Unanswered questions regarding solar wind - magnetosphere interaction
|
|
|
- Sydney Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unanswered questions regarding solar wind - magnetosphere interaction N. Østgaard (1) J.P. Reistad (1), P. Ten6ord (1), K. M. Laundal (1), S. Haaland (1,2), K. Snekvik (1), S. Milan (1,3) 1) Birkeland Centre for Space Science, Department of Physics and Technology, University of Bergen, Allegt 55, N- 5007, Norway 2) Max- Planck InsUtute, GoWngen, Germany 3) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, UK
2 Unsolved questions Why are the aurora in the cojugate hemispheres asymmetric? Two topics: 1. Effects of IMF By 2. Transporal arcs If time: 3. Effects of IMF Bx 2
3 IMF By/clock angle and asymmetric footpoints 6600 substorm onsets by IMAGE and Polar (4671 NH SH) Simultaneous UV aurora in two hemispheres: Asymmetric foot points controlled by IMF Clock angle Østgaard et al, JGR, Østgaard et al, GRL, 2012
4 IMF By penetration : Classical picture Stenbaek-Nielsen and Otto, 1997 Result of reconnecuon, By is transported into closed hemisphere Creates dby/dx in the tail: Ampere s law implies interhemispheric currents 4
5 Revised explanation Stenbaek-Nielsen and Otto, 1997 No interhemispheric currents Only asymmetric currents Lobe pressure not reconnecuon 5
6 Magnetospheric By is induced by IMF By Asymmetric loading of flux and pressure in the lobes This pressure force affects closed field lines Result is an induced By Leads to asymmetric footpoints No need for reconnection, only lobe pressure Response time of ~10 minutes 6
7 Magnetospheric By is induced by IMF By LFM model shows induced By after 10 minutes: How lobe pressure is added on a half sphere 8 Re seen from sun IMF By =0 IMF By >0 7
8 Induced By and dynamics Midtail: 17 Re north Footpoints in banana and orange cell dawn cells Lobe pressure force Tension force In ballance south Finite region of induced By Region of induced By No dissipation and currents close locally 8
9 Induced By and dynamics Near Earth: 6 Re north Less/no lobe pressure Tension force Pressure from Earth (magnetic and particle) Same direction in north Opposite in south Stress released into north up/down currents south Flow in north faster than south removes asymmetry 9 Østgaard et al., 2015 (AGU mon); Ten>ord et al., 2015 (in review process)
10 Summary IMF By IMF By does not penetrate the magnetosphere By is induced by the asymmetric loading of lobe flux Midtail region: forces (tension and lobe pressure) balance and current close locally Near Earth: tension and magnetic/particle pressure from Earth: By>0: same direction in north, opposite in south Alfven wave/magnetic stress released (up down current) into north weaker into south No interhemispheric current but asymmetric currents launched from plasma sheet Flow faster in north than south restoring symmetric footpoints. 10
11 Questions IMF By What is the time scale of this induction? How soon will we see: induced By asymmetric footpoints convection pattern (banana orange cells) LFM model and our own results: 10 minutes Other papers: hours 11
12 Time scale of induced By Østgaard et al.., 2011 Best ordering of delta MLT When SW propagated to 10 Re Which is about 10 min after subsolar point Asymmetries established after 10 min. 12
13 Time scale of induced By South dawnward of North A) South duskward of North B) C) Østgaard et al.., 2011 Two substorms SW propagated to 10 Re which is about 10 min D) E) Delta-MLT follows the By Asymmetries established after 10 min F) 13
14 Time scale of induced By A04209 MOTOBA ET AL.: B Motoba et al., 2010 ACE - clock angle Cluster (X:-12,Y:-3) - By Correlation shows min before By is induced Auroral all-sky images Iceland Antarctica shows delta-mlt consistent with this time delay 14 Asymmetries established after 50 minutes F E 0 a f G t G s S c
15 Time scale of induced By Rong et al., 2015 Cluster sees By at -18.2, -4.4, minutes after OMNI at sub-solar point. Asymmetries established after 55 min 15
16 Questions IMF By What is the time scale of this induction? How soon will we see: induced By asymmetric footpoints convection pattern (banana orange cells) Model (LFM) predicts minutes Alfven waves also indicate minutes Our own results indicate 10 min Some claim it will take hours Rong et al., 2015: 55 min for IMF to induce By component Motoba et al., 2010: 51 minutes 16
17 Polar Arcs Fear et al., Science, Trapped par6cles in theta aurora Cluster passed through the polar arc Time (g): pitch angle distribuuon and electron energy (phase space) double loss- cone and trapped parucles RE S EAR CH R E P O R T S a c d e b f g a 17 h b c i d e f j g h i
18 Non-conjugate polar Arcs Østgaard et al., 2003, 2007 Conjugate imaging: three examples of non- conjugate polar arcs IMF Bx more efficient lobe reconnecuon? 18
19 Non-conjugate polar Arcs 1923:48 UT F12 - southern F14- northern ParUcles from Plasma sheet 19 Polar workshop
20 Non-conjugate polar Arcs Are polar arcs on closed or open field lines Also non- conjugate polar arcs indicate plasma sheet parucles Why then non- conjugate? Asymmetric mapping? into polar arc one hemisphere into the auroral arc in the other 20 Polar workshop
21 IMF Bx region 1 current and duskside aurora 12 May, UT Laundal and Østgaard,
22 IMF BX and dusk side aurora X - 28 The enure IMAGE data set is used X - 28 REISTAD ET AL.: ASYMMETRIC AURORA AND IMF BX REISTAD ET AL.: ASYMMETRIC AURORA AND IMF BX Kolmogorov- Smirnov test: 95% confidence Northern North Hemisphere Northern Hemisphere A A B C BC Nnn mmmm Tension forces IMF Bx negative IMF Bx positive REISTADAND ET IMF AL.: BASYMMETRIC AURORA REISTAD ET AL.: ASYMMETRIC AURORA X AND - 29 IMF BX X D Southern South Figure 2. E D X - 29 E Results of the statistical analysis in the Northern Hemisphere. A: Maps of Southern Figure 2. Results of the statistical analysis in the Northern Hemisphere. A: Maps of Hemispheremedian auroral intensity for IMF Bx negative case. B: Corresponding map for positive Hemisphere A C AB BC median auroral intensity for IMF Bx negative case. B: Corresponding map for positive 22 IMF Bx case. C: The intensity di erence between the two IMF Bx cases. D: Number of Reistad et al., 2014 The ofintensity between the two IMF Bx cases. D: Number of x case. C: level events across the domain. E:IMF The Bsignificance the test di erence that the two distributions
23 IMF Bx effect Small but significant difference in auroral brightness due to IMF Bx Consistent with the explanation of difference in solar wind dynamo efficiency Even small: IMF Bx > 2 nt more than 73% of the time IMF Bz is negative 23
24 Question about IMF Bx One statistical study implies some significance Can this result be confirmed by other measurements? AMPERE data should we looked but have not found? 24
25 Summary of questions 1. What is the time scale of how IMF By induces a By component in the closed hemisphere? 2. How can polar arcs be non-conjugate and on closed field lines? 3. Does IMF Bx (and tilt) lead to significant differences in energy input into the two hemispheres 25
Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Theasymmetricallyaddedfluxto the lobes induces By in the closed magnetosphere AsymmetricFACsarecreatedasa consequence of y directed tension contained in the return flow IMF
RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Theasymmetricallyaddedfluxto the lobes induces By in the closed magnetosphere AsymmetricFACsarecreatedasa consequence of y directed tension contained in the return flow IMF
Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation
 Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation Kyung Sun Park 1, Dae-Young Lee 1, Myeong Joon Kim 1, Rok Soon Kim 2, Kyungsuk
Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation Kyung Sun Park 1, Dae-Young Lee 1, Myeong Joon Kim 1, Rok Soon Kim 2, Kyungsuk
Solar-Wind/Magnetosphere Coupling
 Solar-Wind/Magnetosphere Coupling Joe Borovsky Space Science Institute --- University of Michigan 1. Get a feeling for how the coupling works 2. Get an understanding of how reconnection works 3. Look at
Solar-Wind/Magnetosphere Coupling Joe Borovsky Space Science Institute --- University of Michigan 1. Get a feeling for how the coupling works 2. Get an understanding of how reconnection works 3. Look at
Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System
 Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System Robert Fear 1,2 R.C.Fear@soton.ac.uk 1 Space Environment Physics group University of Southampton 2 Radio & Space Plasma Physics group University of Leicester
Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System Robert Fear 1,2 R.C.Fear@soton.ac.uk 1 Space Environment Physics group University of Southampton 2 Radio & Space Plasma Physics group University of Leicester
Interhemispheric observations of emerging polar cap asymmetries
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja015160, 2010 Interhemispheric observations of emerging polar cap asymmetries K. M. Laundal, 1 N. Østgaard, 1 K.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja015160, 2010 Interhemispheric observations of emerging polar cap asymmetries K. M. Laundal, 1 N. Østgaard, 1 K.
MSSL. Magnetotail Science with Double Star and Cluster
 Magnetotail Science with Double Star and Cluster A.N. Fazakerley 1, A. Marchaudon 1, I. Alexeev 1, C.J. Owen 1, C. M. Carr 2, E. Lucek 2, H Reme 3, J. Watermann 4, G.A. Abel 5 1 :, 2 : ICSTM, 3 : CESR,
Magnetotail Science with Double Star and Cluster A.N. Fazakerley 1, A. Marchaudon 1, I. Alexeev 1, C.J. Owen 1, C. M. Carr 2, E. Lucek 2, H Reme 3, J. Watermann 4, G.A. Abel 5 1 :, 2 : ICSTM, 3 : CESR,
Ion heating during geomagnetic storms measured using energetic neutral atom imaging. Amy Keesee
 Ion heating during geomagnetic storms measured using energetic neutral atom imaging Amy Keesee Outline Motivation Overview of ENA measurements Charge exchange MENA and TWINS ENA instruments Calculating
Ion heating during geomagnetic storms measured using energetic neutral atom imaging Amy Keesee Outline Motivation Overview of ENA measurements Charge exchange MENA and TWINS ENA instruments Calculating
Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm
 ESS 7 Lecture 13 October 27, 2010 Substorms Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm This set of images in the ultra-violet from the Polar satellite shows changes that occur during an auroral substorm.
ESS 7 Lecture 13 October 27, 2010 Substorms Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm This set of images in the ultra-violet from the Polar satellite shows changes that occur during an auroral substorm.
Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling During Storms and Substorms
 Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling During Storms and Substorms Bill Lotko Bin Zhang Oliver Brambles Sheng Xi John Lyon Tian Luo Roger Varney Jeremy Ouellette Mike Wiltberger 2 3 4 CEDAR: Storms
Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling During Storms and Substorms Bill Lotko Bin Zhang Oliver Brambles Sheng Xi John Lyon Tian Luo Roger Varney Jeremy Ouellette Mike Wiltberger 2 3 4 CEDAR: Storms
Magnetospheric Currents at Quiet Times
 Magnetospheric Currents at Quiet Times Robert L. McPherron Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1567 e-mail: rmcpherron@igpp.ucla.edu
Magnetospheric Currents at Quiet Times Robert L. McPherron Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1567 e-mail: rmcpherron@igpp.ucla.edu
Magnetospheric Model Performance during Conjugate Aurora
 18 Magnetospheric Model Performance during Conjugate Aurora William Longley 1, Patricia Reiff 1, Jone Peter Reistad 2, and Nikolai Østgaard 2 Video of Yosemite Talk, URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.15142/t3h01c
18 Magnetospheric Model Performance during Conjugate Aurora William Longley 1, Patricia Reiff 1, Jone Peter Reistad 2, and Nikolai Østgaard 2 Video of Yosemite Talk, URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.15142/t3h01c
Planned talk schedule. Substorm models. Reading: Chapter 9 - SW-Magnetospheric Coupling from Russell book (posted)
 Reading: Chapter 9 - SW-Magnetospheric Coupling from Russell book (posted) Today: Example of dynamics/time variation Review of intro to auroral substorms Substorm models How do we know a substorm is occurring?
Reading: Chapter 9 - SW-Magnetospheric Coupling from Russell book (posted) Today: Example of dynamics/time variation Review of intro to auroral substorms Substorm models How do we know a substorm is occurring?
ESS 200C Aurorae. Lecture 15
 ESS 200C Aurorae Lecture 15 The record of auroral observations dates back thousands of years to Greek and Chinese documents. The name aurora borealis (latin for northern dawn) was coined in 1621 by P.
ESS 200C Aurorae Lecture 15 The record of auroral observations dates back thousands of years to Greek and Chinese documents. The name aurora borealis (latin for northern dawn) was coined in 1621 by P.
Overcoming Uncertainties in the Relation between Source and Aurora
 Unsolved Problems in Magnetospheric Physics Scarborough, UK, 06-12 September 2015 Overcoming Uncertainties in the Relation between Source and Aurora Gerhard Haerendel Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial
Unsolved Problems in Magnetospheric Physics Scarborough, UK, 06-12 September 2015 Overcoming Uncertainties in the Relation between Source and Aurora Gerhard Haerendel Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial
Introduction to the Sun-Earth system Steve Milan
 Introduction to the Sun-Earth system Steve Milan steve.milan@ion.le.ac.uk The solar-terrestrial system Corona is so hot that the Sun s gravity cannot hold it down it flows outwards as the solar wind A
Introduction to the Sun-Earth system Steve Milan steve.milan@ion.le.ac.uk The solar-terrestrial system Corona is so hot that the Sun s gravity cannot hold it down it flows outwards as the solar wind A
G R O U P R E S E A R C H E R S
 SW C O L L A B O R A T I O N J U P I T E R E A R T H G R O U P R E S E A R C H E R S Suwicha Wannawichian Tatphicha Promfu Paparin Jamlongkul Kamolporn Haewsantati 2 SW C O L L A B O R A T I O N C o l
SW C O L L A B O R A T I O N J U P I T E R E A R T H G R O U P R E S E A R C H E R S Suwicha Wannawichian Tatphicha Promfu Paparin Jamlongkul Kamolporn Haewsantati 2 SW C O L L A B O R A T I O N C o l
CROSS POLAR MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA DRIFT AS OBSERVED BY CLUSTER EDI: STATISTICAL RESULTS
 CROSS POLAR MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA DRIFT AS OBSERVED BY CLUSTER EDI: STATISTICAL RESULTS 1 M. Förster 1, S. Haaland 2, G. Paschmann 3, J. B. Baker 4, H. Vaith 5, J.M. Quinn 5, and R. B. Torbert 5 1 Max-Planck
CROSS POLAR MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA DRIFT AS OBSERVED BY CLUSTER EDI: STATISTICAL RESULTS 1 M. Förster 1, S. Haaland 2, G. Paschmann 3, J. B. Baker 4, H. Vaith 5, J.M. Quinn 5, and R. B. Torbert 5 1 Max-Planck
Time history effects at the magnetopause: Hysteresis in power input and its implications to substorm processes
 219 Time history effects at the magnetopause: Hysteresis in power input and its implications to substorm processes M. Palmroth, T. I. Pulkkinen, T. V. Laitinen, H. E. J. Koskinen, and P. Janhunen 1. Introduction
219 Time history effects at the magnetopause: Hysteresis in power input and its implications to substorm processes M. Palmroth, T. I. Pulkkinen, T. V. Laitinen, H. E. J. Koskinen, and P. Janhunen 1. Introduction
Interplanetary magnetic field B x asymmetry effect on auroral brightness
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A8, 10.1029/2001JA000229, 2002 Interplanetary magnetic field B x asymmetry effect on auroral brightness J.-H. Shue, P. T. Newell, K. Liou, and C.-I. Meng
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A8, 10.1029/2001JA000229, 2002 Interplanetary magnetic field B x asymmetry effect on auroral brightness J.-H. Shue, P. T. Newell, K. Liou, and C.-I. Meng
Lecture 12 The Importance of Accurate Solar Wind Measurements
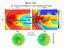 Lecture 12 The Importance of Accurate Solar Wind Measurements The Approach Magnetospheric studies usually are based on a single solar wind monitor. We propagate the solar wind from the observation point
Lecture 12 The Importance of Accurate Solar Wind Measurements The Approach Magnetospheric studies usually are based on a single solar wind monitor. We propagate the solar wind from the observation point
Jim Wild Lancaster University
 Double Star, Cluster, and Ground-based Observations of Magnetic Reconnection During an Interval of Duskward-Oriented IMF Jim Wild Lancaster University S.E. Milan, J.A. Davies, C.M. Carr, M.W. Dunlop, E.
Double Star, Cluster, and Ground-based Observations of Magnetic Reconnection During an Interval of Duskward-Oriented IMF Jim Wild Lancaster University S.E. Milan, J.A. Davies, C.M. Carr, M.W. Dunlop, E.
Statistical study of O + transport from the cusp to the lobes with Cluster CODIF data
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015613, 2010 Statistical study of O + transport from the cusp to the lobes with Cluster CODIF data J. Liao, 1 L. M. Kistler, 1 C. G. Mouikis,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015613, 2010 Statistical study of O + transport from the cusp to the lobes with Cluster CODIF data J. Liao, 1 L. M. Kistler, 1 C. G. Mouikis,
High-latitude aurora during steady northward interplanetary magnetic field and changing IMF B y
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010867, 2005 High-latitude aurora during steady northward interplanetary magnetic field and changing IMF B y J. A. Cumnock 1 Center for Space
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010867, 2005 High-latitude aurora during steady northward interplanetary magnetic field and changing IMF B y J. A. Cumnock 1 Center for Space
Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere. Outline
 Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere P. K. Toivanen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Outline Introduction to large-scale electromagnetic fields Magnetic field geometry Modelling
Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere P. K. Toivanen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Outline Introduction to large-scale electromagnetic fields Magnetic field geometry Modelling
Chapter 8 Geospace 1
 Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Global MHD Eigenmodes of the Outer Magnetosphere
 Global MHD Eigenmodes of the Outer Magnetosphere Andrew Wright UNIVERSITY OF ST ANDREWS Magnetospheric Structure: Cavities and Waveguides The Earth s magnetosphere is structured by magnetic fields and
Global MHD Eigenmodes of the Outer Magnetosphere Andrew Wright UNIVERSITY OF ST ANDREWS Magnetospheric Structure: Cavities and Waveguides The Earth s magnetosphere is structured by magnetic fields and
The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction
 The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction Research seminar on Sun-Earth connections Eija Tanskanen Friday January 27, 2006 12-14 a.m., D115 Outline 1. Basics of the Earth s magnetosphere
The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction Research seminar on Sun-Earth connections Eija Tanskanen Friday January 27, 2006 12-14 a.m., D115 Outline 1. Basics of the Earth s magnetosphere
The Dynamic Magnetosphere. Ioannis A. Daglis. National Observatory of Athens, Greece
 310/1749-42 ICTP-COST-USNSWP-CAWSES-INAF-INFN International Advanced School on Space Weather 2-19 May 2006 The Dynamic Magnetosphere: Reaction to and Consequences of Solar Wind Variations Yannis DAGLIS
310/1749-42 ICTP-COST-USNSWP-CAWSES-INAF-INFN International Advanced School on Space Weather 2-19 May 2006 The Dynamic Magnetosphere: Reaction to and Consequences of Solar Wind Variations Yannis DAGLIS
This is the published version of a paper published in Geophysical Research Letters. Citation for the original published paper (version of record):
 http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Geophysical Research Letters. Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Pitkänen, T., Hamrin, M., Norqvist,
http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Geophysical Research Letters. Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Pitkänen, T., Hamrin, M., Norqvist,
Relation of polar auroral arcs to magnetotail twisting and IMF rotation: a systematic MHD simulation study
 Annales Geophysicae (24) 22: 951 97 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/24-22-951 European Geosciences Union 24 Annales Geophysicae Relation of polar auroral arcs to magnetotail twisting and IMF rotation: a systematic
Annales Geophysicae (24) 22: 951 97 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/24-22-951 European Geosciences Union 24 Annales Geophysicae Relation of polar auroral arcs to magnetotail twisting and IMF rotation: a systematic
Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field
 Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field I. Alexeev, V. Kalegaev The solar wind influence on the magnetospheric state is sufficiently nonlinear
Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field I. Alexeev, V. Kalegaev The solar wind influence on the magnetospheric state is sufficiently nonlinear
Numerical Simulation of Jovian and Kronian Magnetospheric Configuration
 Feb. 16, 2015 Numerical Simulation of Jovian and Kronian Magnetospheric Configuration Keiichiro FUKAZAWA 1, 2 1.Academic Center for Computing and Media Studies, Kyoto University 2.CREST, JST Context Jovian
Feb. 16, 2015 Numerical Simulation of Jovian and Kronian Magnetospheric Configuration Keiichiro FUKAZAWA 1, 2 1.Academic Center for Computing and Media Studies, Kyoto University 2.CREST, JST Context Jovian
Identification of optical auroras caused by mantle precipitation with the aid of particle observations from DMSP satellites
 Article Advances in Polar Science doi: 10.13679/j.advps.2018.4.00233 December 2018 Vol. 29 No. 4: 233-242 Identification of optical auroras caused by mantle precipitation with the aid of particle observations
Article Advances in Polar Science doi: 10.13679/j.advps.2018.4.00233 December 2018 Vol. 29 No. 4: 233-242 Identification of optical auroras caused by mantle precipitation with the aid of particle observations
Earth s Magnetosphere
 Earth s Magnetosphere General Description of the Magnetosphere Shape Pressure Balance The Earth s Magnetic Field The Geodynamo, Magnetic Reversals, Discovery Current Systems Chapman Ferraro Cross Tail
Earth s Magnetosphere General Description of the Magnetosphere Shape Pressure Balance The Earth s Magnetic Field The Geodynamo, Magnetic Reversals, Discovery Current Systems Chapman Ferraro Cross Tail
IMF B Y and the seasonal dependences of the electric field in the inner magnetosphere
 Annales Geophysicae, 23, 2671 2678, 2 SRef-ID: 143276/ag/2-23-2671 European Geosciences Union 2 Annales Geophysicae IMF B Y and the seasonal dependences of the electric field in the inner magnetosphere
Annales Geophysicae, 23, 2671 2678, 2 SRef-ID: 143276/ag/2-23-2671 European Geosciences Union 2 Annales Geophysicae IMF B Y and the seasonal dependences of the electric field in the inner magnetosphere
Ring current formation influenced by solar wind substorm conditions
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014909, 2010 Ring current formation influenced by solar wind substorm conditions M. D. Cash, 1 R. M. Winglee, 1
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014909, 2010 Ring current formation influenced by solar wind substorm conditions M. D. Cash, 1 R. M. Winglee, 1
Magnetic Reconnection
 Magnetic Reconnection? On small scale-lengths (i.e. at sharp gradients), a diffusion region (physics unknown) can form where the magnetic field can diffuse through the plasma (i.e. a breakdown of the frozenin
Magnetic Reconnection? On small scale-lengths (i.e. at sharp gradients), a diffusion region (physics unknown) can form where the magnetic field can diffuse through the plasma (i.e. a breakdown of the frozenin
Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth's bow shock
 Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth's bow shock L. Turc1, P. Escoubet1, D. Fontaine2, E. Kilpua3 1 ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands 2 LPP-CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique-UPMC,
Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth's bow shock L. Turc1, P. Escoubet1, D. Fontaine2, E. Kilpua3 1 ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands 2 LPP-CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique-UPMC,
On the origin of plasma sheet evolution during the substorm growth phase
 On the origin of plasma sheet evolution during the substorm growth phase Evgeny Gordeev Victor Sergeev Maria Shukhtina Viacheslav Merkin Maria Kuznetsova (SPSU) (SPSU) (SPSU) (APL) (GSFC) [Hsieh and Otto,
On the origin of plasma sheet evolution during the substorm growth phase Evgeny Gordeev Victor Sergeev Maria Shukhtina Viacheslav Merkin Maria Kuznetsova (SPSU) (SPSU) (SPSU) (APL) (GSFC) [Hsieh and Otto,
Cluster observations of a magnetic field cavity in the plasma sheet
 Cluster observations of a magnetic field cavity in the plasma sheet N.C. Draper a, M. Lester a, S.W.H. Cowley a, J.-M. Bosqued b, A. Grocott a, J.A. Wild a, Y. Bogdanova c, A.N. Fazakerley c, J.A. Davies
Cluster observations of a magnetic field cavity in the plasma sheet N.C. Draper a, M. Lester a, S.W.H. Cowley a, J.-M. Bosqued b, A. Grocott a, J.A. Wild a, Y. Bogdanova c, A.N. Fazakerley c, J.A. Davies
The Physics of Space Plasmas
 The Physics of Space Plasmas Magnetic Storms and Substorms William J. Burke 14 November 2012 University of Massachusetts, Lowell Lecture 9 Course term-paper topics Geomagnetic Storms: (continued ) Volland-Stern
The Physics of Space Plasmas Magnetic Storms and Substorms William J. Burke 14 November 2012 University of Massachusetts, Lowell Lecture 9 Course term-paper topics Geomagnetic Storms: (continued ) Volland-Stern
Solar wind dependence of the occurrence and motion of polar auroral arcs: A statistical study
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A11, 1362, doi:10.1029/2002ja009245, 2002 Solar wind dependence of the occurrence and motion of polar auroral arcs: A statistical study A. Kullen Royal Institute
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A11, 1362, doi:10.1029/2002ja009245, 2002 Solar wind dependence of the occurrence and motion of polar auroral arcs: A statistical study A. Kullen Royal Institute
The dependence of winter aurora on interplanetary parameters
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A4, 8009, doi:10.1029/2002ja009352, 2003 The dependence of winter aurora on interplanetary parameters J. B. Baker, 1 A. J. Ridley, V. O. Papitashvili, and
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A4, 8009, doi:10.1029/2002ja009352, 2003 The dependence of winter aurora on interplanetary parameters J. B. Baker, 1 A. J. Ridley, V. O. Papitashvili, and
Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter?
 Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter? N. Ganushkina (1, 2), S. Dubyagin (1), I. Sillanpää (1), D.
Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter? N. Ganushkina (1, 2), S. Dubyagin (1), I. Sillanpää (1), D.
RCM Modeling of Penetration Electric Fields During Magnetic Storms
 RCM Modeling of Penetration Electric Fields During Magnetic Storms S. Sazykin, R. A. Wolf, R. W. Spiro, Haystack Workshop on Penetration Electric Fields November 8, 2005 Low Latitude E-field: Massive Undershielding
RCM Modeling of Penetration Electric Fields During Magnetic Storms S. Sazykin, R. A. Wolf, R. W. Spiro, Haystack Workshop on Penetration Electric Fields November 8, 2005 Low Latitude E-field: Massive Undershielding
Polar cap bifurcation during steady-state northward interplanetary magnetic field with j B Y j B Z
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003ja009944, 2004 Polar cap bifurcation during steady-state northward interplanetary magnetic field with j B Y j B Z Masakazu Watanabe, George J.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003ja009944, 2004 Polar cap bifurcation during steady-state northward interplanetary magnetic field with j B Y j B Z Masakazu Watanabe, George J.
Cluster Observations of the Electron Low- Latitude Boundary Layer at Mid-Altitudes
 UCL DEPT. OF SPACE & CLIMATE PHYSICS MULLARD SPACE SCIENCE LABORATORY Cluster Observations of the Electron Low- Latitude Boundary Layer at Mid-Altitudes Y.V. Bogdanova 1, C.J. Owen 1, A.N. Fazakerley 1,
UCL DEPT. OF SPACE & CLIMATE PHYSICS MULLARD SPACE SCIENCE LABORATORY Cluster Observations of the Electron Low- Latitude Boundary Layer at Mid-Altitudes Y.V. Bogdanova 1, C.J. Owen 1, A.N. Fazakerley 1,
Geomagnetic signatures of auroral substorms preceded by pseudobreakups
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013712, 2009 Geomagnetic signatures of auroral substorms preceded by pseudobreakups A. Kullen, 1 S. Ohtani, 2 and T. Karlsson 3 Received 29
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013712, 2009 Geomagnetic signatures of auroral substorms preceded by pseudobreakups A. Kullen, 1 S. Ohtani, 2 and T. Karlsson 3 Received 29
Magnetopause erosion: A global view from MHD simulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A6, 1235, doi:10.1029/2002ja009564, 2003 Magnetopause erosion: A global view from MHD simulation M. Wiltberger High Altitude Observatory, National Center
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A6, 1235, doi:10.1029/2002ja009564, 2003 Magnetopause erosion: A global view from MHD simulation M. Wiltberger High Altitude Observatory, National Center
Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus
 Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus In June 2015, the Sun emitted several M-Class flares over a 2-day period. These flares were concurrent with
Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus In June 2015, the Sun emitted several M-Class flares over a 2-day period. These flares were concurrent with
In-Situ vs. Remote Sensing
 In-Situ vs. Remote Sensing J. L. Burch Southwest Research Institute San Antonio, TX USA Forum on the Future of Magnetospheric Research International Space Science Institute Bern, Switzerland March 24-25,
In-Situ vs. Remote Sensing J. L. Burch Southwest Research Institute San Antonio, TX USA Forum on the Future of Magnetospheric Research International Space Science Institute Bern, Switzerland March 24-25,
What determines when and where reconnection begins
 What determines when and where reconnection begins Robert L. McPherron Invited presentation at Unsolved Problems in Magnetospheric Physics, Scarborough, UK, Sept. 6-12. Factors That Might Affect Tail Reconnection
What determines when and where reconnection begins Robert L. McPherron Invited presentation at Unsolved Problems in Magnetospheric Physics, Scarborough, UK, Sept. 6-12. Factors That Might Affect Tail Reconnection
ESS 200C Lectures 9, 10 and 11 The Magnetosphere
 ESS 00C Lectures 9, 10 and 11 The Magnetosphere The magnetosphere Back in 1930 Chapman and Ferraro foresaw that a planetary magnetic field could provide an effective obstacle to the solar-wind plasma.
ESS 00C Lectures 9, 10 and 11 The Magnetosphere The magnetosphere Back in 1930 Chapman and Ferraro foresaw that a planetary magnetic field could provide an effective obstacle to the solar-wind plasma.
Interplanetary magnetic field control of fast azimuthal flows in the nightside high-latitude ionosphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08102, doi:10.1029/2008gl033545, 2008 Interplanetary magnetic field control of fast azimuthal flows in the nightside high-latitude ionosphere A. Grocott, 1 S. E.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08102, doi:10.1029/2008gl033545, 2008 Interplanetary magnetic field control of fast azimuthal flows in the nightside high-latitude ionosphere A. Grocott, 1 S. E.
Observational Evidence of Component and Antiparallel Reconnection at the Earthʼs Magnetopause
 Observational Evidence of Component and Antiparallel Reconnection at the Earthʼs Magnetopause Stephen A. Fuselier, Karlheinz J. Trattner, Steven M. Petrinec Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center 1
Observational Evidence of Component and Antiparallel Reconnection at the Earthʼs Magnetopause Stephen A. Fuselier, Karlheinz J. Trattner, Steven M. Petrinec Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center 1
A Correlation Study of Steady Magnetospheric Convection in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
 A Correlation Study of Steady Magnetospheric Convection in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres Caroline M. McElhenny 1, Dr. Anna DeJong 1 1 Christopher Newport University Abstract: The purpose of this
A Correlation Study of Steady Magnetospheric Convection in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres Caroline M. McElhenny 1, Dr. Anna DeJong 1 1 Christopher Newport University Abstract: The purpose of this
DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE
 DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE PROF JIM WILD j.wild@lancaster.ac.uk @jim_wild With thanks to: Stan Cowley, Rob Fear & Steve Milan OUTLINE So far: Dungey cycle - the stirring of the magnetosphere
DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE PROF JIM WILD j.wild@lancaster.ac.uk @jim_wild With thanks to: Stan Cowley, Rob Fear & Steve Milan OUTLINE So far: Dungey cycle - the stirring of the magnetosphere
STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM
 Prosiding Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan Penerapan MIPA Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 16 Mei 2009 STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM L. Muhammad
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan Penerapan MIPA Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 16 Mei 2009 STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM L. Muhammad
Sub-Auroral Electric Fields: An Inner Magnetosphere Perspective
 Sub-Auroral Electric Fields: An Inner Magnetosphere Perspective Bob Spiro Rice University 2005 GEM/CEDAR Tutorial 1 Introduction/Outline Introduction/Outline Importance of Sub-Auroral E-Fields Early Models
Sub-Auroral Electric Fields: An Inner Magnetosphere Perspective Bob Spiro Rice University 2005 GEM/CEDAR Tutorial 1 Introduction/Outline Introduction/Outline Importance of Sub-Auroral E-Fields Early Models
Three-dimensional nature of magnetic reconnection X-line in asymmetric current sheets
 Blue Waters symposium 2017 Three-dimensional nature of magnetic reconnection X-line in asymmetric current sheets Yi-Hsin Liu @ NASA- Goddard Space Flight Center William Daughton @ Los Alamos National Lab
Blue Waters symposium 2017 Three-dimensional nature of magnetic reconnection X-line in asymmetric current sheets Yi-Hsin Liu @ NASA- Goddard Space Flight Center William Daughton @ Los Alamos National Lab
Occurrence characteristics of Saturn s radio burst
 Occurrence characteristics of Saturn s radio burst D. Maruno 1, Y. Kasaba 1, T. Kimura 2, A. Morioka 1, B. Cecconi 3 1 Department of Geophysics, Tohoku University 2 ISAS, JAXA 3 LESIA, Observatorire de
Occurrence characteristics of Saturn s radio burst D. Maruno 1, Y. Kasaba 1, T. Kimura 2, A. Morioka 1, B. Cecconi 3 1 Department of Geophysics, Tohoku University 2 ISAS, JAXA 3 LESIA, Observatorire de
Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events
 Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) and Stepan Dubyagin (1) Special thanks to Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez (3) (1) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki,
Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) and Stepan Dubyagin (1) Special thanks to Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez (3) (1) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki,
Lobe cell convection and field-aligned currents poleward of the region 1 current system
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A8, 10.1029/2001JA005041, 2002 Lobe cell convection and field-aligned currents poleward of the region 1 current system S. Eriksson, 1 J. W. Bonnell, 2 L.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A8, 10.1029/2001JA005041, 2002 Lobe cell convection and field-aligned currents poleward of the region 1 current system S. Eriksson, 1 J. W. Bonnell, 2 L.
Magnetic Energy Storage and the Nightside Magnetosphere Ionosphere Coupling
 1 Magnetic Energy Storage and the Nightside Magnetosphere Ionosphere Coupling W. Horton, M. Pekker Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 I. Doxas Dept. of Astrophysical
1 Magnetic Energy Storage and the Nightside Magnetosphere Ionosphere Coupling W. Horton, M. Pekker Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 I. Doxas Dept. of Astrophysical
Intro to magnetosphere (Chap. 8) Schematic of Bow Shock and Foreshock. Flow around planetary magnetic field obstacle. Homework #3 posted
 Intro to magnetosphere (Chap. 8) Homework #3 posted Reading: Finish Chap. 8 of Kallenrode Interaction with solar wind a. Magnetopause b. Structure of magnetosphere - open vs closed c. Convection d. Magnetotail
Intro to magnetosphere (Chap. 8) Homework #3 posted Reading: Finish Chap. 8 of Kallenrode Interaction with solar wind a. Magnetopause b. Structure of magnetosphere - open vs closed c. Convection d. Magnetotail
Simultaneous Geotail and Wind observations of reconnection at the subsolar and tail flank magnetopause
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L09104, doi:10.1029/2006gl025756, 2006 Simultaneous Geotail and Wind observations of reconnection at the subsolar and tail flank magnetopause T. D. Phan, 1 H. Hasegawa,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L09104, doi:10.1029/2006gl025756, 2006 Simultaneous Geotail and Wind observations of reconnection at the subsolar and tail flank magnetopause T. D. Phan, 1 H. Hasegawa,
Effect of solar wind pressure enhancements on storm time ring current asymmetry
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2005ja011019, 2005 Effect of solar wind pressure enhancements on storm time ring current asymmetry Y. Shi, E. Zesta, L. R. Lyons, and A. Boudouridis
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2005ja011019, 2005 Effect of solar wind pressure enhancements on storm time ring current asymmetry Y. Shi, E. Zesta, L. R. Lyons, and A. Boudouridis
Global morphology of substorm growth phases observed by the IMAGE-SI12 imager
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007ja012329, 2007 Global morphology of substorm growth phases observed by the IMAGE-SI12 imager V. Coumans, 1 C. Blockx, 1 J.-C. Gérard, 1 B. Hubert,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007ja012329, 2007 Global morphology of substorm growth phases observed by the IMAGE-SI12 imager V. Coumans, 1 C. Blockx, 1 J.-C. Gérard, 1 B. Hubert,
Convection dynamics and driving mechanism of a small substorm during dominantly IMF By+, Bz+ conditions
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L08803, doi:10.1029/2003gl018878, 2004 Convection dynamics and driving mechanism of a small substorm during dominantly IMF By+, Bz+ conditions Jun Liang, 1 G. J.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L08803, doi:10.1029/2003gl018878, 2004 Convection dynamics and driving mechanism of a small substorm during dominantly IMF By+, Bz+ conditions Jun Liang, 1 G. J.
Relation of substorm disturbances triggered by abrupt solar-wind changes to physics of plasma sheet transport
 1 Relation of substorm disturbances triggered by abrupt solar-wind changes to physics of plasma sheet transport L. R. Lyons, D.-Y. Lee, C.-P. Wang, and S. B. Mende 1. Introduction Abstract: Substorm onset
1 Relation of substorm disturbances triggered by abrupt solar-wind changes to physics of plasma sheet transport L. R. Lyons, D.-Y. Lee, C.-P. Wang, and S. B. Mende 1. Introduction Abstract: Substorm onset
Remote sensing of magnetospheric processes: Lesson 1: Configura7on of the magnetosphere
 Remote sensing of magnetospheric processes: Lesson 1: Configura7on of the magnetosphere AGF-351 Optical methods in auroral physics research UNIS, 24.-25.11.2011 Anita Aikio Dept. Physics University of
Remote sensing of magnetospheric processes: Lesson 1: Configura7on of the magnetosphere AGF-351 Optical methods in auroral physics research UNIS, 24.-25.11.2011 Anita Aikio Dept. Physics University of
sampleess 471/503Research paper titles
 Research Papers Any subject arguably important in Space Physics (Important: clear it with Bob first) Not new research, but synthesis of published research about a topic Pose a question, and provide the
Research Papers Any subject arguably important in Space Physics (Important: clear it with Bob first) Not new research, but synthesis of published research about a topic Pose a question, and provide the
Ionospheric Tomography II: Ionospheric Tomography II: Applications to space weather and the high-latitude ionosphere
 Ionospheric Tomography II: Ionospheric Tomography II: Applications to space weather and the high-latitude ionosphere Why tomography at high latitudes? Why tomography at high latitudes? Magnetic field railway
Ionospheric Tomography II: Ionospheric Tomography II: Applications to space weather and the high-latitude ionosphere Why tomography at high latitudes? Why tomography at high latitudes? Magnetic field railway
Generation and properties of in vivo flux transfer events
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017166, 2012 Generation and properties of in vivo flux transfer events H. Zhang, 1,2,3 M. G. Kivelson, 1,2 V. Angelopoulos, 1,2 K. K. Khurana,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017166, 2012 Generation and properties of in vivo flux transfer events H. Zhang, 1,2,3 M. G. Kivelson, 1,2 V. Angelopoulos, 1,2 K. K. Khurana,
Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (<200 kev) at geostationary orbit
 Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (
Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A12, 1477, doi: /2001ja007546, 2002
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A12, 1477, doi:10.1029/2001ja007546, 2002 Strong interplanetary magnetic field B y -related plasma convection in the ionosphere and cusp field-aligned currents
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. A12, 1477, doi:10.1029/2001ja007546, 2002 Strong interplanetary magnetic field B y -related plasma convection in the ionosphere and cusp field-aligned currents
Cluster results on the magnetotail current sheet structure and dynamics
 Cluster results on the magnetotail current sheet structure and dynamics V. Sergeev, S.Apatenkov (SPbU), A. Runov, W. Baumjohann, R. Nakamura, T. Zhang (IWF), A. Balogh (IC), H. Reme, J.-A. Sauvaud (CESR)
Cluster results on the magnetotail current sheet structure and dynamics V. Sergeev, S.Apatenkov (SPbU), A. Runov, W. Baumjohann, R. Nakamura, T. Zhang (IWF), A. Balogh (IC), H. Reme, J.-A. Sauvaud (CESR)
Properties of Alfvén Waves in the Magnetotail Below 9 R E and Their Relation to Auroral Acceleration and Major Geomagnetic Storms
 Properties of Alfvén Waves in the Magnetotail Below 9 R E and Their Relation to Auroral Acceleration and Major Geomagnetic Storms A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
Properties of Alfvén Waves in the Magnetotail Below 9 R E and Their Relation to Auroral Acceleration and Major Geomagnetic Storms A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
Solar concept of flux transport by interchange reconnection applied to the magnetosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013140, 2008 Solar concept of flux transport by interchange reconnection applied to the magnetosphere V. G. Merkin 1 and N. U. Crooker 1 Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013140, 2008 Solar concept of flux transport by interchange reconnection applied to the magnetosphere V. G. Merkin 1 and N. U. Crooker 1 Received
Solar wind energy transfer and the asymmetric geospace
 Solar wind energy transfer and the asymmetric geospace Paul Tenfjord Dissertation for the degree of Philosophiae Doctor (PhD) Department of Physics and Technology University of Bergen April 2017 Preface
Solar wind energy transfer and the asymmetric geospace Paul Tenfjord Dissertation for the degree of Philosophiae Doctor (PhD) Department of Physics and Technology University of Bergen April 2017 Preface
Open magnetic flux and magnetic flux closure during sawtooth events
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L23301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036374, 2008 Open magnetic flux and magnetic flux closure during sawtooth events B. Hubert, 1 S. E. Milan, 2
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L23301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036374, 2008 Open magnetic flux and magnetic flux closure during sawtooth events B. Hubert, 1 S. E. Milan, 2
Small-scale characteristics of extremely high latitude aurora
 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Small-scale characteristics of extremely high latitude aurora J. A. Cumnock 1,2, L. G. Blomberg
Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Small-scale characteristics of extremely high latitude aurora J. A. Cumnock 1,2, L. G. Blomberg
Simultaneous observations of ionospheric flow and tail reconnection signatures during the substorm expansion phase.
 Simultaneous observations of ionospheric flow and tail reconnection signatures during the substorm expansion phase. M. Lester 1, M. Parkinson 2, J.A. Wild 1, S.E. Milan 1, T. Nagai 3, K.A. McWilliams 4,
Simultaneous observations of ionospheric flow and tail reconnection signatures during the substorm expansion phase. M. Lester 1, M. Parkinson 2, J.A. Wild 1, S.E. Milan 1, T. Nagai 3, K.A. McWilliams 4,
Japanese Sounding Rocket Activity in Scandinavia
 Japanese Sounding Rocket Activity in Scandinavia - Importance of ground-based support - Takumi Abe Institute of Space & Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency NIPR Symposium on Conjugate
Japanese Sounding Rocket Activity in Scandinavia - Importance of ground-based support - Takumi Abe Institute of Space & Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency NIPR Symposium on Conjugate
Small Scale Structures and Motions of Auroral Signatures as Observed From the Ground: a Planned Field Study Using Camera and Radar Observations
 Small Scale Structures and Motions of Auroral Signatures as Observed From the Ground: a Planned Field Study Using Camera and Radar Observations Preliminary Results for Return Current Region Structures
Small Scale Structures and Motions of Auroral Signatures as Observed From the Ground: a Planned Field Study Using Camera and Radar Observations Preliminary Results for Return Current Region Structures
Statistical study of the location and size of the electron edge of the Low-Latitude Boundary Layer as observed by Cluster at mid-altitudes
 European Geosciences Union 2006 Annales Geophysicae Statistical study of the location and size of the electron edge of the Low-Latitude Boundary Layer as observed by Cluster at mid-altitudes Y. V. Bogdanova
European Geosciences Union 2006 Annales Geophysicae Statistical study of the location and size of the electron edge of the Low-Latitude Boundary Layer as observed by Cluster at mid-altitudes Y. V. Bogdanova
Occurrence and properties of substorms associated with pseudobreakups
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015866, 2010 Occurrence and properties of substorms associated with pseudobreakups A. Kullen, 1 T. Karlsson, 1 J. A. Cumnock, 1,2 and T. Sundberg
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015866, 2010 Occurrence and properties of substorms associated with pseudobreakups A. Kullen, 1 T. Karlsson, 1 J. A. Cumnock, 1,2 and T. Sundberg
David versus Goliath 1
 David versus Goliath 1 or A Comparison of the Magnetospheres between Jupiter and Earth 1 David and Goliath is a story from the Bible that is about a normal man (David) who meets a giant (Goliath) Tomas
David versus Goliath 1 or A Comparison of the Magnetospheres between Jupiter and Earth 1 David and Goliath is a story from the Bible that is about a normal man (David) who meets a giant (Goliath) Tomas
Substorm onsets as observed by IMAGE-FUV
 71 Substorm onsets as observed by IMAGE-FUV H. U. Frey and S. B. Mende 1. Introduction Abstract: The FUV instrument observed more than 4000 substorm onsets during the 5.5 years of the IMAGE mission. About
71 Substorm onsets as observed by IMAGE-FUV H. U. Frey and S. B. Mende 1. Introduction Abstract: The FUV instrument observed more than 4000 substorm onsets during the 5.5 years of the IMAGE mission. About
Does the polar cap area saturate?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09107, doi:10.1029/2007gl029357, 2007 Does the polar cap area saturate? V. G. Merkin 1 and C. C. Goodrich 1 Received 15 January 2007;
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09107, doi:10.1029/2007gl029357, 2007 Does the polar cap area saturate? V. G. Merkin 1 and C. C. Goodrich 1 Received 15 January 2007;
Effects of the surface conductivity and IMF strength on dynamics of planetary ions in Mercury s magnetosphere
 1! 5 th SERENA-HEWG workshop (6/16/2014)! Effects of the surface conductivity and IMF strength on dynamics of planetary ions in Mercury s magnetosphere K. Seki 1, M. Yagi 2, Y. Matsumoto 3, N. Terada 4,!
1! 5 th SERENA-HEWG workshop (6/16/2014)! Effects of the surface conductivity and IMF strength on dynamics of planetary ions in Mercury s magnetosphere K. Seki 1, M. Yagi 2, Y. Matsumoto 3, N. Terada 4,!
TAIL RECONNECTION AND PLASMA SHEET FAST FLOWS
 1 TAIL RECONNECTION AND PLASMA SHEET FAST FLOWS Rumi Nakamura, Wolfgang Baumjohann, Andrei Runov, and Yoshihiro Asano Space Research Institute, Austrian Academy of Sciences, Schmiedlstr. 6, A 8042 Graz,
1 TAIL RECONNECTION AND PLASMA SHEET FAST FLOWS Rumi Nakamura, Wolfgang Baumjohann, Andrei Runov, and Yoshihiro Asano Space Research Institute, Austrian Academy of Sciences, Schmiedlstr. 6, A 8042 Graz,
Geophysical Research Letters
 RESEARCH LETTER Key Points: Lobereconnectioncausesanet opening of closed flux if a transpolar arc is present Thisisindicatedbytheintersectionof acuspspotandatranspolararc Thelinkbetweenlobereconnection
RESEARCH LETTER Key Points: Lobereconnectioncausesanet opening of closed flux if a transpolar arc is present Thisisindicatedbytheintersectionof acuspspotandatranspolararc Thelinkbetweenlobereconnection
Received: 30 October 2008 Revised: 4 February 2009 Accepted: 27 February 2009 Published: 2 April Introduction
 Ann. Geophys., 27, 1527 1554, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Plasma flow channels at the dawn/dusk polar cap boundaries:
Ann. Geophys., 27, 1527 1554, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Plasma flow channels at the dawn/dusk polar cap boundaries:
Multipoint observations of substorm pre-onset flows and time sequence in the ionosphere and magnetosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017185, 2012 Multipoint observations of substorm pre-onset flows and time sequence in the ionosphere and magnetosphere Yong Shi, 1 Eftyhia
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017185, 2012 Multipoint observations of substorm pre-onset flows and time sequence in the ionosphere and magnetosphere Yong Shi, 1 Eftyhia
New rms-based planetary geomagnetic activity indices
 New rms-based planetary geomagnetic activity indices M. Menvielle 1,2, J.-J. Valette 3, Mathieu Pau 3, Ch. Lathuillère 4 1 CNRS/INSU, Université Versailles St-Quentin; LATMOS-IPSL, Guyancourt, France 2
New rms-based planetary geomagnetic activity indices M. Menvielle 1,2, J.-J. Valette 3, Mathieu Pau 3, Ch. Lathuillère 4 1 CNRS/INSU, Université Versailles St-Quentin; LATMOS-IPSL, Guyancourt, France 2
Magnetospherically-Generated Ionospheric Electric Fields
 Magnetospherically-Generated Ionospheric Electric Fields Stanislav Sazykin Rice University sazykin@rice.edu June 26, 2005 Sazykin--Ionospheric E-Fields--CEDAR Student Workshop 1 Overall Magnetospheric
Magnetospherically-Generated Ionospheric Electric Fields Stanislav Sazykin Rice University sazykin@rice.edu June 26, 2005 Sazykin--Ionospheric E-Fields--CEDAR Student Workshop 1 Overall Magnetospheric
Stormtime Dynamics of the Magnetosphere near Geosynchronous Altitudes
 Stormtime Dynamics of the Magnetosphere near Geosynchronous Altitudes William J. Burke 1, Meg A. Noah 2 and Jun Yang 2 4 November 214 1. Boston College/ISR 2. University of Massachusetts, Lowell Stormtime
Stormtime Dynamics of the Magnetosphere near Geosynchronous Altitudes William J. Burke 1, Meg A. Noah 2 and Jun Yang 2 4 November 214 1. Boston College/ISR 2. University of Massachusetts, Lowell Stormtime
On the importance of antiparallel reconnection when the dipole tilt and IMF B y are nonzero
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010972, 2006 On the importance of antiparallel reconnection when the dipole tilt and IMF B y are nonzero K. S. Park, 1 T. Ogino, 1 and R. J.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010972, 2006 On the importance of antiparallel reconnection when the dipole tilt and IMF B y are nonzero K. S. Park, 1 T. Ogino, 1 and R. J.
Morphology of the ring current derived from magnetic field observations
 Annales Geophysicae () : 67 95 SRef-ID: 3-576/ag/--67 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Morphology of the ring current derived from magnetic field observations G. Le, C. T. Russell, and K.
Annales Geophysicae () : 67 95 SRef-ID: 3-576/ag/--67 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Morphology of the ring current derived from magnetic field observations G. Le, C. T. Russell, and K.
