NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. High Aitken Nucleus Concentrations above Cloud Tops in the Arctic
|
|
|
- Oliver Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 779 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE High Aitken Nucleus Concentrations above Cloud Tops in the Arctic TIMOTHY J. GARRETT* AND PETER V. HOBBS Atmospheric Sciences Department, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington LAWRENCE F. RADKE National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado 15 December 2000 and 22 April 2001 ABSTRACT Airborne measurements in the Arctic in spring show large increases in the concentrations of particles with diameters below about 0.1 m just above the tops of stratus clouds when the water-vapor mixing ratio is relatively high in these regions. Low temperatures and low particle surface areas may also favor the appearance of these particles. Particles produced above stratus clouds could be a widespread source of aerosol in the Arctic. 1. Introduction Field measurements in middle latitudes have shown that, under appropriate conditions, large concentrations of small (Aitken nuclei) particles can be present above the tops of strauform clouds (Hegg et al. 1990) and in the vicinity of convective clouds (Radke and Hobbs 1991; Hudson and Frisbie 1991; Hudson 1993; Perry and Hobbs 1994). It has been suggested that particles generated near the tops of large convective towers in the Tropics are transported poleward, sink in the subtropics, and thereby supply large numbers of particles to the subtropical troposphere (Raes et al. 1993). Here we report on measurements of high Aitken nucleus concentrations above the tops of stratus clouds in the Arctic, and the conditions that appear to favor their formation. 2. Instrumentation All of the measurements to be described were obtained aboard the University of Washington s (UW) Convair-580 research aircraft in the Arctic in spring * Current affiliation: Department of Meteorology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah. The National Center for Atmospheric Research is sponsored by the National Science Foundation. Corresponding author address: Peter V. Hobbs, Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Box , Seattle, WA phobbs@atmos.washington.edu 2000 as part of the First International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project (ISCCP) Regional Experiment- Arctic Cloud Experiment/Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean (FIRE-ACE/SHEBA) field project (Curry et al. 2000). Aitken nucleus concentrations (defined here as the total concentration of particles with diameters between about m) were measured aboard the UW Convair- 580 using a Thermo Systems Incorporated (TSI) condensation nucleus counter (model 3760). The TSI 3760 uses a laser diode optical particle counter that measures the total number concentration of particles with sizes larger than m diameter, but because of the design of the inlet to this counter particles larger than about 0.3- m diameter were not measured. The inlet to the TSI 3760 on the Convair-580 is designed to remove cloud droplets from the airflow into the laser cavity by passing the airflow through a cyclone separator. The separator removes droplets larger than 5- m diameter from the air flow via impaction, leaving just cloud interstitial aerosol for detection by the TSI Weber et al. (1998) suggested that spuriously high concentrations of Aitken nuclei might be measured from an aircraft flying in clouds due to the fragmentation of cloud drops in aerosol inlets. There is no evidence that this occurred in the measurements described here. Indeed, evidence is to the contrary: in ascent descent porpoise maneuvers in and out of cloud top, there were no significant changes in Aitken nucleus concentrations. A Particle Measuring Systems (PMS) Passive Cavity Aerosol Spectrometer Probe (PCASP) 100X instrument was used to measure size distributions of particles from 0.1- to 3- m diameter. The PCASP was routinely cal American Meteorological Society
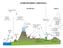
2 780 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 59 ibrated with glass beads and latex spheres. The PCASP dries the sampled aerosol by heating the airstream C before sampling. However, within clouds, droplets are only partially evaporated by the PCASP; therefore the remnants of cloud droplets may artificially enhance the measured concentrations of particles in the tail ( 1 m diameter) of the aerosol spectrum. For this reason, we neglected the contributions that particles 1 m diameter made to the total particle concentrations measured by the PCASP in clouds. A PMS forward scattering spectrometer probe (FSSP) 100 forward light-scattering instrument was used to measure particles and droplets from 2- to 47- m diameters. The total surface area of particles (and droplets in clouds) was derived from the PCASP and FSSP-100 measurements assuming spherical particles. The estimated uncertainty in the surface area measurements is 15% within cloud and 50% out of cloud. The water vapor mixing ratio was measured with an Ophir Corporation model IR-2000 infrared optical hygrometer. This instrument uses the differential water vapor absorption between two beams, one absorbing (2.665 m) and the other nonabsorbing (2.45 m), to directly measure the density of water vapor. The instrument operates at a frequency of 20 Hz with a resolution of better than 1% for water vapor contents greaterthan2gm 3. A reverse-flow inlet is used to prevent liquid water from entering the instrument. However, both beams are absorbed equally by any liquid water that might enter the instrument. Cerni (1994) provides details on the Ophir instrument, which we have used successfully for airborne measurements for many years (e.g., Perry and Hobbs 1996). 3. Results In middle latitudes the cloud-topped marine boundary layer is generally capped by an increase in temperature (i.e., a temperature inversion) and a decrease in dewpoint (Fig. 1a). The Arctic is unusual in that quite frequently both temperature and humidity increase with height over distances of several hundreds of meters above the tops of low-level stratus clouds (Fig. 1b). Increases in humidity above arctic stratus clouds were observed frequently aboard the UW Convair-580 research aircraft during the FIRE ACE/SHEBA field study. Between 20 May and 24 June 2000, 47 vertical profiles of stratus clouds were made in 23 flights. Twenty-seven of these profiles were characterized by increases in humidity over distances of several hundred meters just above the cloud-topped boundary layer, with the watervapor mixing ratio 1 2gkg 1 higher within these regions than in the boundary layer. In each of these 27 cases, there was a significant increase in Aitken nucleus concentrations within the zone of high humidity. In 18 of the remaining 20 cases where there was not an increase in humidity above cloud top, there was also not an increase in Aitken nuclei. In the two cases where there was FIG. 1. Schematics of typical profiles of temperature (T) and dewpoint (T d ) above stratus clouds in (a) midlatitudes and (b) the Arctic. an increase in Aitken nuclei above cloud top in the absence of an increase in humidity, the light-scattering coefficient (indicative of larger particles) was also elevated. This suggests that in these two cases both small and larger particles were enhanced by the (coincidental) occurrence of an arctic haze layer near cloud top. Figure 2 shows three examples of large increases in Aitken nucleus concentrations above the tops of arctic stratus clouds. The most frequently observed scenario was similar to that shown in Fig. 2(i). Here the Aitken nucleus concentration is highest in the temperature inversion immediately above cloud top, where the Aitken nuclei are highly correlated with the water vapor mixing ratio. Since there was not a significant increase in the concentration of particles 0.1 m diameter just above cloud top, the increase in Aitken nuclei was due to enhanced concentrations of particles 0.1 m diameter. A similar scenario is shown in Fig. 2(ii), where the Aitken nuclei are again well-correlated with the water-vapor
3 781 FIG. 2. Three examples of elevated Aitken nucleus concentrations above the tops of arctic stratus clouds. The panels marked a) on the left-hand side show vertical profiles of water-vapor mixing ratio (dashed line) and temperature (solid line). The panels marked b) on the right-hand side show vertical profiles of Aitken nucleus concentrations (solid line), particle concentrations in the accumulation mode (dashed line), and the surface area of the hydrated particles (dotted line). The shaded region represents stratus cloud.
4 782 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 59 FIG. 3. Three examples where elevated Aitken nucleus concentrations were not observed above the tops of arctic stratus clouds. See caption to Fig. 2 for legend.
5 783 mixing ratio, particularly between 0.2 and 0.8 km in altitude. Figure 2(iii) shows another case where high Aitken nucleus concentrations were present above cloud top. In this case, however, the water-vapor mixing ratio increased steadily with altitude, rather than attaining a local maximum above cloud top. Figure 3 shows three cases where high Aitken nucleus concentrations were not observed above cloud top. In each of these three cases, the water vapor mixing ratio was significantly lower than those measured near cloud top for the three cases shown in Fig. 2 where elevated Aitken nucleus concentrations were observed. 4. Discussion The mechanism that has been most commonly proposed to explain the occurrence of high concentrations of small particles in humid air is homogeneous-bimolecular nucleation (HBN) of sulfuric acid solution droplets from H 2 SO 4 and H 2 O vapor (e.g., Itoh et al. 1977; Middleton and King 1978; Roedel 1979; Shaw 1989; Hegg et al. 1990; Raes et al. 1993; Perry and Hobbs 1994; Saxena and Grovenstein 1994). The measurements that we obtained in the Arctic are not sufficient to determine whether HBN, or other possible mechanisms, were responsible for the high particle concentrations above cloud tops since, apart from H 2 O vapor, we did not measure the relevant chemical species. However, the physical conditions under which the high particle concentrations occurred are, in general, consistent with HBN. For example, HBN theory predicts that new particle formation is favored by high humidities, low temperatures, a small preexisting surface area of particles, and high actinic flux: conditions that are common above arctic stratus clouds in spring and summer. Specifically, Figs. 2(i) and 2(ii) show high correlations between Aitken nucleus concentrations above cloud top and the water-vapor mixing ratio. In Fig. 2(iii), the Aitken nucleus concentrations above cloud top peak in a region of increasing water-vapor mixing ratio, but then decrease with increasing altitude above about 0.15 km, even though the water-vapor mixing ratio continues to increase. In terms of HBN theory this could be due to the continual increase of temperature with height shown in Fig. 2(iii). In Figs. 2(i) and 2(iii) the surface areas of the particles are small ( 100 m 2 cm 3 )in the regions where the Aitken nucleus concentrations peak. However, Fig. 2(ii) shows a layer of high Aitken nucleus concentrations within the upper 200 m of the cloud layer itself, where particle surface-area concentrations were m 2 cm 3 (due mainly to supermicron cloud droplets). This is difficult to explain in terms of HBN theory, since high particle surface areas provide a large sink for H 2 SO 4 vapor and therefore limits the nucleation of new particles. However, 5 min prior to the measurements shown in Fig. 2(ii), the cloud top was 200 m lower (at 0.3 km). Therefore, the high Aitken nucleus concentrations shown in Fig. 2(ii) could have formed in the humidity inversion prior to the formation of cloudy air in the moist layer between 0.3 and 0.5 km. In the cases where Aitken nucleus concentrations were not noticeably enhanced above cloud tops (Fig. 3), the water vapor was significantly lower than those measured near cloud top where elevated Aitken nucleus concentrations were measured (Fig. 2). It appears therefore that enhanced humidities are crucial for the formation of high particle concentrations above cloud tops in the Arctic. Regardless of the mechanism(s) responsible for high Aitken nucleus concentrations above cloud tops, the measurements reported here show that this phenomenon is common above the tops of arctic stratus clouds in spring. Since stratus clouds are ubiquitous in the Arctic, this could be a widespread source of small particles in this region. Acknowledgments. This research was supported by NASA Grants NAG1-2079, NCC5-326, NAS , and NAG REFERENCES Cerni, T. A., 1994: An infrared hygrometer for atmospheric research and routine monitoring. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 11, Curry, J. A., and Coauthors, 2000: FIRE arctic clouds experiment. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 81, Hegg, D. A., L. F. Radke, and P. V. Hobbs, 1990: Particle production associated with marine clouds. J. Geophys. Res., 95, Hudson, J. G., 1993: Cloud condensation nuclei near marine cumulus. J. Geophys. Res., 98, , and P. R. Frisbie, 1991: Cloud condensation nuclei near marine stratus. J. Geophys. Res., 96, Itoh, M., K. Takahashi, and M. Kasahara, 1977: The temperature dependence of nucleation of sulfuric acid-water mixture in air. J. Aerosol Sci., 8, Middleton, P., and C. S. Kiang, 1978: A kinetic aerosol model for the formation and growth of secondary sulfuric acid particles. J. Aerosol Sci., 9, Perry, K. D., and P. V. Hobbs, 1994: Further evidence for particle nucleation in clear air adjacent to marine cumulus clouds. J. Geophys. Res., 99, , and, 1996: Influences of isolated cumulus clouds on the humidity of their surroundings. J. Atmos. Sci., 53, Radke, C. F., and P. V. Hobbs, 1991: Humidity and particle fields around some small cumulus clouds. J. Atmos. Sci., 48, Raes, F., R. van Dingenen, J. Wilson, and A. Saltelli, 1993: Cloud condensation nuclei from dimethylsulfide in the natural marine boundary layer: Remote vs. in situ production. Dimethylsulfide Oceans, Atmosphere and Climate, G. Restelli and G. Angeletti, Eds., Kluwer Academic, Roedel, W., 1979: Measurement of sulfuric acid saturated vapor pressure: Implications for aerosol formation by heteromolecular nucleation. J. Aerosol Sci., 10, Saxena, V. K., and J. D. Grovenstein, 1994: The role of clouds in the enhancement of cloud condensation nuclei concentrations. Atmos. Res., 31, Shaw, G. E., 1989: Production of condensation nuclei in clean air by nucleation of H 2 SO 4. Atmos. Environ., 23, Weber, R. J., A. D. Clarke, M. Litchy, J. Li, G. Kok, R. D. Chillawski, and P. H. McMurray, 1998: Spurious aerosol measurements when sampling from aircraft in the vicinity of clouds. J. Geophys. Res., 103,
In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius
 In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius A. S. Frisch and G. Feingold Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere National Oceanic and Atmospheric
In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius A. S. Frisch and G. Feingold Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Impact of new particle formation on the concentrations of aerosols and cloud condensation nuclei around Beijing
 ! JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116, D19208, doi:10.1029/2011jd016025, 2011!! Impact of new particle formation on the concentrations of aerosols and cloud condensation nuclei around Beijing H.
! JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116, D19208, doi:10.1029/2011jd016025, 2011!! Impact of new particle formation on the concentrations of aerosols and cloud condensation nuclei around Beijing H.
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change
 Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Clean air slots amid dense atmospheric pollution in southern Africa
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D13, 8490, doi:10.1029/2002jd002156, 2003 Clean air slots amid dense atmospheric pollution in southern Africa Peter V. Hobbs Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D13, 8490, doi:10.1029/2002jd002156, 2003 Clean air slots amid dense atmospheric pollution in southern Africa Peter V. Hobbs Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS OF MIXED- PHASE CLOUD FORMATION
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS OF MIXED- PHASE CLOUD FORMATION Takuya Tajiri 1*, Katsuya Yamashita 1, Masataka Murakami 1, Narihiro Orikasa 1, Atsushi Saito 1, Tomohiro Nagai 1, Tetsu Sakai 1, and Hiroshi Ishimoto
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS OF MIXED- PHASE CLOUD FORMATION Takuya Tajiri 1*, Katsuya Yamashita 1, Masataka Murakami 1, Narihiro Orikasa 1, Atsushi Saito 1, Tomohiro Nagai 1, Tetsu Sakai 1, and Hiroshi Ishimoto
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CLOUD DROPLET AND AEROSOL NUMBER CONCENTRATIONS FOR CLIMATE MODELS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY, VOL. 16, 94 1-946 (1 996) 551.521.1 l(4) THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CLOUD DROPLET AND AEROSOL NUMBER CONCENTRATIONS FOR CLIMATE MODELS 1. GULTEPE and G. A. ISAAC Cloud
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY, VOL. 16, 94 1-946 (1 996) 551.521.1 l(4) THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CLOUD DROPLET AND AEROSOL NUMBER CONCENTRATIONS FOR CLIMATE MODELS 1. GULTEPE and G. A. ISAAC Cloud
Duncan Axisa*, Amit Teller, Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Roelof Burger National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), Boulder CO USA
 J12.1 AEROSOL - CLOUD INTERACTIONS OVER ISTANBUL, TURKEY AND CENTRAL SAUDI ARABIA Duncan Axisa*, Amit Teller, Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Roelof Burger National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR),
J12.1 AEROSOL - CLOUD INTERACTIONS OVER ISTANBUL, TURKEY AND CENTRAL SAUDI ARABIA Duncan Axisa*, Amit Teller, Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Roelof Burger National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR),
CHAPTER 8. AEROSOLS 8.1 SOURCES AND SINKS OF AEROSOLS
 1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
8. Clouds and Climate
 8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
The Retrieval of Stratus Cloud Droplet Effective Radius with Cloud Radars
 JUNE 00 FRISCH ET AL. 835 The Retrieval of Stratus Cloud Droplet Effective Radius with Cloud Radars SHELBY FRISCH NOAA/Environmental Technology Laboratory, Boulder, Colorado, and Colorado State University,
JUNE 00 FRISCH ET AL. 835 The Retrieval of Stratus Cloud Droplet Effective Radius with Cloud Radars SHELBY FRISCH NOAA/Environmental Technology Laboratory, Boulder, Colorado, and Colorado State University,
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Figure 1: A summary of the validation strategy for C3VP incorporating ground truth (GT) and physical validation (PV).
 3.3 THE CANADIAN CLOUDSAT CALIPSO VALIDATION PROJECT:EVALUATION OF SENSITIVITY AND SUB-PIXEL VARIABILITY OF CLOUDSAT DATA PRODUCTS D. Hudak 1 *, H. Barker 1, K. Strawbridge 1, M. Wolde 2, A. Kankiewicz
3.3 THE CANADIAN CLOUDSAT CALIPSO VALIDATION PROJECT:EVALUATION OF SENSITIVITY AND SUB-PIXEL VARIABILITY OF CLOUDSAT DATA PRODUCTS D. Hudak 1 *, H. Barker 1, K. Strawbridge 1, M. Wolde 2, A. Kankiewicz
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
Precipitation Formation, and RADAR Equation by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio Stel (1)
 PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics Precipitation Formation, and RADAR Equation by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics Precipitation Formation, and RADAR Equation by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
Extinction. Aerosols
 Extinction Extinction is the loss of energy out of a beam of radiation as it propagates. Extinction = absorption + scattering Extinction cross section analogous to the cross-sectional area of absorbers
Extinction Extinction is the loss of energy out of a beam of radiation as it propagates. Extinction = absorption + scattering Extinction cross section analogous to the cross-sectional area of absorbers
Investigations into free tropospheric new particle formation in the central Canadian arctic during the winter/spring transition as part of TOPSE
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. 0, XXXX, doi:10.1029/2002jd002239, 2002 Investigations into free tropospheric new particle formation in the central Canadian arctic during the winter/spring
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. 0, XXXX, doi:10.1029/2002jd002239, 2002 Investigations into free tropospheric new particle formation in the central Canadian arctic during the winter/spring
Cloud-aerosol interactions during autumn over the. Beaufort Sea
 Cloud-aerosol interactions during autumn over the Beaufort Sea James O. Pinto and Judith A. Curry Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department of Aerospace Engineering Sciences University of
Cloud-aerosol interactions during autumn over the Beaufort Sea James O. Pinto and Judith A. Curry Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department of Aerospace Engineering Sciences University of
Importance of vertical velocity variations in the cloud droplet nucleation process of marine stratus clouds
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jd004922, 2005 Importance of vertical velocity variations in the cloud droplet nucleation process of marine stratus clouds Yiran Peng, 1,2 Ulrike
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jd004922, 2005 Importance of vertical velocity variations in the cloud droplet nucleation process of marine stratus clouds Yiran Peng, 1,2 Ulrike
Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes. Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez
 Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093, USA *To whom correspondence
Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093, USA *To whom correspondence
New Particle Formation in the UT/LS:
 New Particle Formation in the UT/LS: Project Overview and Preliminary Results Li-Hao Young 1, David Benson 1, William Montanaro 1, James C. Wilson 2, and Shan-Hu Lee 1 1 Kent State University 2 University
New Particle Formation in the UT/LS: Project Overview and Preliminary Results Li-Hao Young 1, David Benson 1, William Montanaro 1, James C. Wilson 2, and Shan-Hu Lee 1 1 Kent State University 2 University
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model
 Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
HARP Assessment of Uncertainty
 HARP Assessment of Uncertainty The HIAPER Airborne Radiation Package (HARP) was designed to produce accurate measurements of actinic flux and irradiance. The Atmospheric Radiation Group (ARG) at the University
HARP Assessment of Uncertainty The HIAPER Airborne Radiation Package (HARP) was designed to produce accurate measurements of actinic flux and irradiance. The Atmospheric Radiation Group (ARG) at the University
Physio-chemical and Optical Characterization of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol: Implications for Assessing Global Effects
 Physio-chemical and Optical Characterization of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol: Implications for Assessing Global Effects GLOBE Pollution Southern Japan TRACE-P, 2001 Dust Antony Clarke, University
Physio-chemical and Optical Characterization of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol: Implications for Assessing Global Effects GLOBE Pollution Southern Japan TRACE-P, 2001 Dust Antony Clarke, University
Final Review Meteorology
 Final Review Meteorology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is an example of climate? a. A sudden snowstorm resulted
Final Review Meteorology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is an example of climate? a. A sudden snowstorm resulted
Size-distribution of submicron aerosol particles over the Indian Ocean during IFP-99 of INDOEX
 Size-distribution of submicron aerosol particles over the Indian Ocean during IFP-99 of INDOEX P. Murugavel, S. D. Pawar and A. K. Kamra* Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pashan, Pune 411 008,
Size-distribution of submicron aerosol particles over the Indian Ocean during IFP-99 of INDOEX P. Murugavel, S. D. Pawar and A. K. Kamra* Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pashan, Pune 411 008,
Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence)
 1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
SOLAR INFLUENCE ON EARTH S CLIMATE. 1. Introduction
 SOLAR INFLUENCE ON EARTH S CLIMATE NIGEL MARSH and HENRIK SVENSMARK Danish Space Research Institute, Juliane Maries Vej 30, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark Abstract. An increasing number of studies indicate
SOLAR INFLUENCE ON EARTH S CLIMATE NIGEL MARSH and HENRIK SVENSMARK Danish Space Research Institute, Juliane Maries Vej 30, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark Abstract. An increasing number of studies indicate
WEATHER. Review Note Cards
 WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
WEATHER Review Note Cards Thermometer Weather instrument that measures air temperature Units include F, C, and K ESRT 13 Sling Psychrometer Weather instrument that measures relative humidity and dewpoint
Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature
 Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Influences on Insolation Absorption Reflection/Scattering Transmission 1 Absorption An absorber gains energy
Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Influences on Insolation Absorption Reflection/Scattering Transmission 1 Absorption An absorber gains energy
A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time
 WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
Mystery of ice multiplication in warm based precipitating shallow cumulus clouds
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042440, 2010 Mystery of ice multiplication in warm based precipitating shallow cumulus clouds Jiming Sun, 1,2 Parisa
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042440, 2010 Mystery of ice multiplication in warm based precipitating shallow cumulus clouds Jiming Sun, 1,2 Parisa
Evidence that Nitric Acid Increases Relative Humidity in Low-Temperature Cirrus
 Supporting Online Material for: Evidence that Nitric Acid Increases Relative Humidity in Low-Temperature Cirrus Clouds R. S. Gao, P. J. Popp, D. W. Fahey, T. P. Marcy, R. L. Herman, E. M. Weinstock, D.
Supporting Online Material for: Evidence that Nitric Acid Increases Relative Humidity in Low-Temperature Cirrus Clouds R. S. Gao, P. J. Popp, D. W. Fahey, T. P. Marcy, R. L. Herman, E. M. Weinstock, D.
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics
 An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
CU Airborne Multi AXis DOAS
 CU Airborne Multi AXis DOAS Detection of iodine oxide and glyoxal in the tropical free troposphere B. Dix (1), S. Baidar (1,2), J. Bresch (3), R. Volkamer (1,2) 1 Dep. of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University
CU Airborne Multi AXis DOAS Detection of iodine oxide and glyoxal in the tropical free troposphere B. Dix (1), S. Baidar (1,2), J. Bresch (3), R. Volkamer (1,2) 1 Dep. of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University
Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models
 Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models John H. Seinfeld, Principal Investigator California Institute of Technology 1200 E. California Blvd., M/C 210-41 Pasadena, CA 91125 phone:
Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models John H. Seinfeld, Principal Investigator California Institute of Technology 1200 E. California Blvd., M/C 210-41 Pasadena, CA 91125 phone:
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Characterization of ice-particle concentration, size,
 Small Ice Particles in Tropospheric Clouds: Fact or Artifact? Airborne Icing Instrumentation Evaluation Experiment by A. V. Ko r o l e v, E. F. Em e ry, J. W. Str app, S. G. Co b e r, G. A. Is a a c, M.
Small Ice Particles in Tropospheric Clouds: Fact or Artifact? Airborne Icing Instrumentation Evaluation Experiment by A. V. Ko r o l e v, E. F. Em e ry, J. W. Str app, S. G. Co b e r, G. A. Is a a c, M.
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study
 The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
Lecture 3. Background materials. Planetary radiative equilibrium TOA outgoing radiation = TOA incoming radiation Figure 3.1
 Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Final Exam: Monday March 17 3:00-6:00 pm (here in Center 113) Slides from Review Sessions are posted on course website:
 Final Exam: Monday March 17 3:00-6:00 pm (here in Center 113) 35% of total grade Format will be all multiple choice (~70 questions) Final exam will cover entire course - material since 2 nd midterm weighted
Final Exam: Monday March 17 3:00-6:00 pm (here in Center 113) 35% of total grade Format will be all multiple choice (~70 questions) Final exam will cover entire course - material since 2 nd midterm weighted
Title: The Impact of Convection on the Transport and Redistribution of Dust Aerosols
 Authors: Kathryn Sauter, Tristan L'Ecuyer Title: The Impact of Convection on the Transport and Redistribution of Dust Aerosols Type of Presentation: Oral Short Abstract: The distribution of mineral dust
Authors: Kathryn Sauter, Tristan L'Ecuyer Title: The Impact of Convection on the Transport and Redistribution of Dust Aerosols Type of Presentation: Oral Short Abstract: The distribution of mineral dust
Remote sensing of ice clouds
 Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes John H. Seinfeld California Institute of Technology,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes John H. Seinfeld California Institute of Technology,
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
SkyScanner. Deploying fleets of enduring drones to probe atmospheric phenomena " Kicked off on June the 16 th, 2014
 SkyScanner Deploying fleets of enduring drones to probe atmospheric phenomena " Kicked off on June the 16 th, 2014 Project supported by the STAE foundation, 2014 / 2016 Scope of the project" Overall target:
SkyScanner Deploying fleets of enduring drones to probe atmospheric phenomena " Kicked off on June the 16 th, 2014 Project supported by the STAE foundation, 2014 / 2016 Scope of the project" Overall target:
Aerosols AP sizes AP types Sources Sinks Amount and lifetime Aerosol radiative effects. Aerosols. Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21
 Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth s surface. Extends from 9-16 km above Earth s Surface It contains most of the mass of the atmosphere.
 Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
THE EFFECTS OF GIANT CCN ON CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE SAUDI ARABIA PROGRAM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF RAINFALL AUGMENTATION
 J12.2 THE EFFECTS OF GIANT CCN ON CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE SAUDI ARABIA PROGRAM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF RAINFALL AUGMENTATION Amit Teller*, Duncan Axisa, Daniel Breed, and Roelof Bruintjes
J12.2 THE EFFECTS OF GIANT CCN ON CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE SAUDI ARABIA PROGRAM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF RAINFALL AUGMENTATION Amit Teller*, Duncan Axisa, Daniel Breed, and Roelof Bruintjes
Aerosol Basics: Definitions, size distributions, structure
 Aerosol Basics: Definitions, size distributions, structure Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008 Department of Physics, Division of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysics, University of
Aerosol Basics: Definitions, size distributions, structure Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008 Department of Physics, Division of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysics, University of
4.1 SPACE-BASED EVALUATION OF THE AEROSOL INDIRECT EFFECT IN THE ARCTIC
 4.1 SPACE-BASED EVALUATION OF THE AEROSOL INDIRECT EFFECT IN THE ARCTIC Kyle Tietze 1, Timothy J. Garrett 1, Jerôme Rièdi 2, Andreas Stohl 3 1 Univ. of Utah, Dept of Atmospheric Sciences, 2 Laboratoire
4.1 SPACE-BASED EVALUATION OF THE AEROSOL INDIRECT EFFECT IN THE ARCTIC Kyle Tietze 1, Timothy J. Garrett 1, Jerôme Rièdi 2, Andreas Stohl 3 1 Univ. of Utah, Dept of Atmospheric Sciences, 2 Laboratoire
Chapter 2 Available Solar Radiation
 Chapter 2 Available Solar Radiation DEFINITIONS Figure shows the primary radiation fluxes on a surface at or near the ground that are important in connection with solar thermal processes. DEFINITIONS It
Chapter 2 Available Solar Radiation DEFINITIONS Figure shows the primary radiation fluxes on a surface at or near the ground that are important in connection with solar thermal processes. DEFINITIONS It
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review
 Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
Weather & Atmospheric Variables Review Words that are bold, italicized and/or underlined are vocabulary you must KNOW! A) Atmospheric variables: a) Temperature as it relates to: 1) duration of insolation...longer
ON LINE ARCHIVE OF STORM PENETRATING DATA
 ON LINE ARCHIVE OF STORM PENETRATING DATA Matthew Beals, Donna V. Kliche, and Andrew G. Detwiler Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, South Dakota School of Mines and Technology, Rapid City, SD Steve Williams
ON LINE ARCHIVE OF STORM PENETRATING DATA Matthew Beals, Donna V. Kliche, and Andrew G. Detwiler Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, South Dakota School of Mines and Technology, Rapid City, SD Steve Williams
Energy: Warming the earth and Atmosphere. air temperature. Overview of the Earth s Atmosphere 9/10/2012. Composition. Chapter 3.
 Overview of the Earth s Atmosphere Composition 99% of the atmosphere is within 30km of the Earth s surface. N 2 78% and O 2 21% The percentages represent a constant amount of gas but cycles of destruction
Overview of the Earth s Atmosphere Composition 99% of the atmosphere is within 30km of the Earth s surface. N 2 78% and O 2 21% The percentages represent a constant amount of gas but cycles of destruction
NATS 1750 Lecture. Wednesday 28 th November Pearson Education, Inc.
 NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
A solar reflectance method for retrieving the optical thickness and droplet size of liquid water clouds over snow and ice surfaces
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. D14, PAGES 15,185 15,199, JULY 27, 2001 A solar reflectance method for retrieving the optical thickness and droplet size of liquid water clouds over snow
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. D14, PAGES 15,185 15,199, JULY 27, 2001 A solar reflectance method for retrieving the optical thickness and droplet size of liquid water clouds over snow
EVIDENCE FOR NATURAL VARIABILITY IN MARINE STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD PROPERTIES DUE TO CLOUD-AEROSOL INTERACTIONS
 EVIDENCE FOR NATURAL VARIABILITY IN MARINE STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD PROPERTIES DUE TO CLOUD-AEROSOL INTERACTIONS Bruce Albrecht 1, Tarah Sharon 1, Haf Jonsson 2, Patrick Minnis 3, J. Kirk Ayers 4, Mandana M.
EVIDENCE FOR NATURAL VARIABILITY IN MARINE STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD PROPERTIES DUE TO CLOUD-AEROSOL INTERACTIONS Bruce Albrecht 1, Tarah Sharon 1, Haf Jonsson 2, Patrick Minnis 3, J. Kirk Ayers 4, Mandana M.
Observational and Numerical Studies on Turbulent Entrainment-Mixing
 Observational and Numerical Studies on Turbulent Entrainment-Mixing Processes Chunsong Lu 1, 2, Yangang Liu 1, Shengjie Niu 2, Steven Krueger 3, Seong Soo Yum 4, Satoshi Endo 1, Timothy Wagner 5 1. Brookhaven
Observational and Numerical Studies on Turbulent Entrainment-Mixing Processes Chunsong Lu 1, 2, Yangang Liu 1, Shengjie Niu 2, Steven Krueger 3, Seong Soo Yum 4, Satoshi Endo 1, Timothy Wagner 5 1. Brookhaven
Ultrafine Aerosol Size Distribution: A Study of New Particle Formation in the Atmosphere
 . Ultrafine Aerosol Size Distribution: A Study of New Particle Formation in the Atmosphere Report on DOE Grant Number: DE-FG02-9 ler61205 PreDared for: U. S. Department of Energy ATTN: Fred Sienko, Contracting
. Ultrafine Aerosol Size Distribution: A Study of New Particle Formation in the Atmosphere Report on DOE Grant Number: DE-FG02-9 ler61205 PreDared for: U. S. Department of Energy ATTN: Fred Sienko, Contracting
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument.
 1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
1. Which weather map symbol is associated with extremely low air pressure? 2. The diagram below represents a weather instrument. Which weather variable was this instrument designed to measure? A) air pressure
Cloud Brightening and Climate Change
 Cloud Brightening and Climate Change 89 Hannele Korhonen and Antti-Ilari Partanen Contents Definitions... 778 Aerosols and Cloud Albedo... 778 Cloud Brightening with Sea-Salt Aerosol... 779 Climate Effects
Cloud Brightening and Climate Change 89 Hannele Korhonen and Antti-Ilari Partanen Contents Definitions... 778 Aerosols and Cloud Albedo... 778 Cloud Brightening with Sea-Salt Aerosol... 779 Climate Effects
Fluid Circulation Review. Vocabulary. - Dark colored surfaces absorb more energy.
 Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
5) The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 C is called: Page Ref: 69
 Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Chapter 4. Atmospheric Moisture, Condensation, and Clouds. 9/13/2012
 Chapter 4 Atmospheric Moisture, Condensation, and Clouds. The sun s electromagnetic spectrum and some of the descriptive names of each region. The numbers underneath the curve approximate the percent of
Chapter 4 Atmospheric Moisture, Condensation, and Clouds. The sun s electromagnetic spectrum and some of the descriptive names of each region. The numbers underneath the curve approximate the percent of
9/13/2012. Chapter 4. Atmospheric Moisture, Condensation, and Clouds.
 Chapter 2-3 review Chapter 2-3 review Chapter 4 Atmospheric Moisture, Condensation, and Clouds. The sun s electromagnetic spectrum and some of the descriptive names of each region. The numbers underneath
Chapter 2-3 review Chapter 2-3 review Chapter 4 Atmospheric Moisture, Condensation, and Clouds. The sun s electromagnetic spectrum and some of the descriptive names of each region. The numbers underneath
New Insights into Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter
 New Insights into Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter J.A. Ogren, E. Andrews, A. McComiskey, P. Sheridan, A. Jefferson, and M. Fiebig National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/ Earth System Research Laboratory
New Insights into Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter J.A. Ogren, E. Andrews, A. McComiskey, P. Sheridan, A. Jefferson, and M. Fiebig National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/ Earth System Research Laboratory
Research Article Direct Evidence of Reduction of Cloud Water after Spreading Diatomite Particles in Stratus Clouds in Beijing, China
 Meteorology Volume 2010, Article ID 412024, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/412024 Research Article Direct Evidence of Reduction of Cloud Water after Spreading Diatomite Particles in Stratus Clouds in Beijing,
Meteorology Volume 2010, Article ID 412024, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/412024 Research Article Direct Evidence of Reduction of Cloud Water after Spreading Diatomite Particles in Stratus Clouds in Beijing,
The TRMM Precipitation Radar s View of Shallow, Isolated Rain
 OCTOBER 2003 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 1519 The TRMM Precipitation Radar s View of Shallow, Isolated Rain COURTNEY SCHUMACHER AND ROBERT A. HOUZE JR. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
OCTOBER 2003 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 1519 The TRMM Precipitation Radar s View of Shallow, Isolated Rain COURTNEY SCHUMACHER AND ROBERT A. HOUZE JR. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
J2.11 PROPERTIES OF WATER-ONLY, MIXED-PHASE, AND ICE-ONLY CLOUDS OVER THE SOUTH POLE: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 J2.11 PROPERTIES OF WATER-ONLY, MIXED-PHASE, AND ICE-ONLY CLOUDS OVER THE SOUTH POLE: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Mark E. Ellison 1, Von P. Walden 1 *, James R. Campbell 2, and James D. Spinhirne 3 1 University
J2.11 PROPERTIES OF WATER-ONLY, MIXED-PHASE, AND ICE-ONLY CLOUDS OVER THE SOUTH POLE: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Mark E. Ellison 1, Von P. Walden 1 *, James R. Campbell 2, and James D. Spinhirne 3 1 University
Lindzen et al. (2001, hereafter LCH) present
 NO EVIDENCE FOR IRIS BY DENNIS L. HARTMANN AND MARC L. MICHELSEN Careful analysis of data reveals no shrinkage of tropical cloud anvil area with increasing SST AFFILIATION: HARTMANN AND MICHELSEN Department
NO EVIDENCE FOR IRIS BY DENNIS L. HARTMANN AND MARC L. MICHELSEN Careful analysis of data reveals no shrinkage of tropical cloud anvil area with increasing SST AFFILIATION: HARTMANN AND MICHELSEN Department
In-situ observations of aerosol particles remaining from evaporated cirrus crystals: Comparing clean and polluted air masses
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 3, 1037 1049, 2003 Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics In-situ observations of aerosol particles remaining from evaporated cirrus crystals: Comparing clean and polluted air masses M.
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 3, 1037 1049, 2003 Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics In-situ observations of aerosol particles remaining from evaporated cirrus crystals: Comparing clean and polluted air masses M.
Atmospheric ice nuclei concentrations and characteristics constraining the role of biological ice nuclei
 Atmospheric ice nuclei concentrations and characteristics constraining the role of biological ice nuclei Paul J. DeMott, Mathews S. Richardson, Daniel.J. Cziczo,, Anthony J. Prenni and Sonia M. Kreidenweis
Atmospheric ice nuclei concentrations and characteristics constraining the role of biological ice nuclei Paul J. DeMott, Mathews S. Richardson, Daniel.J. Cziczo,, Anthony J. Prenni and Sonia M. Kreidenweis
Hand in Question sheets with answer booklets Calculators allowed Mobile telephones or other devices not allowed
 York University Department of Earth and Space Science and Engineering ESSE 3030 Department of Physics and Astronomy PHYS 3080 Atmospheric Radiation and Thermodynamics Final Examination 2:00 PM 11 December
York University Department of Earth and Space Science and Engineering ESSE 3030 Department of Physics and Astronomy PHYS 3080 Atmospheric Radiation and Thermodynamics Final Examination 2:00 PM 11 December
On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties. Science Systems and Applications, Inc., Hampton, Virginia 2
 JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
Updated H 2 SO 4 -H 2 O binary homogeneous nucleation look-up tables
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010527, 2008 Updated H 2 SO 4 -H 2 O binary homogeneous nucleation look-up tables Fangqun Yu 1 Received 2 June
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010527, 2008 Updated H 2 SO 4 -H 2 O binary homogeneous nucleation look-up tables Fangqun Yu 1 Received 2 June
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21804, doi: /2006gl027150, 2006
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21804, doi:10.1029/2006gl027150, 2006 Influence of aerosols on the shortwave cloud radiative forcing from North Pacific oceanic clouds:
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21804, doi:10.1029/2006gl027150, 2006 Influence of aerosols on the shortwave cloud radiative forcing from North Pacific oceanic clouds:
GPS RO Retrieval Improvements in Ice Clouds
 Joint COSMIC Tenth Data Users Workshop and IROWG-6 Meeting GPS RO Retrieval Improvements in Ice Clouds Xiaolei Zou Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center (ESSIC) University of Maryland, USA September
Joint COSMIC Tenth Data Users Workshop and IROWG-6 Meeting GPS RO Retrieval Improvements in Ice Clouds Xiaolei Zou Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center (ESSIC) University of Maryland, USA September
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Reviewed by Jeff Snider, University of Wyoming, Laramie, USA. Overview
 L.I. Kleinman et al., Aerosol concentration and size distribution measured below, in, and above cloud from the DOE G-1 during VOCALS-REx, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions Reviewed by Jeff
L.I. Kleinman et al., Aerosol concentration and size distribution measured below, in, and above cloud from the DOE G-1 during VOCALS-REx, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions Reviewed by Jeff
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled?
 1 NAME Investigation 2 Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? Introduction As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
1 NAME Investigation 2 Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? Introduction As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Name(s) Period Date. Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled?
 Name(s) Period Date 1 Introduction Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Name(s) Period Date 1 Introduction Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
An Introduction to Climate Modeling
 An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
HIERARCHY OF MICROPHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS SUITABLE FOR CLOUD AND MESOSCALE MODELS.
 HIERARCHY OF MICROPHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS SUITABLE FOR CLOUD AND MESOSCALE MODELS. William D. Hall, Roy M. Rasmussen, and Gregory Thompson National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
HIERARCHY OF MICROPHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS SUITABLE FOR CLOUD AND MESOSCALE MODELS. William D. Hall, Roy M. Rasmussen, and Gregory Thompson National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations. S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences.
 The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
Air Temperature at Ocean Surface Derived from Surface-Level Humidity
 Journal of Oceanography Vol. 51, pp. 619 to 634. 1995 Air Temperature at Ocean Surface Derived from Surface-Level Humidity MASAHISA KUBOTA* and AKIRA SHIKAUCHI** School of Marine Science and Technology,
Journal of Oceanography Vol. 51, pp. 619 to 634. 1995 Air Temperature at Ocean Surface Derived from Surface-Level Humidity MASAHISA KUBOTA* and AKIRA SHIKAUCHI** School of Marine Science and Technology,
Measurement of the Sea Spray Droplet Size Distributions at High Winds
 Measurement of the Sea Spray Droplet Size Distributions at High Winds William E. Asher Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington 1013 NE 40 th Street Seattle, WA 98105 phone: (206) 543-5942
Measurement of the Sea Spray Droplet Size Distributions at High Winds William E. Asher Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington 1013 NE 40 th Street Seattle, WA 98105 phone: (206) 543-5942
A Possible Role for Immersion Freezing in Mixed-phase Stratus Clouds. Gijs de Boer T. Hashino, G.J. Tripoli, and E.W. Eloranta
 A Possible Role for Immersion Freezing in Mixed-phase Stratus Clouds Gijs de Boer T. Hashino, G.J. Tripoli, and E.W. Eloranta Introduction EUREKA BARROW HSRL/MMCR combination - Barrow (8/04-11/04) M-PACE
A Possible Role for Immersion Freezing in Mixed-phase Stratus Clouds Gijs de Boer T. Hashino, G.J. Tripoli, and E.W. Eloranta Introduction EUREKA BARROW HSRL/MMCR combination - Barrow (8/04-11/04) M-PACE
Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida
 Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida Amy Clement Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami IPCC 2007 + findings since the report + discussion of uncertainty
Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida Amy Clement Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami IPCC 2007 + findings since the report + discussion of uncertainty
Aircraft Icing Icing Physics
 Aircraft Icing Icing Physics Prof. Dr. Dept. Aerospace Engineering, METU Fall 2015 Outline Formation of ice in the atmosphere Supercooled water droplets Mechanism of aircraft icing Icing variations Ice
Aircraft Icing Icing Physics Prof. Dr. Dept. Aerospace Engineering, METU Fall 2015 Outline Formation of ice in the atmosphere Supercooled water droplets Mechanism of aircraft icing Icing variations Ice
Investigation of Droplet Size Distributions and Drizzle Formation Using A New Trajectory Ensemble Model. Part II: Lucky Parcels
 VOLUME 66 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S APRIL 2009 Investigation of Droplet Size Distributions and Drizzle Formation Using A New Trajectory Ensemble Model. Part II: Lucky
VOLUME 66 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S APRIL 2009 Investigation of Droplet Size Distributions and Drizzle Formation Using A New Trajectory Ensemble Model. Part II: Lucky
YMC FOR CLIMATE CHANGE AND AIR QUALITY (CCAQ) CENTER of BMKG
 Contribution of CENTER for CLIMATE CHANGE and AIR QUALITY (CCAQ) OF BMKG in the Prepared by Dr. Dodo Gunawan Director FIRST INTERNATIONAL SCIENCE AND PLANNING WORKSHOP ON YMC, SINGAPORE 27-30 JANUARY 2015
Contribution of CENTER for CLIMATE CHANGE and AIR QUALITY (CCAQ) OF BMKG in the Prepared by Dr. Dodo Gunawan Director FIRST INTERNATIONAL SCIENCE AND PLANNING WORKSHOP ON YMC, SINGAPORE 27-30 JANUARY 2015
P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II
 P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II Louis Nguyen*, Patrick Minnis NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA,
P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II Louis Nguyen*, Patrick Minnis NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA,
