Announcements. - Marie Friday 3/17, 4-5pm NatSci2 Annex Plato Sunday, 3/20, 3-4pm, NatSci2 Annex 101
|
|
|
- Willis Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements Please fill out an on-line course evaluation Final Exam: Wednesday, 3/22, 7:30pm - 3 hours - same format, rules as midterm: multiple choice with formula sheet, closed book and notes, bring a #2 pencil and a non-internet-enabled calculator Cumulative: study the midterm material, too Review sessions: - Marie Friday 3/17, 4-5pm NatSci2 Annex Plato Sunday, 3/20, 3-4pm, NatSci2 Annex 101
2 Final Exam Review Review the midterm. There will be material from the first half of the class on the final. The best way to study for that is to review the midterm. Review the homework and reading assignments Go to the TA review sessions Formula sheet will be available and posted on the course web pages.
3 Properties of Thermal Radiation Stefan - Boltzmann Law: Energy output per second per meter 2 on the surface of an object = σt 4 Luminosity = total energy flow into or out of an object Units: Energy/sec or Power, Joules/s or Watts Stefan - Boltzmann Law: Luminosity = Total surface area of object σt 4 Universal constant: σ = 5.7x10-8 J/(s m 2 K 4 )
4 Kirchoff s Laws 1) Dense, opaque objects: continuous spectrum, thermal emission Wavelength 2) Transparent, low-density matter: If too hot to re-absorb photons: emission line spectrum Wavelength
5 Kirchoff s Laws 3) Thermal emission traveling through some other matter? Transparent, cool matter: atoms can re-absorb the light Observe: an absorption line spectrum This is often the spectrum we observe from stars and galaxies (which are made of stars) Exception: hot gas in galaxies, where stars are born or black holes live.
6 Vradial = Δλ = λshift - λrest c λrest λrest Doppler Shift We can measure the velocity (direction and speed) of a light source from its Doppler Shift. Rest Red shift, moving away Larger red shift, moving away faster Blue shift, moving toward you Larger blue shift, moving toward you faster
7 Recap: Nucleosynthesis How do you make energy out of 2 x kg of Hydrogen? One Helium atom is less massive than 4 Hydrogen atoms? 4 H atoms = 4 protons: x kg 1 He atom = 2 protons + 2 neutrons: x kg (less massive by 0.7%) If you stick together Hydrogen atoms to make Helium, the extra mass has to go somewhere. It becomes energy: E = mc 2 Mass and energy are the same thing, and transform back and forth using this equation. Fusing Hydrogen into Helium must release energy
8 Q θ Measuring Distance Distance d to a star with a parallax measurement p of 1 arc second Units for angles: 1 degree = 60 arcminutes = 3600 arcseconds In symbols: 1º = 60 = = 60 d = Q p 206,265 Q θ d = (1 AU) x 206,265 p Define a REALLY convenient unit: 1 Parsec = AU = 3x10 16 m d (parsec) = 1 p (arceconds) d = distance in parsec, p = parallax angle in arcseconds
9 Measuring Masses of Stars What if M1, M2 are both large, like binary stars? Objects always orbit the Center of Mass. CM stays still. M1 and M2 orbit around it. Use: P 2 = 4π 2 G(M1+M2) A 3 Measure P, A, solve for M1+M2
10 Measuring Luminosity Luminosity: total amount of energy put out by an object. Units: Joules/sec Always the same, a property of an object (table, me, star,...) Depends on temperature and surface area of the emitting object Stefan - Boltzmann Law: Luminosity = Total surface area σt 4
11 area of sphere: 4πd 2 Measuring Luminosity What can we measure? Light passing through a patch on the sphere Apparent brightness of an object = Luminosity = L like a star, etc. Surface Area 4πd 2 Apparent brightness depends on distance to the object. Objects that are farther away appear fainter: we collect less energy/sec in our eyes,camera, etc. because our eyes,camera are the same size no matter how far away the star is Luminosity is always the same. It s a property of the star.
12 Measuring Luminosity If we can measure the apparent brightness B and the distance to the star d, we can measure the Luminosity of the star L Measure apparent brightness in some patch of area on the sphere: your eye, a telescope, a camera,... L Apparent brightness B = rearrange: L = B (4πd 2 ) 4πd 2
13 Measuring the Stars Measure Luminosity of a star: total energy output per second, by measuring the apparent brightness and distance L Apparent Brightness = 4πd 2 Temperature: from Wein s Law (wavelength of max photon emission) Chemical composition: matching chemical fingerprints of different atoms to lines in the spectrum Mass: period and distance separation of binary star orbits Distance: parallax Size: from Luminosity and Temperature, using Stefan-Boltzmann law Luminosity = Total surface area σt 4
14 Gravitational Equilibrium in the Sun Pressure = Force Area High temperature (hot): molecules and atoms have lots of kinetic energy (1/2 mv 2 ), so every time an atom changes direction it gets a big acceleration. Lots of force per bounce high pressure. Low temperature (cool): less kinetic energy, less acceleration from every bounce lower pressure Perfect Gas Law: Pressure = k density x temperature Many molecules (high density): many collisions = high pressure Few molecules (low density): few collisions = low pressure k = universal constant perfect : assumes molecules and atoms bounce perfectly in every collision. Chemistry tells us that doesn t always happen: sometimes they stick together and make molecules
15 Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Relations between luminosity, mass, size, temperature and lifetime of stars. Where are most of the stars? On the Main Sequence. Maintain gravitational equilibrium, hold themselves up against gravity by generating energy in their core from nuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium: 4H He + Energy
16 Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Relations between luminosity, mass, size, temperature of stars. Where are all the stars? On the Main Sequence. Main sequence is a sequence in mass: Hot,bright massive stars at top left Cool, faint low-mass stars at bottom right Why?
17 Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Higher mass = more pressure from gravity Star has to generate more energy from nuclear fusion to create more thermal pressure to hold itself up against gravity
18 Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Higher mass = more pressure from gravity Higher mass: Higher core pressure, need Higher core temperature. Need larger rate of energy generation from fusion to hold the star up Lower mass: lower core pressure, lower core temperature. Can counter-act the pressure from gravity with a lower energy generation rate from nuclear fusion.
19 Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Higher mass = more pressure from gravity Higher mass: Higher core pressure, need Higher core temperature. Need larger rate of energy generation from fusion to hold the star up Lower mass: lower core pressure, lower core temperature. Can counter-act the pressure from gravity with a lower energy generation rate from nuclear fusion. main sequence lifetime: tms = M years L M,L in units of solar mass, luminosity
20 Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Higher mass = more pressure from gravity Main sequence: - Powered by nucleosynthesis of H to He - Properties set by mass. High mass: High luminosity Blue = high temperature Large radius Short lifetime Low Mass: Low luminosity Red = cool temperature Small radius Long lifetime
21 High Mass Stars: Post Main Sequence Evolution New fusion cycles initiated as core collapses, never becomes degenerate. Q: When does it stop? A: When fusion of new elements doesn t release energy Mass per particle in the nucleus decreases from H to Fe. Where does it go? It is converted to energy Remember: of 4 H nuclei > 1 He nucleus. Δm = Mass4H - MassHe Eout = Δmc 2 Mass per particle goes down as fusion makes heaver atomic nuclei H, He,... C...Fe...Ag...Pb...U increasing number of particles in nucleus for elements in the periodic table
22 High Mass Stars: Post Main Sequence Evolution Iron (Fe) is the end of the line for fusion. Fe nucleus has lowest mass per particle: no conversion of mass to energy when you add more particles Now gravity can win as the core collapses. Star can t generate energy to hold itself up with thermal pressure. Mass per particle goes down as fusion makes heaver atomic nuclei mass per particle goes up for elements heavier than iron
23 High Mass Stars: Post Main Sequence Evolution Mass per particle (neutron, proton) in the nucleus increases for elements heavier than Fe. Mass per particle of a lead nucleus > Mass per particle of an iron nucleus. Δm = MassFe - MassPb < 0 No energy out by fusing nuclei to make lead How are these elements made? Put energy in during the explosions that end the lives of massive stars Mass per particle goes down as fusion makes heaver atomic nuclei mass per particle goes up for elements heavier than iron H, He,... C...Fe...Ag...Pb...U increasing number of particles in nucleus for elements in the periodic table
24 General Relativity Implication #1: The path of light is always straight, but space is bent by gravity. light crossing event horizon Space curved if the sun were a black hole If mass is dense enough, there is a radius from which light can t escape. Radius of this Event Horizon = Schwarzschild Radius
25 Black Holes Escape velocity: velocity needed to get free of an object s gravitational pull. M = mass, d = distance from the center vescape = 2 G M of the object you want to escape from d For a star, light is emitted at its surface, so d is the radius of the star, R If M is very big and/or R is very small, then Vescape > c, the speed of light. NOTHING can have speed > c, so NOTHING can escape, not even light. Star becomes a Black Hole Artist s rendition, not a real picture
26 Black Holes For any mass define a radius, the Schwarzschild radius Rs, where Vescape = c vescape = 2 G M R Then rearrange: Artist s rendition, not a real picture Rs = 2GM = c 2 ( 2G ) c 2 M If M = Msun, Rs = 3 km So for any star, Rs = 3 km M* Msun
27 Black Holes Black holes in the centers of galaxies can pull in gas from the rest of the galaxy. As the gas falls in the atoms collide. The gas heats up due to friction and the release of gravitational potential energy. The gas emits radiation, though not a thermal spectrum. Can be incredibly bright, out-shine an entire galaxy.
28 Quasars Eventually, realized that quasars are black holes in the centers of galaxies. That huge luminosity is the light from gas that is glowing from the energy it gains as it falls in to the black hole. Infall converts gravitational potential energy to other kinds of energy. Stored in the energy levels of atoms, released as emission line spectra and other interactions
29 Measuring the Size of Quasars
30 Milky Way: Mass What do you expect will happen to the velocity once the circles get big enough to enclose all the stars? A) velocity increase as radius gets larger (green circle and beyond) B) velocity should decrease as radius gets larger (green circle and beyond) Remember, speed of an orbit around mass M:
31 Milky Way: Mass What do you expect will happen to the velocity once the circles get big enough to enclose all the stars? Velocity should decrease at larger radii, just like for the solar system. All the mass is inside the large circles, right?
32 Milky Way: Mass What we measure is wonderfully weird: the velocity stays constant. So mass must still be increasing with radius
33 Milky Way: Mass What we measure is wonderfully weird: the velocity stays constant. So mass must still be increasing with radius
34 Milky Way: Mass We can t see it, but the velocity measurements tell us there is mass at larger distances than all the mass we can see
35 Galaxies in the Universe Light travels at a finite speed (300,000 km/s). Galaxies at large distances light left those galaxies a long time ago. Large distance = large look-back time The distance to Andromeda, the nearest galaxy to the Milky Way (our galaxy), is 2.5 million light-years. Stars in the Andromeda galaxy emitted the light we see when we look at Andromeda today 2.5 million years ago.
36 Distances to Galaxies More luminous Cepheids have longer periods Cepheid Variable This is incredibly useful: if you can measure period, you can learn luminosity of a Cepheid without knowing its distance If you also measure the apparent brightness, you can learn the distance to the Cepheid, and therefore to the star cluster or galaxy it lives in: Period of cycle Cepheid period-luminosity relation B
37 Distances to Galaxies Edwin Hubble (him again) used the inverse square law for light again to measure the distances to other galaxies. Astronomers already knew that the spectra of almost all other galaxies is red-shifted. normal galaxy spectrum. Looks like the sum of many star spectra. More light from bright stars, less from faint stars. This is what we observe. Redshift (z): This is just the Doppler formula for light (Chapter 5)
38 Hubble s Law and the Expanding Universe Hubble s Law v = H0 D H0 = 21 (km/s)/mly H0 = Hubble s Constant, relates distance and velocity Looks like all the galaxies are moving away from us More distant galaxies are moving faster. Space is expanding, so the distance between galaxies is growing. Measure a galaxy s Doppler velocity (redshift), know H0, find its distance from us.
39 Hubble s Law and the Expanding Universe Hubble s Law: v = H0 D 1 has units of seconds = time H0 What time is that? Time since the expansion started. That s the age of the universe. Galaxies that are farther away are going faster. All galaxies take the same amount of time to get where they are now if they all started very close together and the universe expands at a constant rate.
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Black Hole Binary System. Outline - Feb. 25, Constraining the Size of the Region that Contains the Invisible Mass
 Outline - Feb. 25, 2010 Black Hole Binary System Observational evidence for Black Holes (pgs. 600-601) Properties of Stars (Ch. 16) Luminosities (pgs. 519-523) Temperatures (pg. 524) Optical image of Cygnus
Outline - Feb. 25, 2010 Black Hole Binary System Observational evidence for Black Holes (pgs. 600-601) Properties of Stars (Ch. 16) Luminosities (pgs. 519-523) Temperatures (pg. 524) Optical image of Cygnus
Announcements. There is no homework next week. Tuesday s sections (right after the midterm) will be cancelled.
 1 Announcements The Midterm is one week away! Bring: Calculator, scantron (big red form), pencil No notes, cellphones, or books allowed. Homework #4 is due this thursday There is no homework next week.
1 Announcements The Midterm is one week away! Bring: Calculator, scantron (big red form), pencil No notes, cellphones, or books allowed. Homework #4 is due this thursday There is no homework next week.
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam
 Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Lec 9: Stellar Evolution and DeathBirth and. Why do stars leave main sequence? What conditions are required for elements. Text
 1 Astr 102 Lec 9: Stellar Evolution and DeathBirth and Evolution Why do stars leave main sequence? What conditions are required for elements Text besides Hydrogen to fuse, and why? How do stars die: white
1 Astr 102 Lec 9: Stellar Evolution and DeathBirth and Evolution Why do stars leave main sequence? What conditions are required for elements Text besides Hydrogen to fuse, and why? How do stars die: white
Selected Questions from Minute Papers. Outline - March 2, Stellar Properties. Stellar Properties Recap. Stellar properties recap
 Black Holes: Selected Questions from Minute Papers Will all the material in the Milky Way eventually be sucked into the BH at the center? Does the star that gives up mass to a BH eventually get pulled
Black Holes: Selected Questions from Minute Papers Will all the material in the Milky Way eventually be sucked into the BH at the center? Does the star that gives up mass to a BH eventually get pulled
Relative Sizes of Stars. Today Exam#3 Review. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Blackbody Radiation
 Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti
 Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation!
 AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation! Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons
AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation! Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons
Beyond the Solar System 2006 Oct 17 Page 1 of 5
 I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
2) On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find red giant stars? A) upper right B) lower right C) upper left D) lower left
 Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? 1. How
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? 1. How
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24
 Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a. Chapter 34: Cosmology. Cosmology: How the Universe Works
 Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
The Big Bang Theory. Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra
 The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Neutron Stars, Black Holes, Pulsars and More
 Neutron Stars, Black Holes, Pulsars and More October 30, 2002 1) Star Clusters 2) Type II Supernova 3) Neutron Stars 4) Black Holes 5) More Gravity Announcements Extra Credit there is an extra credit assignment
Neutron Stars, Black Holes, Pulsars and More October 30, 2002 1) Star Clusters 2) Type II Supernova 3) Neutron Stars 4) Black Holes 5) More Gravity Announcements Extra Credit there is an extra credit assignment
Galaxies and the expansion of the Universe
 Review of Chapters 14, 15, 16 Galaxies and the expansion of the Universe 5/4/2009 Habbal Astro 110-01 Review Lecture 36 1 Recap: Learning from Light How does light tell us what things are made of? Every
Review of Chapters 14, 15, 16 Galaxies and the expansion of the Universe 5/4/2009 Habbal Astro 110-01 Review Lecture 36 1 Recap: Learning from Light How does light tell us what things are made of? Every
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A
 29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Final Exam December 13, 2010 Form A
 29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Final Exam December 13, 2010 Form A There are 40 questions. Read each question and all of the choices before choosing. Budget your time. No whining. Walk with Ursus!
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Final Exam December 13, 2010 Form A There are 40 questions. Read each question and all of the choices before choosing. Budget your time. No whining. Walk with Ursus!
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27, Section 1. Composition & Temperature. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of Stars
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
ASTRONOMY 1 EXAM 3 a Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 EXAM 3 a Name Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each = 20 pts.) Multiple Choice (25 @ 2 points each = 50 pts.) Essays (choose 3 of 4 @ 10 points each = 30 pt 1.Luminosity D 8.White dwarf
ASTRONOMY 1 EXAM 3 a Name Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each = 20 pts.) Multiple Choice (25 @ 2 points each = 50 pts.) Essays (choose 3 of 4 @ 10 points each = 30 pt 1.Luminosity D 8.White dwarf
Today. Homework Due. Stars. Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions. proton-proton chain. CNO cycle. Stellar Lifetimes
 Today Stars Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions proton-proton chain CNO cycle Stellar Lifetimes Homework Due Stellar Properties Luminosity Surface Temperature Size Mass Composition Stellar Properties
Today Stars Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions proton-proton chain CNO cycle Stellar Lifetimes Homework Due Stellar Properties Luminosity Surface Temperature Size Mass Composition Stellar Properties
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
Chapter 33 The History of a Star. Introduction. Radio telescopes allow us to look into the center of the galaxy. The milky way
 Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
IB Physics - Astronomy
 Solar System Our Solar System has eight planets. The picture below shows their relative sizes, but NOT their relative distances. A planet orbits the sun, and has gravitationally cleared its orbital area
Solar System Our Solar System has eight planets. The picture below shows their relative sizes, but NOT their relative distances. A planet orbits the sun, and has gravitationally cleared its orbital area
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution. How do we observe the life histories of galaxies?
 Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
Notes for Wednesday, July 16; Sample questions start on page 2 7/16/2008
 Notes for Wednesday, July 16; Sample questions start on page 2 7/16/2008 Wed, July 16 MW galaxy, then review. Start with ECP3Ch14 2 through 8 Then Ch23 # 8 & Ch 19 # 27 & 28 Allowed Harlow Shapely to locate
Notes for Wednesday, July 16; Sample questions start on page 2 7/16/2008 Wed, July 16 MW galaxy, then review. Start with ECP3Ch14 2 through 8 Then Ch23 # 8 & Ch 19 # 27 & 28 Allowed Harlow Shapely to locate
ASTR Midterm 1 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 1 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson FIRST MID-TERM EXAM FEBRUARY 16 th 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 1 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson FIRST MID-TERM EXAM FEBRUARY 16 th 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
PHYS 160 Astronomy Take-home Test #4 Fall 2017
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Take-home Test #4 Fall 2017 Instructions: This is a take-home test. The test period starts Monday 11/27/2017 at 2:10pm and ends at Wednesday 11/29/2017 at 1:10pm. The test must represent
PHYS 160 Astronomy Take-home Test #4 Fall 2017 Instructions: This is a take-home test. The test period starts Monday 11/27/2017 at 2:10pm and ends at Wednesday 11/29/2017 at 1:10pm. The test must represent
Hydrogen Lines. What can we learn from light? Spectral Classification. Visible Hydrogen Spectrum Lines: Series. Actual Spectrum from SDSS
 What can we learn from light? Hydrogen Lines Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the! Lower E, Lower f, λ Visible! Higher E, Higher f, λ Visible Hydrogen Spectrum
What can we learn from light? Hydrogen Lines Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the! Lower E, Lower f, λ Visible! Higher E, Higher f, λ Visible Hydrogen Spectrum
TA Final Review. Class Announcements. Objectives Today. Compare True and Apparent brightness. Finding Distances with Cepheids
 Class Announcements Vocab Quiz 4 deadline is Saturday Midterm 4 has started, ends Monday Lab was in the Planetarium. You still need to do the 2 questions Check PS100 webpage, make sure your clicker is
Class Announcements Vocab Quiz 4 deadline is Saturday Midterm 4 has started, ends Monday Lab was in the Planetarium. You still need to do the 2 questions Check PS100 webpage, make sure your clicker is
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008
 Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
To infinity, and beyond!
 stars The night sky is filled with stars that shine at different levels of brightness. The brightness of the stars we observe can be related to the size of the star or its distance from Earth. In order
stars The night sky is filled with stars that shine at different levels of brightness. The brightness of the stars we observe can be related to the size of the star or its distance from Earth. In order
Today. Spectra. Thermal Radiation. Wien s Law. Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Spectra & Composition
 Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
How Do Stars Appear from Earth?
 How Do Stars Appear from Earth? Magnitude: the brightness a star appears to have from Earth Apparent Magnitude depends on 2 things: (actual intrinsic brightness) The color of a star is related to its temperature:
How Do Stars Appear from Earth? Magnitude: the brightness a star appears to have from Earth Apparent Magnitude depends on 2 things: (actual intrinsic brightness) The color of a star is related to its temperature:
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
ASTR : Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)... Study Guide for Midterm 1
 ASTR-1200-01: Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)........................ Study Guide for Midterm 1 The first midterm exam for ASTR-1200 takes place in class on Wednesday, February 13, 2019. The exam covers
ASTR-1200-01: Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)........................ Study Guide for Midterm 1 The first midterm exam for ASTR-1200 takes place in class on Wednesday, February 13, 2019. The exam covers
11/1/16. Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) Important Stuff (Section 002, 1:00 pm) 14.1 White Dwarfs. Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) The Second Midterm is Thursday, November 10 The Second Midterm will be given in a different room: Willey 175 Bring 2 pencils and a photo-id. In accordance with the
Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) The Second Midterm is Thursday, November 10 The Second Midterm will be given in a different room: Willey 175 Bring 2 pencils and a photo-id. In accordance with the
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09. Astronomy 101
 High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
Astronomy 1143 Quiz 2 Review
 Astronomy 1143 Quiz 2 Review Prof. Pradhan October 1, 2018 Light 1. What is light? Light is electromagnetic energy It is both a particle (photon) and a wave 2. How is light created and what can light interact
Astronomy 1143 Quiz 2 Review Prof. Pradhan October 1, 2018 Light 1. What is light? Light is electromagnetic energy It is both a particle (photon) and a wave 2. How is light created and what can light interact
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers
 Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars
 Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? How do we
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? How do we
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Final exam is Wednesday, December 14, in LR 1 VAN at 9:45 am.
 Announcements Final exam is Wednesday, December 14, in LR 1 VAN at 9:45 am. Office hours: Tuesday 9-11 am, 1 2 pm, and 3-4 pm or by appointment in 702 VAN There will be no Astronomy tutorial during finals
Announcements Final exam is Wednesday, December 14, in LR 1 VAN at 9:45 am. Office hours: Tuesday 9-11 am, 1 2 pm, and 3-4 pm or by appointment in 702 VAN There will be no Astronomy tutorial during finals
Astronomy Hour Exam 2 March 10, 2011 QUESTION 1: The half-life of Ra 226 (radium) is 1600 years. If you started with a sample of 100 Ra 226
 Astronomy 101.003 Hour Exam 2 March 10, 2011 QUESTION 1: The half-life of Ra 226 (radium) is 1600 years. If you started with a sample of 100 Ra 226 atoms, approximately how many Ra 226 atoms would be left
Astronomy 101.003 Hour Exam 2 March 10, 2011 QUESTION 1: The half-life of Ra 226 (radium) is 1600 years. If you started with a sample of 100 Ra 226 atoms, approximately how many Ra 226 atoms would be left
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
Chapter 15: Surveying the Stars
 Chapter 15 Lecture Chapter 15: Surveying the Stars Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How
Chapter 15 Lecture Chapter 15: Surveying the Stars Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How
5. A particular star has an angle of parallax of 0.2 arcsecond. What is the distance to this star? A) 50 pc B) 2 pc C) 5 pc D) 0.
 Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
ANSWER KEY. Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe. Telescopes Guided Reading and Study. Characteristics of Stars Guided Reading and Study
 Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
How does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Lifetime of the Sun. Luminosity of the Sun. Radiation Zone. Core 3/30/17
 What is the Sun s structure? From inside out, the layers are: Core Radiation Zone Convection Zone Photosphere Chromosphere Corona How does the Sun shine? The Sun has its own energy source Main difference
What is the Sun s structure? From inside out, the layers are: Core Radiation Zone Convection Zone Photosphere Chromosphere Corona How does the Sun shine? The Sun has its own energy source Main difference
The Universe. But first, let s talk about light! 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 The Universe But first, let s talk about light! Light is fast! The study of light All forms of radiation travel at 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second Since objects in space are so far away,
The Universe But first, let s talk about light! Light is fast! The study of light All forms of radiation travel at 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second Since objects in space are so far away,
Light, Energy and Matter
 Announcements You should see a polling session active if you are using the REEF app. Make sure you are signed in I have thee iclickers to loan out. First come, first served. If you borrow one, please remember
Announcements You should see a polling session active if you are using the REEF app. Make sure you are signed in I have thee iclickers to loan out. First come, first served. If you borrow one, please remember
The Night Sky. The Universe. The Celestial Sphere. Stars. Chapter 14
 The Night Sky The Universe Chapter 14 Homework: All the multiple choice questions in Applying the Concepts and Group A questions in Parallel Exercises. Celestial observation dates to ancient civilizations
The Night Sky The Universe Chapter 14 Homework: All the multiple choice questions in Applying the Concepts and Group A questions in Parallel Exercises. Celestial observation dates to ancient civilizations
Test #2 results. Grades posted in UNM Learn. Along with current grade in the class
 Test #2 results Grades posted in UNM Learn D C B A Along with current grade in the class F Clicker Question: If the Earth had no Moon then what would happen to the tides? A: The tides would not be as strong
Test #2 results Grades posted in UNM Learn D C B A Along with current grade in the class F Clicker Question: If the Earth had no Moon then what would happen to the tides? A: The tides would not be as strong
The Cosmic Perspective. Surveying the Properties of Stars. Surveying the Stars. How do we measure stellar luminosities?
 Surveying the Stars Chapter 15 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we
Surveying the Stars Chapter 15 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we
Midterm Study Guide Astronomy 122
 Midterm Study Guide Astronomy 122 Introduction: 1. How is modern Astronomy different from Astrology? 2. What is the speed of light? Is it constant or changing? 3. What is an AU? Light-year? Parsec? Which
Midterm Study Guide Astronomy 122 Introduction: 1. How is modern Astronomy different from Astrology? 2. What is the speed of light? Is it constant or changing? 3. What is an AU? Light-year? Parsec? Which
A star is at a distance of 1.3 parsecs, what is its parallax?
 Stars Spectral lines from stars Binaries and the masses of stars Classifying stars: HR diagram Luminosity, radius, and temperature Vogt-Russell theorem Main sequence Evolution on the HR diagram A star
Stars Spectral lines from stars Binaries and the masses of stars Classifying stars: HR diagram Luminosity, radius, and temperature Vogt-Russell theorem Main sequence Evolution on the HR diagram A star
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect
 Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect Learning objectives Explain why the wavelength of waves from a moving source depends on the speed of the source. Define Doppler shift. Measure the velocity of
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect Learning objectives Explain why the wavelength of waves from a moving source depends on the speed of the source. Define Doppler shift. Measure the velocity of
PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1
 PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1 PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 2 1 The star alpha-centauri C has moved across the sky by 3853 seconds of arc during the last thousand years - slightly more
PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1 PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 2 1 The star alpha-centauri C has moved across the sky by 3853 seconds of arc during the last thousand years - slightly more
PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1
 PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1 PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 2 1 A steady X-ray signal with sudden bursts lasting a few seconds each is probably caused by a. a supermassive star. b. a
PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1 PHYS103 Sec 901 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 2 1 A steady X-ray signal with sudden bursts lasting a few seconds each is probably caused by a. a supermassive star. b. a
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
 Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Lecture Outline Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 14.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf?
Lecture Outline Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 14.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf?
Spectrographs: instrument to separate white light into the bands of color.
 (BIG BANG PACKET 2) Name: Period: wavelength and lowest frequencies Broadcast waves and microwaves Infrared Rays Wavelength shorter than radio waves The invisible you feel Visible Light You can see The
(BIG BANG PACKET 2) Name: Period: wavelength and lowest frequencies Broadcast waves and microwaves Infrared Rays Wavelength shorter than radio waves The invisible you feel Visible Light You can see The
Stellar Evolution. The lives of low-mass stars. And the lives of massive stars
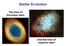 Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars Stars of High Mass High mass stars fuse H He, but do so in a different reaction: the CNO cycle Carbon is a catalyst, speeding
Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars Stars of High Mass High mass stars fuse H He, but do so in a different reaction: the CNO cycle Carbon is a catalyst, speeding
Teacher of the Week DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 Teacher of the Week DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON E-2 STELLAR RADIATION IB Assessment Statements Topic E-2, Stellar Radiation and Stellar Types Energy Source E.2.1.
Teacher of the Week DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON E-2 STELLAR RADIATION IB Assessment Statements Topic E-2, Stellar Radiation and Stellar Types Energy Source E.2.1.
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Types of Stars 1/31/14 O B A F G K M. 8-6 Luminosity. 8-7 Stellar Temperatures
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Nature of Stars For nearby stars - measure distances with parallax 1 AU d p 8-2 Parallax A January ³ d = 1/p (arcsec) [pc] ³ 1pc when p=1arcsec; 1pc=206,265AU=3
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Nature of Stars For nearby stars - measure distances with parallax 1 AU d p 8-2 Parallax A January ³ d = 1/p (arcsec) [pc] ³ 1pc when p=1arcsec; 1pc=206,265AU=3
Astronomy 1144 Exam 3 Review
 Stars and Stellar Classification Astronomy 1144 Exam 3 Review Prof. Pradhan 1. What is a star s energy source, or how do stars shine? Stars shine by fusing light elements into heavier ones. During fusion,
Stars and Stellar Classification Astronomy 1144 Exam 3 Review Prof. Pradhan 1. What is a star s energy source, or how do stars shine? Stars shine by fusing light elements into heavier ones. During fusion,
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. White Dwarfs. What is a white dwarf? Size of a White Dwarf White Dwarfs
 Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Determining the Properties of the Stars
 Determining the Properties of the Stars This set of notes by Nick Strobel covers: The properties of stars--their distances, luminosities, compositions, velocities, masses, radii, and how we determine those
Determining the Properties of the Stars This set of notes by Nick Strobel covers: The properties of stars--their distances, luminosities, compositions, velocities, masses, radii, and how we determine those
Question 1. Question 2. Correct. Chapter 16 Homework. Part A
 Chapter 16 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Following are a number of distinguishing characteristics
Chapter 16 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Following are a number of distinguishing characteristics
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9
 Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3
 October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
White dwarfs are the remaining cores of dead stars. Electron degeneracy pressure supports them against the crush of gravity. The White Dwarf Limit
 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? Seventh
The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? Seventh
Announcements. L! m 3.5 BRIGHT FAINT. Mass Luminosity Relation: Why? Homework#3 will be handed out at the end of this lecture.
 Announcements BRIGHT Homework#3 will be handed out at the end of this lecture. Due October 14 (next Thursday) Review of Mid-term exam will be handed out Tuesday. Mid-term exam will be variants (if not
Announcements BRIGHT Homework#3 will be handed out at the end of this lecture. Due October 14 (next Thursday) Review of Mid-term exam will be handed out Tuesday. Mid-term exam will be variants (if not
Mar 22, INSTRUCTIONS: First ll in your name and social security number (both by printing
 ASTRONOMY 0089: EXAM 2 Class Meets M,W,F, 1:00 PM Mar 22, 1996 INSTRUCTIONS: First ll in your name and social security number (both by printing and by darkening the correct circles). Sign your answer sheet
ASTRONOMY 0089: EXAM 2 Class Meets M,W,F, 1:00 PM Mar 22, 1996 INSTRUCTIONS: First ll in your name and social security number (both by printing and by darkening the correct circles). Sign your answer sheet
Which property of a star would not change if we could observe it from twice as far away? a) Angular size b) Color c) Flux d) Parallax e) Proper Motion
 Exam #1 is in class next monday 25 multiple-choice questions 50 minutes Similar to questions asked in class Review sheet to be posted this week. We will have two 1-hour review sessions Friday 5-6pm (with
Exam #1 is in class next monday 25 multiple-choice questions 50 minutes Similar to questions asked in class Review sheet to be posted this week. We will have two 1-hour review sessions Friday 5-6pm (with
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016
 Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Announcement: Tonight s observing session with Stephanie Ho has been CANCELLED. She has rescheduled it for 8-9pm on Thursday Nov. 3 rd. Hopefully the clouds will part by then. Lecture
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Announcement: Tonight s observing session with Stephanie Ho has been CANCELLED. She has rescheduled it for 8-9pm on Thursday Nov. 3 rd. Hopefully the clouds will part by then. Lecture
Stellar Evolution - Chapter 12 and 13. The Lives and Deaths of Stars White dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes
 Stellar Evolution - Chapter 12 and 13 The Lives and Deaths of Stars White dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes During the early stages of a star formation the objects are called a protostars. The internal
Stellar Evolution - Chapter 12 and 13 The Lives and Deaths of Stars White dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes During the early stages of a star formation the objects are called a protostars. The internal
Exam #2 Review Sheet. Part #1 Clicker Questions
 Exam #2 Review Sheet Part #1 Clicker Questions 1) The energy of a photon emitted by thermonuclear processes in the core of the Sun takes thousands or even millions of years to emerge from the surface because
Exam #2 Review Sheet Part #1 Clicker Questions 1) The energy of a photon emitted by thermonuclear processes in the core of the Sun takes thousands or even millions of years to emerge from the surface because
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars Properties of Stars
 Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? Luminosity:
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? Luminosity:
Characteristics of Stars
 Characteristics of Stars Mass of a Star The mass of a star is the hardest for astronomers to determine and it can only be found based on the gravitational forces and interactions with nearby stars. We
Characteristics of Stars Mass of a Star The mass of a star is the hardest for astronomers to determine and it can only be found based on the gravitational forces and interactions with nearby stars. We
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Spring 2003 Final Exam Review Topics
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Spring 2003 Final Exam Review Topics The final exam will cover material from the whole course (including the galaxies and cosmology material from after Exam 3). The topics
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Spring 2003 Final Exam Review Topics The final exam will cover material from the whole course (including the galaxies and cosmology material from after Exam 3). The topics
The Sun. The Chromosphere of the Sun. The Surface of the Sun
 Key Concepts: Lecture 22: The Sun Basic properties of the Sun The outer layers of the Sun: Chromosphere, Corona Sun spots and solar activity: impact on the Earth Nuclear Fusion: the source of the Sun s
Key Concepts: Lecture 22: The Sun Basic properties of the Sun The outer layers of the Sun: Chromosphere, Corona Sun spots and solar activity: impact on the Earth Nuclear Fusion: the source of the Sun s
HOMEWORK - Chapter 17 The Stars
 Astronomy 20 HOMEWORK - Chapter 7 The Stars Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate sheet
Astronomy 20 HOMEWORK - Chapter 7 The Stars Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate sheet
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Objectives. HR Diagram
 Objectives HR Diagram Questions from Yesterday Centripetal Force perpendicular to the rotation axis Acts to slow down collapse Strongest 90 deg from rotation axis Particles with an angle < 90 feel the
Objectives HR Diagram Questions from Yesterday Centripetal Force perpendicular to the rotation axis Acts to slow down collapse Strongest 90 deg from rotation axis Particles with an angle < 90 feel the
! p. 1. Observations. 1.1 Parameters
 1 Observations 11 Parameters - Distance d : measured by triangulation (parallax method), or the amount that the star has dimmed (if it s the same type of star as the Sun ) - Brightness or flux f : energy
1 Observations 11 Parameters - Distance d : measured by triangulation (parallax method), or the amount that the star has dimmed (if it s the same type of star as the Sun ) - Brightness or flux f : energy
