t 4.0 sec. 2. A bicyclist travels 60.0 kilometers in 3.5 hours. What is the cyclist s average speed?
|
|
|
- Ross Daniels
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Skill Sheet 3.1 Speed Problems This skill sheet will allow you to practice solving speed problems. To determine the speed of an object, you need to know the distance traveled and the time taken to travel that distance. However, by rearranging the formula for speed, v = d/t, you can also determine the distance traveled or the time it took for the object to travel that distance, if you know the speed. For example, Equation Gives you If you know v = d/t speed time and distance d = v t distance speed and time t = d/v time distance and speed 1. Solving problems Solve the following problems using the speed equation. The first problem is done for you. 1. What is the speed of a cheetah that travels meters in 4.0 seconds? speed = d -- = m = t 4.0 sec m sec 2. A bicyclist travels 60.0 kilometers in 3.5 hours. What is the cyclist s average speed? 3. What is the average speed of a car that traveled miles in 5.5 hours? 4. How much time would it take for the sound of thunder to travel 1,500 meters if sound travels at a speed of 330 m/sec? 5. How much time would it take for an airplane to reach its destination if it traveled at an average speed of 790 kilometers/hour for a distance of 4,700 kilometers? 1
2 Skill Sheet 3.1 Speed Problems 6. How far can a person run in 15 minutes if he or she runs at an average speed of 16 km/hr? (HINT: Remember to convert minutes to hours) 7. A snail can move approximately 0.30 meters per minute. How many meters can the snail cover in 15 minutes? 2. Unit conversion So far we have been mostly using the metric system for our problems. Now we will convert to the English system of measurement. Remember that there are 1,609 meters in one mile. Do not forget to include all units and cancel appropriately. These questions refer to problems in Part In problem 1.1, what is the cheetah s speed in miles/hour? m sec 2. In problem 1.5, what is the airplane s speed in miles/ hour? mile 1,609 m 3, 600 sec hour = 63 miles hour 3. In problem 1.6, what is the runner s distance traveled in miles? 4. You know that there are 1,609 meters in a mile. The number of feet in a mile is 5,280. Use these equalities to answer the following problems: a. How many centimeters equals one inch? b. What is the speed of the snail in problem 1.7 in inches per minute? 2
3 Name: Skill Sheet 3.2 Making Line Graphs Graphs allow you to present data in a form that is easily and quickly understood. Graphs are especially good for describing changing data. Here is how a line graph is made. 1. Examine your data Graph data consist of data pairs. Each data pair represents two variables. The independent variable will be plotted on the x- (horizontal) axis and the dependent variable will be plotted on the y-(vertical) axis. It s much easier to find the dependent than the independent variable. Test for the dependent variable by asking yourself which one depends on the other. For example, in a data set of money earned for hours worked, the dependent variable is money earned. That is because the money depends on the hours worked. Use this test to determine the dependent variable in any data set. Next, determine the numerical range between the smallest and largest value for each variable. If you started working with zero hours and worked 60 hours to earn this money, the range for hours would be 60. During this time, if you started with $50 and finished working with $320, the range for dollars would be 270. Be sure to calculate the range for the independent and depend variables separately. 2. Examine your graph Check the space that you will use for your graph. If you are using a piece of graph paper, allow some space on the side and bottom for labels and other information. Now count the number of lines right from the y-axis to nearly the edge of the space. This is the maximum graph space that you have for the independent variable. Repeat this process for the dependent variable by counting the number of lines up from the x-axis to nearly the top of the space. This is the maximum graph space that you have for the dependent variable. 3. Determine the graph scale You are now going to set the scale for the independent and dependent variables. It is important that you calculate the scales separately. The independent and dependent variables usually have different scales. We know that the dependent variable, money, has a range of $270. Now imagine that the graph space has a maximum of 20 lines on the y-axis before it nearly runs off the page. The first line (the x-axis) will be labeled $50. What will the next higher line be labeled? The point here is that if the value is too small, some of the money data will run out of the graph space. But if the value is too large, the plotted line will be small and hard to read. Divide the number of lines into the range to find a starting value. Increase the scale to an easier-to-use scale if necessary. $ lines = $13.50/line Increase to an easier scale: $15/line 1
4 Skill Sheet 3.2 Making Line Graphs Now label the y-axis at $15 per line. It is not necessary to label each line; perhaps each fourth line as a multiple of $60. Repeat this process for the independent variable. 1. Use the above information and the graphic to help you make a graph of the following data: (0, $50), (10, $95), (20, $140), (30, $185), (40, $230), (50, $275), (60, $320). Use your own graph paper or the graph paper on the last page of this skill sheet. 2. Use the data and the graph to determine the amount earned per hour during the 60 hours of work time. 4. Determine the independent and dependent variables Two variables are listed in each row of the first two columns of the table below. Identify the independent and dependent variable in each data pair. Rewrite the data pair under the correct heading in the next two columns of the table. The first data pair is done for you. Data pair not necessarily in order Independent Dependent Temperature Hours of heating Hours of heating Temperature Reaction time Number of people in a family Stream flow rate Tree age Alcohol consumed Cost per week for groceries Amount of rainfall Average height 5. Find the data range Calculate the data range for each variable: Lowest value Highest value Range
5 Skill Sheet 3.2 Making Line Graphs 6. Set the graph scale Using the variable range and the number of lines, calculate the scale for an axis and then determine an easy-touse scale. Write the easy-to-use scale in the column with the heading Adjusted scale. Range Number of lines Range Number of lines Calculated scale Adjusted scale
6 Skill Sheet 3.2 Making Line Graphs Graph paper 4
7 Name: Skill Sheet 3.3A Analyzing Graphs of Motion Without Numbers Graphs change columns of figures into images that are easy to interpret. Position-time and speed-time graphs describe the movement of objects. Here are stories for you to tell as graphs and a graph for you to tell as a story. Both will sharpen your graph interpreting skills. 1. Position-time graphs Data Remember the The Three Little Pigs? The wolf started from his house. Traveled to the straw house. Stayed to blow it down and eat dinner. Traveled to the stick house. Again stayed, blew it down, and ate seconds. Traveled to the brick house. Died in the stew pot at the brick house. The wolf started at his house, and the graph starts at the origin. Each time the wolf moves farther from his house, the line moves upward with passing time. At each pig s house, the line continues to the right but neither rises nor falls, indicating that the wolf has stopped moving relative to his starting point. We can deduce that the pigs houses are generally in a line away from the wolf s house and that the brick house was the farthest away. How would the line look if the brick house were on the way back to the wolf s house? Remember that position refers to the starting point in this case, the wolf s house. 2. Speed-time graphs A speed-time graph displays the speed of an object over time and is based on position-time data. You know that speed is the relationship between distance and time, R = D/T. Look at the first part of the wolf s trip. The line rises steadily to a new position and a new time. It would be easy to calculate a speed for this first leg. What if the wolf traveled this first leg faster? The new line would rise to the same position, but it would take less time. That would make the new line steeper. Here is the speed-time graph for the wolf: The wolf moved at the same speed toward his first two visits. His third trip was slightly slower. Except for this slight difference, the wolf was either at one speed or stopped. That is why this graph is so angular. 1
8 Skill Sheet 3.3A Analyzing Graphs of Motion Without Numbers 3. Stories for you to tell as graphs Read each of the following stories. Then sketch in the line for a position-time graph and a speed-time graph. 1. Little Red Riding Hood. Graph Red Riding Hood's movements. Data: Little Red Riding Hood set out for Grandmother s cottage at a good walking pace. She stopped briefly to talk to the wolf. She walked a bit slower because they were talking as they walked to the wild flowers. She stopped to pick flowers for quite a while. Realizing she was late, Red Riding Hood ran the rest of the way to Grandmother s cottage. 2. The Tortoise and the Hare. Use two lines to graph both the tortoise and the hare. Data: The tortoise and the hare began their race from the combined start-finish line. Quickly outdistancing the tortoise, the hare ran off at a moderate speed. The tortoise took off at a slow but steady speed. The hare, with an enormous lead, stopped for a short nap. With a start, the hare awoke and realized that he had been sleeping for a long time. The hare raced off toward the finish at top speed. Before the hare could catch up, the tortoise s steady pace won the race with an hour to spare. 2
9 Skill Sheet 3.3A Analyzing Graphs of Motion Without Numbers 3. The Skyrocket. Graph the altitude of the rocket. Data: The skyrocket was placed on the launcher. As the rocket motor burned, the rocket flew faster and faster into the sky. The motor burned out; although the rocket began to slow, it continued to coast ever higher. Eventually, the rocket stopped for a split second before it began to fall back to Earth. Gravity pulled the rocket faster and faster toward Earth until a parachute popped out, slowing its descent. The descent ended as the rocket landed gently on the ground. 4. A story to be told from a graph Tim, a student at Cumberland Junior High, was determined to ask Caroline for a movie date. Here are the graphs of his movements from his house to Caroline s. You write the story. 3
10 Name: Skill Sheet 3.3B Analyzing Graphs of Motion With Numbers Speed can be calculated from position-time graphs and distance can be calculated from speed-time graphs. Both calculations rely on the familiar speed equation: R = D/T. 1. Calculating speed from a position-time graph This graph shows position and time for a sailboat starting from its home port as it sailed to a distant island. By studying the line, you can see that the sailboat traveled 10 miles in 2 hours. The speed equation allows us to calculate that the vessel speed during this time was 5 miles per hour. R R = = D T 10 miles 2 hours R = 5 miles/hour, read as 5 miles per hour This result can now be transferred to a speed-time graph. Remember that this speed was measured during the first two hours. The line showing vessel speed is horizontal because the speed was constant during the two-hour period. 2. Calculating distance from a speed-time graph Here is the speed-time graph of the same sailboat later in the voyage. Between the second and third hours, the wind freshened and the sailboat increased its speed to 7 miles per hour. The speed remained 7 miles per hour to the end of the voyage. How far did the sailboat go during this time? We will first calculate the distance traveled between the third and sixth hours. 1
11 Skill Sheet 3.3B Analyzing Graphs of Motion With Numbers On a speed-time graph, distance is equal to the area between the baseline and the plotted line. You know that the area of a rectangle is found with the equation: A = L W. Similarly, multiplying the speed from the y-axis by the time on the x-axis produces distance. Notice how the labels cancel to produce miles: speed time = distance 7 miles/hour ( 6 hours 3 hours) = distance 7 miles/hour 3 hours = distance = 21 miles Now that we have seen how distance is calculated, we can consider the distance covered between hours 2 and 3. The easiest way to visualize this problem is to think in geometric terms. Find the area of the rectangle labeled 1st problem, then find the area of the triangle above, and add the two areas. Area of triangle A Geometry formula Area of rectangle B Geometry formula The area of a triangle is one-half the area of a rectangle. time speed = distance 2 ( 7 miles/hour 5 miles/hour) speed time = distance ( 3 hours 2 hours) = distance = 1 mile 2 5 miles/hour ( 3 hours 2 hours) = distance = 5 miles Add the two areas Area A + Area B = distance 1 miles + 5 mile = distance = 6 miles We can now take the distances found for both sections of the speed graph to complete our position-time graph: 2
12 Skill Sheet 3.3B Analyzing Graphs of Motion With Numbers 3. Practice: Finding speed from position-time graphs For each position-time graph, calculate and plot speed on the speed-time graph to the right. 1. The bicycle trip through hilly country. 2. A walk in the park. 3. Strolling up and down the supermarket aisles. 3
13 Skill Sheet 3.3B Analyzing Graphs of Motion With Numbers 4. Practice: Finding distance from speed-time graphs For each speed-time graph, calculate and plot the distance on the position-time graph to the right. For this practice, assume that movement is always away from the starting position. 1. The honey bee among the flowers. 2. Rover runs the street. 3. The amoeba. 4
Equation... Gives you... If you know... v = d/t speed distance and time. t = d/v time distance and speed
 Name: Date: Velocity and Speed Speed To determine the speed of an object, you need to know the distance traveled and the time taken to travel that distance. However, by rearranging the formula for speed,
Name: Date: Velocity and Speed Speed To determine the speed of an object, you need to know the distance traveled and the time taken to travel that distance. However, by rearranging the formula for speed,
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS
 Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS 31. On the position-time graph below, sketch a plot representing the motion of an object which is.... Label each line with the corresponding letter (e.g., "a", "b",
Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS 31. On the position-time graph below, sketch a plot representing the motion of an object which is.... Label each line with the corresponding letter (e.g., "a", "b",
During the second part of the trip then we travelled at 50 km/hr for hour so x = v avg t =
 PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity. What we asked about
 Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity Outline for this unit: Displacement, Velocity: numerically and graphically Mechanics Lecture 1, Slide 1 What we asked about Would like to see more practice problems
Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity Outline for this unit: Displacement, Velocity: numerically and graphically Mechanics Lecture 1, Slide 1 What we asked about Would like to see more practice problems
Four Types of Motion We ll Study
 Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
CHAPTER 2. Motion Notes
 CHAPTER 2 Motion Notes DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings. DISTANCE Distance
CHAPTER 2 Motion Notes DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings. DISTANCE Distance
Math Exam 1 Answers Fall Circle the LETTER of the correct answer for #1-3.
 Math 1800 Exam 1 Answers Fall 011 Circle the LETTER of the correct answer for #1-. (7 pts)1. An eight inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min; a twelve inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min. Which candle
Math 1800 Exam 1 Answers Fall 011 Circle the LETTER of the correct answer for #1-. (7 pts)1. An eight inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min; a twelve inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min. Which candle
3.3 Acceleration An example of acceleration Definition of acceleration Acceleration Figure 3.16: Steeper hills
 3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
FORCE AND MOTION Study Notes
 FORCE AND MOTION Study Notes FORCE: a push or pull acting on an object. examples of forces are gravity, friction, magnetism, and applied forces. Forces cause an object to change its speed, direction, or
FORCE AND MOTION Study Notes FORCE: a push or pull acting on an object. examples of forces are gravity, friction, magnetism, and applied forces. Forces cause an object to change its speed, direction, or
Physics #1 - Motion Notebook
 Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
2.4 Slope and Rate of Change
 2.4 Slope and Rate of Change Learning Objectives Find positive and negative slopes. Recognize and find slopes for horizontal and vertical lines. Understand rates of change. Interpret graphs and compare
2.4 Slope and Rate of Change Learning Objectives Find positive and negative slopes. Recognize and find slopes for horizontal and vertical lines. Understand rates of change. Interpret graphs and compare
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Describing Mo tion. Speed and Velocity. What is speed?
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1
 Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1 What is a linear equation? It sounds fancy, but linear equation means the same thing as a line. In other words, it s an equation
Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1 What is a linear equation? It sounds fancy, but linear equation means the same thing as a line. In other words, it s an equation
Lesson 2-4: Average vs. Instantaneous Velocity (Revisiting the Tortoise and Hare) Period: Date:
 Name: Period: Date: For this assignment: Re-read the Tortoise vs. the Hare story (2-1) All the needed information is on this assignment or in the reading Every question requires you to go back to previous
Name: Period: Date: For this assignment: Re-read the Tortoise vs. the Hare story (2-1) All the needed information is on this assignment or in the reading Every question requires you to go back to previous
Using Units in Science
 Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Physics Essentials Homework Packet
 Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST **
 Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
MILLIONS AND BILLIONS STUDENT WORKSHEET
 MILLIONS AND BILLIONS STUDENT WORKSHEET Name: Date: Problem 1: A) How tall is a stack of a million sheets of paper? B) How tall is a stack of a billion sheets of paper? 1. I would estimate that the height
MILLIONS AND BILLIONS STUDENT WORKSHEET Name: Date: Problem 1: A) How tall is a stack of a million sheets of paper? B) How tall is a stack of a billion sheets of paper? 1. I would estimate that the height
Chapter 3 The Integral Business Calculus 197
 Chapter The Integral Business Calculus 97 Chapter Exercises. Let A(x) represent the area bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis and vertical lines at t=0 and t=x for the graph in Fig.. Evaluate A(x)
Chapter The Integral Business Calculus 97 Chapter Exercises. Let A(x) represent the area bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis and vertical lines at t=0 and t=x for the graph in Fig.. Evaluate A(x)
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Section 1: Units, Measurements and Error What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Qualitative and Quantitative Descriptions
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Section 1: Units, Measurements and Error What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Qualitative and Quantitative Descriptions
What is Motion? any physical movement or change in position or place, relative to a reference point. Movement. Reference Point
 Motion What is Motion? any physical movement or change in position or place, relative to a reference point Movement Reference Point Distance = how far an object has moved. Measured in meters, kilometers
Motion What is Motion? any physical movement or change in position or place, relative to a reference point Movement Reference Point Distance = how far an object has moved. Measured in meters, kilometers
Homework due Nov 28 Physics
 Homework due Nov 28 Physics Name Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the information and vector diagram below and on your knowledge of physics. A hiker starts at point P and walks 2.0 kilometers
Homework due Nov 28 Physics Name Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the information and vector diagram below and on your knowledge of physics. A hiker starts at point P and walks 2.0 kilometers
Physical Science Chapter 11. Motion
 Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION
 Lab 2 - Introduction to Motion 3 Name Date Partners LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise Objectives To explore how various motions are represented
Lab 2 - Introduction to Motion 3 Name Date Partners LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise Objectives To explore how various motions are represented
Distance And Velocity
 Unit #8 - The Integral Some problems and solutions selected or adapted from Hughes-Hallett Calculus. Distance And Velocity. The graph below shows the velocity, v, of an object (in meters/sec). Estimate
Unit #8 - The Integral Some problems and solutions selected or adapted from Hughes-Hallett Calculus. Distance And Velocity. The graph below shows the velocity, v, of an object (in meters/sec). Estimate
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Representing Motion
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Representing Motion Suggested Videos for Chapter 1 Prelecture Videos Introduction Putting Numbers on Nature Video Tutor Solutions Representing Motion Class Videos Series
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Representing Motion Suggested Videos for Chapter 1 Prelecture Videos Introduction Putting Numbers on Nature Video Tutor Solutions Representing Motion Class Videos Series
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 4. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 4 Physical Science Motion What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Called the Fundamental Science Famous Physicists Galileo Galilei Albert Einstein
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 4 Physical Science Motion What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Called the Fundamental Science Famous Physicists Galileo Galilei Albert Einstein
Introduction to Measurements of Physical Quantities
 1 Goal Introduction to Measurements of Physical Quantities Content Discussion and Activities PHYS 104L The goal of this week s activities is to provide a foundational understanding regarding measurements
1 Goal Introduction to Measurements of Physical Quantities Content Discussion and Activities PHYS 104L The goal of this week s activities is to provide a foundational understanding regarding measurements
Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Please write your CID Colton
 Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
? 4. Like number bonds, a formula is useful because it helps us know what operation to use depending on which pieces of information we have.
 UNIT SIX DECIMALS LESSON 168 PROBLEM-SOLVING You ve covered quite a distance in your journey through our number system, from whole numbers through fractions, to decimals. Today s math mysteries all have
UNIT SIX DECIMALS LESSON 168 PROBLEM-SOLVING You ve covered quite a distance in your journey through our number system, from whole numbers through fractions, to decimals. Today s math mysteries all have
THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY
 THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating
THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations
 1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
Trigonometry Basics. Which side is opposite? It depends on the angle. θ 2. Y is opposite to θ 1 ; Y is adjacent to θ 2.
 Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Grade 7, Unit 2 Practice Problems - Open Up Resources. Lesson 1. Problem 1. Problem 2. Yes, since 3 times 1.5 is 4 and 2 times 1.5 is 3.
 9//7, 0) AM Lesson Problem Which one of these shapes is not like the others? Explain what makes it different by representing each width and height pair with a ratio. C is different from A and B. For both
9//7, 0) AM Lesson Problem Which one of these shapes is not like the others? Explain what makes it different by representing each width and height pair with a ratio. C is different from A and B. For both
Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement
 Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1a.cfm http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1b.cfm
Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1a.cfm http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1b.cfm
Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures
 II-1 Scientific Notation Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures Frequently numbers that occur in physics and other sciences are either very large or very small. For example, the speed of
II-1 Scientific Notation Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures Frequently numbers that occur in physics and other sciences are either very large or very small. For example, the speed of
Items to pick-up: Admit Ticket/Exit Ticket (3) Cornell Note Sheets
 Items to pick-up: Admit Ticket/Exit Ticket (3) Cornell Note Sheets DUE TODAY!!! COMPOSITION NOTEBOOK CHECK (Journal Entries will begin next week) MONDAY AUGUST 8, 2016 All Periods will meet in Lab 2 Admit
Items to pick-up: Admit Ticket/Exit Ticket (3) Cornell Note Sheets DUE TODAY!!! COMPOSITION NOTEBOOK CHECK (Journal Entries will begin next week) MONDAY AUGUST 8, 2016 All Periods will meet in Lab 2 Admit
Section 1: The Definite Integral
 Chapter The Integral Applied Calculus 70 Section : The Definite Integral Distance from Velocity Example Suppose a car travels on a straight road at a constant speed of 40 miles per hour for two hours.
Chapter The Integral Applied Calculus 70 Section : The Definite Integral Distance from Velocity Example Suppose a car travels on a straight road at a constant speed of 40 miles per hour for two hours.
Kinematics A train accelerates from rest at a rate of 2 m/(s*s), for a time of 20 seconds. How much distance does the train cover?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: 1.
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: 1.
Unit 2 - Linear Motion and Graphical Analysis
 Unit 2 - Linear Motion and Graphical Analysis Motion in one dimension is particularly easy to deal with because all the information about it can be encapsulated in two variables: x, the position of the
Unit 2 - Linear Motion and Graphical Analysis Motion in one dimension is particularly easy to deal with because all the information about it can be encapsulated in two variables: x, the position of the
Appearances Can Be Deceiving!
 Appearances Can Be Deceiving! Overview: Students explore the relationship between angular width, actual size, and distance by using their finger, thumb and fist as a unit of angular measurement in this
Appearances Can Be Deceiving! Overview: Students explore the relationship between angular width, actual size, and distance by using their finger, thumb and fist as a unit of angular measurement in this
These worksheets are representative of skills that students will need to be proficient in before
 June 16, 2016 GSMST Physics & Engineering Summer Assignment Greetings! All students enrolled in GSMST s Physics & Engineering class (PhysEng) in the upcoming year are required to complete the following
June 16, 2016 GSMST Physics & Engineering Summer Assignment Greetings! All students enrolled in GSMST s Physics & Engineering class (PhysEng) in the upcoming year are required to complete the following
Physics 8 Monday, September 12, 2011
 Physics 8 Monday, September 12, 2011 If you didn t pick up second half of textbook (starting with Chapter 8) on Friday, you can pick it up now. The bookstore is expecting more clickers to arrive soon (tomorrow?
Physics 8 Monday, September 12, 2011 If you didn t pick up second half of textbook (starting with Chapter 8) on Friday, you can pick it up now. The bookstore is expecting more clickers to arrive soon (tomorrow?
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Problem Set 1
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Car and Bicycle Rider Problem Set 1 A car is driving along a straight line with a speed v 0. At time t = 0 the car is at the
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Car and Bicycle Rider Problem Set 1 A car is driving along a straight line with a speed v 0. At time t = 0 the car is at the
Position and Displacement
 Position and Displacement Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Explain the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity ) Explain the difference between total distance traveled
Position and Displacement Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Explain the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity ) Explain the difference between total distance traveled
Everything Old Is New Again: Connecting Calculus To Algebra Andrew Freda
 Everything Old Is New Again: Connecting Calculus To Algebra Andrew Freda (afreda@deerfield.edu) ) Limits a) Newton s Idea of a Limit Perhaps it may be objected, that there is no ultimate proportion of
Everything Old Is New Again: Connecting Calculus To Algebra Andrew Freda (afreda@deerfield.edu) ) Limits a) Newton s Idea of a Limit Perhaps it may be objected, that there is no ultimate proportion of
Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
 Name Physics Honors Pd Date Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an
Name Physics Honors Pd Date Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an
PHYSICS: the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy and force.
 Car materials: 2 toilet paper rolls 8 water bottle caps 2 straws masking tape 2 4-inch bamboo skewers 5 paper clips 10 toothpicks PHYSICS: the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along
Car materials: 2 toilet paper rolls 8 water bottle caps 2 straws masking tape 2 4-inch bamboo skewers 5 paper clips 10 toothpicks PHYSICS: the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along
Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration. Unit 1: Kinematics
 Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure
Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure
Section Distance and displacment
 Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by both magnitude AND direction
 Unit I: Motion Subunit A: Constant Velocity Chapter 2 Section 1 Texas Physics p. 38-45 Equations Variables, Units NOTES: scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by
Unit I: Motion Subunit A: Constant Velocity Chapter 2 Section 1 Texas Physics p. 38-45 Equations Variables, Units NOTES: scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by
Section 3-1: Relating Graphs to Events Common Core Standards: 8.F.5
 Section 3-1: Relating Graphs to Events Common Core Standards: 8.F.5 Section Objective: To interpret and sketch graphs that represent real world situations. New Vocabulary linear (p. 82): An equation is
Section 3-1: Relating Graphs to Events Common Core Standards: 8.F.5 Section Objective: To interpret and sketch graphs that represent real world situations. New Vocabulary linear (p. 82): An equation is
April 23, 2009 SOLUTIONS SECTION NUMBER:
 MATH 5 FINAL EXAM April, 9 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER:. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.. Do not separate
MATH 5 FINAL EXAM April, 9 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER:. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.. Do not separate
Section 1 Force and Motion: Review
 Section 1 Force and Motion: Review 1. MAIN IDEA How does a motion diagram represent an object s motion? A motion diagram shows the positions of a moving object at equal time intervals. 2. Motion Diagram
Section 1 Force and Motion: Review 1. MAIN IDEA How does a motion diagram represent an object s motion? A motion diagram shows the positions of a moving object at equal time intervals. 2. Motion Diagram
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 1st Semester Review Which best describes the solution(s) for this equation? 3 ( 8x 12) = 33 2x
 Name: Period: ate: lgebra 1 1st Semester Review 2011 1 Which algebraic expression could NOT match the pictorial representation below? 5 Which best describes the solution(s) for this equation? 3 ( 8x 12)
Name: Period: ate: lgebra 1 1st Semester Review 2011 1 Which algebraic expression could NOT match the pictorial representation below? 5 Which best describes the solution(s) for this equation? 3 ( 8x 12)
Post-Algebra II, Pre-Precalculus Summer Packet
 Post-Algebra II, Pre-Precalculus Summer Packet (Concepts epected to be understood upon entering Precalculus course) Name Grade Level School Teacher In order to be successful in a Precalculus course at
Post-Algebra II, Pre-Precalculus Summer Packet (Concepts epected to be understood upon entering Precalculus course) Name Grade Level School Teacher In order to be successful in a Precalculus course at
Unit 1 Our Dynamic Universe
 North Berwick High School Higher Physics Department of Physics Unit 1 Our Dynamic Universe Section 1 Equations of Motion Section 1 Equations of Motion Note Making Make a dictionary with the meanings of
North Berwick High School Higher Physics Department of Physics Unit 1 Our Dynamic Universe Section 1 Equations of Motion Section 1 Equations of Motion Note Making Make a dictionary with the meanings of
Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity
 3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
Chapter 2: Motion a Straight Line
 Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
December 14, SWBAT understand and explain a velocity vs. time graph.
 December 14, 2016 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain a velocity vs. time graph. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. You Review 3. Class Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: Homework: M.10 Graphing
December 14, 2016 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain a velocity vs. time graph. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. You Review 3. Class Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: Homework: M.10 Graphing
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages )
 Name Class Date Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages 328 331) This section defines distance and displacement. Methods of describing motion are presented. Vector addition and subtraction are introduced.
Name Class Date Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages 328 331) This section defines distance and displacement. Methods of describing motion are presented. Vector addition and subtraction are introduced.
Focus Questions: 3-1: Describe how objects speed up and slow down 3-2: Describes how objects change direction
 Motion Graphing Focus Questions: 3-1: Describe how objects speed up and slow down 3-2: Describes how objects change direction Motion Graphing Speed Graphs A typical speed graph will have distance or position
Motion Graphing Focus Questions: 3-1: Describe how objects speed up and slow down 3-2: Describes how objects change direction Motion Graphing Speed Graphs A typical speed graph will have distance or position
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
9/27/12. Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces. Motion and Position. Motion. Distance. Relative Motion
 9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
Physics I P H Y S I C S U N I O N M A T H E M A T I C S. Kinematics. Student Edition
 P H Y S I C S U N I O N M A T H E M A T I C S Physics I Kinematics Student Edition Supported by the National Science Foundation (DRL-0733140) and Science Demo, Ltd. PUM Physics I Kinematics Adapted from:
P H Y S I C S U N I O N M A T H E M A T I C S Physics I Kinematics Student Edition Supported by the National Science Foundation (DRL-0733140) and Science Demo, Ltd. PUM Physics I Kinematics Adapted from:
1.1 Motion and Motion Graphs
 Figure 1 A highway is a good example of the physics of motion in action. kinematics the study of motion without considering the forces that produce the motion dynamics the study of the causes of motion
Figure 1 A highway is a good example of the physics of motion in action. kinematics the study of motion without considering the forces that produce the motion dynamics the study of the causes of motion
Analyzing Motion: Enrichment
 Chapter 2 Analyzing Motion: Enrichment Note to Teachers: The concepts involved in motion position, velocity, acceleration, and time should be developed using the four modes of representation: visual, numeric,
Chapter 2 Analyzing Motion: Enrichment Note to Teachers: The concepts involved in motion position, velocity, acceleration, and time should be developed using the four modes of representation: visual, numeric,
LAB 3 - VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 Name Date Partners L03-1 LAB 3 - VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION OBJECTIVES A cheetah can accelerate from 0 to 50 miles per hour in 6.4 seconds. Encyclopedia of the Animal World A Jaguar can accelerate from
Name Date Partners L03-1 LAB 3 - VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION OBJECTIVES A cheetah can accelerate from 0 to 50 miles per hour in 6.4 seconds. Encyclopedia of the Animal World A Jaguar can accelerate from
On Your Own. Applications. Unit 1. 1 p = 7.5n - 55, where n represents the number of car washes and p represents the profit in dollars.
 Applications 1 p = 7.5n - 55, where n represents the number of car washes and p represents the profit in dollars. 2 t = 0.5 + 2a, where a represents the area of the grass and t represents the time in hours
Applications 1 p = 7.5n - 55, where n represents the number of car washes and p represents the profit in dollars. 2 t = 0.5 + 2a, where a represents the area of the grass and t represents the time in hours
Crossing the Atlantic: Then and Now
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Crossing the Atlantic: Then and Now How has the amount
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Crossing the Atlantic: Then and Now How has the amount
8, x 2. 4and. 4, y 1. y 2. x 1. Name. Part 1: (Skills) Each question is worth 2 points. SHOW ALL WORK IN THE SPACE PROVIDED. 1.
 MATH 099 PRACTICE FINAL EXAMINATION Fall 2016 Name Part 1: (Skills) Each question is worth 2 points. SHOW ALL WORK IN THE SPACE PROVIDED. 1. Determine whether 4, 3 is a solution to the equation 3x 3y 21
MATH 099 PRACTICE FINAL EXAMINATION Fall 2016 Name Part 1: (Skills) Each question is worth 2 points. SHOW ALL WORK IN THE SPACE PROVIDED. 1. Determine whether 4, 3 is a solution to the equation 3x 3y 21
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
graphs, Equations, and inequalities 2
 graphs, Equations, and inequalities You might think that New York or Los Angeles or Chicago has the busiest airport in the U.S., but actually it s Hartsfield-Jackson Airport in Atlanta, Georgia. In 010,
graphs, Equations, and inequalities You might think that New York or Los Angeles or Chicago has the busiest airport in the U.S., but actually it s Hartsfield-Jackson Airport in Atlanta, Georgia. In 010,
Preliminary Physics. Moving About. DUXCollege. Week 2. Student name:. Class code:.. Teacher name:.
 Week 2 Student name:. Class code:.. Teacher name:. DUXCollege Week 2 Theory 1 Present information graphically of: o Displacement vs time o Velocity vs time for objects with uniform and non-uniform linear
Week 2 Student name:. Class code:.. Teacher name:. DUXCollege Week 2 Theory 1 Present information graphically of: o Displacement vs time o Velocity vs time for objects with uniform and non-uniform linear
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
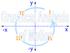 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
(UNIT I) Measuring Activity Name
 (UNIT I) Measuring Activity Name Purpose: To become more familiar with the metric system (SI) of measurement. Make estimates first and then measure it. Pre Lab reading: http://www.cnn.com/tech/space/9909/30/mars.metric.02/#1
(UNIT I) Measuring Activity Name Purpose: To become more familiar with the metric system (SI) of measurement. Make estimates first and then measure it. Pre Lab reading: http://www.cnn.com/tech/space/9909/30/mars.metric.02/#1
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Converting Base Units The Step Stair Method is a simple trick to converting these units. Kilo (k) Hecta (h) Deka (D) Larger unit as you go up the steps! Divide
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Converting Base Units The Step Stair Method is a simple trick to converting these units. Kilo (k) Hecta (h) Deka (D) Larger unit as you go up the steps! Divide
Math 060/Final Exam Review Guide/ / College of the Canyons
 Math 060/Final Exam Review Guide/ 010-011/ College of the Canyons General Information: The final exam is a -hour timed exam. There will be approximately 40 questions. There will be no calculators or notes
Math 060/Final Exam Review Guide/ 010-011/ College of the Canyons General Information: The final exam is a -hour timed exam. There will be approximately 40 questions. There will be no calculators or notes
RELATING GRAPHS TO EVENTS
 RELATING GRAPHS TO EVENTS Independent Variable: The cause variable (the tested variable or input). Always labeled on the x axis of graph. Dependent Variable: The effect variable (output). Always labeled
RELATING GRAPHS TO EVENTS Independent Variable: The cause variable (the tested variable or input). Always labeled on the x axis of graph. Dependent Variable: The effect variable (output). Always labeled
Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions
 Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Neatly sketch the following dot motion diagrams: (a) A particle moving right
Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Neatly sketch the following dot motion diagrams: (a) A particle moving right
Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS. Skills Worksheet. Multiple Choice
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. mass gravity friction weight speed velocity net force newton 1.
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. mass gravity friction weight speed velocity net force newton 1.
Drawing and Interpreting Graphs
 Drawing and Interpreting Graphs Drawing and Interpreting Graphs Scientific Graphs: Most scientific graphs are made as line graphs. The lines on scientific graphs are usually drawn either straight or curved.
Drawing and Interpreting Graphs Drawing and Interpreting Graphs Scientific Graphs: Most scientific graphs are made as line graphs. The lines on scientific graphs are usually drawn either straight or curved.
Algebra 1, Chapter 4 Post Test
 Class: Date: Algebra 1, Chapter 4 Post Test Review 4.1.1: I can represent mathematical relationships using graphs. 1. (2 points) Sketch a graph of the speed of a city bus on a daily route. Label each section.
Class: Date: Algebra 1, Chapter 4 Post Test Review 4.1.1: I can represent mathematical relationships using graphs. 1. (2 points) Sketch a graph of the speed of a city bus on a daily route. Label each section.
Chapter 7. Lesson Lesson 7.1.2
 Chapter 7 Lesson 7.1.1 7-. Customer A should order y=4x instead; Customer B should order y= x+ instead; Customer C s order is correct; Customer D s table is not linear, so the customer should revise his
Chapter 7 Lesson 7.1.1 7-. Customer A should order y=4x instead; Customer B should order y= x+ instead; Customer C s order is correct; Customer D s table is not linear, so the customer should revise his
Displacement and Total Distance Traveled
 Displacement and Total Distance Traveled We have gone over these concepts before. Displacement: This is the distance a particle has moved within a certain time - To find this you simply subtract its position
Displacement and Total Distance Traveled We have gone over these concepts before. Displacement: This is the distance a particle has moved within a certain time - To find this you simply subtract its position
Motion in 1 Dimension
 Motion in 1 Dimension Physics is all about describing motion. For now we are going to discuss motion in 1 dimension, which means either along the x axis or the y axis. To describe an object s motion, we
Motion in 1 Dimension Physics is all about describing motion. For now we are going to discuss motion in 1 dimension, which means either along the x axis or the y axis. To describe an object s motion, we
Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy
 Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy Author: Matthew Kurth Grade Level: pre-ap 6 th grade Science (45 minute class) Sources: CPO Science (Force and Motion) o Curriculum
Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy Author: Matthew Kurth Grade Level: pre-ap 6 th grade Science (45 minute class) Sources: CPO Science (Force and Motion) o Curriculum
0.3 Domain and Range: Relations vs Functions, Domain, Range, and Vertical Line Test Worksheet 3 #1-7
 Unit 0 Check Sheet Function Families Check sheet must be turned in to receive Homework & Quiz points. All quiz corrections must be done for test score to replace quiz scores. No check sheet = No Points.
Unit 0 Check Sheet Function Families Check sheet must be turned in to receive Homework & Quiz points. All quiz corrections must be done for test score to replace quiz scores. No check sheet = No Points.
LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. What is Science? Worksheets CSS AP Physics 1 2015-16 Summer Assignment Part 1 of 3 CHAPTER 1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Scientific Inquiry 1.2 Fundamental Units
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. What is Science? Worksheets CSS AP Physics 1 2015-16 Summer Assignment Part 1 of 3 CHAPTER 1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Scientific Inquiry 1.2 Fundamental Units
Practice Ace Problems
 Unit 5: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 1: Walking Rates Practice Ace Problems Directions: Please complete the necessary problems to earn a maximum of 11 points according to the chart below. Show all
Unit 5: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 1: Walking Rates Practice Ace Problems Directions: Please complete the necessary problems to earn a maximum of 11 points according to the chart below. Show all
Accuracy and Precision Making measurements is an important skill in science.
 Motion Physics Unit Physics is the scientific study of matter and energy and how they interact. topic such as motion, light, electricity, and heat strong rules about using numbers in math Accuracy and
Motion Physics Unit Physics is the scientific study of matter and energy and how they interact. topic such as motion, light, electricity, and heat strong rules about using numbers in math Accuracy and
SECTION 2. Objectives. Describe motion in terms changing velocity. Compare graphical representations of accelerated and nonaccelerated motions.
 SECTION Plan and Prepare Preview Vocabulary Academic Vocabulary Remind students that rate describes how something changes compared to something else. In physics, a rate usually refers to a change over
SECTION Plan and Prepare Preview Vocabulary Academic Vocabulary Remind students that rate describes how something changes compared to something else. In physics, a rate usually refers to a change over
How To Complete and Experiment and Write a Lab Report: Using Questions to Write a Hypothesis With Clear Independent and Dependent Variables
 How To Complete and Experiment and Write a Lab Report: Using Questions to Write a Hypothesis With Clear Independent and Dependent Variables 1 I can How to Write a Hypothesis http://www.myteacherpages.com/webpages/jflynt/portfolio.cfm?subpage=1001394
How To Complete and Experiment and Write a Lab Report: Using Questions to Write a Hypothesis With Clear Independent and Dependent Variables 1 I can How to Write a Hypothesis http://www.myteacherpages.com/webpages/jflynt/portfolio.cfm?subpage=1001394
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
