TABLE OF CONTENTS. Dust Suppression Upgrade 2016 Memorandum Drift Distances and Overspray Considerations File 2270
|
|
|
- Candace Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 PURPOSE OF MEMORANDUM EXECUTIVE SUMMARY GENERAL FACTORS AFFECTING DROPLET DRIFT DISTANCE Droplet size Wind Speed Evaporation SITE SPECIFIC FACTORS AFFECTING DROPLET DRIFT DISTANCE AT NEPTUNE TERMINALS Droplet Size Wind Velocity Evaporation THEORETICAL ESTIMATION OF DRIFT DISTANCE CONCLUSION REFERENCES APPENDIX A Nozzle VMD Droplet APPENDIX B Wind Velocities Page 1 of 15
2 1 PURPOSE OF MEMORANDUM To estimate the theoretical drift distance and possibility of overspray of water droplets generated by the proposed Tower Sprays at Neptune Bulk Terminals (NBT) in North Vancouver, BC 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Drift distances for water droplets depends on droplet size (small droplets drift further than larger ones), the height at which the droplet falls from, the wind velocity, and evaporation. Droplet size depends upon the nozzle design and pressure. In reality, a nozzle produces a range of droplet sizes ranging from very small (comparable to light fog) to very large (comparable to heavy rain). The distribution for these droplet sizes is of log normal type with a relatively small standard distribution. In other words, the number of very small droplets and very large droplets is quite low relative to the total number of droplets that are propelled through the nozzles. In addition, it is important to note that although the number of small droplets is comparable to the number of large droplets, they constitute only a minimal portion of the total propelled volume. Nozzle pressure affects droplet size, with higher pressures producing smaller droplets with consequently greater drift distances. However, the effect of pressure on droplet size is non-linear and there are limits to its effect on droplet size. Wind velocities for the Neptune site can reach 60 km/h, though this is a relatively rare event. The predominant direction is blowing to the east (westerly wind). For overspray concerns, the most vulnerable direction is almost due north, which occurs much less frequently. For the purposes of this memorandum, maximum drift distance analysis was based upon a wind velocity of 45 km/h in a northerly direction. Evaporation, although beneficial in regards to overspray, is not a significant factor for the VMD droplet sizes produced by the proposed nozzles. Analyses for maximum drift distances were performed for the volume median diameter (D v0.5 or VMD) droplet size and for a 10 percentile volume diameter (D v0.1 ) size (see memorandum for terminology details). The analysis indicates that there will not be significant drift beyond the site boundary; although some smaller droplets would leave the site boundary during high wind events (greater than 30 km/h) they would probably, in a worst case scenario, be only a very light mist. The results of the analyses are shown graphically in Figure 7 of the memorandum. If reality trumps the theoretical analyses herein, overspray could be eliminated by increasing the droplet size either by reducing nozzle pressure or, in an extreme situation, by changing out the nozzles to a model that produces larger droplet sizes... Page 2 of 15
3 3 GENERAL FACTORS AFFECTING DROPLET DRIFT DISTANCE The drift distance of a water droplet is a function of it s horizontal velocity and the time spent in the air. The time spent in the air is directly related to the terminal vertical velocity of the water droplet and the height at which it falls from. Vertical terminal velocity and horizontal velocity are determined by: 3.1 Droplet size The size of the droplet effects the vertical velocity at which it falls. A larger droplet will fall at a greater speed than a smaller droplet in the same conditions. When evaluating the average drop size produced by a particular nozzle, the Volume Mean Diameter (VMD) is typically used. The VMD is a value where 50% of the total volume of liquid sprayed is made up of drops with diameters larger than the median value and 50% smaller than the median value (Schick, R.J., 2006). Table 1 below describes water droplets at particular diameters. Table 1: Water Droplet VMD Description (Grisso, R. et al, 2013) For the prevention of dust generation for stockpiles, standard hydraulic nozzles that produce drops between 200 and 1200 μm are generally used. The drop size distribution from most nozzles follow a typical curve, approximately a log normal distribution, as shown in Figure 1 below. Note: the VMD is shown as D V0.5. Also shown is the D V0.1, representing the diameter where 10% and 90% of the total sprayed volume is made up of smaller and larger diameters respectively. Page 3 of 15
4 Figure 1: Typical Drop Size Distribution from Nozzle Drop size and uniformity will vary based on several factors: viscosity of the liquid, the spray nozzle design, flow through the spray nozzle, and the air pressure if two-fluid nozzle are being used (Schick, R.J., 2006). 3.2 Wind Speed The wind speed determines the horizontal velocity of the water droplets. Due to a high drag force on a droplet relative to its size, the horizontal velocity is considered the same as the wind velocity for practical purposes. In other words, the discharge velocity of droplet as it leaves the nozzle is disregarded. 3.3 Evaporation Evaporation can be a factor for very small droplets and /or long fall distances. Page 4 of 15
5 4 SITE SPECIFIC FACTORS AFFECTING DROPLET DRIFT DISTANCE AT NEPTUNE TERMINALS 4.1 Droplet Size The VMD can be affected by the nature of the fluid e.g. viscosity, vapor pressure or temperature extremes. However Neptune Bulk Terminals proposed Spray Towers will operate under fundamental conditions i.e. clean water entering normal atmospheric conditions. Therefore, the VMD can be estimated by considering only the type of nozzle and the water pressure at the nozzle head for a given flow Nozzle Type: There will be two types of nozzles on the Tower Sprays: Whirljet 8-15W which produce a mean droplet diameter of approximately psi and Whirljet 15-15W with a mean droplet diameter of approximately psi (see Appendix A). At a single tower, two-thirds of the nozzles will be 8-15Ws and one-third will be 15-15Ws. The 8-15W droplet drift distance will be investigated further, since they produce smaller droplets and represent the majority of the nozzles. Figure 2: 8-15W Nozzle Drop Size Distribution Two drop sizes will be evaluated: a droplet of the nozzles VMD value (D V0.5 ) and a droplet of the nozzles (D V0.1 ) value. In reference to Table 1, this will evaluate a droplet characteristic of light rain, and a droplet characteristic of a fine drizzle respectively. Page 5 of 15
6 4.1.2 Pressure Droplet drift distance has been estimated using the VMD produced by a design water pressure at the nozzles of 40 psi. VMD is inversely correlated with water pressure. The following equation can be used to estimate the change in VMD with a change in pressure (BETE, 2016): D 2 D 1 = P 2 P (Equation 1) Figure 3 was produced using Eq. 1 and the Spraying Systems data from Appendix A. VMD vs Pressure VMD (μm) Pressure (psi) Figure 3: VMD vs Pressure Since the VMD is inversely correlated with water pressure and the pressure can be modified on site, the VMD can be adjusted within the limits shown. Therefore, if overspray is ever an issue during normal operation, the pressure can be reduced to increase droplet size and thereby shorten the drift distance. Note: the pressure can only be modified within practical limits. For example, the pressure in the Spray Tower piping should never exceed its pressure ratings. On the opposite end of the spectrum, the spray emitting from the nozzles will become a stream as the water pressure approaches zero. 4.2 Vertical Fall Velocity The vertical fall velocity is determined by droplet diameter. As water droplets greater than 100 μm become unstable in a free fall scenario, Stokes Law does not apply. Page 6 of 15
7 Instead, Figure 4 shows the graphed experimental data Gunn & Kinzer s The Terminal Velocity of Fall for Water Droplets in Stagnant Air. 10 Drop Diameter vs Terminal Velocity (Experimental Data) Terminal Vel. (m/s) Drop Diameter (μm) Figure 4: Drop Diameter vs Terminal Velocity As interpolated from the data points presented, the vertical velocity of a 500 μm droplet is 2.06 m/s Note: the leftmost data point is that of 100 μm diameter; all smaller droplets terminal velocities may be calculated using Stokes Law. 4.3 Wind Velocity The historical wind data at the Vancouver Airport can be found in Appendix B. From this data, the following wind speeds can be gathered: Typical day-to-day: ~15 km/h Typical weekly high: ~30 km/h Typical high (gale force): ~45 km/h Westerly winds are the most common winds through the Burrard Inlet. However, to be conservative, we will assume these winds can travel in the path most consequential to overspray when evaluating drift distances. 4.4 Evaporation Water drops that are greater than 300 μm in diameter will experience negligible evaporation from a fall over 1000 m in an atmosphere with a relative humidity as low as 40% (Pruppacher & Page 7 of 15
8 Klett, 1980; Gunn & Kinzer, 1951). Figure 5 below shows the distance a droplet falls before evaporating. Figure 5: Droplet Fall Distance Before Evaporation (The above fall distances assume isothermal conditions with a temperature of 7 C and an ambient saturation ratio of 0.8 (Rogers, 1979). Since the fall distance from the Spray Tower will be no more than 40 m and the VMD is 500 μm, we are basically off the chart ie the effects of evaporation for the VMD can be disregarded. However, very small droplets which theoretically would drift beyond the site boundaries under extreme wind conditions, will evaporate in hot summer weather. This potentially beneficial effect has been disregarded for purposes of this memorandum. Page 8 of 15
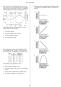
9 5 THEORETICAL ESTIMATION OF DRIFT DISTANCE Theoretical drift distances can be evaluated using the following information from the previous sections: Droplet Diameter using Whirljet 8-15W nozzle at 40 psi - D V0.5 (VMD) = 500 μm; const. vert velocity = 2.06 m/s - D V0.1 = 241 μm; const. vert velocity = 1.09 m/s Constant horizontal velocities = 15 km/h, 30 km/h, 45 km/h Evaporation = negligible Direction = north The drop distance from the Tower Spray nozzles will be approximately 40 m above ground at its base. Figure 6: Critical Droplet Drift Path The critical path was chosen along the profile line A-D. Points of reference along the line are A. Tower spray (closest to public road and residential property) B. Stacker/reclaimer rails C. Keith Road south retaining wall D. Nearest residential housing It is assumed that the spray poles running along the north side of the site will be shut off in southerly (blowing north) winds. Therefore, the possibility of overspray from these spray poles is ignored. Page 9 of 15
10 Figure 7 on the following page shows the profile along reference points A-D along with the projected drift distances during 15km/h, 30 km/h, and 45 km/h winds. Approximate elevations have been found using Google Earth. Page 10 of 15
11 A B C D Figure 7: Droplet Drift Distance Profile (Natural Scale) These drift profiles refer to the travel distance for D V0.5 and D V0.1 droplet sizes. As discussed previously, the nozzles will produce droplet diameters in a distributed manner. There will be droplets that are smaller in diameter than what is shown, and will therefore travel farther. However, the volume of water that these droplets constitute is considered small enough to ignore. Also, it should be readdressed that west is the wind s most primary direction in the Burrard Inlet. In the last year, the wind blew north (direction along the profile line) less than 5% of the time. Page 11 of 15
12 6 CONCLUSION As evident from Figure 7, water droplets from the Spray Towers will not leave the NBT yard in any direction during a 15 km/h wind event; the mean wind velocity in Vancouver. During a 30km/h wind event, which is considered a typical weekly high in Vancouver, a water droplet will travel to approximately the extents of the NBT Yard. During a one-year, 60 km/h wind event, a water droplet could reach the most vulnerable section of road along Keith Road/Low Level Road. However the droplets that make it this far are of very small diameter and will constitute something approximating a fine mist. Under anything other than hurricane force winds, residential properties are not vulnerable to overspray. If it turns out that the Tower Spray nozzles do produce overspray beyond the theoretical drift distance, it will be possible to reduce the drift distance by increasing the droplet size either by manipulating the site pressure, as seen in Figure 3 or, in an extreme case, by changing out the nozzles to a model that produces larger droplets. Page 12 of 15
13 7 REFERENCES BETE, 2016: BETE 0813 Spray Nozzle Catalogue, p 129. Grisso, R. et al, 2013: Nozzle: Selection and Sizing, Publication , p 5. Virgina Cooperative Extension Gunn, R. & G.D. Kinzer, 1949: The Terminal Velocity of Fall for Water Droplets in Stagnant Air, p 243. Journal of Meteorology, Volume 6, US Weather Bureau, Washington, D.C. Gunn, R. & G.D. Kinzer, 1951: The Evaporation, Temperature, and Thermal Relaxation Time of Freely Falling Waterdrops, p 71. Journal of Meteorology, Volume 8, US Weather Bureau, Washington, D.C. Pruppacher, H.R. & J.D. Klett, 1980: Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation, p 445. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordecht, Holland. Rogers, R.R., 1979: A Short Course in Cloud Physics, p 92. Pergamon Press, Oxford, England Schick, R.J., 2006: Spray Technology Reference Guide: Understanding Drop Size, p 16. Spray Analysis and Research Services, Spraying Systems, USA. Page 13 of 15
14 8 APPENDIX A Nozzle VMD Droplet Page 14 of 15
15 9 APPENDIX B Wind Velocities YEARLY WIND SPEED RECORDS (AUG 2015 AUG 2016) 5-YEAR WIND SPEED RECORDS (AUG 2011 AUG 2016) Page 15 of 15
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 2 Weather Patterns Guided Notes Objective(s): 7.E.1.4 Predict weather conditions and patterns based on information obtained from:
 Chapter 2 Weather Patterns Guided Notes Objective(s): 7.E.1.4 Predict weather conditions and patterns based on information obtained from: Weather data collected from direct observations and measurement
Chapter 2 Weather Patterns Guided Notes Objective(s): 7.E.1.4 Predict weather conditions and patterns based on information obtained from: Weather data collected from direct observations and measurement
Weather, Sun/Water Cycle, and Space. Test Review
 Weather, Sun/Water Cycle, and Space Test Review Weather Key Concept 1: Weather conditions can vary and change from day to day. Key Concept 2: We can use tools, such as rain gauges, wind vanes, and thermometers
Weather, Sun/Water Cycle, and Space Test Review Weather Key Concept 1: Weather conditions can vary and change from day to day. Key Concept 2: We can use tools, such as rain gauges, wind vanes, and thermometers
Page 1. Name: 4) State the actual air pressure, in millibars, shown at Miami, Florida on the given weather map.
 Name: Questions 1 and 2 refer to the following: A partial station model and meteorological conditions table, as reported by the weather bureau in the city of Oswego, New York, are shown below. 1) Using
Name: Questions 1 and 2 refer to the following: A partial station model and meteorological conditions table, as reported by the weather bureau in the city of Oswego, New York, are shown below. 1) Using
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars
 Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Go With the Flow From High to Low Investigating Isobars Science 10 Mrs. Purba Air Masses The air over a warm surface can be heated, causing it to rise above more dense air. The result is the formation
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Contents. Section 1: Climate Factors. Section 2: Climate Types. Section 3: Climate Effects
 Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Science Chapter 13,14,15
 Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
PRECIPITATION TYPE AND RAINFALL INTENSITY FROM THE PLUDIX DISDROMETER DURING THE WASSERKUPPE CAMPAIGN
 PRECIPITATION TYPE AND RAINFALL INTENSITY FROM THE PLUDIX DISDROMETER DURING THE WASSERKUPPE CAMPAIGN Clelia Caracciolo1, Franco Prodi1,2, Leo Pio D Adderio2 and Eckhard Lanzinger4 1 University of Ferrara,
PRECIPITATION TYPE AND RAINFALL INTENSITY FROM THE PLUDIX DISDROMETER DURING THE WASSERKUPPE CAMPAIGN Clelia Caracciolo1, Franco Prodi1,2, Leo Pio D Adderio2 and Eckhard Lanzinger4 1 University of Ferrara,
Weather and Climate Review
 Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Weather and Climate Review STUFF YOU NEED TO KNOW and to UNDERSTAND! 1) Because water has a higher specific heat than land, water will warm and cool more slowly than the land will. Because of this: a)
Appendix 2a. Radar Wind Profiler Data
 Appendix 2a. Radar ind Profiler Data Discussion of Radar ind Profiler Data ind profiler data were collected in two modes at four sites, Big Bend, agle Pass, Llano, and Brownsville. (ee chapter 2 for a
Appendix 2a. Radar ind Profiler Data Discussion of Radar ind Profiler Data ind profiler data were collected in two modes at four sites, Big Bend, agle Pass, Llano, and Brownsville. (ee chapter 2 for a
latent heat/humidity
 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Weather. Describing Weather
 Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
Weather Describing Weather What is weather? Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. Have you ever been caught in a rainstorm on what
CLIMATE. UNIT TWO March 2019
 CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
GAW - WCCAP recommendation for aerosol inlets and sampling tubes
 GAW - WCCAP recommendation for aerosol inlets and sampling tubes Alfred Wiedensohler, Wolfram Birmili, Leibniz Institute for Tropospheric Research, Leipzig, Germany John Ogren, NOAA ESRL GMD, Boulder,
GAW - WCCAP recommendation for aerosol inlets and sampling tubes Alfred Wiedensohler, Wolfram Birmili, Leibniz Institute for Tropospheric Research, Leipzig, Germany John Ogren, NOAA ESRL GMD, Boulder,
Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time. It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the
 Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
78% : component of atmosphere! 21% : 1% : Changes depending on origin of air: - originated over - originated over Ozone = O 3 Definition:
 Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Tuesday, September 13, 16
 Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Systems Study Guide:
 Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather vs. Climate. Tucson NWS homepage:
 Weather vs. Climate Tucson NWS homepage: www.nws.noaa.gov/twc/ A Weather Forecaster? Betty claims to know exactly when it s going to rain because her knee starts to hurt. Ms. Betty Martin of Newburgh,
Weather vs. Climate Tucson NWS homepage: www.nws.noaa.gov/twc/ A Weather Forecaster? Betty claims to know exactly when it s going to rain because her knee starts to hurt. Ms. Betty Martin of Newburgh,
Relating Storage Tank Stock Temperature to Meteorological Data
 Relating Storage Tank Stock Temperature to Meteorological Data September 11, 2008 Prepared by: Robert L. Ferry J. Randolph Kissell The TGB Partnership Prepared for: American Petroleum Institute 1220 L
Relating Storage Tank Stock Temperature to Meteorological Data September 11, 2008 Prepared by: Robert L. Ferry J. Randolph Kissell The TGB Partnership Prepared for: American Petroleum Institute 1220 L
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
Snow Measurement Guidelines for National Weather Service Snow Spotters
 Snow Measurement Guidelines for National Weather Service Snow Spotters National Weather Service Forecast Office Northern Indiana October 2004 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Definitions.. 3 Relaying Real
Snow Measurement Guidelines for National Weather Service Snow Spotters National Weather Service Forecast Office Northern Indiana October 2004 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Definitions.. 3 Relaying Real
f= flow rate (m 3 /s) A = cross-sectional area of the pipe (m 2 ) v= flow speed (m/s)
 Fluid Mechanics Flow Rate and Continuity Equation If you have a pipe that is flowing a liquid you will have a flow rate. The flow rate is the volume of fluid that passes any particular point per unit of
Fluid Mechanics Flow Rate and Continuity Equation If you have a pipe that is flowing a liquid you will have a flow rate. The flow rate is the volume of fluid that passes any particular point per unit of
Precipitation Formation, and RADAR Equation by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio Stel (1)
 PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics Precipitation Formation, and RADAR Equation by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics Precipitation Formation, and RADAR Equation by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
Average Weather In March For Fukuoka, Japan
 Average Weather In March For Fukuoka, Japan Location This report describes the typical weather at the Fukuoka Airport (Fukuoka, Japan) weather station over the course of an average March. It is based on
Average Weather In March For Fukuoka, Japan Location This report describes the typical weather at the Fukuoka Airport (Fukuoka, Japan) weather station over the course of an average March. It is based on
Chapter Introduction. Weather. Patterns. Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Final Review Meteorology
 Final Review Meteorology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is an example of climate? a. A sudden snowstorm resulted
Final Review Meteorology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is an example of climate? a. A sudden snowstorm resulted
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long
 Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Meteorological and Dispersion Modelling Using TAPM for Wagerup
 Meteorological and Dispersion Modelling Using TAPM for Wagerup Phase 1: Meteorology Appendix A: Additional modelling details Prepared for: Alcoa World Alumina Australia, P. O. Box 252, Applecross, Western
Meteorological and Dispersion Modelling Using TAPM for Wagerup Phase 1: Meteorology Appendix A: Additional modelling details Prepared for: Alcoa World Alumina Australia, P. O. Box 252, Applecross, Western
How Can You Predict Weather Changes?
 How Can You Predict Weather Changes? How to Predict Weather Meteorologists make weather predictions daily. They use the same processes that you will. They collect weather data. They plot the data on maps.
How Can You Predict Weather Changes? How to Predict Weather Meteorologists make weather predictions daily. They use the same processes that you will. They collect weather data. They plot the data on maps.
A S U M M A RY OF Chemigation Applicatio n Studies
 A S U M M A RY OF Chemigation Applicatio n Studies I n t r o d u c t i o n The incidence and impact of spray drift can be minimized by proper equipment selection and setup, and good application technique.
A S U M M A RY OF Chemigation Applicatio n Studies I n t r o d u c t i o n The incidence and impact of spray drift can be minimized by proper equipment selection and setup, and good application technique.
1. What influence does the Coriolis force have on pressure gradient wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere?
 1. What influence does the Coriolis force have on pressure gradient wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere? A. Pushes wind to the left B. Pushes wind to the right C. Pushes wind up D. Pushes wind backwards
1. What influence does the Coriolis force have on pressure gradient wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere? A. Pushes wind to the left B. Pushes wind to the right C. Pushes wind up D. Pushes wind backwards
Warming Earth and its Atmosphere The Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles
 Warming Earth and its Atmosphere The Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles Or, what happens to the energy received from the sun? First We Need to Understand The Ways in Which Heat Can be Transferred in the Atmosphere
Warming Earth and its Atmosphere The Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles Or, what happens to the energy received from the sun? First We Need to Understand The Ways in Which Heat Can be Transferred in the Atmosphere
The Sun and Water Cycle
 Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
ENVR 116 Introduction to Aerosol Science December 17, 2001 FINAL EXAMINATION
 ENVR 116 Introduction to Aerosol Science December 17, 2001 FINAL EXAMINATION Please answer all questions on the attached sheets Answer Question No. 1 and 4 of the remaining 6 questions. No extra credit
ENVR 116 Introduction to Aerosol Science December 17, 2001 FINAL EXAMINATION Please answer all questions on the attached sheets Answer Question No. 1 and 4 of the remaining 6 questions. No extra credit
Precipitation. Prof. M.M.M. Najim
 Precipitation Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Explain different forms of precipitation Identify different types of rain gauges Measure rainfall using
Precipitation Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Explain different forms of precipitation Identify different types of rain gauges Measure rainfall using
according to and water. High atmospheric pressure - Cold dry air is other air so it remains close to the earth, giving weather.
 EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
Weather: Air Patterns
 Weather: Air Patterns Weather: Air Patterns Weather results from global patterns in the atmosphere interacting with local conditions. You have probably experienced seasonal shifts, such as winter in New
Weather: Air Patterns Weather: Air Patterns Weather results from global patterns in the atmosphere interacting with local conditions. You have probably experienced seasonal shifts, such as winter in New
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
Grade 5 Earth Science. Earth: Our Unique Planet
 Science Matters Grade 5 Earth Science Earth: Our Unique Planet Written By Summer Bray Christine Lindblad Claire Poissonniez Vanessa Scarlett Developed in Conjunction with K-12 Alliance/WestEd Table of
Science Matters Grade 5 Earth Science Earth: Our Unique Planet Written By Summer Bray Christine Lindblad Claire Poissonniez Vanessa Scarlett Developed in Conjunction with K-12 Alliance/WestEd Table of
Precipitation Processes METR σ is the surface tension, ρ l is the water density, R v is the Gas constant for water vapor, T is the air
 Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12)
 Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
I T A T I O N H B I T B T V A O C J K M R S A T M O S P H E R E
 Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Average Weather For Coeur d'alene, Idaho, USA
 Average Weather For Coeur d'alene, Idaho, USA Information courtesy of weatherspark.com Location This report describes the typical weather at the Coeur d'alene Air Terminal (Coeur d'alene, Idaho, United
Average Weather For Coeur d'alene, Idaho, USA Information courtesy of weatherspark.com Location This report describes the typical weather at the Coeur d'alene Air Terminal (Coeur d'alene, Idaho, United
Your Task: Read each slide then use the underlined red or underlined information to fill in your organizer.
 Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
For example an empty bucket weighs 2.0kg. After 7 seconds of collecting water the bucket weighs 8.0kg, then:
 Hydraulic Coefficient & Flow Measurements ELEMENTARY HYDRAULICS National Certificate in Technology (Civil Engineering) Chapter 3 1. Mass flow rate If we want to measure the rate at which water is flowing
Hydraulic Coefficient & Flow Measurements ELEMENTARY HYDRAULICS National Certificate in Technology (Civil Engineering) Chapter 3 1. Mass flow rate If we want to measure the rate at which water is flowing
Unit 5. Seasons and Atmosphere
 Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
Unit 5 Seasons and Atmosphere Standard 1: Revolution Motion of a body along a path around some point in space. Earth s orbit is elliptical Earth s distance from the sun varies Perihelion Earth is closest
Snow Microphysics and the Top-Down Approach to Forecasting Winter Weather Precipitation Type
 Roger Vachalek Journey Forecaster National Weather Service Des Moines, Iowa www.snowcrystals.com Why is Snow Microphysics Important? Numerical Prediction Models better forecast areas of large scale forcing
Roger Vachalek Journey Forecaster National Weather Service Des Moines, Iowa www.snowcrystals.com Why is Snow Microphysics Important? Numerical Prediction Models better forecast areas of large scale forcing
Chapter 2 Available Solar Radiation
 Chapter 2 Available Solar Radiation DEFINITIONS Figure shows the primary radiation fluxes on a surface at or near the ground that are important in connection with solar thermal processes. DEFINITIONS It
Chapter 2 Available Solar Radiation DEFINITIONS Figure shows the primary radiation fluxes on a surface at or near the ground that are important in connection with solar thermal processes. DEFINITIONS It
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore JET STREAM For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore JET STREAM For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid. Clouds form by this process.
 CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns. Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth s surface. Extends from 9-16 km above Earth s Surface It contains most of the mass of the atmosphere.
 Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
Thermal / Solar. When air is warmed it... Rises. Solar Energy. Evaporation. Condensation Forms Clouds
 Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
ARCTIC COASTAL CLIMATIC IMPACT ON DESIGN CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF THE HAMMERFEST LNG PLANT
 ARCTIC COASTAL CLIMATIC IMPACT ON DESIGN CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF THE HAMMERFEST LNG PLANT M. A. Drage 1 and Truls Mølmann 2 1 University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway 2 Barlindhaug Consult AS, Tromsø,
ARCTIC COASTAL CLIMATIC IMPACT ON DESIGN CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF THE HAMMERFEST LNG PLANT M. A. Drage 1 and Truls Mølmann 2 1 University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway 2 Barlindhaug Consult AS, Tromsø,
What is precipitation?
 WEATHER ; - What is precipitation? ; precipitation [prih-sip-uh-tay-shun]: water that falls io the earth from the atmosphere rain gauge instrument used to measure precipitation c? - c? t[gayj]: 'j r r
WEATHER ; - What is precipitation? ; precipitation [prih-sip-uh-tay-shun]: water that falls io the earth from the atmosphere rain gauge instrument used to measure precipitation c? - c? t[gayj]: 'j r r
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
MOISTURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE MEGA PACKET
 NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
NAME: MEGA PACKET 1. A psychrometer is used to determine which weather variables? A) wind speed and wind direction B) percentage of cloud cover and cloud height C) air pressure and air temperature D) relative
ISSUED BY KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA - DOWNLOADED FROM
 CHAPTER -11 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE This chapter deals with Humidity, types of humidity, relative humidity, absolute humidity, specific humidity, dew point, condensation, saturated air, types of precipitation
CHAPTER -11 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE This chapter deals with Humidity, types of humidity, relative humidity, absolute humidity, specific humidity, dew point, condensation, saturated air, types of precipitation
Weather. Describing Weather
 CHAPTER 13 Weather LESSON 1 Describing Weather What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
CHAPTER 13 Weather LESSON 1 Describing Weather What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
MATH 1050Q Mathematical Modeling in the Environment
 MATH 1050Q Mathematical Modeling in the Environment Lecture 18. Basic Physics and Chemistry. Dmitriy Leykekhman Spring 2010 D. Leykekhman - MATH 1050Q Mathematical Modeling in the Environment Course info
MATH 1050Q Mathematical Modeling in the Environment Lecture 18. Basic Physics and Chemistry. Dmitriy Leykekhman Spring 2010 D. Leykekhman - MATH 1050Q Mathematical Modeling in the Environment Course info
Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets
 Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets 1. Too much exposure to can cause skin cancer. B. Ultraviolet radiation 2. The layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth s surface is the 3. Some
Clever Catch Weather Ball Question and Answer Sheets 1. Too much exposure to can cause skin cancer. B. Ultraviolet radiation 2. The layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth s surface is the 3. Some
Week: Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
 Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation formation Rain Ice Lecture 14 Oct 11 2018 1 Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation formation Rain Ice Lecture 14 Oct 11 2018 1 Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 3. Weather vs. Climate
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 3 Weather vs. Climate Definition of Weather Weather: Condition of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. Comprised of: Air temperature: Degree of hotness or coldness
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 3 Weather vs. Climate Definition of Weather Weather: Condition of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. Comprised of: Air temperature: Degree of hotness or coldness
research highlight Wind-Rain Relationships in Southwestern British Columbia Introduction Methodology Figure 2 Lower Mainland meteorological stations
 research highlight June 2007 Technical Series 07-114 Introduction Building envelope failures in southwestern British Columbia has brought to light the strong influence of wind-driven rain on building envelopes.
research highlight June 2007 Technical Series 07-114 Introduction Building envelope failures in southwestern British Columbia has brought to light the strong influence of wind-driven rain on building envelopes.
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CH.15 practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a) climate. c) water cycle. b) weather.
CH.15 practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a) climate. c) water cycle. b) weather.
Earth and Space Science. Teacher s Guide
 Earth and Space Science Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher............................................................. vi Classroom Management....................................................
Earth and Space Science Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher............................................................. vi Classroom Management....................................................
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Explain the parts of the water cycle that are directly connected to weather.
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Anticipation Guide #2
 Weather Systems Anticipation Guide #2 Density differences in the atmosphere are responsible for redistributing earth s heat When air is heated it rises, cools and expands releasing energy mt air masses
Weather Systems Anticipation Guide #2 Density differences in the atmosphere are responsible for redistributing earth s heat When air is heated it rises, cools and expands releasing energy mt air masses
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long
 Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR
 CHAPTER 7 CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The activation temperature of most ice-forming nuclei is 0 C. a. above b. about c. well below 2. Hygroscopic nuclei water
CHAPTER 7 CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The activation temperature of most ice-forming nuclei is 0 C. a. above b. about c. well below 2. Hygroscopic nuclei water
WEATHER. rain. thunder. The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning.
 WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Objectives Understand what causes weather. Explore weather factors related to air. Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Explore weather
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Objectives Understand what causes weather. Explore weather factors related to air. Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Explore weather
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Convection. forced convection when the flow is caused by external means, such as by a fan, a pump, or atmospheric winds.
 Convection The convection heat transfer mode is comprised of two mechanisms. In addition to energy transfer due to random molecular motion (diffusion), energy is also transferred by the bulk, or macroscopic,
Convection The convection heat transfer mode is comprised of two mechanisms. In addition to energy transfer due to random molecular motion (diffusion), energy is also transferred by the bulk, or macroscopic,
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather
 Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Haines ACC science Midterm study guide
 Haines ACC science Midterm study guide Which state of matter is the most common state of matter visible in the universe? a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas d. plasma Molecules flow freely and take the shape of
Haines ACC science Midterm study guide Which state of matter is the most common state of matter visible in the universe? a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas d. plasma Molecules flow freely and take the shape of
Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Science - 4th grade practice test
 Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
Midterm Study Guide: Haines, Manzanares & Soto
 Midterm Study Guide: Haines, Manzanares & Soto 1. High level pushes air masses to new regions. (Wind) Easy 2. How is the atmosphere like a greenhouse? ( Greenhouse gasses trap heat like the walls of a
Midterm Study Guide: Haines, Manzanares & Soto 1. High level pushes air masses to new regions. (Wind) Easy 2. How is the atmosphere like a greenhouse? ( Greenhouse gasses trap heat like the walls of a
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 5 Content: Weather Maps Notes
 Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
