A method for determination of gamma-ray direction in space. Serkan Akkoyun
|
|
|
- Bethany Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A method for determination of gamma-ray direction in space Serkan Akkoyun Cumhuriyet University, Faculty of Science, Department of Physics, Sivas-Turkey 0 Abstract Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are short and most intense bursts of gamma-rays that come from random direction in space. Their origin are still unknown and they originate likely from cosmological distances, probably after birth of a new black hole or death of a giant star. In this work, Geant simulations of a detector array whose aim is to identify gamma-ray directions in space were performed and a method for this identification was developed. The array consists of three quadratic NaI(Tl) scintillators which are facing different directions and the method is based on the difference of the counts registered in these three detectors. By using the method the gamma-ray directions are obtained with 0 o accuracy. This form of the array which can scan three dimensions in space is crucial to pinpoint origin of the GRBs. The array would also be applicable in various fields where identifications of the gamma-ray directions are necessary. Keywords: Gamma-ray direction, GRB, Geant, NaI(Tl) 0 Corresponding author sakkoyun@cumhuriyet.edu.tr, Tel: +000x Preprint submitted to Elsevier September 0, 0
2 Introduction Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are short and intense flashes of photons that come from random direction in space and last from fraction of a second up to few minutes []. The origin of the GRBs are still unknown and they originate from cosmological distances, probably after birth of a new black hole or death of a giant star (hyper/super-nova) []. These bursts emitting in the energy range between about 0. MeV to few MeV often outshine other gamma-ray sources. These short-lived bursts are usually followed by a much longer-lived signal. This socalled "afterglow" [-] emitted at longer wavelengths allows us to pinpoint the origin of the gamma-ray burst that is not possible from the short-lived gamma-ray signal alone. The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, indicating that the explosions are both extremely energetic and rare []. The topic of GRBs has been reviewed over the years in several works [, -]. GRBs remain one of the most interesting objects in high energy astrophysics almost 0 years after their discovery. A new era in GRB studies have been opened about 0 years ago with the launch of the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (CGRO) []. The most significant results came from the all-sky observing by the Burst and Transient Experiment (BATSE) on CGRO complemented by data from the OSSE [], Comptel [] and EGRET [] experiments. The next major discovery was made by satellite BeppoSAX, which was able to produce the first quick and small error boxes of GRBs' positions in the sky []. This allows observing position of GRB several hours or days after their explosion. Nowadays the detections of GRBs are performed by HETE, Integral, Swift and AGILE satellites []. Several techniques have been developed in order to obtain directional information of gamma-rays from GRBs or the other sources [-]. Accurate burst locations are necessary for solving GRB mystery. In this work, new types of a detector array have been designed to obtain directional information of incident gamma-rays from mainly GRBs. This array consists of three quadratic NaI(Tl) detectors which are perpendicular to each other viewing different directions in space. By making use of three energy spectra obtained in these three detectors, determination of gamma-ray direction can be achieved. This array can scan three dimensions in space and identify the location of the bursts within about 0 o accuracy. The detector array would be applicable in various fields such as in measurements of terrestrial gamma-rays [], in determination of the location of missing gamma-emitting radioactive sources, in
3 0 identification of radioactive areas and in explanation dose rate differences found by car-borne measurement.. Experimental setup and method The detector array designed for placing on a satellite is consist of three quadratic NaI(Tl) crystals which are perpendicular each other, as shown in Fig.. In ideal case, the thickness of the detector should be zero in order to perfectly determine gamma-ray directions. Namely as can be seen in Fig..a, in order to obtain directional information of the gamma- rays coming from the source along the z direction, they must hit the whole surface of the detector A and must not hit the detector B and C. In this case, one can say that gamma-rays are measured only by the detector A. But at this time, the detector A will not be able to detect gamma-rays due to its extremely thinness. After several investigations by considering both photopeak efficiencies of each individual detector and efficiency of the array, the dimensions of the detectors were chosen as. cm. Then the total weight of the crystals is 0 g and the estimated total weight of the detectors including electronic and mechanical parts is 00 g. Then after given an optimal thickness to the detectors, in the case of Fig..a, the majority of the gamma-ray counts are registered in the detector A. Still, accurately determinations of the gamma-ray directions are possible. Already, the method developed in this work is based on the relative counts belonging to the different detectors. 0. Simulations The simulation of the detectors and gamma-ray interactions were performed by Geant simulation program []. The detector array mentioned above located in a vacuum environment (denoted by big cubes with dot-dashed lines in Fig.) which represents the space. Due to the big distance between detectors and gamma-ray source, the gamma-ray beams reached to the detectors are considered to be in parallel. It is also assumed that the detectors can measure gamma-rays only by their front and lateral faces due to the electrical and mechanical parts of the detectors are placed on the shielded backside of the detectors. 0
4 0. Method Changing incoming directions of the gamma-ray beams changes the each photopeak counts recorded in three detectors which view different directions in space. The relative responses of the detectors are used for the determination of the gamma-ray directions. Because of the rotational motion of the satellite around the world and itself, it is essential to know measurement moment of the gamma-rays for getting true gamma-ray directions. This rotational motion of the satellite allows scanning entire space in three dimensions by the detector array. According to the method, as an illustration in Fig..a, because of the surface area of the detector A is bigger than that of detector B and C viewing by incoming gammarays, more gamma-rays enter the detector A. Therefore, the photopeak counts belonging to the detector A is expected more than B and C. Eventually in this case, one can predict the incoming direction of the gamma-rays towards the surface of detector A. Similarly in Fig..b and.c, it is easily said that the gamma-ray directions are towards the surface of detector B and C respectively.
5 Fig. Experimental setup with three NaI crystals indicated in different colours. The gammarays enter perpendicularly the detector surfaces A (a), B (b) and C (c). 0. Application of the method In order to determine gamma-ray directions, the photopeak counts in three different detectors were obtained. The photopeak counts registered in detectors A, B and C were indicated by A, B and C. As T represents the total photopeak counts registered in all three detectors, the count ratios A/T, B/T and C/T can be useful for identification of the gamma-ray directions. In this study, the systematics of the angle of incident gamma-ray can be explained
6 0 0 by helping Fig.s. The and angles which are perpendicular to the surface of the detector A are 0 o and 0 o respectively. By increasing, the gamma-ray beam direction rotates counter- clockwise about the y-axis and after rotation of 0 o finally becomes perpendicular to the surface of the detector B. In this situation the final angles are 0 o and 0 o. Besides, the counter-clockwise rotation about the z-axis increases the φ angle. By increasing φ, the gamma-ray beam direction which were perpendicular to the surface of the detector B ( 0 o ) becomes perpendicular to surface of the detector C after rotation of 0 o. The analyses were performed by changing one of the angle by 0 o step while the other is constant. The result were given in Table. and for, and 0 MeV gamma-rays with constant and. As can be clearly seen in the Table., at 0 o and 0 o the detector B and C have their maximum and minimum counts ratios respectively, as expected. By increasing value, the ratio of the detector B decreases while the detector C's increases and reaches their minimum and maximum at 0 o and 0 o for the detector B and C, respectively. This situation seems only for and MeV energy values. But there is an opposite situation for 0 MeV gamma-rays. Due to their long range in this high energy, the thickness of the detector is not enough to efficiently detect them. Besides, the incoming gamma-rays enter the detector A and C by lateral sides and are detected more probably although their surfaces viewed by gamma-rays are smaller. So, while the count ratio belonging to the detector C decreases, the detector B's increases. Furthermore, effect of changing value do not appreciably affect the ratio belonging to the detector A due to the gamma-rays always enter the detector in its lateral side.
7 Table. Changing of photopeak counts ratios by for fixed. Analyses were performed for, and 0 MeV gamma-rays. E ( MeV ) 0 o Photopeak count ratios Angle A/T B/T C/T 0 o o o o o o o o o o o o Similar effect can be seen for effect of changing value in Table.. Maximum count ratio belonging to the detector A and minimum count ratio belonging to the detector B is at 0 o and 0 o as expected. These ratios increase for the detector A and decrease for the detector B with increasing. Finally the ratio belonging to the detector A reaches its minimum at 0 o and 0 o at which the ratio belonging to the detector B is in its maximum. This situation seems only for and MeV energy values and the ratio belonging to the detector C remain almost constant as mentioned above. Thereby in this method, the gamma-ray direction can be determined by using knowledge of the count ratios of each three detector.
8 Table. Changing of photopeak counts ratios by for fixed. Analyses were performed for, and 0 MeV gamma-rays. E ( MeV ) 0 0 o Angle Photopeak count ratios A/T B/T C/T 0 o o o o o o o o o o o o 0, The results are also given for fixed values and different gamma-ray energies in Figs.. In Figs..a and.b, for and MeV gamma-rays and fixed, decreases and increases in count ratios of the detector A and B, respectively, are obviously seen while for the detector C's stays nearly same level. By increasing, the gamma-ray beams shift toward the detector B from A. Therefore, the surface area of the detector A viewed by gamma-rays decreases and the area of the detector B increases. Additionally it is evidently noticed that, the count ratios of A and B have same values around the o and are symmetric on both sides of that point. Moreover, at o and o, all three detector count ratios are equal due to the fact that exact symmetry of the array according to the gamma-ray beams. In Fig..c, for 0 MeV highenergy gamma-rays, an opposite situation appears. Accordingly, the ratio of the detector A increases while the detector B's decreases by increasing, as mentioned before.
9 Fig. The changing of detector photopeak count ratios by θ for MeV (a), MeV (b) and 0 MeV (c) gamma-rays.
10 0 0. Results The plots which can help for determination of the gamma-ray directions were given in Figs.. A/T, B/T and C/T count ratios versus were shown for different values in Figs.a, b and c respectively. As is seen in the Fig..a, the ratios decrease by increasing for 0 o o,0 and 0 o because of shifting gamma-ray beam from surface of the detector A to B. So, the ratios related to detector B increase for same angles (Fig..b). There is a different situation for 0 o. In this case, change of the θ does not alter the ratios, due to the gamma- ray beam stays perpendicular to lateral surface of the detector A and B in every values. From the Fig..c, one can see that the count ratios for every values stay nearly steady even changes. The reason for this is is only associated with the detector A and B, not C. A value which is not used previously in the plots was used for basic test of the success of the method. For MeV gamma-rays and A/T=0,, B/T=0, and C/T=0, ratios, by simultaneous investigation of each three plots (Figs.), the direction of the gamma-rays can be determined by about 0 o deviations from true values of o and 0 o.
11 Fig. The changing of detector photopeak count ratios by θ for A/T (a), B/T (b) and C/T (c).. Conclusions We have performed Geant simulations in order to demonstrate the ability of our designed detection system for identification of the gamma-ray directions. The method is based on the relative counts registered in different detectors in the array. According to the results,
12 directional information of the gamma-rays was obtained by using developed method with 0 o accuracy. Besides the application of the method in space, this array can also be useful for measurements of terrestrial gamma-rays, determination of the location of radioactive sources and explanation dose rate differences found by car-borne measurement 0 0 References [] G.J. Fishman and C.A. Meegan, Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics () -. [] S.E. Woosley and J.S. Bloom,. 00, arxiv:astro-ph/00v. [] L.J. Gou et al., A&A (00) -0. [] B. Zhang, Advances in Space Research 0 (00a) -. [] D. W. Fox, et al., Nature (00) -. [] Ph. Podsiadlowski et al., The Astrophysical Journal 0 (00) L-L0. [] T. Piran, Physics Reports () -. [] J. van Paradijs, et al., Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics (000) -. [] P. Mészáros, Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics 0 (00) -. [0] B. Zhang and P. Mészáros, Inernational Journal of Modern Physics A (00). [] B. Zhang, Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics No. (00b) -0. [] W.N. Johnson et al., The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series () -. [] R.M. Kippen et al., The Astropysical Journal () -. [] D.J. Thompson, et al., Journal of Geophysical Research, 0 No.A PP. () -, 0. [] A. Gomboc, Contemporary Physics No. (0) -. [] R. Aloisio, et al., Astroparticle Physics (0) -. [] Y. Shirakawa, Nucl.Instrum.Meth. Phys. Res. B (00) -. [] T. Tanimori, et al., 00 arxiv:astro-ph/00v. [] K. Fujimoto and Y. Noda, Radioactivity in the Environment (00) -. [0] Y. Shirakawa, Nucl.Instrum.Meth. Phys. Res. B (00) -. [] E. Suarez-Garcia, et al., Nucl.Instrum.Meth. Phys. Res. A (00) -.
13 [] N. Schemm, et al., Proceedings of IEEE Sensors (0) 0-. [] G.J. Fishman, et al., Science () -. [] S. Agostinelli, et al., Nucl.Instrum.Meth. Phys. Res. A 0 (00) 0-0.
Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Astro 129: Chapter 1a
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
The Discovery of Gamma-Ray Bursts
 The Discovery of Gamma-Ray Bursts The serendipitous discovery of Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs) in the late sixties puzzled astronomers for several decades: GRBs are pulses of gamma-ray radiation (typically lasting
The Discovery of Gamma-Ray Bursts The serendipitous discovery of Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs) in the late sixties puzzled astronomers for several decades: GRBs are pulses of gamma-ray radiation (typically lasting
Detectors for 20 kev 10 MeV
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Detectors for 20 kev to 10 MeV Discovery The early years BATSE Fast versus slow bursts Uniformity and log N log S relation BeppoSAX and discovery of afterglows Redshift measurements Connection
Gamma-Ray Bursts Detectors for 20 kev to 10 MeV Discovery The early years BATSE Fast versus slow bursts Uniformity and log N log S relation BeppoSAX and discovery of afterglows Redshift measurements Connection
Rest-frame properties of gamma-ray bursts observed by the Fermi Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor
 Rest-frame properties of gamma-ray bursts observed by the Fermi Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor on behalf of the Fermi/GBM collaboration Max Planck Institute for extraterrestrial Physics, Giessenbachstr. 1., 85748
Rest-frame properties of gamma-ray bursts observed by the Fermi Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor on behalf of the Fermi/GBM collaboration Max Planck Institute for extraterrestrial Physics, Giessenbachstr. 1., 85748
Gamma-ray Astronomy Missions, and their Use of a Global Telescope Network
 Gamma-ray Astronomy Missions, and their Use of a Global Telescope Network The Big Picture Whole sky glows Extreme environments Probes of the Universe CGRO/EGRET All Sky Map Early Gamma-ray Astronomy Gamma-ray
Gamma-ray Astronomy Missions, and their Use of a Global Telescope Network The Big Picture Whole sky glows Extreme environments Probes of the Universe CGRO/EGRET All Sky Map Early Gamma-ray Astronomy Gamma-ray
Construction and Preliminary Application of the Variability Luminosity Estimator
 Construction and Preliminary Application of the Variability Luminosity Estimator arxiv:astro-ph/0103255v2 19 Mar 2001 Daniel E. Reichart 1,2 and Donald Q. Lamb 3 1 Department of Astronomy, California Institute
Construction and Preliminary Application of the Variability Luminosity Estimator arxiv:astro-ph/0103255v2 19 Mar 2001 Daniel E. Reichart 1,2 and Donald Q. Lamb 3 1 Department of Astronomy, California Institute
Position Sensitive Germanium Detectors for the Advanced Compton Telescope
 Position Sensitive Germanium Detectors for the Advanced Compton Telescope R.A. Kroeger 1, W.N. Johnson 1, J.D. Kurfess 1, B.F. Phlips, P.N. Luke 3, M. Momayezi 4, W.K. Warburton 4 1 Naval Research Laboratory,
Position Sensitive Germanium Detectors for the Advanced Compton Telescope R.A. Kroeger 1, W.N. Johnson 1, J.D. Kurfess 1, B.F. Phlips, P.N. Luke 3, M. Momayezi 4, W.K. Warburton 4 1 Naval Research Laboratory,
Science of Compact X-Ray and Gamma-ray Objects: MAXI and GLAST
 Science of Compact X-Ray and Gamma-ray Objects: MAXI and GLAST D. J. Thompson, 1 on behalf of the GLAST LAT Collaboration 1 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 USA E-mail(DJT): David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov
Science of Compact X-Ray and Gamma-ray Objects: MAXI and GLAST D. J. Thompson, 1 on behalf of the GLAST LAT Collaboration 1 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 USA E-mail(DJT): David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov
The Angular Distribution of. COMPTEL Gamma-Ray Bursts. R.M. Kippen, J. Ryan, A. Connors, M. McConnell,
 The Angular Distribution of COMPTEL Gamma-Ray Bursts R.M. Kippen, J. Ryan, A. Connors, M. McConnell, D.H. Hartmann y, C. Winkler z, L.O. Hanlon z, V. Schonfelder x, J. Greiner x, M. Varendor x, W. Collmar
The Angular Distribution of COMPTEL Gamma-Ray Bursts R.M. Kippen, J. Ryan, A. Connors, M. McConnell, D.H. Hartmann y, C. Winkler z, L.O. Hanlon z, V. Schonfelder x, J. Greiner x, M. Varendor x, W. Collmar
MeV Quasar Observations with the. COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory
 MeV Quasar Observations with the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory 1. Introduction Extragalactic gamma-ray astronomy barely existed prior to the launch of the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) but there
MeV Quasar Observations with the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory 1. Introduction Extragalactic gamma-ray astronomy barely existed prior to the launch of the COMPTON Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) but there
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 21 (11/29/06) Detection of Nuclear Radiation: Pulse Height Spectra
 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 21 (11/29/06) Detection of Nuclear Radiation: Pulse Height Spectra References: W. E. Meyerhof, Elements of Nuclear Physics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1967),
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 21 (11/29/06) Detection of Nuclear Radiation: Pulse Height Spectra References: W. E. Meyerhof, Elements of Nuclear Physics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1967),
Gamma-ray Bursts. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Gamma-ray Bursts At the moment, the most important application of the theory of relativistic shock waves is in explaining the radiation from Gamma-ray Burst sources. I will briefly introduce
Chapter 4 Gamma-ray Bursts At the moment, the most important application of the theory of relativistic shock waves is in explaining the radiation from Gamma-ray Burst sources. I will briefly introduce
A NEW GENERATION OF GAMMA-RAY TELESCOPE
 A NEW GENERATION OF GAMMA-RAY TELESCOPE Aleksandar GOSTOJIĆ CSNSM, Orsay, France 11 th Russbach School on Nuclear Astrophysics, March 2014. Introduction: Gamma-ray instruments GROUND BASED: ENERGY HIGHER
A NEW GENERATION OF GAMMA-RAY TELESCOPE Aleksandar GOSTOJIĆ CSNSM, Orsay, France 11 th Russbach School on Nuclear Astrophysics, March 2014. Introduction: Gamma-ray instruments GROUND BASED: ENERGY HIGHER
April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9,
 April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10,
April 13, 2011 Exam 4, Friday. Review sheet posted. Sky Watch 4 due. Review session Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 3.502, right here! Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10,
THE COMPTON EFFECT Last Revised: January 5, 2007
 B2-1 THE COMPTON EFFECT Last Revised: January 5, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: How does the energy of a scattered photon change after an interaction with an electron? INTRODUCTION: When a photon is
B2-1 THE COMPTON EFFECT Last Revised: January 5, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: How does the energy of a scattered photon change after an interaction with an electron? INTRODUCTION: When a photon is
GAMMA RAYS. 1 P a g e
 GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
RXTE Observations of PKS during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst
 RXTE Observations of PKS 2155-304 during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst W. Thomas Vestrand a and P. Sreekumar b a Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824 arxiv:astro-ph/9901404v1
RXTE Observations of PKS 2155-304 during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst W. Thomas Vestrand a and P. Sreekumar b a Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824 arxiv:astro-ph/9901404v1
GAMMA-RAY BURSTS. mentor: prof.dr. Andrej Čadež
 GAMMA-RAY BURSTS author: Uroš Kostić mentor: prof.dr. Andrej Čadež Abstract Gamma-ray bursts (GRB) are sudden, intense flashes of gamma rays which, for a few seconds, light up in otherwise dark gamma-ray
GAMMA-RAY BURSTS author: Uroš Kostić mentor: prof.dr. Andrej Čadež Abstract Gamma-ray bursts (GRB) are sudden, intense flashes of gamma rays which, for a few seconds, light up in otherwise dark gamma-ray
1. GAMMA-RAY BURSTS & 2. FAST RADIO BURSTS
 1. GAMMA-RAY BURSTS & 2. FAST RADIO BURSTS WITH TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR) GAMMA-RAY BURST OBSERVATIONS WITH CTA LESSONS LEARNT FROM FERMI/LAT TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR,
1. GAMMA-RAY BURSTS & 2. FAST RADIO BURSTS WITH TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR) GAMMA-RAY BURST OBSERVATIONS WITH CTA LESSONS LEARNT FROM FERMI/LAT TAM, Pak Hin (Sun Yat-sen University/ICRR,
Using Gamma Ray Bursts to Estimate Luminosity Distances. Shanel Deal
 Using Gamma Ray Bursts to Estimate Luminosity Distances Shanel Deal University of Notre Dame Summer Research Experience for Undergraduate 2013 Program Dr. Peter Garnavich August 2, 2013 Abstract Gamma
Using Gamma Ray Bursts to Estimate Luminosity Distances Shanel Deal University of Notre Dame Summer Research Experience for Undergraduate 2013 Program Dr. Peter Garnavich August 2, 2013 Abstract Gamma
GRB detection at ground level using Water Cerenkov Tanks
 GRB detection at ground level using Water Cerenkov Tanks Hugo Rivera May 21, 2009 Outline 1 Gamma Ray Bursts Discovery BATSE Beppo-SAX SWIFT 2 Water Cherenkov Tanks Single Particle Technique WCD calibration
GRB detection at ground level using Water Cerenkov Tanks Hugo Rivera May 21, 2009 Outline 1 Gamma Ray Bursts Discovery BATSE Beppo-SAX SWIFT 2 Water Cherenkov Tanks Single Particle Technique WCD calibration
The Fermi Zoo : GRB prompt spectra. Michael S. Briggs (Univ. Alabama in Huntsville) for the Fermi GBM & LAT Teams
 The Fermi Zoo : GRB prompt spectra Michael S. Briggs (Univ. Alabama in Huntsville) for the Fermi GBM & LAT Teams Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 1 Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 2 Before Fermi:
The Fermi Zoo : GRB prompt spectra Michael S. Briggs (Univ. Alabama in Huntsville) for the Fermi GBM & LAT Teams Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 1 Multi-Messenger Workshop KIAA 2013 2 Before Fermi:
Gamma-Ray Bursts.
 A Cosmic Gamma-Ray Burst, GRB for short, is a brief, bright flash of gamma-rays lasting typically about 20 seconds that comes from an unpredictable location in the sky. Gamma-Ray Bursts http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap120312.html
A Cosmic Gamma-Ray Burst, GRB for short, is a brief, bright flash of gamma-rays lasting typically about 20 seconds that comes from an unpredictable location in the sky. Gamma-Ray Bursts http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap120312.html
Gamma-Ray Bursts.
 Gamma-Ray Bursts http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap120312.html http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap120310.html A Cosmic Gamma-Ray Burst, GRB for short, is a brief, bright flash of gamma-rays lasting typically about
Gamma-Ray Bursts http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap120312.html http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap120310.html A Cosmic Gamma-Ray Burst, GRB for short, is a brief, bright flash of gamma-rays lasting typically about
Development of a Hard X-Ray Polarimeter for Solar Flares and Gamma-Ray Bursts
 Development of a Hard X-Ray Polarimeter for Solar Flares and Gamma-Ray Bursts M.L. McConnell, D.J. Forrest, J. Macri, M. McClish, M. Osgood, J.M. Ryan, W.T. Vestrand and C. Zanes Space Science Center University
Development of a Hard X-Ray Polarimeter for Solar Flares and Gamma-Ray Bursts M.L. McConnell, D.J. Forrest, J. Macri, M. McClish, M. Osgood, J.M. Ryan, W.T. Vestrand and C. Zanes Space Science Center University
Gamma-Ray Bursts and their Afterglows
 Seminar Ib Gamma-Ray Bursts and their Afterglows Mentor: Izr. prof. dr. Andreja Gomboc Author: Katja Bricman Ljubljana, May 2015 Abstract Gamma ray bursts (GRBs) are short flashes of gamma rays, that can
Seminar Ib Gamma-Ray Bursts and their Afterglows Mentor: Izr. prof. dr. Andreja Gomboc Author: Katja Bricman Ljubljana, May 2015 Abstract Gamma ray bursts (GRBs) are short flashes of gamma rays, that can
Gamma-Ray Bursts from High. Velocity Neutron Stars. Tomasz Bulik and Donald Q. Lamb. Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics. University of Chicago
 Gamma-Ray Bursts from High Velocity Neutron Stars Tomasz Bulik and Donald Q. Lamb Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago 5640 South Ellis Avenue Chicago, IL 60637 We investigate
Gamma-Ray Bursts from High Velocity Neutron Stars Tomasz Bulik and Donald Q. Lamb Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago 5640 South Ellis Avenue Chicago, IL 60637 We investigate
A New Look at the Galactic Diffuse GeV Excess
 A New Look at the Galactic Diffuse GeV Excess Brian Baughman Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics 1 Overview Diffuse gamma-ray emission The Galactic diffuse gamma-ray GeV excess Discussion of the
A New Look at the Galactic Diffuse GeV Excess Brian Baughman Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics 1 Overview Diffuse gamma-ray emission The Galactic diffuse gamma-ray GeV excess Discussion of the
1. Motivation & Detector concept 2. Performance 3. Confirmation experiments 4. Summary
 A. Takada, T. Tanimori, H. Kubo, J. D. Parker, T. Mizumoto, Y. Mizumura, T. Sawano, K. Nakamura, Y. Matsuoka, S. Komura, S. Nakamura, T. Kishimoto, M. Oda, T. Takemura, S. Miyamoto, K. Miuchi, S. Kurosawa
A. Takada, T. Tanimori, H. Kubo, J. D. Parker, T. Mizumoto, Y. Mizumura, T. Sawano, K. Nakamura, Y. Matsuoka, S. Komura, S. Nakamura, T. Kishimoto, M. Oda, T. Takemura, S. Miyamoto, K. Miuchi, S. Kurosawa
Following up Fermi GBM Gamma-Ray Bursts
 Following up Fermi GBM Gamma-Ray Bursts V. Connaughton, and M. S. Briggs University of Alabama, Huntsville A. Goldstein (NASA Postdoctoral Fellow) NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Abstract The Fermi Gamma-Ray
Following up Fermi GBM Gamma-Ray Bursts V. Connaughton, and M. S. Briggs University of Alabama, Huntsville A. Goldstein (NASA Postdoctoral Fellow) NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Abstract The Fermi Gamma-Ray
GRB Spectra and their Evolution: - prompt GRB spectra in the γ-regime
 GRB Spectra and their Evolution: - prompt GRB spectra in the γ-regime Andreas von Kienlin MPE -Gamma 14. November 2003 1 Outline Time averaged GRB spectra Example spectra Instrumental response Band function
GRB Spectra and their Evolution: - prompt GRB spectra in the γ-regime Andreas von Kienlin MPE -Gamma 14. November 2003 1 Outline Time averaged GRB spectra Example spectra Instrumental response Band function
GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY: IMAGING ATMOSPHERIC CHERENKOV TECHNIQUE FABIO ZANDANEL - SESIONES CCD
 GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY: IMAGING ATMOSPHERIC CHERENKOV TECHNIQUE COSMIC RAYS Discovered in 1912 by Victor Hess (Nobel Prize) Messengers from the non-thermal part of the Universe E < 15 ev: galactic E > 17
GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY: IMAGING ATMOSPHERIC CHERENKOV TECHNIQUE COSMIC RAYS Discovered in 1912 by Victor Hess (Nobel Prize) Messengers from the non-thermal part of the Universe E < 15 ev: galactic E > 17
High-Energy Emission from GRBs: First Year Highlights from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 High-Energy Emission from GRBs: First Year Highlights from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Jonathan Granot University of Hertfordshire (Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award Holder) on behalf
High-Energy Emission from GRBs: First Year Highlights from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Jonathan Granot University of Hertfordshire (Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award Holder) on behalf
X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma Ray Bursts
 X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma Ray Bursts John Heise 1,2,Jeanin tzand 2,1,R.MarcKippen 3,andPeterM.Woods 4 1 Space Research Organization Netherlands, Utrecht, NL 3484CA Netherlands 2 Astronomical Institute,
X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma Ray Bursts John Heise 1,2,Jeanin tzand 2,1,R.MarcKippen 3,andPeterM.Woods 4 1 Space Research Organization Netherlands, Utrecht, NL 3484CA Netherlands 2 Astronomical Institute,
PHYS 3650L - Modern Physics Laboratory
 PHYS 3650L - Modern Physics Laboratory Laboratory Advanced Sheet Photon Attenuation 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory exercise are: a. To measure the mass attenuation coefficient at a gamma
PHYS 3650L - Modern Physics Laboratory Laboratory Advanced Sheet Photon Attenuation 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory exercise are: a. To measure the mass attenuation coefficient at a gamma
Development of a new MeV gamma-ray camera
 Development of a new MeV gamma-ray camera ICEPP Symposium February 16, 2004 Hakuba, Nagano, Japan Kyoto University Atsushi Takeda H. Kubo, K. Miuchi, T. Nagayoshi, Y. Okada, R. Orito, A. Takada, T. Tanimori,
Development of a new MeV gamma-ray camera ICEPP Symposium February 16, 2004 Hakuba, Nagano, Japan Kyoto University Atsushi Takeda H. Kubo, K. Miuchi, T. Nagayoshi, Y. Okada, R. Orito, A. Takada, T. Tanimori,
Space Application of Geant4 for the Japanese X-ray X Gamma-ray Mission
 Space Application of Geant4 for the Japanese X-ray X and Gamma-ray Mission Yukikatsu Terada (RIKEN, Japan), Shin Watanabe, Masanobu Ozaki, Tadayuki Takahashi (ISAS/JAXA), and Motohide Kokubun (Univ. of
Space Application of Geant4 for the Japanese X-ray X and Gamma-ray Mission Yukikatsu Terada (RIKEN, Japan), Shin Watanabe, Masanobu Ozaki, Tadayuki Takahashi (ISAS/JAXA), and Motohide Kokubun (Univ. of
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energy Astrophysics Gamma-ray Bursts Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk May 2011 Gamma-ray Bursts - Observations - Long-duration
High Energy Astrophysics Gamma-ray Bursts Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk May 2011 Gamma-ray Bursts - Observations - Long-duration
The Ulysses Supplement to the GRANAT/WATCH Catalog of. Cosmic Gamma-Ray Bursts
 The Ulysses Supplement to the GRANAT/WATCH Catalog of Cosmic Gamma-Ray Bursts K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 arxiv:astro-ph/0001019v1 3
The Ulysses Supplement to the GRANAT/WATCH Catalog of Cosmic Gamma-Ray Bursts K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 arxiv:astro-ph/0001019v1 3
Eric Howell University of Western Australia
 Using temporal distributions of transient events to characterize cosmological source populations AIGO Conference 22-24 February 2010 Eric Howell University of Western Australia Plan Brief overview cosmological
Using temporal distributions of transient events to characterize cosmological source populations AIGO Conference 22-24 February 2010 Eric Howell University of Western Australia Plan Brief overview cosmological
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Interpretation of Early Bursts
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Discovery The early years BATSE Fast versus slow bursts Uniformity and log N log S relation BeppoSAX and discovery of afterglows Redshift measurements Connection of long GRBs to supernovae
Gamma-Ray Bursts Discovery The early years BATSE Fast versus slow bursts Uniformity and log N log S relation BeppoSAX and discovery of afterglows Redshift measurements Connection of long GRBs to supernovae
Early Optical Afterglows of GRBs with 2-m Robotic Telescopes
 Early Optical Afterglows of GRBs with 2-m Robotic Telescopes Andreja Gomboc Faculty of Mathematics and Physics University of Ljubljana on behalf of a larger collaboration led by: ARI, Liverpool John Moores
Early Optical Afterglows of GRBs with 2-m Robotic Telescopes Andreja Gomboc Faculty of Mathematics and Physics University of Ljubljana on behalf of a larger collaboration led by: ARI, Liverpool John Moores
Hydrodynamic Evolution of GRB Afterglow
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 1, No. 4, (2001) 349 356 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Hydrodynamic Evolution of GRB Afterglow Ji-Rong
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 1, No. 4, (2001) 349 356 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Hydrodynamic Evolution of GRB Afterglow Ji-Rong
Tracking and imaging gamma ray experiment (TIGRE) for 1 to 100 MEV gamma ray astronomy
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Space Science Center Institute for the Study of Earth, Oceans, and Space (EOS) 1994 Tracking and imaging gamma ray experiment
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Space Science Center Institute for the Study of Earth, Oceans, and Space (EOS) 1994 Tracking and imaging gamma ray experiment
Extreme Astronomy and Supernovae. Professor Lynn Cominsky Department of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University
 Extreme Astronomy and Supernovae Professor Lynn Cominsky Department of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University What are X- & Gamma rays? Why study X- & gamma rays? Universe as seen by eye is peaceful
Extreme Astronomy and Supernovae Professor Lynn Cominsky Department of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University What are X- & Gamma rays? Why study X- & gamma rays? Universe as seen by eye is peaceful
Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics Astroparticle Physics Lecture 5 Gamma Rays & x-rays Sept. 22, 2015 Sun Kee Kim Seoul National University Gamma ray astronomy gamma ray synchrotron radition
Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics Astroparticle Physics Lecture 5 Gamma Rays & x-rays Sept. 22, 2015 Sun Kee Kim Seoul National University Gamma ray astronomy gamma ray synchrotron radition
Two Space High Energy Astrophysics Missions of China: POLAR & HXMT
 Two Space High Energy Astrophysics Missions of China: POLAR & HXMT Shuang-Nan Zhang ( 张双南 ) Institute of High Energy Physics National Astronomical Observatories of China Chinese Academy of Sciences 1/22
Two Space High Energy Astrophysics Missions of China: POLAR & HXMT Shuang-Nan Zhang ( 张双南 ) Institute of High Energy Physics National Astronomical Observatories of China Chinese Academy of Sciences 1/22
ON GRB PHYSICS REVEALED BY FERMI/LAT
 Proceedings of the 3rd Galileo Xu Guangqi Meeting International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 23 (2013) 223 227 c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194513011343
Proceedings of the 3rd Galileo Xu Guangqi Meeting International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 23 (2013) 223 227 c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194513011343
Gamma Ray Physics in the Fermi era. F.Longo University of Trieste and INFN
 Gamma Ray Physics in the Fermi era F.Longo University of Trieste and INFN Vulcano, May 22, 2018 F.Longo et al. -- 1 Gamma-ray astrophysics above 100 MeV AGILE Fermi 2 Picture of the day, Feb. 28, 2011,
Gamma Ray Physics in the Fermi era F.Longo University of Trieste and INFN Vulcano, May 22, 2018 F.Longo et al. -- 1 Gamma-ray astrophysics above 100 MeV AGILE Fermi 2 Picture of the day, Feb. 28, 2011,
H. Hofer, C. Lechanoine-Leluc, S. Orsi, M. Pohl, D. Rapin, E.Suarez-Garcia
 : a space borne GRB polarimeter G. Lamanna, N. Fouque, R. Hermel, J.P. Vialle LAPP, Université de Savoie, CNRS/IN2P3, Annecy-le-Vieux, France E-mail: giovanni.lamanna@lapp.in2p3.fr H. Hofer, C. Lechanoine-Leluc,
: a space borne GRB polarimeter G. Lamanna, N. Fouque, R. Hermel, J.P. Vialle LAPP, Université de Savoie, CNRS/IN2P3, Annecy-le-Vieux, France E-mail: giovanni.lamanna@lapp.in2p3.fr H. Hofer, C. Lechanoine-Leluc,
The spectacular stellar explosion - GRB A: synchrotron modeling in the wind and the ISM
 The spectacular stellar explosion - GRB 17A: synchrotron moeling in the win an the ISM University of Johannesburg, Department of Physics, Aucklan Park 6, Johannesburg, South Africa E-mail: jessymolkt@uj.ac.za
The spectacular stellar explosion - GRB 17A: synchrotron moeling in the win an the ISM University of Johannesburg, Department of Physics, Aucklan Park 6, Johannesburg, South Africa E-mail: jessymolkt@uj.ac.za
COMPTON OBSERVATORY OBSERVATIONS OF AGN
 COMPTON OBSERVATORY OBSERVATIONS OF AGN J. D. Kurfess Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375 ABSTRACT. The principal results on active galactic nuclei from the Phase 1 observations by the COMPTON
COMPTON OBSERVATORY OBSERVATIONS OF AGN J. D. Kurfess Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375 ABSTRACT. The principal results on active galactic nuclei from the Phase 1 observations by the COMPTON
hν' Φ e - Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous?
 Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous? 2. Briefly discuss dead time in a detector. What factors are important
Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous? 2. Briefly discuss dead time in a detector. What factors are important
First Results of POLAR: A dedicated Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter
 First Results of POLAR: A dedicated Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter DPNC, University of Geneva E-mail: merlin.kole@unige.ch This year marks the 50th anniversary of the first detection of a Gamma-Ray Burst.
First Results of POLAR: A dedicated Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter DPNC, University of Geneva E-mail: merlin.kole@unige.ch This year marks the 50th anniversary of the first detection of a Gamma-Ray Burst.
Development of a 3D-Imaging Calorimeter in LaBr 3 for Gamma-Ray Space Astronomy
 Development of a 3D-Imaging Calorimeter in LaBr 3 for Gamma-Ray Space Astronomy Aleksandar GOSTOJIĆ CSNSM, Orsay, France 7 th New Developmeants In Photodetection, Tours, France, 2014 Introduction: Gamma-ray
Development of a 3D-Imaging Calorimeter in LaBr 3 for Gamma-Ray Space Astronomy Aleksandar GOSTOJIĆ CSNSM, Orsay, France 7 th New Developmeants In Photodetection, Tours, France, 2014 Introduction: Gamma-ray
DETECTABILITY AND MODELING OF HIGH-REDSHIFT GRBS
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics DETECTABILITY AND MODELING OF HIGH-REDSHIFT GRBS A Thesis in Astronomy and Astrophysics by Li-Jun Gou c 007
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics DETECTABILITY AND MODELING OF HIGH-REDSHIFT GRBS A Thesis in Astronomy and Astrophysics by Li-Jun Gou c 007
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy. HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric
 Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
Precise Interplanetary Network Localization of a New Soft. Gamma Repeater, SGR
 Precise Interplanetary Network Localization of a New Soft Gamma Repeater, SGR1627-41 K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 C. Kouveliotou Universities
Precise Interplanetary Network Localization of a New Soft Gamma Repeater, SGR1627-41 K. Hurley University of California, Berkeley, Space Sciences Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720-7450 C. Kouveliotou Universities
Space Astronomy Facilities
 ASI and bi/multilateral Space Astronomy Facilities Paolo Giommi Italian Space Agency, ASI 10 February 2010 COPUOS - Vienna 1 AGILE: an Italian Small Mission AGILE: an Italian small scientific mission Devoted
ASI and bi/multilateral Space Astronomy Facilities Paolo Giommi Italian Space Agency, ASI 10 February 2010 COPUOS - Vienna 1 AGILE: an Italian Small Mission AGILE: an Italian small scientific mission Devoted
Response Function of the BGO and NaI(Tl) Detectors Using Monte Carlo Simulations
 Response Function of the BGO and NaI(Tl) Detectors Using Monte Carlo Simulations 271 I. ORION 1,2 1 AND L. WIELOPOLSKI 2, 1 St. Luke=s/Roosevelt Hospital, Columbia University, New York, NY 10025,USA 2
Response Function of the BGO and NaI(Tl) Detectors Using Monte Carlo Simulations 271 I. ORION 1,2 1 AND L. WIELOPOLSKI 2, 1 St. Luke=s/Roosevelt Hospital, Columbia University, New York, NY 10025,USA 2
Background and Sensitivity Simulation of a Space Based Germanium Compton Telescope
 Background and Sensitivity Simulation of a Space Based Germanium Compton Telescope B. L. Graham George Mason University, Institute for Computational Sciences and Informatics, 4400 University Dr, Fairfax
Background and Sensitivity Simulation of a Space Based Germanium Compton Telescope B. L. Graham George Mason University, Institute for Computational Sciences and Informatics, 4400 University Dr, Fairfax
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 29 May 2000
 Effects of Luminosity Functions Induced by Relativistic Beaming on Statistics of Cosmological Gamma-Ray Bursts Chunglee Kim, Heon-Young Chang, and Insu Yi arxiv:astro-ph/5556v 29 May 2 Korea Institute
Effects of Luminosity Functions Induced by Relativistic Beaming on Statistics of Cosmological Gamma-Ray Bursts Chunglee Kim, Heon-Young Chang, and Insu Yi arxiv:astro-ph/5556v 29 May 2 Korea Institute
1 Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter GAP aboard
 1 Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter GAP aboard the Solar Powered Sail Mission Daisuke Yonetoku, Toshio Murakami, Hirofumi Fujimoto, Tomonori Sakashita (Kanazawa University) Shuichi Gunji, Noriyuki Toukairin
1 Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter GAP aboard the Solar Powered Sail Mission Daisuke Yonetoku, Toshio Murakami, Hirofumi Fujimoto, Tomonori Sakashita (Kanazawa University) Shuichi Gunji, Noriyuki Toukairin
Radiation Detection and Measurement
 Radiation Detection and Measurement June 2008 Tom Lewellen Tkldog@u.washington.edu Types of radiation relevant to Nuclear Medicine Particle Symbol Mass (MeV/c 2 ) Charge Electron e-,! - 0.511-1 Positron
Radiation Detection and Measurement June 2008 Tom Lewellen Tkldog@u.washington.edu Types of radiation relevant to Nuclear Medicine Particle Symbol Mass (MeV/c 2 ) Charge Electron e-,! - 0.511-1 Positron
Effect of Rapid Evolution of Magnetic Tilt Angle of a Newborn Magnetar on Light Curve of Gamma-ray Burst
 Effect of Rapid Evolution of Magnetic Tilt Angle of a Newborn Magnetar on Light Curve of Gamma-ray Burst Department of Physics, Jiangxi Science & Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330013, China E-mail:
Effect of Rapid Evolution of Magnetic Tilt Angle of a Newborn Magnetar on Light Curve of Gamma-ray Burst Department of Physics, Jiangxi Science & Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330013, China E-mail:
Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts
 Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts B.L. Dingus and the Milagro Collaboration Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Maryland, University of California Santa Cruz, University of California
Milagro A TeV Observatory for Gamma Ray Bursts B.L. Dingus and the Milagro Collaboration Los Alamos National Laboratory University of Maryland, University of California Santa Cruz, University of California
INTRODUCTION. As shown in Figure 1a, the phenomena of lightningmesosphere-ionosphere
 ABSTRACT Intense, transient quasi-electrostatic (QE) fields, which exist above the thunderclouds following a positive cloud-to-ground lightning discharge, can produce an upward travelling runaway electron
ABSTRACT Intense, transient quasi-electrostatic (QE) fields, which exist above the thunderclouds following a positive cloud-to-ground lightning discharge, can produce an upward travelling runaway electron
GAMMA-RAY BURST PHYSICS WITH GLAST
 SLAC-PUB-110 October 006 GAMMA-RAY BURST PHYSICS WITH GLAST N. OMODEI INFN sez. Pisa, Edificio C - Polo Fibonacci - Largo B. Pontecorvo, PISA, E-mail: nicola.omodei@pi.infn.it The Gamma-ray Large Area
SLAC-PUB-110 October 006 GAMMA-RAY BURST PHYSICS WITH GLAST N. OMODEI INFN sez. Pisa, Edificio C - Polo Fibonacci - Largo B. Pontecorvo, PISA, E-mail: nicola.omodei@pi.infn.it The Gamma-ray Large Area
Detection and measurement of gamma-radiation by gammaspectroscopy
 Detection and measurement of gamma-radiation by gammaspectroscopy Gamma-radiation is electromagnetic radiation having speed equal to the light in vacuum. As reaching a matter it interact with the different
Detection and measurement of gamma-radiation by gammaspectroscopy Gamma-radiation is electromagnetic radiation having speed equal to the light in vacuum. As reaching a matter it interact with the different
Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments
 Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments David J. Thompson NASA Goddard Space Flight Center GLAST Large Area Telescope Collaboration djt@egret.gsfc.nasa.gov D. Thompson 363 rd Heraeus
Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments David J. Thompson NASA Goddard Space Flight Center GLAST Large Area Telescope Collaboration djt@egret.gsfc.nasa.gov D. Thompson 363 rd Heraeus
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Dec 2003
 Observation and implications of the E peak - E iso correlation in Gamma-Ray Bursts arxiv:astro-ph/0312371v1 15 Dec 2003 J-L. Atteia, G. R. Ricker, D. Q. Lamb, T. Sakamoto, C. Graziani, T. Donaghy, C. Barraud
Observation and implications of the E peak - E iso correlation in Gamma-Ray Bursts arxiv:astro-ph/0312371v1 15 Dec 2003 J-L. Atteia, G. R. Ricker, D. Q. Lamb, T. Sakamoto, C. Graziani, T. Donaghy, C. Barraud
Cosmic Gamma-ray Bursts Studies with Ioffe Institute Konus Experiments
 Cosmic Gamma-ray Bursts Studies with Ioffe Institute Konus Experiments R. L. Aptekar 1, S. V. Golenetskii, D. D. Frederiks, E. P. Mazets and V. D. Palshin Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute St. Petersburg,
Cosmic Gamma-ray Bursts Studies with Ioffe Institute Konus Experiments R. L. Aptekar 1, S. V. Golenetskii, D. D. Frederiks, E. P. Mazets and V. D. Palshin Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute St. Petersburg,
Scintillation Detector
 Scintillation Detector Introduction The detection of ionizing radiation by the scintillation light produced in certain materials is one of the oldest techniques on record. In Geiger and Marsden s famous
Scintillation Detector Introduction The detection of ionizing radiation by the scintillation light produced in certain materials is one of the oldest techniques on record. In Geiger and Marsden s famous
SPECTRAL STUDIES OF GAMMA-RAY BURST PROMPT EMISSION YUKI KANEKO A DISSERTATION
 SPECTRAL STUDIES OF GAMMA-RAY BURST PROMPT EMISSION by YUKI KANEKO A DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in The Department of Physics
SPECTRAL STUDIES OF GAMMA-RAY BURST PROMPT EMISSION by YUKI KANEKO A DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in The Department of Physics
Shallow Decay of X-ray Afterglows in Short GRBs: Energy Injection from a Millisecond Magnetar?
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 7 2007), No. 5, 669 674 http://www.chjaa.org) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Shallow Decay of X-ray Afterglows in Short GRBs: Energy Injection from a Millisecond
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 7 2007), No. 5, 669 674 http://www.chjaa.org) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Shallow Decay of X-ray Afterglows in Short GRBs: Energy Injection from a Millisecond
Dark Matter Particle Explorer: The First Chinese Cosmic Ray and Hard γ-ray Detector in Space
 SPACE SCIENCE ACTIVITIES IN CHINA Dark Matter Particle Explorer: The First Chinese Cosmic Ray and Hard γ-ray Detector in Space AUTHORS CHANG Jin Key Laboratory of Dark Matter and Space Astronomy, Purple
SPACE SCIENCE ACTIVITIES IN CHINA Dark Matter Particle Explorer: The First Chinese Cosmic Ray and Hard γ-ray Detector in Space AUTHORS CHANG Jin Key Laboratory of Dark Matter and Space Astronomy, Purple
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 8 May 2005
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO Vol.?, N.?? arxiv:astro-ph/0505156v1 8 May 2005 Jet Models of X-Ray Flashes D. Q. Lamb( 1 ), T. Q. Donaghy( 1 ) & C. Graziani( 1 ) ( 1 ) Dept. of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of
IL NUOVO CIMENTO Vol.?, N.?? arxiv:astro-ph/0505156v1 8 May 2005 Jet Models of X-Ray Flashes D. Q. Lamb( 1 ), T. Q. Donaghy( 1 ) & C. Graziani( 1 ) ( 1 ) Dept. of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of
NEW SOFT BATSE GRBS AND SPECTRA OF X-RAY RICH BURSTS
 1 NEW SOFT BATSE GRBS AND SPECTRA OF X-RAY RICH BURSTS Yana Tikhomirova 1, Boris Stern 2,1, Alexandra Kozyreva 3, and Juri Poutanen 4 1 Astro Space Centre, P.N. Lebedev Physical Institute, Profsoyuznaya
1 NEW SOFT BATSE GRBS AND SPECTRA OF X-RAY RICH BURSTS Yana Tikhomirova 1, Boris Stern 2,1, Alexandra Kozyreva 3, and Juri Poutanen 4 1 Astro Space Centre, P.N. Lebedev Physical Institute, Profsoyuznaya
High-Energy Spectral Signatures in Gamma-Ray Bursts
 To appear in Proc. of Snowbird TeV Gamma-Ray Workshop ed. B. L. Dingus (AIP, New York, 1999) High-Energy Spectral Signatures in Gamma-Ray Bursts Matthew G. Baring arxiv:astro-ph/9911061v1 4 Nov 1999 Laboratory
To appear in Proc. of Snowbird TeV Gamma-Ray Workshop ed. B. L. Dingus (AIP, New York, 1999) High-Energy Spectral Signatures in Gamma-Ray Bursts Matthew G. Baring arxiv:astro-ph/9911061v1 4 Nov 1999 Laboratory
The Cosmic Microwave Background
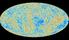 The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
BATSE Evidence for GRB Spectral Features
 BATSE Evidence for GRB Spectral Features M. S. Briggs, D. L. Band, R. D. Preece, G. N. Pendleton, W. S. Paciesas & J. L. Matteson arxiv:astro-ph/9712096v1 5 Dec 1997 Department of Physics, University of
BATSE Evidence for GRB Spectral Features M. S. Briggs, D. L. Band, R. D. Preece, G. N. Pendleton, W. S. Paciesas & J. L. Matteson arxiv:astro-ph/9712096v1 5 Dec 1997 Department of Physics, University of
Theory of the prompt emission of Gamma-Ray Bursts
 Theory of the prompt emission of Gamma-Ray Bursts Department of Physics, NC State University, Raleigh, NC 27695-8202 E-mail: davide_lazzati@ncsu.edu Since their discovery more than 40 years ago the origin
Theory of the prompt emission of Gamma-Ray Bursts Department of Physics, NC State University, Raleigh, NC 27695-8202 E-mail: davide_lazzati@ncsu.edu Since their discovery more than 40 years ago the origin
Gamma-Ray Bursts - I. Stellar Transients / Gamma Ray Bursts I 1
 Gamma-Ray Bursts - I Stellar Transients / Gamma Ray Bursts I 1 Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs).. are brief (10-2 10 +3 s) and bright transients of ~1-10 3 kev radiation happening a few times per day at arbitrary
Gamma-Ray Bursts - I Stellar Transients / Gamma Ray Bursts I 1 Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs).. are brief (10-2 10 +3 s) and bright transients of ~1-10 3 kev radiation happening a few times per day at arbitrary
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 9 Jan 1996
 SKY COVERAGE AND BURST REPETITION arxiv:astro-ph/9601036v1 9 Jan 1996 David L. Band CASS 0111, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093 Received 1995 September 14; accepted 1996 January
SKY COVERAGE AND BURST REPETITION arxiv:astro-ph/9601036v1 9 Jan 1996 David L. Band CASS 0111, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093 Received 1995 September 14; accepted 1996 January
The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi
 INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte 22 February 2012 The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi Elena Pian INAF, Trieste Astronomical Observatory & Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa UNIFIED
INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte 22 February 2012 The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi Elena Pian INAF, Trieste Astronomical Observatory & Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa UNIFIED
Prompt GRB Optical Follow-up Experiments
 Prompt GRB Optical Follow-up Experiments Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, CA USA Upper Limits on the Prompt Optical Emission From G. G. William s PhD thesis (2000) Experimental Goal &
Prompt GRB Optical Follow-up Experiments Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, CA USA Upper Limits on the Prompt Optical Emission From G. G. William s PhD thesis (2000) Experimental Goal &
arxiv: v3 [hep-ph] 6 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v3 [hep-ph] 6 Sep 2016 arxiv: v3 [hep-ph] 6 Sep 2016](/thumbs/85/92554241.jpg) Light speed variation from gamma-ray bursts Haowei Xu a, Bo-Qiang Ma a,b,c,d, a School of Physics and State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Technology, Peking University, Beijing 1871, China b Collaborative
Light speed variation from gamma-ray bursts Haowei Xu a, Bo-Qiang Ma a,b,c,d, a School of Physics and State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Technology, Peking University, Beijing 1871, China b Collaborative
PoS(INTEGRAL 2010)062
 Fermi GBM observations of Terrestrial Gamma Flashes CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville E-mail: valerie@nasa.gov For the GBM TGF Team Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes (TGFs) are brief pulses of energetic
Fermi GBM observations of Terrestrial Gamma Flashes CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville E-mail: valerie@nasa.gov For the GBM TGF Team Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes (TGFs) are brief pulses of energetic
Downward Terrestrial Gamma Flashes Observed at the Telescope Array Surface Detector
 Downward Terrestrial Gamma Flashes Observed at the Telescope Array Surface Detector John Belz University of Utah PACIFIC 2018 Akaigawa, Hokkaido, Japan 20180215 Unknowns In Lightning Production When we
Downward Terrestrial Gamma Flashes Observed at the Telescope Array Surface Detector John Belz University of Utah PACIFIC 2018 Akaigawa, Hokkaido, Japan 20180215 Unknowns In Lightning Production When we
The Compton Effect. Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA (Dated: November 26, 2002)
 The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with BATSE
 9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with CGRO BATSE Large Area Detector (LAD) BATSE 1 of 8 BATSE Colleen A. Wilson (NASA/MSFC), for the BATSE teams at MSFC and Southampton Abstract The hard X-ray
9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with CGRO BATSE Large Area Detector (LAD) BATSE 1 of 8 BATSE Colleen A. Wilson (NASA/MSFC), for the BATSE teams at MSFC and Southampton Abstract The hard X-ray
AGILE GRBs: detections and upper limits
 AGILE GRBs: detections and upper limits Outline AGILE quick review; The GRB search pipeline; The AGILE GRBs; The GRB090618: any clue for the detectability in the E>30 MeV band? The GRB sample in the GRID
AGILE GRBs: detections and upper limits Outline AGILE quick review; The GRB search pipeline; The AGILE GRBs; The GRB090618: any clue for the detectability in the E>30 MeV band? The GRB sample in the GRID
Spectral characteristics of X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma-Ray Bursts observed by HETE-2
 Spectral characteristics of X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma-Ray Bursts observed by HETE-2 Takanori Sakamoto Department of Physics. Graduated School of Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo,
Spectral characteristics of X-ray flashes and X-ray rich Gamma-Ray Bursts observed by HETE-2 Takanori Sakamoto Department of Physics. Graduated School of Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo,
4- Locate the channel number of the peak centroid with the software cursor and note the corresponding energy. Record these values.
 EXPERIMENT 2.1 GAMMA ENERGY CALIBRATION 1- Turn the power supply on to 900 V. Turn the NIM crate on to power the amplifiers. Turn the Oscilloscope on to check the gamma pulses. The main amplifier should
EXPERIMENT 2.1 GAMMA ENERGY CALIBRATION 1- Turn the power supply on to 900 V. Turn the NIM crate on to power the amplifiers. Turn the Oscilloscope on to check the gamma pulses. The main amplifier should
New Scintillators for the Border Monitoring Equipment
 New Scintillators for the Border Monitoring Equipment M. Moszynski a a Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, PL 05-400 Otwock-Swierk, Poland Performance of new scintillators characterized by a high energy
New Scintillators for the Border Monitoring Equipment M. Moszynski a a Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, PL 05-400 Otwock-Swierk, Poland Performance of new scintillators characterized by a high energy
Suzaku-WAM soft gamma-ray all-sky monitor by the earth occultation technique
 Suzaku-WAM soft gamma-ray all-sky monitor by the earth occultation technique C.Kira 1,Y.Fukazawa 1,T.Asano 1, T.Takahashi 1,T.Uehara 1, Y.Hanabata 1, H.Takahashi 1, K.Yamaoka 2,M.Tashiro 3,Y.Terada 3,
Suzaku-WAM soft gamma-ray all-sky monitor by the earth occultation technique C.Kira 1,Y.Fukazawa 1,T.Asano 1, T.Takahashi 1,T.Uehara 1, Y.Hanabata 1, H.Takahashi 1, K.Yamaoka 2,M.Tashiro 3,Y.Terada 3,
Expected and unexpected gamma-ray emission from GRBs in light of AGILE and Fermi. Marco Tavani (INAF & University of Rome Tor Vergata)
 Expected and unexpected gamma-ray emission from GRBs in light of AGILE and Fermi Marco Tavani (INAF & University of Rome Tor Vergata) The EGRET heritage; Outline Description of the AGILE detectors for
Expected and unexpected gamma-ray emission from GRBs in light of AGILE and Fermi Marco Tavani (INAF & University of Rome Tor Vergata) The EGRET heritage; Outline Description of the AGILE detectors for
COMPTEL Observations of the Blazars 3C and CTA 102
 COMPTEL Observations of the Blazars 3C 5.3 and CTA 1 S. Zhang 1,5, W. Collmar 1, V. Schönfelder 1, H. Bloemen, W. Hermsen, M. McConnell 3, K.Bennett, O.R. Williams arxiv:astro-ph/17173v1 1 Jul 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
COMPTEL Observations of the Blazars 3C 5.3 and CTA 1 S. Zhang 1,5, W. Collmar 1, V. Schönfelder 1, H. Bloemen, W. Hermsen, M. McConnell 3, K.Bennett, O.R. Williams arxiv:astro-ph/17173v1 1 Jul 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
How do telescopes "see" on Earth and in space?
 How do telescopes "see" on Earth and in space? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 933 Level 970L TOP IMAGE: The Hubble Space Telescope orbiting in space over Earth. SECOND IMAGE:
How do telescopes "see" on Earth and in space? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 933 Level 970L TOP IMAGE: The Hubble Space Telescope orbiting in space over Earth. SECOND IMAGE:
