AST 103 Ch.1 Our Place in the Universe #2. Prof. Ken Nagamine Dept. of Physics & Astronomy UNLV
|
|
|
- Buddy Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AST 103 Ch.1 Our Place in the Universe #2 Prof. Ken Nagamine Dept. of Physics & Astronomy UNLV 1
2 Ch. 1.2 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: How big is Earth compared to our solar system? How far away are the stars? How big is the Milky Way Galaxy? How big is the universe? How do our lifetimes compare to the age of the universe? 2
3 Quiz Let s reduce the size of the solar system by a factor of 10 billion; the Sun is now the size of a large grapefruit (14cm diameter). How big is Earth on this scale? A. an atom B. a ball point C. a marble D. a golf ball 3
4 The scale of the solar system On a 1-to-10 billion scale: Sun is the size of a large grapefruit (14 cm) Earth is the size of a ball point, 15 meters away. 4
5 How far away are the stars? On our 1-to-10 billion scale, it s just a few minutes walk to Pluto. How far would you have to walk to reach Alpha Centauri? A. 1 mile B. 10 miles C. 100 miles D. the distance across the U.S. (2500 miles) 5
6 How big is the Universe? The Milky Way is one of about 100 billion galaxies stars/galaxy x galaxies = stars As many stars as grains of (dry) sand on all Earth s beaches 6
7 How do our lifetimes compare to the age of the Universe? The Cosmic Calendar: a scale on which we compress the history of the universe into 1 year. 7
8 How do our lifetimes compare to the age of the Universe? The Cosmic Calendar: a scale on which we compress the history of the universe into 1 year. 8
9 What have we learned? How big is Earth compared to our solar system? The distances between planets are huge compared to their sizes on a scale of 1-to-10 billion, Earth is the size of a ball point and the Sun is 15 meters away How far away are the stars? On the same scale, the stars are thousands of km away How big is the Milky Way galaxy? It would take more than 3,000 years to count the stars in the Milky Way Galaxy at a rate of one per second, and they are spread across 100,000 light-years 9
10 What have we learned? How big is the universe? The observable universe is 14 billion lightyears in radius and contains over 100 billion galaxies with a total number of stars comparable to the number of grains of sand on all of Earth s beaches How do our lifetimes compare to the age of the universe? On a cosmic calendar that compresses the history of the Universe into one year, human civilization is just a few seconds old, and a human lifetime is a fraction of a second 10
11 Ch. 1.3 Spaceship Earth Our goals for learning: How is Earth moving in our solar system? How is our solar system moving in the Galaxy? How do galaxies move within the Universe? Are we ever sitting still? 11
12 How is Earth moving in our solar system? Contrary to our perception, we are not sitting still. We are moving with the Earth in several ways, and at surprisingly fast speeds The Earth rotates around its axis once every day. 12
13 Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year: at an average distance of 1 AU 150 million km. with Earth s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris) and rotating in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. 13
14 Our Sun moves randomly relative to the other stars in the local Solar neighborhood typical relative speeds of more than 70,000 km/hr but stars are so far away that we cannot easily notice their motion And orbits the galaxy every 230 million years. 14
15 How do galaxies move within the universe? Galaxies are carried along with the expansion of the Universe. But how did Hubble figure out that the universe is expanding? 15
16 Edwin Hubble discovered that: All galaxies outside our Local Group are moving away from us. The more distant the galaxy, the faster it is racing away. Conclusion: We live in an expanding universe. 16
17 Are we ever sitting still? Earth rotates on axis: > 1,000 km/hr Earth orbits Sun: > 100,000 km/hr Solar system moves among stars: ~ 70,000 km/hr Milky Way rotates: ~ 800,000 km/hr Milky Way moves in Local Group Universe expands 17
18 When we say the universe is expanding, we mean that (A) everything in the universe is growing in size. (B) average distance between galaxies is growing with time. (C) the universe is getting older. (D) all of the above. Quiz 18
19 Quiz Could we see a galaxy that is 20 billion light years away? (A) Yes, if we had a big enough telescope. (B) No, because it would be beyond the bounds of our observable universe. (C) No, because a galaxy could not possibly be that far away. 19
20 Quiz The total number of stars in the observable universe is roughly equivalent to (A) the number of grains of sands on all the beaches on Earth. (B) the number of grains of sands on Miami Beach. (C) infinity. 20
21 What have we learned? How is Earth moving in our solar system? It rotates on its axis once a day and orbit the Sun at a distance of 1 A.U. = 150 million km How is our solar system moving in the Milky Way galaxy? Stars in the Local Neighborhood move randomly relative to one another and orbit the center of the Milky Way in about 230 million years 21
22 What have we learned? How do galaxies move within the universe? All galaxies beyond the Local Group are moving away from us with expansion of the Universe: the more distant they are, the faster they re moving Are we ever sitting still? No! 22
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in
Chapter 1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. A Modern View of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe Chapter Opener 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is
Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe Chapter Opener 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is
Stars. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe. What Objects Do We Find in The Universe? 8/12/2010. Our goals for learning:
 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the past? Can we see the entire universe?
1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the past? Can we see the entire universe?
Chapter 1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. A Modern View of the Universe
 Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe?
Chapter 1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe 1.1 The Scale of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe?
9/5/16. Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM. Astronomy 1001 First Assignments: Chapter 1: A Modern View of the Universe
 9/5/16 Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM Syllabus: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/syllabi/ Lecture notes: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/ lecnotes/ Exams: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/
9/5/16 Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM Syllabus: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/syllabi/ Lecture notes: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/ lecnotes/ Exams: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Star. Chapter 1: Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning:
 Chapter 1: Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our physical place in the Universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the Universe was like
Chapter 1: Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our physical place in the Universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the Universe was like
Chapter 1 Review Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. A Modern View of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe Put these objects in the correct order, from nearest to farthest from Earth: a) The Moon, Mars, the Sun, the nearest
Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition A Modern View of the Universe Put these objects in the correct order, from nearest to farthest from Earth: a) The Moon, Mars, the Sun, the nearest
Bell Ringer. want to do someday? 1. Briefly describe the Doppler effect in one sentence. 2. What do you want to do someday, like, in life?
 Bell Ringer 1. Briefly describe the Doppler effect in one sentence. 2. What do you want to do someday, like, in life? 3. How do you think science might apply to what you want to do someday? SCIENCE MATTERS
Bell Ringer 1. Briefly describe the Doppler effect in one sentence. 2. What do you want to do someday, like, in life? 3. How do you think science might apply to what you want to do someday? SCIENCE MATTERS
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe
 Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 1 TUTORIAL QUIZ
 TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 1 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. If the solar system is scaled down so that the Sun is represented by a basketball, a. a ping-pong ball located 500 feet away would properly represent
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 1 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. If the solar system is scaled down so that the Sun is represented by a basketball, a. a ping-pong ball located 500 feet away would properly represent
Measures of Astronomical Distances. Measures of Astronomical Distances
 Measures of Astronomical Distances Let s view the Universe in terms of kilometers The size of the observable universe is roughly 130,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 km! - Obviously measuring astronomical distances
Measures of Astronomical Distances Let s view the Universe in terms of kilometers The size of the observable universe is roughly 130,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 km! - Obviously measuring astronomical distances
Lecture 3: Chapter 1- Charting the Heavens. Assignment: Read Chapter 1 of Astronomy Today
 Lecture 3: Chapter 1- Charting the Heavens Assignment: Read Chapter 1 of Astronomy Today 1.2 Scientific Theory and the Scientific Method Scientific number notation Measures of Distance 1.2 Scientific
Lecture 3: Chapter 1- Charting the Heavens Assignment: Read Chapter 1 of Astronomy Today 1.2 Scientific Theory and the Scientific Method Scientific number notation Measures of Distance 1.2 Scientific
Welcome Aboard!! CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS. Briefing Welcome to the Cosmic Tour: Some Guide Lines. Lecture 1 Our Place in the Universe
 CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS (Previous) Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 (New) Tuesdays 4:45 to 5:30 Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 YOURNAME 31AUG Welcome Aboard!! AUSTIN AST 301 YOURNAME 31AUG 2.5 MILLION
CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS (Previous) Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 (New) Tuesdays 4:45 to 5:30 Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 YOURNAME 31AUG Welcome Aboard!! AUSTIN AST 301 YOURNAME 31AUG 2.5 MILLION
AST 103 The Solar System
 AST 103 The Solar System Prof. Ken Nagamine Dept. of Physics & Astronomy UNLV Pick up two items from the front table (one each): 1. Syllabus 2. ABCD card 1 Instructor Contact Info Prof. Ken Nagamine Office:
AST 103 The Solar System Prof. Ken Nagamine Dept. of Physics & Astronomy UNLV Pick up two items from the front table (one each): 1. Syllabus 2. ABCD card 1 Instructor Contact Info Prof. Ken Nagamine Office:
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration
 ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 3: Our Place in the Universe [1/19/07] Announcements Scale in the
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 3: Our Place in the Universe [1/19/07] Announcements Scale in the
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1
 Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE (Right answers are reported in red) 1.. A solar system contains a. primarily planets. b. large amounts of gas and dust
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE (Right answers are reported in red) 1.. A solar system contains a. primarily planets. b. large amounts of gas and dust
Astronomy 1010: Survey of Astronomy. University of Toledo Department of Physics and Astronomy
 Astronomy 1010: Survey of Astronomy University of Toledo Department of Physics and Astronomy Information Kathy Shan Office: MH 4008 Phone: 530 2226 Email: kathy.shan@utoledo.edu Email is the best way to
Astronomy 1010: Survey of Astronomy University of Toledo Department of Physics and Astronomy Information Kathy Shan Office: MH 4008 Phone: 530 2226 Email: kathy.shan@utoledo.edu Email is the best way to
It is a very human trait to wonder where we are in this universe. Usually, the only hint of the vastness of the universe comes at night.
 Chapter 01 Part 1 Our Place in Space We all wonder It is a very human trait to wonder where we are in this universe. Usually, the only hint of the vastness of the universe comes at night. There seems to
Chapter 01 Part 1 Our Place in Space We all wonder It is a very human trait to wonder where we are in this universe. Usually, the only hint of the vastness of the universe comes at night. There seems to
The Age of the Universe If the entire age of the Universe were 1 calendar year, then 1 month would be equivalent to roughly 1 billion years
 Astro.101 Sept. 9, 2008 Announcements A few slots are still open in the class; see prof. to sign up Web-page computer has been down; o.k. now Turn in your student contract Don t forget to do the OWL tutorial
Astro.101 Sept. 9, 2008 Announcements A few slots are still open in the class; see prof. to sign up Web-page computer has been down; o.k. now Turn in your student contract Don t forget to do the OWL tutorial
A Cosmic Perspective. Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics
 A Cosmic Perspective Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics Presentation Overview Let s talk about 3 (or 4) important and relevant topics: Me You and your place
A Cosmic Perspective Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics Presentation Overview Let s talk about 3 (or 4) important and relevant topics: Me You and your place
Modern Astronomy Review #1
 Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
The Scale of the Cosmos
 The Scale of the Cosmos Scale defined as relative magnitude. Astronomy deals with objects on a vast range of size scales and time scales. Most of these size and time scales are way beyond our every-day
The Scale of the Cosmos Scale defined as relative magnitude. Astronomy deals with objects on a vast range of size scales and time scales. Most of these size and time scales are way beyond our every-day
The Scale of the Cosmos
 The Scale of the Cosmos Scale defined as relative magnitude. Astronomy deals with objects on a vast range of size scales and time scales. Most of these size and time scales are way beyond our every-day
The Scale of the Cosmos Scale defined as relative magnitude. Astronomy deals with objects on a vast range of size scales and time scales. Most of these size and time scales are way beyond our every-day
Now on to scales in the. Let s change scale by TWO orders of magnitude at a time and see what happens.
 Announcements Read 2.1 (Magnitude & Flux), 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 In-class Quiz #1 on Tuesday, January 29. Homework #2 due in class on Thursday, January 31. Disability Services is in need of a note taker for this
Announcements Read 2.1 (Magnitude & Flux), 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 In-class Quiz #1 on Tuesday, January 29. Homework #2 due in class on Thursday, January 31. Disability Services is in need of a note taker for this
Plan. Questions? Syllabus; administrative details. Some Definitions. An Idea of Scale
 Plan Questions? Syllabus; administrative details Some Definitions An Idea of Scale All material available from http://astroweb.case.edu/ssm/astr101/ which is the primary document for the course (not Canvas).
Plan Questions? Syllabus; administrative details Some Definitions An Idea of Scale All material available from http://astroweb.case.edu/ssm/astr101/ which is the primary document for the course (not Canvas).
Homework. Our Home World! Nights for 1 st Class Sky Observation Exercise (field near Leeds Business School)
 Our Home World! 1 2 All homework will be assigned via the online system MasteringAstronomy. Stay up with class assignments in conjunction with the reading. The course ID for Astr 1020 in MasteringAstronomy
Our Home World! 1 2 All homework will be assigned via the online system MasteringAstronomy. Stay up with class assignments in conjunction with the reading. The course ID for Astr 1020 in MasteringAstronomy
How Did the Universe Begin?
 How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam 1 Physics 101 Fall 2014 Chapters 1-3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Suppose we look at a photograph of many galaxies.
Exam 1 Physics 101 Fall 2014 Chapters 1-3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Suppose we look at a photograph of many galaxies.
ASTR 380. The Universe: the context for Life
 ASTR 380 The Universe: the context for Life Simple facts: The Universe is vast. The Universe is old. The elements for life are wide-spread. Our physical laws appear universal The Universe is mostly empty!
ASTR 380 The Universe: the context for Life Simple facts: The Universe is vast. The Universe is old. The elements for life are wide-spread. Our physical laws appear universal The Universe is mostly empty!
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 6. The Structure and Scale of the Universe
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 6. The Structure and Scale of the Universe
Lecture 2: A Modern View of the Universe!
 Lecture 2: A Modern View of the Universe! Asteroid Ida and satellite Dactyl! Claire Max April 3 rd, 2014 Astro 18: Planets and Planetary Systems UC Santa Cruz Page 1 Topics for this class Some definitions
Lecture 2: A Modern View of the Universe! Asteroid Ida and satellite Dactyl! Claire Max April 3 rd, 2014 Astro 18: Planets and Planetary Systems UC Santa Cruz Page 1 Topics for this class Some definitions
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
The Universe and Galaxies. Adapted from:
 The Universe and Galaxies Adapted from: http://www.west-jefferson.k12.oh.us/earthandspacescience.aspx Astronomy The study of objects and matter outside the Earth s atmosphere and of their physical and
The Universe and Galaxies Adapted from: http://www.west-jefferson.k12.oh.us/earthandspacescience.aspx Astronomy The study of objects and matter outside the Earth s atmosphere and of their physical and
ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System. Course Info. Course Info. Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center
 ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center Instructor: Wes Ryle Course Info In-class Activities/Quizzes (10%) 4 Homework Assignments (15%)
ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center Instructor: Wes Ryle Course Info In-class Activities/Quizzes (10%) 4 Homework Assignments (15%)
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 8. The scale of time and nature of worlds (Page
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 8. The scale of time and nature of worlds (Page
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes
 Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how much bigger in radius is the Sun than the Earth? The ratio of the Sun's radius to the Earth's radius is 1,392,000/12756 = 109.1 How big is an astronomical
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how much bigger in radius is the Sun than the Earth? The ratio of the Sun's radius to the Earth's radius is 1,392,000/12756 = 109.1 How big is an astronomical
Astronomy 1. 10/17/17 - NASA JPL field trip 10/17/17 - LA Griffith Observatory field trip
 Astronomy 1 10/17/17 - NASA JPL field trip 10/17/17 - LA Griffith Observatory field trip CH 1 Here and NOW Where do we fit in the Universe? How-small-we-really-are-in-this-universe Start here: The figure
Astronomy 1 10/17/17 - NASA JPL field trip 10/17/17 - LA Griffith Observatory field trip CH 1 Here and NOW Where do we fit in the Universe? How-small-we-really-are-in-this-universe Start here: The figure
Start with known facts and reasonable guesses. More on order of magnitude Astronomy How many piano tuners are there in Boulder County?
 ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010
 Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Lecture 4: August 30, 2010 How many hospitals are there in the USA? Announcements: First homework has been posted Due Friday (10 th ) First Observatory Opportunity Thursday Night September 2, 8:30pm Will
Lecture 14: Other Galaxies A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath. The Milky Way in the Infrared 3/17/10. NGC 7331: the Milky Way s Twins. Spiral Galaxy bulge halo
 Lecture 14: Other Galaxies A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Our Galaxy: Side View We see our galaxy edge-on Primary features: Disk: young and old stars where we live. Bulge: older stars Halo: oldest stars, globular
Lecture 14: Other Galaxies A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Our Galaxy: Side View We see our galaxy edge-on Primary features: Disk: young and old stars where we live. Bulge: older stars Halo: oldest stars, globular
Science Benchmark: 06 : 04 Standard 04: Stargazing universe, the light-year, speed of light Grade Benchmark Standard Page
 Science Benchmark: 06 : 04 The sun is one of billions of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, that is one of billions of galaxies in the universe. Scientists use a variety of tools to investigate the nature
Science Benchmark: 06 : 04 The sun is one of billions of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, that is one of billions of galaxies in the universe. Scientists use a variety of tools to investigate the nature
Size and Scale of the Universe SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE
 Size and Scale of the Universe SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE Size and Scale of the Universe WHAT IS YOUR COSMIC ADDRESS? # Street City State Country Continent Hemisphere Planet Orbit Star?? Size and Scale
Size and Scale of the Universe SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE Size and Scale of the Universe WHAT IS YOUR COSMIC ADDRESS? # Street City State Country Continent Hemisphere Planet Orbit Star?? Size and Scale
3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was. Timeline of Events 4. This outward expansion
 NOTES BB.notebook The Universe started as a single point of highly concentrated matter 3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was extremely dense Density: the amount of mass contained in a certain
NOTES BB.notebook The Universe started as a single point of highly concentrated matter 3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was extremely dense Density: the amount of mass contained in a certain
Space Cruise & Picture Book
 Space Cruise & Picture Book Learning Target: Recognize that there are enormous distances between objects in space Apply our knowledge of light and space travel to understand this distance. Watch Powers
Space Cruise & Picture Book Learning Target: Recognize that there are enormous distances between objects in space Apply our knowledge of light and space travel to understand this distance. Watch Powers
A MODERN VIEW OF THE UNIVERSE
 A MODERN VIEW OF THE UNIVERSE LEARNING GOALS 1 THE SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe? 2 THE HISTORY OF THE UNIVERSE How did we come to be? How do our lifetimes
A MODERN VIEW OF THE UNIVERSE LEARNING GOALS 1 THE SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe? 2 THE HISTORY OF THE UNIVERSE How did we come to be? How do our lifetimes
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
AST 104 Lab 8: Hubble Deep Field & The Fate of the Universe
 Name: SUID: AST 104 Lab 8: Hubble Deep Field & The Fate of the Universe Introduction: One of the most revered images in all of Astronomy is the so called Hubble Deep Field image. Part of the Hubble Telescope
Name: SUID: AST 104 Lab 8: Hubble Deep Field & The Fate of the Universe Introduction: One of the most revered images in all of Astronomy is the so called Hubble Deep Field image. Part of the Hubble Telescope
A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth. The guitar player Pablo Picasso (1910)
 A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth The guitar player Pablo Picasso (1910) Announcements n Notes from the first lecture are available on the class web site (www.astro.umass.edu/~calzetti/astro100).
A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth The guitar player Pablo Picasso (1910) Announcements n Notes from the first lecture are available on the class web site (www.astro.umass.edu/~calzetti/astro100).
Galaxies and Star Systems
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
A Modern View of the Universe
 . The Scale of the Universe What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe?.2 The History of the Universe How did we come to be? How do our lifetimes compare to the age of the universe? learning
. The Scale of the Universe What is our place in the universe? How big is the universe?.2 The History of the Universe How did we come to be? How do our lifetimes compare to the age of the universe? learning
Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR Astronomy Building. Outline. The Planet Eris? What is a planet?
 Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR 1100-1120 134 Astronomy Building Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwl1@1uiuc1.1edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: W: 11:00 a.m. noon or by appointment This
Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR 1100-1120 134 Astronomy Building Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwl1@1uiuc1.1edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: W: 11:00 a.m. noon or by appointment This
How Old is the Universe? How Do We Know It s So Old?
 How Old is the Universe? Until recently, astronomers estimated that the Big Bang occurred between 12 and 14 billion years ago. To put this in perspective, our own Solar System is thought to be 4.5 billion
How Old is the Universe? Until recently, astronomers estimated that the Big Bang occurred between 12 and 14 billion years ago. To put this in perspective, our own Solar System is thought to be 4.5 billion
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy
 Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
What is the difference between a galaxy and a solar system?
 What is the difference between a galaxy and a solar system? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.19.17 Word Count 819 Level 970L An image of the Milky Way galaxy taken In celebration of the International
What is the difference between a galaxy and a solar system? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.19.17 Word Count 819 Level 970L An image of the Milky Way galaxy taken In celebration of the International
Astronomy 103: First Exam
 Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp September 21, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer Mercury What is the closest Planet to the
Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp September 21, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer Mercury What is the closest Planet to the
What is a supernova? They Outshine Their Entire Galaxy. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 675 Level 840L
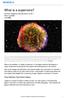 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 675 Level 840L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 675 Level 840L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)
 Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math
 ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lectures 2 & 3 1 Prep For Today (is now due) L3 Reading (If you haven t already): Required: BBBHNM: Chapter 1-4 Recommended: (BHOT: Chap. 1-3, SHU: Chap. 1-2, TOE: Chap.
ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lectures 2 & 3 1 Prep For Today (is now due) L3 Reading (If you haven t already): Required: BBBHNM: Chapter 1-4 Recommended: (BHOT: Chap. 1-3, SHU: Chap. 1-2, TOE: Chap.
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
 AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos
 An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos What is Astronomy? 50 years ago, astronomy was the study of everything outside Earth s atmosphere: the planets, the Sun, stars, galaxies, the
An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos What is Astronomy? 50 years ago, astronomy was the study of everything outside Earth s atmosphere: the planets, the Sun, stars, galaxies, the
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
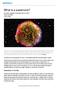 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Back of chapters have additional Resources and various tutorials to help you getting acquainted With the subject Also exercises you can do for extra
 Astronomy 100 Instructor: Prof. Irv Robbins Office:1N, room 233 Office Phone:982-2818 Observatory 982-3260 e-mail: profirobbins@aol.com Course requirements are at the Observatory Web site Via CSI web site
Astronomy 100 Instructor: Prof. Irv Robbins Office:1N, room 233 Office Phone:982-2818 Observatory 982-3260 e-mail: profirobbins@aol.com Course requirements are at the Observatory Web site Via CSI web site
The Universe April 2, Lecture 2 1
 Beyond Our Comfort Zone Direct Experience: 10-5 to 10 5 meters Dust grain may have 0.01 mm = 10 micron diameter View from mountaintop may extend 100 km Experts may claim comfort with 10-7 to 10 7 m Optical
Beyond Our Comfort Zone Direct Experience: 10-5 to 10 5 meters Dust grain may have 0.01 mm = 10 micron diameter View from mountaintop may extend 100 km Experts may claim comfort with 10-7 to 10 7 m Optical
5. What force holds the different astronomical systems described in this section together? What other forces exist in nature?
 SUMMARY The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is one of about a hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way, two other similar size galaxies, and dozens
SUMMARY The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is one of about a hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way, two other similar size galaxies, and dozens
Ch. 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Ch. 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 1 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? 2 What does the universe look
Ch. 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself 1 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the universe look like from Earth? Why do stars rise and set? 2 What does the universe look
The Universe and Galaxies
 The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
Astronomy 9 Concepts of the Cosmos
 Astronomy 9 Concepts of the Cosmos Monday/Wednesday, 1:30-2:45 pm, Cabot Auditorium LECTURE 2: I.Our Place in the Universe Lecture on Mon., Feb. 1 st Pre-course Test - REQUIRED! (if you want the attendance
Astronomy 9 Concepts of the Cosmos Monday/Wednesday, 1:30-2:45 pm, Cabot Auditorium LECTURE 2: I.Our Place in the Universe Lecture on Mon., Feb. 1 st Pre-course Test - REQUIRED! (if you want the attendance
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
THE SIZE AND STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE
 THE SIZE AND STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE when considering the facts in this presentation, keep in mind: Earth s diameter (distance across center at widest point) approximately = 8,000 miles (12,800 kilometers)
THE SIZE AND STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE when considering the facts in this presentation, keep in mind: Earth s diameter (distance across center at widest point) approximately = 8,000 miles (12,800 kilometers)
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
ASTRONOMY QUIZ NUMBER 1
 ASTRONOMY QUIZ NUMBER. You read in an astronomy atlas that an object has a negative right ascension. You immediately conclude that A) the object is located in the Southern Sky. B) the object is located
ASTRONOMY QUIZ NUMBER. You read in an astronomy atlas that an object has a negative right ascension. You immediately conclude that A) the object is located in the Southern Sky. B) the object is located
WHAT WE KNOW. Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So..
 ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
Agenda for Ast 309N, Sep. 27. Measuring Masses from Binary Stars
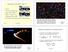 Agenda for Ast 309N, Sep. 27 Quiz 3 The role of stellar mass Ages of star clusters Exam 1, Thurs. Oct. 4 Study guide out on 9/28 Next topic: brown dwarfs and extrasolar planets 1 This image of the central
Agenda for Ast 309N, Sep. 27 Quiz 3 The role of stellar mass Ages of star clusters Exam 1, Thurs. Oct. 4 Study guide out on 9/28 Next topic: brown dwarfs and extrasolar planets 1 This image of the central
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
The Cosmological Distance Ladder. It's not perfect, but it works!
 The Cosmological Distance Ladder It's not perfect, but it works! First, we must know how big the Earth is. Next, we must determine the scale of the solar system. Copernicus (1543) correctly determined
The Cosmological Distance Ladder It's not perfect, but it works! First, we must know how big the Earth is. Next, we must determine the scale of the solar system. Copernicus (1543) correctly determined
How do telescopes "see" on Earth and in space?
 How do telescopes "see" on Earth and in space? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 933 Level 970L TOP IMAGE: The Hubble Space Telescope orbiting in space over Earth. SECOND IMAGE:
How do telescopes "see" on Earth and in space? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 933 Level 970L TOP IMAGE: The Hubble Space Telescope orbiting in space over Earth. SECOND IMAGE:
Cambridge University Press Origins of Life in the Universe Robert Jastrow and Michael Rampino Excerpt More information PART I
 PART I The Universe CHAPTER 1 Our place in the Universe The realm of the galaxies All life as we know it exists within the bounds of the single planet that we call home. For centuries mankind has gazed
PART I The Universe CHAPTER 1 Our place in the Universe The realm of the galaxies All life as we know it exists within the bounds of the single planet that we call home. For centuries mankind has gazed
Astronomers discover an active, bright galaxy "in its infancy"
 Astronomers discover an active, bright galaxy "in its infancy" By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.18.15 Word Count 825 The galaxy EGS-zs8-1, the most distant galaxy yet seen, was discovered
Astronomers discover an active, bright galaxy "in its infancy" By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.18.15 Word Count 825 The galaxy EGS-zs8-1, the most distant galaxy yet seen, was discovered
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 13. Midterm review February 4th, 2008 1. Astronomy
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 13. Midterm review February 4th, 2008 1. Astronomy
Astronomy. Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe.
 Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
Nucleus Hydrogen nucleus. hydrogen. helium
 1. (a) Once formed, a star can have a stable life for billions of years. Describe the two main forces at work in the star during this period of stability. 1.... 2.... What happens to a star once this stable
1. (a) Once formed, a star can have a stable life for billions of years. Describe the two main forces at work in the star during this period of stability. 1.... 2.... What happens to a star once this stable
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
 AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it
 Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET # 3
 ASTRONOMY 294Z: The History of the Universe Professor Barbara Ryden SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET # 3 1) [20 points] You are given a ticket for running a red traffic light. For an observer halted at the light,
ASTRONOMY 294Z: The History of the Universe Professor Barbara Ryden SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET # 3 1) [20 points] You are given a ticket for running a red traffic light. For an observer halted at the light,
The cause and development of cosmic background radiation
 Background Radiation 1 The cause and development of cosmic background radiation A paper by: Dipl. Ing. Matthias Krause, (CID) Cosmological Independent Department, Germany, 2009 Objective The objective
Background Radiation 1 The cause and development of cosmic background radiation A paper by: Dipl. Ing. Matthias Krause, (CID) Cosmological Independent Department, Germany, 2009 Objective The objective
Writing very large numbers
 19.1 Tools of Astronomers Frequently in the news we hear about discoveries that involve space. Since the 1970s, space probes have been sent to all of the planets in the solar system and we have seen them
19.1 Tools of Astronomers Frequently in the news we hear about discoveries that involve space. Since the 1970s, space probes have been sent to all of the planets in the solar system and we have seen them
V. M. Slipher ( ) was an astronomer who worked at Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona. In 1909 he began studying the spectrum of the
 Hubble s Law V. M. Slipher (1875-1969) was an astronomer who worked at Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona. In 1909 he began studying the spectrum of the Andromeda Nebula. He found that that object
Hubble s Law V. M. Slipher (1875-1969) was an astronomer who worked at Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona. In 1909 he began studying the spectrum of the Andromeda Nebula. He found that that object
Answers. The Universe. Year 10 Science Chapter 6
 Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
Chapter 20 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology 20.1 Islands of Stars Our goals for learning: How are the lives of galaxies connected with the history of the universe? What are the three major
Chapter 20 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology 20.1 Islands of Stars Our goals for learning: How are the lives of galaxies connected with the history of the universe? What are the three major
Revision Guide for Chapter 12
 Revision Guide for Chapter 12 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes The speed of light... 4 Doppler effect... 4 Expansion of the Universe... 5 Microwave background radiation... 5 Galaxy... 6 Summary
Revision Guide for Chapter 12 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes The speed of light... 4 Doppler effect... 4 Expansion of the Universe... 5 Microwave background radiation... 5 Galaxy... 6 Summary
The Hubble Deep Field
 The Hubble Deep Field Introduction This is a picture of the Hubble Deep Field (HDF). The deepest image of the sky ever taken, it was made in 1996 using the Hubble Space Telescope by effectively leaving
The Hubble Deep Field Introduction This is a picture of the Hubble Deep Field (HDF). The deepest image of the sky ever taken, it was made in 1996 using the Hubble Space Telescope by effectively leaving
