Stochastic resonance in the absence and presence of external signals for a chemical reaction
|
|
|
- Juliana Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 Stochastic resonance in the absence and presence of external signals for a chemical reaction Lingfa Yang, Zhonghuai Hou, and Houwen Xin a) Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, , People s Republic of China Received 27 August 1998; accepted 4 November 1998 A catalytic reduction of NO with CO on Pt 100 surface is adopted to study its response under random perturbation. Noise-induced oscillations and noise-induced frequency shifts have been observed when the system works in the vicinity of the oscillatory region and meanwhile is subjected to random modulation of its feeding speed. Stochastic resonance behavior can be recognized from the noise-induced peak in the power spectrum even though in the absence of external signals. The numerical results have been obtained near supercritical Hopf bifurcation points, but are not confined to the classification of bifurcation. When the system falls into bistable regions, noise can help an external weak signal to induce state-to-state transitions and also shows a stochastic resonance behavior except for the case that the system has an isolated bifurcation scheme American Institute of Physics. S I. INTRODUCTION Random noise can be beneficial to the formation of order, rather than destroy it. This paradoxical point of view has been increasingly reported in many nonlinear systems recently, and gradually accepted by many scientists. Stochastic resonance SR is one of the most prominent phenomena in which noise represents a useful tool to improve the detection of a weak signal, to transport its random energy to enhance the signal oscillation. The concept of SR was originally proposed by Benzi et al. 1 to account for the periodicity in Earth s ice ages, but has since been shown to occur in many systems such as in physical sensitive devices and sensory neuron systems. 2 The notion of SR has been widened to include many different mechanisms. The unifying feature of all these systems is the increased sensitivity to small perturbations at an optimal noise level and the existence of a resonance peak on the plot of signal-to-noise SNR versus noise intensity. The effect of SR requires three basic ingredients: 3 a suitable nonlinear system, a weak signal and a source of noise. In studying SR, the signal is adopted generally as an external input modulation of a nonlinear system, then, one looks at the periodic contribution of the output at the same frequency as input. Recently, Hu et al. 4 took the initiative to present a kind of SR in an autonomous system without external periodic force, which we here call autonomous stochastic resonance ASR. Near the oscillatory region they find a noise-induced oscillation and a noise-induced shift in frequency. Their results were reexamined later by Rappel et al. 5 and ascribed to the nonuniformity of the limit cycle. We particularly notice that in their studies the oscillation is terminated by a saddle-node bifurcation and Rappel et al. 5 draw the conclusion that one would not expect to find this a Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; electronic mail: lfyang@ustc.edu.cn type of stochastic resonance in systems whose oscillations are created by a Hopf bifurcation. We are afraid that we can not accept this viewpoint. In this paper, we present an ASR behavior which can occur in a chemical reaction whose oscillations are both created and ended by supercritical Hopf bifurcation. In addition, the frequency shifts are found, but the shift direction tends to the opposite direction as that indicated in Refs. 4 and 5. SR phenomena have been studied mainly in bistable systems in the past years. It therefore gives a wrong impression: All bistable systems can show SR if the input is modulated properly by an external periodic signal and a suitable level of noise. Our present study shows that this conclusion is not universal, because some bistable systems can definitely not show SR. It is the bifurcation scheme that accounts for the occurrence of SR. In this paper, we present a bifurcation scheme, which can change from an isolated circle to a mushroomlike shape through a transcritical bifurcation. The result shows that the response of the reaction is much different before and after the bifurcation when the system is subjected to external modulations. Up to now, almost all the studies on SR, both theoretically and experimentally, have concentrated on physical or biophysical systems, but few of them involve chemical reactions except experimental studies by Schneider s group in homogeneous reactions 6 8 and our recent numerical results 9 in a surface catalytic reaction Pt 110 /CO O 2. In this paper, we adopt a reaction of catalytic reduction of NO with CO on a Pt single crystal surface that has been thoroughly investigated in the past decades. 10 The reaction exhibits an abundance of kinetic behaviors including sustained rate oscillations and pattern formations, and its reaction model has been well organized and shows a series of interesting bifurcation schemes /99/110(7)/3591/5/$ American Institute of Physics
2 3592 J. Chem. Phys., Vol. 110, No. 7, 15 February 1999 Yang, Hou, and Xin II. THE MODEL AND ITS BIFURCATION SCHEME The reaction of Pt 100 /NO CO proceeding in an ultrahigh vacuum chamber is well understood see Ref. 10 and references cited therein. The mechanism can be described by the following steps: 10,13 CO gas * CO ad, I NO gas * NO ad, NO ad * N ad O ad, 2N ad N 2 gas 2*, II III IV CO ad O ad CO 2 gas 2*. V The adsorption of CO gas or NO gas requires a vacant site; in the opposite direction, the desorption of CO ad or NO ad releases an adsorption site I, II. Following the adsorption of NO gas, the dissociation of adsorbed NO requires another free adsorption site. Therefore, this step is regarded as a rate-limiting one III. The following two reactions IV and V produce gas species which are removed from the surface immediately and release two adsorption sites each. The competition between the vacant sites consumption in I, II, and III and their supply in IV and V shows an autocatalytic behavior. Certainly, this scheme neglects N 2 O formation because it is unstable in low pressure or room temperature. Imbihl et al. 11 have built a three-variable model from reactions I to V to describe adsorbate coverages CO for adsorbed CO, NO for adsorbed NO, O for adsorbed oxygen. That is, d CO dt 1 p CO 1 CO NO 2 CO 3 CO O, 1 d NO dt 1 p NO 1 CO NO 4 NO 5 NO empty, 2 d O dt 5 NO empty 3 CO O, with empty max 1 CO NO O CO,NO O,0. All the coefficients of adsorption (k 1 ), desorption (k 2 and k 4 ), dissociation (k 5 ) and combination (k 3 and k 7 ), have been listed in Refs. 11 and 12, which were originally taken from experimental data. Because of the repulsive interaction between adsorbed CO and NO, their desorptions become easy. Their temperature dependence is expressed via the Arrhenius law, k 2,4 2,4 exp( E NO,CO /RT), and their active energy barriers, E NO,CO act E NO,CO act 0 6 NO CO 2, decrease with the increase of the surface coverage. When NO,CO exceeds NO,CO 0.61, and adsorbed oxygen exceeds O 0.4, no free sites provide for NO ad dissociation, and the reaction is inhibited. 3 FIG. 1. Bifurcation diagrams show the existence of an isolated branch of the steady-state solution as p NO is varied as bifurcation parameter before a transcritical bifurcation occurs a and the existence of a mushroomlike multiple steady-state solution after the transcritical bifurcation occurs b. When p NO is modulated, the reaction shows kinetic hysteresis marked by loop ABCD and loop EFGH in b. In contrast, there is not any hysteresis in the isola a. The existence range for kinetic oscillations is terminated by two supercritical Hopf bifurcation points h1 and h2. The amplitude of the oscillations the upper and lower turning points is represented by the dash lines. The legends for a are also suitable for b. The kinetic behavior of this model can be understood by its bifurcation scheme. First, one can get a steady state fixed point by solving the equations d CO /dt 0, d NO /dt 0 and d O /dt 0. Then, one can get its stability using a linear stability analysis method. A fixed point should fall into one of the kinds: a stable or unstable node, a stable or unstable focus, or a saddle point. Here we show the system s multistability in one-dimensional bifurcation diagrams see Fig. 1, which agrees well with Imbihl s results. 11 The low branch has an oscillatory region that both starts and terminates both by supercritical Hopf bifurcation. The amplitude of the oscillations the upper and lower turning points represented in Fig. 1 is obtained from the numerical integration of Eqs Keeping p CO mbar, we notice there exists a transcritical bifurcation at about T 415 K. At low temperature, the low isolated region separates with the upper branch Fig. 1 a. With the increase of temperature, the upper branch approaches the isolated region and finally touches it to cause a transcritical bifurcation. The diagram seems mushroom-like see Fig. 1 b. We pay special attention to these two cases: before and after the transcritical bifurcation, to study their different responses under external perturbations.
3 J. Chem. Phys., Vol. 110, No. 7, 15 February 1999 Yang, Hou, and Xin 3593 FIG. 2. Noise-induced oscillation on power spectrum. The background line is obtained directly from FFT. The white overlay curve is a smoothing curve from adjacent averaging of 100 points. FIG. 3. The signal-to-noise ratio: SNR evaluated from the power spectrum versus noise level. The constant partial pressure p (a), 4.75 b and 3.05 c in units of 10 7 mbar for different locations in Fig. 1 a. Each curve displays a peak for stochastic resonance. III. COHERENT MOTION AND STOCHASTIC RESONANCE RESPONSE The time evolution of many nonlinear systems shows nonuniformity. In some parts of the trajectory the system evolves quickly, but in other parts it goes slowly. This reveals an interior asymmetry of a nonlinear system. When the asymmetric system is subjected to a zero-mean symmetric perturbation, its response may show a coherent motion to some extent. A Gaussian-type white noise has a zero mean value (t) 0, and its correlation (t) (t ) 2D (t t ) is a white spectrum. It is often adopted to simulate internal fluctuation or external uncertainty. As usual, the response of a nonlinear system to a white noise input is no longer a white spectrum. If we modify the reaction conditions carefully so that the system works near the oscillatory region but not in the region, presenting noise to the control parameters may induce an oscillatory motion. By power spectrum analysis of the output, a noise-induced peak can be found. With an increase of noise level, the peak becomes broad but higher first and then collapses at high noise level. We give another definition of the SNR as the height of the peak over its half-width, because a sharp and high peak is much more recognized. A resonancelike behavior can be obtained from the curve of the SNR to the noise level. Because this performance appears in the absence of an external signal, one calls it autonomous stochastic resonance ASR. In contrast with SR in a general sense, ASR can be understood as the noise resonating with the intrinsic signal instead of the external signal. Figure 2 shows a noise-induced oscillation peak in the power spectrum at the frequency corresponding to the intrinsic oscillation. It is a response of the system to external noise input p NO 1 t p 0, where is noise intensity. The nonperturbation pressure of NO is p mbar. It is apparently out of the oscillatory region marked by h1, p NO mbar, and h2, p NO mbar. For a small noise, the noiseinduced peak is sharp but low. At increasing noise level, it becomes high but broad. By power spectrum analysis of the output, we plot the SNR as a function of noise level in Fig. 3 a. The curve shows clearly a SR peak at If the constant pressure becomes closer to the oscillatory region, for example, p mbar, the SR peak becomes higher and shifts to low level of noise see Fig. 3 b. Atthe other end of the oscillatory region, p mbar, the noise-induced oscillation can also be found, and the response also has a SR peak shown in Fig. 3 c. However, the SR peak is very small and appears at very small noise because too much noise can result in a jump from the isola to the opposite stable state, but the reverse process never happens. Figure 4 displays the frequency shift of the noiseinduced oscillation peak. With the increase of noise level, the peak shifts to lower frequency, not to higher frequency as indicated in Refs. 4 and 5 IV. STOCHASTIC RESONANCE WITH EXTERNAL SIGNAL A general feature of a system exhibiting stochastic resonance is its increased sensitivity to small perturbations when an appropriate dose of noise is added. In its simplest form, SR occurs in a bistable system driven by a periodic external force. The periodic force raises two potential wells alternately; when the noise is sufficiently strong, the overdamped particle can jump over the potential barrier. The key point is that the external signal, itself, is not strong enough to cause any transitions or excitations; the increasing noise helps the transitions or excitations gradually, makes them true, and can make the transition synchronized with weak perturbation. FIG. 4. Frequency shift of the noise-induced oscillation peak as a function of the noise level. The plot and the insert plot corresponds to Figs. 3 b and 3 c, respectively. The lines are only drawn to guide the eyes.
4 3594 J. Chem. Phys., Vol. 110, No. 7, 15 February 1999 Yang, Hou, and Xin However, a too strong noise counteracts the aforementioned correlation, thereby reducing the response. So there exists a SR peak with the increase of noise level. Now the question is whether all bistable systems can show a SR behavior. Bifurcation schemes for low-dimension systems generally fall into four basic classes: S type, Z type, isolated, and mushroomlike. The two stable states, corresponding to a stable node, a focus or a stable limit cycle surrounding an unstable focus, are usually separated by a saddle point. Hysteresis behavior can occur as modulation of the control parameter for the other three cases except for the isolated bifurcation scheme. Figure 1 a displays an isolated bifurcation where the bistable region is clearly shown within two saddle-node bifurcation sn1 and sn2, and the low branch is isolated. Under a strong modulation, the low branch may lose its stability to jump up to the high branch. However, the inverse process never occurs. In these circumstances, one never expects to have a general SR response. After a transcritical bifurcation, the isola develops into a mushroomlike scheme shown in Fig. 1 b. This bifurcation diagram exhibits two hysteresis regions when the system is subjected to external modulation. At p mbar, we applied a small periodic signal amplitude, frequency f s ) together with a Gaussian noise component intensity. That is, p NO 1 sin 2 f s t t p 0. For 0.03, f s 1/400s 1, and let the noise be added 100 times per signal period. The integration of the ODEs lasts not less than 100 signal periods. We adopt a fast Fourier transform FFT power spectrum analysis method to analyze one of the state variables, for example, CO. Then, the SNR can be obtained from the spectrum. Figure 5 a shows the results. As the noise level is increased, a SR peak can be recognized at about In parallel to the above, we choose another site p mbar to study SR. Let 0.12, f s 1/1500s 1, and the other conditions remain unchanged. We obtain a similar SNR curve shown in Fig. 5 b. As shown in Fig. 1 b, the kinetic behaviors for the two bistable regions are much different. In the loop ABCD, both the upper branch AB and the low branch CD are stable steady states. In contrast, in another loop EFGH, EF still keeps a stable steady state, but most of the branch GH falls into the oscillatory region. In the absence of noise, one can find mixed-mode oscillations and rich phase-locking phenomena in power spectrum under external periodic modulation. However, the local dynamical difference, regardless of the difference between a steady state and an oscillatory state, has no influence on the occurrence of SR. V. CONCLUSION A typical surface chemical reaction Pt 100 /CO NO is adopted to study its dynamical response under random perturbation in the absence and presence of external periodic weak modulation. Resonance behavior can be found for both of them. First, the reaction exhibits an oscillatory region that is both created and ended by continuous Hopf bifurcation. As FIG. 5. SNR output as the function of noise level. Locating p 0 5.3(a) and 3.3 b in units 10 7 mbar, the system works corresponding to the loop ABCD and the loop EFGH in Fig. 1, respectively. Both show a stochastic resonance peak. the NO pressure approaches the oscillatory region, we apply a Gaussian type noise to modify the feeding system of partial pressure of NO. Noise-induced oscillations and noiseinduced frequency have been found, and the response may display an autonomous stochastic resonance behavior that shows the positive effect of the noise. Our numerical results have revealed these nonlinear phenomena are constant regardless of a Hopf bifurcation or a saddle-node bifurcation coming into or out of the intrinsic oscillations. Second, stochastic resonance in bistable regions has been found. Each stable state may relate to a stable node, or a stable focus, even an unstable focus but existing a stable limit cycle. This difference does not present an obstacle to the occurrence of stochastic resonance. However, if the bifurcation scheme has an isolated branch causing the transition between the two stable states to be inreversible, one never expects to observe the stochastic resonance behavior in general sense. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Laboratory of Theoretical and Computational Chemistry of China. 1 R. Benzi, S. Sutera, and A. Vulpiani, J. Phys. A 14, L K. Wiesenfeld and F. Moss, Nature London 373, L. Gammaitoni, P. Hanggi, P. Jung, and F. Marchesoni, Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, G. Hu, T. Ditzinger, C. Z. Ning, and H. Haken, Phys. Rev. Lett. 71,
5 J. Chem. Phys., Vol. 110, No. 7, 15 February 1999 Yang, Hou, and Xin W. J. Rappel and S. H. Stroget, Phys. Rev. E 50, A. Guderian, G. Decher, K.-P. Zeyer, and F. W. Schneider, J. Phys. Chem. 100, A. Forster, M. Merget, and F. W. Schneider, J. Phys. Chem. 100, W. Hohmann, J. Muller, and F. W. Schneider, J. Phys. Chem. 100, L. Yang, Z. Hou, and H. Xin, J. Chem. Phys. 109, R. Imbihl and G. Ertl, Chem. Rev. 95, R. Imbihl, T. Fink, and K. Krischer, J. Chem. Phys. 96, T. Fink, K. Krischer, and R. Imbihl, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 10, T. Fink, J.-P. Dath, R. Imbihl, and G. Ertl, J. Chem. Phys. 95,
Stochastic resonance of electrochemical aperiodic spike trains
 Stochastic resonance of electrochemical aperiodic spike trains P. Parmananda, 1 Gerardo J. Escalera Santos, 1 M. Rivera, 1 and Kenneth Showalter 2 1 Facultad de Ciencias, UAEM, Avenida Universidad 1001,
Stochastic resonance of electrochemical aperiodic spike trains P. Parmananda, 1 Gerardo J. Escalera Santos, 1 M. Rivera, 1 and Kenneth Showalter 2 1 Facultad de Ciencias, UAEM, Avenida Universidad 1001,
Noise-enhanced propagation in a dissipative chain of triggers
 Noise-enhanced propagation in a dissipative chain of triggers S. Morfu.C. Comte.M. Bilbault and P. Marquié Université de Bourgogne, LE2I, (F.R.E.) C.N.R.S. 2309 BP 40-210 DION cedex, FRANCE email: smorfu@u-bourgogne.fr
Noise-enhanced propagation in a dissipative chain of triggers S. Morfu.C. Comte.M. Bilbault and P. Marquié Université de Bourgogne, LE2I, (F.R.E.) C.N.R.S. 2309 BP 40-210 DION cedex, FRANCE email: smorfu@u-bourgogne.fr
Vibrational resonance
 Published in J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 33, L433 L438 (2000). LETTER TO THE EDITOR Vibrational resonance P S Landa andpvemcclintock Department of Physics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119899 Moscow,
Published in J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 33, L433 L438 (2000). LETTER TO THE EDITOR Vibrational resonance P S Landa andpvemcclintock Department of Physics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119899 Moscow,
Cooperative Effects of Noise and Coupling on Stochastic Dynamics of a Membrane-Bulk Coupling Model
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 51 (2009) pp. 455 459 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 51, No. 3, March 15, 2009 Cooperative Effects of Noise and Coupling on Stochastic Dynamics
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 51 (2009) pp. 455 459 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 51, No. 3, March 15, 2009 Cooperative Effects of Noise and Coupling on Stochastic Dynamics
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 80 1 JUNE 1998 NUMBER 22 Field-Induced Stabilization of Activation Processes N. G. Stocks* and R. Mannella Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Pisa, and Istituto Nazionale
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 80 1 JUNE 1998 NUMBER 22 Field-Induced Stabilization of Activation Processes N. G. Stocks* and R. Mannella Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Pisa, and Istituto Nazionale
Lecture 4: Importance of Noise and Fluctuations
 Lecture 4: Importance of Noise and Fluctuations Jordi Soriano Fradera Dept. Física de la Matèria Condensada, Universitat de Barcelona UB Institute of Complex Systems September 2016 1. Noise in biological
Lecture 4: Importance of Noise and Fluctuations Jordi Soriano Fradera Dept. Física de la Matèria Condensada, Universitat de Barcelona UB Institute of Complex Systems September 2016 1. Noise in biological
Ordering periodic spatial structures by non-equilibrium uctuations
 Physica A 277 (2000) 327 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Ordering periodic spatial structures by non-equilibrium uctuations J.M.G. Vilar a;, J.M. Rub b a Departament de F sica Fonamental, Facultat de
Physica A 277 (2000) 327 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Ordering periodic spatial structures by non-equilibrium uctuations J.M.G. Vilar a;, J.M. Rub b a Departament de F sica Fonamental, Facultat de
STOCHASTIC RESONANCE IN MONOSTABLE SYSTEMS
 Published in J. Phys. A: Mat. Gen. 26, L385-39 (1993). STOCHASTIC RESONANCE IN MONOSTABLE SYSTEMS N G Stocks, N D Stein and P V E McClintock School of Physics and Materials, Lancaster University, Lancaster,
Published in J. Phys. A: Mat. Gen. 26, L385-39 (1993). STOCHASTIC RESONANCE IN MONOSTABLE SYSTEMS N G Stocks, N D Stein and P V E McClintock School of Physics and Materials, Lancaster University, Lancaster,
Effects of colored noise on stochastic resonance in a bistable system subject to multiplicative and additive noise
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 63, 031107 Effects of colored noise on stochastic resonance in a bistable system subject to multiplicative and additive noise Ya Jia, 1, * Xiao-ping Zheng, 1 Xiang-ming Hu, 1
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 63, 031107 Effects of colored noise on stochastic resonance in a bistable system subject to multiplicative and additive noise Ya Jia, 1, * Xiao-ping Zheng, 1 Xiang-ming Hu, 1
Nonlinear Stochastic Resonance with subthreshold rectangular pulses arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 2004.
![Nonlinear Stochastic Resonance with subthreshold rectangular pulses arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 2004. Nonlinear Stochastic Resonance with subthreshold rectangular pulses arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 2004.](/thumbs/72/67240881.jpg) Nonlinear Stochastic Resonance with subthreshold rectangular pulses arxiv:cond-mat/4163v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 4 Jesús Casado-Pascual, José Gómez-Ordóñez, and Manuel Morillo Física Teórica, Universidad
Nonlinear Stochastic Resonance with subthreshold rectangular pulses arxiv:cond-mat/4163v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 15 Jan 4 Jesús Casado-Pascual, José Gómez-Ordóñez, and Manuel Morillo Física Teórica, Universidad
Evidence for structure sensitivity in the high pressure CO NO reaction over Pd(111) and Pd(100)
 Evidence for structure sensitivity in the high pressure CO NO reaction over Pd(111) and Pd(100) Scott M. Vesecky, Peijun Chen, Xueping Xu, and D. Wayne Goodman a) Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University,
Evidence for structure sensitivity in the high pressure CO NO reaction over Pd(111) and Pd(100) Scott M. Vesecky, Peijun Chen, Xueping Xu, and D. Wayne Goodman a) Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University,
arxiv: v1 [nlin.cd] 22 Aug 2016
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.cd] 22 Aug 2016 arxiv: v1 [nlin.cd] 22 Aug 2016](/thumbs/90/103054586.jpg) The Two Dynamical States of a Driven Underdamped Classical Pendulum: An Analog Simulation Experiment Ivan Skhem Sawkmie and Mangal C. Mahato Department of Physics, North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong-793022,
The Two Dynamical States of a Driven Underdamped Classical Pendulum: An Analog Simulation Experiment Ivan Skhem Sawkmie and Mangal C. Mahato Department of Physics, North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong-793022,
Problem Set Number 2, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
 Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
= F ( x; µ) (1) where x is a 2-dimensional vector, µ is a parameter, and F :
 1 Bifurcations Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 A bifurcation is a qualitative change
1 Bifurcations Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 A bifurcation is a qualitative change
On the mystery of differential negative resistance
 On the mystery of differential negative resistance Sebastian Popescu, Erzilia Lozneanu and Mircea Sanduloviciu Department of Plasma Physics Complexity Science Group Al. I. Cuza University 6600 Iasi, Romania
On the mystery of differential negative resistance Sebastian Popescu, Erzilia Lozneanu and Mircea Sanduloviciu Department of Plasma Physics Complexity Science Group Al. I. Cuza University 6600 Iasi, Romania
HSND-2015, IPR. Department of Physics, University of Burdwan, Burdwan, West Bengal.
 New kind of deaths: Oscillation Death and Chimera Death HSND-2015, IPR Dr. Tanmoy Banerjee Department of Physics, University of Burdwan, Burdwan, West Bengal. Points to be discussed Oscillation suppression
New kind of deaths: Oscillation Death and Chimera Death HSND-2015, IPR Dr. Tanmoy Banerjee Department of Physics, University of Burdwan, Burdwan, West Bengal. Points to be discussed Oscillation suppression
Bifurcations and global stability of synchronized stationary states in the Kuramoto model for oscillator populations
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 16218 Bifurcations and global stability of synchronized stationary states in the Kuramoto model for oscillator populations J. A. Acebrón, 1,2, * A. Perales, 3 and R. Spigler
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 16218 Bifurcations and global stability of synchronized stationary states in the Kuramoto model for oscillator populations J. A. Acebrón, 1,2, * A. Perales, 3 and R. Spigler
Effect of common noise on phase synchronization in coupled chaotic oscillators
 CHAOS 17, 013105 2007 Effect of common noise on phase synchronization in coupled chaotic oscillators Kwangho Park Department of Electrical Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona 85287 Ying-Cheng
CHAOS 17, 013105 2007 Effect of common noise on phase synchronization in coupled chaotic oscillators Kwangho Park Department of Electrical Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona 85287 Ying-Cheng
Effects of thermal noise on transport in soliton ratchet systems
 Effects of thermal noise on transport in soliton ratchet systems With L. Morales, V. Stehr, P. Müller (Bayreuth) A. Sanchez (Madrid), N.R. Quintero (Sevilla) A.R. Bishop (Los Alamos) J. Buceta, K. Lindenberg
Effects of thermal noise on transport in soliton ratchet systems With L. Morales, V. Stehr, P. Müller (Bayreuth) A. Sanchez (Madrid), N.R. Quintero (Sevilla) A.R. Bishop (Los Alamos) J. Buceta, K. Lindenberg
arxiv: v1 [nlin.ps] 21 Sep 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.ps] 21 Sep 2008 arxiv: v1 [nlin.ps] 21 Sep 2008](/thumbs/94/122087967.jpg) Stochastic Resonance in the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam Chain George Miloshevich, Ramaz Khomeriki,, Stefano Ruffo () Physics Department, Tbilisi State University, 8 Tbilisi (Georgia) () Max-Planck-Institut fur Physik
Stochastic Resonance in the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam Chain George Miloshevich, Ramaz Khomeriki,, Stefano Ruffo () Physics Department, Tbilisi State University, 8 Tbilisi (Georgia) () Max-Planck-Institut fur Physik
Modelling Research Group
 Modelling Research Group The Importance of Noise in Dynamical Systems E. Staunton, P.T. Piiroinen November 20, 2015 Eoghan Staunton Modelling Research Group 2015 1 / 12 Introduction Historically mathematicians
Modelling Research Group The Importance of Noise in Dynamical Systems E. Staunton, P.T. Piiroinen November 20, 2015 Eoghan Staunton Modelling Research Group 2015 1 / 12 Introduction Historically mathematicians
Stochastic resonance in a monostable system driven by square-wave signal and dichotomous noise
 Stochastic resonance in a monostable system driven by square-wave signal and dichotomous noise Guo Feng( 郭锋 ) a), Luo Xiang-Dong( 罗向东 ) a), Li Shao-Fu( 李少甫 ) a), and Zhou Yu-Rong( 周玉荣 ) b) a) School of
Stochastic resonance in a monostable system driven by square-wave signal and dichotomous noise Guo Feng( 郭锋 ) a), Luo Xiang-Dong( 罗向东 ) a), Li Shao-Fu( 李少甫 ) a), and Zhou Yu-Rong( 周玉荣 ) b) a) School of
2 Department of Physics, Saratov State University, Astrahanskaya 83, Saratov, Russia
 Experimental Studies Of The Non-Adiabatic Escape Problem M. Arrayas 1, I.A. Khovanov 2, D.G. Luchinsky 1, R. Mannella 3, P.V.E. McClintock 1, M. Greenall 1, H. Sabbagh 4 1 Department of Physics, Lancaster
Experimental Studies Of The Non-Adiabatic Escape Problem M. Arrayas 1, I.A. Khovanov 2, D.G. Luchinsky 1, R. Mannella 3, P.V.E. McClintock 1, M. Greenall 1, H. Sabbagh 4 1 Department of Physics, Lancaster
Time Delay Induced Stochastic Resonance in One Species Competition Ecosystem without a Periodic Signal
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 57 (2012) 619 623 Vol. 57, No. 4, April 15, 2012 Time Delay Induced Stochastic Resonance in One Species Competition Ecosystem without a Periodic Signal WANG Xiu-Hua ( ), 1 BAI Li (Ü
Commun. Theor. Phys. 57 (2012) 619 623 Vol. 57, No. 4, April 15, 2012 Time Delay Induced Stochastic Resonance in One Species Competition Ecosystem without a Periodic Signal WANG Xiu-Hua ( ), 1 BAI Li (Ü
Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014
![Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014 Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014](/thumbs/73/69324282.jpg) Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise Denis S. Goldobin arxiv:148.135v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 214 Department of Physics, University of Potsdam, Postfach 61553, D-14415 Potsdam,
Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise Denis S. Goldobin arxiv:148.135v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 214 Department of Physics, University of Potsdam, Postfach 61553, D-14415 Potsdam,
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator
 Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
Signal amplification in NbN superconducting resonators via stochastic resonance
 Physics Letters A 370 (2007) 449 453 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Signal amplification in NbN superconducting resonators via stochastic resonance Baleegh Abdo, Eran Segev, Oleg Shtempluck, Eyal Buks Microelectronics
Physics Letters A 370 (2007) 449 453 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Signal amplification in NbN superconducting resonators via stochastic resonance Baleegh Abdo, Eran Segev, Oleg Shtempluck, Eyal Buks Microelectronics
Simple approach to the creation of a strange nonchaotic attractor in any chaotic system
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 59, NUMBER 5 MAY 1999 Simple approach to the creation of a strange nonchaotic attractor in any chaotic system J. W. Shuai 1, * and K. W. Wong 2, 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 59, NUMBER 5 MAY 1999 Simple approach to the creation of a strange nonchaotic attractor in any chaotic system J. W. Shuai 1, * and K. W. Wong 2, 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Effect of various periodic forces on Duffing oscillator
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 351 356 Effect of various periodic forces on Duffing oscillator V RAVICHANDRAN 1, V CHINNATHAMBI 1, and S RAJASEKAR
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 351 356 Effect of various periodic forces on Duffing oscillator V RAVICHANDRAN 1, V CHINNATHAMBI 1, and S RAJASEKAR
Nonlinear systems, chaos and control in Engineering
 Nonlinear systems, chaos and control in Engineering Module 1 block 3 One-dimensional nonlinear systems Cristina Masoller Cristina.masoller@upc.edu http://www.fisica.edu.uy/~cris/ Schedule Flows on the
Nonlinear systems, chaos and control in Engineering Module 1 block 3 One-dimensional nonlinear systems Cristina Masoller Cristina.masoller@upc.edu http://www.fisica.edu.uy/~cris/ Schedule Flows on the
Simple Explanation of Fermi Arcs in Cuprate Pseudogaps: A Motional Narrowing Phenomenon
 Simple Explanation of Fermi Arcs in Cuprate Pseudogaps: A Motional Narrowing Phenomenon ABSTRACT: ARPES measurements on underdoped cuprates above the superconducting transition temperature exhibit the
Simple Explanation of Fermi Arcs in Cuprate Pseudogaps: A Motional Narrowing Phenomenon ABSTRACT: ARPES measurements on underdoped cuprates above the superconducting transition temperature exhibit the
Coherence of Noisy Oscillators with Delayed Feedback Inducing Multistability
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Coherence of Noisy Oscillators with Delayed Feedback Inducing Multistability To cite this article: Anastasiya V Pimenova and Denis S Goldobin 2016
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Coherence of Noisy Oscillators with Delayed Feedback Inducing Multistability To cite this article: Anastasiya V Pimenova and Denis S Goldobin 2016
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS. Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations
 TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
Problem Set Number 02, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2018)
 Problem Set Number 0, 18.385j/.036j MIT (Fall 018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room -337, Cambridge, MA 0139) September 6, 018 Due October 4, 018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math. Problem Set
Problem Set Number 0, 18.385j/.036j MIT (Fall 018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room -337, Cambridge, MA 0139) September 6, 018 Due October 4, 018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math. Problem Set
Networks in systems biology
 Networks in systems biology Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson) Networks in systems
Networks in systems biology Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson) Networks in systems
Atomic-Scale Friction in Xe/Ag and N2/Pb ]
![Atomic-Scale Friction in Xe/Ag and N2/Pb ] Atomic-Scale Friction in Xe/Ag and N2/Pb ]](/thumbs/74/70046007.jpg) Intermitional Journal of Thermophysics, Vol. 19, No. 3, 1998 Atomic-Scale Friction in Xe/Ag and N2/Pb ] A. Dayo2 and J. Krim3, 4 Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and electrical resistivity measurements
Intermitional Journal of Thermophysics, Vol. 19, No. 3, 1998 Atomic-Scale Friction in Xe/Ag and N2/Pb ] A. Dayo2 and J. Krim3, 4 Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and electrical resistivity measurements
Self-induced stochastic resonance in excitable systems
 Physica D 210 (2005) 227 240 Self-induced stochastic resonance in excitable systems Cyrill B. Muratov a,, Eric Vanden-Eijnden b, Weinan E c a Department of Mathematical Sciences, New Jersey Institute of
Physica D 210 (2005) 227 240 Self-induced stochastic resonance in excitable systems Cyrill B. Muratov a,, Eric Vanden-Eijnden b, Weinan E c a Department of Mathematical Sciences, New Jersey Institute of
arxiv:q-bio/ v1 [q-bio.sc] 11 Jan 2006
![arxiv:q-bio/ v1 [q-bio.sc] 11 Jan 2006 arxiv:q-bio/ v1 [q-bio.sc] 11 Jan 2006](/thumbs/89/98614469.jpg) arxiv:q-bio/0601013v1 [q-bio.sc] 11 Jan 2006 Effect of channel block on the spiking activity of excitable membranes in a stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley model G. Schmid, I. Goychuk and P. Hänggi Institut für
arxiv:q-bio/0601013v1 [q-bio.sc] 11 Jan 2006 Effect of channel block on the spiking activity of excitable membranes in a stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley model G. Schmid, I. Goychuk and P. Hänggi Institut für
Spatiotemporal multiple coherence resonances and calcium waves in a coupled hepatocyte system
 Vol 18 No 3, March 2009 c 2009 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2009/18(03)/0872-09 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Spatiotemporal multiple coherence resonances and calcium waves in a coupled hepatocyte
Vol 18 No 3, March 2009 c 2009 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2009/18(03)/0872-09 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Spatiotemporal multiple coherence resonances and calcium waves in a coupled hepatocyte
Genetic transcriptional regulatory model driven by the time-correlated noises
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 40, no. 3, September, 010 95 Genetic transcriptional regulatory model driven by the time-correlated noises Xiao-miao Zhang, Bao-quan Ai, and Jian-wen Xiong Laboratory
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 40, no. 3, September, 010 95 Genetic transcriptional regulatory model driven by the time-correlated noises Xiao-miao Zhang, Bao-quan Ai, and Jian-wen Xiong Laboratory
Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber
 Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber J.C. Ji, N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box, Broadway,
Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber J.C. Ji, N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box, Broadway,
Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator
 Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator This paper has been published in Journal of Sound and Vibration vol. 5 issue - 8 pp.-. J.C. Ji N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering University
Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator This paper has been published in Journal of Sound and Vibration vol. 5 issue - 8 pp.-. J.C. Ji N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering University
ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 121 133, 2009 ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING M. Aleshams Department of Electrical and Computer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 121 133, 2009 ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING M. Aleshams Department of Electrical and Computer
Clearly the passage of an eigenvalue through to the positive real half plane leads to a qualitative change in the phase portrait, i.e.
 Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
Aperiodic stochastic resonance and phase synchronization
 Physics Letters A 326 (2004) 391 396 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Aperiodic stochastic resonance and phase synchronization Kwangho Park a, Ying-Cheng Lai a,b,, Zonghua Liu a, Arje Nachman c a Department
Physics Letters A 326 (2004) 391 396 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Aperiodic stochastic resonance and phase synchronization Kwangho Park a, Ying-Cheng Lai a,b,, Zonghua Liu a, Arje Nachman c a Department
Scaling and crossovers in activated escape near a bifurcation point
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 69, 061102 (2004) Scaling and crossovers in activated escape near a bifurcation point D. Ryvkine, M. I. Dykman, and B. Golding Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 69, 061102 (2004) Scaling and crossovers in activated escape near a bifurcation point D. Ryvkine, M. I. Dykman, and B. Golding Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University,
A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations,
 Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Reliability of Bulk Power Systems (cont d)
 Reliability of Bulk Power Systems (cont d) Important requirements of a reliable electric power service Voltage and frequency must be held within close tolerances Synchronous generators must be kept running
Reliability of Bulk Power Systems (cont d) Important requirements of a reliable electric power service Voltage and frequency must be held within close tolerances Synchronous generators must be kept running
Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system
 Vol 17 No 7, July 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(07)/2446-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system Wang Liang( ), Xu Wei( ), and
Vol 17 No 7, July 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(07)/2446-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system Wang Liang( ), Xu Wei( ), and
One Dimensional Dynamical Systems
 16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
arxiv:chao-dyn/ v1 20 May 1994
 TNT 94-4 Stochastic Resonance in Deterministic Chaotic Systems A. Crisanti, M. Falcioni arxiv:chao-dyn/9405012v1 20 May 1994 Dipartimento di Fisica, Università La Sapienza, I-00185 Roma, Italy G. Paladin
TNT 94-4 Stochastic Resonance in Deterministic Chaotic Systems A. Crisanti, M. Falcioni arxiv:chao-dyn/9405012v1 20 May 1994 Dipartimento di Fisica, Università La Sapienza, I-00185 Roma, Italy G. Paladin
Coherence and stochastic resonance in a two-state system
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 6 JUNE 2000 Coherence and stochastic resonance in a two-state system Benjamin Lindner and Lutz Schimansky-Geier Humboldt-University at Berlin, Invalidenstrasse 110,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 6 JUNE 2000 Coherence and stochastic resonance in a two-state system Benjamin Lindner and Lutz Schimansky-Geier Humboldt-University at Berlin, Invalidenstrasse 110,
A Novel Three Dimension Autonomous Chaotic System with a Quadratic Exponential Nonlinear Term
 ETASR - Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol., o.,, 9-5 9 A Novel Three Dimension Autonomous Chaotic System with a Quadratic Exponential Nonlinear Term Fei Yu College of Information Science
ETASR - Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol., o.,, 9-5 9 A Novel Three Dimension Autonomous Chaotic System with a Quadratic Exponential Nonlinear Term Fei Yu College of Information Science
arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 4 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 4 Nov 2009 arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 4 Nov 2009](/thumbs/93/113261052.jpg) One-bit stochastic resonance storage device S. A. Ibáñez 1 P. I. Fierens 1 G. A. Patterson 2 R. P. J. Perazzo 1 D. F. Grosz 1,2,3 November 17, 2018 arxiv:0911.0878v1 [nlin.ao] 4 Nov 2009 Abstract The increasing
One-bit stochastic resonance storage device S. A. Ibáñez 1 P. I. Fierens 1 G. A. Patterson 2 R. P. J. Perazzo 1 D. F. Grosz 1,2,3 November 17, 2018 arxiv:0911.0878v1 [nlin.ao] 4 Nov 2009 Abstract The increasing
Enhancing aperiodic stochastic resonance through noise modulation
 CHAOS VOLUME 8, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1998 Enhancing aperiodic stochastic resonance through noise modulation Carson C. Chow Center for BioDynamics and Department of Mathematics, Boston University, Boston,
CHAOS VOLUME 8, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1998 Enhancing aperiodic stochastic resonance through noise modulation Carson C. Chow Center for BioDynamics and Department of Mathematics, Boston University, Boston,
MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation
 MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation 1 Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions When we were considering one-dimensional systems, we saw that subtle changes in parameter
MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation 1 Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions When we were considering one-dimensional systems, we saw that subtle changes in parameter
Spatial coherence resonance in excitable biochemical media induced by internal noise
 Biophysical Chemistry 128 (2007) 210 214 http://www.elsevier.com/locate/biophyschem Spatial coherence resonance in excitable biochemical media induced by internal noise Marko Gosak, Marko Marhl, Matjaž
Biophysical Chemistry 128 (2007) 210 214 http://www.elsevier.com/locate/biophyschem Spatial coherence resonance in excitable biochemical media induced by internal noise Marko Gosak, Marko Marhl, Matjaž
Neural Excitability in a Subcritical Hopf Oscillator with a Nonlinear Feedback
 Neural Excitability in a Subcritical Hopf Oscillator with a Nonlinear Feedback Gautam C Sethia and Abhijit Sen Institute for Plasma Research, Bhat, Gandhinagar 382 428, INDIA Motivation Neural Excitability
Neural Excitability in a Subcritical Hopf Oscillator with a Nonlinear Feedback Gautam C Sethia and Abhijit Sen Institute for Plasma Research, Bhat, Gandhinagar 382 428, INDIA Motivation Neural Excitability
Phase Locking. 1 of of 10. The PRC's amplitude determines which frequencies a neuron locks to. The PRC's slope determines if locking is stable
 Printed from the Mathematica Help Browser 1 1 of 10 Phase Locking A neuron phase-locks to a periodic input it spikes at a fixed delay [Izhikevich07]. The PRC's amplitude determines which frequencies a
Printed from the Mathematica Help Browser 1 1 of 10 Phase Locking A neuron phase-locks to a periodic input it spikes at a fixed delay [Izhikevich07]. The PRC's amplitude determines which frequencies a
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
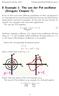 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Gomplex Behavior in Asymmetric Plasma Divided by a Magnetic Filter
 J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol.4 (2001) 60H04 Gomplex Behavior in Asymmetric Plasma Divided by a Magnetic Filter ohi Kazuo, NAITOU Hiroshi*, TAUCHI Yasushi, FUKUMASA Osamu and ITOH Kimitakar Department
J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol.4 (2001) 60H04 Gomplex Behavior in Asymmetric Plasma Divided by a Magnetic Filter ohi Kazuo, NAITOU Hiroshi*, TAUCHI Yasushi, FUKUMASA Osamu and ITOH Kimitakar Department
The correlation between stochastic resonance and the average phase-synchronization time of a bistable system driven by colour-correlated noises
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 19, No. 1 (010) 01050 The correlation between stochastic resonance and the average phase-synchronization time of a bistable system driven by colour-correlated noises Dong Xiao-Juan(
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 19, No. 1 (010) 01050 The correlation between stochastic resonance and the average phase-synchronization time of a bistable system driven by colour-correlated noises Dong Xiao-Juan(
Effect of Non Gaussian Noises on the Stochastic Resonance-Like Phenomenon in Gated Traps. Abstract
 Effect of Non Gaussian Noises on the Stochastic Resonance-Like Phenomenon in Gated Traps Jorge A. Revelli 1 Alejandro D. Sánchez 2, and Horacio S. Wio 1 1) Grupo de Física Estadística Centro Atómico Bariloche
Effect of Non Gaussian Noises on the Stochastic Resonance-Like Phenomenon in Gated Traps Jorge A. Revelli 1 Alejandro D. Sánchez 2, and Horacio S. Wio 1 1) Grupo de Física Estadística Centro Atómico Bariloche
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6. Target waves in the complex Ginzburg-Landau equation
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 2000 Target waves in the complex Ginzburg-Landau equation Matthew Hendrey, Keeyeol Nam, Parvez Guzdar,* and Edward Ott University of Maryland, Institute for
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 2000 Target waves in the complex Ginzburg-Landau equation Matthew Hendrey, Keeyeol Nam, Parvez Guzdar,* and Edward Ott University of Maryland, Institute for
ME 680- Spring Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems
 ME 680- Spring 2014 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems 1 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems Logistic equation: n = rn(1 n) velocity function Equilibria or fied points : initial conditions
ME 680- Spring 2014 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems 1 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems Logistic equation: n = rn(1 n) velocity function Equilibria or fied points : initial conditions
Mathematical Analysis of Bursting Electrical Activity in Nerve and Endocrine Cells
 Mathematical Analysis of Bursting Electrical Activity in Nerve and Endocrine Cells Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University
Mathematical Analysis of Bursting Electrical Activity in Nerve and Endocrine Cells Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University
CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION
 CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 143 CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 6.1 Introduction Based on the previous three experimental chapters dealing
CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 143 CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 6.1 Introduction Based on the previous three experimental chapters dealing
Cubic autocatalytic reaction diffusion equations: semi-analytical solutions
 T&T Proof 01PA003 2 January 2002 10.1098/rspa.2001.0899 Cubic autocatalytic reaction diffusion equations: semi-analytical solutions By T. R. Marchant School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics, The University
T&T Proof 01PA003 2 January 2002 10.1098/rspa.2001.0899 Cubic autocatalytic reaction diffusion equations: semi-analytical solutions By T. R. Marchant School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics, The University
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time. delay
 Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Statistical Properties of a Ring Laser with Injected Signal and Backscattering
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (2001) pp. 87 92 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 1, January 15, 2001 Statistical Properties of a Ring Laser with Injected Signal and Backscattering
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (2001) pp. 87 92 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 1, January 15, 2001 Statistical Properties of a Ring Laser with Injected Signal and Backscattering
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Early version, also known as pre-print
 Erzgraber, H, Krauskopf, B, & Lenstra, D (2004) Compound laser modes of mutually delay-coupled lasers : bifurcation analysis of the locking region Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication
Erzgraber, H, Krauskopf, B, & Lenstra, D (2004) Compound laser modes of mutually delay-coupled lasers : bifurcation analysis of the locking region Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication
Linear and nonlinear approximations for periodically driven bistable systems
 Invited Paper Linear and nonlinear approximations for periodically driven bistable systems Alexander A. Dubkov a, Bernardo Spagnolo b, and Davide Valenti b a Radiophysics Department, Nizhni Novgorod State
Invited Paper Linear and nonlinear approximations for periodically driven bistable systems Alexander A. Dubkov a, Bernardo Spagnolo b, and Davide Valenti b a Radiophysics Department, Nizhni Novgorod State
The influence of noise on two- and three-frequency quasi-periodicity in a simple model system
 arxiv:1712.06011v1 [nlin.cd] 16 Dec 2017 The influence of noise on two- and three-frequency quasi-periodicity in a simple model system A.P. Kuznetsov, S.P. Kuznetsov and Yu.V. Sedova December 19, 2017
arxiv:1712.06011v1 [nlin.cd] 16 Dec 2017 The influence of noise on two- and three-frequency quasi-periodicity in a simple model system A.P. Kuznetsov, S.P. Kuznetsov and Yu.V. Sedova December 19, 2017
arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017](/thumbs/74/70757831.jpg) Feature-rich bifurcations in a simple electronic circuit Debdipta Goswami 1, and Subhankar Ray 2, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
Feature-rich bifurcations in a simple electronic circuit Debdipta Goswami 1, and Subhankar Ray 2, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
Oscillatory Turing Patterns in a Simple Reaction-Diffusion System
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 50, No. 1, January 2007, pp. 234 238 Oscillatory Turing Patterns in a Simple Reaction-Diffusion System Ruey-Tarng Liu and Sy-Sang Liaw Department of Physics,
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 50, No. 1, January 2007, pp. 234 238 Oscillatory Turing Patterns in a Simple Reaction-Diffusion System Ruey-Tarng Liu and Sy-Sang Liaw Department of Physics,
Effects of Atomic Coherence and Injected Classical Field on Chaotic Dynamics of Non-degenerate Cascade Two-Photon Lasers
 Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing China) 48 2007) pp. 288 294 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 48 No. 2 August 15 2007 Effects of Atomic Coherence and Injected Classical Field on Chaotic Dynamics of
Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing China) 48 2007) pp. 288 294 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 48 No. 2 August 15 2007 Effects of Atomic Coherence and Injected Classical Field on Chaotic Dynamics of
Time-periodic forcing of Turing patterns in the Brusselator model
 Time-periodic forcing of Turing patterns in the Brusselator model B. Peña and C. Pérez García Instituto de Física. Universidad de Navarra, Irunlarrea, 1. 31008-Pamplona, Spain Abstract Experiments on temporal
Time-periodic forcing of Turing patterns in the Brusselator model B. Peña and C. Pérez García Instituto de Física. Universidad de Navarra, Irunlarrea, 1. 31008-Pamplona, Spain Abstract Experiments on temporal
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Phase-Locked Loop? The phase-locked loop (PLL) is an electronic system which has numerous important applications. It consists of three elements forming a feedback loop:
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Phase-Locked Loop? The phase-locked loop (PLL) is an electronic system which has numerous important applications. It consists of three elements forming a feedback loop:
Signal Modeling, Statistical Inference and Data Mining in Astrophysics
 ASTRONOMY 6523 Spring 2013 Signal Modeling, Statistical Inference and Data Mining in Astrophysics Course Approach The philosophy of the course reflects that of the instructor, who takes a dualistic view
ASTRONOMY 6523 Spring 2013 Signal Modeling, Statistical Inference and Data Mining in Astrophysics Course Approach The philosophy of the course reflects that of the instructor, who takes a dualistic view
Lecture 12: Transcritical flow over an obstacle
 Lecture 12: Transcritical flow over an obstacle Lecturer: Roger Grimshaw. Write-up: Erinna Chen June 22, 2009 1 Introduction The flow of a fluid over an obstacle is a classical and fundamental problem
Lecture 12: Transcritical flow over an obstacle Lecturer: Roger Grimshaw. Write-up: Erinna Chen June 22, 2009 1 Introduction The flow of a fluid over an obstacle is a classical and fundamental problem
8 Ecosystem stability
 8 Ecosystem stability References: May [47], Strogatz [48]. In these lectures we consider models of populations, with an emphasis on the conditions for stability and instability. 8.1 Dynamics of a single
8 Ecosystem stability References: May [47], Strogatz [48]. In these lectures we consider models of populations, with an emphasis on the conditions for stability and instability. 8.1 Dynamics of a single
Active Vibration Control for A Bilinear System with Nonlinear Velocity Time-delayed Feedback
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol III, WCE, July - 5,, London, U.K. Active Vibration Control for A Bilinear System with Nonlinear Velocity Time-delayed Feedback X. Gao, Q. Chen Abstract
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol III, WCE, July - 5,, London, U.K. Active Vibration Control for A Bilinear System with Nonlinear Velocity Time-delayed Feedback X. Gao, Q. Chen Abstract
Phase Desynchronization as a Mechanism for Transitions to High-Dimensional Chaos
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (2001) pp. 682 688 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 6, June 15, 2001 Phase Desynchronization as a Mechanism for Transitions to High-Dimensional
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (2001) pp. 682 688 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 6, June 15, 2001 Phase Desynchronization as a Mechanism for Transitions to High-Dimensional
Lecture 5. Outline: Limit Cycles. Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles. Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps
 Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps Limit
Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps Limit
Phase Synchronization of Coupled Rossler Oscillators: Amplitude Effect
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 47 (2007) pp. 265 269 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 47, No. 2, February 15, 2007 Phase Synchronization of Coupled Rossler Oscillators: Amplitude Effect
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 47 (2007) pp. 265 269 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 47, No. 2, February 15, 2007 Phase Synchronization of Coupled Rossler Oscillators: Amplitude Effect
On the Dynamics of Delayed Neural Feedback Loops. Sebastian Brandt Department of Physics, Washington University in St. Louis
 On the Dynamics of Delayed Neural Feedback Loops Sebastian Brandt Department of Physics, Washington University in St. Louis Overview of Dissertation Chapter 2: S. F. Brandt, A. Pelster, and R. Wessel,
On the Dynamics of Delayed Neural Feedback Loops Sebastian Brandt Department of Physics, Washington University in St. Louis Overview of Dissertation Chapter 2: S. F. Brandt, A. Pelster, and R. Wessel,
Semi-analytical solutions for cubic autocatalytic reaction-diffusion equations; the effect of a precursor chemical
 ANZIAM J. 53 (EMAC211) pp.c511 C524, 212 C511 Semi-analytical solutions for cubic autocatalytic reaction-diffusion equations; the effect of a precursor chemical M. R. Alharthi 1 T. R. Marchant 2 M. I.
ANZIAM J. 53 (EMAC211) pp.c511 C524, 212 C511 Semi-analytical solutions for cubic autocatalytic reaction-diffusion equations; the effect of a precursor chemical M. R. Alharthi 1 T. R. Marchant 2 M. I.
Monte Carlo simulation of thin-film growth on a surface with a triangular lattice
 Vacuum 52 (1999) 435 440 Monte Carlo simulation of thin-film growth on a surface with a triangular lattice Wei Helin*, Liu Zuli, Yao Kailun Department of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,
Vacuum 52 (1999) 435 440 Monte Carlo simulation of thin-film growth on a surface with a triangular lattice Wei Helin*, Liu Zuli, Yao Kailun Department of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,
Analysis of Stochastic Resonance Phenomenon in Wind Induced Vibration of a Girder POSPÍŠIL Stanislav 1,a and NÁPRSTEK Jiří 1,b
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2014-08-18 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 617, pp 285-290 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.617.285 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Analysis of Stochastic Resonance
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2014-08-18 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 617, pp 285-290 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.617.285 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Analysis of Stochastic Resonance
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
Scaling of noisy fluctuations in complex networks and applications to network prediction
 Scaling of noisy fluctuations in complex networks and applications to network prediction Wen-Xu Wang, Qingfei Chen, Liang Huang, Ying-Cheng Lai,,2 and Mary Ann F. Harrison 3 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Scaling of noisy fluctuations in complex networks and applications to network prediction Wen-Xu Wang, Qingfei Chen, Liang Huang, Ying-Cheng Lai,,2 and Mary Ann F. Harrison 3 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Complex Patterns in a Simple System
 Complex Patterns in a Simple System arxiv:patt-sol/9304003v1 17 Apr 1993 John E. Pearson Center for Nonlinear Studies Los Alamos National Laboratory February 4, 2008 Abstract Numerical simulations of a
Complex Patterns in a Simple System arxiv:patt-sol/9304003v1 17 Apr 1993 John E. Pearson Center for Nonlinear Studies Los Alamos National Laboratory February 4, 2008 Abstract Numerical simulations of a
Biophysical Journal Volume 92 May
 Biophysical Journal Volume 92 May 2007 3407 3424 3407 Dynamics of a Minimal Model of Interlocked Positive and Negative Feedback Loops of Transcriptional Regulation by camp-response Element Binding Proteins
Biophysical Journal Volume 92 May 2007 3407 3424 3407 Dynamics of a Minimal Model of Interlocked Positive and Negative Feedback Loops of Transcriptional Regulation by camp-response Element Binding Proteins
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations
 7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
WEAK SIGNAL DETECTION BASED ON TWO DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC RESONANCE. Leonardo Barbini, Matthew O. T. Cole, Andrew J. Hillis, Jonathan L.
 WEAK SIGNAL DETECTION BASED ON TWO DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC RESONANCE Leonardo Barbini, Matthew O. T. Cole, Andrew J. Hillis, Jonathan L. du Bois University of Bath Department of Mechanical Engineering Claverton
WEAK SIGNAL DETECTION BASED ON TWO DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC RESONANCE Leonardo Barbini, Matthew O. T. Cole, Andrew J. Hillis, Jonathan L. du Bois University of Bath Department of Mechanical Engineering Claverton
CHAPTER 6 HOPF-BIFURCATION IN A TWO DIMENSIONAL NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 CHAPTER 6 HOPF-BIFURCATION IN A TWO DIMENSIONAL NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION [Discussion on this chapter is based on our paper entitled Hopf-Bifurcation Ina Two Dimensional Nonlinear Differential Equation,
CHAPTER 6 HOPF-BIFURCATION IN A TWO DIMENSIONAL NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION [Discussion on this chapter is based on our paper entitled Hopf-Bifurcation Ina Two Dimensional Nonlinear Differential Equation,
Maps, electron-clouds in RHIC and first-order phase-transitions
 C-A/AP/#197 April 005 Maps, electron-clouds in RHIC and first-order phase-transitions P. Thieberger, U. Iriso and S. Peggs Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory Upton, NY 11973
C-A/AP/#197 April 005 Maps, electron-clouds in RHIC and first-order phase-transitions P. Thieberger, U. Iriso and S. Peggs Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory Upton, NY 11973
Krauskopf, B., Erzgraber, H., & Lenstra, D. (2006). Dynamics of semiconductor lasers with filtered optical feedback.
 Krauskopf, B, Erzgraber, H, & Lenstra, D (26) Dynamics of semiconductor lasers with filtered optical feedback Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in Explore Bristol Research
Krauskopf, B, Erzgraber, H, & Lenstra, D (26) Dynamics of semiconductor lasers with filtered optical feedback Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in Explore Bristol Research
DYNAMICS OF THREE COUPLED VAN DER POL OSCILLATORS WITH APPLICATION TO CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS
 Proceedings of IDETC/CIE 2005 ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference September 24-28, 2005, Long Beach, California USA DETC2005-84017
Proceedings of IDETC/CIE 2005 ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference September 24-28, 2005, Long Beach, California USA DETC2005-84017
Problem Sheet 1.1 First order linear equations;
 Problem Sheet 1 First order linear equations; In each of Problems 1 through 8 find the solution of the given initial value problem 5 6 7 8 In each of Problems 9 and 10: (a) Let be the value of for which
Problem Sheet 1 First order linear equations; In each of Problems 1 through 8 find the solution of the given initial value problem 5 6 7 8 In each of Problems 9 and 10: (a) Let be the value of for which
