Chemo-dynamical disk modeling. Ivan Minchev Leibniz-Institut fur Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)
|
|
|
- Ronald McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemo-dynamical disk modeling Ivan Minchev Leibniz-Institut fur Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)
2 Talk outline Effect of disk asymmetries on disk dynamics. Radial migration in galactic disks. Chemo-dynamical disk modeling. Chemo-kinematic observational constraints.
3 Resonances in galactic disks Corotation resonance (CR) Inner and outer Lindblad resonances (ILR and OLR)
4 Resonances in galactic disks For a flat rotation curve Lindblad resonances are given by Corotation is at For a 2-armed spiral structure or a bar m=2. For a 4-armed spiral m=4. Inner and Outer Lindblad resonances
5 Stellar orbits near resonances m=4 at Near OLR OLR Near m=2 Corotation (CR) Single spiral wave Outside OLR+CR Inside OLR+CR 2 spiral waves
6 Radial migration
7 N-body Tree-SPH Disk expands due to strong angular momentum transport outwards (Minchev et al. 2012a). Formation of a pseudobulge Simulations by P. Di Matteo
8 Power spectrograms reveal multiple patterns Overlap of bar and spiral creates transient stellar mass clumps! Sa model Existence of multiple patterns in disks long known in simulations: Tagger et al. (1987) Signet et al. (1988) Quillen et al. (2011) Minchev et al. (2012a) and in observations: Elemegreen et al. (1992) Rix & Rieke (1993) Meidt et al. (2009) Minchev et al. (2012a) Interaction between the bar and the spiral when reconnecting
9 Power spectrograms reveal multiple patterns Time Quasi-steady spiral patterns of multiplicity 1-4 Minchev et al. (2012a)
10 Chemo-dynamical evolution modeling of the Milky Way
11 Classical chemical evolution modeling Classical chemical evolution models (Matteucci & Francois 1989; Prantzos & Aubert 1995; Chiappini et al. 1997, 2001). Stars assumed to die close to their birth places. 4 kpc 2 kpc 8 kpc 14 kpc 12 kpc
12 Classical chemical evolution modeling hampered by radial migration Stars move away from their birth places (Sellwood and Binney 2002). 4 kpc 2 kpc 8 kpc 14 kpc 12 kpc MCM13 model
13 Classical chemical evolution modeling hampered by radial migration Stars move away from their birth places (Sellwood and Binney 2002). 4 kpc 2 kpc 8 kpc 14 kpc 12 kpc mean MCM13 model
14 Classical chemical evolution modeling hampered by radial migration Stars move away from their birth places (Sellwood and Binney 2002). 4 kpc 2 kpc We need to recover the migration efficiency as a function of Galactic radius and time. 14 kpc mean 8 kpc 12 kpc t=6.7 Gyr Stellar density MCM13 model Bar resonances
15 Disk formation in cosmological simulations Traditionally a challenge (e.g., Navarro and Benz 1991; Abadi et al., 2003): Extreme angular momentum loss during mergers. Overly-concentrated mass distributions and massive bulges. Abadi et al. (2003)
16 Recent improvements Increase in resolution and better modeling of star formation and feedback produce MW-mass galaxies with reduced bulge fractions (e.g., Agertz et al. 2011; Guedes et al. 2011; Martig et al. 2012). However, no chemical treatment! Milky Way disk morphology not easily reproducible in fully cosmological simulations. Guedes et al. (2011)
17 Recent improvements in chemical enrichment Simulations including chemical treatment Raiteri et al. (1996), Mosconi et al. (2001), Lia et al. (2002), Kawata and Gibson (2003), Kobayashi (2004), Scannapieco et al. (2005), Martínez-Serrano et al. (2008), Oppenheimer and Davé (2008), Wiersma et al. (2009), Few et al. (2012) Encouraging results recently global observed trends reproduced: The mass-metallicity relation (e.g., Kobayashi et al. 2007) Metallicity trends between different galactic components (e.g., Tissera et al. 2012) However, still a challenge to reproduce the properties of the Milky Way, e.g., the typical metallicities of the different components Tissera et al. (2012).
18 Recent improvements in chemical enrichment Simulations including chemical treatment Raiteri et al. (1996), Mosconi et al. (2001), Lia et al. (2002), Kawata and Gibson (2003), Kobayashi (2004), Scannapieco et al. (2005), Martínez-Serrano et al. (2008), Oppenheimer and Davé (2008), Wiersma et al. (2009), Disk Few et al. (2012) Aquarius simulations Spheroid Inner halo Encouraging results recently global observed trends reproduced: Outer halo The mass-metallicity relation (e.g., Kobayashi et al. 2007) Metallicity trends between different galactic components (e.g., Tissera et al. 2012) However, still a challenge to reproduce the properties of the Milky Way, e.g., the typical metallicities of the different components Tissera et al. (2012). Tissera et al. (2012)
19 Seek an alternative approach to circumvent problems with fully self-consistent simulations Radial migration must be considered in the disk s chemical evolution (Sellwood and Binney 2002, Schonrich and Binnery 2009a,b). Use present day Milky Way disk morphology and kinematics as constraints
20 Ingredients A high-resolution simulation of a disk assembly in the cosmological context: Gas infall form filaments and gas-rich mergers Merger activity decreasing toward redshift zero Disk properties at redshift zero consistent with the dynamics and morphology of the Milky Way: The presence of a Milky Way-size bar A small bulge Bar s Outer Lindblad Resonance at ~2.5 disk scale-lengths A detailed chemical evolution model: Matching several observational constraints in the Milky Way.
21 Galactic disk assembly in the cosmological context Simulation in cosmological context Martig et al. (2009, 2012) Stars born hot at high redshift: Similar to Brook et al. (2012), Stinson et al. (2013), Bird et al. (2013) Simulations by M. Martig
22 Chemical model Constrained by: The solar and present day abundances of more than 30 elements The present SFR The current stellar, gas and total mass densities at the solar vicinity The present day supernovae rates of type II and Ia The metallicity distribution of G-dwarf stars Similar to Chiappini (2009) Only thin disk chemistry used!
23 Origin and metallicity distributions of local stars max z <3 kpc 7<r<9 kpc Minchev, Chiappini & Martig (2013) Older populations arrive from progressively smaller galactic radii due to their longer exposure to migration.
24 Origin and metallicity distributions of local stars kpc kpc
25 Increase of disk scale-length with age: A legacy of inside-out formation Simulations with strong merger activity at high redshift Bovy et al. (2012a) Radial migration cannot compete with inside-out formation. Martig et al. (2014a)
26 The metallicity distribution z < 40 pc z > 500 pc Adibekyan et al. (2012) 0.1< z kpc 7.9<r<8.1 kpc SEGUE, DR9, Brauer et al. (2014) 0.5< z <3 kpc 6<r<10 kpc MCM13 Model = 0 dex Shift For both model and observations the MDF peak shifts to lower [Fe/H] with distance from the disk plane
27 The [Fe/H]-[O/Fe] relation Kinematical selection of thin- and thick-disk populations Ramírez et al. (2013) Thick disk Thin disk
28 The [Fe/H]-[O/Fe] relation Kinematical selection of thin- and thick-disk populations Ramírez et al. (2013) Thick disk Thin disk Minchev et al Model Thick disk Thin disk
29 The age-[α/fe] relation Haywood et al. (2013) This model Mean model
30 The Rotational velocity - Metallicity relation Model Navarro et al. (2011) All Significant migration in model, yet flat relation for thin disk.
31 Scale-height distribution of mono-abundance subpopulations Bovy et al. (2012), SEGUE data Model data SEGUE G-dwarfs Bovy et al. (2012) kpc z <3 kpc 6<r<10 kpc Model disk Scale-heights
32 A new chemo-kinematic relation can recover the disk merger history
33 Vertical velocity dispersion as a fn of [Mg/Fe] in RAVE RAVE Giants, SN>65 7<r<9 kpc z <0.6 kpc 4755 stars Velocity dispersion drops at [Mg/Fe] > 0.4 dex Minchev + RAVE (2014)
34 Vertical velocity dispersion as a fn of [Mg/Fe] in RAVE Minchev + RAVE (2014) RAVE Giants, SN>65 7<r<9 kpc z <0.6 kpc 4755 stars Separate into [Fe/H] sub-populations [Fe/H] dex Velocity dispersion drops at the high-[mg/fe] end for each metallicity sub-population
35 Vertical velocity dispersion as a fn of [Mg/Fe] in RAVE Minchev + RAVE (2014) RAVE Giants, SN>65 7<r<9 kpc z <0.6 kpc 4755 stars Separate into [Fe/H] sub-populations [Fe/H] dex Velocity dispersion drops at the high-[mg/fe] end for each metallicity sub-population
36 Model 7<r<9 kpc 0.2< z <0.6 kpc Origin of stars currently in the solar neighborhood
37 Model 7<r<9 kpc 0.2< z <0.6 kpc Origin of stars currently in the solar neighborhood [Fe/H] dex
38 Model 7<r<9 kpc 0.2< z <0.6 kpc Origin of stars currently in the solar neighborhood [Fe/H] Model 7<r<9 kpc 0.2< z <0.6 kpc dex For a given metallicity bin, stars coming from the inner disc are kinematically colder and older.
39 Cool old stars arrive from inner disk during mergers Model 7<r<9 kpc, 0.2< z <0.6 kpc Gyr Old stars coming from the inner disk are cooler than locally born stars by up to 30 km/s. rfinal Slope becomes negative for the last several Gyr (no significant mergers). Explains inversion of vel. dispersion - [Mg/Fe] relation in RAVE and SEGUE G-dwarf data.
40 Cool old stars arrive from inner disk during mergers Model 7<r<9 kpc, 0.2< z <0.6 kpc Gyr Model Old stars 7<r<9 coming kpc from the inner disk are 0.2< z <0.6 cooler kpcthan locally born stars by up to 30 km/s. rfinal Slope becomes negative for the last several Gyr (no significant mergers). Explains inversion of vel. dispersion - [Mg/Fe] relation in RAVE and SEGUE G-dwarf data.
41 Summary Great improvements in chemo-dynamics in cosmological simulations, however, still hard to apply to Milky Way. Important for disk models to match the Milky Way morphology today. Our chemo-dynamical model explains everything. Great care taken in defining properly the solar neighborhood. More than 30 elements available for doing Galactic Archeology (e.g., GALAH, APOGEE, 4MOST, Gaia). Decline in velocity dispersion found in RAVE and SEGUE at [α/fe] 0.4 dex. Can be related to perturbations from satellite-disk interactions over the Galaxy lifetime. Extragalactic Archaeology will be made possible with the E-ELT!
42 Summary Great improvements in chemo-dynamics in cosmological simulations, however, still hard to apply to Milky Way. Important for disk models to match the Milky Way morphology today. Our chemo-dynamical model explains everything consistent with a wide range of observational constraints. Great care taken in defining properly the solar neighborhood. More than 30 elements available for doing Galactic Archeology (e.g., GALAH, APOGEE, 4MOST, Gaia). Decline in velocity dispersion found in RAVE and SEGUE at [α/fe] 0.4 dex. Can be related to perturbations from satellite-disk interactions over the Galaxy lifetime. Extragalactic Archaeology will be made possible with the E-ELT!
Galaxy simulations in the Gaia era. Ivan Minchev Leibniz-Institut fur Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)
 Galaxy simulations in the Gaia era Ivan Minchev Leibniz-Institut fur Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP) What we think our Galaxy looks like GCS data (Hipparcos satellite) - the only pre-gaia sample with good proper
Galaxy simulations in the Gaia era Ivan Minchev Leibniz-Institut fur Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP) What we think our Galaxy looks like GCS data (Hipparcos satellite) - the only pre-gaia sample with good proper
PATRICIA B. TISSERA. Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics Argentina
 PATRICIA B. TISSERA Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics Argentina i Observational motivations Model Results GALAXY FORMATION In the last years, studies of chemical elements obtained in the Local
PATRICIA B. TISSERA Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics Argentina i Observational motivations Model Results GALAXY FORMATION In the last years, studies of chemical elements obtained in the Local
Galaxy Evolution at High Resolution: The New View of the Milky Way's Disc. Jo Bovy (University of Toronto; Canada Research Chair)
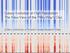 Galaxy Evolution at High Resolution: The New View of the Milky Way's Disc Jo Bovy (University of Toronto; Canada Research Chair) WHY THE MILKY WAY? WHY THE MILKY WAY? Detailed measurements of position,
Galaxy Evolution at High Resolution: The New View of the Milky Way's Disc Jo Bovy (University of Toronto; Canada Research Chair) WHY THE MILKY WAY? WHY THE MILKY WAY? Detailed measurements of position,
Distribution of Mass in the Milky Way Galaxy, Leiden, July Laura V. Sales. Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, Groningen, The Netherlands
 Distribution of Mass in the Milky Way Galaxy, Leiden, 13-17 July 2009 Laura V. Sales Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, Groningen, The Netherlands Outline - Brief review of thick disk formation scenarios:
Distribution of Mass in the Milky Way Galaxy, Leiden, 13-17 July 2009 Laura V. Sales Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, Groningen, The Netherlands Outline - Brief review of thick disk formation scenarios:
The Structure and Substructure of the Milky Way Galaxy Discs. Rosemary Wyse
 The Structure and Substructure of the Milky Way Galaxy Discs Rosemary Wyse Hiroshima, 30 th November 2016 The Fossil Record: Galactic Archaeology Studying low-mass old stars near-field cosmology There
The Structure and Substructure of the Milky Way Galaxy Discs Rosemary Wyse Hiroshima, 30 th November 2016 The Fossil Record: Galactic Archaeology Studying low-mass old stars near-field cosmology There
THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY DISK
 THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY DISK 1. The simple picture of disk evolution: independent ring evolution, successes and failures 2. The dynamical picture: stars (and gas) moving around 3. A model
THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY DISK 1. The simple picture of disk evolution: independent ring evolution, successes and failures 2. The dynamical picture: stars (and gas) moving around 3. A model
The role of radial migration in shaping the stellar populations of spiral galaxies
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 25, 64 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Supplementi The role of radial migration in shaping the stellar populations of spiral galaxies R. Roškar Insititute for Theoretical Physics, University
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 25, 64 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Supplementi The role of radial migration in shaping the stellar populations of spiral galaxies R. Roškar Insititute for Theoretical Physics, University
Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE
 IAU Symposium 330 Nice, 27. April 2017 Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE Wilma Trick (MPIA, Heidelberg) Hans-Walter Rix (MPIA) Jo Bovy (Uni Toronto) Open Questions
IAU Symposium 330 Nice, 27. April 2017 Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE Wilma Trick (MPIA, Heidelberg) Hans-Walter Rix (MPIA) Jo Bovy (Uni Toronto) Open Questions
Secular Evolution of Galaxies
 Secular Evolution of Galaxies Outline:!Disk size evolution! Bar fraction vs mass & color! AM transfers, radial migrations! Bulges, thick disks Françoise Combes Durham, 19 July 2011 Two modes to assemble
Secular Evolution of Galaxies Outline:!Disk size evolution! Bar fraction vs mass & color! AM transfers, radial migrations! Bulges, thick disks Françoise Combes Durham, 19 July 2011 Two modes to assemble
Following the evolution of the Galactic disc with Open Clusters
 Following the evolution of the Galactic disc with Open Clusters Laura Magrini INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri With Nikos Prantzos and the GES collaboration (in particular Lorenzo Spina, Sofia
Following the evolution of the Galactic disc with Open Clusters Laura Magrini INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri With Nikos Prantzos and the GES collaboration (in particular Lorenzo Spina, Sofia
The HERMES project. Reconstructing Galaxy Formation. Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU. The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012
 The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk
 Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk omas Bensby Lund Observatory, Department of Astronomy and eoretical Physics Discovery of thick disks (Burstein 1979, ApJ, 234, 829) Discovery of the Galactic
Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk omas Bensby Lund Observatory, Department of Astronomy and eoretical Physics Discovery of thick disks (Burstein 1979, ApJ, 234, 829) Discovery of the Galactic
Galactic archaeology with the RAdial Velocity Experiment
 Galactic archaeology with the RAdial Velocity Experiment Georges Kordopatis & RAVE collaboration Leibniz-Institute for Astrophysics, Potsdam Multi-Object Spectroscopy in the next decade: Big questions,
Galactic archaeology with the RAdial Velocity Experiment Georges Kordopatis & RAVE collaboration Leibniz-Institute for Astrophysics, Potsdam Multi-Object Spectroscopy in the next decade: Big questions,
Gaia ITNG2013 School, Tenerife. Ken Freeman, Lecture 2: the thin disk
 Gaia ITNG2013 School, Tenerife Ken Freeman, Lecture 2: the thin disk September 2013 The Thick Disk Thick disk Most spirals (including our Galaxy) have a second thicker disk component The thick disk and
Gaia ITNG2013 School, Tenerife Ken Freeman, Lecture 2: the thin disk September 2013 The Thick Disk Thick disk Most spirals (including our Galaxy) have a second thicker disk component The thick disk and
ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY. The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm
 ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm Halo abundance patterns and stellar yields Standard chemical evolution of solar
ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm Halo abundance patterns and stellar yields Standard chemical evolution of solar
DOES THE MILKY WAY HAVE AN ACCRETED DISK COMPONENT?
 DOES THE MILKY WAY HAVE AN ACCRETED DISK COMPONENT? Gregory Ruchti Lund Observatory!!!! in collaboration with: Justin Read, Sofia Feltzing, Thomas Bensby, Antonio Pipino ACCRETED STARS Our current cosmology
DOES THE MILKY WAY HAVE AN ACCRETED DISK COMPONENT? Gregory Ruchti Lund Observatory!!!! in collaboration with: Justin Read, Sofia Feltzing, Thomas Bensby, Antonio Pipino ACCRETED STARS Our current cosmology
The Thick Thin Disk and the Thin Thick Disk: a New Paradigm from Gaia
 The Thick Thin Disk and the Thin Thick Disk: a New Paradigm from Gaia Michael Hayden Alejandra Recio-Blanco, Patrick de Laverny, Sarunas Mikolaitis, Guillaume Guiglion, Anastasia Titarenko Observatoire
The Thick Thin Disk and the Thin Thick Disk: a New Paradigm from Gaia Michael Hayden Alejandra Recio-Blanco, Patrick de Laverny, Sarunas Mikolaitis, Guillaume Guiglion, Anastasia Titarenko Observatoire
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy
 Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
GALAXIES 626. The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution:
 GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
Chemical evolution of the Galactic disk using Open Clusters
 Chemical evolution of the Galactic disk using Open Clusters ICC Winter Meeting Feb 2017 1. Galactic Archaeology Unravel the formation and evolution of the Milky Way (MW) Resolved stars provide a fossil
Chemical evolution of the Galactic disk using Open Clusters ICC Winter Meeting Feb 2017 1. Galactic Archaeology Unravel the formation and evolution of the Milky Way (MW) Resolved stars provide a fossil
Cosmologia locale: origine e storia della Via Lattea
 Cosmologia locale: origine e storia della Via Lattea Mario G. Lattanzi (OATo) & Michele Bellazzini (OABo) Roma, 14 feb 2013 L Italia in Gaia, INAF Hq Collaborators Anna Curir Alessandro Spagna Francesca
Cosmologia locale: origine e storia della Via Lattea Mario G. Lattanzi (OATo) & Michele Bellazzini (OABo) Roma, 14 feb 2013 L Italia in Gaia, INAF Hq Collaborators Anna Curir Alessandro Spagna Francesca
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Radial migration of the Sun in the Milky Way: a statistical study
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu2094 Radial migration of the Sun in the Milky Way: a statistical study C. A. Martínez-Barbosa, A. G. A. Brown and S. Portegies Zwart Leiden Observatory, Leiden University, PO Box 9513
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu2094 Radial migration of the Sun in the Milky Way: a statistical study C. A. Martínez-Barbosa, A. G. A. Brown and S. Portegies Zwart Leiden Observatory, Leiden University, PO Box 9513
Correlations between stellar dynamics and metallicity in the discs
 Correlations between stellar dynamics and metallicity in the discs Semi-analytic chemodynamical model of the Milky Way Jan Rybizki (Supervisor: Andreas Just) Astronomisches Rechen-Institut - Zentrum für
Correlations between stellar dynamics and metallicity in the discs Semi-analytic chemodynamical model of the Milky Way Jan Rybizki (Supervisor: Andreas Just) Astronomisches Rechen-Institut - Zentrum für
The Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment. Ricardo Schiavon
 The Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment Ricardo Schiavon CS20, Boston, August 1st, 2018 Overview paper: Majewski, Schiavon et al. (2017) APOGEE at a Glance Dual hemisphere spectroscopic
The Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment Ricardo Schiavon CS20, Boston, August 1st, 2018 Overview paper: Majewski, Schiavon et al. (2017) APOGEE at a Glance Dual hemisphere spectroscopic
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
The structure and formation of the Milky Way disks
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 25, 11 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Supplementi The structure and formation of the Milky Way disks M. Haywood GEPI, Observatoire de Paris, CNRS, Université Paris Diderot, 5 place
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 25, 11 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Supplementi The structure and formation of the Milky Way disks M. Haywood GEPI, Observatoire de Paris, CNRS, Université Paris Diderot, 5 place
Exploring the structure and evolu4on of the Milky Way disk
 Exploring the structure and evolu4on of the Milky Way disk Results from the Gaia-ESO survey and plans for 4MOST Thomas Bensby Dept. of Astronomy and Theore3cal Physics Lund University Sweden Chemistry
Exploring the structure and evolu4on of the Milky Way disk Results from the Gaia-ESO survey and plans for 4MOST Thomas Bensby Dept. of Astronomy and Theore3cal Physics Lund University Sweden Chemistry
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 Jan 2018](/thumbs/74/70960060.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. gradient_across_spirals c ESO 2018 January 29, 2018 Stellar metallicity variations across spiral arms in disk galaxies with multiple populations S. Khoperskov 1,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. gradient_across_spirals c ESO 2018 January 29, 2018 Stellar metallicity variations across spiral arms in disk galaxies with multiple populations S. Khoperskov 1,
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars. Young Sun Lee
![Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars. Young Sun Lee Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars. Young Sun Lee](/thumbs/83/87302303.jpg) Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars Young Sun Lee Research Group Meeting on June 16, 2010 Outline Introduction Why [α/fe]? Determination of [α/fe] Validation of estimate of [α/fe]
Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars Young Sun Lee Research Group Meeting on June 16, 2010 Outline Introduction Why [α/fe]? Determination of [α/fe] Validation of estimate of [α/fe]
Epicycles the short form.
 Homework Set 3 Due Sept 9 CO 4.15 just part (a). (see CO pg. 908) CO 4.1 CO 4.36 (a),(b) CO 5.14 (assume that Sun currently has its max. u velocity.) CO 5.16 (Keplerian orbit = orbit around a point mass)
Homework Set 3 Due Sept 9 CO 4.15 just part (a). (see CO pg. 908) CO 4.1 CO 4.36 (a),(b) CO 5.14 (assume that Sun currently has its max. u velocity.) CO 5.16 (Keplerian orbit = orbit around a point mass)
Gaia-LSST Synergy. A. Vallenari. INAF, Padova
 Gaia-LSST Synergy A. Vallenari INAF, Padova The Galaxy view Unveiling the complex history of the MW assembly and internal evolution is still one of the main interest of astrophysics However the specific
Gaia-LSST Synergy A. Vallenari INAF, Padova The Galaxy view Unveiling the complex history of the MW assembly and internal evolution is still one of the main interest of astrophysics However the specific
Small Scale Structure in the Galaxy. Alice Quillen (University of Rochester)
 Small Scale Structure in the Galaxy Alice Quillen (University of Rochester) Morphology of the Milky Way Distances uncertain. Projection is difficult. Cartoons favor 2 or 4 armed symmetrical structures
Small Scale Structure in the Galaxy Alice Quillen (University of Rochester) Morphology of the Milky Way Distances uncertain. Projection is difficult. Cartoons favor 2 or 4 armed symmetrical structures
The chemical evolution of the Milky Way
 The chemical evolution of the Milky Way Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Trieste E-mail: matteucci@oats.inaf.it Emanuele Spitoni Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Trieste E-mail: spitoni@oats.inaf.it
The chemical evolution of the Milky Way Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Trieste E-mail: matteucci@oats.inaf.it Emanuele Spitoni Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Trieste E-mail: spitoni@oats.inaf.it
Constraints on secular evolution in unbarred spiral galaxies: understanding bulge and disk formation
 Constraints on secular evolution in unbarred spiral galaxies: understanding bulge and disk formation July 10 th 2012 Marja Kristin Seidel Jesús Falcón - Barroso Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias www.iac.es/project/traces
Constraints on secular evolution in unbarred spiral galaxies: understanding bulge and disk formation July 10 th 2012 Marja Kristin Seidel Jesús Falcón - Barroso Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias www.iac.es/project/traces
Galactic Bulge Science
 Galactic Bulge Science Ken Freeman Australian National University ngcfht meeting Hilo, Mar 27-29 2013 NGC 5746 1 The Galactic bulge was long thought to be a merger product. We now know that boxy bulges
Galactic Bulge Science Ken Freeman Australian National University ngcfht meeting Hilo, Mar 27-29 2013 NGC 5746 1 The Galactic bulge was long thought to be a merger product. We now know that boxy bulges
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history
 Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Chemo-Dynamical evolution of dwarf spheroidal galaxies
 11 th Russbach School on Nuclear Astrophysics Chemo-Dynamical evolution of dwarf spheroidal galaxies Yutaka Hirai! (The University of Tokyo, NAOJ)! Jun Hidaka (NAOJ), Takayuki R. Saitoh (Titech),! Michiko
11 th Russbach School on Nuclear Astrophysics Chemo-Dynamical evolution of dwarf spheroidal galaxies Yutaka Hirai! (The University of Tokyo, NAOJ)! Jun Hidaka (NAOJ), Takayuki R. Saitoh (Titech),! Michiko
THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS. B. Barbuy
 THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS B. Barbuy IAG - Universidade de São Paulo Outline: Interest of studies on Galactic bulge and globulars Data available on metallicity,, kinematics in field
THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS B. Barbuy IAG - Universidade de São Paulo Outline: Interest of studies on Galactic bulge and globulars Data available on metallicity,, kinematics in field
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Constraining the Milky Way assembly history with Galactic Archaeology
 Astronomische Nachrichten, 17 October 2018 Constraining the Milky Way assembly history with Galactic Archaeology Ludwig Biermann Award Lecture 2015 I. Minchev arxiv:1701.07034v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2017
Astronomische Nachrichten, 17 October 2018 Constraining the Milky Way assembly history with Galactic Archaeology Ludwig Biermann Award Lecture 2015 I. Minchev arxiv:1701.07034v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2017
Tristan Cantat-Gaudin
 Open Clusters in the Milky Way with Gaia ICCUB Winter Meeting 1-2 Feb 2018, Barcelona Tristan Cantat-Gaudin Carme Jordi, Antonella Vallenari, Laia Casamiquela, and Gaia people in Barcelona and around the
Open Clusters in the Milky Way with Gaia ICCUB Winter Meeting 1-2 Feb 2018, Barcelona Tristan Cantat-Gaudin Carme Jordi, Antonella Vallenari, Laia Casamiquela, and Gaia people in Barcelona and around the
Low-velocity streams in the solar neighbourhood caused by the Galactic bar
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 407, 2122 2130 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17060.x Low-velocity streams in the solar neighbourhood caused by the Galactic bar I. Minchev, C. Boily, A. Siebert and O. Bienayme
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 407, 2122 2130 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17060.x Low-velocity streams in the solar neighbourhood caused by the Galactic bar I. Minchev, C. Boily, A. Siebert and O. Bienayme
The Gaia-ESO Spectroscopic Survey. Survey Co-PIs. Gerry Gilmore (IoA, Cambridge) & Sofia Randich (INAF/Arcetri) >300 CoIs
 The Gaia-ESO Spectroscopic Survey Survey Co-PIs Gerry Gilmore (IoA, Cambridge) & Sofia Randich (INAF/Arcetri) >300 CoIs Gaia-ESO survey context and motivations (conclusions and key words of several talks)
The Gaia-ESO Spectroscopic Survey Survey Co-PIs Gerry Gilmore (IoA, Cambridge) & Sofia Randich (INAF/Arcetri) >300 CoIs Gaia-ESO survey context and motivations (conclusions and key words of several talks)
Migration and kinematics in growing disc galaxies with thin and thick discs
 MNRAS, 1 22 (217) Preprint 12 November 217 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3. Migration and kinematics in growing disc galaxies with thin and thick discs Michael Aumer, James Binney and Ralph Schönrich
MNRAS, 1 22 (217) Preprint 12 November 217 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3. Migration and kinematics in growing disc galaxies with thin and thick discs Michael Aumer, James Binney and Ralph Schönrich
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
Spiral Structure. m ( Ω Ω gp ) = n κ. Closed orbits in non-inertial frames can explain the spiral pattern
 Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Modelling the Milky Way: challenges in scientific computing and data analysis. Matthias Steinmetz
 Modelling the Milky Way: challenges in scientific computing and data analysis Matthias Steinmetz Can we form disk galaxies? 3 Not really Formation of disks has been notoriously difficult Feedback? Resolution?
Modelling the Milky Way: challenges in scientific computing and data analysis Matthias Steinmetz Can we form disk galaxies? 3 Not really Formation of disks has been notoriously difficult Feedback? Resolution?
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jun 2010
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jun 2010 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jun 2010](/thumbs/86/94897285.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 31 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) An observer s view of simulated galaxies: disc-to-total ratios, bars, and (pseudo-)bulges arxiv:1001.4890v3
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 31 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) An observer s view of simulated galaxies: disc-to-total ratios, bars, and (pseudo-)bulges arxiv:1001.4890v3
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8
 The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context
 IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al
IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al
The Milky Way in the cosmological context. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago
 The Milky Way in the cosmological context Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Milky Way and Its Stars, KITP, 2 February 2015 Cosmological context: hierarchical structure formation from a Gaussian
The Milky Way in the cosmological context Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Milky Way and Its Stars, KITP, 2 February 2015 Cosmological context: hierarchical structure formation from a Gaussian
Renegades in the Solar neighborhood
 Title Renegades in the Solar neighborhood Ana Bonaca ITC Fellow Harvard University // Charlie Conroy // // Andrew Wetzel // Origin of the halo stars: In situ Eggen, Lynden-Bell & Sandage (1962) Accretion
Title Renegades in the Solar neighborhood Ana Bonaca ITC Fellow Harvard University // Charlie Conroy // // Andrew Wetzel // Origin of the halo stars: In situ Eggen, Lynden-Bell & Sandage (1962) Accretion
Coordinate Systems! The geometry of the stream requires an oblate near-spherical halo!
 Milky Way Galaxy (blue/ white points and orange bulge) with the Sun (yellow sphere), inner and outer Sgr stream models (yellow/red points respectively), Monoceros tidal stream model(violet points), and
Milky Way Galaxy (blue/ white points and orange bulge) with the Sun (yellow sphere), inner and outer Sgr stream models (yellow/red points respectively), Monoceros tidal stream model(violet points), and
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
WEAVE Galactic Surveys
 WEAVE Galactic Surveys A. Vallenari INAF, Padova On behalf of the Science Team Overview WEAVE Surveys Milky Way Surveys WEAVE Characteristics Project structure Primary Science Surveys There are six primary
WEAVE Galactic Surveys A. Vallenari INAF, Padova On behalf of the Science Team Overview WEAVE Surveys Milky Way Surveys WEAVE Characteristics Project structure Primary Science Surveys There are six primary
Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg, Germany. The evolution history of the extended solar neighbourhood
 Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg, Germany The evolution history of the extended solar neighbourhood Andreas Just Kseniia Sysoliatina, Ioanna Koutsouridou Content Dynamical disc model Local model
Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg, Germany The evolution history of the extended solar neighbourhood Andreas Just Kseniia Sysoliatina, Ioanna Koutsouridou Content Dynamical disc model Local model
Impacts of a flaring star-forming disc and stellar radial mixing on the vertical metallicity gradient
 Advance Access publication 2016 September 16 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2363 Impacts of a flaring star-forming disc and stellar radial mixing on the vertical metallicity gradient Daisuke Kawata, 1 Robert J.
Advance Access publication 2016 September 16 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2363 Impacts of a flaring star-forming disc and stellar radial mixing on the vertical metallicity gradient Daisuke Kawata, 1 Robert J.
Evolution of galactic discs: multiple patterns, radial migration and disc outskirts
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa September 21, 2012 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Evolution of galactic discs: multiple patterns, radial migration and disc outskirts I. Minchev 1, B.
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa September 21, 2012 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Evolution of galactic discs: multiple patterns, radial migration and disc outskirts I. Minchev 1, B.
Lecture 28: Spiral Galaxies Readings: Section 25-4, 25-5, and 26-3
 Lecture 28: Spiral Galaxies Readings: Section 25-4, 25-5, and 26-3 Key Ideas: Disk & Spheroid Components Old Stars in Spheroid Old & Young Stars in Disk Rotation of the Disk: Differential Rotation Pattern
Lecture 28: Spiral Galaxies Readings: Section 25-4, 25-5, and 26-3 Key Ideas: Disk & Spheroid Components Old Stars in Spheroid Old & Young Stars in Disk Rotation of the Disk: Differential Rotation Pattern
1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions
 26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
Probing the history of star formation in the Local Group using the galactic fossil record
 Probing the history of star formation in the Local Group using the galactic fossil record Brian O Shea (Michigan State University) Collaborators: Tim Beers, Carolyn Peruta, Monica Derris (MSU), Jason Tumlinson
Probing the history of star formation in the Local Group using the galactic fossil record Brian O Shea (Michigan State University) Collaborators: Tim Beers, Carolyn Peruta, Monica Derris (MSU), Jason Tumlinson
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Gaia DR2 and/versus RAVE DR5: application for the semi-analytic thin disk model
 Gaia DR2 and/versus RAVE DR5: application for the semi-analytic thin disk model Speaker: Supervisor: Kseniia Sysoliatina (ARI) Prof. Dr. Andreas Just Gaia DR2 workshop Heidelberg, Outline (1) Comparison
Gaia DR2 and/versus RAVE DR5: application for the semi-analytic thin disk model Speaker: Supervisor: Kseniia Sysoliatina (ARI) Prof. Dr. Andreas Just Gaia DR2 workshop Heidelberg, Outline (1) Comparison
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
stelle e galassie primordiali
 stelle e galassie primordiali Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma Matteo de Bennassuti, PhD INAF/OAR Stefania Marassi, Pdoc INAF/OAR Luca Graziani, Pdoc INAF/OAR Rosa Valiante, Pdoc
stelle e galassie primordiali Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma Matteo de Bennassuti, PhD INAF/OAR Stefania Marassi, Pdoc INAF/OAR Luca Graziani, Pdoc INAF/OAR Rosa Valiante, Pdoc
r-process enrichment traced by Pu and Ba near the sun and in the Draco
 r-process enrichment traced by Pu and Ba near the sun and in the Draco Takuji Tsujimoto (Nat. Aston. Obs. Jap.) capturing electromagnetic waves earth archives stellar spectra meteorites deep-sea crusts
r-process enrichment traced by Pu and Ba near the sun and in the Draco Takuji Tsujimoto (Nat. Aston. Obs. Jap.) capturing electromagnetic waves earth archives stellar spectra meteorites deep-sea crusts
Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia
 Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Chengqun Yang Contents 1 Stellar Halo
Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Chengqun Yang Contents 1 Stellar Halo
Basics of Galactic chemical evolution
 Basics of Galactic chemical evolution The chemical abundances of stars provide important clues as to the evolutionary history of a galaxy. Astronomers usually refer to chemical elements other than hydrogen
Basics of Galactic chemical evolution The chemical abundances of stars provide important clues as to the evolutionary history of a galaxy. Astronomers usually refer to chemical elements other than hydrogen
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Barred Galaxies. Morphology Gas in barred galaxies Dynamics: pattern speed Theory: secular evolution, resonances
 Barred Galaxies Morphology Gas in barred galaxies Dynamics: pattern speed Theory: secular evolution, resonances NGC1300: SB(s) fig.6 NGC1512: SB(r) fig.3 NGC2523: SB(r) fig.2 Dust lanes NGC 1300 Star formation
Barred Galaxies Morphology Gas in barred galaxies Dynamics: pattern speed Theory: secular evolution, resonances NGC1300: SB(s) fig.6 NGC1512: SB(r) fig.3 NGC2523: SB(r) fig.2 Dust lanes NGC 1300 Star formation
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
Overview of Dynamical Modeling. Glenn van de Ven
 Overview of Dynamical Modeling Glenn van de Ven glenn@mpia.de 1 Why dynamical modeling? -- mass total mass stellar systems key is to their evolution compare luminous mass: constrain DM and/or IMF DM radial
Overview of Dynamical Modeling Glenn van de Ven glenn@mpia.de 1 Why dynamical modeling? -- mass total mass stellar systems key is to their evolution compare luminous mass: constrain DM and/or IMF DM radial
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Evolution of galactic discs: multiple patterns, radial migration, and disc outskirts
 A&A 548, A126 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219198 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics Evolution of galactic discs: multiple patterns, radial migration, and disc outskirts I. Minchev 1, B. Famaey 2,3,
A&A 548, A126 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219198 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics Evolution of galactic discs: multiple patterns, radial migration, and disc outskirts I. Minchev 1, B. Famaey 2,3,
Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback. Romain Teyssier
 Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback Romain Teyssier KITP 2011: Monster Inc. Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Feedback and galaxy formation - The role of AGN feedback in Milky Way halos
Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback Romain Teyssier KITP 2011: Monster Inc. Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Feedback and galaxy formation - The role of AGN feedback in Milky Way halos
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
PE#4: It contains some useful diagrams and formula which we ll use today
 Sep 6, 2017 Overview of the MW PE#4: It contains some useful diagrams and formula which we ll use today HW#2 is due next Wed and is now posted. Don t wait for the last minute to start it. Includes a short
Sep 6, 2017 Overview of the MW PE#4: It contains some useful diagrams and formula which we ll use today HW#2 is due next Wed and is now posted. Don t wait for the last minute to start it. Includes a short
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
(Present and) Future Surveys for Metal-Poor Stars
 (Present and) Future Surveys for Metal-Poor Stars Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics SDSS 1 Why the Fascination
(Present and) Future Surveys for Metal-Poor Stars Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics SDSS 1 Why the Fascination
Search for streams in thick disk and halo of the Milky Way
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Search for streams in thick disk and halo of the Milky Way To cite this article: Dian Puspita Triani and M Ikbal Arifyanto 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Search for streams in thick disk and halo of the Milky Way To cite this article: Dian Puspita Triani and M Ikbal Arifyanto 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 27 May 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 27 May 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 27 May 2015](/thumbs/86/94706484.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Paper Kubryk c ESO 2018 March 7, 2018 Evolution of the Milky Way with radial motions of stars and gas I. The solar neighbourhood and the thin and thick disks M.
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Paper Kubryk c ESO 2018 March 7, 2018 Evolution of the Milky Way with radial motions of stars and gas I. The solar neighbourhood and the thin and thick disks M.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Nov 1999
 Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
How Massive is the Milky Way?
 How Massive is the Milky Way? See also: Klypin et al. (2002) Simon s talk Matthias Steinmetz Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Overview Spectroscopic Surveys of the MW Geneva-Copenhagen, SDSS, RAVE Mass
How Massive is the Milky Way? See also: Klypin et al. (2002) Simon s talk Matthias Steinmetz Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Overview Spectroscopic Surveys of the MW Geneva-Copenhagen, SDSS, RAVE Mass
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
Overview of Gaia-ESO Survey results based on high-resolution spectra of FGK-type stars Rodolfo Smiljanic! (Gaia-ESO WG11 co-coordinator)
 Overview of Gaia-ESO Survey results based on high-resolution spectra of FGK-type stars Rodolfo Smiljanic! (Gaia-ESO WG11 co-coordinator) The Gaia-ESO Survey http://www.gaia-eso.eu Public spectroscopic
Overview of Gaia-ESO Survey results based on high-resolution spectra of FGK-type stars Rodolfo Smiljanic! (Gaia-ESO WG11 co-coordinator) The Gaia-ESO Survey http://www.gaia-eso.eu Public spectroscopic
Is the Milky Way ringing? The hunt for high-velocity streams
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 396, L56 L60 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00661.x Is the Milky Way ringing? The hunt for high-velocity streams I. Minchev, 1 A. C. Quillen, 2 M. Williams, 3,4 K. C. Freeman,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 396, L56 L60 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00661.x Is the Milky Way ringing? The hunt for high-velocity streams I. Minchev, 1 A. C. Quillen, 2 M. Williams, 3,4 K. C. Freeman,
Galaxies. With a touch of cosmology
 Galaxies With a touch of cosmology Types of Galaxies Spiral Elliptical Irregular Spiral Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Disk component where the spiral arms are Interstellar medium Star formation Spheroidal
Galaxies With a touch of cosmology Types of Galaxies Spiral Elliptical Irregular Spiral Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Disk component where the spiral arms are Interstellar medium Star formation Spheroidal
Age and abundance structure of the central sub-kpc of the Milky Way
 Age and abundance structure of the central sub-kpc of the Milky Way Thomas Bensby Department of Astronomy and THeoretical Physics Sweden MBD collaboration (Microlensed Bulge Dwarf) Sofia Feltzing Thomas
Age and abundance structure of the central sub-kpc of the Milky Way Thomas Bensby Department of Astronomy and THeoretical Physics Sweden MBD collaboration (Microlensed Bulge Dwarf) Sofia Feltzing Thomas
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Jun 2017](/thumbs/72/67479888.jpg) The Impact of Stellar Migration on disk Outskirts Victor P. Debattista, Rok Roškar, Sarah R. Loebman arxiv:1706.01996v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Jun 2017 Abstract Stellar migration, whether due to trapping by transient
The Impact of Stellar Migration on disk Outskirts Victor P. Debattista, Rok Roškar, Sarah R. Loebman arxiv:1706.01996v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Jun 2017 Abstract Stellar migration, whether due to trapping by transient
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2018](/thumbs/92/110840737.jpg) Local Stellar Kinematics from RAVE data VIII. Effects of the Galactic Disc Perturbations on Stellar Orbits of Red Clump Stars arxiv:1801.02170v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2018 Ö. Önal Taş 1 S. Bilir 1 O. Plevne
Local Stellar Kinematics from RAVE data VIII. Effects of the Galactic Disc Perturbations on Stellar Orbits of Red Clump Stars arxiv:1801.02170v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2018 Ö. Önal Taş 1 S. Bilir 1 O. Plevne
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
Matthias Steinmetz. 16 Oct 2012 Science from the Next Generation Imaging and Spectroscopic Surveys 1
 Matthias Steinmetz 16 Oct 2012 Science from the Next Generation Imaging and Spectroscopic Surveys 1 The RAVE Survey Spectroscopic high latitude survey of the MW 9 < I < 13 GAIA spectral range and resolution
Matthias Steinmetz 16 Oct 2012 Science from the Next Generation Imaging and Spectroscopic Surveys 1 The RAVE Survey Spectroscopic high latitude survey of the MW 9 < I < 13 GAIA spectral range and resolution
Myung Gyoon Lee. With Ho Seong Hwang (CfA) and Hong Soo Park (NAOJ) (Dept of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University)
 Myung Gyoon Lee (Dept of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University) With Ho Seong Hwang (CfA) and Hong Soo Park (NAOJ) 2013. 10. 22 Dynamics of Disk Galaxies, The 7 th Korean Astrophysics Workshop,
Myung Gyoon Lee (Dept of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University) With Ho Seong Hwang (CfA) and Hong Soo Park (NAOJ) 2013. 10. 22 Dynamics of Disk Galaxies, The 7 th Korean Astrophysics Workshop,
