Jamming by compressing a system of granular crosses
|
|
|
- Maude Farmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jamming by compressing a system of granular crosses Hu Zheng, Dong Wang, Jonathan Barés, Robert Behringer To cite this version: Hu Zheng, Dong Wang, Jonathan Barés, Robert Behringer. Jamming by compressing a system of granular crosses. Powders and Grains 2017, Jul 2017, Montpellier, France. Powders and Grains 2017 proceedings. < <hal > HAL Id: hal Submitted on 31 Mar 2017 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access archive for the deposit and dissemination of scientific research documents, whether they are published or not. The documents may come from teaching and research institutions in France or abroad, or from public or private research centers. L archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des établissements d enseignement et de recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires publics ou privés.
2 Jamming by compressing a system of granular crosses Hu Zheng 1,2, Dong Wang 2, Jonathan Barés 2,3, Robert Behringer 2, 1 School of Earth Science and Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing , China; 2 Department of Physics, Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA 3 Laboratoire de Mécanique et de Génie Civil de Montpellier, Université de Montpellier, France. Abstract. A disordered stress-free granular packing can be jammed, transformed into a mechanically rigid structure, by increasing the density of particles or by applying shear deformation. The jamming behavior of systems made of 2D circular discs has been investigated in detail, but very little is known about jamming for non-spherical particles, and particularly, non-convex particles. Here, we perform an experimental study on jamming by compression of a system of quasi-2d granular crosses made of photo-elastic crosses. We measure the pressure evolution during cyclic compression and decompression. The Jamming packing fraction of these quasi-2d granular crosses is φ J 0.475, which is much smaller than the value φ J 0.84 for-2d granular disks. The packing fraction shifts systematically to higher values under compressive cycling, corresponding to systematic shifts in the stress-strain response curves. Associated with these shifts are rotations of the crosses, with minimal changes in their centers of mass. 1 Introduction Granular materials can be easily found in nature and in industrial applications. They have gas-like, liquid-like or solid-like properties depending on their density or shear stress [1 4]. Many industrial devices exploit these state properties, and a number of geo-hazards involve uncontrolled state changes. For example, in controlled flow in an industrial process, such as in a hopper, gas-like or liquidlike states are desirable [5]. On the other hand, most geo-hazards, like landslide or debris flow occur when a jammed solid state transitions to a liquid-like state [6, 7]. Hence, it is very important to understand the granular phase properties, and the transitions between fluid and solid, i.e. unjammed or jammed, states. Characterizing the jamming transition in disordered granular systems has attracted significant interest [2, 8 12]. Liu and Nagel [8] hypothesized a zero temperature jamming phase diagram. In a space of shear stress, τ and packing fraction, φ, they proposed jammed states for τ < τ Y (φ), where the yield stress curve, τ Y (φ), is a monotonically increasing curve that intersects the φ axis at φ J. This proposal was substantiated by O Hern et al. using numerical simulations of frictionless discs. These studies used protocols that produced macroscopically isotropic states. Recently, Bi et al. [2] showed that for frictional disks, jammed states occur below the frictionless isotropic φ J. They used a protocol consisting of shear strain applied hz64@phy.duke.edu dw148@phy.edu.ed jb@jonathan-bares.eu bob@phy.duke.edu to an initially unjammed (stress-free) isotropic state. In a range φ S < φ < φ J, they found that increasing shear strain led from unjammed states to fragile and then robustly shear jammed states, where the last two states are characterized by non-zero shear stress. The isotropic jamming point of a two dimensional frictionless disc granular system is φ 0.84 [9, 13]. However, most of the experiments and simulations of jamming have focused on simple geometry particles like discs and spheres or at least on convex particles. Hence the focus of the present experiments is on non-convex crossshaped particles. Role of particle shape has been recognized as significant in controlling the microstucture of various granular materials [1, 14 16]. For instance, Athanassidis et al. [17] have shown that the macroscopic mechanical properties of a granular material can be controlled by tuning the grain shape via a 3D printing approach to make different shape particles including tetrahedra, octahedra, and dodecahedra[17]. And several authors have shown that 3D systems of rods [18] or of non-convex particles, such as staples, or star-shaped particles have interlocking or entangled states that are mechanically stable [19 21]. For instance, star-shaped non-convex particles, i.e. hexapods are interesting to both granular science and architecture design. These particles form stable granular aggregates by pouring [22]. Zhao et al. [21] conducted laboratory experiments to show the stability and structure of poured hexapod packings by varying the arm length and coefficient of friction between particles. However, experimental methods generally cannot detect the internal details of such packings, or the forces between particles, which
3 (b) 3 camera motor 3 6 UV light 9 polarizer UV light photoelastic particles Plexiglas table Unit: mm (d) polarizer LED light Figure 1. : Sketch of cross particle geometry. (b): Photoelastic response generated by compressing a cross particle along each arm. : Schematic of uniaxial compression, using the biaxial apparatus. (d): Sketch of biaxial compression. The gravity direction is given by g. are important for understanding their mechanical properties. The photo-elastic method, used here, is an effective experimental technique to study 2D granular materials [10, 23 26] because it provides access to the forces, and hence local pressure on each particle. We combine this technique with direct visualiation of particle displacements and rotations. The latter is particulary important for crosses as they gradually evolve to lower stress states at a given φ under cyclic compression/decompression. We apply strain with a bi-axial apparatus [2, 27] which allows controlled strains in two directions, as in Fig. 1 and (d). 2 Experimental techniques and protocols Figure 2. Experimental apparatus and typical experimental image data. : Schematic of the experimental apparatus, side view. Light from an LED source passes through a first circular polarizer, then through the transparent base of the apparatus and the particles. A stepper motor rotates a polarizer into or out of the line of sight of the camera, yielding polarized or non-polarized images. (b): Image with only UV light from above. Fluorescent bars on the arms yield the cross orientation. : Image with normal light and without the second polarizer. These images are used to detect particle positions. (d): Polarized image used to measure the pressure inside of the each particle. fringe patterns, as typified by Fig. 1 (b). In particular, the concentrated intensity variation close to a contact point gives a measure of the force at a contact, and helps determine the existence of contacts. The density of fringes corresponds to the magnitude of the force: the more fringes, the bigger the force. Fig. 1 (b) shows a photo-elastic image of a cross particle subjected to compression in all four directions, as indicated by the arrows. We use the G2 method [23] as measure of the fringe density, and hence of the forces acting on a particle. The G2 value is defined as the pixel-wise intensity gradient in the photo-elastic digital image. Moreover, the actual contact force can also be calculated in principle based on a complex fringe patternfitting algorithm pioneered by Majmudar [27]. In this paper, we only use G2 as a measure of the pressure of each particle, which has been demonstrated to be a one-to-one function of pressure at the particle scale [28]. 2.1 Experimental techniques 2.2 Experimental apparatus Specifically, the experiments are conducted using photoelastic crosses in a two dimensional bi-axial apparatus. We cyclically compress this system through the isotropic jamming point, and then decompress the system to the original boundary configuration. The geometry of the crosses, cut out of a 6.35mm thick photo-elastic sheet by water-jet cutting, is shown in Fig. 1. The length of each arm is 18cm, from the center of cross to the edge. The end of each arm is a semicircle and the corner between two neighbor arms is arc-shaped to avoid force concentration. The radii of the semicircle and arc is 3cm. The friction coefficient between crosses is 0.7. The particle photo-elastic property allows us to measure the forces acting on them via digital images of the The experimental apparatus performed bi-axial and uniaxial compression. An illustration of the system is shown in Fig 2. The photo-elastic cross particles are placed on a transparent Plexiglas table in a horizontal plane, such that gravity plays no role in the granular behavior, other than through weak friction with the base (0.36 ± 0.04). Four UV tube lights illuminate the UV-fluorescent ink on the top of each cross (Fig. 2 (b)), allowing us to track the position and orientation of each cross. An LED array provides homogeneous light from below. A circular polarizer sheet on the top of the LED array polarizes the light. A second crossed polarizer is rotated into or out of position in front of a camera, providing normal and polarized images (Fig. 2 and (d)). The camera (Canon R 70D)
4 23.5 has a resolution of pixels, corresponding to 31, 000 pix2 per cross. AvrG2 [AU] We compressed the system quasi-statically in steps of 1mm. After each step, we obtained three images, one with only UV light, one polarized and a normal image with light from the LED array. The initial size of the shear box was cm crosses were placed in the shear box. Before compressing the system, we ensured that there was no initial stress in the system, which meant that no fringes were visible in the polarized image of the initial state. Unicompress Bicompress (b) 18 2 AvrG [AU] 2.3 Protocol Nc Results and discussion We focus on the jamming transition where we contrast system properties that were achieved by compressing either uniaxially or isotropically, i.e. biaxially. Below, we distinguish these two protocols by unicompression or bicompression. For these two protocols, we determined the contact number, the force chain network, and the system pressure, and used these properties to characterize the jamming transition. The system pressure (G2 ) evolution as a function of the packing fraction for multiple compression cycles is shown in Fig. 3. The blue line corresponds to unicompression and the red one to bicompression. The green region indicates the transition area of the granular crosses from an unjammed to a jammed state. Manifestly, the jamming point is not a unique function of packing fraction, and it also depends on the compression protocol. The difference between unicompression and bicompression can be seen from the inset images in Fig. 3. The force chain network generated by unicompressing is more anisotropic than the Figure 4. : Maximum G2 at the highest packing fraction of each compression circle. Note that the maximum compressions and vertical scales are different for the two compression protocols. The maximum G2 decays with Nc, the number of compression cycles for both experimental methods. Alternatively, this can be seen as an increase in φ J as a function of Nc. (b): Photo-elastic image when the system firstly reached the maximum packing fraction, φmax = 48%. : Photo-elastic image at the maximum packing fraction after 43 shearing cycles. The white bar in (b) indicates 10cm. (b) and share the same scale. bicompression case, reflecting the more anisotropic character of unicompression. The difficulty of rearrangement in the cross packing also caused a relative fast G2 development by unicompressing with a slope of about 7.8. For the bicompression system, the slope of G2 is about 7.2, and the system evolution is smoother. The crosses move little during cyclic compression, G2 decays over multiple cycles, as seen in 2D disc system [13] and in simulations of frictionless spheres [? ]. However, G2 appears to reach a plateau, within moderate fluctuations, for large enough Nc for bicompression, although not necessarily for unicompressions. Fig. 4 (b) and show the force chain networks at the packing fraction, φ = 48%. The photo-elastic response at cycle 43 is slightly weaker than after the first cycle. Figure 3. System pressure, expressed by G2 in arbitrary units, vs. compressive strain for multiple cycles. Insets: Image indicated by red arrow is a photo-elastic image at the jamming point for unicompressing while the one indicated by blue arrow is for bicompression. The force chain networks of the two images indicate that a more isotropic network occurs for the bicompression case. The green area shows the jamming transition zone. We compared the position and orientation of each cross in the unicompression system, as shown in Fig. 5, to see that the position of each particle changes very little, even after 43 compression cycles; consequently, the coarse-grain density also changes little over the 43 cycles. However, the particle orientations change substantially. It is reasonable to conclude that the pressure decay at the maximum packing fraction is strongly correlated with changes in the particle orientations.
5 Figure 5. Positions and orientations of the crosses for unicompression initially (red crosses) and after 43 compression cycles (green crosses). 4 Conclusion We have experimentally investigated the jamming transition of a packing formed from 2D photoelastic crosses subject to multiple cycles of compression that is either uniaxial or biaxial. The jamming point of this system is between 47.5% and 48.0%, and the specific jamming density is sensitive to details of the compression protocol, including the cycle number and whether the compression is unixial of biaxial. The rate of increase of G 2 with φ is higher for unicompression than for bicompression. Several measures are sensitive to the cycle number, including the jamming point and the pressure at a given packing fraction two properties that are correlated. There is little change in the positions of individual particles, but there is significant rotation of crosses during the course of multiple cycles, and this rotation provides a mechanism for stress relaxation. Acknowledgements and References This work is supported by NSF Grant No.DMR , NASA Grant No. NNX15AD38G, the W.M. Keck Foundation and a RT-MRSEC fellowship. HZ thanks NSFC Grant No and the NSF(Jiangsu, China) Grant No. BK for financial support. References [1] H.M. Jaeger, S.R. Nagel, R.P. Behringer, Reviews of Modern Physics 68, 1259 (1996) [2] D. Bi, J. Zhang, B. Chakraborty, R.P. Behringer, Nature 480, 355 (2011) [3] M. van Hecke, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 22, (2010) [4] Alexander O.N. Siemens, Martin van Hecke, Physica A 389, 4255 (2010) [5] J. Tang, R.P. Behringer, Europhysics Letters 114, (2016) [6] G.Q. Chen, R.Q. Huang, Q. Xu, T. Li, M. Zhu, Journal of Mountain Science 10, 532 (2013) [7] H. Zheng, Y. Huang, Environmental Earth Sciences 73, 4853 (2015) [8] A.J. Liu, S.R. Nagel, Nature 396, 21 (1998) [9] C.S. O Hern, L.E. Silbert, A.J. Liu, S.R. Nagel, PHYSICAL REVIEW E 68, (2003) [10] R. Behringer, D. Bi, B. Chakraborty, S. Henkes, R.R.Hartley, Physical Review Letters 101, (2008) [11] J. Ren, J.A. Dijksman, R.P. Behringer, Physical Review Letters 110, (2013) [12] H. Zheng, J.A. Dijksman, R.P. Behringer, Europhysics Letters 107, (2014) [13] T. Majmudar, M. Sperl, S. Luding, R. Behringer, Physical review letters 95, (2007) [14] J. Duran, Sands, powdersm and Grains: An Introduction to Physics of Granular Materials (Springer, Berlin, 1999) [15] D.M. Wood, Soil Behavior and Critical State Soil Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990) [16] E. Azéma, F. Radjaï, R. Peyroux, G. Saussine, Physical Review E 76, (2007) [17] A. Athanassiadis, M. Miskin, P. Kaplan, N. Rodenberg, S. Lee, J. Merritt, E. Brown, J. Amend, H. Lipson, H. Jaeger, Soft Matter 10, 48 (201) [18] K. Desmond, S.V. Franklin, PHYSICAL REVIEW E 73, (2006) [19] C. Schreck, N. Xu, O HernaC.S., Soft Matter 6, 2960 (2010) [20] T. Marschall, S. Franklin, S. Teitel, Granular Matter 17, 121 (2015) [21] Y. Zhao, Kevin Liu, Matthew Zheng, Jonathan Barés, Karola Dierichs, Achim Menges, Robert P. Behringer, Granular Matter 18, 1 (2016) [22] K. Dierichs, A. Menges, Architectural Design 85, 86 (2015) [23] D. Howell, R.P. Behringer, C. Veje, Physical Review Letter 82, 5241 (1999) [24] J. Geng, D. Howell, E. Longhi, R.P. Behringer, G. Reydellet, L. Vanel, E. Clément, S. Luding, Physical Review Letter 87, (2001) [25] A.H. Clark, R.P. Behringer, Europhysics Letters 101, (2013) [26] A.H. Clark, A.J. Petersen, R.P. Behringer, Physical Review E 89, (2014) [27] T.S. Majmudar, R.P. Behringer, Nature 435, 1079 (2005) [28] M. Cox, D. Wang, J. Barés, R.P. Behringer, Europhysics Letters 115, (2016)
Self-organized magnetic particles to tune the mechanical behavior of a granular system
 Self-organized magnetic particles to tune the mechanical behavior of a granular system Meredith Cox, Dong Wang, Jonathan Barés, Robert Behringer To cite this version: Meredith Cox, Dong Wang, Jonathan
Self-organized magnetic particles to tune the mechanical behavior of a granular system Meredith Cox, Dong Wang, Jonathan Barés, Robert Behringer To cite this version: Meredith Cox, Dong Wang, Jonathan
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2015](/thumbs/95/125520951.jpg) Self-organized magnetic particles to tune the mechanical behaviour of a granular system arxiv:1511.02219v1 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2015 Meredith Cox, 1 Dong Wang, 1 Jonathan Barés, 1 and Robert P. Behringer
Self-organized magnetic particles to tune the mechanical behaviour of a granular system arxiv:1511.02219v1 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2015 Meredith Cox, 1 Dong Wang, 1 Jonathan Barés, 1 and Robert P. Behringer
Quasistatic behavior and force transmission in packing of irregular polyhedral particles
 Quasistatic behavior and force transmission in packing of irregular polyhedral particles Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine To cite this version: Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine.
Quasistatic behavior and force transmission in packing of irregular polyhedral particles Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine To cite this version: Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine.
Structure of hexapod 3D packings: understanding the global stability from the local organization
 Structure of hexapod 3D packings: understanding the global stability from the local organization Jonathan Barés, Yuchen Zhao, Mathieu Renouf, Karola Dierichs, Robert Behringer To cite this version: Jonathan
Structure of hexapod 3D packings: understanding the global stability from the local organization Jonathan Barés, Yuchen Zhao, Mathieu Renouf, Karola Dierichs, Robert Behringer To cite this version: Jonathan
Rolling and sliding dynamics in centrifugal spreading
 Rolling and sliding dynamics in centrifugal spreading F. Rioual, E. Piron, E. Tijskens To cite this version: F. Rioual, E. Piron, E. Tijskens. Rolling and sliding dynamics in centrifugal spreading. Applied
Rolling and sliding dynamics in centrifugal spreading F. Rioual, E. Piron, E. Tijskens To cite this version: F. Rioual, E. Piron, E. Tijskens. Rolling and sliding dynamics in centrifugal spreading. Applied
Smart Bolometer: Toward Monolithic Bolometer with Smart Functions
 Smart Bolometer: Toward Monolithic Bolometer with Smart Functions Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia, Olivier De Sagazan To cite this version: Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia,
Smart Bolometer: Toward Monolithic Bolometer with Smart Functions Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia, Olivier De Sagazan To cite this version: Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia,
Methylation-associated PHOX2B gene silencing is a rare event in human neuroblastoma.
 Methylation-associated PHOX2B gene silencing is a rare event in human neuroblastoma. Loïc De Pontual, Delphine Trochet, Franck Bourdeaut, Sophie Thomas, Heather Etchevers, Agnes Chompret, Véronique Minard,
Methylation-associated PHOX2B gene silencing is a rare event in human neuroblastoma. Loïc De Pontual, Delphine Trochet, Franck Bourdeaut, Sophie Thomas, Heather Etchevers, Agnes Chompret, Véronique Minard,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 2006](/thumbs/82/86963356.jpg) The Jamming Transition in Granular Systems arxiv:cond-mat/61645v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 26 T. S. Majmudar 1, M. Sperl 1, S. Luding 2, R.P. Behringer 1 1 Duke University, Department of Physics, Box 935,
The Jamming Transition in Granular Systems arxiv:cond-mat/61645v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 26 T. S. Majmudar 1, M. Sperl 1, S. Luding 2, R.P. Behringer 1 1 Duke University, Department of Physics, Box 935,
A micromechanical approach to describe internal erosion effects in soils
 A micromechanical approach to describe internal erosion effects in soils Luc Scholtès, Pierre-Yves Hicher, Luc Sibille To cite this version: Luc Scholtès, Pierre-Yves Hicher, Luc Sibille. A micromechanical
A micromechanical approach to describe internal erosion effects in soils Luc Scholtès, Pierre-Yves Hicher, Luc Sibille To cite this version: Luc Scholtès, Pierre-Yves Hicher, Luc Sibille. A micromechanical
Bimodal Character of Stress Transmission in Granular Packings
 Bimodal Character of Stress Transmission in Granular Packings Farhang Radjai, Dietrich Wolf, Michel Jean, Jean Jacques Moreau To cite this version: Farhang Radjai, Dietrich Wolf, Michel Jean, Jean Jacques
Bimodal Character of Stress Transmission in Granular Packings Farhang Radjai, Dietrich Wolf, Michel Jean, Jean Jacques Moreau To cite this version: Farhang Radjai, Dietrich Wolf, Michel Jean, Jean Jacques
DEM modeling of penetration test in static and dynamic conditions
 DEM modeling of penetration test in static and dynamic conditions Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul To cite this version: Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul. DEM modeling of penetration
DEM modeling of penetration test in static and dynamic conditions Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul To cite this version: Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul. DEM modeling of penetration
A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser s theorem
 A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser s theorem Rédoane Daoudi To cite this version: Rédoane Daoudi. A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser
A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser s theorem Rédoane Daoudi To cite this version: Rédoane Daoudi. A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser
A Simple Model for Cavitation with Non-condensable Gases
 A Simple Model for Cavitation with Non-condensable Gases Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène Mathis To cite this version: Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène
A Simple Model for Cavitation with Non-condensable Gases Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène Mathis To cite this version: Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène
Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window
 Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window Christophe Barras To cite this version: Christophe Barras. Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window. Société Française d Acoustique. Acoustics 12, Apr 12, Nantes,
Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window Christophe Barras To cite this version: Christophe Barras. Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window. Société Française d Acoustique. Acoustics 12, Apr 12, Nantes,
On The Exact Solution of Newell-Whitehead-Segel Equation Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method
 On The Exact Solution of Newell-Whitehead-Segel Equation Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori, Akbar Nazari-Golshan To cite this version: S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori,
On The Exact Solution of Newell-Whitehead-Segel Equation Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori, Akbar Nazari-Golshan To cite this version: S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori,
Case report on the article Water nanoelectrolysis: A simple model, Journal of Applied Physics (2017) 122,
 Case report on the article Water nanoelectrolysis: A simple model, Journal of Applied Physics (2017) 122, 244902 Juan Olives, Zoubida Hammadi, Roger Morin, Laurent Lapena To cite this version: Juan Olives,
Case report on the article Water nanoelectrolysis: A simple model, Journal of Applied Physics (2017) 122, 244902 Juan Olives, Zoubida Hammadi, Roger Morin, Laurent Lapena To cite this version: Juan Olives,
Easter bracelets for years
 Easter bracelets for 5700000 years Denis Roegel To cite this version: Denis Roegel. Easter bracelets for 5700000 years. [Research Report] 2014. HAL Id: hal-01009457 https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01009457
Easter bracelets for 5700000 years Denis Roegel To cite this version: Denis Roegel. Easter bracelets for 5700000 years. [Research Report] 2014. HAL Id: hal-01009457 https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01009457
Stator/Rotor Interface Analysis for Piezoelectric Motors
 Stator/Rotor Interface Analysis for Piezoelectric Motors K Harmouch, Yves Bernard, Laurent Daniel To cite this version: K Harmouch, Yves Bernard, Laurent Daniel. Stator/Rotor Interface Analysis for Piezoelectric
Stator/Rotor Interface Analysis for Piezoelectric Motors K Harmouch, Yves Bernard, Laurent Daniel To cite this version: K Harmouch, Yves Bernard, Laurent Daniel. Stator/Rotor Interface Analysis for Piezoelectric
IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESISTANCE
 IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESISTANCE V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar To cite this version: V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar. IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESIS- TANCE. THERMINIC 2007,
IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESISTANCE V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar To cite this version: V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar. IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESIS- TANCE. THERMINIC 2007,
New Basis Points of Geodetic Stations for Landslide Monitoring
 New Basis Points of Geodetic Stations for Landslide Monitoring V Riabchii, M Tregub, Yankin To cite this version: V Riabchii, M Tregub, Yankin. New Basis Points of Geodetic Stations for Landslide Monitoring.
New Basis Points of Geodetic Stations for Landslide Monitoring V Riabchii, M Tregub, Yankin To cite this version: V Riabchii, M Tregub, Yankin. New Basis Points of Geodetic Stations for Landslide Monitoring.
Lorentz force velocimetry using small-size permanent magnet systems and a multi-degree-of-freedom force/torque sensor
 Lorentz force velocimetry using small-size permanent magnet systems and a multi-degree-of-freedom force/torque sensor D Hernández, C Karcher To cite this version: D Hernández, C Karcher. Lorentz force
Lorentz force velocimetry using small-size permanent magnet systems and a multi-degree-of-freedom force/torque sensor D Hernández, C Karcher To cite this version: D Hernández, C Karcher. Lorentz force
A numerical study of the penetration test at constant rod velocity
 A numerical study of the penetration test at constant rod velocity Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul To cite this version: Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul. A numerical study
A numerical study of the penetration test at constant rod velocity Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul To cite this version: Quoc Anh Tran, Bastien Chevalier, Pierre Breul. A numerical study
Evolution of the cooperation and consequences of a decrease in plant diversity on the root symbiont diversity
 Evolution of the cooperation and consequences of a decrease in plant diversity on the root symbiont diversity Marie Duhamel To cite this version: Marie Duhamel. Evolution of the cooperation and consequences
Evolution of the cooperation and consequences of a decrease in plant diversity on the root symbiont diversity Marie Duhamel To cite this version: Marie Duhamel. Evolution of the cooperation and consequences
Sound intensity as a function of sound insulation partition
 Sound intensity as a function of sound insulation partition S. Cvetkovic, R. Prascevic To cite this version: S. Cvetkovic, R. Prascevic. Sound intensity as a function of sound insulation partition. Journal
Sound intensity as a function of sound insulation partition S. Cvetkovic, R. Prascevic To cite this version: S. Cvetkovic, R. Prascevic. Sound intensity as a function of sound insulation partition. Journal
Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English strategy ( )
 Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English strategy (1997-2010) Johan P Mackenbach To cite this version: Johan P Mackenbach. Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English
Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English strategy (1997-2010) Johan P Mackenbach To cite this version: Johan P Mackenbach. Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English
Thomas Lugand. To cite this version: HAL Id: tel
 Contribution à la Modélisation et à l Optimisation de la Machine Asynchrone Double Alimentation pour des Applications Hydrauliques de Pompage Turbinage Thomas Lugand To cite this version: Thomas Lugand.
Contribution à la Modélisation et à l Optimisation de la Machine Asynchrone Double Alimentation pour des Applications Hydrauliques de Pompage Turbinage Thomas Lugand To cite this version: Thomas Lugand.
Dissipation measurements during ultrasonic fatigue tests
 Dissipation measurements during ultrasonic fatigue tests Antoine Blanche, Nicolas Ranc, Véronique Favier, André Chrysochoos To cite this version: Antoine Blanche, Nicolas Ranc, Véronique Favier, André
Dissipation measurements during ultrasonic fatigue tests Antoine Blanche, Nicolas Ranc, Véronique Favier, André Chrysochoos To cite this version: Antoine Blanche, Nicolas Ranc, Véronique Favier, André
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
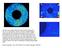 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Comment on: Sadi Carnot on Carnot s theorem.
 Comment on: Sadi Carnot on Carnot s theorem. Jacques Arnaud, Laurent Chusseau, Fabrice Philippe To cite this version: Jacques Arnaud, Laurent Chusseau, Fabrice Philippe. Comment on: Sadi Carnot on Carnot
Comment on: Sadi Carnot on Carnot s theorem. Jacques Arnaud, Laurent Chusseau, Fabrice Philippe To cite this version: Jacques Arnaud, Laurent Chusseau, Fabrice Philippe. Comment on: Sadi Carnot on Carnot
Natural convection of magnetic fluid inside a cubical enclosure under magnetic gravity compensation
 Natural convection of magnetic fluid inside a cubical enclosure under magnetic gravity compensation Zuo-Sheng Lei, Sheng-Yang Song, Chun-Long Xu, Jia-Hong Guo To cite this version: Zuo-Sheng Lei, Sheng-Yang
Natural convection of magnetic fluid inside a cubical enclosure under magnetic gravity compensation Zuo-Sheng Lei, Sheng-Yang Song, Chun-Long Xu, Jia-Hong Guo To cite this version: Zuo-Sheng Lei, Sheng-Yang
On size, radius and minimum degree
 On size, radius and minimum degree Simon Mukwembi To cite this version: Simon Mukwembi. On size, radius and minimum degree. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, DMTCS, 2014, Vol. 16 no.
On size, radius and minimum degree Simon Mukwembi To cite this version: Simon Mukwembi. On size, radius and minimum degree. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, DMTCS, 2014, Vol. 16 no.
Simultaneous Induction Heating and Electromagnetic Stirring of a Molten Glass Bath
 Simultaneous Induction Heating and Electromagnetic Stirring of a Molten Glass Bath V Fireteanu, E Rousset, E Chauvin, N Chouard To cite this version: V Fireteanu, E Rousset, E Chauvin, N Chouard. Simultaneous
Simultaneous Induction Heating and Electromagnetic Stirring of a Molten Glass Bath V Fireteanu, E Rousset, E Chauvin, N Chouard To cite this version: V Fireteanu, E Rousset, E Chauvin, N Chouard. Simultaneous
Towards an active anechoic room
 Towards an active anechoic room Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède To cite this version: Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède. Towards an active
Towards an active anechoic room Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède To cite this version: Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède. Towards an active
Some approaches to modeling of the effective properties for thermoelastic composites
 Some approaches to modeling of the ective properties for thermoelastic composites Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov To cite this version: Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov.
Some approaches to modeling of the ective properties for thermoelastic composites Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov To cite this version: Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov.
Full-order observers for linear systems with unknown inputs
 Full-order observers for linear systems with unknown inputs Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu To cite this version: Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu. Full-order observers
Full-order observers for linear systems with unknown inputs Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu To cite this version: Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu. Full-order observers
Strain localization and cyclic damage of polyurethane foam cylinders: experimental tests and theoretical model
 Strain localization and cyclic damage of polyurethane foam cylinders: experimental tests and theoretical model Giampiero Pampolini, Gianpietro Del Piero To cite this version: Giampiero Pampolini, Gianpietro
Strain localization and cyclic damage of polyurethane foam cylinders: experimental tests and theoretical model Giampiero Pampolini, Gianpietro Del Piero To cite this version: Giampiero Pampolini, Gianpietro
Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm
 Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold To cite this version: Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold. Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm. Information Processing
Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold To cite this version: Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold. Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm. Information Processing
Theoretical calculation of the power of wind turbine or tidal turbine
 Theoretical calculation of the power of wind turbine or tidal turbine Pierre Lecanu, Joel Breard, Dominique Mouazé To cite this version: Pierre Lecanu, Joel Breard, Dominique Mouazé. Theoretical calculation
Theoretical calculation of the power of wind turbine or tidal turbine Pierre Lecanu, Joel Breard, Dominique Mouazé To cite this version: Pierre Lecanu, Joel Breard, Dominique Mouazé. Theoretical calculation
Observation of negative line tensions from Plateau border regions in dry foam films
 Observation of negative line tensions from Plateau border regions in dry foam s J.-C. Géminard, A. Żywocinski, F. Caillier, P. Oswald To cite this version: J.-C. Géminard, A. Żywocinski, F. Caillier, P.
Observation of negative line tensions from Plateau border regions in dry foam s J.-C. Géminard, A. Żywocinski, F. Caillier, P. Oswald To cite this version: J.-C. Géminard, A. Żywocinski, F. Caillier, P.
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian Block-Matrices
 On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 015 HAL Id: hal-0131860
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 015 HAL Id: hal-0131860
From Unstructured 3D Point Clouds to Structured Knowledge - A Semantics Approach
 From Unstructured 3D Point Clouds to Structured Knowledge - A Semantics Approach Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida, Frank Boochs, Christophe Nicolle To cite this version: Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida,
From Unstructured 3D Point Clouds to Structured Knowledge - A Semantics Approach Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida, Frank Boochs, Christophe Nicolle To cite this version: Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida,
Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab
 Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab G. Laveissiere To cite this version: G. Laveissiere. Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab. Compton Scattering from Low to High Momentum Transfer, Mar
Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab G. Laveissiere To cite this version: G. Laveissiere. Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab. Compton Scattering from Low to High Momentum Transfer, Mar
RHEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION OF RAYLEIGH DAMPING
 RHEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION OF RAYLEIGH DAMPING Jean-François Semblat To cite this version: Jean-François Semblat. RHEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION OF RAYLEIGH DAMPING. Journal of Sound and Vibration, Elsevier,
RHEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION OF RAYLEIGH DAMPING Jean-François Semblat To cite this version: Jean-François Semblat. RHEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION OF RAYLEIGH DAMPING. Journal of Sound and Vibration, Elsevier,
On infinite permutations
 On infinite permutations Dmitri G. Fon-Der-Flaass, Anna E. Frid To cite this version: Dmitri G. Fon-Der-Flaass, Anna E. Frid. On infinite permutations. Stefan Felsner. 2005 European Conference on Combinatorics,
On infinite permutations Dmitri G. Fon-Der-Flaass, Anna E. Frid To cite this version: Dmitri G. Fon-Der-Flaass, Anna E. Frid. On infinite permutations. Stefan Felsner. 2005 European Conference on Combinatorics,
A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion
 A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim To cite this version: Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim. A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion. ICASSP 007, Apr 007, Honolulu,
A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim To cite this version: Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim. A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion. ICASSP 007, Apr 007, Honolulu,
Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement
 Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement N.-E. Khélifa To cite this version: N.-E. Khélifa. Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement. Measurement. Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement, May 2007, Smolenice,
Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement N.-E. Khélifa To cite this version: N.-E. Khélifa. Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement. Measurement. Water Vapour Effects in Mass Measurement, May 2007, Smolenice,
Approximation SEM-DG pour les problèmes d ondes elasto-acoustiques
 Approximation SEM-DG pour les problèmes d ondes elasto-acoustiques Helene Barucq, Henri Calandra, Aurélien Citrain, Julien Diaz, Christian Gout To cite this version: Helene Barucq, Henri Calandra, Aurélien
Approximation SEM-DG pour les problèmes d ondes elasto-acoustiques Helene Barucq, Henri Calandra, Aurélien Citrain, Julien Diaz, Christian Gout To cite this version: Helene Barucq, Henri Calandra, Aurélien
Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore
 Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore Anaïs Rolez To cite this version: Anaïs Rolez. Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore. Article destiné à l origine à la Revue de l Institut National
Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore Anaïs Rolez To cite this version: Anaïs Rolez. Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore. Article destiné à l origine à la Revue de l Institut National
How Can Grains Jam under Shear?
 How Can Grains Jam under Shear? Bob Behringer, September 8, 2017 Collaborators: Jonathan Baras, Cacey Bester-Stevens, Max Bi, Nicolas Brodu, Abe Clark, Corentin Coulais, Julien Dervaux, Joshua Dijksman,
How Can Grains Jam under Shear? Bob Behringer, September 8, 2017 Collaborators: Jonathan Baras, Cacey Bester-Stevens, Max Bi, Nicolas Brodu, Abe Clark, Corentin Coulais, Julien Dervaux, Joshua Dijksman,
On measurement of mechanical properties of sound absorbing materials
 On measurement of mechanical properties of sound absorbing materials Nicolas Dauchez, Manuel Etchessahar, Sohbi Sahraoui To cite this version: Nicolas Dauchez, Manuel Etchessahar, Sohbi Sahraoui. On measurement
On measurement of mechanical properties of sound absorbing materials Nicolas Dauchez, Manuel Etchessahar, Sohbi Sahraoui To cite this version: Nicolas Dauchez, Manuel Etchessahar, Sohbi Sahraoui. On measurement
The beam-gas method for luminosity measurement at LHCb
 The beam-gas method for luminosity measurement at LHCb P. Hopchev To cite this version: P. Hopchev. The beam-gas method for luminosity measurement at LHCb. XLVth Rencontres de Moriond: Electroweak Interactions
The beam-gas method for luminosity measurement at LHCb P. Hopchev To cite this version: P. Hopchev. The beam-gas method for luminosity measurement at LHCb. XLVth Rencontres de Moriond: Electroweak Interactions
Nonlocal computational methods applied to composites structures
 Nonlocal computational methods applied to composites structures Norbert Germain, Frédéric Feyel, Jacques Besson To cite this version: Norbert Germain, Frédéric Feyel, Jacques Besson. Nonlocal computational
Nonlocal computational methods applied to composites structures Norbert Germain, Frédéric Feyel, Jacques Besson To cite this version: Norbert Germain, Frédéric Feyel, Jacques Besson. Nonlocal computational
Solubility prediction of weak electrolyte mixtures
 Solubility prediction of weak electrolyte mixtures Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang Yuan To cite this version: Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang
Solubility prediction of weak electrolyte mixtures Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang Yuan To cite this version: Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang
AC Transport Losses Calculation in a Bi-2223 Current Lead Using Thermal Coupling With an Analytical Formula
 AC Transport Losses Calculation in a Bi-2223 Current Lead Using Thermal Coupling With an Analytical Formula Kévin Berger, Jean Lévêque, Denis Netter, Bruno Douine, Abderrezak Rezzoug To cite this version:
AC Transport Losses Calculation in a Bi-2223 Current Lead Using Thermal Coupling With an Analytical Formula Kévin Berger, Jean Lévêque, Denis Netter, Bruno Douine, Abderrezak Rezzoug To cite this version:
Uniform and gradually varied flows in compound channel versus free mixing layers
 Uniform and gradually varied flows in compound channel versus free mixing layers S. Proust, J.N. Fernandes, N. Riviere, J.B. Leal, Y. Peltier, A.H. Cardoso To cite this version: S. Proust, J.N. Fernandes,
Uniform and gradually varied flows in compound channel versus free mixing layers S. Proust, J.N. Fernandes, N. Riviere, J.B. Leal, Y. Peltier, A.H. Cardoso To cite this version: S. Proust, J.N. Fernandes,
Application of Regularized Digital Images Correlation Analysis to the Tensile Test of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy
 Application of Regularized Digital Images Correlation Analysis to the Tensile Test of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Xuyang Chang, Mame Daro Fall, Karine Lavernhe Taillard, Olivier Hubert To cite this version:
Application of Regularized Digital Images Correlation Analysis to the Tensile Test of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Xuyang Chang, Mame Daro Fall, Karine Lavernhe Taillard, Olivier Hubert To cite this version:
Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic
 Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic. Licence. France.
Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic. Licence. France.
Thermo-mechanical modelling of the aircraft tyre cornering
 Thermo-mechanical modelling of the aircraft tyre cornering Lama Elias-Birembaux, Iulian Rosu, Frédéric Lebon To cite this version: Lama Elias-Birembaux, Iulian Rosu, Frédéric Lebon. Thermo-mechanical modelling
Thermo-mechanical modelling of the aircraft tyre cornering Lama Elias-Birembaux, Iulian Rosu, Frédéric Lebon To cite this version: Lama Elias-Birembaux, Iulian Rosu, Frédéric Lebon. Thermo-mechanical modelling
The magnetic field diffusion equation including dynamic, hysteresis: A linear formulation of the problem
 The magnetic field diffusion equation including dynamic, hysteresis: A linear formulation of the problem Marie-Ange Raulet, Benjamin Ducharne, Jean-Pierre Masson, G. Bayada To cite this version: Marie-Ange
The magnetic field diffusion equation including dynamic, hysteresis: A linear formulation of the problem Marie-Ange Raulet, Benjamin Ducharne, Jean-Pierre Masson, G. Bayada To cite this version: Marie-Ange
Stickelberger s congruences for absolute norms of relative discriminants
 Stickelberger s congruences for absolute norms of relative discriminants Georges Gras To cite this version: Georges Gras. Stickelberger s congruences for absolute norms of relative discriminants. Journal
Stickelberger s congruences for absolute norms of relative discriminants Georges Gras To cite this version: Georges Gras. Stickelberger s congruences for absolute norms of relative discriminants. Journal
L institution sportive : rêve et illusion
 L institution sportive : rêve et illusion Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar To cite this version: Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar. L institution sportive : rêve et illusion. Revue
L institution sportive : rêve et illusion Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar To cite this version: Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar. L institution sportive : rêve et illusion. Revue
On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph
 On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph Julien Bensmail To cite this version: Julien Bensmail. On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph. 2012. HAL Id:
On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph Julien Bensmail To cite this version: Julien Bensmail. On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph. 2012. HAL Id:
Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration
 Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration A. Semenov To cite this version: A. Semenov. Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1994, 04 (C5), pp.c7-251-c7-254.
Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration A. Semenov To cite this version: A. Semenov. Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1994, 04 (C5), pp.c7-251-c7-254.
Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images
 Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images. Philica, Philica,
Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images. Philica, Philica,
b-chromatic number of cacti
 b-chromatic number of cacti Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva To cite this version: Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva. b-chromatic number
b-chromatic number of cacti Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva To cite this version: Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva. b-chromatic number
Biaxial tension on polymer in thermoforming range
 Biaxial tension on polymer in thermoforming range Simon Becker, Christelle Combeaud, Francis Fournier, J. Rodriguez, Noëlle Billon To cite this version: Simon Becker, Christelle Combeaud, Francis Fournier,
Biaxial tension on polymer in thermoforming range Simon Becker, Christelle Combeaud, Francis Fournier, J. Rodriguez, Noëlle Billon To cite this version: Simon Becker, Christelle Combeaud, Francis Fournier,
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian Block-Matrices
 On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 016 HAL Id: hal-0131860
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 016 HAL Id: hal-0131860
Exogenous input estimation in Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems
 Exogenous input estimation in Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de Wit, Franck Quaine, Violaine Cahouet To cite this version: Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de
Exogenous input estimation in Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de Wit, Franck Quaine, Violaine Cahouet To cite this version: Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de
LAWS OF CRYSTAL-FIELD DISORDERNESS OF Ln3+ IONS IN INSULATING LASER CRYSTALS
 LAWS OF CRYSTAL-FIELD DISORDERNESS OF Ln3+ IONS IN INSULATING LASER CRYSTALS A. Kaminskii To cite this version: A. Kaminskii. LAWS OF CRYSTAL-FIELD DISORDERNESS OF Ln3+ IONS IN INSULAT- ING LASER CRYSTALS.
LAWS OF CRYSTAL-FIELD DISORDERNESS OF Ln3+ IONS IN INSULATING LASER CRYSTALS A. Kaminskii To cite this version: A. Kaminskii. LAWS OF CRYSTAL-FIELD DISORDERNESS OF Ln3+ IONS IN INSULAT- ING LASER CRYSTALS.
A new approach of the concept of prime number
 A new approach of the concept of prime number Jamel Ghannouchi To cite this version: Jamel Ghannouchi. A new approach of the concept of prime number. 4 pages. 24. HAL Id: hal-3943 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-3943
A new approach of the concept of prime number Jamel Ghannouchi To cite this version: Jamel Ghannouchi. A new approach of the concept of prime number. 4 pages. 24. HAL Id: hal-3943 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-3943
A Simple Proof of P versus NP
 A Simple Proof of P versus NP Frank Vega To cite this version: Frank Vega. A Simple Proof of P versus NP. 2016. HAL Id: hal-01281254 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01281254 Submitted
A Simple Proof of P versus NP Frank Vega To cite this version: Frank Vega. A Simple Proof of P versus NP. 2016. HAL Id: hal-01281254 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01281254 Submitted
Stress Dependency on the Ultrasonic Wave Velocity and Attenuation of Fe-C System
 Stress Dependency on the Ultrasonic Wave Velocity and Attenuation of Fe-C System S. Takahashi, K. Takahashi To cite this version: S. Takahashi, K. Takahashi. Stress Dependency on the Ultrasonic Wave Velocity
Stress Dependency on the Ultrasonic Wave Velocity and Attenuation of Fe-C System S. Takahashi, K. Takahashi To cite this version: S. Takahashi, K. Takahashi. Stress Dependency on the Ultrasonic Wave Velocity
Diurnal variation of tropospheric temperature at a tropical station
 Diurnal variation of tropospheric temperature at a tropical station K. Revathy, S. R. Prabhakaran Nayar, B. V. Krishna Murthy To cite this version: K. Revathy, S. R. Prabhakaran Nayar, B. V. Krishna Murthy.
Diurnal variation of tropospheric temperature at a tropical station K. Revathy, S. R. Prabhakaran Nayar, B. V. Krishna Murthy To cite this version: K. Revathy, S. R. Prabhakaran Nayar, B. V. Krishna Murthy.
Jamming for a 2D granular material
 PAPER www.rsc.org/softmatter Soft Matter Jamming for a 2D granular material Jie Zhang, T. S. Majmudar,x M. Sperl{ and R. P. Behringer* Received 6th January 2010, Accepted 19th May 2010 First published
PAPER www.rsc.org/softmatter Soft Matter Jamming for a 2D granular material Jie Zhang, T. S. Majmudar,x M. Sperl{ and R. P. Behringer* Received 6th January 2010, Accepted 19th May 2010 First published
On the beam deflection method applied to ultrasound absorption measurements
 On the beam deflection method applied to ultrasound absorption measurements K. Giese To cite this version: K. Giese. On the beam deflection method applied to ultrasound absorption measurements. Journal
On the beam deflection method applied to ultrasound absorption measurements K. Giese To cite this version: K. Giese. On the beam deflection method applied to ultrasound absorption measurements. Journal
The FLRW cosmological model revisited: relation of the local time with th e local curvature and consequences on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
 The FLRW cosmological model revisited: relation of the local time with th e local curvature and consequences on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle Nathalie Olivi-Tran, Paul M Gauthier To cite this version:
The FLRW cosmological model revisited: relation of the local time with th e local curvature and consequences on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle Nathalie Olivi-Tran, Paul M Gauthier To cite this version:
Modeling of Electromagmetic Processes in Wire Electric Discharge Machining
 Modeling of Electromagmetic Processes in Wire Electric Discharge Machining V.M. Volgin, V.V. Lyubimov, V.D. Kukhar To cite this version: V.M. Volgin, V.V. Lyubimov, V.D. Kukhar. Modeling of Electromagmetic
Modeling of Electromagmetic Processes in Wire Electric Discharge Machining V.M. Volgin, V.V. Lyubimov, V.D. Kukhar To cite this version: V.M. Volgin, V.V. Lyubimov, V.D. Kukhar. Modeling of Electromagmetic
Impulse response measurement of ultrasonic transducers
 Impulse response measurement of ultrasonic transducers F. Kadlec To cite this version: F. Kadlec. Impulse response measurement of ultrasonic transducers. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1994, 04 (C5),
Impulse response measurement of ultrasonic transducers F. Kadlec To cite this version: F. Kadlec. Impulse response measurement of ultrasonic transducers. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1994, 04 (C5),
Determination of absorption characteristic of materials on basis of sound intensity measurement
 Determination of absorption characteristic of materials on basis of sound intensity measurement R. Prascevic, A. Milosevic, S. Cvetkovic To cite this version: R. Prascevic, A. Milosevic, S. Cvetkovic.
Determination of absorption characteristic of materials on basis of sound intensity measurement R. Prascevic, A. Milosevic, S. Cvetkovic To cite this version: R. Prascevic, A. Milosevic, S. Cvetkovic.
Direct strain and slope measurement using 3D DSPSI
 Direct strain and slope measurement using 3D DSPSI Jérôme Molimard, Wajdi Dandach, Pascal Picart To cite this version: Jérôme Molimard, Wajdi Dandach, Pascal Picart. Direct strain and slope measurement
Direct strain and slope measurement using 3D DSPSI Jérôme Molimard, Wajdi Dandach, Pascal Picart To cite this version: Jérôme Molimard, Wajdi Dandach, Pascal Picart. Direct strain and slope measurement
STATISTICAL ENERGY ANALYSIS: CORRELATION BETWEEN DIFFUSE FIELD AND ENERGY EQUIPARTITION
 STATISTICAL ENERGY ANALYSIS: CORRELATION BETWEEN DIFFUSE FIELD AND ENERGY EQUIPARTITION Thibault Lafont, Alain Le Bot, Nicolas Totaro To cite this version: Thibault Lafont, Alain Le Bot, Nicolas Totaro.
STATISTICAL ENERGY ANALYSIS: CORRELATION BETWEEN DIFFUSE FIELD AND ENERGY EQUIPARTITION Thibault Lafont, Alain Le Bot, Nicolas Totaro To cite this version: Thibault Lafont, Alain Le Bot, Nicolas Totaro.
Finite element computation of leaky modes in straight and helical elastic waveguides
 Finite element computation of leaky modes in straight and helical elastic waveguides Khac-Long Nguyen, Fabien Treyssede, Christophe Hazard, Anne-Sophie Bonnet-Ben Dhia To cite this version: Khac-Long Nguyen,
Finite element computation of leaky modes in straight and helical elastic waveguides Khac-Long Nguyen, Fabien Treyssede, Christophe Hazard, Anne-Sophie Bonnet-Ben Dhia To cite this version: Khac-Long Nguyen,
Self Field Effect Compensation in an HTS Tube
 Self Field Effect Compensation in an HTS Tube Bruno Douine, Kévin Berger, Jean Lévêque, Denis Netter, Olivia Arbey, Nancy Barthelet To cite this version: Bruno Douine, Kévin Berger, Jean Lévêque, Denis
Self Field Effect Compensation in an HTS Tube Bruno Douine, Kévin Berger, Jean Lévêque, Denis Netter, Olivia Arbey, Nancy Barthelet To cite this version: Bruno Douine, Kévin Berger, Jean Lévêque, Denis
Quantum efficiency and metastable lifetime measurements in ruby ( Cr 3+ : Al2O3) via lock-in rate-window photothermal radiometry
 Quantum efficiency and metastable lifetime measurements in ruby ( Cr 3+ : Al2O3) via lock-in rate-window photothermal radiometry A. Mandelis, Z. Chen, R. Bleiss To cite this version: A. Mandelis, Z. Chen,
Quantum efficiency and metastable lifetime measurements in ruby ( Cr 3+ : Al2O3) via lock-in rate-window photothermal radiometry A. Mandelis, Z. Chen, R. Bleiss To cite this version: A. Mandelis, Z. Chen,
Quasi-periodic solutions of the 2D Euler equation
 Quasi-periodic solutions of the 2D Euler equation Nicolas Crouseilles, Erwan Faou To cite this version: Nicolas Crouseilles, Erwan Faou. Quasi-periodic solutions of the 2D Euler equation. Asymptotic Analysis,
Quasi-periodic solutions of the 2D Euler equation Nicolas Crouseilles, Erwan Faou To cite this version: Nicolas Crouseilles, Erwan Faou. Quasi-periodic solutions of the 2D Euler equation. Asymptotic Analysis,
A numerical analysis of chaos in the double pendulum
 A numerical analysis of chaos in the double pendulum Tomasz Stachowiak, Toshio Okada To cite this version: Tomasz Stachowiak, Toshio Okada. A numerical analysis of chaos in the double pendulum. Chaos,
A numerical analysis of chaos in the double pendulum Tomasz Stachowiak, Toshio Okada To cite this version: Tomasz Stachowiak, Toshio Okada. A numerical analysis of chaos in the double pendulum. Chaos,
Particle-in-cell simulations of high energy electron production by intense laser pulses in underdense plasmas
 Particle-in-cell simulations of high energy electron production by intense laser pulses in underdense plasmas Susumu Kato, Eisuke Miura, Mitsumori Tanimoto, Masahiro Adachi, Kazuyoshi Koyama To cite this
Particle-in-cell simulations of high energy electron production by intense laser pulses in underdense plasmas Susumu Kato, Eisuke Miura, Mitsumori Tanimoto, Masahiro Adachi, Kazuyoshi Koyama To cite this
Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions
 Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions Guo-Niu Han To cite this version: Guo-Niu Han Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions The Ramanujan Journal, 009, 9 p HAL Id: hal-00395690
Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions Guo-Niu Han To cite this version: Guo-Niu Han Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions The Ramanujan Journal, 009, 9 p HAL Id: hal-00395690
Eddy-Current Effects in Circuit Breakers During Arc Displacement Phase
 Eddy-Current Effects in Circuit Breakers During Arc Displacement Phase Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier, V. Mazauric, Yann Le Floch, Patrice Labie To cite this version: Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier,
Eddy-Current Effects in Circuit Breakers During Arc Displacement Phase Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier, V. Mazauric, Yann Le Floch, Patrice Labie To cite this version: Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier,
AN INTERNAL FRICTION PEAK DUE TO HYDROGEN-DISLOCATION INTERACTION IN NICKEL
 AN INTERNAL FRICTION PEAK DUE TO HYDROGEN-DISLOCATION INTERACTION IN NICKEL K. Tanaka, T. Atsumi, M. Yamada To cite this version: K. Tanaka, T. Atsumi, M. Yamada. AN INTERNAL FRICTION PEAK DUE TO HYDROGEN-
AN INTERNAL FRICTION PEAK DUE TO HYDROGEN-DISLOCATION INTERACTION IN NICKEL K. Tanaka, T. Atsumi, M. Yamada To cite this version: K. Tanaka, T. Atsumi, M. Yamada. AN INTERNAL FRICTION PEAK DUE TO HYDROGEN-
A remark on a theorem of A. E. Ingham.
 A remark on a theorem of A. E. Ingham. K G Bhat, K Ramachandra To cite this version: K G Bhat, K Ramachandra. A remark on a theorem of A. E. Ingham.. Hardy-Ramanujan Journal, Hardy-Ramanujan Society, 2006,
A remark on a theorem of A. E. Ingham. K G Bhat, K Ramachandra To cite this version: K G Bhat, K Ramachandra. A remark on a theorem of A. E. Ingham.. Hardy-Ramanujan Journal, Hardy-Ramanujan Society, 2006,
Nodal and divergence-conforming boundary-element methods applied to electromagnetic scattering problems
 Nodal and divergence-conforming boundary-element methods applied to electromagnetic scattering problems M. Afonso, Joao Vasconcelos, Renato Mesquita, Christian Vollaire, Laurent Nicolas To cite this version:
Nodal and divergence-conforming boundary-element methods applied to electromagnetic scattering problems M. Afonso, Joao Vasconcelos, Renato Mesquita, Christian Vollaire, Laurent Nicolas To cite this version:
Evaluation of transverse elastic properties of fibers used in composite materials by laser resonant ultrasound spectroscopy
 Evaluation of transverse elastic properties of fibers used in composite materials by laser resonant ultrasound spectroscopy Denis Mounier, Christophe Poilâne, Cécile Bûcher, Pascal Picart To cite this
Evaluation of transverse elastic properties of fibers used in composite materials by laser resonant ultrasound spectroscopy Denis Mounier, Christophe Poilâne, Cécile Bûcher, Pascal Picart To cite this
Near-Earth Asteroids Orbit Propagation with Gaia Observations
 Near-Earth Asteroids Orbit Propagation with Gaia Observations David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot To cite this version: David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot. Near-Earth Asteroids
Near-Earth Asteroids Orbit Propagation with Gaia Observations David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot To cite this version: David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot. Near-Earth Asteroids
Basic concepts and models in continuum damage mechanics
 Basic concepts and models in continuum damage mechanics Djimedo Kondo, Hélène Welemane, Fabrice Cormery To cite this version: Djimedo Kondo, Hélène Welemane, Fabrice Cormery. Basic concepts and models
Basic concepts and models in continuum damage mechanics Djimedo Kondo, Hélène Welemane, Fabrice Cormery To cite this version: Djimedo Kondo, Hélène Welemane, Fabrice Cormery. Basic concepts and models
Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic based on Fitting and Smullyan
 Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic based on Fitting and Smullyan Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic
Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic based on Fitting and Smullyan Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic
Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems
 Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert To cite this version: Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert. Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems. Proceedings
Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert To cite this version: Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert. Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems. Proceedings
Interactions of an eddy current sensor and a multilayered structure
 Interactions of an eddy current sensor and a multilayered structure Thanh Long Cung, Pierre-Yves Joubert, Eric Vourc H, Pascal Larzabal To cite this version: Thanh Long Cung, Pierre-Yves Joubert, Eric
Interactions of an eddy current sensor and a multilayered structure Thanh Long Cung, Pierre-Yves Joubert, Eric Vourc H, Pascal Larzabal To cite this version: Thanh Long Cung, Pierre-Yves Joubert, Eric
Improved Adaptive Resolution Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Improved Adaptive Resolution Molecular Dynamics Simulation Iuliana Marin, Virgil Tudose, Anton Hadar, Nicolae Goga, Andrei Doncescu To cite this version: Iuliana Marin, Virgil Tudose, Anton Hadar, Nicolae
Improved Adaptive Resolution Molecular Dynamics Simulation Iuliana Marin, Virgil Tudose, Anton Hadar, Nicolae Goga, Andrei Doncescu To cite this version: Iuliana Marin, Virgil Tudose, Anton Hadar, Nicolae
Improvement of YBCO Superconductor Magnetic Shielding by Using Multiple Bulks
 Improvement of YCO Superconductor Magnetic Shielding by Using Multiple ulks runo Douine, Gaël Malé, Thierry Lubin, Smail Meani, ean Lévêque, Kévin erger To cite this version: runo Douine, Gaël Malé, Thierry
Improvement of YCO Superconductor Magnetic Shielding by Using Multiple ulks runo Douine, Gaël Malé, Thierry Lubin, Smail Meani, ean Lévêque, Kévin erger To cite this version: runo Douine, Gaël Malé, Thierry
