On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems
|
|
|
- Crystal George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT)
2 High level comments
3 High level comments Many modern queueing systems are large scale
4 High level comments Many modern queueing systems are large scale Operating optimally requires large scale resources
5 High level comments Many modern queueing systems are large scale Operating optimally requires large scale resources It is of interest to understand the best performance under limited resources availability
6 High level comments Many modern queueing systems are large scale Operating optimally requires large scale resources It is of interest to understand the best performance under limited resources availability In this work we study Join-the-Shortest-Queue (JSQ) policy in heavy traffic and compare it with M/M/N design Dispatching policies with limited memory and limited information exchange in many server queueing systems
7 Join the Shortest Queue in heavy traffic n n parallel servers Exp(1) service Pois(nλ n ) arrival. λ n = 1 β/ n. Choose any shortest queue upon arrival Compare with M/M/N - global buffer, join the smallest workload
8 Join the Shortest Queue in heavy traffic n n parallel servers Exp(1) service Pois(nλ n ) arrival. λ n = 1 β/ n. Choose any shortest queue upon arrival Compare with M/M/N - global buffer, join the smallest workload
9 Join the Shortest Queue in heavy traffic n n parallel servers Exp(1) service Pois(nλ n ) arrival. λ n = 1 β/ n. Choose any shortest queue upon arrival Compare with M/M/N - global buffer, join the smallest workload
10 Prior work on JSQ: fixed number of servers Winston 77 : JSQ is the optimal policy if customers are routed to servers immedaitely. Foschini and Salz 78 : diffusion limit for heavy traffic with fixed number of servers. Mukherjee, Borst, van Leeuwaarden and Whiting 15: a combination of JSQ with a Supermarket Model.
11 Notation Q n i (t) is the number of servers with queue length at least i, including those in service n Q n 1 (t) Qn 2 (t) 0 Q i (t) Q i+1 (t) is the number of servers with exactly i customers n Q n 1 (t) is the number of idle servers X n 1 (t) = (Qn 1 (t) n)/ n, X n i (t) = Q n i (t)/ n
12 Main result described qualitatively
13 Main result described qualitatively: queues
14 Main result described qualitatively: queues
15 Main result described qualitatively: queues O ( n ) idle servers and O ( n ) servers with exactly one customer waiting
16 Main result described qualitatively: queues O ( n ) idle servers and O ( n ) servers with exactly one customer waiting Upon rescaling, they form a 2-dimensional reflected Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process
17 Main result described qualitatively: queues O ( n ) idle servers and O ( n ) servers with exactly one customer waiting Upon rescaling, they form a 2-dimensional reflected Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process Longer queues disappear in constant time
18 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times
19 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times Two possibilities for arriving customer:
20 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times Two possibilities for arriving customer: At least one idle server, so zero wait No idle servers, join queue behind one customer, so wait Exp(1)
21 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times Two possibilities for arriving customer: At least one idle server, so zero wait No idle servers, join queue behind one customer, so wait Exp(1) Aggregate waiting time for customers arriving in [0, t] is O ( n )
22 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times Two possibilities for arriving customer: At least one idle server, so zero wait No idle servers, join queue behind one customer, so wait Exp(1) Aggregate waiting time for customers arriving in [0, t] is O ( n ) Order n arrivals in [0, t]
23 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times Two possibilities for arriving customer: At least one idle server, so zero wait No idle servers, join queue behind one customer, so wait Exp(1) Aggregate waiting time for customers arriving in [0, t] is O ( n ) Order n arrivals in [0, t] Fraction of customers who wait: O ( 1/ n )
24 Main result described qualitatively: waiting times Two possibilities for arriving customer: At least one idle server, so zero wait No idle servers, join queue behind one customer, so wait Exp(1) Aggregate waiting time for customers arriving in [0, t] is O ( n ) Order n arrivals in [0, t] Fraction of customers who wait: O ( 1/ n ) Average waiting time O ( 1/ n ) - same as for M/M/N.
25 JSQ as a reflected process Fix k 3, b R k, y D k. Theorem There exists a unique solution x(t) to the integral equation x(t) = b + y(t) + (x(t))dt + U(t) 0 1{x(t) }du(t) = 0, This is a variation on a result of Pang, Talreja, and Whitt 07.
26 An integral equation For k 3, B R +, b R k, y D k, there is a unique solution (x, u) to x 1 (t) = b 1 + y 1 (t) + x 2 (t) = b 2 + y 2 (t) + x i (t) = b i + y i (t) + x k (t) = b k + y k (t) + t 0 t 0 t 0 t 0 ( x 1 (s) + x 2 (s))ds u 1 (t) ( x 2 (s) + x 3 (s))ds + u 1 (t) u 2 (t), ( x i (s) + x i+1 (s))ds, 3 i k 1, x k (s)ds, x 1 (t) 0, 0 x 2 (t) B, x i (t) 0, u 1 (t), u 2 (t) 0, t 0, 0 1{x 1 (t) < 0}du 1 (t) = 0, 0 1{x 2 (t) < B}du 2 (t) = 0.
27 JSQ heavy traffic limit Theorem (Main Result) Suppose X n (0) X(0) with X n k+1 (0) = 0. Then X n X where X 1 0, X i 0, i 2, and nondecreasing U 1 0 such that X 1 (t) = X 1 (0) + t 2W (t) βt + X 2 (t) = X 2 (0) + U 1 (t) + X i (t) = X i (0) + X k (t) = X k (0) + 0 = 0 t 0 t 0 t 0 0 ( X 1 (s) + X 2 (s)) ds U 1 (t), ( X 2 (s) + X 3 (s))ds, ( X i (s) + X i+1 (s))ds, 3 i k 1, X k (s)ds, X i (t) = 0, i k + 1, 1{X 1 (t) < 0}dU 1 (t), where W is a standard Brownian motion.
28 Proof outline Introduce truncated approximation of system. show that the truncated system converges to the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process. Show the original and truncated systems have same behavior whp.
29 Truncated model n n 1 Initially no queue longer than k. Reject any arrival when ˆQ 2 n (t) = n. ˆQ i n (t), i 3 decreases monotonically in t. n
30 Truncated model n n 1 Initially no queue longer than k. Reject any arrival when ˆQ 2 n (t) = n. ˆQ i n (t), i 3 decreases monotonically in t. n
31 Connecting truncated and untruncated Since Q2 n (0) < n, truncated system and full system are identical until the first time ˆQ 2 n (t) = n. The weak convergence of the truncated system ˆX n X implies ( ) P sup ˆQ 2 n (s) n 0. 0 s t This further implies X n X.
32 Open questions Waiting time distribution for a customer arriving at time t Steady state of the limiting system Convergence of steady state in n-th system to steady state of limiting system (interchange of limits) General service times distribution
33 Dispatching with limited memory and information exchange Resource Constrained Pull Based (RCPB) policy Dispatcher 15,3,28,6,87 15 n parallel servers. Exp(1) service. Pois(λn) arrival. λ < 1. Dispatcher can store up to C IDs of idle servers. Idle servers send reminders at rate µ. Job is assigned to an idle server, if at least one idle server ID is available. Otherwise u.a.r.
34 Some relevant literature Badonnel and Burgess 08: Pull-based load balancing Stolyar 15: Pull-based load distribution in heterogeneous systems Literature on Supermarket Model
35 Main results: positive S N (t) = (Q i (t)/n, i 1), Q i (t) - number of servers with length i. 0 M(t) C - number of tokens at Dispatcher.
36 Main results: positive S N (t) = (Q i (t)/n, i 1), Q i (t) - number of servers with length i. 0 M(t) C - number of tokens at Dispatcher. Theorem
37 Main results: positive S N (t) = (Q i (t)/n, i 1), Q i (t) - number of servers with length i. 0 M(t) C - number of tokens at Dispatcher. Theorem ODE (Fluid model limit) S N (t) N s(t).
38 Main results: positive S N (t) = (Q i (t)/n, i 1), Q i (t) - number of servers with length i. 0 M(t) C - number of tokens at Dispatcher. Theorem ODE (Fluid model limit) S N (t) N s(t). s(t) s.
39 Main results: positive S N (t) = (Q i (t)/n, i 1), Q i (t) - number of servers with length i. 0 M(t) C - number of tokens at Dispatcher. Theorem ODE (Fluid model limit) S N (t) N s(t). s(t) s. Interchange of limits: S N (t) t π N N s.
40 Description of the equilibrium Theorem The equilibrium is given by P0 = 0 k C ( ) µ(1 λ) k λ s i = λ (λp 0 )i 1, i 1 E[Delay] = λp 0 1 λp0. 1,
41 Uniformly bounded delay in λ 1
42 Uniformly bounded delay in λ 1 Note: as λ 1, the effective rate of messages decreases (1 λ)µ.
43 Uniformly bounded delay in λ 1 Note: as λ 1, the effective rate of messages decreases (1 λ)µ. Given a budget ν (1 λ)µ and memory size C, how does the delay scale as λ 1?
44 Uniformly bounded delay in λ 1 Note: as λ 1, the effective rate of messages decreases (1 λ)µ. Given a budget ν (1 λ)µ and memory size C, how does the delay scale as λ 1? Theorem The delay is uniformly bounded in λ: sup E[Delay] λ<1 1 k C ν k 1.
45 Uniformly bounded delay in λ 1 Note: as λ 1, the effective rate of messages decreases (1 λ)µ. Given a budget ν (1 λ)µ and memory size C, how does the delay scale as λ 1? Theorem The delay is uniformly bounded in λ: sup E[Delay] λ<1 1 k C Note: For the supermarket model E[Delay] 1 ( ) 1 log d log. 1 λ ν k 1.
46 Lower bound on delays for general policies queries messages Dispatcher Dispatcher memory capacity C log n. Dispatcher queries some servers upon arrivals. Servers send messages to Dispatcher. Memory state is updated at events.
47 Lower bound on delays for general policies Theorem Every symmetric dispatching policy induces a delay bounded away from zero: for every λ < 1 lim inf E[Delay π π ] > 0.
48 Thank you.
Load Balancing in Distributed Service System: A Survey
 Load Balancing in Distributed Service System: A Survey Xingyu Zhou The Ohio State University zhou.2055@osu.edu November 21, 2016 Xingyu Zhou (OSU) Load Balancing November 21, 2016 1 / 29 Introduction and
Load Balancing in Distributed Service System: A Survey Xingyu Zhou The Ohio State University zhou.2055@osu.edu November 21, 2016 Xingyu Zhou (OSU) Load Balancing November 21, 2016 1 / 29 Introduction and
DELAY, MEMORY, AND MESSAGING TRADEOFFS IN DISTRIBUTED SERVICE SYSTEMS
 DELAY, MEMORY, AND MESSAGING TRADEOFFS IN DISTRIBUTED SERVICE SYSTEMS By David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5 th September, 2017 We consider the
DELAY, MEMORY, AND MESSAGING TRADEOFFS IN DISTRIBUTED SERVICE SYSTEMS By David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5 th September, 2017 We consider the
David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis, Martin Zubeldia
 This article was downloaded by: [148.251.232.83] On: 16 August 218, At: :1 Publisher: Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) INFORMS is located in Maryland, USA Stochastic
This article was downloaded by: [148.251.232.83] On: 16 August 218, At: :1 Publisher: Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) INFORMS is located in Maryland, USA Stochastic
arxiv: v1 [cs.pf] 22 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.pf] 22 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.pf] 22 Dec 2017](/thumbs/92/109331375.jpg) Scalable Load Balancing in etworked Systems: Universality Properties and Stochastic Coupling Methods Mark van der Boor 1, Sem C. Borst 1,2, Johan S.H. van Leeuwaarden 1, and Debankur Mukherjee 1 1 Eindhoven
Scalable Load Balancing in etworked Systems: Universality Properties and Stochastic Coupling Methods Mark van der Boor 1, Sem C. Borst 1,2, Johan S.H. van Leeuwaarden 1, and Debankur Mukherjee 1 1 Eindhoven
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems
 Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
A LOWER BOUND ON THE QUEUEING DELAY IN RESOURCE CONSTRAINED LOAD BALANCING
 A LOWER BOUND ON THE QUEUEING DELAY IN RESOURCE CONSTRAINED LOAD BALANCING By David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia Massachusetts Institute of Technology 8 th July, 2018 We consider the
A LOWER BOUND ON THE QUEUEING DELAY IN RESOURCE CONSTRAINED LOAD BALANCING By David Gamarnik, John N. Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia Massachusetts Institute of Technology 8 th July, 2018 We consider the
MODELING WEBCHAT SERVICE CENTER WITH MANY LPS SERVERS
 MODELING WEBCHAT SERVICE CENTER WITH MANY LPS SERVERS Jiheng Zhang Oct 26, 211 Model and Motivation Server Pool with multiple LPS servers LPS Server K Arrival Buffer. Model and Motivation Server Pool with
MODELING WEBCHAT SERVICE CENTER WITH MANY LPS SERVERS Jiheng Zhang Oct 26, 211 Model and Motivation Server Pool with multiple LPS servers LPS Server K Arrival Buffer. Model and Motivation Server Pool with
arxiv: v2 [math.pr] 14 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v2 [math.pr] 14 Feb 2017 arxiv: v2 [math.pr] 14 Feb 2017](/thumbs/73/69157751.jpg) Large-scale Join-Idle-Queue system with general service times arxiv:1605.05968v2 [math.pr] 14 Feb 2017 Sergey Foss Heriot-Watt University EH14 4AS Edinburgh, UK and Novosibirsk State University s.foss@hw.ac.uk
Large-scale Join-Idle-Queue system with general service times arxiv:1605.05968v2 [math.pr] 14 Feb 2017 Sergey Foss Heriot-Watt University EH14 4AS Edinburgh, UK and Novosibirsk State University s.foss@hw.ac.uk
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
Universality of Power-of-$d$ Load Balancing in Many- Server Systems Mukherjee, D.; Borst, S.C.; van Leeuwaarden, J.S.H.; Whiting, P.A.
 Universality of Power-of-$d$ Load Balancing in Many- Server Systems Mukherjee, D.; Borst, S.C.; van Leeuwaarden, J.S.H.; Whiting, P.A. Published in: arxiv Published: //6 Document Version Accepted manuscript
Universality of Power-of-$d$ Load Balancing in Many- Server Systems Mukherjee, D.; Borst, S.C.; van Leeuwaarden, J.S.H.; Whiting, P.A. Published in: arxiv Published: //6 Document Version Accepted manuscript
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective. Ward Whitt. IEOR Department. Columbia University
 Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits. IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015
 Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
State Space Collapse in Many-Server Diffusion Limits of Parallel Server Systems. J. G. Dai. Tolga Tezcan
 State Space Collapse in Many-Server Diffusion imits of Parallel Server Systems J. G. Dai H. Milton Stewart School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia
State Space Collapse in Many-Server Diffusion imits of Parallel Server Systems J. G. Dai H. Milton Stewart School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia
BRAVO for QED Queues
 1 BRAVO for QED Queues Yoni Nazarathy, The University of Queensland Joint work with Daryl J. Daley, The University of Melbourne, Johan van Leeuwaarden, EURANDOM, Eindhoven University of Technology. Applied
1 BRAVO for QED Queues Yoni Nazarathy, The University of Queensland Joint work with Daryl J. Daley, The University of Melbourne, Johan van Leeuwaarden, EURANDOM, Eindhoven University of Technology. Applied
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Control of Fork-Join Networks in Heavy-Traffic
 in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
 UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
Designing load balancing and admission control policies: lessons from NDS regime
 Designing load balancing and admission control policies: lessons from NDS regime VARUN GUPTA University of Chicago Based on works with : Neil Walton, Jiheng Zhang ρ K θ is a useful regime to study the
Designing load balancing and admission control policies: lessons from NDS regime VARUN GUPTA University of Chicago Based on works with : Neil Walton, Jiheng Zhang ρ K θ is a useful regime to study the
Maximum pressure policies for stochastic processing networks
 Maximum pressure policies for stochastic processing networks Jim Dai Joint work with Wuqin Lin at Northwestern Univ. The 2011 Lunteren Conference Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) MPPs January 18, 2011 1 / 55 Outline
Maximum pressure policies for stochastic processing networks Jim Dai Joint work with Wuqin Lin at Northwestern Univ. The 2011 Lunteren Conference Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) MPPs January 18, 2011 1 / 55 Outline
Overflow Networks: Approximations and Implications to Call-Center Outsourcing
 Overflow Networks: Approximations and Implications to Call-Center Outsourcing Itai Gurvich (Northwestern University) Joint work with Ohad Perry (CWI) Call Centers with Overflow λ 1 λ 2 Source of complexity:
Overflow Networks: Approximations and Implications to Call-Center Outsourcing Itai Gurvich (Northwestern University) Joint work with Ohad Perry (CWI) Call Centers with Overflow λ 1 λ 2 Source of complexity:
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues
 Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
This lecture is expanded from:
 This lecture is expanded from: HIGH VOLUME JOB SHOP SCHEDULING AND MULTICLASS QUEUING NETWORKS WITH INFINITE VIRTUAL BUFFERS INFORMS, MIAMI Nov 2, 2001 Gideon Weiss Haifa University (visiting MS&E, Stanford)
This lecture is expanded from: HIGH VOLUME JOB SHOP SCHEDULING AND MULTICLASS QUEUING NETWORKS WITH INFINITE VIRTUAL BUFFERS INFORMS, MIAMI Nov 2, 2001 Gideon Weiss Haifa University (visiting MS&E, Stanford)
Operations Research Letters. Instability of FIFO in a simple queueing system with arbitrarily low loads
 Operations Research Letters 37 (2009) 312 316 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Operations Research Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/orl Instability of FIFO in a simple queueing
Operations Research Letters 37 (2009) 312 316 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Operations Research Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/orl Instability of FIFO in a simple queueing
Scheduling: Queues & Computation
 Scheduling: Queues Computation achieving baseline performance efficiently Devavrat Shah LIDS, MIT Outline Two models switched network and bandwidth sharing Scheduling: desirable performance queue-size
Scheduling: Queues Computation achieving baseline performance efficiently Devavrat Shah LIDS, MIT Outline Two models switched network and bandwidth sharing Scheduling: desirable performance queue-size
Servers. Rong Wu. Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Canada. Douglas G. Down
 MRRK-SRPT: a Scheduling Policy for Parallel Servers Rong Wu Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Canada Douglas G. Down Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University,
MRRK-SRPT: a Scheduling Policy for Parallel Servers Rong Wu Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Canada Douglas G. Down Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 22 12/09/2013. Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.7J Fall 213 Lecture 22 12/9/213 Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion Content. 1. G/G/1 queueing system 2. One dimensional reflection mapping
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.7J Fall 213 Lecture 22 12/9/213 Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion Content. 1. G/G/1 queueing system 2. One dimensional reflection mapping
Stein s Method for Steady-State Approximations: A Toolbox of Techniques
 Stein s Method for Steady-State Approximations: A Toolbox of Techniques Anton Braverman Based on joint work with Jim Dai (Cornell), Itai Gurvich (Cornell), and Junfei Huang (CUHK). November 17, 2017 Outline
Stein s Method for Steady-State Approximations: A Toolbox of Techniques Anton Braverman Based on joint work with Jim Dai (Cornell), Itai Gurvich (Cornell), and Junfei Huang (CUHK). November 17, 2017 Outline
State-dependent and Energy-aware Control of Server Farm
 State-dependent and Energy-aware Control of Server Farm Esa Hyytiä, Rhonda Righter and Samuli Aalto Aalto University, Finland UC Berkeley, USA First European Conference on Queueing Theory ECQT 2014 First
State-dependent and Energy-aware Control of Server Farm Esa Hyytiä, Rhonda Righter and Samuli Aalto Aalto University, Finland UC Berkeley, USA First European Conference on Queueing Theory ECQT 2014 First
Designing a Telephone Call Center with Impatient Customers
 Designing a Telephone Call Center with Impatient Customers with Ofer Garnett Marty Reiman Sergey Zeltyn Appendix: Strong Approximations of M/M/ + Source: ErlangA QEDandSTROG FIAL.tex M/M/ + M System Poisson
Designing a Telephone Call Center with Impatient Customers with Ofer Garnett Marty Reiman Sergey Zeltyn Appendix: Strong Approximations of M/M/ + Source: ErlangA QEDandSTROG FIAL.tex M/M/ + M System Poisson
Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types
 Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types Yue Hu (DRO, Columbia Business School) Joint work with Prof. Carri Chan (DRO, Columbia Business School) and Prof. Jing Dong (DRO, Columbia Business School) Motivation
Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types Yue Hu (DRO, Columbia Business School) Joint work with Prof. Carri Chan (DRO, Columbia Business School) and Prof. Jing Dong (DRO, Columbia Business School) Motivation
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1
 Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1 Mor Armony 2 Avishai Mandelbaum 3 June 25, 2008 Abstract Motivated by call centers,
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1 Mor Armony 2 Avishai Mandelbaum 3 June 25, 2008 Abstract Motivated by call centers,
Minimizing response times and queue lengths in systems of parallel queues
 Minimizing response times and queue lengths in systems of parallel queues Ger Koole Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Vrije Universiteit, De Boelelaan 1081a, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Minimizing response times and queue lengths in systems of parallel queues Ger Koole Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Vrije Universiteit, De Boelelaan 1081a, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
Distributed Join-the-Idle-Queue for Low Latency Cloud Services
 Distributed Join-the-Idle-Queue for Low Latency Cloud Services Chunpu Wang, Chen Feng, Member, IEEE and Julian Cheng, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv:79.9v [cs.dc] 8 Sep 7 Abstract Low latency is highly desirable
Distributed Join-the-Idle-Queue for Low Latency Cloud Services Chunpu Wang, Chen Feng, Member, IEEE and Julian Cheng, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv:79.9v [cs.dc] 8 Sep 7 Abstract Low latency is highly desirable
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Control of Many-Server Queueing Systems in Heavy Traffic. Gennady Shaikhet
 Control of Many-Server Queueing Systems in Heavy Traffic Gennady Shaikhet Control of Many-Server Queueing Systems in Heavy Traffic Research Thesis In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Control of Many-Server Queueing Systems in Heavy Traffic Gennady Shaikhet Control of Many-Server Queueing Systems in Heavy Traffic Research Thesis In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No., January February 23, pp. 228 243 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/.287/opre.2.29 23 INFORMS Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No., January February 23, pp. 228 243 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/.287/opre.2.29 23 INFORMS Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems
A Diffusion Approximation for Stationary Distribution of Many-Server Queueing System In Halfin-Whitt Regime
 A Diffusion Approximation for Stationary Distribution of Many-Server Queueing System In Halfin-Whitt Regime Mohammadreza Aghajani joint work with Kavita Ramanan Brown University APS Conference, Istanbul,
A Diffusion Approximation for Stationary Distribution of Many-Server Queueing System In Halfin-Whitt Regime Mohammadreza Aghajani joint work with Kavita Ramanan Brown University APS Conference, Istanbul,
Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing
 Submitted to Management Science manuscript MS-251-27 Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing Rishi Talreja, Ward Whitt Department of
Submitted to Management Science manuscript MS-251-27 Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing Rishi Talreja, Ward Whitt Department of
Tales of Time Scales. Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ
 Tales of Time Scales Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ New Book Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues Springer 2001 I won t
Tales of Time Scales Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ New Book Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues Springer 2001 I won t
Multi-layered Round Robin Routing for Parallel Servers
 Multi-layered Round Robin Routing for Parallel Servers Douglas G. Down Department of Computing and Software McMaster University 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, ON L8S 4L7, Canada downd@mcmaster.ca 905-525-9140
Multi-layered Round Robin Routing for Parallel Servers Douglas G. Down Department of Computing and Software McMaster University 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, ON L8S 4L7, Canada downd@mcmaster.ca 905-525-9140
Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers
 Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers Mor Armony Amy R. Ward 2 October 6, 2 Abstract In a call center, arriving customers must be routed to available
Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers Mor Armony Amy R. Ward 2 October 6, 2 Abstract In a call center, arriving customers must be routed to available
Asymptotic Coupling of an SPDE, with Applications to Many-Server Queues
 Asymptotic Coupling of an SPDE, with Applications to Many-Server Queues Mohammadreza Aghajani joint work with Kavita Ramanan Brown University March 2014 Mohammadreza Aghajanijoint work Asymptotic with
Asymptotic Coupling of an SPDE, with Applications to Many-Server Queues Mohammadreza Aghajani joint work with Kavita Ramanan Brown University March 2014 Mohammadreza Aghajanijoint work Asymptotic with
Queues with Many Servers and Impatient Customers
 MATHEMATICS OF OPERATIOS RESEARCH Vol. 37, o. 1, February 212, pp. 41 65 ISS 364-765X (print) ISS 1526-5471 (online) http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/moor.111.53 212 IFORMS Queues with Many Servers and Impatient
MATHEMATICS OF OPERATIOS RESEARCH Vol. 37, o. 1, February 212, pp. 41 65 ISS 364-765X (print) ISS 1526-5471 (online) http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/moor.111.53 212 IFORMS Queues with Many Servers and Impatient
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Section 1.2: A Single Server Queue
 Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/25/17. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
M/G/1 and Priority Queueing
 M/G/1 and Priority Queueing Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 5229: Advanced Compute Networks Outline PASTA M/G/1 Workload and FIFO Delay Pollaczek Khinchine Formula
M/G/1 and Priority Queueing Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 5229: Advanced Compute Networks Outline PASTA M/G/1 Workload and FIFO Delay Pollaczek Khinchine Formula
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
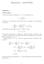 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Dynamic Matching Models
 Dynamic Matching Models Ana Bušić Inria Paris - Rocquencourt CS Department of École normale supérieure joint work with Varun Gupta, Jean Mairesse and Sean Meyn 3rd Workshop on Cognition and Control January
Dynamic Matching Models Ana Bušić Inria Paris - Rocquencourt CS Department of École normale supérieure joint work with Varun Gupta, Jean Mairesse and Sean Meyn 3rd Workshop on Cognition and Control January
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Technical Appendix for: When Promotions Meet Operations: Cross-Selling and Its Effect on Call-Center Performance
 Technical Appendix for: When Promotions Meet Operations: Cross-Selling and Its Effect on Call-Center Performance In this technical appendix we provide proofs for the various results stated in the manuscript
Technical Appendix for: When Promotions Meet Operations: Cross-Selling and Its Effect on Call-Center Performance In this technical appendix we provide proofs for the various results stated in the manuscript
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements
 The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour
 On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour This paper is motivated by two phenomena observed in many queueing systems in practice. The first is the partitioning of server capacity
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour This paper is motivated by two phenomena observed in many queueing systems in practice. The first is the partitioning of server capacity
Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network. Haifa Statistics Seminar May 5, 2008
 Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network Yoni Nazarathy Gideon Weiss Haifa Statistics Seminar May 5, 2008 1 Outline 1 Preview of Results 2 Introduction Queueing
Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network Yoni Nazarathy Gideon Weiss Haifa Statistics Seminar May 5, 2008 1 Outline 1 Preview of Results 2 Introduction Queueing
Gideon Weiss University of Haifa. Joint work with students: Anat Kopzon Yoni Nazarathy. Stanford University, MSE, February, 2009
 Optimal Finite Horizon Control of Manufacturing Systems: Fluid Solution by SCLP (separated continuous LP) and Fluid Tracking using IVQs (infinite virtual queues) Stanford University, MSE, February, 29
Optimal Finite Horizon Control of Manufacturing Systems: Fluid Solution by SCLP (separated continuous LP) and Fluid Tracking using IVQs (infinite virtual queues) Stanford University, MSE, February, 29
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 1, January February 2011, pp. 50 65 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5901 0050 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1100.0878 2011 INFORMS Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 1, January February 2011, pp. 50 65 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5901 0050 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1100.0878 2011 INFORMS Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service
Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network
 Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network Yoni Nazarathy a,1, Gideon Weiss a,1 a Department of Statistics, The University of Haifa, Mount Carmel 31905, Israel.
Positive Harris Recurrence and Diffusion Scale Analysis of a Push Pull Queueing Network Yoni Nazarathy a,1, Gideon Weiss a,1 a Department of Statistics, The University of Haifa, Mount Carmel 31905, Israel.
A Semiconductor Wafer
 M O T I V A T I O N Semi Conductor Wafer Fabs A Semiconductor Wafer Clean Oxidation PhotoLithography Photoresist Strip Ion Implantation or metal deosition Fabrication of a single oxide layer Etching MS&E324,
M O T I V A T I O N Semi Conductor Wafer Fabs A Semiconductor Wafer Clean Oxidation PhotoLithography Photoresist Strip Ion Implantation or metal deosition Fabrication of a single oxide layer Etching MS&E324,
Chapter 2. Poisson Processes. Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 Chapter 2. Poisson Processes Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Outline Introduction to Poisson Processes Definition of arrival process Definition
Chapter 2. Poisson Processes Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Outline Introduction to Poisson Processes Definition of arrival process Definition
ANALYSIS OF THE LAW OF THE ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR THE IDLE TIME OF A CUSTOMER IN MULTIPHASE QUEUES
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 66 No. 2 2011, 183-190 ANALYSIS OF THE LAW OF THE ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR THE IDLE TIME OF A CUSTOMER IN MULTIPHASE QUEUES Saulius Minkevičius
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 66 No. 2 2011, 183-190 ANALYSIS OF THE LAW OF THE ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR THE IDLE TIME OF A CUSTOMER IN MULTIPHASE QUEUES Saulius Minkevičius
Linear Model Predictive Control for Queueing Networks in Manufacturing and Road Traffic
 Linear Model Predictive Control for ueueing Networks in Manufacturing and Road Traffic Yoni Nazarathy Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne. Joint work with: Erjen Lefeber (manufacturing), Hai
Linear Model Predictive Control for ueueing Networks in Manufacturing and Road Traffic Yoni Nazarathy Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne. Joint work with: Erjen Lefeber (manufacturing), Hai
Performance analysis of queueing systems with resequencing
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI SALERNO Dipartimento di Matematica Dottorato di Ricerca in Matematica XIV ciclo - Nuova serie Performance analysis of queueing systems with resequencing Candidato: Caraccio Ilaria
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI SALERNO Dipartimento di Matematica Dottorato di Ricerca in Matematica XIV ciclo - Nuova serie Performance analysis of queueing systems with resequencing Candidato: Caraccio Ilaria
A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers
 UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS. Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ Murray Hill, NJ 07974
 LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS by Daniel P. Heyman Ward Whitt Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ 07701 Murray Hill, NJ 07974 May 11, 1988 ABSTRACT We study the
LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS by Daniel P. Heyman Ward Whitt Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ 07701 Murray Hill, NJ 07974 May 11, 1988 ABSTRACT We study the
A Joining Shortest Queue with MAP Inputs
 The Eighth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 09) Zhangjiajie, China, September 20 22, 2009 Copyright 2009 ORSC & APORC, pp. 25 32 A Joining Shortest Queue with
The Eighth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 09) Zhangjiajie, China, September 20 22, 2009 Copyright 2009 ORSC & APORC, pp. 25 32 A Joining Shortest Queue with
Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem
 Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Convexity Properties of Loss and Overflow Functions
 Convexity Properties of Loss and Overflow Functions Krishnan Kumaran?, Michel Mandjes y, and Alexander Stolyar? email: kumaran@lucent.com, michel@cwi.nl, stolyar@lucent.com? Bell Labs/Lucent Technologies,
Convexity Properties of Loss and Overflow Functions Krishnan Kumaran?, Michel Mandjes y, and Alexander Stolyar? email: kumaran@lucent.com, michel@cwi.nl, stolyar@lucent.com? Bell Labs/Lucent Technologies,
Strategic Dynamic Jockeying Between Two Parallel Queues
 Strategic Dynamic Jockeying Between Two Parallel Queues Amin Dehghanian 1 and Jeffrey P. Kharoufeh 2 Department of Industrial Engineering University of Pittsburgh 1048 Benedum Hall 3700 O Hara Street Pittsburgh,
Strategic Dynamic Jockeying Between Two Parallel Queues Amin Dehghanian 1 and Jeffrey P. Kharoufeh 2 Department of Industrial Engineering University of Pittsburgh 1048 Benedum Hall 3700 O Hara Street Pittsburgh,
Statistics 150: Spring 2007
 Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour
 On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour Bin Hu Saif Benjaafar Department of Operations and Management Science, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan at Ann Arbor,
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour Bin Hu Saif Benjaafar Department of Operations and Management Science, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan at Ann Arbor,
Scheduling I. Today. Next Time. ! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms. ! Advanced topics on scheduling
 Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue
 A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue Robert C. Hampshire Heinz School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University hamp@andrew.cmu.edu William A. Massey Department of
A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue Robert C. Hampshire Heinz School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University hamp@andrew.cmu.edu William A. Massey Department of
Periodic Load Balancing
 Queueing Systems 0 (2000)?? 1 Periodic Load Balancing Gisli Hjálmtýsson a Ward Whitt a a AT&T Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Building 103, Florham Park, NJ 07932-0971 E-mail: {gisli,wow}@research.att.com Queueing
Queueing Systems 0 (2000)?? 1 Periodic Load Balancing Gisli Hjálmtýsson a Ward Whitt a a AT&T Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Building 103, Florham Park, NJ 07932-0971 E-mail: {gisli,wow}@research.att.com Queueing
Classical Queueing Models.
 Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Critical Thresholds for Dynamic Routing in Queueing Networks
 Queueing Systems 42, 297 316, 2002 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Critical Thresholds for Dynamic Routing in Queueing Networks YIH-CHOUNG TEH Department of Statistics,
Queueing Systems 42, 297 316, 2002 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Critical Thresholds for Dynamic Routing in Queueing Networks YIH-CHOUNG TEH Department of Statistics,
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries
 A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries Dan-Cristian Tomozei Joint work with Jean-Yves Le Boudec CCW, Sedona AZ, 07/11/2012 Demand Response by Quantity = distribution network operator may interrupt
A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries Dan-Cristian Tomozei Joint work with Jean-Yves Le Boudec CCW, Sedona AZ, 07/11/2012 Demand Response by Quantity = distribution network operator may interrupt
Online Supplement to Creating Work Breaks From Available Idleness
 Online Supplement to Creating Work Breaks From Available Idleness Xu Sun and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University New York, NY, 127 September 7,
Online Supplement to Creating Work Breaks From Available Idleness Xu Sun and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University New York, NY, 127 September 7,
arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 5 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 5 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 5 Aug 2013](/thumbs/86/94917496.jpg) BRAVO for many-server QED systems with finite buffers Daryl J. Daley, Johan S.H. van Leeuwaarden, Yoni Nazarathy arxiv:38.933v [math.pr] 5 Aug 23 September 7, 28 Abstract This paper demonstrates the occurrence
BRAVO for many-server QED systems with finite buffers Daryl J. Daley, Johan S.H. van Leeuwaarden, Yoni Nazarathy arxiv:38.933v [math.pr] 5 Aug 23 September 7, 28 Abstract This paper demonstrates the occurrence
Erlang-C = M/M/N. agents. queue ACD. arrivals. busy ACD. queue. abandonment BACK FRONT. lost calls. arrivals. lost calls
 Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
Topics in queueing theory
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 217 Topics in queueing theory Keguo Huang Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 217 Topics in queueing theory Keguo Huang Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd
λ 2 1 = 2 = 2 2 2P 1 =4P 2 P 0 + P 1 + P 2 =1 P 0 =, P 1 =, P 2 = ρ 1 = P 1 + P 2 =, ρ 2 = P 1 + P 2 =
 Urban Operations Research Compiled by James S. Kang Fall 001 Quiz Solutions 1//001 Problem 1 (Larson, 001) 1 (a) One is tempted to say yes by setting ρ = Nµ = =.But = is not the rate at which customers
Urban Operations Research Compiled by James S. Kang Fall 001 Quiz Solutions 1//001 Problem 1 (Larson, 001) 1 (a) One is tempted to say yes by setting ρ = Nµ = =.But = is not the rate at which customers
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement
 Submitted to imanufacturing & Service Operations Management manuscript MSOM-11-370.R3 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement (Authors names blinded
Submitted to imanufacturing & Service Operations Management manuscript MSOM-11-370.R3 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement (Authors names blinded
Estimation of arrival and service rates for M/M/c queue system
 Estimation of arrival and service rates for M/M/c queue system Katarína Starinská starinskak@gmail.com Charles University Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Department of Probability and Mathematical Statistics
Estimation of arrival and service rates for M/M/c queue system Katarína Starinská starinskak@gmail.com Charles University Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Department of Probability and Mathematical Statistics
EE 368. Weeks 3 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
Queueing systems. Renato Lo Cigno. Simulation and Performance Evaluation Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1
 Queueing systems Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Queues A Birth-Death process is well modeled by a queue Indeed queues can be used to
Queueing systems Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Queues A Birth-Death process is well modeled by a queue Indeed queues can be used to
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
SCHEDULING PARALLEL SERVERS IN THE NONDEGENERATE SLOWDOWN DIFFUSION REGIME: ASYMPTOTIC OPTIMALITY RESULTS 1
 The Annals of Applied Probability 214, Vol. 24, No. 2, 76 81 DOI: 1.1214/13-AAP935 Institute of Mathematical Statistics, 214 SCHEDULING PARALLEL SERVERS IN THE NONDEGENERATE SLOWDOWN DIFFUSION REGIME:
The Annals of Applied Probability 214, Vol. 24, No. 2, 76 81 DOI: 1.1214/13-AAP935 Institute of Mathematical Statistics, 214 SCHEDULING PARALLEL SERVERS IN THE NONDEGENERATE SLOWDOWN DIFFUSION REGIME:
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
The Behavior of a Multichannel Queueing System under Three Queue Disciplines
 The Behavior of a Multichannel Queueing System under Three Queue Disciplines John K Karlof John Jenkins November 11, 2002 Abstract In this paper we investigate a multichannel channel queueing system where
The Behavior of a Multichannel Queueing System under Three Queue Disciplines John K Karlof John Jenkins November 11, 2002 Abstract In this paper we investigate a multichannel channel queueing system where
Retrial queue for cloud systems with separated processing and storage units
 Retrial queue for cloud systems with separated processing and storage units Tuan Phung-Duc Department of Mathematical and Computing Sciences Tokyo Institute of Technology Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Retrial queue for cloud systems with separated processing and storage units Tuan Phung-Duc Department of Mathematical and Computing Sciences Tokyo Institute of Technology Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Single-Server Service-Station (G/G/1)
 Service Engineering July 997 Last Revised January, 006 Single-Server Service-Station (G/G/) arrivals queue 000000000000 000000000000 departures Arrivals A = {A(t), t 0}, counting process, e.g., completely
Service Engineering July 997 Last Revised January, 006 Single-Server Service-Station (G/G/) arrivals queue 000000000000 000000000000 departures Arrivals A = {A(t), t 0}, counting process, e.g., completely
Chapter 6 Queueing Models. Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation
 Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Service Level Agreements in Call Centers: Perils and Prescriptions
 Service Level Agreements in Call Centers: Perils and Prescriptions Joseph M. Milner Joseph L. Rotman School of Management University of Toronto Tava Lennon Olsen John M. Olin School of Business Washington
Service Level Agreements in Call Centers: Perils and Prescriptions Joseph M. Milner Joseph L. Rotman School of Management University of Toronto Tava Lennon Olsen John M. Olin School of Business Washington
Continuous Time Processes
 page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
