ON CONVEXITY OF HELE- SHAW CELLS Ibrahim W. Rabha Institute of Mathematical Sciences, University Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
|
|
|
- Gregory Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROMAI J., v.8, no.1(2012), ON CONVEXITY OF HELE- SHAW CELLS Ibrahim W. Rabha Institute of Mathematical Sciences, University Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract The main aim of this paper is to apply methods of the theory of univalent functions and geometric functions to some problems of fluid mechanics. We study the time evolution of the free boundary of a viscous fluid for planar flows in Hele- Shaw cells under injection; we prove the invariance in time of convexity of complex order for two basic cases: the inner problem and the outer problem. Keywords: free boundary problem, conformal map, complex analysis, univalent functions, unit disk, Hele-Shaw cells, Hadamard product, convex function, convex of complex order MSC: 30C45,76S05, 76D INTRODUCTION One of the basic models is a fluid flow in a Hele-Shaw cell. Hele-Shaw [1] first described his cell, which was an experimental device for studying fluid flow by pumping a viscous liquid into the gap between two closely-separated glass plates. Using dye-lines, he was able to observe the flow patterns generated when the flow was impeded by various kinds of obstacles, such as aerofoil sections, placed between the plates. If the displacing fluid has lower viscosity than the displaced fluid the interface will develop hydrodynamical instability which results in highly ramified patterns [2-4]. This phenomenon is known as viscous fingering, and it may also occur when elasticity of the fluids acts as another driving mechanism [5-7]. Pattern formation of similar type has been observed in a variety of non equilibrium systems besides viscous fingering, such as crystal growth [8], electrodeposition [9] and solidification [10]. The canonical mathematical model for Hele-Shaw flows is Darcy s law, where the flow velocity is proportional to the pressure gradient: Darcy Law : v n (z) H(z); z γ(t), where v n is the velocity of the curve, γ(t) is a simple planar curve - boundary of a simply-connected domain and H(z) is the normal gradient of a solution of the Dirichlet problem in a fluid domain D with a source (a sink) at a distant location (often at infinity). Under the assumption that the flow is incompressible, the pressure field satisfies a Laplace s equation; therefore, such an evolution of the free interface is also called Laplacian growth process. The method of conformal mapping resides its 93
2 94 Ibrahim W. Rabha strength of transforming the generally difficult task of solving a moving-free boundary problem into finding solutions to a single differential equation of an analytic function on a fixed domain, usually the half plane or the interior of the unit disk. Indeed, the simply connected domains are preserved in rotating cell [11]. Recently, the stability of this method was considered in [12]. The time evolution of the free boundary of a viscous fluid for planar flows in Hele- Shaw cells under injection was studied by many authors. By using methods of univalent functions theory, they proved that certain geometric properties (such as starlikeness, directional convexity Φ like and E family) are preserved in time [13-20]. In fact, as any zero-surface tension problem is timer-eversible, blow-up solutions can be generated by injecting with a non-smooth free boundary and then reversing the sequence of solutions so obtained. This procedure can reveal unexpected features, an example being the waiting time that can occur when injection takes place into an initial domain with a corner [21]. The analysis of this situation again involves the Baiocchi transform of the pressure, and this device is also instrumental in the analysis of allowable cusps in injection problems [22]. In this paper, we continue their study by proving the invariance in time of another geometric property. We study the time evolution of the free boundary of a viscous fluid for planar flows in Hele- Shaw cells under injection. Applying methods from the theories of univalent functions and geometric functions; we prove the invariance in time of convexity of complex order property for two basic cases: the inner problem and the outer problem. 2. HELE-SHAW CELLS PROBLEM We study the flow of a viscous fluid in a planar Hele-Shaw cell under injection through a source (of constant strength Q, Q < 0 in case of injection) which is situated at the origin. Suppose that for the initial time, the phase domain Ω 0 occupied by the fluid is simply connected and bounded by a smooth curve Γ 0. The evolution of the phase domains Ω(t), Ω(0) = Ω 0 is described by an auxiliary conformal mapping f (ζ, t), f (ζ, 0) = f 0 (ζ) on the unit disk U := {z C : z < 1} onto Ω(t), Γ(t) = Ω(t) normalized by f (0, t) = 0, f (0, t) > 0. We denote the derivatives by f (z, t) = f z and f (z, t) = f t, where t is the time parameter. The function f (ζ, 0) = f 0(ζ) poses a parametrization of Γ 0 = { f 0 (e iθ ), θ [0, 2π)}, while the moving boundary is parameterized by Γ(t) = { f (e iθ, t), θ [0, 2π)}. This mapping satisfies the equation (see [23-27]) R[ f (ζ, t)ζ f (ζ, t)] = Q 2π, ζ = eiθ. (1) In the case of the problem of injection Q < 0 of the fluid into a bounded simply connected with small surface tension γ > 0, the Polubarinova-Galin equation [18] is of the form:
3 On convexity of Hele- Shaw cells 95 where R[ f (ζ, t)ζ f (ζ, t)] = Q 2π + γh[ik θ (eiθ, t)](θ), ζ = e iθ, (2) k(e iθ, t) = 1 f (e iθ, t) R( 1 + eiθ f (e iθ, t) ), θ [0, 2π), f (e iθ, t) k θ (eiθ, t) = I( e2iθ S f (e iθ, t) f (e iθ ),, t) S f = ( f f ) 1 2 ( f f )2 is the Schwarzian derivative, and H[Φ](θ) is the Hilbert transform given by H[Φ](θ) = 1 π P.V. θ 2π (PV denotes the Cauchy principal value) satisfying where 0 Φ(e iθ ) 1 e i(θ θ ) dθ θ [ik θ (eiθ, t)](θ) = H[iA](θ), A(ζ) = ( 1 )[ ( R 2ζ 2 f S f (ζ)+ζ( f (ζ) (ζ) f (ζ) ) ζ( f (ζ) f (ζ) )( f (ζ) f (ζ) ) ) +I ( ζ f (ζ)) Iζ 2 f S f (ζ) ]. (ζ) The case of unbounded domain with bounded complement virtues as the dynamics of a contracting bubble in a Hele-Shaw cell since the fluid occupies a neighborhood of infinity and injection (of constant strength Q < 0) is supposed to take place at infinity. Again, we denote by Ω(t) the domain occupied by the fluid at the moment t, Γ(t) = Ω(t). By using the Riemann mapping theorem, the domain Ω(t) can be described by a univalent function F(ζ, t) from the exterior of the unit disk U = {ζ : ζ > 1} onto Ω(t). The equation satisfied by the free boundary is [16,18] for the zero tension surface model and R[Ḟ(ζ, t)ζf (ζ, t)] = Q 2π, ζ = eiθ, (3) R[Ḟ(ζ, t)ζf (ζ, t)] = Q 2π γh[ik θ (eiθ, t)](θ), ζ = e iθ, (4) for the small surface tension model.
4 96 Ibrahim W. Rabha 3. THE INNER PROBLEM Let us define the classes of convex functions which will parameterize our phase domains. If a function f (z) maps U onto a convex domain and f (0) = 0, then we say that f (z) is a convex function. A necessary and sufficient condition for a function f to be convex is the inequality R(1 + z f (z) f (z) ) > 0. In this section, we impose the invariance in time of convex of complex order for the inner problem. Starting with an initial bounded domain Ω(0) which is convex of complex order, we prove that at each moment t [0, T) the domain Ω(t) is convex of complex order. Definition 3.1. Let f be a holomorphic function on U such that f (0) = 0, f (0) 0. A function f is called convex of complex order b (b C\{0}) if it satisfies the following inequality R{1 + 1 b (z f (z) f 1)} > 0, (z U). (z) We denoted this class C(b). Definition 3.2. A simply connected domain Ω C is convex in the direction of the real axis R if each line parallel to R either misses Ω or the intersection with Ω is a connected set. If a function f (ζ) maps U(the unit disk) onto a domain which is convex in the direction of the real axis, f (0) = 0, then we say that f (z) is a convex function in the direction of the real axis and denote the class of such function by C R and by C R (b) for convex of complex order in the direction of the real axis. Theorem 3.1. Let Q < 0 and f 0 C R (b) on U and univalent in U. Let f (ζ, t) be the classical solution of the Polubarinova-Galin equation (1) with the initial condition f (ζ, 0) = f 0 (ζ). Moreover, let Ω := t [0,T) Ω(t) = t [0,T) f (U, t), where T is the blow-up time. If Rb = 2 and 1 < Ib < 2 then f (ζ, t) C R (b) in the direction of the real axis R for ζ [ɛ, 1), 0 < ɛ < 1. Proof. Assume that there exists a complex number such that which satisfies the equality ζ 0 := (e iθ 0 ) b, ζ0 1 ( arg ζ 0 b f (ζ 0, t 0 ) ) b = π 2 (or π ), b 0 2 and for ɛ > 0 there is t > t 0 and θ (θ 0 ɛ, θ 0 + ɛ) such that arg ζ ( b f (ζ, t) ) b π 2 (or π 2 ).
5 Then for ζ = (e iθ ) b, which yields Since f (e i( b )θ, t) 0 we obtain ( θ arg(eiθ ) b b f (e On convexity of Hele- Shaw cells 97 i( b R { b [ζ f (ζ, t 0 ) f (ζ, t 0 ) )θ, t) ) b 0, 1] } > 0. Iζ 0 (b f (ζ 0, t 0 )) b > 0. Since ζ 0 is a critical point then we deduce that and We put r θ arg ei( )θ( b b f (e arg ei( )θ( b b f (re i( b i( b )θ, t) ) b )θ, t) ) b R ( b [ζ 0 f (ζ 0, t 0 ) f (ζ 0, t 0 ) I ( b [ζ 0 f (ζ 0, t 0 ) f (ζ 0, t 0 ) = 0 θ=θ0,t=t 0 0. θ=θ0,t=t 0,r=1 1] ) = 0, 1] ) > 0. Equality does not hold for the last assertion because the level lines preserve the property of being convex in the direction of R. By the assumptions Rb = 2 and Ib < 2, we obtain R ( 1 + ζ 0 f (ζ 0, t 0 )) = 0, (5) f (ζ 0, t 0 ) Then we derive I ( 1 + ζ 0 f (ζ 0, t 0 ) f (ζ 0, t 0 ) ) > 0. (6) t arg ζ(b f (ζ, t)) b 1 = I t f (ζ, t) b 1 f (ζ, t). (7) By differentiating the Polubarinova-Galin equation with respect to θ for ζ = 1, we obtain or I ( f (ζ, t) t f (ζ, t) ζ f (ζ, t) f (ζ, t) ζ 2 f (ζ, t) f (ζ, t) ) = 0 f (ζ, t) 2 I ( t f (ζ, t) f (ζ, t) ζ f (ζ, t) f (ζ, t) ζ 2 f (ζ, t) f (ζ, t) ) = 0
6 98 Ibrahim W. Rabha and consequently, we have f (ζ, t) 2 I 1 t f (ζ, t) b 1 f = I 1 (ζ, t) b 1 ζ f (ζ, t) f (ζ, t) ( ζ f (ζ, t) f 1 ) (ζ, t) Substituting (1) and (5) in last equation, we have t arg ζ( b f (ζ, t) ) b = ζ=ζ0,t=t 0 Q 2π f (ζ 0, t 0 ) 2 I 1 (ζ f (ζ 0, t 0 ) b 1 f + 1 ). (ζ 0, t 0 ) The right-hand side of this equality is strictly negative because of (6) and Ib > 1. Hence arg ζ ( b f (ζ, t) ) b < π 2 for t close to t 0 and in a neighborhood of θ 0 and this is a contradiction. 4. THE OUTER PROBLEM In this section, we obtain the invariance in time of the same geometric property (denoted by C(b)) for the outer problem (injection at infinity). Here we prove that our problem preserves geometric properties of domains with C(b) complements. Let us suppose that the complement of the fluid domain contains the origin and is in the class C(b) with respect to the origin at the initial instant, we have the following definition: Definition 4.1. Let F be a holomorphic function on U such that F(ζ) = aζ + a 0 + a 1 ζ +..., a 0. The C(b) is defined so that R{1 + 1 b (zf (z) F (z) 1)} > 0, ζ U. (8) Straightforward computations give the following facts: Remark 4.1. (a) If the function F belongs to the C(b) in U then the function f : U C given by is a member in C(b) on U. f (z) = 1 F( 1 z 0, f (0) = 0 z ),
7 On convexity of Hele- Shaw cells 99 (b) If the function f belongs to the C(b) in U then the function F : U C given by F(ζ) = 1 f ( 1 ζ 0, ζ ), is a member in C(b) on U. (c) If F C(b), then it is univalent on U. Theorem 4.1. Let Q < 0 and F 0 be a function which is in the class C(b) on U and univalent in U. Let F(ζ, t) be the classical solution of the Polubarinova-Galin equation (3) with the initial condition F(ζ, 0) = F 0 (ζ). Moreover, let Ω := t [0,T) Ω(t) = t [0,T) F(U, t), where T is the blow-up time. If If Rb = 2 and 1 < Ib < 2 then F(ζ, t) is in C(b). Proof. By assuming the function f (ζ, t) = 1/F( 1 ζ ), the Polubarinova-Galin equation (3) can be rewritten in terms of f as follows: R[ f (ζ, t)ζ f Q f (ζ, t) 4 (ζ, t)] =, ζ = 1. (9) 2π According to the previous remark, the function F(ζ, t), ζ U is in C(b) if and only if f (ζ, t), ζ U is in C(b). Thus, it suffices to prove that the functions f (ζ, t), ζ U, t [0, T), is in C(b). Suppose by contrary that the previous statement is not true. Then there exist t 0 0 and ζ 0 = e iθ 0 such that equations (5-7) are held. Calculation gives t arg ζ( b f (ζ, t) ) b = Q f (ζ 0, t 0 ) 2 I 1 (ζ f (ζ 0, t 0 ) ζ=ζ0,t=t 0 2π b 1 f + 1 ). (ζ 0, t 0 ) The right-hand side of this equality is strictly negative because of (6) and Ib > 1. Hence arg ζ ( b f (ζ, t) ) b < π 2 for t close to t 0 and in a neighborhood of θ 0 or arg[1 + 1 b (eiθ f (e iθ, t) f (e iθ, t) 1)] < π 2 and this is a contradiction. Hence f (ζ, t), ζ U is in the C(b) and consequently F(ζ, t), ζ U is in C(b).
8 100 Ibrahim W. Rabha 5. CONCLUSION We imposed sufficient conditions for convexity of Hele- Shaw Cells in complex domain. This problem was studied by Gustafsson, Friedman, Hohlov, Markina, Prokhorov, Vasil ev and others. We considered a modification of a logarithmic antiderivative of the convex of complex order. The functional that assumed here taking the form ζ ( b f (ζ, t) ) b such that Rb = 2 and 1 < Ib < 2. This functional satisfied ( arg ζ 0 b f (ζ 0, t 0 ) ) b = π 2 (or π ), b 0 2 where ζ 0 := (e iθ 0 ) b, ζ0 1. References [1] H.S. Hele-Shaw, The flow of water, Nature, 58(1898), [2] P. Saffman, G. I. Taylor, The penetration of a fluid into a porous medium or Hele-Shaw cell containing a more viscous fluid, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 245(1958), [3] L. Paterson, Radial fingering in a Hele-Shaw cell, J. Fluid Mech. 113(1981), [4] D. Bensimon, Stability of viscous fingering, Phys. Rev., A 33(1986), [5] E. Lemaire, P. Levitz, G. Daccord, H. Damme, From viscous fingering to viscoelastic fracturing, Phys. Rev. Lett., 67(1991), [6] T. Podgorski, M. C. Sostarecz, S. Zorman, A. Belmonte, Fingering instabilities of a reactive micellar interface, Physical Review E, 76( )(2007), 1-6. [7] S. Mora, M. Manna, Saffman-Taylor instability of viscoelastic uids: From viscous fingering to elastic fractures, Physical Review E, 81(026305) (2010), [8] J. Langer, Instabilities and pattern formation in crystal growth, Rev. Mod. Phys., 52(1980), [9] M. Matsushita, M. Sano, Y. Hayakawa, H. Honjo, Y. Sawada, Fractal structures of zinc metal leaves grown by electrodeposition, Phys. Rev. Lett., 53(1984), [10] J. Hunt, Pattern formation in solidification, Materials Science & Technology, 15(1999), [11] V.M. Entov, P.I. Etingof, D. Ya, Kleinbock, On nonlinear interface dynamics in Hele-Shaw flows, Eur. J. Appl. Math., 6(1995), [12] A. He, A. Belmonte, Inertial effects on viscous fingering in the complex plane, J. Fluid Mech., 668(2011), [13] Y. E. Hohlov, D. V. Prokhorov, A. J. Vasil ev, On geometrical properties of free boundaries in the Hele-Shaw flows moving boundary problem, Lobachevskii Journal of Mathematics, 1(1998), [14] K. Kornev, A. Vasil ev, Geometric properties of the solutions of a Hele-Shaw type equation, Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 128, 9(2000), [15] D. Prokhorov, A. Vasil ev, Convex dynamics in Hele-Shaw cells, International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences, 31, 11(2002), [16] A. Vasil ev, Univalent functions in the dynamics of viscous flows, Computational Methods and Function Theory, 1, 2(2001),
9 On convexity of Hele- Shaw cells 101 [17] A. Vasil ev, Univalent functions in two-dimensional free boundary problems, Acta Applicandae Mathematicae, 79, 3(2003), [18] A. Vasil ev, I. Markina, On the geometry of Hele-Shaw flows with small surface tension, Interfaces and Free Boundaries, 5, 2(2003), [19] P. Curt, D. Fericean, A Special class of univalent functions in Hele-Shaw flow problems, Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID , [20] R.W. Ibrahim, On Geometric Properties for Hele- Shaw Cells, Complex Variables and Elliptic Equations. To appear. [21] J.R. King,, A.A. Lacey, J.L. Vazquez, Persistence of corners in free boundaries in Hele-Shaw flow, Europ. J. Appl. Math., 6(1995), [22] S.D Howison, Cusp development in Hele-Shaw flow with a free surface, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 46(1986), [23] L. A. Galin, Unsteady filtration with a free surface, Doklady Akademii Nauk USSR, 47(1945), , (Russian). [24] P. Y. Polubarinova-Kochina, On a problem of the motion of the contour of a petroleum shell, Doklady Akademii Nauk USSR, 47(1945), , (Russian). [25] P. J. Poloubarinova-Kochina, Concerning unsteady motions in the theory of filtration, 9, 1(1945), 79-90, (in Russian). [26] L. Fejer, Mechanische Quadraturen mit positiven Cotesschen Zahlen, Math. Zeitschrift, 37, 2 (1933), [27] B. Gustafsson, A. Vasil ev, Conformal and Potential Analysis in Hele-Shaw Cells, Advances in Mathematical Fluid Mechanics, Birkhäuser, Basel, Switzerland, 2006.
Inertial effects on viscous fingering in the complex plane
 J. Fluid Mech. (011), vol. 668, pp. 436 445. c Cambridge University Press 011 doi:10.1017/s0011010005859 Inertial effects on viscous fingering in the complex plane ANDONG HE 1 AND ANDREW BELMONTE 1, 1
J. Fluid Mech. (011), vol. 668, pp. 436 445. c Cambridge University Press 011 doi:10.1017/s0011010005859 Inertial effects on viscous fingering in the complex plane ANDONG HE 1 AND ANDREW BELMONTE 1, 1
On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell
 On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell Gelu Paşa Abstract. In this paper we study the linear stability of the displacement of two incompressible Stokes fluids in a 3D
On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell Gelu Paşa Abstract. In this paper we study the linear stability of the displacement of two incompressible Stokes fluids in a 3D
Classical solutions for the quasi-stationary Stefan problem with surface tension
 Classical solutions for the quasi-stationary Stefan problem with surface tension Joachim Escher, Gieri Simonett We show that the quasi-stationary two-phase Stefan problem with surface tension has a unique
Classical solutions for the quasi-stationary Stefan problem with surface tension Joachim Escher, Gieri Simonett We show that the quasi-stationary two-phase Stefan problem with surface tension has a unique
CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES. Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles
 CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Scientific questions Chemical reactions can induce changes in viscosity or density
CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Scientific questions Chemical reactions can induce changes in viscosity or density
Two-dimensional Stokes and Hele-Shaw flows with free surfaces
 Under consideration for publication in Euro. Jnl of Applied Mathematics 1 Two-dimensional Stokes and Hele-Shaw flows with free surfaces L. J. CUMMINGS 1, S. D. HOWISON 1, and J. R. KING 2 1 Mathematical
Under consideration for publication in Euro. Jnl of Applied Mathematics 1 Two-dimensional Stokes and Hele-Shaw flows with free surfaces L. J. CUMMINGS 1, S. D. HOWISON 1, and J. R. KING 2 1 Mathematical
Interface Dynamics for Quasi- Stationary Stefan Problem
 Interface Dynamics for Quasi- Stationary Stefan Problem R. Andrushkiw Department of Mathematical Sciences New Jersey Institute of Technology Newark, New Jersey 7 USA V. Gafiychuk Institute of Computer
Interface Dynamics for Quasi- Stationary Stefan Problem R. Andrushkiw Department of Mathematical Sciences New Jersey Institute of Technology Newark, New Jersey 7 USA V. Gafiychuk Institute of Computer
approach to Laplacian Growth Problems in 2-D
 Conformal Mapping and Boundary integral approach to Laplacian Growth Problems in 2-D Saleh Tanveer (Ohio State University) Collaborators: X. Xie, J. Ye, M. Siegel Idealized Hele-Shaw flow model Gap averaged
Conformal Mapping and Boundary integral approach to Laplacian Growth Problems in 2-D Saleh Tanveer (Ohio State University) Collaborators: X. Xie, J. Ye, M. Siegel Idealized Hele-Shaw flow model Gap averaged
On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a Boundary Point
 Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 261, 649 664 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7564, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 261, 649 664 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7564, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a
Hele-Shaw Flows and Classical Potential Theory. Lavi Karp. Department of Mathematics, ORT Braude College P.O. Box 78, Karmiel 21982, Israel
 Hele-Shaw Flows and Classical Potential Theory Lavi Karp Department of Mathematics, ORT Braude College P.O. Box 78, Karmiel 21982, Israel 1 1 The Mathematical Model We consider a flow of a homogeneous
Hele-Shaw Flows and Classical Potential Theory Lavi Karp Department of Mathematics, ORT Braude College P.O. Box 78, Karmiel 21982, Israel 1 1 The Mathematical Model We consider a flow of a homogeneous
From Hele-Shaw Problems to Integrable Sytems
 From Hele-Shaw Problems to Integrable Sytems 1898 2006 Sam Howison, OCIAM, Oxford University ISIAM, Madrid, September 2006 1 History 2 HS Hele-Shaw, inventor of the Hele-Shaw cell (and the variable-pitch
From Hele-Shaw Problems to Integrable Sytems 1898 2006 Sam Howison, OCIAM, Oxford University ISIAM, Madrid, September 2006 1 History 2 HS Hele-Shaw, inventor of the Hele-Shaw cell (and the variable-pitch
Numerical solution of Hele-Shaw flows driven by a quadrupole
 Euro. Jnl of Applied Mathematics (1997), vol. 8, pp. 551 566. c 1997 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 551 Numerical solution of Hele-Shaw flows driven by a quadrupole E. D. KELLY
Euro. Jnl of Applied Mathematics (1997), vol. 8, pp. 551 566. c 1997 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 551 Numerical solution of Hele-Shaw flows driven by a quadrupole E. D. KELLY
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent functions with opening angle at infinity
 A SHARP BOUND FOR THE SCHWARZIAN DERIVATIVE OF CONCAVE FUNCTIONS BAPPADITYA BHOWMIK AND KARL-JOACHIM WIRTHS Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent
A SHARP BOUND FOR THE SCHWARZIAN DERIVATIVE OF CONCAVE FUNCTIONS BAPPADITYA BHOWMIK AND KARL-JOACHIM WIRTHS Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
A NOTE ON UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS WITH FINITELY MANY COEFFICIENTS. Abstract
 A NOTE ON UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS WITH FINITELY MANY COEFFICIENTS M. Darus, R.W. Ibrahim Abstract The main object of this article is to introduce sufficient conditions of univalency for a class of analytic
A NOTE ON UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS WITH FINITELY MANY COEFFICIENTS M. Darus, R.W. Ibrahim Abstract The main object of this article is to introduce sufficient conditions of univalency for a class of analytic
ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS
 ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Daoud Bshouty, Dept. of Mathematics, Technion Inst. of Technology, 3200 Haifa, Israel, and Allen Weitsman, Dept. of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, IN 47907
ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Daoud Bshouty, Dept. of Mathematics, Technion Inst. of Technology, 3200 Haifa, Israel, and Allen Weitsman, Dept. of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, IN 47907
On Classes of Analytic Functions Associated by a Parametric Linear Operator in a Complex Domain
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: A. Physical and Computational Sciences 54 (3): 257 267 (207) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 258-4245 (print), 258-4253 (online) Pakistan Academy
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: A. Physical and Computational Sciences 54 (3): 257 267 (207) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 258-4245 (print), 258-4253 (online) Pakistan Academy
Topology of Quadrature Domains
 Topology of Quadrature Domains Seung-Yeop Lee (University of South Florida) August 12, 2014 1 / 23 Joint work with Nikolai Makarov Topology of quadrature domains (arxiv:1307.0487) Sharpness of connectivity
Topology of Quadrature Domains Seung-Yeop Lee (University of South Florida) August 12, 2014 1 / 23 Joint work with Nikolai Makarov Topology of quadrature domains (arxiv:1307.0487) Sharpness of connectivity
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
Cesáro partial sums of certain analytic functions
 JIA_30_edited [0/06 19:18] 1/8 Cesáro partial sums of certain analytic functions 1 abha W Ibrahim and Maslina Darus 1 Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
JIA_30_edited [0/06 19:18] 1/8 Cesáro partial sums of certain analytic functions 1 abha W Ibrahim and Maslina Darus 1 Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Surface Tension Effect on a Two Dimensional. Channel Flow against an Inclined Wall
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 007, no. 7, 313-36 Surface Tension Effect on a Two Dimensional Channel Flow against an Inclined Wall A. Merzougui *, H. Mekias ** and F. Guechi ** * Département de
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 007, no. 7, 313-36 Surface Tension Effect on a Two Dimensional Channel Flow against an Inclined Wall A. Merzougui *, H. Mekias ** and F. Guechi ** * Département de
Part IB. Complex Analysis. Year
 Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
ULAM STABILITY OF BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM
 Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 37(2 (213, Pages 287 297. ULAM STABILITY OF BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM RABHA W. IBRAHIM Abstract. In this paper we present and discuss different types of Ulam stability:
Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 37(2 (213, Pages 287 297. ULAM STABILITY OF BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM RABHA W. IBRAHIM Abstract. In this paper we present and discuss different types of Ulam stability:
DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR GENERALIZED BY FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES
 Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 1787-2413 Vol. 12 (2011), No. 2, pp. 167 184 DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR GENERALIZED BY FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES RABHA W. IBRAHIM AND M. DARUS Received March 30, 2010 Abstract.
Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 1787-2413 Vol. 12 (2011), No. 2, pp. 167 184 DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR GENERALIZED BY FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES RABHA W. IBRAHIM AND M. DARUS Received March 30, 2010 Abstract.
INTEGRAL MEANS OF UNIVALENT SOLUTION FOR FRACTIONAL EQUATION IN COMPLEX PLANE. Rabha W. Ibrahim and Maslina Darus
 Acta Universitatis Apulensis ISSN: 1582-5329 No. 23/21 pp. 39-47 INTEGRAL MEANS OF UNIVALENT SOLUTION FOR FRACTIONAL EQUATION IN COMPLEX PLANE Rabha W. Ibrahim and Maslina Darus Abstract. Integral means
Acta Universitatis Apulensis ISSN: 1582-5329 No. 23/21 pp. 39-47 INTEGRAL MEANS OF UNIVALENT SOLUTION FOR FRACTIONAL EQUATION IN COMPLEX PLANE Rabha W. Ibrahim and Maslina Darus Abstract. Integral means
The universality class of diffusion-limited aggregation and viscous fingering
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 October 2006 Europhys. Lett., 76 (2), pp. 257 263 (2006) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2006-10246-x The universality class of diffusion-limited aggregation and viscous fingering J. Mathiesen
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 October 2006 Europhys. Lett., 76 (2), pp. 257 263 (2006) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2006-10246-x The universality class of diffusion-limited aggregation and viscous fingering J. Mathiesen
Three Extremal Problems for Hyperbolically Convex Functions
 Three Extremal Problems for Hyperbolically Convex Functions Roger W. Barnard, Kent Pearce, and G. Brock Williams Dedicated to the memory of Walter Hengartner. Keywords. Hyperbolically convex functions,
Three Extremal Problems for Hyperbolically Convex Functions Roger W. Barnard, Kent Pearce, and G. Brock Williams Dedicated to the memory of Walter Hengartner. Keywords. Hyperbolically convex functions,
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk 1
 The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk Michael Dorff and Ted Suffridge Abstract The class S H consists of univalent, harmonic, and sense-preserving functions f in the unit disk,,
The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk Michael Dorff and Ted Suffridge Abstract The class S H consists of univalent, harmonic, and sense-preserving functions f in the unit disk,,
Partial Density Functions and Hele-Shaw Flow
 Partial Density Functions and Hele-Shaw Flow Jackson Van Dyke University of California, Berkeley jayteeveedee@berkeley.edu August 14, 2017 Jackson Van Dyke (UCB) Partial Density Functions August 14, 2017
Partial Density Functions and Hele-Shaw Flow Jackson Van Dyke University of California, Berkeley jayteeveedee@berkeley.edu August 14, 2017 Jackson Van Dyke (UCB) Partial Density Functions August 14, 2017
A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF A MONOTONE SCHEME FOR THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION 1. INTRODUCTION
 A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF A MONOTONE SCHEME FOR THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION GERARD AWANOU AND LEOPOLD MATAMBA MESSI ABSTRACT. We give a proof of existence of a solution to the discrete problem
A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF A MONOTONE SCHEME FOR THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION GERARD AWANOU AND LEOPOLD MATAMBA MESSI ABSTRACT. We give a proof of existence of a solution to the discrete problem
THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM
 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM ALEXANDER WAUGH Abstract. This paper aims to provide all necessary details to give the standard modern proof of the Riemann Mapping Theorem utilizing normal families of functions.
THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM ALEXANDER WAUGH Abstract. This paper aims to provide all necessary details to give the standard modern proof of the Riemann Mapping Theorem utilizing normal families of functions.
ON POLYHARMONIC UNIVALENT MAPPINGS
 ON POLYHARMONIC UNIVALENT MAPPINGS J. CHEN, A. RASILA and X. WANG In this paper, we introduce a class of complex-valued polyharmonic mappings, denoted by HS pλ, and its subclass HS 0 pλ, where λ [0, ]
ON POLYHARMONIC UNIVALENT MAPPINGS J. CHEN, A. RASILA and X. WANG In this paper, we introduce a class of complex-valued polyharmonic mappings, denoted by HS pλ, and its subclass HS 0 pλ, where λ [0, ]
Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings
 Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings Antti Rasila Helsinki University of Technology antti.rasila@tkk.fi (Mainly based on P. Duren s book Harmonic mappings in the plane) Helsinki Analysis Seminar,
Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings Antti Rasila Helsinki University of Technology antti.rasila@tkk.fi (Mainly based on P. Duren s book Harmonic mappings in the plane) Helsinki Analysis Seminar,
The computation of zeros of Ahlfors map for doubly connected regions
 The computation of zeros of Ahlfors map for doubly connected regions Kashif Nazar, Ali W. K. Sangawi, Ali H. M. Murid, and Yeak Su Hoe Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings 1750, 020007 (2016); doi: 10.1063/1.4954520
The computation of zeros of Ahlfors map for doubly connected regions Kashif Nazar, Ali W. K. Sangawi, Ali H. M. Murid, and Yeak Su Hoe Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings 1750, 020007 (2016); doi: 10.1063/1.4954520
Numerical Range in C*-Algebras
 Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 6, No. 2, (2012), 91-98 Numerical Range in C*-Algebras M. T. Heydari Yasouj University Abstract. Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and let S be the state space of
Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 6, No. 2, (2012), 91-98 Numerical Range in C*-Algebras M. T. Heydari Yasouj University Abstract. Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and let S be the state space of
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2003 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
Harmonic Mappings for which Second Dilatation is Janowski Functions
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 3, 2013, no. 8, 617-624 Harmonic Mappings for which Second Dilatation is Janowski Functions Emel Yavuz Duman İstanbul Kültür University Department of Mathematics and Computer
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 3, 2013, no. 8, 617-624 Harmonic Mappings for which Second Dilatation is Janowski Functions Emel Yavuz Duman İstanbul Kültür University Department of Mathematics and Computer
= 2 x y 2. (1)
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
CONFORMAL MODELS AND FINGERPRINTS OF PSEUDO-LEMNISCATES
 CONFORMAL MODELS AND FINGERPRINTS OF PSEUDO-LEMNISCATES TREVOR RICHARDS AND MALIK YOUNSI Abstract. We prove that every meromorphic function on the closure of an analytic Jordan domain which is sufficiently
CONFORMAL MODELS AND FINGERPRINTS OF PSEUDO-LEMNISCATES TREVOR RICHARDS AND MALIK YOUNSI Abstract. We prove that every meromorphic function on the closure of an analytic Jordan domain which is sufficiently
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002](/thumbs/74/69829551.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0212257v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 International Journal of Modern Physics B c World Scientific Publishing Company VISCOUS FINGERING IN MISCIBLE, IMMISCIBLE AND REACTIVE FLUIDS PATRICK
arxiv:cond-mat/0212257v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 International Journal of Modern Physics B c World Scientific Publishing Company VISCOUS FINGERING IN MISCIBLE, IMMISCIBLE AND REACTIVE FLUIDS PATRICK
MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY
 MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. About 2 2. Complex Numbers 2 3. Fundamental inequalities 2 4. Continuously differentiable functions
MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. About 2 2. Complex Numbers 2 3. Fundamental inequalities 2 4. Continuously differentiable functions
Finger competition dynamics in rotating Hele-Shaw cells
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 70, 066308 (2004) Finger competition dynamics in rotating Hele-Shaw cells Hermes Gadêlha and José A. Miranda* Laboratório de Física Teórica e Computacional, Departamento de Física, Universidade
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 70, 066308 (2004) Finger competition dynamics in rotating Hele-Shaw cells Hermes Gadêlha and José A. Miranda* Laboratório de Física Teórica e Computacional, Departamento de Física, Universidade
Boundary Decomposition of the Bergman Kernel
 Boundary Decomposition of the Bergman Kernel Steven G. Krantz 1 Abstract: We study the Bergman kernel on a domain having smooth boundary with several connected components, and relate it to the Bergman
Boundary Decomposition of the Bergman Kernel Steven G. Krantz 1 Abstract: We study the Bergman kernel on a domain having smooth boundary with several connected components, and relate it to the Bergman
Research Article Hyperbolically Bi-Lipschitz Continuity for 1/ w 2 -Harmonic Quasiconformal Mappings
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 569481, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/569481 Research Article Hyperbolically Bi-Lipschitz Continuity for 1/ w 2 -Harmonic Quasiconformal
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 569481, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/569481 Research Article Hyperbolically Bi-Lipschitz Continuity for 1/ w 2 -Harmonic Quasiconformal
Microlocal Methods in X-ray Tomography
 Microlocal Methods in X-ray Tomography Plamen Stefanov Purdue University Lecture I: Euclidean X-ray tomography Mini Course, Fields Institute, 2012 Plamen Stefanov (Purdue University ) Microlocal Methods
Microlocal Methods in X-ray Tomography Plamen Stefanov Purdue University Lecture I: Euclidean X-ray tomography Mini Course, Fields Institute, 2012 Plamen Stefanov (Purdue University ) Microlocal Methods
Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature
 Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Abstract We give optimal bounds of the height, curvature, area and enclosed volume of K-surfaces in R 3 bounding a
Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Abstract We give optimal bounds of the height, curvature, area and enclosed volume of K-surfaces in R 3 bounding a
Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary
 Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary David Chopp and John A. Velling December 1, 2003 Abstract Let γ be a Jordan curve in S 2, considered as the ideal
Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary David Chopp and John A. Velling December 1, 2003 Abstract Let γ be a Jordan curve in S 2, considered as the ideal
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics part 2: hydrodynamics dynamic contact angle? lubrication: Cox-Voinov theory maximum speed for instability corner shape? dimensional analysis: speed U position r viscosity η pressure
contact line dynamics part 2: hydrodynamics dynamic contact angle? lubrication: Cox-Voinov theory maximum speed for instability corner shape? dimensional analysis: speed U position r viscosity η pressure
ONE PROBLEM OF THE BENDING OF A PLATE FOR A CURVILINEAR QUADRANGULAR DOMAIN WITH A RECTILINEAR CUT. Kapanadze G., Gulua B.
 Seminar of I. Veua Institute of Applied Mathematics REPORTS, Vol. 42, 2016 ONE PROBLEM OF THE BENDING OF A PLATE FOR A CURVILINEAR QUADRANGULAR DOMAIN WITH A RECTILINEAR CUT Kapanadze G., Gulua B. Abstract.
Seminar of I. Veua Institute of Applied Mathematics REPORTS, Vol. 42, 2016 ONE PROBLEM OF THE BENDING OF A PLATE FOR A CURVILINEAR QUADRANGULAR DOMAIN WITH A RECTILINEAR CUT Kapanadze G., Gulua B. Abstract.
Cesàro Sum Approximation of Outer Functions. R.W. Barnard, K. Pearce
 Cesàro Sum Approximation of Outer Functions R.W. Barnard, K. Pearce Department of Mathematics and Statistics Texas Tech University barnard@math.ttu.edu, pearce@math.ttu.edu J. Cima Department of Mathematics
Cesàro Sum Approximation of Outer Functions R.W. Barnard, K. Pearce Department of Mathematics and Statistics Texas Tech University barnard@math.ttu.edu, pearce@math.ttu.edu J. Cima Department of Mathematics
SOME SUBCLASSES OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY GENERALIZED DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR. Maslina Darus and Imran Faisal
 Acta Universitatis Apulensis ISSN: 1582-5329 No. 29/212 pp. 197-215 SOME SUBCLASSES OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY GENERALIZED DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR Maslina Darus and Imran Faisal Abstract. Let A denote
Acta Universitatis Apulensis ISSN: 1582-5329 No. 29/212 pp. 197-215 SOME SUBCLASSES OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY GENERALIZED DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR Maslina Darus and Imran Faisal Abstract. Let A denote
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADPO10919 TITLE: Pattern Selection: Nonsingular Saffman-Taylor Finger and its Dynamic Evolution with Zero Surface Tension DISTRIBUTION:
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADPO10919 TITLE: Pattern Selection: Nonsingular Saffman-Taylor Finger and its Dynamic Evolution with Zero Surface Tension DISTRIBUTION:
Finite-time singularity formation for Euler vortex sheet
 Finite-time singularity formation for Euler vortex sheet Daniel Coutand Maxwell Institute Heriot-Watt University Oxbridge PDE conference, 20-21 March 2017 Free surface Euler equations Picture n N x Ω Γ=
Finite-time singularity formation for Euler vortex sheet Daniel Coutand Maxwell Institute Heriot-Watt University Oxbridge PDE conference, 20-21 March 2017 Free surface Euler equations Picture n N x Ω Γ=
Norwegian University of Science and Technology N-7491 Trondheim, Norway
 QUASICONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 48 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1999 WHAT IS A DISK? KARI HAG Norwegian University of Science and
QUASICONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 48 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1999 WHAT IS A DISK? KARI HAG Norwegian University of Science and
Harmonic Mappings and Shear Construction. References. Introduction - Definitions
 Harmonic Mappings and Shear Construction KAUS 212 Stockholm, Sweden Tri Quach Department of Mathematics and Systems Analysis Aalto University School of Science Joint work with S. Ponnusamy and A. Rasila
Harmonic Mappings and Shear Construction KAUS 212 Stockholm, Sweden Tri Quach Department of Mathematics and Systems Analysis Aalto University School of Science Joint work with S. Ponnusamy and A. Rasila
Generalised Separable Solution of Double Phase Flow through Homogeneous Porous Medium in Vertical Downward Direction Due to Difference in Viscosity
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 932-9466 Vol. 8, Issue (June 203), pp. 305-37 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Generalised Separable Solution
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 932-9466 Vol. 8, Issue (June 203), pp. 305-37 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Generalised Separable Solution
Convolutions of harmonic right half-plane mappings
 Open Math. 06; 4 789 800 Open Mathematics Open Access Research Article YingChun Li and ZhiHong Liu* Convolutions of harmonic right half-plane mappings OI 0.55/math-06-0069 Received March, 06; accepted
Open Math. 06; 4 789 800 Open Mathematics Open Access Research Article YingChun Li and ZhiHong Liu* Convolutions of harmonic right half-plane mappings OI 0.55/math-06-0069 Received March, 06; accepted
Conformal Mapping Lecture 20 Conformal Mapping
 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
UNIFORM APPROXIMATION BY b HARMONIC FUNCTIONS
 UNIFORM APPROXIMATION BY b HARMONIC FUNCTIONS JOHN T. ANDERSON Abstract. The Mergelyan and Ahlfors-Beurling estimates for the Cauchy transform give quantitative information on uniform approximation by
UNIFORM APPROXIMATION BY b HARMONIC FUNCTIONS JOHN T. ANDERSON Abstract. The Mergelyan and Ahlfors-Beurling estimates for the Cauchy transform give quantitative information on uniform approximation by
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Existence of Ulam Stability for Iterative Fractional Differential Equations Based on Fractional Entropy
 Entropy 215, 17, 3172-3181; doi:1.339/e1753172 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 199-43 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Existence of Ulam Stability for Iterative Fractional Differential Equations Based on
Entropy 215, 17, 3172-3181; doi:1.339/e1753172 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 199-43 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Existence of Ulam Stability for Iterative Fractional Differential Equations Based on
INDEX. Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem, for sequences, boundary points, bounded functions, 142 bounded sets, 42 43
 INDEX Abel s identity, 131 Abel s test, 131 132 Abel s theorem, 463 464 absolute convergence, 113 114 implication of conditional convergence, 114 absolute value, 7 reverse triangle inequality, 9 triangle
INDEX Abel s identity, 131 Abel s test, 131 132 Abel s theorem, 463 464 absolute convergence, 113 114 implication of conditional convergence, 114 absolute value, 7 reverse triangle inequality, 9 triangle
Blow-up of solutions for the sixth-order thin film equation with positive initial energy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 4 journal of October 05 physics pp. 577 58 Blow-up of solutions for the sixth-order thin film equation with positive initial energy WENJUN LIU and KEWANG
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 4 journal of October 05 physics pp. 577 58 Blow-up of solutions for the sixth-order thin film equation with positive initial energy WENJUN LIU and KEWANG
Modelling of interfaces and free boundaries
 University of Regensburg Regensburg, March 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Obstacle problems 3 Stefan problem 4 Shape optimization Introduction What is a free boundary problem? Solve a partial differential
University of Regensburg Regensburg, March 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Obstacle problems 3 Stefan problem 4 Shape optimization Introduction What is a free boundary problem? Solve a partial differential
The Complex Analysis Behind Smirnov s Theorem
 The Complex Analysis Behind Smirnov s Theorem Elizabeth Gillaspy March 15, 2010 Abstract Smirnov s celebrated proof [6] of the conformal invariance of critical site percolation on the triangular grid relies
The Complex Analysis Behind Smirnov s Theorem Elizabeth Gillaspy March 15, 2010 Abstract Smirnov s celebrated proof [6] of the conformal invariance of critical site percolation on the triangular grid relies
A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR HYPERBOLICALLY CONVEX FUNCTIONS
 A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR HYPERBOLICALLY CONVEX FUNCTIONS ROGER W. BARNARD, G. LENNY ORNAS, AND KENT PEARCE Abstract. In this paper we describe a variational method, based on Julia s formula for the Hadamard
A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR HYPERBOLICALLY CONVEX FUNCTIONS ROGER W. BARNARD, G. LENNY ORNAS, AND KENT PEARCE Abstract. In this paper we describe a variational method, based on Julia s formula for the Hadamard
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data
 On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS. C φ 2 e = lim sup w 1
 ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS PEKKA NIEMINEN AND EERO SAKSMAN Abstract. We give a negative answer to a conjecture of J. E. Shapiro concerning compactness of the dierence of
ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS PEKKA NIEMINEN AND EERO SAKSMAN Abstract. We give a negative answer to a conjecture of J. E. Shapiro concerning compactness of the dierence of
Diffusion-Limited Aggregation on Curved Surfaces
 Diffusion-Limited Aggregation on Curved Surfaces The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Choi,
Diffusion-Limited Aggregation on Curved Surfaces The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Choi,
Free-surface potential flow of an ideal fluid due to a singular sink
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Free-surface potential flow of an ideal fluid due to a singular sink To cite this article: A A Mestnikova and V N Starovoitov 216 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Free-surface potential flow of an ideal fluid due to a singular sink To cite this article: A A Mestnikova and V N Starovoitov 216 J. Phys.: Conf.
Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains
 Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains Ken-ichi Sakan (Osaka City Univ., Japan) Dariusz Partyka (The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Poland)
Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains Ken-ichi Sakan (Osaka City Univ., Japan) Dariusz Partyka (The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Poland)
On sandwich theorems for p-valent functions involving a new generalized differential operator
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 60(015), No. 3, 395 40 On sandwich theorems for p-valent functions involving a new generalized differential operator T. Al-Hawary, B.A. Frasin and M. Darus Abstract. A new
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 60(015), No. 3, 395 40 On sandwich theorems for p-valent functions involving a new generalized differential operator T. Al-Hawary, B.A. Frasin and M. Darus Abstract. A new
DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION ASSOCIATED WITH NEW GENERALIZED DERIVATIVE OPERATOR
 ROMAI J., v.12, no.1(2016), 77 89 DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION ASSOCIATED WITH NEW GENERALIZED DERIVATIVE OPERATOR Anessa Oshah, Maslina Darus School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology,
ROMAI J., v.12, no.1(2016), 77 89 DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION ASSOCIATED WITH NEW GENERALIZED DERIVATIVE OPERATOR Anessa Oshah, Maslina Darus School of Mathematical Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology,
Geometry-Fitted Fourier-Mellin Transform Pairs
 Geometry-Fitted Fourier-Mellin Transform Pairs Darren Crowdy Abstract The construction of novel Fourier/Mellin-type transform pairs that are tailor-made for given planar regions within the special class
Geometry-Fitted Fourier-Mellin Transform Pairs Darren Crowdy Abstract The construction of novel Fourier/Mellin-type transform pairs that are tailor-made for given planar regions within the special class
Richard F. Bass Krzysztof Burdzy University of Washington
 ON DOMAIN MONOTONICITY OF THE NEUMANN HEAT KERNEL Richard F. Bass Krzysztof Burdzy University of Washington Abstract. Some examples are given of convex domains for which domain monotonicity of the Neumann
ON DOMAIN MONOTONICITY OF THE NEUMANN HEAT KERNEL Richard F. Bass Krzysztof Burdzy University of Washington Abstract. Some examples are given of convex domains for which domain monotonicity of the Neumann
Non-trivial pinning threshold for an evolution equation involving long range interactions
 Non-trivial pinning threshold for an evolution equation involving long range interactions Martin Jesenko joint work with Patrick Dondl Workshop: New trends in the variational modeling of failure phenomena
Non-trivial pinning threshold for an evolution equation involving long range interactions Martin Jesenko joint work with Patrick Dondl Workshop: New trends in the variational modeling of failure phenomena
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
SOME PROPERTIES OF A SUBCLASS OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY A GENERALIZED SRIVASTAVA-ATTIYA OPERATOR. Nagat. M. Mustafa and Maslina Darus
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS NIŠ) Ser. Math. Inform. Vol. 27 No 3 2012), 309 320 SOME PROPERTIES OF A SUBCLASS OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY A GENERALIZED SRIVASTAVA-ATTIYA OPERATOR Nagat. M. Mustafa and Maslina
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS NIŠ) Ser. Math. Inform. Vol. 27 No 3 2012), 309 320 SOME PROPERTIES OF A SUBCLASS OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY A GENERALIZED SRIVASTAVA-ATTIYA OPERATOR Nagat. M. Mustafa and Maslina
PROBLEMS. (b) (Polarization Identity) Show that in any inner product space
 1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
Higher Orders Instability of a Hollow Jet Endowed with Surface Tension
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 2, No. (2008) 69 78 c Technical University of Lodz Higher Orders Instability of a Hollow Jet Endowed with Surface Tension Ahmed E. Radwan Mathematics Department,
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 2, No. (2008) 69 78 c Technical University of Lodz Higher Orders Instability of a Hollow Jet Endowed with Surface Tension Ahmed E. Radwan Mathematics Department,
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I
 MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
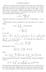 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
For an imposed stress history consisting of a rapidly applied step-function jump in
 Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
STABILITY OF THE INTERFACE BETWEEN TWO IMMISCIBLE FLUIDS IN POROUS MEDIA
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20032003), No. 25, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp) STABILITY OF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20032003), No. 25, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp) STABILITY OF
Generalization of some extremal problems on non-overlapping domains with free poles
 doi: 0478/v006-0-008-9 A N N A L E S U N I V E R S I T A T I S M A R I A E C U R I E - S K Ł O D O W S K A L U B L I N P O L O N I A VOL LXVII, NO, 03 SECTIO A IRYNA V DENEGA Generalization of some extremal
doi: 0478/v006-0-008-9 A N N A L E S U N I V E R S I T A T I S M A R I A E C U R I E - S K Ł O D O W S K A L U B L I N P O L O N I A VOL LXVII, NO, 03 SECTIO A IRYNA V DENEGA Generalization of some extremal
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models
 Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
Laplacian Growth and Diffusion Limited Aggregation: Different Universality Classes
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Benny Davidovitch 2001 Laplacian Growth and Diffusion Limited Aggregation: Different Universality Classes Felipe Barra Benny Davidovitch, University
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Benny Davidovitch 2001 Laplacian Growth and Diffusion Limited Aggregation: Different Universality Classes Felipe Barra Benny Davidovitch, University
The Rayleigh-Taylor condition for the evolution of irrotational fluid interfaces.
 The Rayleigh-Taylor condition for the evolution of irrotational fluid interfaces. Antonio Cordoba Universidad Autonoma de Madrid ctra. de Colmenar Viejo, Km. 15 28049 Madrid e-mail: antonio.cordoba@uam.es
The Rayleigh-Taylor condition for the evolution of irrotational fluid interfaces. Antonio Cordoba Universidad Autonoma de Madrid ctra. de Colmenar Viejo, Km. 15 28049 Madrid e-mail: antonio.cordoba@uam.es
Complex Analysis for F2
 Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian UNDER NONHOMOGENEOUS NEUMANN BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 210, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 210, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian
WELL-POSEDNESS OF A RIEMANN HILBERT
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 42, 207, 4 47 WELL-POSEDNESS OF A RIEMANN HILBERT PROBLEM ON d-regular QUASIDISKS Eric Schippers and Wolfgang Staubach University of Manitoba, Department
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 42, 207, 4 47 WELL-POSEDNESS OF A RIEMANN HILBERT PROBLEM ON d-regular QUASIDISKS Eric Schippers and Wolfgang Staubach University of Manitoba, Department
On the Poisson Integral of Step Functions and Minimal Surfaces. Allen Weitsman
 On the Poisson Integral of Step Functions and Minimal Surfaces Allen Weitsman Abstract. Applications of minimal surface methods are made to obtain information about univalent harmonic mappings. In the
On the Poisson Integral of Step Functions and Minimal Surfaces Allen Weitsman Abstract. Applications of minimal surface methods are made to obtain information about univalent harmonic mappings. In the
MULTICENTRIC CALCULUS AND THE RIESZ PROJECTION
 JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND APPROXIMATION THEORY J. Numer. Anal. Approx. Theory, vol. 44 (2015) no. 2, pp. 127 145 ictp.acad.ro/jnaat MULTICENTRIC CALCULUS AND THE RIESZ PROJECTION DIANA APETREI
JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND APPROXIMATION THEORY J. Numer. Anal. Approx. Theory, vol. 44 (2015) no. 2, pp. 127 145 ictp.acad.ro/jnaat MULTICENTRIC CALCULUS AND THE RIESZ PROJECTION DIANA APETREI
STRONG DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION AND SUPERORDINATION OF NEW GENERALIZED DERIVATIVE OPERATOR. Anessa Oshah and Maslina Darus
 Korean J. Math. 23 2015, No. 4, pp. 503 519 http://dx.doi.org/10.11568/jm.2015.23.4.503 STRONG DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION AND SUPERORDINATION OF NEW GENERALIZED DERIVATIVE OPERATOR Anessa Oshah and Maslina
Korean J. Math. 23 2015, No. 4, pp. 503 519 http://dx.doi.org/10.11568/jm.2015.23.4.503 STRONG DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION AND SUPERORDINATION OF NEW GENERALIZED DERIVATIVE OPERATOR Anessa Oshah and Maslina
Bergman spaces and differential geometry
 Bergman spaces and differential geometry Haakan Hedenmalm (KTH, Stockholm) Updated version - 2013 Geometries induced by the Bergman kernel Bergman s geometric idea Stefan Bergman s idea here was to let
Bergman spaces and differential geometry Haakan Hedenmalm (KTH, Stockholm) Updated version - 2013 Geometries induced by the Bergman kernel Bergman s geometric idea Stefan Bergman s idea here was to let
Radius of close-to-convexity and fully starlikeness of harmonic mappings
 Complex Variables and Elliptic Equations, 014 Vol. 59, No. 4, 539 55, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17476933.01.759565 Radius of close-to-convexity and fully starlikeness of harmonic mappings David Kalaj a,
Complex Variables and Elliptic Equations, 014 Vol. 59, No. 4, 539 55, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17476933.01.759565 Radius of close-to-convexity and fully starlikeness of harmonic mappings David Kalaj a,
Scaling limits of anisotropic random growth models
 Scaling limits of anisotropic random growth models Amanda Turner Department of Mathematics and Statistics Lancaster University (Joint work with Fredrik Johansson Viklund and Alan Sola) Overview 1 Generalised
Scaling limits of anisotropic random growth models Amanda Turner Department of Mathematics and Statistics Lancaster University (Joint work with Fredrik Johansson Viklund and Alan Sola) Overview 1 Generalised
