relative error?
50 42 Chapter 7. Linear Approximations and Differentials 9. When blood flows along a blood vessel, Poiseuille s Law states that the flux F (the volume of blood per unit time that flows past a given point) is proportional to the fourth power of the radius R of the blood vessel: F = kr 4. A partially clogged artery can be expanded by an operation called angioplasty, in which a balloon-tipped catheter is inflated inside the artery to widen it and restore the normal blood flow. Show that the relative change in F is about four times the relative change in R. How will a 5% increase in the radius affect the flow of blood?
51 Suppose that you don t have a formula for f, but you know that f(2) = 4 and f (x) = x for all x. Use a linear approximation to estimate f(1.95) and f(2.05). Are your estimates too large or too small? Explain.
52 44 Chapter 7. Linear Approximations and Differentials 11. Show that the length of the portion of any tangent line to the astroid x 2/3 + y 2/3 = 4 cut off by the coordinate axes is constant. You can also find a link on my web page to a version of this graph with a slider to move the point of tangency along the curve:
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29,
 MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 125: Exam 3 Review
 Math 125: Exam 3 Review Since we re using calculators, to keep the playing field level between all students, I will ask that you refrain from using certain features of your calculator, including graphing.
Math 125: Exam 3 Review Since we re using calculators, to keep the playing field level between all students, I will ask that you refrain from using certain features of your calculator, including graphing.
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems A) 4 B) 2 C) 1 D) 0 E) 2 A) 9 B) 12 C) 14 D) 21 E) 40
 Extreme Values in an Interval AP Calculus BC 1. The absolute maximum value of x = f ( x) x x 1 on the closed interval, 4 occurs at A) 4 B) C) 1 D) 0 E). The maximum acceleration attained on the interval
Extreme Values in an Interval AP Calculus BC 1. The absolute maximum value of x = f ( x) x x 1 on the closed interval, 4 occurs at A) 4 B) C) 1 D) 0 E). The maximum acceleration attained on the interval
Math 2413 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/2016
 Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
MATH 122 FALL Final Exam Review Problems
 MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
Math 241 Final Exam, Spring 2013
 Math 241 Final Exam, Spring 2013 Name: Section number: Instructor: Read all of the following information before starting the exam. Question Points Score 1 5 2 5 3 12 4 10 5 17 6 15 7 6 8 12 9 12 10 14
Math 241 Final Exam, Spring 2013 Name: Section number: Instructor: Read all of the following information before starting the exam. Question Points Score 1 5 2 5 3 12 4 10 5 17 6 15 7 6 8 12 9 12 10 14
Final Exam Review. MATH Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri. Name:. Show all your work.
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
2. Find the intervals where function is increasing and decreasing. Then find all relative extrema.
 MATH 1071Q Exam #2 Review Fall 2011 1. Find the elasticity at the given points and determine whether demand is inelastic, elastic, or unit elastic. Explain the significance of your answer. (a) x = 10 2p
MATH 1071Q Exam #2 Review Fall 2011 1. Find the elasticity at the given points and determine whether demand is inelastic, elastic, or unit elastic. Explain the significance of your answer. (a) x = 10 2p
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20. ), and f(a + 1).
 Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation
 2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
Math 121: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 11: Final Exam Review Sheet The Final Exam will be given on Thursday, March 1 from 10:30 am 1:30 pm. The exam is cumulative and will cover chapters 1.1-1.3, 1.5, 1.6,.1-.6, 3.1-3.6,
Exam Information Math 11: Final Exam Review Sheet The Final Exam will be given on Thursday, March 1 from 10:30 am 1:30 pm. The exam is cumulative and will cover chapters 1.1-1.3, 1.5, 1.6,.1-.6, 3.1-3.6,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A
 Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math Practice Final - solutions
 Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not
 Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Purdue University Study Guide for MA Credit Exam
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 16010 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA16010. The credit exam is a two-hour long exam with multiple choice questions. No books or
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 16010 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA16010. The credit exam is a two-hour long exam with multiple choice questions. No books or
Chapter 5. Increasing and Decreasing functions Theorem 1: For the interval (a,b) f (x) f(x) Graph of f + Increases Rises - Decreases Falls
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 First Derivative and Graphs Objectives: The student will be able to identify increasing and decreasing functions and local extrema The student will be able to apply the first derivative
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 First Derivative and Graphs Objectives: The student will be able to identify increasing and decreasing functions and local extrema The student will be able to apply the first derivative
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
3. Go over old quizzes (there are blank copies on my website try timing yourself!)
 final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
Math 115 Second Midterm March 25, 2010
 Math 115 Second Midterm March 25, 2010 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 8 problems.
Math 115 Second Midterm March 25, 2010 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 8 problems.
The University of British Columbia Final Examination - December 11, 2013 Mathematics 104/184 Time: 2.5 hours. LAST Name.
 The University of British Columbia Final Examination - December 11, 2013 Mathematics 104/184 Time: 2.5 hours LAST Name First Name Signature Student Number MATH 104 or MATH 184 (Circle one) Section Number:
The University of British Columbia Final Examination - December 11, 2013 Mathematics 104/184 Time: 2.5 hours LAST Name First Name Signature Student Number MATH 104 or MATH 184 (Circle one) Section Number:
Introduction to Calculus
 Introduction to Calculus Contents 1 Introduction to Calculus 3 11 Introduction 3 111 Origin of Calculus 3 112 The Two Branches of Calculus 4 12 Secant and Tangent Lines 5 13 Limits 10 14 The Derivative
Introduction to Calculus Contents 1 Introduction to Calculus 3 11 Introduction 3 111 Origin of Calculus 3 112 The Two Branches of Calculus 4 12 Secant and Tangent Lines 5 13 Limits 10 14 The Derivative
Practice A Exam 3. November 14, 2018
 Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 10250 Elem. of Calc. I Name: Instructor: Practice A Exam November 14, 2018 This exam is in 2 parts on 11 pages and contains 15 problems worth a total
Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 10250 Elem. of Calc. I Name: Instructor: Practice A Exam November 14, 2018 This exam is in 2 parts on 11 pages and contains 15 problems worth a total
Math 115 Second Midterm Exam
 Math 115 Second Midterm Exam November 14, 006 Name: Instructor: SOLUTIONS Section Number: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin.. This exam has 8 pages including this cover. There are 7
Math 115 Second Midterm Exam November 14, 006 Name: Instructor: SOLUTIONS Section Number: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin.. This exam has 8 pages including this cover. There are 7
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
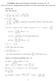 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
F. KEEP YOUR BUBBLE SHEET COVERED AT ALL TIMES.
 UF UNIVERSITY of Department of Mathematics FLORIDA MAC 2233 Exam 2A Spring 2017 A. Sign your bubble sheet on the back at the bottom in ink. B. In pencil, write and encode in the spaces indicated: 1) Name
UF UNIVERSITY of Department of Mathematics FLORIDA MAC 2233 Exam 2A Spring 2017 A. Sign your bubble sheet on the back at the bottom in ink. B. In pencil, write and encode in the spaces indicated: 1) Name
Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 28, 2015
 Math 110 4. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 8, 015 1. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute the derivative of f(x = 1 at x = a. 1 + x Inserting the function into
Math 110 4. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 8, 015 1. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute the derivative of f(x = 1 at x = a. 1 + x Inserting the function into
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Study guide for the Math 115 final Fall 2012
 Study guide for the Math 115 final Fall 2012 This study guide is designed to help you learn the material covered on the Math 115 final. Problems on the final may differ significantly from these problems
Study guide for the Math 115 final Fall 2012 This study guide is designed to help you learn the material covered on the Math 115 final. Problems on the final may differ significantly from these problems
Math Exam 03 Review
 Math 10350 Exam 03 Review 1. The statement: f(x) is increasing on a < x < b. is the same as: 1a. f (x) is on a < x < b. 2. The statement: f (x) is negative on a < x < b. is the same as: 2a. f(x) is on
Math 10350 Exam 03 Review 1. The statement: f(x) is increasing on a < x < b. is the same as: 1a. f (x) is on a < x < b. 2. The statement: f (x) is negative on a < x < b. is the same as: 2a. f(x) is on
Exam Review Sheets Combined
 Exam Review Sheets Combined Fall 2008 1 Fall 2007 Exam 1 1. For each part, if the statement is always true, circle the printed capital T. If the statement is sometimes false, circle the printed capital
Exam Review Sheets Combined Fall 2008 1 Fall 2007 Exam 1 1. For each part, if the statement is always true, circle the printed capital T. If the statement is sometimes false, circle the printed capital
Math 115 Second Midterm Exam
 Math 115 Second Midterm Exam November 14, 2006 Name: Instructor: Section Number: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 8 pages including this cover. There are 7 questions.
Math 115 Second Midterm Exam November 14, 2006 Name: Instructor: Section Number: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 8 pages including this cover. There are 7 questions.
Math 211 Business Calculus TEST 3. Question 1. Section 2.2. Second Derivative Test.
 Math 211 Business Calculus TEST 3 Question 1. Section 2.2. Second Derivative Test. p. 1/?? Math 211 Business Calculus TEST 3 Question 1. Section 2.2. Second Derivative Test. Question 2. Section 2.3. Graph
Math 211 Business Calculus TEST 3 Question 1. Section 2.2. Second Derivative Test. p. 1/?? Math 211 Business Calculus TEST 3 Question 1. Section 2.2. Second Derivative Test. Question 2. Section 2.3. Graph
The Princeton Review AP Calculus BC Practice Test 1
 8 The Princeton Review AP Calculus BC Practice Test CALCULUS BC SECTION I, Part A Time 55 Minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION Directions: Solve each
8 The Princeton Review AP Calculus BC Practice Test CALCULUS BC SECTION I, Part A Time 55 Minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION Directions: Solve each
Find all points where the function is discontinuous. 1) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - 1) 2) f(x) =
 Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
5. Find the intercepts of the following equations. Also determine whether the equations are symmetric with respect to the y-axis or the origin.
 MATHEMATICS 1571 Final Examination Review Problems 1. For the function f defined by f(x) = 2x 2 5x find the following: a) f(a + b) b) f(2x) 2f(x) 2. Find the domain of g if a) g(x) = x 2 3x 4 b) g(x) =
MATHEMATICS 1571 Final Examination Review Problems 1. For the function f defined by f(x) = 2x 2 5x find the following: a) f(a + b) b) f(2x) 2f(x) 2. Find the domain of g if a) g(x) = x 2 3x 4 b) g(x) =
( ) as a fraction. If both numerator and denominator are
 A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
Math 210 Midterm #2 Review
 Math 210 Mierm #2 Review Related Rates In general, the approach to a related rates problem is to first determine which quantities in the problem you care about or have relevant information about. Then
Math 210 Mierm #2 Review Related Rates In general, the approach to a related rates problem is to first determine which quantities in the problem you care about or have relevant information about. Then
CALCULUS I: FIU FINAL EXAM PROBLEM COLLECTION: VERSION WITHOUT ANSWERS
 CALCULUS I: FIU FINAL EXAM PROBLEM COLLECTION: VERSION WITHOUT ANSWERS FIU MATHEMATICS FACULTY NOVEMBER 2017 Contents 1. Limits and Continuity 1 2. Derivatives 4 3. Local Linear Approximation and differentials
CALCULUS I: FIU FINAL EXAM PROBLEM COLLECTION: VERSION WITHOUT ANSWERS FIU MATHEMATICS FACULTY NOVEMBER 2017 Contents 1. Limits and Continuity 1 2. Derivatives 4 3. Local Linear Approximation and differentials
MA 125 CALCULUS I FALL 2006 December 08, 2006 FINAL EXAM. Name (Print last name first):... Instructor:... Section:... PART I
 CALCULUS I, FINAL EXAM 1 MA 125 CALCULUS I FALL 2006 December 08, 2006 FINAL EXAM Name (Print last name first):............................................. Student ID Number:...........................
CALCULUS I, FINAL EXAM 1 MA 125 CALCULUS I FALL 2006 December 08, 2006 FINAL EXAM Name (Print last name first):............................................. Student ID Number:...........................
Bonus Homework and Exam Review - Math 141, Frank Thorne Due Friday, December 9 at the start of the final exam.
 Bonus Homework and Exam Review - Math 141, Frank Thorne (thornef@mailbox.sc.edu) Due Friday, December 9 at the start of the final exam. It is strongly recommended that you do as many of these problems
Bonus Homework and Exam Review - Math 141, Frank Thorne (thornef@mailbox.sc.edu) Due Friday, December 9 at the start of the final exam. It is strongly recommended that you do as many of these problems
e) Find the average revenue when 100 units are made and sold.
 Math 142 Week in Review Set of Problems Week 7 1) Find the derivative, y ', if a) y=x 5 x 3/2 e 4 b) y= 1 5 x 4 c) y=7x 2 0.5 5 x 2 d) y=x 2 1.5 x 10 x e) y= x7 5x 5 2 x 4 2) The price-demand function
Math 142 Week in Review Set of Problems Week 7 1) Find the derivative, y ', if a) y=x 5 x 3/2 e 4 b) y= 1 5 x 4 c) y=7x 2 0.5 5 x 2 d) y=x 2 1.5 x 10 x e) y= x7 5x 5 2 x 4 2) The price-demand function
Calculus I (Math 241) (In Progress)
 Calculus I (Math 241) (In Progress) The following is a collection of Calculus I (Math 241) problems. Students may expect that their final exam is comprised, more or less, of one problem from each section,
Calculus I (Math 241) (In Progress) The following is a collection of Calculus I (Math 241) problems. Students may expect that their final exam is comprised, more or less, of one problem from each section,
Math 251 Final Exam Review Fall 2016
 Below are a set of review problems that are, in general, at least as hard as the problems you will see on the final eam. You should know the formula for area of a circle, square, and triangle. All other
Below are a set of review problems that are, in general, at least as hard as the problems you will see on the final eam. You should know the formula for area of a circle, square, and triangle. All other
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions
 Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically
 Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically Foundation Concepts: Limit Left-hand limit Right-hand limit 1 = 1 = tiny big Practice: 1. What can we say about lim,. f(x)? a) If lim, 3 4 f(x)=7
Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically Foundation Concepts: Limit Left-hand limit Right-hand limit 1 = 1 = tiny big Practice: 1. What can we say about lim,. f(x)? a) If lim, 3 4 f(x)=7
MLC Practice Final Exam. Recitation Instructor: Page Points Score Total: 200.
 Name: PID: Section: Recitation Instructor: DO NOT WRITE BELOW THIS LINE. GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. Page Points Score 3 20 4 30 5 20 6 20 7 20 8 20 9 25 10 25 11 20 Total: 200 Page 1 of 11 Name: Section:
Name: PID: Section: Recitation Instructor: DO NOT WRITE BELOW THIS LINE. GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. Page Points Score 3 20 4 30 5 20 6 20 7 20 8 20 9 25 10 25 11 20 Total: 200 Page 1 of 11 Name: Section:
dx dt = x 2 x = 120
 Solutions to Review Questions, Exam. A child is flying a kite. If the kite is 90 feet above the child s hand level and the wind is blowing it on a horizontal course at 5 feet per second, how fast is the
Solutions to Review Questions, Exam. A child is flying a kite. If the kite is 90 feet above the child s hand level and the wind is blowing it on a horizontal course at 5 feet per second, how fast is the
MATH 2053 Calculus I Review for the Final Exam
 MATH 05 Calculus I Review for the Final Exam (x+ x) 9 x 9 1. Find the limit: lim x 0. x. Find the limit: lim x + x x (x ).. Find lim x (x 5) = L, find such that f(x) L < 0.01 whenever 0 < x
MATH 05 Calculus I Review for the Final Exam (x+ x) 9 x 9 1. Find the limit: lim x 0. x. Find the limit: lim x + x x (x ).. Find lim x (x 5) = L, find such that f(x) L < 0.01 whenever 0 < x
Calculus 437 Semester 1 Review Chapters 1, 2, and 3 January 2016
 Name: Class: Date: Calculus 437 Semester 1 Review Chapters 1, 2, and 3 January 2016 Short Answer 1. Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether calculus is required.
Name: Class: Date: Calculus 437 Semester 1 Review Chapters 1, 2, and 3 January 2016 Short Answer 1. Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether calculus is required.
Math 115 Test 1 Sample Problems for Dr. Hukle s Class
 Mat 5 Test Sample Problems for Dr. Hukle s Class. Demand for a Jayawk pen at te Union is known to be D(p) = 26 pens per mont wen te selling p price is p dollars and eac p 3. A supplier for te bookstore
Mat 5 Test Sample Problems for Dr. Hukle s Class. Demand for a Jayawk pen at te Union is known to be D(p) = 26 pens per mont wen te selling p price is p dollars and eac p 3. A supplier for te bookstore
MA 125 CALCULUS I SPRING 2007 April 27, 2007 FINAL EXAM. Name (Print last name first):... Student ID Number (last four digits):...
 CALCULUS I, FINAL EXAM 1 MA 125 CALCULUS I SPRING 2007 April 27, 2007 FINAL EXAM Name (Print last name first):............................................. Student ID Number (last four digits):........................
CALCULUS I, FINAL EXAM 1 MA 125 CALCULUS I SPRING 2007 April 27, 2007 FINAL EXAM Name (Print last name first):............................................. Student ID Number (last four digits):........................
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. is continuous.
 Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
See animations and interactive applets of some of these at. Fall_2009/Math123/Notes
 MA123, Chapter 7 Word Problems (pp. 125-153) Chapter s Goal: In this chapter we study the two main types of word problems in Calculus. Optimization Problems. i.e., max - min problems Related Rates See
MA123, Chapter 7 Word Problems (pp. 125-153) Chapter s Goal: In this chapter we study the two main types of word problems in Calculus. Optimization Problems. i.e., max - min problems Related Rates See
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 2) h(x) = x2-5x + 5
 Assignment 7 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the derivative of f(x) given below, determine the critical points of f(x).
Assignment 7 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the derivative of f(x) given below, determine the critical points of f(x).
Puxi High School Examinations Semester 1, AP Calculus (BC) Part 1. Wednesday, December 16 th, :45 pm 3:15 pm.
 Puxi High School Examinations Semester 1, 2009 2010 AP Calculus (BC) Part 1 Wednesday, December 16 th, 2009 12:45 pm 3:15 pm Time: 45 minutes Teacher: Mr. Surowski Testing Site: HS Gymnasium Student Name:
Puxi High School Examinations Semester 1, 2009 2010 AP Calculus (BC) Part 1 Wednesday, December 16 th, 2009 12:45 pm 3:15 pm Time: 45 minutes Teacher: Mr. Surowski Testing Site: HS Gymnasium Student Name:
Puxi High School Examinations Semester 1, AP Calculus (BC) Part 1. Wednesday, December 16 th, :45 pm 3:15 pm.
 Puxi High School Examinations Semester 1, 2009 2010 AP Calculus (BC) Part 1 Wednesday, December 16 th, 2009 12:45 pm 3:15 pm Time: 45 minutes Teacher: Mr. Surowski Testing Site: HS Gymnasium Student Name:
Puxi High School Examinations Semester 1, 2009 2010 AP Calculus (BC) Part 1 Wednesday, December 16 th, 2009 12:45 pm 3:15 pm Time: 45 minutes Teacher: Mr. Surowski Testing Site: HS Gymnasium Student Name:
Applications of Derivatives
 Applications of Derivatives Big Ideas Connecting the graphs of f, f, f Differentiability Continuity Continuity Differentiability Critical values Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: Hypothesis: If f is
Applications of Derivatives Big Ideas Connecting the graphs of f, f, f Differentiability Continuity Continuity Differentiability Critical values Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: Hypothesis: If f is
Math 221 Exam II Tuesday Mar 23 5:30-7:00 PM Answers
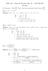 Math 221 Exam II Tuesday Mar 23 5:30-7:00 PM Answers I. (25 points.) Find. Note: The book sometimes writes D xy for. (a) y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 Answer: Let u = x 2 x + 1. Then y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 = u 7 so = d
Math 221 Exam II Tuesday Mar 23 5:30-7:00 PM Answers I. (25 points.) Find. Note: The book sometimes writes D xy for. (a) y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 Answer: Let u = x 2 x + 1. Then y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 = u 7 so = d
Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications
 Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications Summary: The main purpose of this chapter is to use the derivative as a tool to assist in the graphing of functions and for solving optimization problems.
Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications Summary: The main purpose of this chapter is to use the derivative as a tool to assist in the graphing of functions and for solving optimization problems.
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review
 MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
Final Exam Review (Section 8.3 and Review of Other Sections)
 c Kathryn Bollinger, April 29, 2014 1 Final Exam Review (Section 8.3 and Review of Other Sections) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the material covered throughout
c Kathryn Bollinger, April 29, 2014 1 Final Exam Review (Section 8.3 and Review of Other Sections) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the material covered throughout
Math 115 Final Exam April 28, 2014
 On my honor, as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Signed: Math 115 Final Exam April 8, 014 Name: Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you
On my honor, as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Signed: Math 115 Final Exam April 8, 014 Name: Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you
3. (1.2.13, 19, 31) Find the given limit. If necessary, state that the limit does not exist.
 Departmental Review for Survey of Calculus Revised Fall 2013 Directions: All work should be shown and all answers should be exact and simplified (unless stated otherwise) to receive full credit on the
Departmental Review for Survey of Calculus Revised Fall 2013 Directions: All work should be shown and all answers should be exact and simplified (unless stated otherwise) to receive full credit on the
Exam A. Exam 3. (e) Two critical points; one is a local maximum, the other a local minimum.
 1.(6 pts) The function f(x) = x 3 2x 2 has: Exam A Exam 3 (a) Two critical points; one is a local minimum, the other is neither a local maximum nor a local minimum. (b) Two critical points; one is a local
1.(6 pts) The function f(x) = x 3 2x 2 has: Exam A Exam 3 (a) Two critical points; one is a local minimum, the other is neither a local maximum nor a local minimum. (b) Two critical points; one is a local
MLC Practice Final Exam
 Name: Section: Recitation/Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through. Show all your work on the standard response
Name: Section: Recitation/Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through. Show all your work on the standard response
Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions
 39 Algebra 2 Honors Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Section 2.1: Use Properties of Exponents Evaluate each expression (3 4 ) 2 ( 5 8 ) 3 ( 2) 3 ( 2) 9 ( a2 3 ( y 2 ) 5 y 2 y 12 rs
39 Algebra 2 Honors Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Section 2.1: Use Properties of Exponents Evaluate each expression (3 4 ) 2 ( 5 8 ) 3 ( 2) 3 ( 2) 9 ( a2 3 ( y 2 ) 5 y 2 y 12 rs
Review for the Final Exam
 Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Part A: Short Answer Questions
 Math 111 Practice Exam Your Grade: Fall 2015 Total Marks: 160 Instructor: Telyn Kusalik Time: 180 minutes Name: Part A: Short Answer Questions Answer each question in the blank provided. 1. If a city grows
Math 111 Practice Exam Your Grade: Fall 2015 Total Marks: 160 Instructor: Telyn Kusalik Time: 180 minutes Name: Part A: Short Answer Questions Answer each question in the blank provided. 1. If a city grows
Doug Clark The Learning Center 100 Student Success Center learningcenter.missouri.edu Overview
 Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
Chapter 4. Section Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 - Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: The student will be able to calculate the derivative of e x and of lnx. The student will be able to compute the
Chapter 4 Section 4.2 - Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: The student will be able to calculate the derivative of e x and of lnx. The student will be able to compute the
4. a b c d e 14. a b c d e. 5. a b c d e 15. a b c d e. 6. a b c d e 16. a b c d e. 7. a b c d e 17. a b c d e. 9. a b c d e 19.
 MA1 Elem. Calculus Spring 017 Final Exam 017-0-0 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use an ACT-approved calculator during
MA1 Elem. Calculus Spring 017 Final Exam 017-0-0 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use an ACT-approved calculator during
2.6 Related Rates. The Derivative as a Rate of Change. = ft related rates 175
 2.6 related rates 175 2.6 Related Rates Throughout the next several tions we ll look at a variety of applications of derivatives. Probably no single application will be of interest or use to everyone,
2.6 related rates 175 2.6 Related Rates Throughout the next several tions we ll look at a variety of applications of derivatives. Probably no single application will be of interest or use to everyone,
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM
 MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM March 31, 2009 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM March 31, 2009 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.
College Algebra: Midterm Review
 College Algebra: A Missive from the Math Department Learning College Algebra takes effort on your part as the student. Here are some hints for studying that you may find useful. Work Problems If you do,
College Algebra: A Missive from the Math Department Learning College Algebra takes effort on your part as the student. Here are some hints for studying that you may find useful. Work Problems If you do,
Derivatives and Rates of Change
 Sec.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change A. Slope of Secant Functions rise Recall: Slope = m = = run Slope of the Secant Line to a Function: Examples: y y = y1. From this we are able to derive: x x x1 m y
Sec.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change A. Slope of Secant Functions rise Recall: Slope = m = = run Slope of the Secant Line to a Function: Examples: y y = y1. From this we are able to derive: x x x1 m y
B) Increasing on (-1, ); Decreasing on (-, -1) C) Increasing on (-, -1); Decreasing on (-1, ) D) Increasing on (-, 1); Decreasing on (1, ) 2) 2)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine the intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, and constant. 1) 1) Increasing
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine the intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, and constant. 1) 1) Increasing
D) Increasing on (-1, ); Decreasing on (-, -1) B) Increasing on (-, -1); Decreasing on (-1, ) C) Increasing on (-, 1); Decreasing on (1, ) 2) 2)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine the intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, and constant. 1) 1) Increasing
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine the intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, and constant. 1) 1) Increasing
Fall 2009 Math 113 Final Exam Solutions. f(x) = 1 + ex 1 e x?
 . What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
. What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
Exam 3 Practice Problems
 MATH1214 Exam 3 Practice Problems 1. Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of f(x) = x 3 + 3x 2 9x 7 on each of the following intervals (a) [ 6, 4] (b) [ 4, 2] (c) [ 2, 2] 2. Find the absolute
MATH1214 Exam 3 Practice Problems 1. Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of f(x) = x 3 + 3x 2 9x 7 on each of the following intervals (a) [ 6, 4] (b) [ 4, 2] (c) [ 2, 2] 2. Find the absolute
Math 115 Final Exam April 24, 2017
 On my honor, as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Initials: Do not write in this area Your Initials Only: Math 5 Final Exam April 2, 207 Your U-M ID #
On my honor, as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Initials: Do not write in this area Your Initials Only: Math 5 Final Exam April 2, 207 Your U-M ID #
4.1 & 4.2 Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives. for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number f()
 4.1 & 4. Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives Definition A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if f ( c) f ( x) for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number
4.1 & 4. Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives Definition A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if f ( c) f ( x) for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number
Answer Key. Calculus I Math 141 Fall 2003 Professor Ben Richert. Exam 2
 Answer Key Calculus I Math 141 Fall 2003 Professor Ben Richert Exam 2 November 18, 2003 Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem
Answer Key Calculus I Math 141 Fall 2003 Professor Ben Richert Exam 2 November 18, 2003 Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem
DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
 AP Calculus AB Exam SECTION I: Multiple Choice 016 DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time 1 hour, 45 minutes Number of Questions 45 Percent of Total Score 50% Writing
AP Calculus AB Exam SECTION I: Multiple Choice 016 DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time 1 hour, 45 minutes Number of Questions 45 Percent of Total Score 50% Writing
MA 123 Recitation Activity Sheets
 MA 123 Recitation Activity Sheets You will need to bring this packet with you to recitation each week. Some of the exercises included in this packet closely follow the lecture material and homework problems.
MA 123 Recitation Activity Sheets You will need to bring this packet with you to recitation each week. Some of the exercises included in this packet closely follow the lecture material and homework problems.
Exam 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation. x3 + y3 = 5 A)
Exam 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation. x3 + y3 = 5 A)
APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES
 94 APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES Chapter 6 With the Calculus as a key, Mathematics can be successfully applied to the explanation of the course of Nature. WHITEHEAD 6. Introduction In Chapter 5, we have learnt
94 APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES Chapter 6 With the Calculus as a key, Mathematics can be successfully applied to the explanation of the course of Nature. WHITEHEAD 6. Introduction In Chapter 5, we have learnt
Final Exam 12/11/ (16 pts) Find derivatives for each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 1+ x e + e π [Do not simplify your answer.
 Math 105 Final Exam 1/11/1 Name Read directions carefully and show all your work. Partial credit will be assigned based upon the correctness, completeness, and clarity of your answers. Correct answers
Math 105 Final Exam 1/11/1 Name Read directions carefully and show all your work. Partial credit will be assigned based upon the correctness, completeness, and clarity of your answers. Correct answers
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
No calculators, cell phones or any other electronic devices can be used on this exam. Clear your desk of everything excepts pens, pencils and erasers.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS. Do not open your exam until told to do so. No calculators, cell phones or any other electronic devices can be used on this exam. Clear
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS. Do not open your exam until told to do so. No calculators, cell phones or any other electronic devices can be used on this exam. Clear
NO CALCULATOR 1. Find the interval or intervals on which the function whose graph is shown is increasing:
 AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 5 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 5 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
Applied Calculus I. Review Solutions. Qaisar Latif. October 25, 2016
 Applied Calculus I Review Solutions Qaisar Latif October 25, 2016 2 Homework 1 Problem 1. The number of people living with HIV infections increased worldwide approximately exponentially from 2.5 million
Applied Calculus I Review Solutions Qaisar Latif October 25, 2016 2 Homework 1 Problem 1. The number of people living with HIV infections increased worldwide approximately exponentially from 2.5 million
Implicit Differentiation
 Week 6. Implicit Differentiation Let s say we want to differentiate the equation of a circle: y 2 + x 2 =9 Using the techniques we know so far, we need to write the equation as a function of one variable
Week 6. Implicit Differentiation Let s say we want to differentiate the equation of a circle: y 2 + x 2 =9 Using the techniques we know so far, we need to write the equation as a function of one variable
, find the value(s) of a and b which make f differentiable at bx 2 + x if x 2 x = 2 or explain why no such values exist.
 Math 171 Exam II Summary Sheet and Sample Stuff (NOTE: The questions posed here are not necessarily a guarantee of the type of questions which will be on Exam II. This is a sampling of questions I have
Math 171 Exam II Summary Sheet and Sample Stuff (NOTE: The questions posed here are not necessarily a guarantee of the type of questions which will be on Exam II. This is a sampling of questions I have
