The Brown Dwarf - Exoplanet Connection
|
|
|
- Rodney Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Brown Dwarf - Exoplanet Connection Adam J. Burgasser 1/ 2 ( MIT> + UCSD>)
2 what is a brown dwarf? Sun Brown dwarf Jupiter Low-mass objects with properties intermediate between stars and planets. Failed stars - form like stars, found as isolated systems, can host their own planetary systems Super-Jupiters - do not fuse hydrogen, sizes comparable to Jupiter, planetary atmospheres
3 Effective Temperature (K) no fusion of any element Planemos Brown Dwarfs Stars sustained H-burning M (Z dependent) insufficient H-burning models from Burrows et al. (2001) Time (Gyr)
4 spectral types M dwarfs ( K) magnetically active, only the youngest brown dwarfs are classified M-type L dwarfs ( K) molecule-rich atmospheres contain clouds of hot dirt and other condensates T dwarfs ( ? K) coldest known brown dwarfs, atmospheres contain CH 4 and NH 3 gases
5 Brown dwarf & Planetary Spectra M dwarf L dwarf T dwarf Jupiter T eff 3000 K 1700 K 700 K 125 K Marley & Leggett (2008) data from Cushing et al. (2005,2007)
6 Overview Similarites between brown dwarf and exoplanet atmospheres Differences between brown dwarf and exoplanet atmospheres Focus on condensate cloud formation/ evolution
7 Similarities Compact radii (R BD ~ R jup for t > 100 Myr) Cool atmospheres (T eff ~ K) Similar (but not identical) surface gravities
8 Chabrier et al. (2008) models by Baraffe et al. (2003)
9 Similarities Compact radii (R BD ~ R jup for t > 100 Myr) Cool atmospheres (T eff ~ K) Similar (but not identical) surface gravities
10 Hot Exoplanets GJ 436b T eq (A = 0.3) 2000 K 1750 K 1550 K 1400 K 1250 K 1100 K 1000 K 950 K 850 K 750 K Cool Brown Dwarfs L dwarfs K T dwarfs 600?-1300 K Fortney et al. (2008) 575 K ULAS 1335 (Burningham 2009 Adam et J. Burgasser al. 2008)
11 Cold Brown Dwarfs 2MASS T eff = 600 K, L = 10-6 L sun brown dwarf binary (Burgasser et al. 2008)
12 Similarities Compact radii (R BD ~ R jup for t > 100 Myr) Cool atmospheres (T eff ~ K) Similar (but not identical) surface gravities
13 2500 Equilibrium chemical planets 1 Myr transitions at 1 bar (Lodders & Fegley 2006) OGLE-TR-56b 13 M Jup brown dwarfs 75 M Jup M9 L0 Equilibrium/Effective Temperature (K) VO(g)/V(s) TiO(g)/Ti-x(s) Li(g)/LiCl(s) CO/CH 4 K(g)/KCl(s) N 2 /NH 3 1 M Jup OGLE-TR-132b GJ 436b Beta Pic b HR 8799c/d HR 8799b AB Pic B 2M1207B HAT-P-2b CoRoT-Exo-3b ULAS Gyr Gl 618.1B Gl 584C Gl 570D L5 T0 T5 T8 Approximate Brown Dwarf Spectral Type Scale 500 Form b Y? H 2 O(g)/H 2 O(s) Evolutionary models from Burrows et al. (1997, 2001) Log Surface Gravity (cgs) Burgasser 2009 Adam et al. J. (2009) Burgasser
14 Differences Metallicities: [M/H] ~ (BDs) vs. [M/H] ~ (JSUN) No external drivers for brown dwarf atmospheres wind, jets & inversions? Rotation rates: Jup: 11 hr, BD: ~4 hr: influences magnetic activity, surface winds
15 1.5 L0 1.0 M0 M1 M2M3 M4 M5 M6 M7 M8 M9 0.5 LSR MASS J-K s SSSPM J SDSS J MASS J MASS J GAIA Cond-Phoenix models log g = i -J Burgasser et al. (2009) see also Scholz et al. (2004,2008); Lepine et al. (2003,2005,2007)
16 Differences Metallicities: [M/H] ~ (BDs) vs. [M/H] ~ (JSUN) No external drivers for brown dwarf atmospheres winds, jets & inversions? Rotation rates: Jup: 11 hr, BD: ~4 hr: influences magnetic activity, surface winds
17 Ups And b Harrington et al. (2006) HD189733b Knutson et al. (2007) Harrington et al. (2006); Cowan et al. (2007); Knutson et al. (2007,2009)
18 Thermal inversions in exoplanet spectra Burrows et al. (2007); Fortney et al. (2008) also Deming et al. (2005); Richardson et al. (2007); Knutson et al. (2008)
19 exoplanets with & without stratospheres Fortney et al. (2008)
20 Differences Metallicities: [M/H] ~ (BDs) vs. [M/H] ~ (JSUN) No external drivers for brown dwarf atmospheres winds, jets & inversions? Rotation rates: Jup: 11 hr, BD: ~4 hr: influences magnetic activity, surface winds
21 Brown Dwarfs are Dizzy 80 km/s max (P<1.5 hr) 30 km/s typical (P<4 hr) 10 km/s floor (P<12 hr) (similar to Jupiter) 3 km/s (P~3d) Hot EPs Reiners & Basri (2008) see also Mohanty et al. (2002), Mohanty & Basri (2003), Bailer- Jones (2004); Reiners & Basri (2006), Blake et al. (2007)
22 Detailed Physics Revealed in Brown Dwarf Atmospheres Warm (high J) molecular opacities Heavily pressure-broadened line profiles Condensate grain and cloud formation Vertical mixing and non-equilibrium chemistry
23 Detailed Physics Revealed in Brown Dwarf Atmospheres Warm (high J) molecular opacities Heavily pressure-broadened line profiles Condensate grain and cloud formation Vertical mixing and non-equilibrium chemistry
24 Condensation in BD Atmospheres At the atmospheric temperatures and pressures of late-m and L dwarfs, several gaseous species form condensates. Marley et al. (2002) e.g.: TiO TiO 2 (s), CaTiO 3 (s) VO VO(s) Fe Fe(l) SiO SiO 2 (s), MgSiO 3 (s)
25 Lodders & Fegley (2006)
26 Condensation Disappearance of TiO & VO bands signals transition between M and L spectral classes. Removal of opacity strengthens other features, notably alkalis Kirkpatrick et al. (1999)
27 L dwarfs Cloudy model Cloud-free model T dwarfs Chabrier et al. (2000) See also Ackerman & Marley (2001); Allard et al. (2001); Cooper et al. (2003); Helling et al. (2008)
28 Direct detection of condensates Excess absorption at 8-11 µm is coincident with silicate features, grain sizes < 1 µm. Cushing et al. (2006) see also Burgasser et al. (2007); Helling et al. (2007); Looper et al. (2008)
29 Clouds in L Dwarfs ~L7 ~T7 ~Y? photosphere Ackerman & Marley (2001) see also Allard et al. (2001); Cooper et al. (2003); Helling et al. (2008)
30 Cloud Variations Burgasser et al. (2008) see also McLean et al. (2003); Knapp et al. (2004); Cruz et al. (2007); Cushing et al. (2008)
31 the good the ugly Δm ~ 0.01 mag Temporal variations? While there are clear indications of periodic variability in a few sources, they are weak and often aperiodic. Clarke et al. (2002); Goldman et al. (2008) See also Bailer-Jones & Mundt (1999, 2001); Bailer- Jones (2002, 2008); Bailer-Jones et al. (2003); Gelino et al. (2002); Enoch et al. (2003); Koen (2003,2004, 2005, 2006, 2008); Caballero et al. (2004); Morales- Calderon et al. (2006)
32 L dwarfs Cloudy model Cloud-free model T dwarfs Cloud depletion Chabrier et al. (2000) See also Ackerman & Marley (2001); Allard et al. (2001); Cooper et al. (2003); Helling et al. (2008)
33 M J L/T transition J-band bump J-K Burrows et al. (2006) s color See also Dahn et al. (1999); Ackerman & Marley (2001); Marley et al. (2002); Tinney et al. (2003); Tsuji (2003,2005); Saumon & Marley (2008)
34 Flux-reversal binaries Liu et al. (2006); Burgasser et al. (2006) See also Gizis et al. (2003); Cruz et al. (2004); Burgasser (2007,2008); Looper et al. (2008)
35 What Drives Cloud Loss? 5 µm Sudden change in sedimentation efficiency? Break-up of clouds? (cf. Jupiter) Compression of clouds? Transition T eff varies with log g, [M/H], other Several warm EPs have L/T transition T eff s
36 Rhines Length = R (U/2V eq cos ) 1/ R Scale at which east-west rotation causes elongation of turbulence; banding scale Rossby Deformation Radius = NH/2 sin 0.1 R Scale over which pressure perturbations are tempered by Coriolis forces: vortex scale Jupiter, Saturn << 1; Hot Jupiters 1 brown dwarfs probably have global structures
37 Summary Brown dwarfs & exoplanets share physical properties, but differ in fundamental ways care must be taken in drawing analogies Condensate clouds are prominent in brown dwarf & exoplanet atmospheres, dynamical (mixing) effects must be considered for both evolution & structure
Cloud Formation & Dynamics in Cool Stellar & Planetary Atmospheres
 + Cloud Formation & Dynamics in Cool Stellar & Planetary Atmospheres Adam J. Burgasser UC San Diego/MIT + Clouds are a universal characteristic of low temperature stars/brown dwarfs (particularly L dwarfs),
+ Cloud Formation & Dynamics in Cool Stellar & Planetary Atmospheres Adam J. Burgasser UC San Diego/MIT + Clouds are a universal characteristic of low temperature stars/brown dwarfs (particularly L dwarfs),
Brown dwarfs and hot young planets
 Brown dwarfs and hot young planets D. Saumon Los Alamos National Laboratory Images: Cassini; Marois et al. (2008) 2009 Sagan Exoplanet Summer Workshop, 21 July 2009 LA-UR-09-04365 Brown dwarfs and hot
Brown dwarfs and hot young planets D. Saumon Los Alamos National Laboratory Images: Cassini; Marois et al. (2008) 2009 Sagan Exoplanet Summer Workshop, 21 July 2009 LA-UR-09-04365 Brown dwarfs and hot
Atmosphere Models. Mark Marley, Didier Saumon, Jonathan Fortney, Richard Freedman, Katharina Lodders
 Atmosphere Models Mark Marley, Didier Saumon, Jonathan Fortney, Richard Freedman, Katharina Lodders 1 Today Brief atmosphere review Correctly deriving companion properties Some new cloud results: holes
Atmosphere Models Mark Marley, Didier Saumon, Jonathan Fortney, Richard Freedman, Katharina Lodders 1 Today Brief atmosphere review Correctly deriving companion properties Some new cloud results: holes
The atmosphere of Exoplanets AND Their evolutionary properties. I. Baraffe
 The atmosphere of Exoplanets AND Their evolutionary properties I. Baraffe I) Properties of cool atmospheres: 1) Atmospheric chemistry 2) Main opacity sources 3) Non solar composition 4) Non equilibrium
The atmosphere of Exoplanets AND Their evolutionary properties I. Baraffe I) Properties of cool atmospheres: 1) Atmospheric chemistry 2) Main opacity sources 3) Non solar composition 4) Non equilibrium
Substellar Atmospheres II. Dust, Clouds, Meteorology. PHY 688, Lecture 19 Mar 11, 2009
 Substellar Atmospheres II. Dust, Clouds, Meteorology PHY 688, Lecture 19 Mar 11, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture substellar atmospheres: opacity, LTE, chemical species, metallicity Dust, Clouds,
Substellar Atmospheres II. Dust, Clouds, Meteorology PHY 688, Lecture 19 Mar 11, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture substellar atmospheres: opacity, LTE, chemical species, metallicity Dust, Clouds,
Cloud Formation and Dynamics in Cool Dwarf and Hot Exoplanetary Atmospheres
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Cloud Formation and Dynamics in Cool Dwarf and Hot Exoplanetary Atmospheres Adam J. Burgasser 1,2 1 Center of Astrophysics and Space Sciences, Department
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Cloud Formation and Dynamics in Cool Dwarf and Hot Exoplanetary Atmospheres Adam J. Burgasser 1,2 1 Center of Astrophysics and Space Sciences, Department
Substellar Atmospheres. PHY 688, Lecture 18 Mar 9, 2009
 Substellar Atmospheres PHY 688, Lecture 18 Mar 9, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture the Kepler mission launched successfully results P < 1 month planets by September 09 giant planet interiors comparison
Substellar Atmospheres PHY 688, Lecture 18 Mar 9, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture the Kepler mission launched successfully results P < 1 month planets by September 09 giant planet interiors comparison
The coolest halo subdwarfs - the oldest brown dwarfs?
 Conference on The Milky Way and the Local Group Now and in the Gaia Era, University of Heidelberg, August 31 September 4, 2009 The coolest halo subdwarfs - the oldest brown dwarfs? Ralf-Dieter Scholz Astrophysikalisches
Conference on The Milky Way and the Local Group Now and in the Gaia Era, University of Heidelberg, August 31 September 4, 2009 The coolest halo subdwarfs - the oldest brown dwarfs? Ralf-Dieter Scholz Astrophysikalisches
The Galactic Orbits of Ultracool Subdwarfs
 The Galactic Orbits of Ultracool Subdwarfs Adam J. Burgasser UC San Diego/MIT Robyn Sanderson (MIT) Adam Burgasser, Andrew West, John Bochanski (MIT) and Jackie Faherty (AMNH/SUNY Stony Brook) Nitya Kallivayalil
The Galactic Orbits of Ultracool Subdwarfs Adam J. Burgasser UC San Diego/MIT Robyn Sanderson (MIT) Adam Burgasser, Andrew West, John Bochanski (MIT) and Jackie Faherty (AMNH/SUNY Stony Brook) Nitya Kallivayalil
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets. PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009
 Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture hot Jupiters; transiting planets primary eclipses and atmospheric
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture hot Jupiters; transiting planets primary eclipses and atmospheric
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets. PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009
 Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture: atmospheric temperature structure of irradiated planets isothermal
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture: atmospheric temperature structure of irradiated planets isothermal
1. Chemistry of Low Mass Substellar Objects
 1. Chemistry of Low Mass Substellar Objects Katharina Lodders 1 & Bruce Fegley, Jr. 1 Abstract: Brown dwarfs is the collective name for objects more massive than giant planets such as Jupiter but less
1. Chemistry of Low Mass Substellar Objects Katharina Lodders 1 & Bruce Fegley, Jr. 1 Abstract: Brown dwarfs is the collective name for objects more massive than giant planets such as Jupiter but less
Research paper assignment
 Research paper assignment Review of research that interests you, more focused than discussions in class Include references and figures Final format should be PDF (try LaTeX!) Concise! < 5000 words Steps:
Research paper assignment Review of research that interests you, more focused than discussions in class Include references and figures Final format should be PDF (try LaTeX!) Concise! < 5000 words Steps:
Outstanding Issues in Our Understanding of L, T, and Y Dwarfs
 14 th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun ASP Conference Series, Vol. 384, c 2008 Gerard T. van Belle, ed. Outstanding Issues in Our Understanding of L, T, and Y Dwarfs J. Davy
14 th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun ASP Conference Series, Vol. 384, c 2008 Gerard T. van Belle, ed. Outstanding Issues in Our Understanding of L, T, and Y Dwarfs J. Davy
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 19 Aug 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 19 Aug 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 19 Aug 2008](/thumbs/89/99068046.jpg) The Evolution of L and T Dwarfs in Color-Magnitude Diagrams D. Saumon Los Alamos National Laboratory, PO Box 1663, Mail Stop F663, Los Alamos, NM 87545 arxiv:0808.2611v1 [astro-ph] 19 Aug 2008 dsaumon@lanl.gov
The Evolution of L and T Dwarfs in Color-Magnitude Diagrams D. Saumon Los Alamos National Laboratory, PO Box 1663, Mail Stop F663, Los Alamos, NM 87545 arxiv:0808.2611v1 [astro-ph] 19 Aug 2008 dsaumon@lanl.gov
ATMOSPHERIC PARAMETERS OF FIELD L AND T DWARFS 1
 The Astrophysical Journal, 678:1372Y1395, 2008 May 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. ATMOSPHERIC PARAMETERS OF FIELD L AND T DWARFS 1 Michael C. Cushing,
The Astrophysical Journal, 678:1372Y1395, 2008 May 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. ATMOSPHERIC PARAMETERS OF FIELD L AND T DWARFS 1 Michael C. Cushing,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Jan 2001
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** T Dwarf Discoveries by 2MASS Adam J. Burgasser California Institute of Technology, MSC 103-33, Pasadena, CA 91125 arxiv:astro-ph/0101242v1
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** T Dwarf Discoveries by 2MASS Adam J. Burgasser California Institute of Technology, MSC 103-33, Pasadena, CA 91125 arxiv:astro-ph/0101242v1
Characterization of Exoplanets in the mid-ir with JWST & ELTs
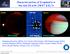 Characterization of Exoplanets in the mid-ir with JWST & ELTs Jupiter HR8799 Saturn VLT/ISAAC VLT/NACO Cassini/VIMS Wolfgang Brandner (MPIA), Eric Pantin (CEA Saclay), Ralf Siebenmorgen (ESO), Carolina
Characterization of Exoplanets in the mid-ir with JWST & ELTs Jupiter HR8799 Saturn VLT/ISAAC VLT/NACO Cassini/VIMS Wolfgang Brandner (MPIA), Eric Pantin (CEA Saclay), Ralf Siebenmorgen (ESO), Carolina
The Role of Clouds in Brown Dwarf and Extrasolar Giant Planet Atmospheres
 Planetary Systems in the Universe: Observation, Formation and Evolution ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 1999 A.J. Penny, P. Artymowicz, A.-M. Lagrange, and S.S. Russell, eds. The Role of Clouds in
Planetary Systems in the Universe: Observation, Formation and Evolution ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 1999 A.J. Penny, P. Artymowicz, A.-M. Lagrange, and S.S. Russell, eds. The Role of Clouds in
Characterizing the Atmospheres of Extrasolar Planets. Julianne I. Moses (Space Science Institute)
 Characterizing the Atmospheres of Extrasolar Planets Julianne I. Moses (Space Science Institute) Intern Brown Bag, 18 June 2014 1795 Confirmed Exoplanets as of 16 June 2014 hot Jupiters Jupiter Super Earths
Characterizing the Atmospheres of Extrasolar Planets Julianne I. Moses (Space Science Institute) Intern Brown Bag, 18 June 2014 1795 Confirmed Exoplanets as of 16 June 2014 hot Jupiters Jupiter Super Earths
Silicate Atmospheres, Clouds, and Fractional Vaporization of Hot Earth-like Exoplanets
 Silicate Atmospheres, Clouds, and Fractional Vaporization of Hot Earth-like Exoplanets Laura Schaefer and Bruce Fegley, Jr. Planetary Chemistry Laboratory Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences Washington
Silicate Atmospheres, Clouds, and Fractional Vaporization of Hot Earth-like Exoplanets Laura Schaefer and Bruce Fegley, Jr. Planetary Chemistry Laboratory Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences Washington
Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects
 Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects Channon Visscher Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA UHCL Spring Seminar Series 2010 Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt Outline introduction to substellar
Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects Channon Visscher Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA UHCL Spring Seminar Series 2010 Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt Outline introduction to substellar
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Dec 2006
 Infrared observations of a mid-l dwarf with strong Hα emission Basmah Riaz and John E. Gizis Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716; basmah@udel.edu, gizis@udel.edu
Infrared observations of a mid-l dwarf with strong Hα emission Basmah Riaz and John E. Gizis Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716; basmah@udel.edu, gizis@udel.edu
Modeling UV photo- chemistry and clouds in the atmosphere of exoplanets
 Modeling UV photo- chemistry and clouds in the atmosphere of exoplanets P. Tremblin, B. Drummond, P. Mourier, D. Amundsen, N. Mayne, I. Baraffe (Exeter), J. Manners (Met-office) In collaboration with O.
Modeling UV photo- chemistry and clouds in the atmosphere of exoplanets P. Tremblin, B. Drummond, P. Mourier, D. Amundsen, N. Mayne, I. Baraffe (Exeter), J. Manners (Met-office) In collaboration with O.
The Nature of Variability in Early L Dwarfs
 The Nature of Variability in Early L Dwarfs J. E. Gizis 1 1 University of Delaware. Dep. of Physics and Astronomy, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA Abstract. The M/L transition features the onset of dust formation,
The Nature of Variability in Early L Dwarfs J. E. Gizis 1 1 University of Delaware. Dep. of Physics and Astronomy, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA Abstract. The M/L transition features the onset of dust formation,
Cloud Condensation Chemistry. in Low-Mass Objects. Katharina Lodders Washington University, St. Louis
 Cloud Condensation Chemistry in Low-Mass Objects Katharina Lodders Washington University, St. Louis For a recent review on this topic, see Lodders & Fegley 2006, Astrophysics Update 2, Springer, p. 1 ff.
Cloud Condensation Chemistry in Low-Mass Objects Katharina Lodders Washington University, St. Louis For a recent review on this topic, see Lodders & Fegley 2006, Astrophysics Update 2, Springer, p. 1 ff.
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY. Planets around white dwarfs Matt Burleigh
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Planets around white dwarfs Matt Burleigh Contents Original motivation DODO - results from our direct imaging survey Where do we go next? The role for E-ELT Direct imaging
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Planets around white dwarfs Matt Burleigh Contents Original motivation DODO - results from our direct imaging survey Where do we go next? The role for E-ELT Direct imaging
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, KITP Public Lecture
 Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
BINARIES AND THE L DWARF/ T DWARF TRANSITION
 The Astrophysical Journal, 659:655 674, 2007 April 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A BINARIES AND THE L DWARF/ T DWARF TRANSITION Adam J. Burgasser
The Astrophysical Journal, 659:655 674, 2007 April 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A BINARIES AND THE L DWARF/ T DWARF TRANSITION Adam J. Burgasser
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview. PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009
 Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Masses and Radii. PHY 688, Lecture 10
 Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Masses and Radii PHY 688, Lecture 10 Outline Review of previous lecture brown dwarf effective temperatures finding cool brown dwarfs current problem: what are the coolest
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Masses and Radii PHY 688, Lecture 10 Outline Review of previous lecture brown dwarf effective temperatures finding cool brown dwarfs current problem: what are the coolest
950 K black body K black body
 Infrared Spectroscopy of Brown Dwarfs: the onset of CH 4 absorption in L dwarfs and the L/T transition T. R. Geballe 1,K.S.Noll 2,S.K.Leggett 3, G. R. Knapp 4,X.Fan 4,andD. Golimowski 5 1 Gemini Observatory,
Infrared Spectroscopy of Brown Dwarfs: the onset of CH 4 absorption in L dwarfs and the L/T transition T. R. Geballe 1,K.S.Noll 2,S.K.Leggett 3, G. R. Knapp 4,X.Fan 4,andD. Golimowski 5 1 Gemini Observatory,
CLOUDS, GRAVITY, AND METALLICITY IN BLUE L DWARFS: THE CASE OF 2MASS J
 The Astrophysical Journal, 674:451Y465, 2008 February 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A CLOUDS, GRAVITY, AND METALLICITY IN BLUE L DWARFS: THE CASE
The Astrophysical Journal, 674:451Y465, 2008 February 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A CLOUDS, GRAVITY, AND METALLICITY IN BLUE L DWARFS: THE CASE
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity. PHY 688, Lecture 11
 Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity PHY 688, Lecture 11 Outline Review of previous lecture binary stars and brown dwarfs (sub)stellar dynamical masses and radii Surface gravity stars,
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity PHY 688, Lecture 11 Outline Review of previous lecture binary stars and brown dwarfs (sub)stellar dynamical masses and radii Surface gravity stars,
ULTRACOOL DWARFS. Ya. V. Pavlenko
 ULTRACOOL DWARFS Ya. V. Pavlenko Main Astronomical Observatory, NAS of Ukraine 27 Akademika Zabolotnoho Str., 03680 Kyiv, Ukraine e-mail: yp@mao.kiev.ua We present results of modelling of spectra of M-,
ULTRACOOL DWARFS Ya. V. Pavlenko Main Astronomical Observatory, NAS of Ukraine 27 Akademika Zabolotnoho Str., 03680 Kyiv, Ukraine e-mail: yp@mao.kiev.ua We present results of modelling of spectra of M-,
Searching for Binary Y dwarfs with the Gemini GeMS Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics System
 Searching for Binary Y dwarfs with the Gemini GeMS Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics System Daniela Opitz 1,2, Chris Tinney 1,2 1 Exoplanetary Science Group, School of Physics, University of New South Wales,
Searching for Binary Y dwarfs with the Gemini GeMS Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics System Daniela Opitz 1,2, Chris Tinney 1,2 1 Exoplanetary Science Group, School of Physics, University of New South Wales,
Substellar Interiors. PHY 688, Lecture 13
 Substellar Interiors PHY 688, Lecture 13 Outline Review of previous lecture curve of growth: dependence of absorption line strength on abundance metallicity; subdwarfs Substellar interiors equation of
Substellar Interiors PHY 688, Lecture 13 Outline Review of previous lecture curve of growth: dependence of absorption line strength on abundance metallicity; subdwarfs Substellar interiors equation of
Rotation and activity in low-mass stars
 Rotation and activity in low-mass stars ät öttingen Outline I. Introduction: Magnetic activity and why we care about it II. III. Spin-up and spin-down: Rotational evolution of sun-like stars Magnetic field
Rotation and activity in low-mass stars ät öttingen Outline I. Introduction: Magnetic activity and why we care about it II. III. Spin-up and spin-down: Rotational evolution of sun-like stars Magnetic field
ULAS J : A BLUE T DWARF COMPANION TO A BLUE L DWARF
 ULAS J141623.94+134836.3: A BLUE T DWARF COMPANION TO A BLUE L DWARF The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
ULAS J141623.94+134836.3: A BLUE T DWARF COMPANION TO A BLUE L DWARF The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Brown Dwarfs in the Era of WISE. Michael Cushing University of Toledo
 Brown Dwarfs in the Era of WISE Michael Cushing University of Toledo WISE at 5 2015-Feb-10 Brown dwarfs were baked into WISE From the 1998 proposal for the Next Generation Sky Survey (NGSS): The primary
Brown Dwarfs in the Era of WISE Michael Cushing University of Toledo WISE at 5 2015-Feb-10 Brown dwarfs were baked into WISE From the 1998 proposal for the Next Generation Sky Survey (NGSS): The primary
A dozen years of hot exoplanet atmospheric investigations. Results from a large HST program. David K. Sing. #acrosshr Cambridge.
 A dozen years of hot exoplanet atmospheric investigations Results from a large HST program David K. Sing #acrosshr Cambridge ] 1 Aug 2014 Outline Introduction to Transit Spectroscopy Highlight 3 Science
A dozen years of hot exoplanet atmospheric investigations Results from a large HST program David K. Sing #acrosshr Cambridge ] 1 Aug 2014 Outline Introduction to Transit Spectroscopy Highlight 3 Science
Exoplanets Atmospheres. Characterization of planetary atmospheres. Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging
 Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jun 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jun 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jun 2011](/thumbs/90/104330845.jpg) Draft version October 5, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 2/16/10 MODEL ATMOSPHERES FOR MASSIVE GAS GIANTS WITH THICK CLOUDS: APPLICATION TO THE HR 8799 PLANETS AND PREDICTIONS FOR
Draft version October 5, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 2/16/10 MODEL ATMOSPHERES FOR MASSIVE GAS GIANTS WITH THICK CLOUDS: APPLICATION TO THE HR 8799 PLANETS AND PREDICTIONS FOR
Coupling chemistry and radiative transfer with global circulation models
 Coupling chemistry and radiative transfer with global circulation models P. Tremblin, B. Drummond, P. Mourier, D. Amundsen, N. Mayne, I. Baraffe (Exeter), J. Manners (Met-office) In collaboration with
Coupling chemistry and radiative transfer with global circulation models P. Tremblin, B. Drummond, P. Mourier, D. Amundsen, N. Mayne, I. Baraffe (Exeter), J. Manners (Met-office) In collaboration with
Direct imaging characterisation of (exo-) planets with METIS
 Direct imaging characterisation of (exo-) planets with METIS Jupiter HR8799 Saturn VLT/ISAAC VLT/NACO Cassini/VIMS Wolfgang Brandner (MPIA) with contributions by Ian Crossfield, Lisa Kaltenegger (MPIA),
Direct imaging characterisation of (exo-) planets with METIS Jupiter HR8799 Saturn VLT/ISAAC VLT/NACO Cassini/VIMS Wolfgang Brandner (MPIA) with contributions by Ian Crossfield, Lisa Kaltenegger (MPIA),
CLOUDLESS ATMOSPHERES FOR L/T DWARFS AND EXTRA-SOLAR GIANT PLANETS
 CLOUDLESS ATMOSPHERES FOR L/T DWARFS AND EXTRA-SOLAR GIANT PLANETS P Tremblin, David Skålid Amundsen, G Chabrier, I Baraffe, B Drummond, S Hinkley, P Mourier, O Venot To cite this version: P Tremblin,
CLOUDLESS ATMOSPHERES FOR L/T DWARFS AND EXTRA-SOLAR GIANT PLANETS P Tremblin, David Skålid Amundsen, G Chabrier, I Baraffe, B Drummond, S Hinkley, P Mourier, O Venot To cite this version: P Tremblin,
The formation of giant planets: Constraints from interior models
 The formation of giant planets: Constraints from interior models Tristan Guillot Observatoire de la Côte d Azur www.obs-nice.fr/guillot (Guillot, Ann. Rev. Earth & Plan. Sci. 2005 & Saas-Fee course 2001,
The formation of giant planets: Constraints from interior models Tristan Guillot Observatoire de la Côte d Azur www.obs-nice.fr/guillot (Guillot, Ann. Rev. Earth & Plan. Sci. 2005 & Saas-Fee course 2001,
New Dimensions of Stellar Atmosphere Modelling
 New Dimensions of Stellar Atmosphere Modelling Derek Homeier 1,2 France Allard 1,3 Bernd Freytag 1 1 CRAL/École Normale Supérieure de Lyon 2 Förderkreis Planetarium Göttingen e.v. 3 Institut d Astrophysique
New Dimensions of Stellar Atmosphere Modelling Derek Homeier 1,2 France Allard 1,3 Bernd Freytag 1 1 CRAL/École Normale Supérieure de Lyon 2 Förderkreis Planetarium Göttingen e.v. 3 Institut d Astrophysique
Characterization of Transiting Planet Atmospheres
 Characterization of Transiting Planet Atmospheres Heather Knutson Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, Caltech A Bird s-eye View of Exoplanet Atmospheres Limited information available for individual
Characterization of Transiting Planet Atmospheres Heather Knutson Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, Caltech A Bird s-eye View of Exoplanet Atmospheres Limited information available for individual
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets
 Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
A SPITZER INFRARED SPECTROGRAPH SPECTRAL SEQUENCE OF M, L, AND T DWARFS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 648:614Y628, 2006 September 1 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A SPITZER INFRARED SPECTROGRAPH SPECTRAL SEQUENCE OF M, L, AND
The Astrophysical Journal, 648:614Y628, 2006 September 1 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A SPITZER INFRARED SPECTROGRAPH SPECTRAL SEQUENCE OF M, L, AND
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 19 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 19 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 19 Aug 2015](/thumbs/83/88348827.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Baudinoetal_7aout c ESO 8 August 7, 8 Interpreting the photometry and spectroscopy of directly imaged planets: a new atmospheric model applied to β Pictoris b and
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Baudinoetal_7aout c ESO 8 August 7, 8 Interpreting the photometry and spectroscopy of directly imaged planets: a new atmospheric model applied to β Pictoris b and
What s Interesting about Low-Mass Stars? Agenda for Ast 309N, Oct. 9. Evidence for Activity in Low-Mass Stars. More Evidence for Activity
 Agenda for Ast 309N, Oct. 9 Results of class poll, 10/02 Brown dwarfs: formation; observed properties Video on exoplanet discoveries, circa 2008 Card activity: exoplanets around red dwarfs What s Interesting
Agenda for Ast 309N, Oct. 9 Results of class poll, 10/02 Brown dwarfs: formation; observed properties Video on exoplanet discoveries, circa 2008 Card activity: exoplanets around red dwarfs What s Interesting
Young Jupiters are faint: new models of the early evolution of giant planets
 Astron. Nachr. / AN 326, No. 10, 925 929 (2005) /DOI10.1002/asna.200510465 Young Jupiters are faint: new models of the early evolution of giant planets J.J. FORTNEY 1,M.S.MARLEY 1,O.HUBICKYJ 1,2,P.BODENHEIMER
Astron. Nachr. / AN 326, No. 10, 925 929 (2005) /DOI10.1002/asna.200510465 Young Jupiters are faint: new models of the early evolution of giant planets J.J. FORTNEY 1,M.S.MARLEY 1,O.HUBICKYJ 1,2,P.BODENHEIMER
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 7 Jun 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 7 Jun 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 7 Jun 2014](/thumbs/78/77870493.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. main c ESO 2014 June 10, 2014 The Brown dwarf Atmosphere Monitoring (BAM) Project I: The largest near-ir monitoring survey of L & T dwarfs P. A. Wilson 1, A. Rajan
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. main c ESO 2014 June 10, 2014 The Brown dwarf Atmosphere Monitoring (BAM) Project I: The largest near-ir monitoring survey of L & T dwarfs P. A. Wilson 1, A. Rajan
A METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF THE COLDEST KNOWN BROWN DWARFS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 639:1095 1113, 2006 March 10 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A A METHOD FO DETEMINING THE PHYSICAL POPETIES OF THE COLDEST KNOWN
The Astrophysical Journal, 639:1095 1113, 2006 March 10 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A A METHOD FO DETEMINING THE PHYSICAL POPETIES OF THE COLDEST KNOWN
Atmospheric Dynamics of Exoplanets: Status and Opportunities
 Atmospheric Dynamics of Exoplanets: Status and Opportunities Adam Showman University of Arizona Collaborators: Jonathan Fortney, Lorenzo Polvani, Yuan Lian, Mark Marley, Nikole Lewis, Daniel Perez-Becker,
Atmospheric Dynamics of Exoplanets: Status and Opportunities Adam Showman University of Arizona Collaborators: Jonathan Fortney, Lorenzo Polvani, Yuan Lian, Mark Marley, Nikole Lewis, Daniel Perez-Becker,
New Tools for Understanding Exoplanet Atmospheres from Spectroscopy. Caroline Morley 2016 Sagan Fellow Harvard University
 New Tools for Understanding Exoplanet Atmospheres from Spectroscopy Caroline Morley 2016 Sagan Fellow Harvard University As a Sagan Fellow, I will use new techniques to retrieve planet compositions and
New Tools for Understanding Exoplanet Atmospheres from Spectroscopy Caroline Morley 2016 Sagan Fellow Harvard University As a Sagan Fellow, I will use new techniques to retrieve planet compositions and
A high-contrast adaptiveoptics imaging search for brown dwarfs
 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file: Albert_Abraham_Michelson2.jpg A high-contrast adaptiveoptics imaging search for brown dwarfs http://nexsci.caltech.edu/sagan/ Katie Morzinski UC Santa Cruz/Center for
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file: Albert_Abraham_Michelson2.jpg A high-contrast adaptiveoptics imaging search for brown dwarfs http://nexsci.caltech.edu/sagan/ Katie Morzinski UC Santa Cruz/Center for
Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses
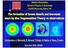 Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses from ~3 M J to ~200 M J (0.2M ) Defining stars, brown dwarfs Stars and planets Objects formed by gravitational instability on a dynamical
Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses from ~3 M J to ~200 M J (0.2M ) Defining stars, brown dwarfs Stars and planets Objects formed by gravitational instability on a dynamical
Probing the physical properties of directly imaged gas giant exoplanets through polarization
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 417, 2874 2881 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19448.x Probing the physical properties of directly imaged gas giant exoplanets through polarization Mark S. Marley 1 and Sujan
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 417, 2874 2881 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19448.x Probing the physical properties of directly imaged gas giant exoplanets through polarization Mark S. Marley 1 and Sujan
Probing the physical properties of directly imaged gas giant exoplanets through polarization
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 417, 2874 2881 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19448.x Probing the physical properties of directly imaged gas giant exoplanets through polarization Mark S. Marley 1 and Sujan
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 417, 2874 2881 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19448.x Probing the physical properties of directly imaged gas giant exoplanets through polarization Mark S. Marley 1 and Sujan
OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS
 OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS Subhanjoy Mohanty (Spitzer Fellow, Harvard University) Gibor Basri, Ray Jayawardhana, Antonella Natta David Barrado y Navascués,
OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS Subhanjoy Mohanty (Spitzer Fellow, Harvard University) Gibor Basri, Ray Jayawardhana, Antonella Natta David Barrado y Navascués,
Carbon- rich Exoplanets
 Carbon- rich Exoplanets Nikku Madhusudhan Princeton University Exploring Strange New Worlds: From Giant Planets to Super Earths Flagstaff, AZ. May 04, 2011 Overview 1. WASP-12b and the need for a second
Carbon- rich Exoplanets Nikku Madhusudhan Princeton University Exploring Strange New Worlds: From Giant Planets to Super Earths Flagstaff, AZ. May 04, 2011 Overview 1. WASP-12b and the need for a second
7. Our Solar System. Planetary Orbits to Scale. The Eight Planetary Orbits
 7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
Substellar objects: Brown dwarfs and extrasolar planets
 Substellar objects: Brown dwarfs and extrasolar planets Basic information Class web site: http://www.mpia-hd.mpg.de/homes/goldman/course/ Material: slides, bibliography, useful links Max-Planck-Institut
Substellar objects: Brown dwarfs and extrasolar planets Basic information Class web site: http://www.mpia-hd.mpg.de/homes/goldman/course/ Material: slides, bibliography, useful links Max-Planck-Institut
Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry. Johannes Sahlmann ESA Research Fellow at ESAC
 Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry ESA Research Fellow at ESAC Who s Who, Paris - 2 July 215 IS MASS A GOOD DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATOR? 2MASSWJ127334 393254 first image of a
Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry ESA Research Fellow at ESAC Who s Who, Paris - 2 July 215 IS MASS A GOOD DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATOR? 2MASSWJ127334 393254 first image of a
Giant planets. Giant planets of the Solar System. Giant planets. Gaseous and icy giant planets
 Giant planets of the Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Giant planets Effective temperature Low values with respect to the rocky planets of the Solar System Below the condensation
Giant planets of the Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Giant planets Effective temperature Low values with respect to the rocky planets of the Solar System Below the condensation
Exoplanets and their Atmospheres. Josh Destree ATOC /22/2010
 Exoplanets and their Atmospheres Josh Destree ATOC 3500 4/22/2010 Outline What is an exoplanet? Why do we care? Detecting exoplanets Exoplanets compared to planets in the solar system Exoplanet atmospheres
Exoplanets and their Atmospheres Josh Destree ATOC 3500 4/22/2010 Outline What is an exoplanet? Why do we care? Detecting exoplanets Exoplanets compared to planets in the solar system Exoplanet atmospheres
Comple(ng the Nearby Stellar and Substellar Census with WISE and 2MASS. John Gizis Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware
 Comple(ng the Nearby Stellar and Substellar Census with WISE and 2MASS John Gizis Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Collaborators Phil Castro Hugh Harris, Fred Vrba A. Burgasser,
Comple(ng the Nearby Stellar and Substellar Census with WISE and 2MASS John Gizis Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Collaborators Phil Castro Hugh Harris, Fred Vrba A. Burgasser,
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12)
 Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Silicate cloud formation in the atmospheres of close-in super-earths and gas giants
 Silicate cloud formation in the atmospheres of close-in super-earths and gas giants by Gourav Mahapatra Student number: 4413385 in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Silicate cloud formation in the atmospheres of close-in super-earths and gas giants by Gourav Mahapatra Student number: 4413385 in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection
 4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2017 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2017](/thumbs/86/93619239.jpg) Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 UNIFORM ATMOSPHERIC RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS OF ULTRACOOL DWARFS II: PROPERTIES OF 11 T-DWARFS Michael R. Line
Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 UNIFORM ATMOSPHERIC RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS OF ULTRACOOL DWARFS II: PROPERTIES OF 11 T-DWARFS Michael R. Line
Planetary Temperatures
 Planetary Temperatures How does Sunlight heat a planet with no atmosphere? This is similar to our dust grain heating problem First pass: Consider a planet of radius a at a distance R from a star of luminosity
Planetary Temperatures How does Sunlight heat a planet with no atmosphere? This is similar to our dust grain heating problem First pass: Consider a planet of radius a at a distance R from a star of luminosity
ON THE NATURE OF THE UNIQUE H-EMITTING T DWARF 2MASS J
 The Astrophysical Journal, 655:522Y527, 2007 January 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A ON THE NATURE OF THE UNIQUE H-EMITTING T DWARF 2MASS J12373919+6526148
The Astrophysical Journal, 655:522Y527, 2007 January 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A ON THE NATURE OF THE UNIQUE H-EMITTING T DWARF 2MASS J12373919+6526148
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section VI
 ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section VI Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section VI Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Sep 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Sep 2014](/thumbs/92/110579217.jpg) Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia (PASA) c Astronomical Society of Australia 2018; published by Cambridge University Press. doi: 10.1017/pasa.2018.xxx. The Dawes Review 3: The Atmospheres
Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia (PASA) c Astronomical Society of Australia 2018; published by Cambridge University Press. doi: 10.1017/pasa.2018.xxx. The Dawes Review 3: The Atmospheres
I C and R C band time-series observations of some bright ultracool dwarfs
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 360, 1132 1142 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09119.x I C and R C band time-series observations of some bright ultracool dwarfs Chris Koen 1,2 1 Department of Statistics,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 360, 1132 1142 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09119.x I C and R C band time-series observations of some bright ultracool dwarfs Chris Koen 1,2 1 Department of Statistics,
CONTENT EXPECTATIONS
 THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
Today. Jovian planets
 Today Jovian planets Global Wind Patterns Heat transport Global winds blow in distinctive patterns: Equatorial: E to W Mid-latitudes: W to E High latitudes: E to W 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Circulation
Today Jovian planets Global Wind Patterns Heat transport Global winds blow in distinctive patterns: Equatorial: E to W Mid-latitudes: W to E High latitudes: E to W 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Circulation
LINE AND MEAN OPACITIES FOR ULTRACOOL DWARFS AND EXTRASOLAR PLANETS
 The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 174:504 513, 2008 February # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. rinted in U.S.A. A LINE AND MEAN OACITIES FOR ULTRACOOL DWARFS AND
The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 174:504 513, 2008 February # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. rinted in U.S.A. A LINE AND MEAN OACITIES FOR ULTRACOOL DWARFS AND
1 Exoplanet Chemistry
 1 Exoplanet Chemistry Katharina Lodders Planetary Chemistry Laboratory, Dept. Of Earth & Planetary Sciences and McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences, Washington University, One Brookings Drive, Saint
1 Exoplanet Chemistry Katharina Lodders Planetary Chemistry Laboratory, Dept. Of Earth & Planetary Sciences and McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences, Washington University, One Brookings Drive, Saint
6. Interstellar Medium. Emission nebulae are diffuse patches of emission surrounding hot O and
 6-1 6. Interstellar Medium 6.1 Nebulae Emission nebulae are diffuse patches of emission surrounding hot O and early B-type stars. Gas is ionized and heated by radiation from the parent stars. In size,
6-1 6. Interstellar Medium 6.1 Nebulae Emission nebulae are diffuse patches of emission surrounding hot O and early B-type stars. Gas is ionized and heated by radiation from the parent stars. In size,
AST 248. Is Pluto a Planet?
 AST 248 Is Pluto a Planet? And what is a planet, anyways? N = N * f s f p n h f l f i f c L/T What is a Star? A star supports stable Hydrogen fusion Upper mass limit: about 120 M above that radiation pressure
AST 248 Is Pluto a Planet? And what is a planet, anyways? N = N * f s f p n h f l f i f c L/T What is a Star? A star supports stable Hydrogen fusion Upper mass limit: about 120 M above that radiation pressure
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 23 May 2001
 The Limiting Effects of Dust in Brown Dwarf Model Atmospheres France Allard arxiv:astro-ph/0104256v2 23 May 2001 Centre de Recherche Astronomique de Lyon (CRAL), Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon, Lyon,
The Limiting Effects of Dust in Brown Dwarf Model Atmospheres France Allard arxiv:astro-ph/0104256v2 23 May 2001 Centre de Recherche Astronomique de Lyon (CRAL), Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon, Lyon,
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology
 Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
Extrasolar Planets: Ushering in the Era of Comparative Exoplanetology A. Sozzetti INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino Detection/Characterization Detection (Visible): - Doppler spectroscopy (95%) -
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets. 4.1 Expected properties of extrasolar planets. Sizes of gas giants, brown dwarfs & low-mass stars
 4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies The H-R Diagram review So far: Stars on Main Sequence (MS) Next: - Pre MS (Star Birth) - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Star Birth We start
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies The H-R Diagram review So far: Stars on Main Sequence (MS) Next: - Pre MS (Star Birth) - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Star Birth We start
Observa6ons of Brown Dwarfs
 Observa6ons of Brown Dwarfs Image credit: Don Dixon Kevin L. Luhman Penn State University 0 2 211 M J Log 10 (L/L sun ) 4 6 1 M J 13 M J 73 M J 0.3 M J 8 Burrows et al. 1997 10 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10
Observa6ons of Brown Dwarfs Image credit: Don Dixon Kevin L. Luhman Penn State University 0 2 211 M J Log 10 (L/L sun ) 4 6 1 M J 13 M J 73 M J 0.3 M J 8 Burrows et al. 1997 10 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10
Brown Dwarfs. Planets
 Low-mass Stars and Brown Dwarfs Beyond the Solar Neighborhood: Diversity, number densities, masses, ages, metallicities, and kinematics for the dominant baryonic component of the Galaxy. Kelle Cruz (1),
Low-mass Stars and Brown Dwarfs Beyond the Solar Neighborhood: Diversity, number densities, masses, ages, metallicities, and kinematics for the dominant baryonic component of the Galaxy. Kelle Cruz (1),
SDSS J AB: A NOVEL T DWARF BINARY FOUND WITH KECK LASER GUIDE STAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS AND THE POTENTIAL ROLE OF BINARITY IN THE L/T TRANSITION 1
 The Astrophysical Journal, 647:1393Y1404, 2006 August 20 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SDSS J1534+1615AB: A NOVEL T DWARF BINARY FOUND WITH KECK LASER
The Astrophysical Journal, 647:1393Y1404, 2006 August 20 # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SDSS J1534+1615AB: A NOVEL T DWARF BINARY FOUND WITH KECK LASER
Brown dwarfs in their infancy and some other remaining bits
 Brown dwarfs in their infancy and some other remaining bits Brown dwarf disks Observed photometry Dereddened photometry December 11, 2006 field M dwarfs without disk! different photometric systems! Jayawardhana
Brown dwarfs in their infancy and some other remaining bits Brown dwarf disks Observed photometry Dereddened photometry December 11, 2006 field M dwarfs without disk! different photometric systems! Jayawardhana
Structure and evolution of (giant) exoplanets: some news from the theoretical front. I. Baraffe University of Exeter
 Structure and evolution of (giant) exoplanets: some news from the theoretical front I. Baraffe University of Exeter I) Structure of Jupiter and Saturn II) Exoplanets: Interior structure and evolutionary
Structure and evolution of (giant) exoplanets: some news from the theoretical front I. Baraffe University of Exeter I) Structure of Jupiter and Saturn II) Exoplanets: Interior structure and evolutionary
PLANETARY RADII ACROSS FIVE ORDERS OF MAGNITUDE IN MASS AND STELLAR INSOLATION: APPLICATION TO TRANSITS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 659:1661 1672, 2007 April 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. PLANETARY RADII ACROSS FIVE ORDERS OF MAGNITUDE IN MASS AND STELLAR
The Astrophysical Journal, 659:1661 1672, 2007 April 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. PLANETARY RADII ACROSS FIVE ORDERS OF MAGNITUDE IN MASS AND STELLAR
OPTICAL AND NEAR-INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY OF THE L SUBDWARF SDSS J
 OPTICAL AND NEAR-INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY OF THE L SUBDWARF SDSS J125637.13-022452.4 The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
OPTICAL AND NEAR-INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY OF THE L SUBDWARF SDSS J125637.13-022452.4 The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground
 The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
From Brown Dwarfs to Super-Earths: An Observational Study of Weather and Atmospheric Composition
 UNIVERSITY OF EXETER From Brown Dwarfs to Super-Earths: An Observational Study of Weather and Atmospheric Composition Submitted by Paul Anthony Wilson to the University of Exeter as a thesis for the degree
UNIVERSITY OF EXETER From Brown Dwarfs to Super-Earths: An Observational Study of Weather and Atmospheric Composition Submitted by Paul Anthony Wilson to the University of Exeter as a thesis for the degree
