Constraining the Diffusion Coefficient with HAWC TeV Gamma-Ray Observations of Two Nearby Pulsar Wind Nebulae
|
|
|
- Lawrence Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TeV Gamma-Ray Observations of Two Nearby Pulsar Wind Nebulae Los Alamos National Laboratory Rubén López-Coto Max-Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics Francisco Salesa Greus The Henryk Niewiadomski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences For the HAWC Collaboration Nearby electron/positron accelerators, mostly Pulsar Wind Nebulae (PWNe), have been proposed as potential origins of the positron excess above 10 GeV. The HAWC Observatory reveals two very extended sources spatially coincident with two nearby middle-aged pulsars: Geminga and PSR B , suggesting ultra-relativistic electrons/positrons accelerated in our backyard. Morphological studies on these two PWNe provide a constraint on the diffusion coefficient at HAWC energies. In this poster, we will present the model development and morphological studies on these PWNe, and the derived diffusion coefficient that best fits the data. 35th International Cosmic Ray Conference ICRC July, 2017 Bexco, Busan, Korea Speaker. For a complete author list, see c Copyright owned by the author(s) under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
2 1. Introduction Launched into orbit in 2006, the PAMELA detector discovered an excess in the positron fraction at energies above 10 GeV as compared to theoretical models of positron production [1]. This anomalous observation has been confirmed with high precision by Fermi Large Area Telescope (Fermi-LAT) [2] and Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) [3]. It was proposed that this overabundance of positrons could be a consequence of the annihilation or decay of dark matter, but an alternative explanation is that the positron excess is due to nearby electron/positron accelerators. Pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe), known as efficient electron/positron accelerators, were postulated as sources of the positron excess [4][5]. At 250 pc and 288 pc, Geminga (PSR J ) and PSR B are two of the nearest pulsars to earth, and this proximity combined with their relatively advanced age make them important candidates contributing to the locally measured electron and positron flux. Ultra-relativistic electrons and positrons cool down via inverse Compton scattering (ICS) and synchrotron. TeV gamma ray can be produced through IC scattering off lower energy photons, e.g. cosmic microwave background. The extended TeV PWN with a size of 2.8 ± 0.8 around Geminga was reported by the Milagro experiment [6]. Weak evidence (2.2σ) of this large nebula emission was reported by the Tibet air shower array [7], but IACT observations using standard analysis techniques have only provided upper limits. In Fermi-LAT data, the Geminga pulsar is one of the brightest sources in the GeV sky but there is no unambiguous evidence of the existence of a surrounding nebula at GeV energies. In this contribution, we will demonstrate the method of morphological analysis on the extended TeV emission around Geminga and PSR B in order to constraint the particle diffusion and to estimate the contribution from these sources to the local flux of electrons and positrons measured near earth. 2. Diffusion Coefficient Both Geminga and PSR B are middle-aged pulsars, with relatively low magnetic field, and the modulation to the surrounding interstellar medium (ISM) due to the particle acceleration by these sources is low. Therefore we consider the scenario that the accelerated particles diffuse isotropically into the ISM. In order to constrain the electron and positron flux that reach the Earth from these two pulsars, we need to know how fast these particles diffuse in the ISM, referred as diffusion coefficient. It is a property of a medium and depends on the energy of the particles, D(E e ) = D 0 (E e /10GeV) δ (2.1) where the typical value of the diffusion index δ is 1/3 and D 0 is the diffusion coefficient at 10 GeV. The diffuse coefficient has been measured from the Boron-Carbon ratio in hadronic cosmic rays. Figure 1 summarizes the diffusion coefficients as a function of energy from different measurements. However, the diffusion coefficient measured from the Boron-Carbon ratio is the average value encountered over very long lifetime of hadronic cosmic rays which are expected to have spent much of that time in the Galactic halo. The local diffusion coefficient could be different. The 2
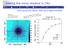
3 D [cm^2/s] Energy [GeV] Figure 1: Diffusion coefficients from different measurements: blue [8], green [9], black [10], [4], and yellow [11]. measurement on the source size around these two nearby pulsars will provide a constraint on the local diffusion coefficient in the ISM. 3. HAWC Observations The High Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) Observatory, located in central Mexico at 4100 m above sea level, is sensitive to gamma rays between 100 GeV and 100 TeV. Thanks to its large field of view of 2 steradians, HAWC has a good sensitivity to extended sources such as pulsar wind nebulae. With 17 month of data, two very extended sources are detected spatially coincident with Geminga and PSR B [12]. Figure 2 shows the significance map in the region around these two pulsars convolved with point spread function. From Figure 2, there is clearly extended emission beyond the point spread function of HAWC around both pulsars, showing evidence of electrons and positrons diffuse away from the source into the ISM. We can use the size of the extended sources to constrain the diffusion coefficient. On the studies of extended sources, the most commonly used morphological models are disk and Gaussian models. However, with these models, there is no direct connection from the model parameters to the physical parameters. In this work, we develop a particle diffusion model and apply it to the HAWC data. 4. Diffusion Model The TeV gamma-ray morphology is determined assuming a model where electrons and positrons diffuse isotropically away from the source into the ISM. They produce TeV gamma rays through ICS off low energy photons in the ISM, i.e. cosmic microwave background (CMB), infrared, and 3
4 Constraining the Diffusion Coefficient with HAWC optical photons. We hereafter obtain an approximated formula for the gamma-ray emission of the diffusion electron positron cloud which we will use to constrain the size of both HAWC sources. In case of continuous injection of electrons (and positrons) from a point source at a constant rate Q0 Ee Γ, the radial distribution of the electrons with energy Ee at an instant t and distance r from the source is given by equation 21 of [13], f (t, r, Ee ) = Q0 Ee Γ r er f c( ) 4πD(Ee )r rd (4.1) where D(Ee ) is the diffusion coefficient as a function of electron energy Ee and rd is the diffusion radius, up to which the electron efficiently diffuse to. They are defined as, D(Ee ) = D0 (Ee /10 GeV )δ rd = 2 p D(Ee )te (4.2) The typical diffusion index δ is 1/3 and is fixed in this analysis. te is the smaller of two timescales: the injection time t (in this case the age of the pulsar) and the electron cooling time tcool, which is a function of election energy and target photon energy, tcool = 1 me c2 4/3cσT γ µb + µ ph /(1 + 4γε0 )3/2 (4.3) where σt is the Thomson cross section, γ is the Lorentz factor of electrons, µb = B2 /8π is the energy density in the magnetic field, and µ ph is the energy density of target photon field with average energy ε0 per photon. Equation 4.3 takes into the account the energy loss of electrons due to both synchrotron in magnetic field and ICS off low energy photons. For the elections that 4 Figure 2: The significance map convolved with point spread function in the region around Geminga and PSR B with 17 months of HAWC data.
5 produce TeV gamma rays through ICS, where the Klein-Nishina effects are important [14], the ICS off infrared and optical photons in the ISM is highly suppressed, leaving only CMB photons as important targets. At these energies, the cooling time is much shorter than the age of these two pulsars. Therefore t E in equation 4.2 can be replaced by t cool. Integrating the energy distribution of electrons and positrons along the observer s line of sight, and considering the gamma rays produced through ICS, we obtain the morphology of gamma rays as a function of the distance d. An analytical approximation is found on this numerical integral, With a source distance of d src, equation 4.5 becomes, f d = π 3/2 r d (d r d ) exp( d2 ) (4.4) r 2 d f θ = π 3/2 θ d (θ θ d ) exp( θ2 ) (4.5) where θ is the angular distance from the pulsar and θ d = r d /r source 180 /π is the diffusion angle. Combined with equation 4.5, 4.2, and 4.3, the diffusion angle is a function of electron energy E e and the target field, θ d = θ 0 ( E e ) δ 1 B 2 /8π + µ ph /(1 + 4ε 0 E e0 /m e c 2 ) 3/2 2 E e0 B 2 /8π + µ ph /(1 + 4ε 0 E e /m e c 2 ) 3/2 (4.6) where θ 0 is the diffusion angle at the pivot energy of E e 0. The relation between the mean electron and gamma ray energy is given by [15], θ 2 d < E e > 17 < E γ > log 10(<E γ >/TeV ) The pivot energy E e0 is chosen to be 100 TeV in this analysis, which corresponds to 20 TeV gamma rays. Figure 3 compares the radial profile as a function of the distance from the pulsar from three morphological models. We then fit the gamma-ray emission around Geminga and PSR B with the diffusion model defined in equation 4.5 and 4.6 using the Multi-Mission Maximum Likelihood framework [16], and calculate the diffusion coefficient of 100 TeV electrons based on the obtained diffusion angle from the likelihood fit. (4.7) 5. Results and Discussion HAWC observations reveal two very extended TeV gamma-ray sources spatially coincident with Geminga and PSR , suggesting ultra-relativistic electrons and positrons accelerated in our neighborhood. The results of the analysis on these two sources and the obtained diffusion coefficient will be presented at ICRC2017. The implication on the positron contribution of these sources to the local flux can be found in other two proceedings for this conference [17] [18]. 5
6 Surface Brightness [Arbitrary Unit] Disk Gaussian Diffusion Distance from Pulsar [pc] Figure 3: Radial profiles of three morphological models: disk, Gaussian, and diffusion model. Acknowledgments We acknowledge the support from: the US National Science Foundation (NSF); the US Department of Energy Office of High-Energy Physics; the Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) program of Los Alamos National Laboratory; Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT), México (grants , , , , , , , , , ), Laboratorio Nacional HAWC de rayos gamma; L OREAL Fellowship for Women in Science 2014; Red HAWC, México; DGAPA-UNAM (grants IG100317, IN111315, IN , IA102715, , IA102917); VIEP-BUAP; PIFI 2012, 2013, PROFOCIE 2014, 2015;the University of Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation; the Institute of Geophysics, Planetary Physics, and Signatures at Los Alamos National Laboratory; Polish Science Centre grant DEC-2014/13/B/ST9/945; Coordinación de la Investigación Científica de la Universidad Michoacana. Thanks to Luciano Díaz and Eduardo Murrieta for technical support. References [1] Adriani et al., An anomalous positron abundance in cosmic rays with energies GeV, Nature 458 (2009) 607 [2] Abdo, A. A. et al., Measurement of the Cosmic Ray e + + e Spectrum from 20 GeV to 1 TeV with the Fermi Large Area Telescope, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 (2009) [ ] [3] Aguilar et al., First Result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station: Precision Measurement of the Positron Fraction in Primary Cosmic Rays of GeV, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013)
7 [4] Yüksel, H., Kistler, M. D., & Stanev, T., TeV Gamma Rays from Geminga and the Origin of the GeV Positron Excess, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 (2009) [ ] [5] Hooper, D., Blasi, P., & Dario Serpico, P., Pulsars as the sources of high energy cosmic ray positrons, Cosmology Astropart. Phys. 1 (2009) 025 [ ] [6] Abdo, A. A. et al., TeV Gamma-Ray Sources from a Survey of the Galactic Plane with Milagro, Astrophys. J. 664 (2007) 91 [7] Amenomori, M. et al., Observation of TeV Gamma Rays from the Fermi Bright Galactic Sources with the Tibet Air Shower Array, Astrophys. J. Lett. 709 (2010) 6 [8] Strong, A. W. & Moskalenko, I. V., Propagation of cosmic-ray nucleons in the Galaxy, Astrophys. J 212 (1998) 228 [astro-ph/ ] [9] Delahaye, T. et al., Positrons from dark matter annihilation in the galactic halo: Theoretical uncertainties, Phys. Rev. D 77 (2008) [ ] [10] Yin, P. et al., Pulsar interpretation for the AMS-02 result, Phys. Rev. D 88 (2013) [ ] [11] Adriani, O. et al, Measurement of Boron and Carbon Fluxes in Cosmic Rays with the PAMELA Experiment, Astrophys. J. 791 (2014) 93 [ ] [12] The HAWC Collaboration, Abeysekara, A. U. et al., The 2HWC HAWC Observatory Gamma-Ray Catalog, Astrophys. J. 843 (2017) 40 [ ] [13] Atoyan, A. M., Aharonian, F. A. & Völk, H. J., Electrons and positrons in the galactic cosmic rays, Phys. Rev. D 52 (1995) 3265 [14] Moderksi, R. M. et al., Klein-Nishina effects in the spectra of non-thermal sources immersed in external radiation fields, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 364 (2005) 1488 [astro-ph/ ] [15] Aharonian, F. A., Very high energy cosmic gamma radiation : A crucial window on the extreme Universe, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd. (2004) ISBN [16] Vianello, G. et al., The Multi-Mission Maximum Likelihood framework (3ML), in Proceedings of ICRC2015 (2015) [ ] [17] Salesa Greus, F. et al, Constraining the Origin of Local Positrons with HAWC TeV Gamma-Ray Observations of Two Nearby Pulsar Wind Nebulae, in Proceedings of ICRC2017 (2017) [18] Lopez-Coto, R. et al, in Proceedings of ICRC2017 (2017) 7
HAWC Observation of Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 HAWC Observation of Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae a, and H. Zhou a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics, Michigan Technological University 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI,
HAWC Observation of Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae a, and H. Zhou a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics, Michigan Technological University 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI,
Correlated GeV TeV Gamma-Ray Emission from Extended Sources in the Cygnus Region
 Correlated GeV TeV Gamma-Ray Emission from Extended Sources in the Cygnus Region Michigan Technological University E-mail: bhona@mtu.edu A. Robare Michigan Technological University E-mail: alrobare@mtu.edu
Correlated GeV TeV Gamma-Ray Emission from Extended Sources in the Cygnus Region Michigan Technological University E-mail: bhona@mtu.edu A. Robare Michigan Technological University E-mail: alrobare@mtu.edu
Probing Cosmic-ray Propagation with TeV Gamma Rays from the Sun Using the HAWC Observatory
 Probing Cosmic-ray Propagation with TeV Gamma Rays from the Sun Using the HAWC Observatory For the HAWC Collaboration University of Rochester E-mail: mnisa@ur.rochester.edu Cosmic rays in the inner solar
Probing Cosmic-ray Propagation with TeV Gamma Rays from the Sun Using the HAWC Observatory For the HAWC Collaboration University of Rochester E-mail: mnisa@ur.rochester.edu Cosmic rays in the inner solar
Gamma Emission from Large Galactic Structures
 Michigan Technological University E-mail: hfleisch@mtu.edu Hugo Alberto Ayala Solares The Pennsylvania State University E-mail: hgayala@psu.edu Petra Huentemeyer Michigan Technological University E-mail:
Michigan Technological University E-mail: hfleisch@mtu.edu Hugo Alberto Ayala Solares The Pennsylvania State University E-mail: hgayala@psu.edu Petra Huentemeyer Michigan Technological University E-mail:
PoS(ICRC2017)750. Detection of vertical muons with the HAWC water Cherenkov detectors and it s application to gamma/hadron discrimination
 Detection of vertical muons with the HAWC water Cherenkov detectors and it s application to gamma/hadron discrimination Ariel Zúñiga a, Alberto Hernández a,b, Aldo Miranda c, Ana P. Vizcaya a, Andrés Sandoval
Detection of vertical muons with the HAWC water Cherenkov detectors and it s application to gamma/hadron discrimination Ariel Zúñiga a, Alberto Hernández a,b, Aldo Miranda c, Ana P. Vizcaya a, Andrés Sandoval
Observations of the Crab Nebula with Early HAWC Data
 Observations of the Crab Nebula with Early HAWC Data a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics, Pennsylvania State University, 16802 University Park, PA, USA b For a complete author list,
Observations of the Crab Nebula with Early HAWC Data a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics, Pennsylvania State University, 16802 University Park, PA, USA b For a complete author list,
PoS(ICRC2017)394. New gamma/hadron separation parameters for a neural network for HAWC
 New gamma/hadron separation parameters for a neural network for HAWC E. Bourbeau a, b,i. Torres b, E. Moreno c for the HAWC Collaboration d a McGill University, 45 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, Quebec,
New gamma/hadron separation parameters for a neural network for HAWC E. Bourbeau a, b,i. Torres b, E. Moreno c for the HAWC Collaboration d a McGill University, 45 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, Quebec,
X-ray/gamma-ray flux correlations in the BL Lac Mrk 421 using HAWC data. For acomplete author list, see
 X-ray/gamma-ray flux correlations in the L Lac Mrk 421 using HAWC data Instituto de Física, UNAM E-mail: jagarcia@fisica.unam.mx M. M. González Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM E-mail: magda@astro.unam.mx
X-ray/gamma-ray flux correlations in the L Lac Mrk 421 using HAWC data Instituto de Física, UNAM E-mail: jagarcia@fisica.unam.mx M. M. González Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM E-mail: magda@astro.unam.mx
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars
 Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
Detection of Nearly-Horizontal Muons with the HAWC Observatory
 Detection of Nearly-Horizontal Muons with the HAWC Observatory Ahron S. Barber a, David B. Kieda a and R. Wayne Springer a* for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Detection of Nearly-Horizontal Muons with the HAWC Observatory Ahron S. Barber a, David B. Kieda a and R. Wayne Springer a* for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere
 On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
Latest news from the High Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Latest news from the High Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory To cite this article: A González Muñoz and HAWC Collaboration 2016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Latest news from the High Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory To cite this article: A González Muñoz and HAWC Collaboration 2016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Bright gamma-ray sources observed by DArk Matter Particle Explorer
 Bright gamma-ray sources observed by DArk Matter Particle Explorer a, Kai-Kai Duan ab, Zhao-Qiang Shen ab, Zun-Lei Xu a, and Simone Garrappa c on behalf of the DAMPE collaboration a Key Laboratory of Dark
Bright gamma-ray sources observed by DArk Matter Particle Explorer a, Kai-Kai Duan ab, Zhao-Qiang Shen ab, Zun-Lei Xu a, and Simone Garrappa c on behalf of the DAMPE collaboration a Key Laboratory of Dark
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 19 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 19 Oct 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 19 Oct 2017](/thumbs/74/69797920.jpg) and Muon Bundles for the HAWC Observatory with CORSIKA arxiv:1710.06971v1 [astro-ph.he] 19 Oct 2017 Ahron S. Barber a, David B. Kieda a and a and for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and
and Muon Bundles for the HAWC Observatory with CORSIKA arxiv:1710.06971v1 [astro-ph.he] 19 Oct 2017 Ahron S. Barber a, David B. Kieda a and a and for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and
HAWC and the cosmic ray quest
 HAWC and the cosmic ray quest J.C. Arteaga-Velázquez for the HAWC Collaboration Instituto de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Michoacana, Mexico Structure of the talk: 1) The HAWC gamma-ray observatory
HAWC and the cosmic ray quest J.C. Arteaga-Velázquez for the HAWC Collaboration Instituto de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Michoacana, Mexico Structure of the talk: 1) The HAWC gamma-ray observatory
Gamma ray and antiparticles (e + and p) as tools to study the propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy
 Gamma ray and antiparticles (e + and p) as tools to study the propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy INFN Sez. La Sapienza, Rome, Italy E-mail: paolo.lipari@roma1.infn.it The spectra of cosmic rays observed
Gamma ray and antiparticles (e + and p) as tools to study the propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy INFN Sez. La Sapienza, Rome, Italy E-mail: paolo.lipari@roma1.infn.it The spectra of cosmic rays observed
PoS(ICRC2015)1001. Gamma Hadron Separation using Pairwise Compactness Method with HAWC
 Gamma Hadron Separation using Pairwise Compactness Method with HAWC a and Stefan Westerhoff a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and WIPAC, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI,
Gamma Hadron Separation using Pairwise Compactness Method with HAWC a and Stefan Westerhoff a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and WIPAC, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI,
First Light with the HAWC Gamma-Ray Observatory
 , for the HAWC Collaboration Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center (WIPAC) and Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI 53706, USA E-mail: westerhoff@wisc.edu The High-Altitude
, for the HAWC Collaboration Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center (WIPAC) and Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI 53706, USA E-mail: westerhoff@wisc.edu The High-Altitude
PoS(NEUTEL2017)079. Blazar origin of some IceCube events
 Blazar origin of some IceCube events Sarira Sahu Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Circuito Exterior, C.U., A. Postal 70-543, 04510 México DF, México. Astrophysical
Blazar origin of some IceCube events Sarira Sahu Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Circuito Exterior, C.U., A. Postal 70-543, 04510 México DF, México. Astrophysical
A-Exam: e + e Cosmic Rays and the Fermi Large Array Telescope
 A-Exam: e + e Cosmic Rays and the Fermi Large Array Telescope Walter Hopkins Physics Department, Cornell University. The Fermi Large Area Telescope is a particle detector in space with an effective collecting
A-Exam: e + e Cosmic Rays and the Fermi Large Array Telescope Walter Hopkins Physics Department, Cornell University. The Fermi Large Area Telescope is a particle detector in space with an effective collecting
PoS(ICRC2017)512. Detection of Near Horizontal Muons with the HAWC Observatory
 with the HAWC Observatory Ahron S. Barber a, David B. Kieda a and a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA b For a complete author
with the HAWC Observatory Ahron S. Barber a, David B. Kieda a and a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA b For a complete author
Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC. Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations
 Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations Snowpack 2010 Milagro and HAWC Milagro was a first generation wide-field gamma-ray telescope: Proposed in 1990
Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations Snowpack 2010 Milagro and HAWC Milagro was a first generation wide-field gamma-ray telescope: Proposed in 1990
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
Galactic diffuse gamma-rays
 Galactic diffuse gamma-rays Masaki Mori Department of Physics, College of Science & Engineering, Ritsumeikan University 1 July 31, 2009, Dept. Astronomy, Kyoto University GeV gamma-ray sky by EGRET Compton
Galactic diffuse gamma-rays Masaki Mori Department of Physics, College of Science & Engineering, Ritsumeikan University 1 July 31, 2009, Dept. Astronomy, Kyoto University GeV gamma-ray sky by EGRET Compton
PoS(ICRC2017)740. Observing the Galactic Plane with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. CTA consortium represented by Roberta Zanin and Jamie Holder
 Observing the Galactic Plane with the Cherenkov Telescope Array CTA consortium represented by and Jamie Holder E-mail: robertazanin@gmail.com The Cherenkov Telescope Array is a next generation ground-based
Observing the Galactic Plane with the Cherenkov Telescope Array CTA consortium represented by and Jamie Holder E-mail: robertazanin@gmail.com The Cherenkov Telescope Array is a next generation ground-based
The electron spectrum from annihilation of Kaluza-Klein dark matter in the Galactic halo
 The electron spectrum from annihilation of Kaluza-Klein dark matter in the Galactic halo Satoshi Tsuchida Affiliation: Department of Physical Sciences, Ritsumeikan University E-mail: rp005076@ed.ritsumei.ac.jp
The electron spectrum from annihilation of Kaluza-Klein dark matter in the Galactic halo Satoshi Tsuchida Affiliation: Department of Physical Sciences, Ritsumeikan University E-mail: rp005076@ed.ritsumei.ac.jp
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale)
 Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
A Galaxy in VHE Gamma-rays: Observations of the Galactic Plane with the H.E.S.S. array
 : Observations of the Galactic Plane with the H.E.S.S. array Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany E-mail: daniel.parsons@mpi-hd.mpg.de P. Bordas Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg,
: Observations of the Galactic Plane with the H.E.S.S. array Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany E-mail: daniel.parsons@mpi-hd.mpg.de P. Bordas Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg,
Observing TeV Gamma Rays from the Jet Interaction Regions of SS 433 with HAWC
 Observing TeV Gamma Rays from the Jet Interaction Regions of SS 433 with HAWC Chang Dong Rho University of Rochester TeVPA 2018 Berlin, Germany 08/28/2018 Overview 2 Microquasars as sources of TeV gamma
Observing TeV Gamma Rays from the Jet Interaction Regions of SS 433 with HAWC Chang Dong Rho University of Rochester TeVPA 2018 Berlin, Germany 08/28/2018 Overview 2 Microquasars as sources of TeV gamma
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments
 Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
HAWC Status & Galactic Science
 HAWC Status & Galactic Science HAWC photo from March 2014. Currently 243 of 300 tanks are built, " 192 are filled with water, and 143 are taking data nearly continuously.! Brenda Dingus, LANL US Spokesperson
HAWC Status & Galactic Science HAWC photo from March 2014. Currently 243 of 300 tanks are built, " 192 are filled with water, and 143 are taking data nearly continuously.! Brenda Dingus, LANL US Spokesperson
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges
 Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Diffuse TeV emission from the Cygnus region
 Diffuse TeV emission from the Cygnus region References: Discovery of TeV gamma-ray emission from the Cygnus region of the Galaxy Abdo et al., astro-ph/0611691 Dissecting the Cygnus region with TeV gamma
Diffuse TeV emission from the Cygnus region References: Discovery of TeV gamma-ray emission from the Cygnus region of the Galaxy Abdo et al., astro-ph/0611691 Dissecting the Cygnus region with TeV gamma
Galactic diffuse neutrino component in the astrophysical excess measured by the IceCube experiment
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 40 C (2017) 140 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2017-17140-4 Colloquia: SciNeGHE 2016 Galactic diffuse neutrino component in the astrophysical excess measured by the IceCube experiment D. Grasso( 1 ),
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 40 C (2017) 140 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2017-17140-4 Colloquia: SciNeGHE 2016 Galactic diffuse neutrino component in the astrophysical excess measured by the IceCube experiment D. Grasso( 1 ),
VERITAS Prospects for Geminga Pulsar
 VERITAS Prospects for Geminga Pulsar Emily Harris University of Pittsburgh, Department of Physics and Astronomy Columbia University, Nevis Laboratories (Dated: August 7, 2018) Recent observations of the
VERITAS Prospects for Geminga Pulsar Emily Harris University of Pittsburgh, Department of Physics and Astronomy Columbia University, Nevis Laboratories (Dated: August 7, 2018) Recent observations of the
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays
 The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Dark Matter Signatures in the Gamma-ray Sky Austin, Texas 7-8 May 2012 arxiv:0908.0195
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Dark Matter Signatures in the Gamma-ray Sky Austin, Texas 7-8 May 2012 arxiv:0908.0195
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 10 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 10 Sep 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 10 Sep 2017](/thumbs/89/98892400.jpg) Observation of radio galaxies with HAWC arxiv:1709.02025v2 [astro-ph.he] 10 Sep 2017, Rubén Alfaro Instituto de Física, UNAM, Ciudad de México, México. E-mail: daniel_avila5@ciencias.unam.mx, ruben@fisica.unam.mx
Observation of radio galaxies with HAWC arxiv:1709.02025v2 [astro-ph.he] 10 Sep 2017, Rubén Alfaro Instituto de Física, UNAM, Ciudad de México, México. E-mail: daniel_avila5@ciencias.unam.mx, ruben@fisica.unam.mx
Astrophysical issues in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation?
 Astrophysical issues +/ in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation? Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics University of Torino and INFN Collab: Torino: R. Lineros, F.
Astrophysical issues +/ in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation? Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics University of Torino and INFN Collab: Torino: R. Lineros, F.
Pulsars and Pulsar-Wind Nebulae: TeV to X-Ray Connection. Oleg Kargaltsev (University of Florida) George Pavlov (Penn State University)
 Pulsars and Pulsar-Wind Nebulae: TeV to X-Ray Connection Oleg Kargaltsev (University of Florida) George Pavlov (Penn State University) Pulsar Wind Nebulae. All active pulsars emit relativistic winds c
Pulsars and Pulsar-Wind Nebulae: TeV to X-Ray Connection Oleg Kargaltsev (University of Florida) George Pavlov (Penn State University) Pulsar Wind Nebulae. All active pulsars emit relativistic winds c
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission
 The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Origin of the Galactic Cosmic Radiation
 The Origin of the Galactic Cosmic Radiation A White Paper submitted to the Stars and Stellar Evolution Science Panel of Astro2010 - The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey Corresponding Author: G.
The Origin of the Galactic Cosmic Radiation A White Paper submitted to the Stars and Stellar Evolution Science Panel of Astro2010 - The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey Corresponding Author: G.
The VERITAS Survey of the Cygnus Region of the Galaxy
 The VERITAS Survey of the Cygnus Region of the Galaxy for the VERITAS collaboration University of California, Los Angeles E-mail: apopkow@ucla.edu The Cygnus region is a very active region of our Galaxy
The VERITAS Survey of the Cygnus Region of the Galaxy for the VERITAS collaboration University of California, Los Angeles E-mail: apopkow@ucla.edu The Cygnus region is a very active region of our Galaxy
Using the Fermi-LAT to Search for Indirect Signals from Dark Matter Annihilation
 Using the Fermi-LAT to Search for Indirect Signals from Dark Matter Annihilation Tim Linden UC - Santa Cruz Representing the Fermi-LAT Collaboration with acknowledgements to: Brandon Anderson, Elliott
Using the Fermi-LAT to Search for Indirect Signals from Dark Matter Annihilation Tim Linden UC - Santa Cruz Representing the Fermi-LAT Collaboration with acknowledgements to: Brandon Anderson, Elliott
Potential Neutrino Signals from Galactic γ-ray Sources
 Potential Neutrino Signals from Galactic γ-ray Sources, Christian Stegmann Felix Aharonian, Jim Hinton MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Madison WI, August 28 31, 2006 TeV γ-ray Sources as Potential ν Sources
Potential Neutrino Signals from Galactic γ-ray Sources, Christian Stegmann Felix Aharonian, Jim Hinton MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Madison WI, August 28 31, 2006 TeV γ-ray Sources as Potential ν Sources
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park
 99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants
 Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants Marianne Lemoine-Goumard (CENBG, Université Bordeaux, CNRS-IN2P3, France) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT and HESS Collaborations
Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants Marianne Lemoine-Goumard (CENBG, Université Bordeaux, CNRS-IN2P3, France) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT and HESS Collaborations
Arrival directions of the highest-energy cosmic rays detected by the Pierre Auger Observatory
 Arrival directions of the highest-energy cosmic rays detected by the Pierre Auger Observatory a for the Pierre Auger Collaboration b a Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Arrival directions of the highest-energy cosmic rays detected by the Pierre Auger Observatory a for the Pierre Auger Collaboration b a Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Prospects for Observations of Very Extended and Diffuse Sources with VERITAS. Josh Cardenzana
 Prospects for Observations of Very Extended and Diffuse Sources with VERITAS Josh Cardenzana New era of synergy ~0.5 at 1GeV to 10 GeV) Fermi ~0.15 at 150GeV to 1 TeV) VERITAS ~0.5 at 1TeV
Prospects for Observations of Very Extended and Diffuse Sources with VERITAS Josh Cardenzana New era of synergy ~0.5 at 1GeV to 10 GeV) Fermi ~0.15 at 150GeV to 1 TeV) VERITAS ~0.5 at 1TeV
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Cosmic Ray Electrons with CTA. R.D. Parsons
 Cosmic Ray Electrons with CTA R.D. Parsons Cosmic Ray Electrons In addi:on to the well known hadronic component of cosmic rays there is a more poorly understood electronic component Has a lower flux than
Cosmic Ray Electrons with CTA R.D. Parsons Cosmic Ray Electrons In addi:on to the well known hadronic component of cosmic rays there is a more poorly understood electronic component Has a lower flux than
Dark Matter Particle Explorer and Its First Results
 0254-6124/2018/38(5)-610 05 Chin. J. Space Sci. Ξ ΛΠΠ CHANG Jin. Dark Matter Particle Explorer and its first results. Chin. J. Space Sci., 2018, 38(5): 610-614. DOI:10.11728/cjss2018. 05.610 Dark Matter
0254-6124/2018/38(5)-610 05 Chin. J. Space Sci. Ξ ΛΠΠ CHANG Jin. Dark Matter Particle Explorer and its first results. Chin. J. Space Sci., 2018, 38(5): 610-614. DOI:10.11728/cjss2018. 05.610 Dark Matter
Spectra of Cosmic Rays
 Spectra of Cosmic Rays Flux of relativistic charged particles [nearly exactly isotropic] Particle density Power-Law Energy spectra Exponent (p, Nuclei) : Why power laws? (constraint on the dynamics of
Spectra of Cosmic Rays Flux of relativistic charged particles [nearly exactly isotropic] Particle density Power-Law Energy spectra Exponent (p, Nuclei) : Why power laws? (constraint on the dynamics of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Jul 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 14 Jul 2017](/thumbs/96/127585275.jpg) Cosmogenic gamma-rays and neutrinos constrain UHECR source models Department of Astrophysics/IMAPP, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands E-mail: a.vanvliet@astro.ru.nl arxiv:1707.04511v1 [astro-ph.he]
Cosmogenic gamma-rays and neutrinos constrain UHECR source models Department of Astrophysics/IMAPP, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands E-mail: a.vanvliet@astro.ru.nl arxiv:1707.04511v1 [astro-ph.he]
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants
 Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
What Can GLAST Say About the Origin of Cosmic Rays in Other Galaxies
 SLAC-PUB-8660 October 2000 astro-ph/0003407 What Can GLAST Say About the Origin of Cosmic Rays in Other Galaxies Seth Digelaxb, Igor V. Moskalenko xc, and Jonathan F. Ormes, P. Sreekumard. and P. Roger
SLAC-PUB-8660 October 2000 astro-ph/0003407 What Can GLAST Say About the Origin of Cosmic Rays in Other Galaxies Seth Digelaxb, Igor V. Moskalenko xc, and Jonathan F. Ormes, P. Sreekumard. and P. Roger
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.:
 PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
Solar Event Simulations using the HAWC Scaler System
 Solar Event Simulations using the HAWC Scaler System a, Alejandro Lara a and Rogelio Caballero-Lopez a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Instituto de Geofisica, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico
Solar Event Simulations using the HAWC Scaler System a, Alejandro Lara a and Rogelio Caballero-Lopez a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Instituto de Geofisica, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico
Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS
 Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Presented by Nahee Park What do we want to learn? Are SNRs the main accelerators of the Galactic cosmic rays? Efficiency of cosmic-ray acceleration? Maximum
Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Presented by Nahee Park What do we want to learn? Are SNRs the main accelerators of the Galactic cosmic rays? Efficiency of cosmic-ray acceleration? Maximum
Gamma-Ray Astronomy from the Ground
 Gamma-Ray Astronomy from the Ground Dieter Horns University of Hamburg Introduction - summary Many new Results from ICRC 2015 No we haven't discovered dark matter, yet Yes we have discovered sources of
Gamma-Ray Astronomy from the Ground Dieter Horns University of Hamburg Introduction - summary Many new Results from ICRC 2015 No we haven't discovered dark matter, yet Yes we have discovered sources of
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration
 Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling
 Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts
 Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts B.L. Dingus and the Milagro Collaboration Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Maryland, University of California Santa Cruz, University of California
Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts B.L. Dingus and the Milagro Collaboration Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Maryland, University of California Santa Cruz, University of California
Cosmic-ray propagation in the light of the Myriad model
 Cosmic-ray propagation in the light of the Myriad model Y. Genolini,, P. Serpico and R. Taillet LAPTh & Université Savoie Mont Blanc E-mail: genolini@lapth.cnrs.fr, salati@lapth.cnrs.fr A hardening of
Cosmic-ray propagation in the light of the Myriad model Y. Genolini,, P. Serpico and R. Taillet LAPTh & Université Savoie Mont Blanc E-mail: genolini@lapth.cnrs.fr, salati@lapth.cnrs.fr A hardening of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Nov 2017](/thumbs/79/80331948.jpg) HAWC response to atmospheric electricity activity arxiv:1711.04202v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Nov 2017 Instituto de Geofísica, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México E-mail: alara@igeofisica.unam.mx Graciela
HAWC response to atmospheric electricity activity arxiv:1711.04202v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Nov 2017 Instituto de Geofísica, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México E-mail: alara@igeofisica.unam.mx Graciela
Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S.
 Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S. Christopher van Eldik (for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration) MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany TeVPA '09, SLAC, July 2009 The Centre of the Milky
Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S. Christopher van Eldik (for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration) MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany TeVPA '09, SLAC, July 2009 The Centre of the Milky
Study of Performance Improvement for Air Shower Array with Surface Water Cherenkov Detectors
 Study of Performance Improvement for Air Shower Array with Surface Water Cherenkov Detectors, a K. Hibino, b T. K. Sako, cd T. Asaba, e Y. Katayose e and M. Ohnishi c a College of Industrial Technology,
Study of Performance Improvement for Air Shower Array with Surface Water Cherenkov Detectors, a K. Hibino, b T. K. Sako, cd T. Asaba, e Y. Katayose e and M. Ohnishi c a College of Industrial Technology,
Can blazar flares be triggered by the VHE gamma-rays from the surrounding of a supermassive black hole?
 Can blazar flares be triggered by the VHE gamma-rays from the surrounding of a supermassive black hole? Department of Astrophysics, University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland E-mail: p.banasinski@uni.lodz.pl Wlodek
Can blazar flares be triggered by the VHE gamma-rays from the surrounding of a supermassive black hole? Department of Astrophysics, University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland E-mail: p.banasinski@uni.lodz.pl Wlodek
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J
 H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
stringent constraint on galactic positron production
 stringent constraint on galactic positron production the ohio state university Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 071102 (2006) [astro-ph/0512411] in collaboration with john beacom Workshop on TeV Particle Astrophysics
stringent constraint on galactic positron production the ohio state university Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 071102 (2006) [astro-ph/0512411] in collaboration with john beacom Workshop on TeV Particle Astrophysics
Recent Results from the HAWC Gamma Ray Observatory. Jordan Goodman University of Maryland February 2018
 Recent Results from the HAWC Gamma Ray Observatory Jordan Goodman University of Maryland February 2018 High Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory J. Goodman - University of Maryland - HAWC Winter 2018 2
Recent Results from the HAWC Gamma Ray Observatory Jordan Goodman University of Maryland February 2018 High Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory J. Goodman - University of Maryland - HAWC Winter 2018 2
Non-thermal emission from pulsars experimental status and prospects
 Non-thermal emission from pulsars experimental status and prospects # γ!"# $%&'() TeV γ-ray astrophysics with VERITAS ( $γ" *$%&'() The charged cosmic radiation - how it all began... Discovery: Victor
Non-thermal emission from pulsars experimental status and prospects # γ!"# $%&'() TeV γ-ray astrophysics with VERITAS ( $γ" *$%&'() The charged cosmic radiation - how it all began... Discovery: Victor
White dwarf pulsar as Possible Cosmic Ray Electron-Positron Factories
 White dwarf pulsar as Possible Cosmic Ray Electron-Positron Factories 2010 7/9 Kazumi Kashiyama (Kyoto University) Kunihito Ioka & Norita Kawanaka (KEK) arxiv:1009.1141 (submitted to PRD) http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/topstory/2007/whitedwarf_pulsar.html
White dwarf pulsar as Possible Cosmic Ray Electron-Positron Factories 2010 7/9 Kazumi Kashiyama (Kyoto University) Kunihito Ioka & Norita Kawanaka (KEK) arxiv:1009.1141 (submitted to PRD) http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/topstory/2007/whitedwarf_pulsar.html
MILAGRO. 1 The Milagro detector. SABRINA CASANOVA for THE MILAGRO COLLABORATION. Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM, 87545, US
 SURVEYING THE TEV SKY WITH MILAGRO SABRINA CASANOVA for THE MILAGRO COLLABORATION Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM, 87545, US Abstract A wide field of view, high duty factor TeV gamma-ray
SURVEYING THE TEV SKY WITH MILAGRO SABRINA CASANOVA for THE MILAGRO COLLABORATION Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM, 87545, US Abstract A wide field of view, high duty factor TeV gamma-ray
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs
 Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 5 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 5 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 5 Sep 2017](/thumbs/93/111088092.jpg) VHE gamma-ray study of the composite SNR MSH 15-52 with H.E.S.S. arxiv:1709.01422v1 [astro-ph.he] 5 Sep 2017 LUPM, CNRS-IN2P3 / University of Montpellier, France E-mail: michelle.tsirou@etu.umontpellier.fr
VHE gamma-ray study of the composite SNR MSH 15-52 with H.E.S.S. arxiv:1709.01422v1 [astro-ph.he] 5 Sep 2017 LUPM, CNRS-IN2P3 / University of Montpellier, France E-mail: michelle.tsirou@etu.umontpellier.fr
Combined Search for Neutrinos from Dark Matter Annihilation in the Galactic Center using IceCube and ANTARES
 Combined Search for Neutrinos from Dark Matter Annihilation in the Galactic Center using IceCube and ANTARES The IceCube and ANTARES Collaborations htt p : //icecube.wisc.edu/collaboration/authors/icrc17_icecube
Combined Search for Neutrinos from Dark Matter Annihilation in the Galactic Center using IceCube and ANTARES The IceCube and ANTARES Collaborations htt p : //icecube.wisc.edu/collaboration/authors/icrc17_icecube
Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars
 Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars Marie-Hélène Grondin CENBG, Bordeaux (France) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing
Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars Marie-Hélène Grondin CENBG, Bordeaux (France) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing
Discovery of TeV Gamma-ray Emission Towards Supernova Remnant SNR G Last Updated Tuesday, 30 July :01
 Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
Galactic Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission
 Galactic Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission The Bright Gamma-Ray Sky 7 th AGILE Workshop 29 Sep - 1 Oct, 2009 Stanley D. Hunter NASA/GSFC stanley.d.hunter@nasa.gov Galactic Diffuse Emission The beginning: OSO
Galactic Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission The Bright Gamma-Ray Sky 7 th AGILE Workshop 29 Sep - 1 Oct, 2009 Stanley D. Hunter NASA/GSFC stanley.d.hunter@nasa.gov Galactic Diffuse Emission The beginning: OSO
Observing Galactic Sources at GeV & TeV Energies (A Short Summary)
 1 Observing Galactic Sources at GeV & TeV Energies (A Short Summary) Tülün Ergin Univ. of Massachusetts, Amherst Air Cherenkov Telescopes 2 Past IACTs: HEGRA, Whipple, CANGAROO Present/Future IACTs: H.E.S.S.,
1 Observing Galactic Sources at GeV & TeV Energies (A Short Summary) Tülün Ergin Univ. of Massachusetts, Amherst Air Cherenkov Telescopes 2 Past IACTs: HEGRA, Whipple, CANGAROO Present/Future IACTs: H.E.S.S.,
Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics
 Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) The extreme Universe viewed in very high energy gamma-rays, Kashiwa 09/25/2012 OUTLINE
Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) The extreme Universe viewed in very high energy gamma-rays, Kashiwa 09/25/2012 OUTLINE
Supernova Remnants as Cosmic Ray Accelerants. By Jamie Overbeek Advised by Prof. J. Finley
 Supernova Remnants as Cosmic Ray Accelerants By Jamie Overbeek Advised by Prof. J. Finley Cosmic Rays Discovered by Victor Hess in 1911 during a balloon flight through Austria He used an electroscope to
Supernova Remnants as Cosmic Ray Accelerants By Jamie Overbeek Advised by Prof. J. Finley Cosmic Rays Discovered by Victor Hess in 1911 during a balloon flight through Austria He used an electroscope to
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays
 The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration UCLA Dark Matter 2012 Marina del Rey 22-24 February 2012 arxiv:0908.0195 Gamma
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration UCLA Dark Matter 2012 Marina del Rey 22-24 February 2012 arxiv:0908.0195 Gamma
Supernova Remnants and Cosmic. Rays
 Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
PoS(ICRC2015)432. Simulation Study On High Energy Electron and Gamma-ray Detection With the Newly Upgraded Tibet ASgamma Experiment
 Simulation Study On High Energy Electron and Gamma-ray Detection With the Newly Upgraded Tibet ASgamma Experiment Xu Chen a, D. Chen b, J. Huang a, H. B. Jin b, L. M. Zhai a,b, M. Shibata c, Y. Katayose
Simulation Study On High Energy Electron and Gamma-ray Detection With the Newly Upgraded Tibet ASgamma Experiment Xu Chen a, D. Chen b, J. Huang a, H. B. Jin b, L. M. Zhai a,b, M. Shibata c, Y. Katayose
High Energy Emissions from the PSR /SS2883 Binary System
 High Energy Emissions from the PSR1259 63/SS2883 Binary System A. Kawachi, T. Naito and S. Nagataki Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Chiba 277-8582, Japan Faculty of Management Information,
High Energy Emissions from the PSR1259 63/SS2883 Binary System A. Kawachi, T. Naito and S. Nagataki Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Chiba 277-8582, Japan Faculty of Management Information,
A pulsar wind nebula associated with PSR J as the powering source of TeV J
 A pulsar wind nebula associated with PSR J2032+4127 as the powering source of TeV J2032+4130 Javier Moldón Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy Extreme Astrophysics in an Ever-Changing Universe Crete,
A pulsar wind nebula associated with PSR J2032+4127 as the powering source of TeV J2032+4130 Javier Moldón Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy Extreme Astrophysics in an Ever-Changing Universe Crete,
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University, 567 Wilson Rd., East Lansing, MI 48824, USA
 EPJ Web of Conferences 116, 11004 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/201611611004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 Results from IceCube Tyce DeYoung a for the IceCube Collaboration Dept.
EPJ Web of Conferences 116, 11004 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/201611611004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 Results from IceCube Tyce DeYoung a for the IceCube Collaboration Dept.
A Summary of recent Updates in the Search for Cosmic Ray Sources using the IceCube Detector
 A Summary of recent Updates in the Search for Cosmic Ray Sources using the IceCube Detector The IceCube Collaboration E-mail: tessa.carver@unige.ch In 2012 the IceCube detector observed the first clear
A Summary of recent Updates in the Search for Cosmic Ray Sources using the IceCube Detector The IceCube Collaboration E-mail: tessa.carver@unige.ch In 2012 the IceCube detector observed the first clear
Concentration of Kaluza Klein dark matter in the Galactic center: constraints from gamma ray signals
 Concentration of Kaluza Klein dark matter in the Galactic center: constraints from gamma ray signals Satoshi Tsuchida Department of Physics, Osaka City University, 3 3 138 Sugimoto, Sumiyoshi ku, Osaka
Concentration of Kaluza Klein dark matter in the Galactic center: constraints from gamma ray signals Satoshi Tsuchida Department of Physics, Osaka City University, 3 3 138 Sugimoto, Sumiyoshi ku, Osaka
Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering
 Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering Gabrijela Zaharijaš Oskar Klein Center, Stockholm University Work with A. Sellerholm, L. Bergstrom, J. Edsjo on behalf
Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering Gabrijela Zaharijaš Oskar Klein Center, Stockholm University Work with A. Sellerholm, L. Bergstrom, J. Edsjo on behalf
Search for GeV neutrinos associated with solar flares with IceCube
 Search for GeV neutrinos associated with solar flares with IceCube The IceCube Collaboration http://icecube.wisc.edu/collaboration/authors/icrc17_icecube E-mail: gdewasse@icecube.wisc.edu Since the end
Search for GeV neutrinos associated with solar flares with IceCube The IceCube Collaboration http://icecube.wisc.edu/collaboration/authors/icrc17_icecube E-mail: gdewasse@icecube.wisc.edu Since the end
Probing the Pulsar Wind in the TeV Binary System
 Probing the Pulsar Wind in the TeV Binary System -PSR B1259-63/SS2883- Jumpei Takata (University of Hong Kong) Ronald Taam (TIARA, Taiwan) 1 Outline 1, Introduction -TeV binaries -Fermi observation -PSR
Probing the Pulsar Wind in the TeV Binary System -PSR B1259-63/SS2883- Jumpei Takata (University of Hong Kong) Ronald Taam (TIARA, Taiwan) 1 Outline 1, Introduction -TeV binaries -Fermi observation -PSR
Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays
 Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Gamma-Ray Astronomy with a Wide Field of View detector operated at Extreme Altitude in the Southern Hemisphere.
 Gamma-Ray Astronomy with a Wide Field of View detector operated at Extreme Altitude in the Southern Hemisphere., S. Miozzi, R. Santonico INFN - Rome Tor Vergata, Italy E-mail: disciascio@roma.infn.it P.
Gamma-Ray Astronomy with a Wide Field of View detector operated at Extreme Altitude in the Southern Hemisphere., S. Miozzi, R. Santonico INFN - Rome Tor Vergata, Italy E-mail: disciascio@roma.infn.it P.
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A
 An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2017](/thumbs/80/81228175.jpg) in the inner heliosphere arxiv:1712.09745v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2017 Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Stanford University, Stanford,
in the inner heliosphere arxiv:1712.09745v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2017 Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Stanford University, Stanford,
Gamma rays from supernova remnants in clumpy environments.! Stefano Gabici APC, Paris
 Gamma rays from supernova remnants in clumpy environments!! Stefano Gabici APC, Paris Overview of the talk Galactic cosmic rays Gamma rays from supernova remnants Hadronic or leptonic? The role of gas
Gamma rays from supernova remnants in clumpy environments!! Stefano Gabici APC, Paris Overview of the talk Galactic cosmic rays Gamma rays from supernova remnants Hadronic or leptonic? The role of gas
