Predictive Understanding of the Oceans' Wind-Driven Circulation on Interdecadal Time Scales
|
|
|
- Moses Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CCPP Mtg. Seattle, Oct , 2004 Predictive Understanding of the Oceans' Wind-Driven Circulation on Interdecadal Time Scales Michael Ghil Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Dept. and IGPP, UCLA Roger Temam Mathematics Dept. and ISCAM, Indiana University Motivation 1. Anthropogenic effects on climate act on a complex system characterized by natural variability on many space and time scales. 2. The ocean s wind-driven & thermohaline circulation exhibit interannual & interdecadal oscillations. 3. We concentrate on the wind-driven circulation, subject to fixed atmospheric forcings as well as coupled to atmospheric variability. Work with H. Dijkstra (CSU), Y. Feliks (IIBR, Israel, & UCLA), K. Ide (UCLA), G. Loeper (U. of Nice, France), E. Simonnet (INLN, France, & UCLA), L. Sushama (UQAM, Canada) & T. Tachim-Medjo (Florida Intl. U.)
2 Outline A. Dynamical results 1. Double-gyre results (ocean only) prescribed wind stress QG, SW & PE models, agreement with 7-yr period in NAO observations periodic wind stress effect on inertial recirculation 2. Effects of oceanic thermal front on atmosphere barotropic baroclinic B. Numerical results (see also poster) 1. High-order approximations for PE models 2. Expansion in the H/L aspect ratio 3. Inertial algorithms for the PEs
3 ! "#$% &'(( ) +*,&-.0/ : ;=<?>A@.BDCFEGIHB JLKNM <O@.PRQ KS;=TOJU8 : KNJWVX<OJLJWKS;=T ;ZY T[<OM B\H]KNV^P@_HB JL<O@QJ Basin size: 2000 x 2000 x 5 km (grid: 14 km, 15 layers) 2 1 Lateral viscosity: 80 m s, Thermal diffusivity: 2 m s density deviation Z=0 Z= 1300 m Z= 2600 m MAX = e+00 MIN = e MAX = e 01 MIN = e MAX = e 03 MIN = e Z= 4000 m MAX = e+00 MIN = e MAX = e 04 MIN = e Z (15 m) MAX = e 01 MIN = e Z (15 m)
4 ! "#$% &'(( ) +*,&-.0/ Basin size: 2000 km x 2000 km, depth: 4 km Re1 = 3333 Re2 = Rt1 = Rt2 = 000 Nb layers: 10 1 Barotropic Ψ 1 surface density deviationρ y 0.5 y x x Depth (m) ρ (kg m 3 ) Total vertical density at (0.5,0.5) 465
5 ! "#$% &'(( ) +*,&-.0/ Kinetic Energy SSA Reconstruction Data Vector vec, RC Vector ssarcvec, M=296 Original Reconstruction MEM Spectrum Data Vector ssarcvec,m= y 2.8 y ;:=<>:@?=ACBEDGFHACIKJL:@M BF+NPO$ACMQSR?=ACBUTWV A,MX 8KYZA,?@?\[^]#_` AaObFBU<c[;X F+?@Jd 79e fkrza,jb:g_hy [6<c[;N?@:@M:@NiX j;mzas<>:@nj k 7>lm_nojqprBF+?=AaO2:\[sM ]L:tOY O2Y F nh_j ul[vbo2y;_hwxo?=acm6o2:@nw[sjbn:@?@?=aao2:\[sm k 465
6
7 References (papers that benefited from DOE support for in blue; DOEsupported team members in red) Dijkstra, H. A., and M. Ghil, 2004: Low-frequency variability of the large-scale ocean circulation: A dynamical systems approach, Rev. Geophys., sub judice. Feliks, Y., M. Ghil, and E. Simonnet, 2004a: Low-frequency variability in the midlatitude atmosphere induced by an oceanic thermal front, J. Atmos. Sci., 61(9), Feliks, Y., M. Ghil, and E. Simonnet, 2004b: Low-frequency variability in the mid-latitude baroclinic atmosphere induced by an oceanic thermal front, J. Atmos. Sci., to be submitted. Feliks, Y., M. Ghil, and E. Simonnet, 2004c: Interannual and interdecadal oscillations in a coupled ocean atmosphere model. in preparation. Ghil, M., Y. Feliks, and L. Sushama, 2002: Baroclinic and barotropic aspects of the wind-driven ocean circulation, Physica D, 167, Simonnet, E., 2004: Quantization of the low-frequency variability of the double-gyre circulation in the presence of bottom friction, J. Phys. Oceanogr., to be submitted. Simonnet, E., M. Ghil, K. Ide, R. Temam, and S. Wang, 2003a: Lowfrequency variability in shallow-water models of the wind-driven ocean circulation. Part I: Steady-state solutions. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 33,
8 Simonnet, E., M. Ghil, K. Ide, R. Temam, and S. Wang, 2003b: Lowfrequency variability in shallow-water models of the wind-driven ocean circulation. Part II: Time-dependent solutions. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 33, Simonnet, E., T. Tachim-Medjo, and R. Temam, 2003c: Barotropic baroclinic formulation of the primitive equations of the ocean. Appl. Analysis, 82, Simonnet, E., M. Ghil, and H.A. Dijkstra, 2004a: Homoclinic bifurcations in the quasi-geostrophic double-gyre circulation. J. Mar. Res., submitted. Simonnet, E., M. Ghil, and H.A. Dijkstra, 2004b: Quasi-homoclinic behavior of the barotropic quasi-geostrophic double-gyre circulation. Chaos, to be submitted. Simonnet, E., T. Tachim-Medjo, and R. Temam, 2004c: Barotropicbaroclinic formulation of the primitive equations of the ocean, Applicable Analysis, 82: Simonnet, E., T. Tachim-Medjo, and R. Temam, 2004d: Higher-order approximation equations for the primitive equations of the ocean, Proc. Erice Conf. PDEs (J.-L. Lions & G. Stampacchia Festschrift), in press. Simonnet, E., T. Tachim-Medjo, and R. Temam, 2004e: On the order of magnitude of the baroclinic flow in the primitive equations of the ocean. Annali Mat. Pura Applicata, to appear. Sushama, L. U., K. Ide and M. Ghil, 2004: Spatio-temporal variability in a mid-latitude ocean basin subject to periodic wind forcing, J. Mar. Res., to be submitted.
LFV in a mid-latitude coupled model:
 LFV in a mid-latitude coupled model: Gulf Stream influence on the NAO M. Ghil 1,2, E. Simonnet 3, Y. Feliks 1,4 1 Dept. of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences and IGPP, UCLA, USA. 2 Geosciences Dept. and
LFV in a mid-latitude coupled model: Gulf Stream influence on the NAO M. Ghil 1,2, E. Simonnet 3, Y. Feliks 1,4 1 Dept. of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences and IGPP, UCLA, USA. 2 Geosciences Dept. and
Spatio-temporal variability in a mid-latitude ocean basin subject to periodic wind forcing
 Spatio-temporal variability in a mid-latitude ocean basin subject to periodic wind forcing L. Sushama 1, 2, K. Ide 3 and M. Ghil 3, 4 1 Ouranos Consortium, Montreal, Canada 2 Department of Earth and Atmospheric
Spatio-temporal variability in a mid-latitude ocean basin subject to periodic wind forcing L. Sushama 1, 2, K. Ide 3 and M. Ghil 3, 4 1 Ouranos Consortium, Montreal, Canada 2 Department of Earth and Atmospheric
Thermosolutal Convection at Infinite Prandtl Number with or without rotation: Bifurcation and Stability in Physical Space
 1/29 Thermosolutal Convection at Infinite Prandtl Number with or without rotation: Bifurcation and Stability in Physical Space Jungho Park Department of Mathematics New York Institute of Technology SIAM
1/29 Thermosolutal Convection at Infinite Prandtl Number with or without rotation: Bifurcation and Stability in Physical Space Jungho Park Department of Mathematics New York Institute of Technology SIAM
A highly nonlinear coupled mode of. decadal-to-interdecadal variability in a mid-latitude. ocean atmosphere model. Part I: Phenomenology
 A highly nonlinear coupled mode of decadal-to-interdecadal variability in a mid-latitude ocean atmosphere model. Part I: Phenomenology S. Kravtsov 1, W. K. Dewar 2, P. Berloff 3, J. C. McWilliams, and
A highly nonlinear coupled mode of decadal-to-interdecadal variability in a mid-latitude ocean atmosphere model. Part I: Phenomenology S. Kravtsov 1, W. K. Dewar 2, P. Berloff 3, J. C. McWilliams, and
Low-Frequency Variability in Shallow-Water Models of the Wind-Driven Ocean Circulation. Part I: Steady-State Solutions 1
 Low-Frequency Variability in Shallow-Water Models of the Wind-Driven Ocean Circulation. Part I: Steady-State Solutions 1 Eric Simonnet 2 Université Paris-Sud Michael Ghil, Kayo Ide University of California,
Low-Frequency Variability in Shallow-Water Models of the Wind-Driven Ocean Circulation. Part I: Steady-State Solutions 1 Eric Simonnet 2 Université Paris-Sud Michael Ghil, Kayo Ide University of California,
Physica D 2889 (2002) Baroclinic and barotropic aspects of the wind-driven ocean circulation
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Abstract Physica D 2889 (2002) 1 35 Baroclinic and barotropic aspects of the wind-driven ocean circulation M. Ghil, Y. Feliks
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Abstract Physica D 2889 (2002) 1 35 Baroclinic and barotropic aspects of the wind-driven ocean circulation M. Ghil, Y. Feliks
Propagation of wind and buoyancy forced density anomalies in the North Pacific: Dependence on ocean model resolution
 Ocean Modelling 16 (2007) 277 284 Short Communication Propagation of wind and buoyancy forced density anomalies in the North Pacific: Dependence on ocean model resolution LuAnne Thompson *, Jordan Dawe
Ocean Modelling 16 (2007) 277 284 Short Communication Propagation of wind and buoyancy forced density anomalies in the North Pacific: Dependence on ocean model resolution LuAnne Thompson *, Jordan Dawe
A highly nonlinear coupled mode of decadal variability in a mid-latitude ocean atmosphere model
 Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 43 (2007) 123 150 A highly nonlinear coupled mode of decadal variability in a mid-latitude ocean atmosphere model S. Kravtsov a,d,, W.K. Dewar b, P. Berloff c, J.C. McWilliams
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 43 (2007) 123 150 A highly nonlinear coupled mode of decadal variability in a mid-latitude ocean atmosphere model S. Kravtsov a,d,, W.K. Dewar b, P. Berloff c, J.C. McWilliams
The Nile River Records Revisited: How good were Joseph's predictions?
 The Nile River Records Revisited: How good were Joseph's predictions? Michael Ghil Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, and University of California, Los Angeles Joint work with Yizhak Feliks, IIBR, and Dmitri
The Nile River Records Revisited: How good were Joseph's predictions? Michael Ghil Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, and University of California, Los Angeles Joint work with Yizhak Feliks, IIBR, and Dmitri
The atmospheric circulation over the North Atlantic. as induced by the SST field
 1 The atmospheric circulation over the North Atlantic as induced by the SST field Yizhak Feliks 1, Michael Ghil 2,3 and Andrew W. Robertson 4 Dept. of Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences and Institute of Geophysics
1 The atmospheric circulation over the North Atlantic as induced by the SST field Yizhak Feliks 1, Michael Ghil 2,3 and Andrew W. Robertson 4 Dept. of Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences and Institute of Geophysics
On a Wind-Driven, Double-Gyre, Quasi-Geostrophic Ocean Model: Numerical Simulations and Structural Analysis 1
 Journal of Computational Physics 155, 387 409 (1999) Article ID jcph.1999.6344, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On a Wind-Driven, Double-Gyre, Quasi-Geostrophic Ocean Model: Numerical
Journal of Computational Physics 155, 387 409 (1999) Article ID jcph.1999.6344, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On a Wind-Driven, Double-Gyre, Quasi-Geostrophic Ocean Model: Numerical
Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability
 Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability J. H. LaCasce, University of Oslo J. Pedlosky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution P. E. Isachsen, Norwegian Meteorological
Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability J. H. LaCasce, University of Oslo J. Pedlosky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution P. E. Isachsen, Norwegian Meteorological
Sensitivity of an Ocean Model to Details of Stochastic Forcing
 Sensitivity of an Ocean Model to Details of Stochastic Forcing Cécile Penland and Philip Sura NOAA-CIRES/Climate Diagnostics Center, Boulder CO 80305-3328 Abstract We review the sensitivity of a double-gyre
Sensitivity of an Ocean Model to Details of Stochastic Forcing Cécile Penland and Philip Sura NOAA-CIRES/Climate Diagnostics Center, Boulder CO 80305-3328 Abstract We review the sensitivity of a double-gyre
P-Vector Inverse Method Evaluated Using the Modular Ocean Model (MOM)
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 54, pp. 185 to 198. 1998 P-Vector Inverse Method Evaluated Using the Modular Ocean Model (MOM) PETER C. CHU 1, CHENWU FAN 1 and WENJU CAI 2 1 Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey,
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 54, pp. 185 to 198. 1998 P-Vector Inverse Method Evaluated Using the Modular Ocean Model (MOM) PETER C. CHU 1, CHENWU FAN 1 and WENJU CAI 2 1 Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey,
Instability of a coastal jet in a two-layer model ; application to the Ushant front
 Instability of a coastal jet in a two-layer model ; application to the Ushant front Marc Pavec (1,2), Xavier Carton (1), Steven Herbette (1), Guillaume Roullet (1), Vincent Mariette (2) (1) UBO/LPO, 6
Instability of a coastal jet in a two-layer model ; application to the Ushant front Marc Pavec (1,2), Xavier Carton (1), Steven Herbette (1), Guillaume Roullet (1), Vincent Mariette (2) (1) UBO/LPO, 6
North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/25, and 1/50
 North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/2, and 1/ Xiaobiao Xu and Eric Chassignet Center for ocean-atmospheric prediction studies Florida State University Motivation Numerical models
North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/2, and 1/ Xiaobiao Xu and Eric Chassignet Center for ocean-atmospheric prediction studies Florida State University Motivation Numerical models
Sergey Kravtsov B.S., Physics and Mathematics, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Russia.
 Sergey Kravtsov University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Department of Mathematical Sciences Atmospheric Sciences Group P. O. Box 413, Milwaukee, WI 53201 kravtsov@uwm.edu; 414-477-3306 https://uwm.edu/math/people/kravtsov-sergey
Sergey Kravtsov University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Department of Mathematical Sciences Atmospheric Sciences Group P. O. Box 413, Milwaukee, WI 53201 kravtsov@uwm.edu; 414-477-3306 https://uwm.edu/math/people/kravtsov-sergey
RESEARCH STATEMENT. 1. dynamic bifurcation theories in fluid dynamics and geophysical fluid dynamics,
 1 OBJECTIVES AND SCIENTIFIC TASKS One of the primary goals in climate dynamics is to document through careful theoretical and numerical studies the presence of climate low frequency variability, to verify
1 OBJECTIVES AND SCIENTIFIC TASKS One of the primary goals in climate dynamics is to document through careful theoretical and numerical studies the presence of climate low frequency variability, to verify
Impacts of natural disasters on a dynamic economy
 Impacts of natural disasters on a dynamic economy Andreas Groth Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris in cooperation with Michael Ghil, Stephane Hallegatte, Patrice Dumas, Yizhak Feliks, Andrew W. Robertson
Impacts of natural disasters on a dynamic economy Andreas Groth Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris in cooperation with Michael Ghil, Stephane Hallegatte, Patrice Dumas, Yizhak Feliks, Andrew W. Robertson
The Turbulent Oscillator: A Mechanism of Low-Frequency Variability
 The Turbulent Oscillator: A Mechanism of Low-Frequency Variability of the Wind-Driven Ocean Gyres People: Pavel Berloff 1,2 Andy Hogg 3 William Dewar 4 Institutions: 1 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution,
The Turbulent Oscillator: A Mechanism of Low-Frequency Variability of the Wind-Driven Ocean Gyres People: Pavel Berloff 1,2 Andy Hogg 3 William Dewar 4 Institutions: 1 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution,
Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L20601, doi:10.1029/2008gl035490, 2008 Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean Denis L. Volkov, 1 Tong Lee, 1 and Lee-Lueng Fu 1 Received 28 July 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L20601, doi:10.1029/2008gl035490, 2008 Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean Denis L. Volkov, 1 Tong Lee, 1 and Lee-Lueng Fu 1 Received 28 July 2008;
The Bremen NOAC observing system in the subpolar North Atlantic
 US AMOC 2014, Seattle The Bremen NOAC observing system in the subpolar North Atlantic Dagmar Kieke, Monika Rhein, Achim Roessler, Christian Mertens, Reiner Steinfeldt, and Linn Schneider NOAC North Atlantic
US AMOC 2014, Seattle The Bremen NOAC observing system in the subpolar North Atlantic Dagmar Kieke, Monika Rhein, Achim Roessler, Christian Mertens, Reiner Steinfeldt, and Linn Schneider NOAC North Atlantic
Conference on Teleconnections in the Atmosphere and Oceans November 2008
 1968-38 Conference on Teleconnections in the Atmosphere and Oceans 17-20 November 2008 Mid-latitude - MJO teleconnection over East Asia in the Northern winter KIM Baekmin Yonsei University Dept. of Atmospheric
1968-38 Conference on Teleconnections in the Atmosphere and Oceans 17-20 November 2008 Mid-latitude - MJO teleconnection over East Asia in the Northern winter KIM Baekmin Yonsei University Dept. of Atmospheric
Midlatitude Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction in an. Idealized Coupled Model. Department of Atmospheric Sciences and
 Midlatitude Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction in an Idealized Coupled Model S. Kravtsov 1 and A. W. Robertson Department of Atmospheric Sciences and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics University
Midlatitude Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction in an Idealized Coupled Model S. Kravtsov 1 and A. W. Robertson Department of Atmospheric Sciences and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics University
Four-Gyre Circulation in a Barotropic Model with Double-Gyre Wind Forcing
 1461 Four-Gyre Circulation in a Barotropic Model with Double-Gyre Wind Forcing RICHARD J. GREATBATCH Department of Oceanography, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B. T. NADIGA Earth and
1461 Four-Gyre Circulation in a Barotropic Model with Double-Gyre Wind Forcing RICHARD J. GREATBATCH Department of Oceanography, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B. T. NADIGA Earth and
BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere. Potential temperature θ. Rossby Ertel potential vorticity
 BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere Need to introduce a new measure of the buoyancy Potential temperature θ In a compressible fluid, the relevant measure
BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere Need to introduce a new measure of the buoyancy Potential temperature θ In a compressible fluid, the relevant measure
General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be
 General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be a bonus) is well written (take your time to edit) shows
General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be a bonus) is well written (take your time to edit) shows
Large-Scale, Low-Frequency Variability in Wind-Driven Ocean Gyres
 1925 Large-Scale, Low-Frequency Variability in Wind-Driven Ocean Gyres PAVEL S. BERLOFF AND JAMES C. MCWILLIAMS Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los
1925 Large-Scale, Low-Frequency Variability in Wind-Driven Ocean Gyres PAVEL S. BERLOFF AND JAMES C. MCWILLIAMS Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Contents
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Contents
Low-frequency climate variability: a dynamical systems a approach
 Low-frequency climate variability: a dynamical systems a approach Henk Broer Rijksuniversiteit Groningen http://www.math.rug.nl/ broer 19 October 2006 Page 1 of 40 1. Variability at low-frequencies Making
Low-frequency climate variability: a dynamical systems a approach Henk Broer Rijksuniversiteit Groningen http://www.math.rug.nl/ broer 19 October 2006 Page 1 of 40 1. Variability at low-frequencies Making
Stability of meridionally-flowing grounded abyssal currents in the ocean
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VII 93 Stability of meridionally-flowing grounded abyssal currents in the ocean G. E. Swaters Applied Mathematics Institute, Department of Mathematical & Statistical Sciences
Advances in Fluid Mechanics VII 93 Stability of meridionally-flowing grounded abyssal currents in the ocean G. E. Swaters Applied Mathematics Institute, Department of Mathematical & Statistical Sciences
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC FLUID DYNAMICS
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC FLUID DYNAMICS Fundamentals and Large-scale Circulation G E O F F R E Y K. V A L L I S Princeton University, New Jersey CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS An asterisk indicates more advanced
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC FLUID DYNAMICS Fundamentals and Large-scale Circulation G E O F F R E Y K. V A L L I S Princeton University, New Jersey CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS An asterisk indicates more advanced
Identifying a Damped Oscillatory Thermohaline Mode in a General Circulation Model Using an Adjoint Model
 AUGUST 2001 SIRKES AND TZIPERMAN 2297 Identifying a Damped Oscillatory Thermohaline Mode in a General Circulation Model Using an Adjoint Model ZIV SIRKES Center for Ocean and Atmospheric Modeling, The
AUGUST 2001 SIRKES AND TZIPERMAN 2297 Identifying a Damped Oscillatory Thermohaline Mode in a General Circulation Model Using an Adjoint Model ZIV SIRKES Center for Ocean and Atmospheric Modeling, The
Variability of Atlantic Ocean heat transport and its effects on the atmosphere
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N., February 3 Variability of Atlantic Ocean heat transport and its effects on the atmosphere Buwen Dong and Rowan T. Sutton Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N., February 3 Variability of Atlantic Ocean heat transport and its effects on the atmosphere Buwen Dong and Rowan T. Sutton Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department
primitive equation simulation results from a 1/48th degree resolution tell us about geostrophic currents? What would high-resolution altimetry
 Scott 2008: Scripps 1 What would high-resolution altimetry tell us about geostrophic currents? results from a 1/48th degree resolution primitive equation simulation Robert B. Scott and Brian K. Arbic The
Scott 2008: Scripps 1 What would high-resolution altimetry tell us about geostrophic currents? results from a 1/48th degree resolution primitive equation simulation Robert B. Scott and Brian K. Arbic The
Influence of forced near-inertial motion on the kinetic energy of a nearly-geostrophic flow
 Abstract Influence of forced near-inertial motion on the kinetic energy of a nearly-geostrophic flow Stephanne Taylor and David Straub McGill University stephanne.taylor@mail.mcgill.ca The effect of forced
Abstract Influence of forced near-inertial motion on the kinetic energy of a nearly-geostrophic flow Stephanne Taylor and David Straub McGill University stephanne.taylor@mail.mcgill.ca The effect of forced
Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation
 Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation Lecture 9 by Andrew Wells We have so far considered boundary layers adjacent to physical boundaries. However, it is also possible to find boundary layers
Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation Lecture 9 by Andrew Wells We have so far considered boundary layers adjacent to physical boundaries. However, it is also possible to find boundary layers
Ocean surface circulation
 Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
Low-Frequency Variability in the Midlatitude Atmosphere Induced by an Oceanic Thermal Front
 VOL. 61, NO. 9 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1MAY 4 Low-Frequency Variability in the Midlatitude Atmosphere Induced by an Oceanic Thermal Front YIZHAK FELIKS, * MICHAEL GHIL, AND ERIC SIMONNET #
VOL. 61, NO. 9 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1MAY 4 Low-Frequency Variability in the Midlatitude Atmosphere Induced by an Oceanic Thermal Front YIZHAK FELIKS, * MICHAEL GHIL, AND ERIC SIMONNET #
arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 15 Jun 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 15 Jun 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 15 Jun 2010](/thumbs/89/98943322.jpg) CLIMATE DYNAMICS AND FLUID MECHANICS: NATURAL VARIABILITY AND RELATED UNCERTAINTIES arxiv:1006.2864v1 [math.ds] 15 Jun 2010 Michael Ghil Département Terre-Atmosphère-Océan, Laboratoire de Météorologie
CLIMATE DYNAMICS AND FLUID MECHANICS: NATURAL VARIABILITY AND RELATED UNCERTAINTIES arxiv:1006.2864v1 [math.ds] 15 Jun 2010 Michael Ghil Département Terre-Atmosphère-Océan, Laboratoire de Météorologie
Internal Wave Modeling in Oceanic General Circulation Models
 Internal Wave Modeling in Oceanic General Circulation Models Flavien Gouillon, Eric P. Chassignet Center for Ocean - Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida State University Introduction One of the
Internal Wave Modeling in Oceanic General Circulation Models Flavien Gouillon, Eric P. Chassignet Center for Ocean - Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida State University Introduction One of the
The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system
 The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU), Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
The global ocean circulation: an elegant dynamical system Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU), Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
Contents. Parti Fundamentals. 1. Introduction. 2. The Coriolis Force. Preface Preface of the First Edition
 Foreword Preface Preface of the First Edition xiii xv xvii Parti Fundamentals 1. Introduction 1.1 Objective 3 1.2 Importance of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics 4 1.3 Distinguishing Attributes of Geophysical
Foreword Preface Preface of the First Edition xiii xv xvii Parti Fundamentals 1. Introduction 1.1 Objective 3 1.2 Importance of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics 4 1.3 Distinguishing Attributes of Geophysical
OCN660 - Ocean Waves. Course Purpose & Outline. Doug Luther. OCN660 - Syllabus. Instructor: x65875
 OCN660 - Ocean Waves Course Purpose & Outline Instructor: Doug Luther dluther@hawaii.edu x65875 This introductory course has two objectives: to survey the principal types of linear ocean waves; and, to
OCN660 - Ocean Waves Course Purpose & Outline Instructor: Doug Luther dluther@hawaii.edu x65875 This introductory course has two objectives: to survey the principal types of linear ocean waves; and, to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
A Kuroshio Extension System Model Study: Decadal Chaotic Self-Sustained Oscillations
 AUGUST 2006 P I E R I N I 1605 A Kuroshio Extension System Model Study: Decadal Chaotic Self-Sustained Oscillations STEFANO PIERINI Dipartimento di Scienze per l Ambiente, Università di Napoli Parthenope,
AUGUST 2006 P I E R I N I 1605 A Kuroshio Extension System Model Study: Decadal Chaotic Self-Sustained Oscillations STEFANO PIERINI Dipartimento di Scienze per l Ambiente, Università di Napoli Parthenope,
2. Baroclinic Instability and Midlatitude Dynamics
 2. Baroclinic Instability and Midlatitude Dynamics Midlatitude Jet Stream Climatology (Atlantic and Pacific) Copyright 26 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without
2. Baroclinic Instability and Midlatitude Dynamics Midlatitude Jet Stream Climatology (Atlantic and Pacific) Copyright 26 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without
PAPER 333 FLUID DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday, 1 June, 2016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm Draft 21 June, 2016 PAPER 333 FLUID DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total.
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday, 1 June, 2016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm Draft 21 June, 2016 PAPER 333 FLUID DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total.
Activity #2 - Major Ocean Surface Currents
 Activity #2 - Major Ocean Surface Currents Concepts # 3 & 6 # 3 Atmospheric cells and ocean gyres redistribute heat from low to high latitudes, which influences climate, weather, and ocean temperature.
Activity #2 - Major Ocean Surface Currents Concepts # 3 & 6 # 3 Atmospheric cells and ocean gyres redistribute heat from low to high latitudes, which influences climate, weather, and ocean temperature.
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation
 Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Transformed Eulerian Mean
 Chapter 15 Transformed Eulerian Mean In the last few lectures we introduced some fundamental ideas on 1) the properties of turbulent flows in rotating stratified environments, like the ocean and the atmosphere,
Chapter 15 Transformed Eulerian Mean In the last few lectures we introduced some fundamental ideas on 1) the properties of turbulent flows in rotating stratified environments, like the ocean and the atmosphere,
Modeling the Formation and Offshore Transport of Dense Water from High-Latitude Coastal Polynyas
 Modeling the Formation and Offshore Transport of Dense Water from High-Latitude Coastal Polynyas David C. Chapman Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2792 fax: (508)
Modeling the Formation and Offshore Transport of Dense Water from High-Latitude Coastal Polynyas David C. Chapman Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2792 fax: (508)
Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Geometry of the ocean 1/17/2018. Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations?
 Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations? Observations? Patterns? Observations? Patterns? Geometry of the ocean Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Continental Continental Basin
Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations? Observations? Patterns? Observations? Patterns? Geometry of the ocean Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Continental Continental Basin
Spreading of near-inertial energy in a 1/12 model of the North Atlantic Ocean
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L10609, doi:10.1029/2007gl029895, 2007 Spreading of near-inertial energy in a 1/12 model of the North Atlantic Ocean Xiaoming Zhai, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L10609, doi:10.1029/2007gl029895, 2007 Spreading of near-inertial energy in a 1/12 model of the North Atlantic Ocean Xiaoming Zhai, 1
THE WIND-DRIVEN OCEAN CIRCULATION: APPLYING DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS THEORY TO A CLIMATE PROBLEM. Michael Ghil
 Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number 0X, XX 200X doi:10.3934/xx.xx.xx.xx pp. X XX THE WIND-DRIVEN OCEAN CIRCULATION: APPLYING DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS THEORY TO A CLIMATE PROBLEM Michael Ghil
Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number 0X, XX 200X doi:10.3934/xx.xx.xx.xx pp. X XX THE WIND-DRIVEN OCEAN CIRCULATION: APPLYING DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS THEORY TO A CLIMATE PROBLEM Michael Ghil
On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time
 Hamburg Workshop 215 On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time Xiaoming Zhai Centre for Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia With David Marshall,
Hamburg Workshop 215 On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time Xiaoming Zhai Centre for Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia With David Marshall,
Impact of Typhoons on the Western Pacific Ocean DRI: Numerical Modeling of Ocean Mixed Layer Turbulence and Entrainment at High Winds
 Impact of Typhoons on the Western Pacific Ocean DRI: Numerical Modeling of Ocean Mixed Layer Turbulence and Entrainment at High Winds Ramsey R. Harcourt Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington,
Impact of Typhoons on the Western Pacific Ocean DRI: Numerical Modeling of Ocean Mixed Layer Turbulence and Entrainment at High Winds Ramsey R. Harcourt Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington,
ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 )
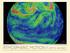 http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
LOW-FREQUENCY VARIABILITY OF THE LARGE-SCALE OCEAN CIRCULATION: A DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS APPROACH
 LOW-FREQUENCY VARIABILITY OF THE LARGE-SCALE OCEAN CIRCULATION: A DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS APPROACH Henk A. Dijkstra 1 Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State University Fort Collins, U.S.A. Michael
LOW-FREQUENCY VARIABILITY OF THE LARGE-SCALE OCEAN CIRCULATION: A DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS APPROACH Henk A. Dijkstra 1 Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State University Fort Collins, U.S.A. Michael
Global Weak Solution of Planetary Geostrophic Equations with Inviscid Geostrophic Balance
 Global Weak Solution o Planetary Geostrophic Equations with Inviscid Geostrophic Balance Jian-Guo Liu 1, Roger Samelson 2, Cheng Wang 3 Communicated by R. Temam) Abstract. A reormulation o the planetary
Global Weak Solution o Planetary Geostrophic Equations with Inviscid Geostrophic Balance Jian-Guo Liu 1, Roger Samelson 2, Cheng Wang 3 Communicated by R. Temam) Abstract. A reormulation o the planetary
I. Variability of off-shore thermocline depth and western boundary current. Rui Xin Huang *+ & Qinyan Liu +$
 Meridional circulation in the western coastal zone: I. Variability of off-shore thermocline depth and western boundary current transport on interannual and decadal time scales Rui Xin Huang *+ & Qinyan
Meridional circulation in the western coastal zone: I. Variability of off-shore thermocline depth and western boundary current transport on interannual and decadal time scales Rui Xin Huang *+ & Qinyan
The general circulation: midlatitude storms
 The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
Macroturbulent cascades of energy and enstrophy in models and observations of planetary atmospheres
 Macroturbulent cascades of energy and enstrophy in models and observations of planetary atmospheres Peter Read + Roland Young + Fachreddin Tabataba-Vakili + Yixiong Wang [Dept. of Physics, University of
Macroturbulent cascades of energy and enstrophy in models and observations of planetary atmospheres Peter Read + Roland Young + Fachreddin Tabataba-Vakili + Yixiong Wang [Dept. of Physics, University of
Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification
 Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification Stamen Dolaptchiev & Rupert Klein Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification Stamen Dolaptchiev & Rupert Klein Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
Quasigeostrophic Dynamics of the Western Boundary Current
 OCTOBER 1999 BERLOFF AND MCWILLIAMS 607 Quasigeostrophic Dynamics of the Western Boundary Current PAVEL S. BERLOFF AND JAMES C. MCWILLIAMS Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
OCTOBER 1999 BERLOFF AND MCWILLIAMS 607 Quasigeostrophic Dynamics of the Western Boundary Current PAVEL S. BERLOFF AND JAMES C. MCWILLIAMS Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
Long-Term Variability of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water in Response to Spin-Up of the Subtropical Gyre
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 279 to 290, 2003 Long-Term Variability of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water in Response to Spin-Up of the Subtropical Gyre TAMAKI YASUDA* and YOSHITERU KITAMURA
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 279 to 290, 2003 Long-Term Variability of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water in Response to Spin-Up of the Subtropical Gyre TAMAKI YASUDA* and YOSHITERU KITAMURA
Dissipative Selection of Low-Frequency Modes in a Reduced-Gravity Basin
 127 Dissipative Selection of Low-Frequency Modes in a Reduced-Gravity Basin PAOLA CESSI AND FRANÇOIS PRIMEAU Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California (Manuscript received 28 September
127 Dissipative Selection of Low-Frequency Modes in a Reduced-Gravity Basin PAOLA CESSI AND FRANÇOIS PRIMEAU Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California (Manuscript received 28 September
2/15/2012. Earth System Science II EES 717 Spring 2012
 Earth System Science II EES 717 Spring 2012 1. The Earth Interior Mantle Convection & Plate Tectonics 2. The Atmosphere - Climate Models, Climate Change and Feedback Processes 3. The Oceans Circulation;
Earth System Science II EES 717 Spring 2012 1. The Earth Interior Mantle Convection & Plate Tectonics 2. The Atmosphere - Climate Models, Climate Change and Feedback Processes 3. The Oceans Circulation;
3.3 Classification Diagrams Estuarine Zone Coastal Lagoons References Physical Properties and Experiments in
 Contents 1 Introduction to Estuary Studies... 1 1.1 Why to Study Estuaries?.... 1 1.2 Origin and Geological Age... 4 1.3 Definition and Terminology... 7 1.4 Policy and Actions to Estuary Preservation....
Contents 1 Introduction to Estuary Studies... 1 1.1 Why to Study Estuaries?.... 1 1.2 Origin and Geological Age... 4 1.3 Definition and Terminology... 7 1.4 Policy and Actions to Estuary Preservation....
The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment
 The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment Norman A. Phillips (1956) Presentation by Lukas Strebel and Fabian Thüring Goal of the Model Numerically predict the mean state of the
The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment Norman A. Phillips (1956) Presentation by Lukas Strebel and Fabian Thüring Goal of the Model Numerically predict the mean state of the
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. El Niño Southern Oscillation and North Atlantic Oscillation Control of Climate in Puerto Rico
 2713 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE El Niño Southern Oscillation and North Atlantic Oscillation Control of Climate in Puerto Rico BJÖRN A. MALMGREN Department of Earth Sciences, University of Göteborg, Goteborg,
2713 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE El Niño Southern Oscillation and North Atlantic Oscillation Control of Climate in Puerto Rico BJÖRN A. MALMGREN Department of Earth Sciences, University of Göteborg, Goteborg,
Models of Marginal Seas Partially Enclosed by Islands
 Models of Marginal Seas Partially Enclosed by Islands Roxana C. Wajsowicz Dept. of Meteorology University of Maryland 3433 Computer and Space Science Building College Park, MD 20852 Phone: (301) 405-5396
Models of Marginal Seas Partially Enclosed by Islands Roxana C. Wajsowicz Dept. of Meteorology University of Maryland 3433 Computer and Space Science Building College Park, MD 20852 Phone: (301) 405-5396
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
Islands in Zonal Flow*
 689 Islands in Zonal Flow* MICHAEL A. SPALL Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 1 April 003, in final form 9 June 003)
689 Islands in Zonal Flow* MICHAEL A. SPALL Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 1 April 003, in final form 9 June 003)
Buoyancy-forced circulations in shallow marginal seas
 Journal of Marine Research, 63, 729 752, 2005 Buoyancy-forced circulations in shallow marginal seas by Michael A. Spall 1 ABSTRACT The properties of water mass transformation and the thermohaline circulation
Journal of Marine Research, 63, 729 752, 2005 Buoyancy-forced circulations in shallow marginal seas by Michael A. Spall 1 ABSTRACT The properties of water mass transformation and the thermohaline circulation
Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea
 Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea Olga Trusenkova V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia PICES 2014 Annual Meeting, 16-26 October 2014, Korea, Yeosu Deep
Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea Olga Trusenkova V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia PICES 2014 Annual Meeting, 16-26 October 2014, Korea, Yeosu Deep
The Beaufort Gyre: Models, Observations, & Truth
 The Beaufort Gyre: Models, Observations, & Truth Michael Steele, Jinlun Zhang, & Wendy Ermold PSC / APL / U of WA Seattle WA 7 th AOMIP workshop GFDL, Princeton, NJ June 14-15, 2004 Abstract We have performed
The Beaufort Gyre: Models, Observations, & Truth Michael Steele, Jinlun Zhang, & Wendy Ermold PSC / APL / U of WA Seattle WA 7 th AOMIP workshop GFDL, Princeton, NJ June 14-15, 2004 Abstract We have performed
Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.
![Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz. Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.](/thumbs/88/117265944.jpg) Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
The Dynamics of a Simple Baroclinic Model of the Wind-Driven Circulation
 FEBRUARY 1998 BERLOFF AND MEACHAM 361 The Dynamics of a Simple Baroclinic Model of the Wind-Driven Circulation P. BERLOFF Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles,
FEBRUARY 1998 BERLOFF AND MEACHAM 361 The Dynamics of a Simple Baroclinic Model of the Wind-Driven Circulation P. BERLOFF Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles,
8 3D transport formulation
 8 3D transport formulation 8.1 The QG case We consider the average (x; y; z; t) of a 3D, QG system 1. The important distinction from the zonal mean case is that the mean now varies with x, or (more generally)
8 3D transport formulation 8.1 The QG case We consider the average (x; y; z; t) of a 3D, QG system 1. The important distinction from the zonal mean case is that the mean now varies with x, or (more generally)
On the Propagation of Baroclinic Waves in the General Circulation
 VOLUME 30 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY NOVEMBER 2000 On the Propagation of Baroclinic Waves in the General Circulation WILLIAM K. DEWAR Department of Oceanography and Supercomputer Computations Research
VOLUME 30 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY NOVEMBER 2000 On the Propagation of Baroclinic Waves in the General Circulation WILLIAM K. DEWAR Department of Oceanography and Supercomputer Computations Research
OCEANIC SUBMESOSCALE SAMPLING WITH WIDE-SWATH ALTIMETRY. James C. McWilliams
 . OCEANIC SUBMESOSCALE SAMPLING WITH WIDE-SWATH ALTIMETRY James C. McWilliams Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Institute of Geophysics & Planetary Physics U.C.L.A. Recall the long-standing
. OCEANIC SUBMESOSCALE SAMPLING WITH WIDE-SWATH ALTIMETRY James C. McWilliams Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Institute of Geophysics & Planetary Physics U.C.L.A. Recall the long-standing
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B
 Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Modeling the atmosphere of Jupiter
 Modeling the atmosphere of Jupiter Bruce Turkington UMass Amherst Collaborators: Richard S. Ellis (UMass Professor) Andrew Majda (NYU Professor) Mark DiBattista (NYU Postdoc) Kyle Haven (UMass PhD Student)
Modeling the atmosphere of Jupiter Bruce Turkington UMass Amherst Collaborators: Richard S. Ellis (UMass Professor) Andrew Majda (NYU Professor) Mark DiBattista (NYU Postdoc) Kyle Haven (UMass PhD Student)
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes
 Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
climate system and its subcomponents: the atmosphere, ocean, land surface, Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A A general description of the Earth
 Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
On Derivation and Interpretation of Kuo Eliassen Equation
 1 On Derivation and Interpretation of Kuo Eliassen Equation Jun-Ichi Yano 1 1 GAME/CNRM, Météo-France and CNRS, 31057 Toulouse Cedex, France Manuscript submitted 22 September 2010 The Kuo Eliassen equation
1 On Derivation and Interpretation of Kuo Eliassen Equation Jun-Ichi Yano 1 1 GAME/CNRM, Météo-France and CNRS, 31057 Toulouse Cedex, France Manuscript submitted 22 September 2010 The Kuo Eliassen equation
Climate/Ocean dynamics
 Interannual variations of the East-Kamchatka and East-Sakhalin Currents volume transports and their impact on the temperature and chemical parameters in the Okhotsk Sea Andrey G. Andreev V.I. Il ichev
Interannual variations of the East-Kamchatka and East-Sakhalin Currents volume transports and their impact on the temperature and chemical parameters in the Okhotsk Sea Andrey G. Andreev V.I. Il ichev
Changes in the Ventilation of the Southern Oceans, and links to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Changes in the Ventilation of the Southern Oceans, and links to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Darryn W. Waugh Dept of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University Collaborators: Francois Primeau,
Changes in the Ventilation of the Southern Oceans, and links to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Darryn W. Waugh Dept of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University Collaborators: Francois Primeau,
Dynamics of Downwelling in an Eddy-Resolving Convective Basin
 OCTOBER 2010 S P A L L 2341 Dynamics of Downwelling in an Eddy-Resolving Convective Basin MICHAEL A. SPALL Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 11 March
OCTOBER 2010 S P A L L 2341 Dynamics of Downwelling in an Eddy-Resolving Convective Basin MICHAEL A. SPALL Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 11 March
Optimal Surface Salinity Perturbations of the Meridional Overturning and Heat Transport in a Global Ocean General Circulation Model
 DECEMBER 2008 S É V E L L E C E T A L. 2739 Optimal Surface Salinity Perturbations of the Meridional Overturning and Heat Transport in a Global Ocean General Circulation Model FLORIAN SÉVELLEC, THIERRY
DECEMBER 2008 S É V E L L E C E T A L. 2739 Optimal Surface Salinity Perturbations of the Meridional Overturning and Heat Transport in a Global Ocean General Circulation Model FLORIAN SÉVELLEC, THIERRY
Tracer transport in a sea of vortices
 Tracer transport in a sea of vortices A. Provenzale ISAC-CNR, Torino and CIMA, Savona, Italy Work done with: Annalisa Bracco, Jost von Hardenberg, Claudia Pasquero A. Babiano, E. Chassignet, Z. Garraffo,
Tracer transport in a sea of vortices A. Provenzale ISAC-CNR, Torino and CIMA, Savona, Italy Work done with: Annalisa Bracco, Jost von Hardenberg, Claudia Pasquero A. Babiano, E. Chassignet, Z. Garraffo,
Eddies, Waves, and Friction: Understanding the Mean Circulation in a Barotropic Ocean Model
 Eddies, Waves, and Friction: Understanding the Mean Circulation in a Barotropic Ocean Model Baylor Fox-Kemper Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Program, Princeton University and NOAA Climate and Global
Eddies, Waves, and Friction: Understanding the Mean Circulation in a Barotropic Ocean Model Baylor Fox-Kemper Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Program, Princeton University and NOAA Climate and Global
Climatic changes in the troposphere, stratosphere and lower mesosphere in
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Climatic changes in the troposphere, stratosphere and lower mesosphere in 1979-2016 To cite this article: Y P Perevedentsev et al
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Climatic changes in the troposphere, stratosphere and lower mesosphere in 1979-2016 To cite this article: Y P Perevedentsev et al
Ocean Eddy Dynamics in a Coupled Ocean Atmosphere Model*
 MAY 2007 B E R L O F F E T A L. 1103 Ocean Eddy Dynamics in a Coupled Ocean Atmosphere Model* P. BERLOFF Physical Oceanography Department, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts,
MAY 2007 B E R L O F F E T A L. 1103 Ocean Eddy Dynamics in a Coupled Ocean Atmosphere Model* P. BERLOFF Physical Oceanography Department, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts,
