Advancing the Utility of Small Satellites with the Development of a Hybrid Electric-Laser Propulsion (HELP) System
|
|
|
- Clarence Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advancing the Utility of Small Satellites with the Development of a Hybrid Electric-Laser Propulsion (HELP) System Dr. Rachel Leach, Gerry Murphy & Tom Adams Design_Net Engineering LLC August 12,
2 Contents Introduction - Application Performance Parameter Space - Imposed System Requirements - Anticipated Thruster Solution Performance Metric Spectrum of Thruster technologies Significance of Performance Metrics - Satellite Launch Cost - Payload Mass - Mission Lifetime Tunable T & I sp System Limitations of current micro-thrusters Proposed HELP Design Solution Conclusions August 12,
3 Introduction Many upcoming ambitious missions (scientific, military) Require complex precision subsystems, formation flying satellites & new generation of highly capable micro-sats Area of advancement in Development of µn thrusters: Provide fine pointing control, long-term maneuvers, orbit change, & station keeping for both grand scientific missions & small satellites LISA, GAMMA, MAXIM, LIRE, TPF, SIM, SAR concepts. Solution: Tunable/Configurable thruster HELP system August 12,
4 Application Performance Parameter Space Range of challenging performance metrics associated to selection of operation tasks Mission Operation Task / Comment Driving Requirement Parameter/Range Robotic service work done with proximity operations (<1m separation) and done over a long period of time High V, Precise Control of position T < 1 µn with ms response time plus high I sp Provide full 3-axis control & fine position control for constellation configuration maintenance Precision thrust T < 10 µn High positional accuracy - Spacecraft control to fractions of λ Precision thrust control MIB < 10 µn-s ± 0.1 µn-s, High BW Oppose drag & enable orbit raising (dependent on drag assumptions & maneuvering periods) Spacecraft rearrangements in constellation Coarse thrust and high Isp T > 0.1 mn I sp > 5000 s Spacecraft tip-off recovery Coarse thrust range & control T= µn T control ± 1 µn Example 1 yr V Straw-man mission for 100kg S/C 600Km orbit 1 yr mission lifetime V budget Mission V budget Total= 270 m/s Formation initialization over a 30 day maneuver period Formation maneuver V 30 m/s Over 1 yr life in 600 Km orbit Stationkeeping/drag V 40 m/s Nominal 30 day maneuver period (depends on altitude change) Orbit adjustment V 50 m/s Deorbit at end of mission (dependent on orbit altitude) Deorbit V 150 m/s August 12,
5 Imposed System Req s Application Performance Parameter Space In-space robotic assembly of modular structures Routine spacecraft repositioning and rescue services Use of formations of satellites Provide fine pointing control, long-term maneuvers, orbit change, & station keeping Today Multiple thruster subsystems req d to enable System Engineering Issues Increased mass, power and volume Increased system complexity Many missions are simply NOT possible with existing technology August 12,
6 Significance of Performance Metrics: Isp Propellant mass decreases with higher I sp Or Or Enabling greater payload mass factor 20 gain (cf. HELP & uppt) Increased mission lifetime Decreased launch costs (1 kg $10k to $30k) Required Thruster System Propellant Mass [kg] Required Thruster System Propellant Mass for "Example 1 yr Straw-man mission for 100kg Spacecraft" as a function of System Isp Isp (seconds) HELP System mission dv 270 m.s-1 uppt System mission dv 270 m.s-1 Colloid System mission dv 270 m.s-1 FEEP System mission dv 270 m.s-1 Chemical System mission dv 270 m.s-1 ulpt System mission dv 270 m.s-1 3 kg August 12,
7 Significance of Performance S/C drift (positional control) & associated V req. improves with finer MIB Good Positional control Important for FF Missions & SAR systems (< nm) & S/C pointing control improves with finer MIB Important for Precision pointing telescopes (< milli- to micro-arcsec) Spacecraft Drift [m] Metrics: Precision 1.0E E E E E E E-13 Spacecraft Drift for "Example 1 yr Straw-man mission for 100kg Spacecraft" as a function of Thruster System MIB Mission dv 270 m/s HELP System, PRF=1kHz uppt System, PRF=2Hz Colloid System, PRF=10kHz FEEP System, PRF=10kHz ulpt System, PRF=80Hz uppt System FEEP System Colloid System ulpt System HELP System No fill = Pointing error Filled = Drift error 1.0E E E E E-04 Thruster System Minimum Impulse Bit (N.Seconds) 1.0E E E E E E E E-08 Spacecraft Pointing Error [arcsec] August 12,
8 Significance of Performance Metrics: Noise S/C stability improves with lower thrust noise Important for Grand Scientific Missions - Drag-Free GW & relativity missions RMS Acceleration [m.s -2 ] 3.000E E E E E-10 RMS Acceleration for "Example DF 100kg Spacecraft" as a function of Thruster noise level Accelermeter positional readout noise Xn = 1e-11 m.hz^-0.5 HELP System, fn=1e-8 N Colloid System, fn=1e-7, Hz FEEP System, fn=1e-7, > 0.01 Hz 5.000E E E E E E E E E E-07 Thruster noise, Fn [N.Hz -0.5 ] August 12,
9 Significance of Performance Metrics: Thrust S/C maneuver time decreases with higher Thrust Fast maneuver times Important for Reconnaissance Missions Longer maneuver times may be permissible for deorbiting Altitude [km] Spacecraft De-Orbit Rate for "Example 1 yr Straw-man mission for 100kg Spacecraft" as a function of System DeltaV HELP dv 100 ms-1 per month HELP dv 10 ms-1 per month HELP dv 5 ms-1 per month Time [months] August 12,
10 Significance of Performance Metrics Currently NO system capitalizing on all benefits associated with various performance metrics Attractive thruster solution Single configurable propulsion Tunable Thrust & Isp System On-orbit Adjustment to suit varying needs of a mission Proposed Hybrid Electric-Laser Propulsion (HELP) System is projected to realize this vision Accrued Advantages Minimize S/C bus requirements Reduces dry weight, Reduces complexity Reduces cost. August 12,
11 State of Practice Current micro-thruster options µppt, Colloid, FEEP, µlpt etc. Limitations of Current micro-thruster technology Poor Repeatability, Inefficiency in Propellant & Power, Low I sp, High Noise; Poor component lifetime, Use of High voltage systems or Contamination etc. Developed for particular application & have finite performance metrics eliminating wide use Nature of small-sats imposes need for component technologies that are Low cost, Compact, Efficient, Long life, High V Development of a new enabling, configurable, high-precision micro-thruster option required to raise utility of small-sats HELP System August 12,
12 HELP Thruster Design HELP Design Objectives Improve thruster ablation repeatability, energy coupling efficiency, I sp, & T/P Optimize thrust plume collimation Enable pulsed & pseudo-steady-state continuous operation modes Improve reliability & lifetime Improve scalability for a wide range of applications Have ability to tune key performance metrics on orbit as required August 12,
13 HELP Thruster Design cont. Novel System Design Features The HELP system will: Employ an advanced laser To ablate the target propellant to form a highly ionized plasma Use high-temperature plasma containment & electromagnetic collimation techniques To optimize I sp & thrust, & minimize contamination & cross-coupling effects Employ a designer propellant with enabling characteristics A novel propellant feed system To ensure repeatability & efficient propellant usage August 12,
14 HELP Thruster Design cont. HELP system comprises of 4 functional subsystems 1) Laser Ablation subsystem, 2) Plasma Collimation subsystem, 3) Propellant Feed subsystem, 4) Control & Power Conversion subsystem 4 Subsystems are housed in 2 discrete & easily connected units Electronics & Control Components Unit & Modular Propellant Pod Unit This physical layout enables robotic servicing HELP system operation entails 3 sub-processes Propellant feed maintains viscosity of fuel to allow feed to target ablation area Laser Ablation operates & controls lasers Plasma collimation operates & controls collimating EM field August 12,
15 HELP Thruster Design cont. HELP System Block Diagram August 12,
16 HELP Thruster Design cont. Conceptual HELP Thruster Unit Design Modular honeycomb fashion of propellant pods facilitates ganging Size of multi-pod system is configurable & scaleable to application Through ganging of singular HELP systems one can provide higher thrust levels to support additional tasks This physical layout enables greater operational flexibility & applicability Multiple Configuration System August 12,
17 HELP Thruster Design cont. Conceptual HELP Thruster Unit Design Hexagonal design of propellant pods facilitates ganging & multi-component use Use selection of propellants with varying atomic masses Use selection of lasers with different operation characteristics P, I, τ, λ, d Use multiple lasers per pod Enabling greater performance metric ranges This physical layout enables greater operational flexibility & applicability Multiple Configuration System High atomic mass propellant Low atomic mass propellant August 12,
18 HELP Thruster Design cont. Estimated Performance Characteristics Propulsion System Type Thruster Operation Modes Thrust Range (tunable & scaleable with pod design) [µn] HELP: Multi-pod config (single) Specific Impulse [s] 500 >20,000 System Efficiency % 30 Req. mission propellant mass ( V 270 m/s, 100kg S/C) [kg] Pseudo-Continuous or Pulsed 175 > 10,000 (25 - >1,000) T/P ratio [µn/w] 5 > 200 Minimum Impulse Bit [N s] < 2.5e -8 System Mass (excl. supporting electronics & propellant) [kg] (0.045) scalable <5.4 Estimated values, Not measured P = m v P W August 12, F = C m m v P W C m = momentum coupling coefficient, P= incident power, W= incident laser energy
19 Comparison of Thruster Performance Characteristics Propulsion System Type µppt FEEP Hall µlpt Colloid HELP Thruster Operation Modes Pulsed Continuous or Pulsed Pulsed Thrust Range [µn] , >1000 Specific Impulse [s] > 20,000 Minimum Impulse Bit [N s] 1e -5 1e -3 T/P ratio [µn/w] > 200 System Mass (excl. supporting electronics & propellant) [kg] 0.12 System Efficiency % Design Simplistic Complex Complex Simplistic Simplistic Simplistic Life Limiting Element Spark Plug Continuous or Pulsed <10e Cathode 1 Cathode August 12, e Propellant Continuous or Pulsed 0.5e Cathode Pseudo-Continuous or Pulsed < 2.5e Propellant Estimated values
20 Conclusions No superior micro-propulsion system suitable for wide range of cases is presently available Current systems have been designed for a Specific Application & are leaders for that niche As such have limited performance metrics eliminating their wide appeal & use Also nearing mature states & max. potential no sig. future improvement Great variety of missions envisioned Driving NEED for alternative enabling, configurable, high-precision technology! Desired attributes: T/P ratio of Colloid I sp of FEEP Ease of integration of PPT Non-contaminating characteristics of cold gas HELP system is expected fulfill this ideology & more Help raise the Utility of Small Sats August 12,
21 Acknowledgements August 12,
Propulsion means for CubeSats
 Propulsion means for CubeSats C. Scharlemann and D. Krejci 2009 CubeSat Developers Workshop, San Louis Obispo, CA Welcome to the Austrian Research Centers Space Propulsion & Advanced Concepts Staff: 11
Propulsion means for CubeSats C. Scharlemann and D. Krejci 2009 CubeSat Developers Workshop, San Louis Obispo, CA Welcome to the Austrian Research Centers Space Propulsion & Advanced Concepts Staff: 11
Electric Propulsion Survey: outlook on present and near future technologies / perspectives. by Ing. Giovanni Matticari
 Electric Propulsion Survey: outlook on present and near future technologies / perspectives by Ing. Giovanni Matticari Electric Propulsion: a concrete reality on many S/C GOCE ARTEMIS ARTEMIS SMART-1 EP
Electric Propulsion Survey: outlook on present and near future technologies / perspectives by Ing. Giovanni Matticari Electric Propulsion: a concrete reality on many S/C GOCE ARTEMIS ARTEMIS SMART-1 EP
Electrospray Propulsion Systems for Small Satellites
 Electrospray Propulsion Systems for Small Satellites Douglas Spence, Eric Ehrbar, Nate Rosenblad, Nate Demmons, Tom Roy, Samuel Hoffman, Dan Williams, Vlad Hruby Busek Co. Inc. 11 Tech Circle, Natick,
Electrospray Propulsion Systems for Small Satellites Douglas Spence, Eric Ehrbar, Nate Rosenblad, Nate Demmons, Tom Roy, Samuel Hoffman, Dan Williams, Vlad Hruby Busek Co. Inc. 11 Tech Circle, Natick,
Pico-Satellite Orbit Control by Vacuum Arc Thrusters as Enabling Technology for Formations of Small Satellites
 1/25 Pico-Satellite Orbit Control by Vacuum Arc Thrusters as Enabling Technology for Formations of Small Satellites Igal Kronhaus, Mathias Pietzka, Klaus Schilling, Jochen Schein Department of Computer
1/25 Pico-Satellite Orbit Control by Vacuum Arc Thrusters as Enabling Technology for Formations of Small Satellites Igal Kronhaus, Mathias Pietzka, Klaus Schilling, Jochen Schein Department of Computer
Electric Rocket Engine System R&D
 Electric Rocket Engine System R&D In PROITERES, a powered flight by an electric rocket engine is planed; that is, orbital transfer will be carried out with a pulsed plasma thruster (PPT). We introduce
Electric Rocket Engine System R&D In PROITERES, a powered flight by an electric rocket engine is planed; that is, orbital transfer will be carried out with a pulsed plasma thruster (PPT). We introduce
Low Cost Helicon Propulsion System for CubeSat future mission scenarios. T4i - University of Padova D.Pavarin
 Low Cost Helicon Propulsion System for CubeSat future mission scenarios T4i - University of Padova D.Pavarin Centro di Ateneo Studi e Attività Spaziali University of Padova Padova, Italy Technology for
Low Cost Helicon Propulsion System for CubeSat future mission scenarios T4i - University of Padova D.Pavarin Centro di Ateneo Studi e Attività Spaziali University of Padova Padova, Italy Technology for
Review of Micro-Propulsion Ablative Devices
 Review of Micro-Propulsion Ablative Devices Michael Keidar and Iain D. Boyd Aerospace Engineering, University of Michigan Ann Arbor 48109 USA Funded by Air Force Office of Scientific Research through grant
Review of Micro-Propulsion Ablative Devices Michael Keidar and Iain D. Boyd Aerospace Engineering, University of Michigan Ann Arbor 48109 USA Funded by Air Force Office of Scientific Research through grant
PROGRESS ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A PULSED PLASMA THRUSTER FOR THE ASTER MISSION
 PROGRESS ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A PULSED PLASMA THRUSTER FOR THE ASTER MISSION IEPC-2013-318 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington,
PROGRESS ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A PULSED PLASMA THRUSTER FOR THE ASTER MISSION IEPC-2013-318 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington,
Systems Engineering in Venus Satellite
 Systems Engineering in Venus Satellite How to benefit from system engineering process in designing a microsatellite Jacob Herscovitz Venus Project Manager RAFAEL - Israel 1 Presentation Contents Introduction
Systems Engineering in Venus Satellite How to benefit from system engineering process in designing a microsatellite Jacob Herscovitz Venus Project Manager RAFAEL - Israel 1 Presentation Contents Introduction
LISA Pathfinder Coldgas Thrusters
 LISA Pathfinder Coldgas Thrusters Joseph Martino/Eric Plagnol - LPF collaboration Lisa Symposium September 2016 Zurich Outline System Description External Disturbances and thruster noise In Flight dedicated
LISA Pathfinder Coldgas Thrusters Joseph Martino/Eric Plagnol - LPF collaboration Lisa Symposium September 2016 Zurich Outline System Description External Disturbances and thruster noise In Flight dedicated
Helicon Plasma Thruster Persepective and At University of Padua
 Helicon Plasma Thruster Persepective and Development status and future development At University of Padua D.Pavarin, M.Manente, F.Trezzolani, A.Selmo, M.Magarotto, E.Toson Outline Helicon Thruster overview
Helicon Plasma Thruster Persepective and Development status and future development At University of Padua D.Pavarin, M.Manente, F.Trezzolani, A.Selmo, M.Magarotto, E.Toson Outline Helicon Thruster overview
A Regional Microsatellite Constellation with Electric Propulsion In Support of Tuscan Agriculture
 Berlin, 20 th - 24 th 2015 University of Pisa 10 th IAA Symposium on Small Satellites for Earth Observation Student Conference A Regional Microsatellite Constellation with Electric Propulsion In Support
Berlin, 20 th - 24 th 2015 University of Pisa 10 th IAA Symposium on Small Satellites for Earth Observation Student Conference A Regional Microsatellite Constellation with Electric Propulsion In Support
Miniature Vacuum Arc Thruster with Controlled Cathode Feeding
 Miniature Vacuum Arc Thruster with Controlled Cathode Feeding Igal Kronhaus and Matteo Laterza Aerospace Plasma Laboratory, Faculty of Aerospace Engineering, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology,
Miniature Vacuum Arc Thruster with Controlled Cathode Feeding Igal Kronhaus and Matteo Laterza Aerospace Plasma Laboratory, Faculty of Aerospace Engineering, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology,
LISA Pathfinder measuring pico-meters and femto-newtons in space
 LISA Pathfinder measuring pico-meters and femto-newtons in space M Hewitson for the LPF team Barcelona, February 15th 2012 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space Push down to
LISA Pathfinder measuring pico-meters and femto-newtons in space M Hewitson for the LPF team Barcelona, February 15th 2012 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space 2 Observing from Space Push down to
Propellant Loading Effects on Ferroelectric Plasma Thruster Performance and Possible Applications
 Propellant Loading Effects on Ferroelectric Plasma Thruster Performance and Possible Applications IEPC-29-177 Presented at the 31st International Electric Propulsion Conference, University of Michigan
Propellant Loading Effects on Ferroelectric Plasma Thruster Performance and Possible Applications IEPC-29-177 Presented at the 31st International Electric Propulsion Conference, University of Michigan
High-Power Plasma Propulsion at NASA-MSFC
 High-Power Plasma Propulsion at NASA-MSFC January 2012 Dr. Kurt Polzin (kurt.a.polzin@nasa.gov) Propulsion Research and Development Laboratory NASA - Marshall Space Flight Center Basics of Rocketry Rocket
High-Power Plasma Propulsion at NASA-MSFC January 2012 Dr. Kurt Polzin (kurt.a.polzin@nasa.gov) Propulsion Research and Development Laboratory NASA - Marshall Space Flight Center Basics of Rocketry Rocket
A Colloid Engine Accelerator Concept Update
 A Colloid Engine Accelerator Concept Update D. Kirtley ERC, Inc. Edwards AFB, CA J. M. Fife U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory Edwards AFB, CA A concept for a colloid engine with an electrodynamic linear
A Colloid Engine Accelerator Concept Update D. Kirtley ERC, Inc. Edwards AFB, CA J. M. Fife U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory Edwards AFB, CA A concept for a colloid engine with an electrodynamic linear
Multiple Thruster Propulsion Systems Integration Study. Rusakol, A.V..Kocherpin A.V..Semenkm A.V.. Tverdokhlebov S.O. Garkusha V.I.
 IEPC-97-130 826 Multiple Thruster Propulsion Systems Integration Study Rusakol, A.V..Kocherpin A.V..Semenkm A.V.. Tverdokhlebov S.O. Garkusha V.I. Central Research Institute of Machine Building (TsNIIMASH)
IEPC-97-130 826 Multiple Thruster Propulsion Systems Integration Study Rusakol, A.V..Kocherpin A.V..Semenkm A.V.. Tverdokhlebov S.O. Garkusha V.I. Central Research Institute of Machine Building (TsNIIMASH)
Electric Propulsion. An short introduction to plasma and ion spacecraft propulsion. S. Barral. Instytut Podstawowych Problemów Techniki - PAN
 Electric Propulsion An short introduction to plasma and ion spacecraft propulsion S. Barral Instytut Podstawowych Problemów Techniki - PAN sbarral@ippt.gov.pl S. Barral (IPPT-PAN) Electric Propulsion 1
Electric Propulsion An short introduction to plasma and ion spacecraft propulsion S. Barral Instytut Podstawowych Problemów Techniki - PAN sbarral@ippt.gov.pl S. Barral (IPPT-PAN) Electric Propulsion 1
Preliminary Development of an Experimental Lightweight Pulsed Plasma Thruster for Solar Sail Attitude Control
 Preliminary Development of an Experimental Lightweight Pulsed Plasma Thruster for Solar Sail Attitude Control Kevin Pryor, Bong Wie, and Pavlos Mikellides Arizona State University 18 th Annual AIAA/USU
Preliminary Development of an Experimental Lightweight Pulsed Plasma Thruster for Solar Sail Attitude Control Kevin Pryor, Bong Wie, and Pavlos Mikellides Arizona State University 18 th Annual AIAA/USU
Low Thrust Mission Trajectories to Near Earth Asteroids
 Low Thrust Mission Trajectories to Near Earth Asteroids Pratik Saripalli Graduate Research Assistant, College Park, Maryland, 20740, USA Eric Cardiff NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland,
Low Thrust Mission Trajectories to Near Earth Asteroids Pratik Saripalli Graduate Research Assistant, College Park, Maryland, 20740, USA Eric Cardiff NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland,
DESIGNED TO OUTPERFORM. Morpheus Space The Cradle of Innovation
 DESIGNED TO OUTPERFORM Morpheus Space The Cradle of Innovation 2 Morpheus Space nanofeep HIGHEST EFFICIENCY Dynamic Thrust Range 1 µn - 40 µn Nominal Thrust 20 µn Specific Impulse 3000 to 8500 s Propellant
DESIGNED TO OUTPERFORM Morpheus Space The Cradle of Innovation 2 Morpheus Space nanofeep HIGHEST EFFICIENCY Dynamic Thrust Range 1 µn - 40 µn Nominal Thrust 20 µn Specific Impulse 3000 to 8500 s Propellant
Spacecraft motion and attitude control in the high elliptic orbit
 Spacecraft motion and attitude control in the high elliptic orbit IEC-2007-30 resented at the 30 th International Electric ropulsion Conference, Florence, Italy V.A. bukhov *, A.I. okryshkin, G.A. opov
Spacecraft motion and attitude control in the high elliptic orbit IEC-2007-30 resented at the 30 th International Electric ropulsion Conference, Florence, Italy V.A. bukhov *, A.I. okryshkin, G.A. opov
APPT Propulsion System for Small Satellites
 APPT Propulsion System for Small Satellites IEPC-2005-111 Presented at the 29 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Princeton University, Nikolay N. Antropov * and Garry A. Popov (1)Research
APPT Propulsion System for Small Satellites IEPC-2005-111 Presented at the 29 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Princeton University, Nikolay N. Antropov * and Garry A. Popov (1)Research
Evaluation of Pulsed Plasma Thruster System for µ-lab Sat II *
 Evaluation of Pulsed Plasma Thruster System for µ-lab Sat II * Haruki TAKEGAHARA, Miwa IGARASHI, Naoki KUMAGAI, Kensuke SATO, and Kouji TAMURA Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Technology, Dept. of Aerospace
Evaluation of Pulsed Plasma Thruster System for µ-lab Sat II * Haruki TAKEGAHARA, Miwa IGARASHI, Naoki KUMAGAI, Kensuke SATO, and Kouji TAMURA Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Technology, Dept. of Aerospace
Pulsed Plasma Thruster Propulsion Technology for Small Satellite
 Pulsed Plasma Thruster Propulsion Technology for Small Satellite Garry A. Popov, Nikolay N. Antropov Research Institute of Applied Mechanics and Electrodynamics, 4, Volokolamskoye shosse, Moscow, 125810,
Pulsed Plasma Thruster Propulsion Technology for Small Satellite Garry A. Popov, Nikolay N. Antropov Research Institute of Applied Mechanics and Electrodynamics, 4, Volokolamskoye shosse, Moscow, 125810,
Parametric family of the PlaS-type thrusters: development status and future activities
 Parametric family of the PlaS-type thrusters: development status and future activities IEPC-2017-39 Presented at the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Parametric family of the PlaS-type thrusters: development status and future activities IEPC-2017-39 Presented at the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Rocket Propulsion Overview
 Rocket Propulsion Overview Seitzman Rocket Overview-1 Rocket Definition Rocket Device that provides thrust to a vehicle by accelerating some matter (the propellant) and exhausting it from the rocket Most
Rocket Propulsion Overview Seitzman Rocket Overview-1 Rocket Definition Rocket Device that provides thrust to a vehicle by accelerating some matter (the propellant) and exhausting it from the rocket Most
Plasma Behaviours and Magnetic Field Distributions of a Short-Pulse Laser-Assisted Pulsed Plasma Thruster
 Plasma Behaviours and Magnetic Field Distributions of a Short-Pulse Laser-Assisted Pulsed Plasma Thruster IEPC-2015-91325 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International Symposium on Space Technology
Plasma Behaviours and Magnetic Field Distributions of a Short-Pulse Laser-Assisted Pulsed Plasma Thruster IEPC-2015-91325 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International Symposium on Space Technology
Minimum Energy Trajectories for Techsat 21 Earth Orbiting Clusters
 Minimum Energy Trajectories for Techsat 1 Earth Orbiting Clusters Edmund M. C. Kong SSL Graduate Research Assistant Prof David W. Miller Director, MIT Space Systems Lab Space 1 Conference & Exposition
Minimum Energy Trajectories for Techsat 1 Earth Orbiting Clusters Edmund M. C. Kong SSL Graduate Research Assistant Prof David W. Miller Director, MIT Space Systems Lab Space 1 Conference & Exposition
Stanford, Space Gravity Research Group
 Stanford, Space Gravity Research Group John W. Conklin, Sasha Buchman, and Robert Byer Gravitational science Earth observation: Geodesy, aeronomy Gravity-waves 1 Space Gravity Technology Development Drag-free
Stanford, Space Gravity Research Group John W. Conklin, Sasha Buchman, and Robert Byer Gravitational science Earth observation: Geodesy, aeronomy Gravity-waves 1 Space Gravity Technology Development Drag-free
AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 ORBIT MANEUVER FOR RESPONSIVE COVERAGE USING ELECTRIC PROPULSION THESIS Timothy S. Hall, Captain, USAF AFIT/GSS/ENY/10-M04 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Wright-Patterson
ORBIT MANEUVER FOR RESPONSIVE COVERAGE USING ELECTRIC PROPULSION THESIS Timothy S. Hall, Captain, USAF AFIT/GSS/ENY/10-M04 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Wright-Patterson
Asteroid Impact Mission AIM Workshop. Electric Propulsion for Attitude & Orbit Control
 Asteroid Impact Mission AIM Workshop Electric Propulsion for Attitude & Orbit Control ESA, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 22-23 February 2016 Christophe R. Koppel Consulting Ind., 75008 Paris, France
Asteroid Impact Mission AIM Workshop Electric Propulsion for Attitude & Orbit Control ESA, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 22-23 February 2016 Christophe R. Koppel Consulting Ind., 75008 Paris, France
The division of energy sources and the working substance in electric propulsioncan determines the range of applicability of electro jet propulsion sys
 Vacuum Arc thruster development for Horyu-4 satellite KaterynaAheieva, Shingo Fuchikami, Hiroshi Fukuda, Tatsuo Shimizu, Kazuhiro Toyoda, Mengu Cho Kyushu Institute of Technology1 N589502a@mail.kyutech.jp
Vacuum Arc thruster development for Horyu-4 satellite KaterynaAheieva, Shingo Fuchikami, Hiroshi Fukuda, Tatsuo Shimizu, Kazuhiro Toyoda, Mengu Cho Kyushu Institute of Technology1 N589502a@mail.kyutech.jp
Recent Advances and Low cost concept for the Gamma-Ray Lens Project MAX
 . Page 1 Recent Advances and Low cost concept for the Gamma-Ray Lens Project MAX ---- F. Arbusti a, P. Attina b X. Leyre a, M. Sghedoni a a Alcatel Alenia Space - Cannes - France. b Alcatel Alenia Space
. Page 1 Recent Advances and Low cost concept for the Gamma-Ray Lens Project MAX ---- F. Arbusti a, P. Attina b X. Leyre a, M. Sghedoni a a Alcatel Alenia Space - Cannes - France. b Alcatel Alenia Space
MagBeam: R. Winglee, T. Ziemba, J. Prager, B. Roberson, J Carscadden Coherent Beaming of Plasma. Separation of Power/Fuel from Payload
 MagBeam: R. Winglee, T. Ziemba, J. Prager, B. Roberson, J Carscadden Coherent Beaming of Plasma Separation of Power/Fuel from Payload Fast, cost-efficient propulsion for multiple missions Plasma Propulsion
MagBeam: R. Winglee, T. Ziemba, J. Prager, B. Roberson, J Carscadden Coherent Beaming of Plasma Separation of Power/Fuel from Payload Fast, cost-efficient propulsion for multiple missions Plasma Propulsion
11.1 Survey of Spacecraft Propulsion Systems
 11.1 Survey of Spacecraft Propulsion Systems 11.1 Survey of Spacecraft Propulsion Systems In the progressing Space Age, spacecrafts such as satellites and space probes are the key to space exploration,
11.1 Survey of Spacecraft Propulsion Systems 11.1 Survey of Spacecraft Propulsion Systems In the progressing Space Age, spacecrafts such as satellites and space probes are the key to space exploration,
Space Travel on a Shoestring: CubeSat Beyond LEO
 Space Travel on a Shoestring: CubeSat Beyond LEO Massimiliano Vasile, Willem van der Weg, Marilena Di Carlo Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Strathclyde, Glasgow 5th Interplanetary
Space Travel on a Shoestring: CubeSat Beyond LEO Massimiliano Vasile, Willem van der Weg, Marilena Di Carlo Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Strathclyde, Glasgow 5th Interplanetary
PlaS-40 Development Status: New Results
 PlaS-40 Development Status: New Results IEPC-2015-99/ISTS-2015-b-9 Presented at Joint Conference of 30 th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science 34 th International Electric Propulsion
PlaS-40 Development Status: New Results IEPC-2015-99/ISTS-2015-b-9 Presented at Joint Conference of 30 th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science 34 th International Electric Propulsion
Operating Envelopes of Thrusters with Anode Layer
 Operating Envelopes of Thrusters with Anode Layer Semenkin A.V., Tverdokhlebov S.O., Garkusha V.I., Kochergin A.V., Chislov G.O., Shumkin B.V., Solodukhin A.V., Zakharenkov L.E. ABSTRACT The operational
Operating Envelopes of Thrusters with Anode Layer Semenkin A.V., Tverdokhlebov S.O., Garkusha V.I., Kochergin A.V., Chislov G.O., Shumkin B.V., Solodukhin A.V., Zakharenkov L.E. ABSTRACT The operational
Plasma Propulsion in Space Eduardo Ahedo
 Plasma Propulsion in Space Eduardo Ahedo Professor of Aerospace Engineering Plasmas and Space Propulsion Team Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain Outline Space propulsion has been the domain of chemical
Plasma Propulsion in Space Eduardo Ahedo Professor of Aerospace Engineering Plasmas and Space Propulsion Team Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain Outline Space propulsion has been the domain of chemical
The Integrated Structural Electrodynamic Propulsion (ISEP) Experiment
 The Integrated Structural Electrodynamic Propulsion (ISEP) Experiment Nestor Voronka, Robert Hoyt, Tyrel Newton, Ian Barnes Brian Gilchrist (UMich( UMich), Keith Fuhrhop (UMich) TETHERS UNLIMITED, INC.
The Integrated Structural Electrodynamic Propulsion (ISEP) Experiment Nestor Voronka, Robert Hoyt, Tyrel Newton, Ian Barnes Brian Gilchrist (UMich( UMich), Keith Fuhrhop (UMich) TETHERS UNLIMITED, INC.
Shally Saraf, Stanford University
 LAser GRavitational-wave ANtenna in GEocentric Orbit Shally Saraf, Stanford University for the LAGRANGE team Background LAser GRavitational-wave ANtenna in GEocentric Orbit was proposed originally as a
LAser GRavitational-wave ANtenna in GEocentric Orbit Shally Saraf, Stanford University for the LAGRANGE team Background LAser GRavitational-wave ANtenna in GEocentric Orbit was proposed originally as a
The post launch assessment review confirmed the following previous assertions about the mission status:
 1 GRACE Newsletter No. 2 August 15, 2003 Topics: http://www.csr.utexas/grace/ http://www.gfz-potsdam.de/grace 1. Editorial 2. Major events in Mission Operations since last Newsletter 3. Current status
1 GRACE Newsletter No. 2 August 15, 2003 Topics: http://www.csr.utexas/grace/ http://www.gfz-potsdam.de/grace 1. Editorial 2. Major events in Mission Operations since last Newsletter 3. Current status
INVESTIGATION OF PULSED PLASMA THRUSTERS FOR SPACECRAFT ATTITUDE CONTROL
 IEPC-97-128 813 INVESTIGATION OF PULSED PLASMA THRUSTERS FOR SPACECRAFT ATTITUDE CONTROL N.J. Meckel, R.J. Cassady, R.D. Osborne, W.A. Hoskins, R.M. Myers PRIMEX Aerospace Company Redmond, WA. ABSTRACT
IEPC-97-128 813 INVESTIGATION OF PULSED PLASMA THRUSTERS FOR SPACECRAFT ATTITUDE CONTROL N.J. Meckel, R.J. Cassady, R.D. Osborne, W.A. Hoskins, R.M. Myers PRIMEX Aerospace Company Redmond, WA. ABSTRACT
XENON RESISTOJETS AS SECONDARY PROPULSION ON EP SPACECRAFTS AND PERFORMANCE RESULTS OF RESISTOJETS USING XENON
 XENON RESISTOJETS AS SECONDARY PROPULSION ON EP SPACECRAFTS AND PERFORMANCE RESULTS OF RESISTOJETS USING XENON D. Nicolini (a), D. Robertson (a), E. Chesta (a), G. Saccoccia (a), D. Gibbon (b), A. Baker
XENON RESISTOJETS AS SECONDARY PROPULSION ON EP SPACECRAFTS AND PERFORMANCE RESULTS OF RESISTOJETS USING XENON D. Nicolini (a), D. Robertson (a), E. Chesta (a), G. Saccoccia (a), D. Gibbon (b), A. Baker
An Architecture of Modular Spacecraft with Integrated Structural Electrodynamic Propulsion (ISEP)
 NIAC 7 th Annual Meeting Tucson, Arizona October 18 th, 2006 An Architecture of Modular Spacecraft with Integrated Structural Electrodynamic Propulsion (ISEP) Nestor Voronka, Robert Hoyt, Brian Gilchrist,
NIAC 7 th Annual Meeting Tucson, Arizona October 18 th, 2006 An Architecture of Modular Spacecraft with Integrated Structural Electrodynamic Propulsion (ISEP) Nestor Voronka, Robert Hoyt, Brian Gilchrist,
Performance Characteristics of Electrothermal Pulsed Plasma Thrusters with Insulator-Rod-Arranged Cavities and Teflon-Alternative Propellants
 Performance Characteristics of Electrothermal Pulsed Plasma Thrusters with Insulator-Rod-Arranged Cavities and Teflon-Alternative Propellants IEPC-2007-337 Presented at the 30 th International Electric
Performance Characteristics of Electrothermal Pulsed Plasma Thrusters with Insulator-Rod-Arranged Cavities and Teflon-Alternative Propellants IEPC-2007-337 Presented at the 30 th International Electric
IV. Rocket Propulsion Systems. A. Overview
 IV. Rocket Propulsion Systems A. Overview by J. M. Seitzman for AE 4451 Jet and Rocket Propulsion Seitzman Rocket Overview-1 Rocket Definition Rocket Device that provides thrust to a vehicle by accelerating
IV. Rocket Propulsion Systems A. Overview by J. M. Seitzman for AE 4451 Jet and Rocket Propulsion Seitzman Rocket Overview-1 Rocket Definition Rocket Device that provides thrust to a vehicle by accelerating
PPT development for Nanosatellites applications: experimental results
 PPT development for Nanosatellites applications: experimental results IEPC-213-198 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington, D.C.
PPT development for Nanosatellites applications: experimental results IEPC-213-198 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington, D.C.
Figure 1. View of ALSAT-2A spacecraft
 ALSAT-2A TRANSFER AND FIRST YEAR OPERATIONS M. Kameche (1), A.H. Gicquel (2), D. Joalland (3) (1) CTS/ASAL, 1 Avenue de la Palestine, BP 13, Arzew 31200 Oran, Algérie, email:mo_kameche@netcourrier.com
ALSAT-2A TRANSFER AND FIRST YEAR OPERATIONS M. Kameche (1), A.H. Gicquel (2), D. Joalland (3) (1) CTS/ASAL, 1 Avenue de la Palestine, BP 13, Arzew 31200 Oran, Algérie, email:mo_kameche@netcourrier.com
SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES
 SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES Rob Hoyt Tethers Unlimited, Inc. The orbital debris population and its potential for continued rapid growth presents a significant threat to DoD, NASA, commercial,
SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES Rob Hoyt Tethers Unlimited, Inc. The orbital debris population and its potential for continued rapid growth presents a significant threat to DoD, NASA, commercial,
LAUNCH SYSTEMS. Col. John Keesee. 5 September 2003
 LAUNCH SYSTEMS Col. John Keesee 5 September 2003 Outline Launch systems characteristics Launch systems selection process Spacecraft design envelope & environments. Each student will Lesson Objectives Understand
LAUNCH SYSTEMS Col. John Keesee 5 September 2003 Outline Launch systems characteristics Launch systems selection process Spacecraft design envelope & environments. Each student will Lesson Objectives Understand
(b) Analyzed magnetic lines Figure 1. Steady state water-cooled MPD thruster.
 A. MPD thruster In this study, as one of the In-Space Propulsion projects by JAXA (Japan Aerospace exploration Agency), a practical MPD propulsion system was investigated. We planned to develop MPD thrusters
A. MPD thruster In this study, as one of the In-Space Propulsion projects by JAXA (Japan Aerospace exploration Agency), a practical MPD propulsion system was investigated. We planned to develop MPD thrusters
Fusion-Enabled Pluto Orbiter and Lander
 Fusion-Enabled Pluto Orbiter and Lander Presented by: Stephanie Thomas DIRECT FUSION DRIVE Team Members Stephanie Thomas Michael Paluszek Princeton Satellite Systems 6 Market St. Suite 926 Plainsboro,
Fusion-Enabled Pluto Orbiter and Lander Presented by: Stephanie Thomas DIRECT FUSION DRIVE Team Members Stephanie Thomas Michael Paluszek Princeton Satellite Systems 6 Market St. Suite 926 Plainsboro,
Optimal Control based Time Optimal Low Thrust Orbit Raising
 Optimal Control based Time Optimal Low Thrust Orbit Raising Deepak Gaur 1, M. S. Prasad 2 1 M. Tech. (Avionics), Amity Institute of Space Science and Technology, Amity University, Noida, U.P., India 2
Optimal Control based Time Optimal Low Thrust Orbit Raising Deepak Gaur 1, M. S. Prasad 2 1 M. Tech. (Avionics), Amity Institute of Space Science and Technology, Amity University, Noida, U.P., India 2
An introduction to the plasma state in nature and in space
 An introduction to the plasma state in nature and in space Dr. L. Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid The plasma state of condensed matter
An introduction to the plasma state in nature and in space Dr. L. Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid The plasma state of condensed matter
Micro Pulsed Plasma Thruster Development
 Micro Pulsed Plasma Thruster Development IEPC-7-15 Presented at the 3 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Florence, Italy September 17-, 7 S. J. Pottinger * and C. A. Scharlemann Austrian
Micro Pulsed Plasma Thruster Development IEPC-7-15 Presented at the 3 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Florence, Italy September 17-, 7 S. J. Pottinger * and C. A. Scharlemann Austrian
Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements
 Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
IAC-13,C4,P,44.p1,x17254 THE DYNAMIC OPERATON OF A HIGH Q EMDRIVE MICROWAVE THRUSTER. Roger Shawyer C.Eng. MIET. FRAeS. SPR Ltd UK
 IAC-13,C4,P,44.p1,x1754 THE DYNAMIC OPERATON OF A HIGH Q EMDRIVE MICROWAVE THRUSTER Roger Shawyer C.Eng. MIET. FRAeS SPR Ltd UK sprltd@emdrive.com ABSTRACT The static operation of an EmDrive microwave
IAC-13,C4,P,44.p1,x1754 THE DYNAMIC OPERATON OF A HIGH Q EMDRIVE MICROWAVE THRUSTER Roger Shawyer C.Eng. MIET. FRAeS SPR Ltd UK sprltd@emdrive.com ABSTRACT The static operation of an EmDrive microwave
Analytical Modeling of a Microthruster System for Nanosatellite Applications
 Master of Science Thesis Analytical Modeling of a Microthruster System for Nanosatellite Applications Veronica Wallängen Department of Theoretical Physics, School of Engineering Sciences Royal Institute
Master of Science Thesis Analytical Modeling of a Microthruster System for Nanosatellite Applications Veronica Wallängen Department of Theoretical Physics, School of Engineering Sciences Royal Institute
Performance characteristics are based on customer requirements. As such, they are not representative of component capabilities or limitations.
 ADN Micro Propulsion System 13066300-01 The VACCO / ECAPS CubeSat ADN Delta-V Propulsion System is a high performance micro propulsion system (MiPS) specifically designed for CubeSats. The ADN Delta-V
ADN Micro Propulsion System 13066300-01 The VACCO / ECAPS CubeSat ADN Delta-V Propulsion System is a high performance micro propulsion system (MiPS) specifically designed for CubeSats. The ADN Delta-V
Experimental study of a high specific impulse plasma thruster PlaS-120
 Experimental study of a high specific impulse plasma thruster PlaS-120 IEPC-2015-154 /ISTS-2015-b-154 Presented at Joint Conference of 30 th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science 34 th
Experimental study of a high specific impulse plasma thruster PlaS-120 IEPC-2015-154 /ISTS-2015-b-154 Presented at Joint Conference of 30 th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science 34 th
OPERATION PECULIARITIES OF HALL THRUSTER WITH POWER kw AT HIGH DISCHARGE VOLTAGES
 OPERATION PECULIARITIES OF HALL THRUSTER WITH POWER 1.5 2.0 kw AT HIGH DISCHARGE VOLTAGES M.B. Belikov, N.V. Blinov, O.A. Gorshkov, R.N. Rizakhanov, A.A. Shagayda Keldysh Research Center 125438, Moscow,
OPERATION PECULIARITIES OF HALL THRUSTER WITH POWER 1.5 2.0 kw AT HIGH DISCHARGE VOLTAGES M.B. Belikov, N.V. Blinov, O.A. Gorshkov, R.N. Rizakhanov, A.A. Shagayda Keldysh Research Center 125438, Moscow,
Lunar Flashlight Project
 ABSTRACT Recent observations of the Moon with the Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3), Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and other evidence suggest
ABSTRACT Recent observations of the Moon with the Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3), Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and other evidence suggest
Micro Electric Propulsion Technology for Small Satellites: Design, Testing and In-Orbit Operations
 SSC13-III-9 Micro Electric Propulsion Technology for Small Satellites: Design, Testing and In-Orbit Operations V.J. Lappas, T. Harle, A. Knoll, P. Shaw University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH P. Bianco
SSC13-III-9 Micro Electric Propulsion Technology for Small Satellites: Design, Testing and In-Orbit Operations V.J. Lappas, T. Harle, A. Knoll, P. Shaw University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH P. Bianco
Mission Design Options for Solar-C Plan-A
 Solar-C Science Definition Meeting Nov. 18, 2008, ISAS Mission Design Options for Solar-C Plan-A Y. Kawakatsu (JAXA) M. Morimoto (JAXA) J. A. Atchison (Cornell U.) J. Kawaguchi (JAXA) 1 Introduction 2
Solar-C Science Definition Meeting Nov. 18, 2008, ISAS Mission Design Options for Solar-C Plan-A Y. Kawakatsu (JAXA) M. Morimoto (JAXA) J. A. Atchison (Cornell U.) J. Kawaguchi (JAXA) 1 Introduction 2
GP-B Attitude and Translation Control. John Mester Stanford University
 GP-B Attitude and Translation Control John Mester Stanford University 1 The GP-B Challenge Gyroscope (G) 10 7 times better than best 'modeled' inertial navigation gyros Telescope (T) 10 3 times better
GP-B Attitude and Translation Control John Mester Stanford University 1 The GP-B Challenge Gyroscope (G) 10 7 times better than best 'modeled' inertial navigation gyros Telescope (T) 10 3 times better
New electric propulsion technologies investigation by simulation
 New electric propulsion technologies investigation by simulation Mario Merino Equipo de Propulsión Espacial por Plasmas (EP2) Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM) Contents The EP2 group and their activities
New electric propulsion technologies investigation by simulation Mario Merino Equipo de Propulsión Espacial por Plasmas (EP2) Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM) Contents The EP2 group and their activities
BravoSat: Optimizing the Delta-V Capability of a CubeSat Mission. with Novel Plasma Propulsion Technology ISSC 2013
 BravoSat: Optimizing the Delta-V Capability of a CubeSat Mission with Novel Plasma Propulsion Technology Sara Spangelo, NASA JPL, Caltech Benjamin Longmier, University of Michigan Interplanetary Small
BravoSat: Optimizing the Delta-V Capability of a CubeSat Mission with Novel Plasma Propulsion Technology Sara Spangelo, NASA JPL, Caltech Benjamin Longmier, University of Michigan Interplanetary Small
High Pulse Repetition Frequency Operation of Low-power short-pulse Plasma Thruster
 High Pulse Repetition Frequency Operation of Low-power short-pulse Plasma Thruster IEPC-2015-91035 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science 34th International
High Pulse Repetition Frequency Operation of Low-power short-pulse Plasma Thruster IEPC-2015-91035 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science 34th International
483 Lecture. Space Mission Requirements. February11, Definition Examples Dos/ Don ts Traceability
 483 Lecture Space Mission February11, 2012 Photo Credit:: http://www.spacewallpapers.info/cool-space-wallpaper What s a Requirement? ification? Requirement A concept independent statement of a mix of needs,
483 Lecture Space Mission February11, 2012 Photo Credit:: http://www.spacewallpapers.info/cool-space-wallpaper What s a Requirement? ification? Requirement A concept independent statement of a mix of needs,
Electric Propulsion Research and Development at NASA-MSFC
 Electric Propulsion Research and Development at NASA-MSFC November 2014 Early NEP concept for JIMO mission Dr. Kurt Polzin (kurt.a.polzin@nasa.gov) Propulsion Research and Development Laboratory NASA -
Electric Propulsion Research and Development at NASA-MSFC November 2014 Early NEP concept for JIMO mission Dr. Kurt Polzin (kurt.a.polzin@nasa.gov) Propulsion Research and Development Laboratory NASA -
Modular Low Earth Orbital-Hub DLR Vision 2025
 The Space Congress Proceedings 2016 (44th) The Journey: Further Exploration for Universal Opportunities May 25th, 10:45 AM Modular Low Earth Orbital-Hub DLR Vision 2025 Dr. Oliver Romberg German Space
The Space Congress Proceedings 2016 (44th) The Journey: Further Exploration for Universal Opportunities May 25th, 10:45 AM Modular Low Earth Orbital-Hub DLR Vision 2025 Dr. Oliver Romberg German Space
CubeSat Propulsion Using Electrospray Thrusters
 SSC09-II-6 CubeSat Propulsion Using Electrospray Thrusters Tom Roy, Vlad Hruby, Nathan Rosenblad, Peter Rostler and Douglas Spence Busek Co. Inc. 11 Tech Circle, Natick, MA 01760; 508-655-5565 troy@busek.com,
SSC09-II-6 CubeSat Propulsion Using Electrospray Thrusters Tom Roy, Vlad Hruby, Nathan Rosenblad, Peter Rostler and Douglas Spence Busek Co. Inc. 11 Tech Circle, Natick, MA 01760; 508-655-5565 troy@busek.com,
Abstract. Objectives. Theory
 A Proposal to Develop a Two-Stage Gridless Ion Thruster with Closed Electron Drift Richard R. Hofer Plasmadynamics and Electric Propulsion Laboratory (PEPL) Department of Aerospace Engineering University
A Proposal to Develop a Two-Stage Gridless Ion Thruster with Closed Electron Drift Richard R. Hofer Plasmadynamics and Electric Propulsion Laboratory (PEPL) Department of Aerospace Engineering University
QB50 Proposed Deployment ConOps. Dan Oltrogge Center for Space Standards and Innovation Co-Lead, QB50 Orbit Dynamics Working Group
 QB50 Proposed Deployment ConOps Dan Oltrogge Center for Space Standards and Innovation Co-Lead, QB50 Orbit Dynamics Working Group 25 Apr 2014 Proposed QB50 Deployment ConOps Want to develop and characterize
QB50 Proposed Deployment ConOps Dan Oltrogge Center for Space Standards and Innovation Co-Lead, QB50 Orbit Dynamics Working Group 25 Apr 2014 Proposed QB50 Deployment ConOps Want to develop and characterize
Mission to Mars. MAE 598: Design Optimization Final Project. By: Trevor Slawson, Jenna Lynch, Adrian Maranon, and Matt Catlett
 Mission to Mars MAE 598: Design Optimization Final Project By: Trevor Slawson, Jenna Lynch, Adrian Maranon, and Matt Catlett Motivation Manned missions beyond low Earth orbit have not occurred since Apollo
Mission to Mars MAE 598: Design Optimization Final Project By: Trevor Slawson, Jenna Lynch, Adrian Maranon, and Matt Catlett Motivation Manned missions beyond low Earth orbit have not occurred since Apollo
Make Your Cubesat Overnight and Put it in Any Orbit (Well almost)
 Make Your Cubesat Overnight and Put it in Any Orbit (Well almost) Jim White, Walter Holemans, Planetary Systems Inc. Dr. Adam Huang, University of Arkansas RAMPART Summary Main Components The Promise of
Make Your Cubesat Overnight and Put it in Any Orbit (Well almost) Jim White, Walter Holemans, Planetary Systems Inc. Dr. Adam Huang, University of Arkansas RAMPART Summary Main Components The Promise of
Thermal Radiation Studies for an Electron-Positron Annihilation Propulsion System
 Thermal Radiation Studies for an Electron-Positron Annihilation Propulsion System Jonathan A. Webb Embry Riddle Aeronautical University Prescott, AZ 8631 Recent studies have shown the potential of antimatter
Thermal Radiation Studies for an Electron-Positron Annihilation Propulsion System Jonathan A. Webb Embry Riddle Aeronautical University Prescott, AZ 8631 Recent studies have shown the potential of antimatter
LISA mission design. Guido Mueller. APS April Meeting, Jan 30th, 2017, Washington DC
 LISA mission design Guido Mueller University of Florida APS April Meeting, Jan 30th, 2017, Washington DC 1 L3 from ESA s perspective 2013: Selection of L3 Science Theme by ESA The Gravitational Universe
LISA mission design Guido Mueller University of Florida APS April Meeting, Jan 30th, 2017, Washington DC 1 L3 from ESA s perspective 2013: Selection of L3 Science Theme by ESA The Gravitational Universe
Asteroid Payload Express Architecture for Low- Cost and Frequent ProspecFng of NEOs
 Asteroid Payload Express Architecture for Low- Cost and Frequent ProspecFng of NEOs Dr. Rob Hoyt Jeffrey Slostad, Lenny Paritsky, Nestor Voronka, Todd Moser, Greg Jimmerson Tethers Unlimited, Inc 11711
Asteroid Payload Express Architecture for Low- Cost and Frequent ProspecFng of NEOs Dr. Rob Hoyt Jeffrey Slostad, Lenny Paritsky, Nestor Voronka, Todd Moser, Greg Jimmerson Tethers Unlimited, Inc 11711
Canadian Advanced Nanospace experiment 2 Orbit Operations:
 Canadian Advanced Nanospace experiment 2 Orbit Operations: One Year of Pushing the Nanosat Performance Envelope Karan Sarda Cordell Grant, Stuart Eagleson Daniel D. Kekez, Amee Shah Robert E. Zee Space
Canadian Advanced Nanospace experiment 2 Orbit Operations: One Year of Pushing the Nanosat Performance Envelope Karan Sarda Cordell Grant, Stuart Eagleson Daniel D. Kekez, Amee Shah Robert E. Zee Space
Electric Propulsion for Space Travel
 Electric Propulsion for Space Travel Sarah Cusson Ph.D. Candidate NASA Space Technology Research Fellow University of Michigan Plasmadynamics and Electric Propulsion Laboratory Agenda History of electric
Electric Propulsion for Space Travel Sarah Cusson Ph.D. Candidate NASA Space Technology Research Fellow University of Michigan Plasmadynamics and Electric Propulsion Laboratory Agenda History of electric
Gravitational & Planetary Research Program
 2012 Gravitational & Planetary Research Program Goals Why? Relativity, Gravitational Waves, Geodesy, Aeronomy Space Technology Education and Training: STEM Team Who? NASA Universities Industry Foreign
2012 Gravitational & Planetary Research Program Goals Why? Relativity, Gravitational Waves, Geodesy, Aeronomy Space Technology Education and Training: STEM Team Who? NASA Universities Industry Foreign
Chapter 4: Spacecraft Propulsion System Selection
 S.1 Introduction - 1 - Chapter 4: Spacecraft Propulsion System Selection The selection of the best propulsion system for a given spacecraft missions is a complex process. Selection criteria employed in
S.1 Introduction - 1 - Chapter 4: Spacecraft Propulsion System Selection The selection of the best propulsion system for a given spacecraft missions is a complex process. Selection criteria employed in
SSC01-IX th Annual/USU Conference on Small Satellites
 An RF Plasma Thruster for Use in Small Satellites New England Space Works, Inc., 24 Swift Road, Framingham, MA 01702 (508)620-6667 LynnOlson@compuserve.com SSC01-IX-7 Abstract. New England Space Works
An RF Plasma Thruster for Use in Small Satellites New England Space Works, Inc., 24 Swift Road, Framingham, MA 01702 (508)620-6667 LynnOlson@compuserve.com SSC01-IX-7 Abstract. New England Space Works
Nanoparticle Electric Propulsion for Space Exploration
 Nanoparticle Electric Propulsion for Space Exploration Thomas M. Liu 1, Louis D. Musinski 2, Prashant R. Patel 3, Alec D. Gallimore 4, Brian E. Gilchrist 5, Michael Keidar 6 1,3,4,6 Aerospace Engineering,
Nanoparticle Electric Propulsion for Space Exploration Thomas M. Liu 1, Louis D. Musinski 2, Prashant R. Patel 3, Alec D. Gallimore 4, Brian E. Gilchrist 5, Michael Keidar 6 1,3,4,6 Aerospace Engineering,
Development of stationary plasma thruster SPT-230 with discharge power of kw
 Development of stationary plasma thruster SPT-230 with discharge power of 10...15 kw IEPC-2017-548 Presented at the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Development of stationary plasma thruster SPT-230 with discharge power of 10...15 kw IEPC-2017-548 Presented at the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
ASPECT Spectral Imager CubeSat Mission to Didymos
 ASPECT Spectral Imager CubeSat Mission to Didymos Kestilä A. 1),Näsilä A. 2), Kohout T. 3),Tikka T. 1),Granvik M. 3) 1. Aalto University, Finland. 2. Technical Research Center of Finland, Finland 3. Helsinki
ASPECT Spectral Imager CubeSat Mission to Didymos Kestilä A. 1),Näsilä A. 2), Kohout T. 3),Tikka T. 1),Granvik M. 3) 1. Aalto University, Finland. 2. Technical Research Center of Finland, Finland 3. Helsinki
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
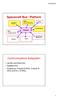 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
The ResistoJet as a simple and cost-effective propulsion system for nano- and microsatellites
 1st IAA Latin American Symposium on Small Satellites Advanced Technologies and Distributed Systems March 7-10, 2017 IAA-LA-13-03 The ResistoJet as a simple and cost-effective propulsion system for nano-
1st IAA Latin American Symposium on Small Satellites Advanced Technologies and Distributed Systems March 7-10, 2017 IAA-LA-13-03 The ResistoJet as a simple and cost-effective propulsion system for nano-
AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Equation Chapter 1 Section 1 CONTAMINATION STUDY OF A MICRO PULSED PLASMA THRUSTER THESIS Ceylan Kesenek, 1 ST Lt, TUAF AFIT/GA/ENY/08-M03 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE
Equation Chapter 1 Section 1 CONTAMINATION STUDY OF A MICRO PULSED PLASMA THRUSTER THESIS Ceylan Kesenek, 1 ST Lt, TUAF AFIT/GA/ENY/08-M03 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE
Research and Development on Coaxial Pulsed Plasma Thruster with Feed Mechanism
 Research and Development on Coaxial Pulsed Plasma er with Feed Mechanism IEPC-2009-255 Presented at the 31st International Electric Propulsion Conference, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA
Research and Development on Coaxial Pulsed Plasma er with Feed Mechanism IEPC-2009-255 Presented at the 31st International Electric Propulsion Conference, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA
DAVID: Diminutive Asteroid Visitor with Ion Drive A Cubesat Asteroid Mission
 DAVID: Diminutive Asteroid Visitor with Ion Drive A Cubesat Asteroid Mission Geoffrey A. Landis NASA Glenn Research Center COMPASS Team at NASA Glenn: Steve Oleson, Melissa McGuire, Aloysius Hepp, James
DAVID: Diminutive Asteroid Visitor with Ion Drive A Cubesat Asteroid Mission Geoffrey A. Landis NASA Glenn Research Center COMPASS Team at NASA Glenn: Steve Oleson, Melissa McGuire, Aloysius Hepp, James
IMPACT OF SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION REQUIREMENTS ON THE MISSION DESIGN OF ESA SPACECRAFT
 IMPACT OF SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION REQUIREMENTS ON THE MISSION DESIGN OF ESA SPACECRAFT Rüdiger Jehn (1), Florian Renk (1) (1 ) European Space Operations Centre, Robert-Bosch-Str. 5, 64293 Darmstadt, Germany,
IMPACT OF SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION REQUIREMENTS ON THE MISSION DESIGN OF ESA SPACECRAFT Rüdiger Jehn (1), Florian Renk (1) (1 ) European Space Operations Centre, Robert-Bosch-Str. 5, 64293 Darmstadt, Germany,
1. (a) Describe the difference between over-expanded, under-expanded and ideallyexpanded
 Code No: R05322106 Set No. 1 1. (a) Describe the difference between over-expanded, under-expanded and ideallyexpanded rocket nozzles. (b) While on its way into orbit a space shuttle with an initial mass
Code No: R05322106 Set No. 1 1. (a) Describe the difference between over-expanded, under-expanded and ideallyexpanded rocket nozzles. (b) While on its way into orbit a space shuttle with an initial mass
New Worlds Observer Final Report Appendix E. Section E: Starshades Subsection E.6: Starshade Spacecraft Lead Author: Amy Lo
 Section E: Starshades Subsection E.6: Starshade Spacecraft Lead Author: Amy Lo Introduction Starshade Spacecraft Functional Requirements The main function of the starshade spacecraft is to: 1) support
Section E: Starshades Subsection E.6: Starshade Spacecraft Lead Author: Amy Lo Introduction Starshade Spacecraft Functional Requirements The main function of the starshade spacecraft is to: 1) support
Thrust Balance Characterization of a 200W Quad Confinement Thruster for High Thrust Regimes
 Thrust Balance Characterization of a 200W Quad Confinement Thruster for High Thrust Regimes IEPC-2013-155 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University
Thrust Balance Characterization of a 200W Quad Confinement Thruster for High Thrust Regimes IEPC-2013-155 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University
Six-Axis Monopropellant Propulsion System for Pico-Satellites
 Six-Axis Monopropellant Propulsion System for Pico-Satellites Mariella Creaghan, Orland Lamce, and Cody Slater 14 October 2015 Overview Background Spacecraft Capabilities Thruster System Design Ground
Six-Axis Monopropellant Propulsion System for Pico-Satellites Mariella Creaghan, Orland Lamce, and Cody Slater 14 October 2015 Overview Background Spacecraft Capabilities Thruster System Design Ground
