Sensitivity of Tropical Tropospheric Temperature to Sea Surface Temperature Forcing
|
|
|
- George Simmons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensitivity of Tropical Tropospheric Temperature to Sea Surface Temperature Forcing Hui Su, J. David Neelin and Joyce E. Meyerson Introduction During El Niño, there are substantial tropospheric temperature anomalies across the entire tropical band associated with the warming of sea surface temperature (SST) in the central and eastern Pacific. What is the relationship between tropical tropospheric temperature response and SST forcing? What is the most important contribution in setting these tropospheric temperature anomalies? Does the relatively small region which has warm SST anomalies added to high climatological SST dominate? Or is it more dependent on the whole region of warm SST anomalies? The Quasi-equilibrium Tropical Circulation Model (QTCM) forced with subregions of SST anomalies is used to investigate the mechanisms for tropical tropospheric temperature anomalies during ENSO. Quasi-equilibrium Tropical Circulation Model (V2.2): The QTCM is an intermediate complexity atmospheric circulation model that makes use of properties of a "quasi-equilibrium moist convective closure". It includes nonlinear advection, Betts-Miller convective adjustment, cloud-radiative interaction, and a simple land model. General Approach In addition to simulations with observed SST from , we conducted simulations with specified SST distributions based on climatological SST plus subregions of SST anomalies observed during an El Niño event. For each distribution, ensemble mean of 10 simulations with slightly different initial conditions are constructed. Anomalies are defined by subtracting the ensemble mean of 10 control runs with climatological SST. The responses in precipitation and tropospheric temperature anomalies are examined. Because the tropospheric temperature response extends throughout the tropics even when SST anomaly forcing is localized, the behavior of the tropical average value is of interest.
2 1. (a) SST Anomaly (C) JFM 1998 Reynolds 2. (a) SST Anomaly (C) NDJ 1994/95 Reynolds (b) Precip. Anomaly (mm day -1 ) JFM 1998 Xie-Arkin (b) Precip. Anomaly (mm day -1 ) NDJ 1994/95 Xie-Arkin (c) Temp. Anomaly (C) ( mb) JFM 1998 NCEP (c) Temp. Anomaly (C) ( mb) NDJ 1994/95 NCEP Figure 1. Observed (a) sea surface temperature (SST) in C, (b) precipitation in mm/day and (c) tropospheric temperature ( mb average) anomalies in C for January-March Figure 2. As in Fig. 1 but for November January 1995.
3 3. (a) Precip. Anomaly JFM (a) Precip. Anomaly NDJ '94/' (b) Temp. Anomaly ( hpa) JFM 1998 (b) Temp. Anomaly ( hpa) NDJ '94/' Figure 3. Model-simulated precipitation (mm/day) and tropospheric temperature ( mb average, in C) anomalies for JFM 1998 from the run using observed SST from Figure 4. As in Fig. 1 but for NDJ 1994/95.
4 5. (a) Precip. Anomaly JFM 1998 ENSOPAC - CLIM 6. (a) Precip. Anomaly JFM 1998 ENSOPAC.sum4 - CLIM (b) Temp. Anomaly ( hpa) JFM 1998 (b) Temp. Anomaly ( hpa) JFM Figure 5. QTCM response to positive SST anomalies during JFM The JFM positive-only portion of the SST anomalies are specified in the region indicated by a dark outline. (a) Precipitation anomaly (mm/day). (b) Tropospheric temperature ( mb average) in C. Figure 6. The sum of QTCM response to each of the four subregions of positive SST anomalies during JFM The four subregions are indicated by dark outlines. (a) Precipitation anomaly (mm/day). (b) Tropospheric temperature ( mb average) in C.
5 7. (a) Precip. Anomaly JFM 1998 ENSOPAC.g4.1 - CLIM 8. (a) Precip. Anomaly JFM 1998 ENSOPAC.l2b - CLIM (b) Temp. Anomaly ( hpa) JFM 1998 (b) Temp. Anomaly ( hpa) JFM Figure 7. QTCM response to one of the four subregions of positive SST anomalies during JFM The subregion is indicated by a dark outline. (a) Precipitation anomaly (mm/day). (b) Tropospheric temperature ( mb average) in C. Figure 8. QTCM response to a small subregion of positive SST anomalies taken from the JFM 1998 El Niño case. The subregion is indicated by a dark outline. (a) Precipitation anomaly (mm/day). (b) Tropospheric temperature ( mb average) in C.
6 9. SST' Forcing SST' Forcing 120E W 60W Tropical average tropospheric temperature anomaly (C) S - 25N Average 120E W 60W SST' Forcing SST' Forcing 120E W 60W SST' dxdy Forcing Area (10 12 C. m 2 ) 120E W 60W Figure 9. Tropical averaged (25S-25N) tropospheric temperature anomalies versus the spatial integral of SST anomaly forcing for a number of experiments with subregions of the 1998 JFM El Niño SST anomaly. The side-panels show examples of the SST anomaly forcing used in the experiments.
7 10. Tropical average tropospheric temperature anomaly ( C) Tropical average SST anomaly ( C) Figure 10. Tropical averaged (25S- 25N) tropospheric temperature anomalies versus tropical averaged SST anomalies for NCAR/NCEP reanalysis ( ), MSU temperature ( ) and QTCM simulation using observed SST from The solid lines are the linear fits to the three datasets. The slopes of three lines are shown in lower-left corner. NCEP m = 1.45 QTCM m = 1.36 MSU m = S - 25 N average
8 11. Tropical average tropospheric temperature ( C) 0 60E 120E W 60W Climatology precipitation JFM JFM ' Tropical average tropospheric temperature ( C) Climatology precipitation SON 0 60E 120E W 60W SON ' Tropical average precipitation anomaly (mm/day) Tropical Average SST anomaly ( C) Tropical Average SST anomaly ( C) Tropical average precipitation anomaly (mm/day) Tropical Average SST anomaly ( C) 4.0C C 1.0C 2.0C 2.5C Tropical Average SST anomaly ( C) 5.0C Figure 11. Tropical averaged (25S-25N) tropospheric temperature anomalies and precipitation anomalies versus tropical averaged SST anomalies for simulations with uniform SST anomalies of amplitude 0.01C up to 5C added to climatological SST in three subregions. The regions are indicated by dark outlines and marked 1, 3 and 4 based on the four subregion experiments for the JFM 1998 El Niño. Climatological precipitation during JFM is displayed on top of the figure. Dots show results of the experiments with linear fits given by solid lines. Dashed lines show linearization for small SST anomalies. The numbers next to the linear fits are corresponding slopes. Figure 12. Same as Fig. 11 but for experiments over a climatologically non-precipitating region, as indicated by dark outline in climatological precipitation map. In the lower panel, numbers next to the dots are the amplitudes of SST anomalies added in the subregion.
9 13. Sensitivity parameter to SSTA (C C -1 (10-12 m -2 )) % 30% 34% 22% 0 JFM '98 60E 120E W 60W 0 Percentage of tropospheric temperature anomalies 14. Sensitivity parameter to SSTA (C C -1 (10-12 m -2 )) % 29% 21% 15% 0 NDJ '94/'95 60E 120E W 60W 0 Percentage of tropospheric temperature anomalies Figure 13. Two measures of the sensitivity parameter of tropical-average tropospheric temperature to SST anomaly in each of four subregions of 1998 JFM positive SST anomalies. The upper numbers are the amount of tropospheric temperature anomalies in degree C per unit SST forcing in Cx10 12 m 2 (amplitude x area). The lower numbers are the fraction of the average tropospheric temperature anomaly contributed by each subregion. Figure 14. As in Fig. 11 but for the NDJ 1994/95 case.
10 Analytical explanation Simplifications based on atm. model moist static energy equation Main feature: integrating over large regions typical of tropospheric temperature response averages out transport terms Consider perturbations from mean state Cloud radiative forcing as a feedback: Averaged over a large horizontal area Precip (convective heating) by moisture budget: Net radiative fluxes linear with Approximate balance Sensible and latent heat fluxes Using
11 Examples of El Niño simulation Compared to observations (Fig.1 and Fig. 2), the QTCM reproduces major precipitation and tropospheric temperature responses to El Niño SSTs for a very strong El Niño event, 1997/98 and a relatively weak event, 1994/95 (Fig. 3 and Fig. 4). In Fig 5, only positive SST anomalies in the tropical Pacific from JFM 1998 are used to force the model (run ENSOPAC). It is clear that the ENSOPAC run captures most of the response in precipitation and tropospheric temperature. We then subdivide the positiveonly region into subregions and force the model with SST anomalies from each subregion only. Atmospheric response to subregions of El Niño SST Figure 6 illustrates the sum of the responses from four subregions of similar size from west to east. The sums of individual runs are similar to the single ENSOPAC run (Fig. 5). However, negative precipitation anomalies are found within the positive SST anomaly region, at the boundaries of the subregions. This is because nonlinear advection effects come into play when strong gradients are artificially created in the subdivision processes. The nonlinear effect is more prominent in precipitation field than the tropospheric temperature field, as the temperature distribution more closely resembles the ENSOPAC experiment. Figure 7 shows the results from one of the four subregions of SST anomaly runs. It is clear that the positive precipitation anomalies are strongly localized to the warm SST anomalies, while the tropospheric temperature displays broad warming in the whole tropical band. Figure 8 is another example of a subdivided SST anomaly experiment, in which only the positive SST anomalies within two degrees of the equator in the central Pacific are retained. Again, the precipitation anomaly is highly localized within the area of positive SST anomaly. The tropospheric temperature anomaly, on the other hand, is spread over a wide region in tropics. The distribution is similar to that of the entire SST anomaly in Fig. 5, although weaker (note the contour interval differs). The temperature anomalies are typical of wave response to localized heating source.
12 Approximate linearity of tropospheric temperature Model As illustrated in Fig. 9, there is a remarkable degree of linearity of the response of tropical tropospheric temperature to El Niño SST anomalies, despite the large range of regional size and spatial patterns sampled. Clearly, it matters how large the area of SST anomaly is, and regions other than the central Pacific do contribute. We note that this applies only to very large-scale aspects of the tropospheric temperature pattern. The precipitation response, for instance, in this model has the same strong nonlinearity at the edges of convection zones seen in observations. Approximate linearity of tropospheric temperature Observations For comparison, we examined the relationship between tropical averaged (25S-25N) tropospheric temperature anomalies versus tropical averaged SST anomalies for NCAR/NCEP reanalysis and Microwave Sounding Unit Channel 2-3 temperature. The results are displayed in Fig. 10 with the QTCM result from the 17 year run from Although the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis and MSU temperature anomalies have more scatter than the model results, the linearity is quite prominent. The slope of the model linear fit is surprisingly close to those of the two independent observational datasets. They are approximately 1.4 C of tropical averaged tropospheric temperature per degree C of tropical averaged SST forcing.
13 Nonlinearity In order to further examine the linearity in the tropospheric temperature response to SST forcing, we conducted experiments with uniform SST anomalies of amplitude 0.01 C up to 5 C in specific regions. The results are shown in Fig. 11 and Fig. 12. In Fig. 11, subregion 1 is climatologically precipitating, while regions 3 and 4 are the mixtures of the precipitating and low-precipitation regions. In Fig. 12, the target area is a climatologically non-precipitating region. Over precipitating regions, the linear fits from all experiments of a particular region capture 80-90% of the actual model response. Even the linear fit from the smaller SST anomaly experiments, which corresponds to the analytical linear model predicted temperature response to SST forcing, would produce about 70-80% of the actual model response. The deviation due to nonlinear effects accounts for only 20-30% of the total response. Precipitation response is also largely linear in the three areas. The slopes of tropospheric temperature anomaly versus tropical averaged SST forcing decrease from region 1 to regions 3 and 4. Over a climatologically non-precipitating region (Fig. 12), nonlinearity in precipitation response is dramatic. The tropical averaged precipitation anomalies are virtually zero until the added SST anomalies are more than 2 C and increase more rapidly for large SST anomalies. The tropical averaged tropospheric temperature response is still quite linear for the whole range of SST anomalies. Sensitivity parameters for subregions Figure 13 provides two measures of sensitivity parameter of the tropical averaged tropospheric temperature response to tropical SST forcing. The sensitivity is noticeably larger in the central Pacific region where absolute SST is higher, but it does not become small in other regions. Since the middle two of the four regions have larger SST anomalies, these actually contribute more to the JFM 1998 tropospheric temperature anomaly. Similar results are obtained in experiments based on NDJ 94/95 El Niño event (Fig. 14). In this case, the highest percentage contribution came from the subregion in the central Pacific because the warmest SST anomalies were concentrated there. However, the sensitivity parameter over the eastern-most subregion is not small.
14 Conclusions El Niño forced strong precipitation anomalies are local to the origin of positive SST anomalies. On the other hand, tropospheric temperature anomalies spread much further. Tropical tropospheric temperature response is approximately linear with the spatial integral of SST forcing both area coverage and magnitude of SST anomalies matter! Nonlinearity in tropical averaged tropospheric temperature response can be modest even when precipitation response is highly nonlinear. Subregions of warm SST anomalies contribute fairly evenly to tropospheric temperature anomalies, while regions over climatological warm water (i.e. Central Pacific) are slightly more sensitive. University of California, Los Angeles Department of Atmospheric Sciences and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics This work was supported in part by National Science Foundation Grant ATM and National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration Grant NA86-GP0314.
Tropical Tropospheric Temperature and Precipitation Response to Sea Surface Temperature Forcing
 Tropical Tropospheric Temperature and Precipitation Response to Sea Surface Temperature Forcing Hui Su and J. David Neelin Department of Atmospheric Sciences, and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
Tropical Tropospheric Temperature and Precipitation Response to Sea Surface Temperature Forcing Hui Su and J. David Neelin Department of Atmospheric Sciences, and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
Mechanisms for Lagged Atmospheric Response to ENSO SST Forcing*
 15 OCTOBER 2005 S U E T A L. 4195 Mechanisms for Lagged Atmospheric Response to ENSO SST Forcing* HUI SU, J. DAVID NEELIN, AND JOYCE E. MEYERSON Department of Atmospheric Sciences, and Institute of Geophysics
15 OCTOBER 2005 S U E T A L. 4195 Mechanisms for Lagged Atmospheric Response to ENSO SST Forcing* HUI SU, J. DAVID NEELIN, AND JOYCE E. MEYERSON Department of Atmospheric Sciences, and Institute of Geophysics
Moist Teleconnection Mechanisms for the Tropical South American and Atlantic Sector*
 3928 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 18 Moist Teleconnection Mechanisms for the Tropical South American and Atlantic Sector* J. DAVID NEELIN AND HUI SU Department of Atmospheric Sciences, and Institute
3928 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 18 Moist Teleconnection Mechanisms for the Tropical South American and Atlantic Sector* J. DAVID NEELIN AND HUI SU Department of Atmospheric Sciences, and Institute
ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO and
 Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Dynamical versus Land-Surface Factors in the African Monsoon
 http://www.atmos.ucla.edu/~csi Dynamical versus Land-Surface Factors in the African Monsoon J. David Neelin,, UCLA Collaborators: Chia Chou, Academia Sinica, Taiwan; Hui Su, UCLA; Ning Zeng, U. Maryland
http://www.atmos.ucla.edu/~csi Dynamical versus Land-Surface Factors in the African Monsoon J. David Neelin,, UCLA Collaborators: Chia Chou, Academia Sinica, Taiwan; Hui Su, UCLA; Ning Zeng, U. Maryland
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions and El Niño Lisa Goddard
 Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions and El Niño Lisa Goddard Advanced Training Institute on Climatic Variability and Food Security 2002 July 9, 2002 Coupled Behavior in tropical Pacific SST Winds Upper Ocean
Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions and El Niño Lisa Goddard Advanced Training Institute on Climatic Variability and Food Security 2002 July 9, 2002 Coupled Behavior in tropical Pacific SST Winds Upper Ocean
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for. monsoon research. H. Annamalai
 Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS. Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 1850
 CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data
 Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L15706, doi:10.1029/2005gl023010, 2005 East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon Toru Terao Faculty
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L15706, doi:10.1029/2005gl023010, 2005 East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon Toru Terao Faculty
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Role of the East Sea SST variability in the atmospheric circulation in the North Pacific.
 Role of the East Sea SST variability in the atmospheric circulation in the North Pacific. Hyodae Seo, Young-Oh Kwon, Jong-Jin Park Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution KORDI-WHOI Workshop, Cheju, Korea,
Role of the East Sea SST variability in the atmospheric circulation in the North Pacific. Hyodae Seo, Young-Oh Kwon, Jong-Jin Park Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution KORDI-WHOI Workshop, Cheju, Korea,
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements
 Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial
 8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
El Niño, South American Monsoon, and Atlantic Niño links as detected by a. TOPEX/Jason Observations
 El Niño, South American Monsoon, and Atlantic Niño links as detected by a decade of QuikSCAT, TRMM and TOPEX/Jason Observations Rong Fu 1, Lei Huang 1, Hui Wang 2, Paola Arias 1 1 Jackson School of Geosciences,
El Niño, South American Monsoon, and Atlantic Niño links as detected by a decade of QuikSCAT, TRMM and TOPEX/Jason Observations Rong Fu 1, Lei Huang 1, Hui Wang 2, Paola Arias 1 1 Jackson School of Geosciences,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2571 Mechanisms of change in ENSO-induced tropical Pacific rainfall variability in a warming climate Ping Huang and Shang-Ping Xie Comparison with the results
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2571 Mechanisms of change in ENSO-induced tropical Pacific rainfall variability in a warming climate Ping Huang and Shang-Ping Xie Comparison with the results
Predictability and prediction of the North Atlantic Oscillation
 Predictability and prediction of the North Atlantic Oscillation Hai Lin Meteorological Research Division, Environment Canada Acknowledgements: Gilbert Brunet, Jacques Derome ECMWF Seminar 2010 September
Predictability and prediction of the North Atlantic Oscillation Hai Lin Meteorological Research Division, Environment Canada Acknowledgements: Gilbert Brunet, Jacques Derome ECMWF Seminar 2010 September
ENSO Outlook by JMA. Hiroyuki Sugimoto. El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate. Alessandra Giannini
 Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate Alessandra Giannini alesall@iri.columbia.edu Outline: Intro/Motivation: demand-driven science, use of seasonal climate prediction, adaptation to climate
Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate Alessandra Giannini alesall@iri.columbia.edu Outline: Intro/Motivation: demand-driven science, use of seasonal climate prediction, adaptation to climate
ALASKA REGION CLIMATE OUTLOOK BRIEFING. December 22, 2017 Rick Thoman National Weather Service Alaska Region
 ALASKA REGION CLIMATE OUTLOOK BRIEFING December 22, 2017 Rick Thoman National Weather Service Alaska Region Today s Outline Feature of the month: Autumn sea ice near Alaska Climate Forecast Basics Climate
ALASKA REGION CLIMATE OUTLOOK BRIEFING December 22, 2017 Rick Thoman National Weather Service Alaska Region Today s Outline Feature of the month: Autumn sea ice near Alaska Climate Forecast Basics Climate
Assessing the Climate-Scale Variability and Seasonal Predictability of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America
 Assessing the Climate-Scale Variability and Seasonal Predictability of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Alexander Gershunov, Tamara Shulgina, Marty Ralph, David Lavers CW3E
Assessing the Climate-Scale Variability and Seasonal Predictability of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Alexander Gershunov, Tamara Shulgina, Marty Ralph, David Lavers CW3E
Basic mechanism for abrupt monsoon transitions
 Basic mechanism for abrupt monsoon transitions Anders Levermann, Jacob Schewe, Vladimir Petoukhov, and Hermann Held Earth System Analysis, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam, Germany,
Basic mechanism for abrupt monsoon transitions Anders Levermann, Jacob Schewe, Vladimir Petoukhov, and Hermann Held Earth System Analysis, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam, Germany,
Second-Order Draft Chapter 10 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
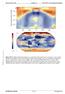 Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Tropical precipitation change under global warming
 Tropical precipitation change under global warming J. D. Neelin *, C. Chou **, M. Munnich *, H. Su *, J. Meyerson *, C. Holloway *, U. Lohmann ***, J. Feichter **** * Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences & Inst.
Tropical precipitation change under global warming J. D. Neelin *, C. Chou **, M. Munnich *, H. Su *, J. Meyerson *, C. Holloway *, U. Lohmann ***, J. Feichter **** * Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences & Inst.
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
Regional Tropical Precipitation Change Mechanisms in ECHAM4/OPYC3 under Global Warming*
 1SEPTEMBER 2006 C H O U E T A L. 4207 Regional Tropical Precipitation Change Mechanisms in ECHAM4/OPYC3 under Global Warming* CHIA CHOU Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
1SEPTEMBER 2006 C H O U E T A L. 4207 Regional Tropical Precipitation Change Mechanisms in ECHAM4/OPYC3 under Global Warming* CHIA CHOU Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
Multiple Equilibria in a Cloud Resolving Model: Using the Weak Temperature Gradient Approximation to Understand Self-Aggregation 1
 Multiple Equilibria in a Cloud Resolving Model: Using the Weak Temperature Gradient Approximation to Understand Self-Aggregation 1 Sharon Sessions, Satomi Sugaya, David Raymond, Adam Sobel New Mexico Tech
Multiple Equilibria in a Cloud Resolving Model: Using the Weak Temperature Gradient Approximation to Understand Self-Aggregation 1 Sharon Sessions, Satomi Sugaya, David Raymond, Adam Sobel New Mexico Tech
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013
 1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
1 Why the Atlantic was surprisingly quiet in 2013 by William Gray and Phil Klotzbach Preliminary Draft - March 2014 (Final draft by early June) ABSTRACT This paper discusses the causes of the unusual dearth
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections. Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542
 Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
On the Coexistence of an Evaporation Minimum and Precipitation Maximum in the Warm Pool
 1003 On the Coexistence of an Evaporation Minimum and Precipitation Maximum in the Warm Pool ADAM H. SOBEL Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, and Department of Earth and Environmental
1003 On the Coexistence of an Evaporation Minimum and Precipitation Maximum in the Warm Pool ADAM H. SOBEL Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, and Department of Earth and Environmental
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific
 Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forecasting. Theory Types Examples
 Forecasting Theory Types Examples How Good Are Week Out Weather Forecasts? For forecasts greater than nine days out, weather forecasters do WORSE than the climate average forecast. Why is there predictability
Forecasting Theory Types Examples How Good Are Week Out Weather Forecasts? For forecasts greater than nine days out, weather forecasters do WORSE than the climate average forecast. Why is there predictability
Towards Stochastic Deep Convective Parameterization
 Towards Stochastic Deep Convective Parameterization Johnny Wei-Bing Lin and J. David Neelin University of Chicago, Department of the Geophysical Sciences 5734 S. Ellis Ave., Chicago, IL 60637, USA jlin@geosci.uchicago.edu
Towards Stochastic Deep Convective Parameterization Johnny Wei-Bing Lin and J. David Neelin University of Chicago, Department of the Geophysical Sciences 5734 S. Ellis Ave., Chicago, IL 60637, USA jlin@geosci.uchicago.edu
Atmospheric humidity and clouds - what can we learn from stratospheric water? Stephan Fueglistaler
 Atmospheric humidity and clouds - what can we learn from stratospheric water? Stephan Fueglistaler The stratosphere is the driest place in the atmosphere as we know it. This workshop is about "Convection,
Atmospheric humidity and clouds - what can we learn from stratospheric water? Stephan Fueglistaler The stratosphere is the driest place in the atmosphere as we know it. This workshop is about "Convection,
Geographic variability in the export of moist static energy and vertical motion profiles in the tropical Pacific
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L17810, doi:10.1029/2006gl026672, 2006 Geographic variability in the export of moist static energy and vertical motion profiles in the tropical Pacific L. E. Back
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L17810, doi:10.1029/2006gl026672, 2006 Geographic variability in the export of moist static energy and vertical motion profiles in the tropical Pacific L. E. Back
Supplementary Material for. Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability
 1 2 Supplementary Material for Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability 3 4 Jie He 1, Clara Deser 2 & Brian J. Soden 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. Princeton University, and NOAA/Geophysical
1 2 Supplementary Material for Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability 3 4 Jie He 1, Clara Deser 2 & Brian J. Soden 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. Princeton University, and NOAA/Geophysical
East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 91 97 East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model ZENG Xian-Feng 1, 2, LI Bo 1, 2, FENG Lei
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 91 97 East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model ZENG Xian-Feng 1, 2, LI Bo 1, 2, FENG Lei
Winter Steve Todd Meteorologist In Charge National Weather Service Portland, OR
 Winter 07-08 Steve Todd Meteorologist In Charge National Weather Service Portland, OR Overview Winter Weather Outlook How to stay informed Winter Outlook LaNina conditions are present across the tropical
Winter 07-08 Steve Todd Meteorologist In Charge National Weather Service Portland, OR Overview Winter Weather Outlook How to stay informed Winter Outlook LaNina conditions are present across the tropical
How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical marine stratus and stratocumulus regions
 Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June to September) Issued in May 2014
 Ministry of Earth Sciences Earth System Science Organization India Meteorological Department WMO Regional Climate Centre (Demonstration Phase) Pune, India Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June
Ministry of Earth Sciences Earth System Science Organization India Meteorological Department WMO Regional Climate Centre (Demonstration Phase) Pune, India Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June
Role of the Indian Ocean SST anomalies in the coupling of the Atmosphere and Ocean
 Role of the Indian Ocean SST anomalies in the coupling of the Atmosphere and Ocean C.Perigaud (*),J.D.Neelin (UCLA) and J. McCreary (IPRC) (* CALTECH/Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA91109; 818-354-8203;
Role of the Indian Ocean SST anomalies in the coupling of the Atmosphere and Ocean C.Perigaud (*),J.D.Neelin (UCLA) and J. McCreary (IPRC) (* CALTECH/Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA91109; 818-354-8203;
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Impacts of Recent El Niño Modoki on Extreme Climate Conditions In East Asia and the United States during Boreal Summer
 Impacts of Recent El Niño Modoki on Extreme Climate Conditions In East Asia and the United States during Boreal Summer Hengyi Weng 1, Karumuri Ashok 1, Swadhin Behera 1, Suryachandra A. Rao 1 and Toshio
Impacts of Recent El Niño Modoki on Extreme Climate Conditions In East Asia and the United States during Boreal Summer Hengyi Weng 1, Karumuri Ashok 1, Swadhin Behera 1, Suryachandra A. Rao 1 and Toshio
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Delayed Response of the Extratropical Northern Atmosphere to ENSO: A Revisit *
 Delayed Response of the Extratropical Northern Atmosphere to ENSO: A Revisit * Ruping Mo Pacific Storm Prediction Centre, Environment Canada, Vancouver, BC, Canada Corresponding author s address: Ruping
Delayed Response of the Extratropical Northern Atmosphere to ENSO: A Revisit * Ruping Mo Pacific Storm Prediction Centre, Environment Canada, Vancouver, BC, Canada Corresponding author s address: Ruping
WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA
 WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA INTRODUCTION A good understanding of the causes of climate variability depend, to the large extend, on the precise knowledge of the functioning of the
WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA INTRODUCTION A good understanding of the causes of climate variability depend, to the large extend, on the precise knowledge of the functioning of the
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
The Texas drought. Kingtse Mo Climate Prediction Center NWS/NCEP/NOAA
 The 2011-2012 Texas drought Kingtse Mo Climate Prediction Center NWS/NCEP/NOAA 1 outline Evolution of the 2011-2012 Texas drought Climatology and historical perspective The 2011 drought Onset Feedback
The 2011-2012 Texas drought Kingtse Mo Climate Prediction Center NWS/NCEP/NOAA 1 outline Evolution of the 2011-2012 Texas drought Climatology and historical perspective The 2011 drought Onset Feedback
An OLR perspective on El Niño and La Niña impacts on seasonal weather anomalies
 An OLR perspective on El Niño and La Niña impacts on seasonal weather anomalies Andy Chiodi & Ed Harrison Univ. of WA (JISAO) and NOAA/PMEL Seattle, USA An Outgoing-Longwave-Radiation (OLR) Perspective
An OLR perspective on El Niño and La Niña impacts on seasonal weather anomalies Andy Chiodi & Ed Harrison Univ. of WA (JISAO) and NOAA/PMEL Seattle, USA An Outgoing-Longwave-Radiation (OLR) Perspective
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica
 Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
C
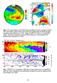 C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: August 2009
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO
 11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS 587.. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). (+) ( ) EOF 1 of SST (+)
11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS 587.. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). (+) ( ) EOF 1 of SST (+)
Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific subtropical high
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS Apr 2006
 Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
ABSTRACT 2 DATA 1 INTRODUCTION
 16B.7 MODEL STUDY OF INTERMEDIATE-SCALE TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES AND COMPARISON TO TWP-ICE CAM- PAIGN OBSERVATIONS. S. Evan 1, M. J. Alexander 2 and J. Dudhia 3. 1 University of Colorado, Boulder,
16B.7 MODEL STUDY OF INTERMEDIATE-SCALE TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES AND COMPARISON TO TWP-ICE CAM- PAIGN OBSERVATIONS. S. Evan 1, M. J. Alexander 2 and J. Dudhia 3. 1 University of Colorado, Boulder,
Moist dynamics of tropical convection zones in monsoons, teleconnections and global warming
 Moist dynamics of tropical convection zones in monsoons, teleconnections and global warming J. David Neelin* Collaborators: Chia Chou**, Hui Su*, Katrina Hales*, Chris Holloway* *Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences
Moist dynamics of tropical convection zones in monsoons, teleconnections and global warming J. David Neelin* Collaborators: Chia Chou**, Hui Su*, Katrina Hales*, Chris Holloway* *Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences
Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
SEASONAL ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS RELATED TO HURRICANE ACTIVITY IN THE NORTHEAST PACIFIC BASIN
 SEASONAL ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS RELATED TO HURRICANE ACTIVITY IN THE NORTHEAST PACIFIC BASIN Jennifer M. Collins Department of Geography and Geosciences Bloomsburg University Bloomsburg, PA 17815 jcollins@bloomu.edu
SEASONAL ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS RELATED TO HURRICANE ACTIVITY IN THE NORTHEAST PACIFIC BASIN Jennifer M. Collins Department of Geography and Geosciences Bloomsburg University Bloomsburg, PA 17815 jcollins@bloomu.edu
Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for August 2015 January 2016
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for August 2015 January 2016 BUSAN, 24 July 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for August 2015 January 2016 (ASONDJ) at the APEC Climate
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for Pacific Islands for August 2015 January 2016 BUSAN, 24 July 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for August 2015 January 2016 (ASONDJ) at the APEC Climate
Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere Coupling and Their Potential Use in Seasonal to Decadal Climate Predictions
 US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry
 lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring
 Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations
 Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations Spencer A. Hill Yi Ming, Isaac Held, Leo Donner, Ming Zhao Motivations Severe uncertainty in rainfall response
Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations Spencer A. Hill Yi Ming, Isaac Held, Leo Donner, Ming Zhao Motivations Severe uncertainty in rainfall response
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Intensification of Northern Hemisphere Subtropical Highs in a Warming Climate Wenhong Li, Laifang Li, Mingfang Ting, and Yimin Liu 1. Data and Methods The data used in this study consists of the atmospheric
Intensification of Northern Hemisphere Subtropical Highs in a Warming Climate Wenhong Li, Laifang Li, Mingfang Ting, and Yimin Liu 1. Data and Methods The data used in this study consists of the atmospheric
Chap.11 Nonlinear principal component analysis [Book, Chap. 10]
![Chap.11 Nonlinear principal component analysis [Book, Chap. 10] Chap.11 Nonlinear principal component analysis [Book, Chap. 10]](/thumbs/84/91178120.jpg) Chap.11 Nonlinear principal component analysis [Book, Chap. 1] We have seen machine learning methods nonlinearly generalizing the linear regression method. Now we will examine ways to nonlinearly generalize
Chap.11 Nonlinear principal component analysis [Book, Chap. 1] We have seen machine learning methods nonlinearly generalizing the linear regression method. Now we will examine ways to nonlinearly generalize
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
Air-sea humidity effects on the generation of tropical Atlantic SST anomalies during the ENSO events
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L19702, doi:10.1029/2006gl027238, 2006 Air-sea humidity effects on the generation of tropical Atlantic SST anomalies during the ENSO events
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L19702, doi:10.1029/2006gl027238, 2006 Air-sea humidity effects on the generation of tropical Atlantic SST anomalies during the ENSO events
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview
 The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) Why has the weather been so violent?
 WEATHER TOPICS Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) 2009 Why has the weather been so violent? As can be seen by the following forecast map, the Fall Transition and early Winter Season of
WEATHER TOPICS Analysis of Fall Transition Season (Sept-Early Dec) 2009 Why has the weather been so violent? As can be seen by the following forecast map, the Fall Transition and early Winter Season of
La Niña impacts on global seasonal weather anomalies: The OLR perspective. Andrew Chiodi and Ed Harrison
 La Niña impacts on global seasonal weather anomalies: The OLR perspective Andrew Chiodi and Ed Harrison Outline Motivation Impacts of the El Nino- Southern Oscillation (ENSO) on seasonal weather anomalies
La Niña impacts on global seasonal weather anomalies: The OLR perspective Andrew Chiodi and Ed Harrison Outline Motivation Impacts of the El Nino- Southern Oscillation (ENSO) on seasonal weather anomalies
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN
 JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
WCRP/CLIVAR efforts to understand El Niño in a changing climate
 WCRP/CLIVAR efforts to understand El Niño in a changing climate Eric Guilyardi IPSL/LOCEAN, Paris & NCAS-Climate, U. Reading Thanks to Andrew Wittenberg, Mike McPhaden, Matthieu Lengaigne 2015 El Niño
WCRP/CLIVAR efforts to understand El Niño in a changing climate Eric Guilyardi IPSL/LOCEAN, Paris & NCAS-Climate, U. Reading Thanks to Andrew Wittenberg, Mike McPhaden, Matthieu Lengaigne 2015 El Niño
P1.16 ADIABATIC LAPSE RATES IN TORNADIC ENVIRONMENTS
 P1.16 ADIABATIC LAPSE RATES IN TORNADIC ENVIRONMENTS Matthew D. Parker Convective Storms Group, The Mesoscale Nexus in Atmospheric Sciences North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION
P1.16 ADIABATIC LAPSE RATES IN TORNADIC ENVIRONMENTS Matthew D. Parker Convective Storms Group, The Mesoscale Nexus in Atmospheric Sciences North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION
SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate
 SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate Chris Reason Oceanography Dept, Univ. Cape Town Overview of southern African climate and tropical Atlantic SST South American monsoon, Benguela
SE Atlantic SST variability and southern African climate Chris Reason Oceanography Dept, Univ. Cape Town Overview of southern African climate and tropical Atlantic SST South American monsoon, Benguela
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN
 MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
Connecting tropics and extra-tropics: interaction of physical and dynamical processes in atmospheric teleconnections
 Connecting tropics and extra-tropics: interaction of physical and dynamical processes in atmospheric teleconnections Franco Molteni, Tim Stockdale, Laura Ferranti European Centre for Medium-Range Weather
Connecting tropics and extra-tropics: interaction of physical and dynamical processes in atmospheric teleconnections Franco Molteni, Tim Stockdale, Laura Ferranti European Centre for Medium-Range Weather
3.4 THE IMPACT OF CONVECTIVE PARAMETERIZATION SCHEMES ON CLIMATE SENSITIVITY
 3.4 THE IMPACT OF CONVECTIVE PARAMETERIZATION SCHEMES ON CLIMATE SENSITIVITY David J. Karoly*, Lance M. Leslie and Diandong Ren School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK and Mark Leplastrier
3.4 THE IMPACT OF CONVECTIVE PARAMETERIZATION SCHEMES ON CLIMATE SENSITIVITY David J. Karoly*, Lance M. Leslie and Diandong Ren School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK and Mark Leplastrier
Environment and Climate Change Canada / GPC Montreal
 Environment and Climate Change Canada / GPC Montreal Assessment, research and development Bill Merryfield Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis (CCCma) with contributions from colleagues at
Environment and Climate Change Canada / GPC Montreal Assessment, research and development Bill Merryfield Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis (CCCma) with contributions from colleagues at
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
