Name Class Date. Chapter 23 Touring Our Solar System Investigation 23
|
|
|
- Ellen Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 23 Touring Our Solar System Investigation 23 Exploring Orbits Introduction In 1609, the German mathematician and astronomer Johannes Kepler deciphered a major puzzle of the solar system. The strange back-andforth motions of the planets in the sky were nearly impossible to predict until Kepler figured out the true shapes of the planetary orbits around the sun. Orbits were always believed to be circular, but Kepler used mathematics to discover they were actually elliptical. An ellipse is an oval that is characterized by two quantities. The first quantity is the width of the ellipse, which is called the major axis. The second quantity is called the eccentricity, which is a measure of how stretched out the ellipse is. Eccentricity is defined by the distance between two mathematically determined points within the ellipse called the foci. For planets, one focus of their orbital ellipse is the sun. The other is an empty point in space. The orbit of each planet is an ellipse, but each planet s elliptical orbit has different major axes and eccentricities. Once Kepler understood the proper nature of orbits, the movements of the planets in the sky could be predicted with precision. In this investigation, you will draw ellipses, calculate their eccentricities, observe an interesting property of ellipses, and compare the ellipses you draw with the orbital eccentricities of Earth and other planets in the solar system. Major axis Focus Focal length Figure 1 Problem What do the elliptical orbits of the planets look like? Sun (at focus) Pre-Lab Discussion Read the entire investigation. Then work with a partner to answer the following questions. 1. Predicting Each planet s orbit is shaped like an ellipse. Predict whether the shapes of the planet s orbits will be more circular or more elongated. Earth Science Lab Manual 145
2 2. Applying Concepts What is the one thing that the elliptical orbits of all planets, asteroids, and most comets have in common? 3. Controlling Variables What is the independent variable for the ellipses you will draw? 4. Controlling Variables What are the dependent variables for the ellipses you will draw? 5. Designing Experiments What purpose do the two pushpins serve in this investigation? Materials (per pair of students) 3 sheets of paper heavy corrugated cardboard ( 50 cm 60 cm) 2 pushpins metric ruler string, 30 cm long 5 colored pencils cellophane tape calculator Earth Science Lab Manual 146
3 Safety Be careful when handling sharp objects. Note all safety symbols next to the steps in the Procedure and review the meaning of each symbol by referring to the safety symbol guide on page xiii. Procedure Part A: Drawing Ellipses and Calculating Eccentricity 1. Fold a sheet of paper in half lengthwise. Flatten it out again. 2. Place the paper on the cardboard and measure 5 cm from the center of the page. Place one pushpin at the 5 cm mark. Measure 5 cm to the other side of the center of the paper and place a pushpin there. The pushpins should be 10 cm apart. CAUTION: Be careful when handling the pins; they can puncture skin. 3. Label one of the pushpins as the sun. 4. Tie the string in a loop and place it around the pins. Using one of the colored pencils, gently pull the string tight. Keep the string tight without pulling the pins out of the cardboard. Carefully drag the pencil around the pins to draw an ellipse, as shown in Figure 2. P Sun 5. Using the same colored pencil, draw a circle around the pin that is not labeled as the sun. Remove the pin. 6. Use the metric ruler to measure the length of the major axis and focal length. Record these values in Data Table Reposition the second pin so that it is now 8.0 cm from the other pin. Repeat Steps 4 through 6, using a different colored pencil. 8. Repeat Step 7, using distances of 6.0 cm, 4.0 cm, and 2.0 cm between the pins. As the focal length for each ellipse becomes smaller, you may need to tape additional sheets of paper above and below the original sheet of paper to draw the entire ellipse. Earth Science Lab Manual 147
4 9. The eccentricity for each ellipse is calculated by dividing the focal length by the length of the major axis: focal length eccentricity major axis Calculate the eccentricity for each ellipse. Record the values in Data Table Label each ellipse on your diagram with its matching eccentricity. Observations DATA TABLE 1 Ellipse (Color) Major Axis (cm) Focal Length (cm) Eccentricity Part B: Observing Properties of Ellipses 11. Choose one of the ellipses you made on your diagram and label the foci A and B respectively. 12. Choose a point anywhere on the ellipse and label it C. 13. Measure the length of the lines AC and BC in centimeters. Record your measurements in Data Table Repeat Steps 12 and 13, placing point C at three different points on the ellipse. Carefully measure lines AC and BC and record your measurements in Data Table 2. DATA TABLE 2 Position of C Length of AC Length of BC Length of AC BC Earth Science Lab Manual 148
5 Analysis and Conclusions 1. Compare and Contrast Compare the following values for planetary eccentricities to those you calculated for your ellipses. What can you state about the orbits of the various planets? Planet Eccentricity Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Inferring What shape would you make if both pushpins were placed at a single central point? What would be the focal length and eccentricity of this shape? 3. Observing What did you discover in Part B about the sums of lines AC and BC for your ellipse? Generalize your findings as a basic law of ellipses. Earth Science Lab Manual 149
6 4. Drawing Conclusions Did your results from this activity confirm your original prediction? Explain why or why not. 5. Inferring What body in the solar system do you think is one focus of the moon s orbit? 6. Inferring How would you modify this activity to offer a better sense of planetary orbits? Go Further Research the orbits of smaller bodies in the solar system such as asteroids or comets. Use the materials from this investigation and researched values for the major axis and eccentricity to produce drawings of the orbits of these objects. Include in your report your drawings and all values used. Earth Science Lab Manual 150
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #39 ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #39 ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION Our sun is not exactly in the center of the orbits of the planets, and therefore the planetary orbits are not circular.
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #39 ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION Our sun is not exactly in the center of the orbits of the planets, and therefore the planetary orbits are not circular.
Earth Science Unit 6: Astronomy Period: Date: Elliptical Orbits
 Earth Science Name: Unit 6: Astronomy Period: Date: Lab # 5 Elliptical Orbits Objective: To compare the shape of the earth s orbit (eccentricity) with the orbits of and with a circle. other planets Focus
Earth Science Name: Unit 6: Astronomy Period: Date: Lab # 5 Elliptical Orbits Objective: To compare the shape of the earth s orbit (eccentricity) with the orbits of and with a circle. other planets Focus
Lesson 1 The Structure of the Solar System
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: PARTNERS: Lab # ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Our sun is not exactly in the center of the orbits of the planets, and therefore the planetary orbits are
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: PARTNERS: Lab # ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Our sun is not exactly in the center of the orbits of the planets, and therefore the planetary orbits are
5. How did Copernicus s model solve the problem of some planets moving backwards?
 MODELS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM Reading Guide: Chapter 27.2 (read text pages 691-694) 1k. Recognize the cumulative nature of scientific evidence. 1n. Know that when an observation does not agree with an accepted
MODELS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM Reading Guide: Chapter 27.2 (read text pages 691-694) 1k. Recognize the cumulative nature of scientific evidence. 1n. Know that when an observation does not agree with an accepted
ASTRO 1050 LAB #3: Planetary Orbits and Kepler s Laws
 ASTRO 1050 LAB #3: Planetary Orbits and Kepler s Laws ABSTRACT Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), a German mathematician and astronomer, was a man on a quest to discover order and harmony in the solar system.
ASTRO 1050 LAB #3: Planetary Orbits and Kepler s Laws ABSTRACT Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), a German mathematician and astronomer, was a man on a quest to discover order and harmony in the solar system.
,.~ Readlng ~ What,~,~~ is a geocentric system? Chapter3 J 73
 Earth at the Center When the ancient Greeks watched the stars move across the sky, they noticed that the patterns of the stars didn t change. Although the stars seemed to move, they stayed in the same
Earth at the Center When the ancient Greeks watched the stars move across the sky, they noticed that the patterns of the stars didn t change. Although the stars seemed to move, they stayed in the same
Unit: Planetary Science
 Orbital Motion Kepler s Laws GETTING AN ACCOUNT: 1) go to www.explorelearning.com 2) click on Enroll in a class (top right hand area of screen). 3) Where it says Enter class Code enter the number: MLTWD2YAZH
Orbital Motion Kepler s Laws GETTING AN ACCOUNT: 1) go to www.explorelearning.com 2) click on Enroll in a class (top right hand area of screen). 3) Where it says Enter class Code enter the number: MLTWD2YAZH
Patterns in the Solar System (Chapter 18)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Patterns in the Solar System (Chapter 18) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and meter stick.
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Patterns in the Solar System (Chapter 18) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and meter stick.
Investigating the Solar System
 Investigating the Solar System This Workbook belongs to: Our Local Star: The Sun Location in The Solar System Interesting Facts 1. 2. 3. 4. Name of Star: THE SUN 5. Draw and Color your own Sun in the blank
Investigating the Solar System This Workbook belongs to: Our Local Star: The Sun Location in The Solar System Interesting Facts 1. 2. 3. 4. Name of Star: THE SUN 5. Draw and Color your own Sun in the blank
Gravity and the Orbits of Planets
 Gravity and the Orbits of Planets 1. Gravity Galileo Newton Earth s Gravity Mass v. Weight Einstein and General Relativity Round and irregular shaped objects 2. Orbits and Kepler s Laws ESO Galileo, Gravity,
Gravity and the Orbits of Planets 1. Gravity Galileo Newton Earth s Gravity Mass v. Weight Einstein and General Relativity Round and irregular shaped objects 2. Orbits and Kepler s Laws ESO Galileo, Gravity,
Reading Preview. Models of the Universe What is a geocentric model?
 Section 1 Observing the Solar System 1 Observing the Solar System Objectives After this lesson, students will be able to J.3.1.1 Identify the geocentric and heliocentric systems. J.3.1.2 Recognize how
Section 1 Observing the Solar System 1 Observing the Solar System Objectives After this lesson, students will be able to J.3.1.1 Identify the geocentric and heliocentric systems. J.3.1.2 Recognize how
Gravity and Orbits 4.2 CAN YOU EXPLAIN IT? you explore the lesson, gather evidence about how solar system bodies behave.
 4.2 Gravity and Orbits An orrery is a physical model of the relative motions of the planets. CAN YOU EXPLAIN IT? FIGURE 1: Mercury s transit of the sun in 2016 Gather Evidence As you explore the lesson,
4.2 Gravity and Orbits An orrery is a physical model of the relative motions of the planets. CAN YOU EXPLAIN IT? FIGURE 1: Mercury s transit of the sun in 2016 Gather Evidence As you explore the lesson,
Astronomy Ideas. 1. Meteors and craters. Assignments. Materials and Equipment
 Astronomy Ideas Assignments 1. Meteors and craters Materials and Equipment Different-sized objects that are nearly spherical (at least 3 total), such a rubber ball, a baseball, and a piece of roundish
Astronomy Ideas Assignments 1. Meteors and craters Materials and Equipment Different-sized objects that are nearly spherical (at least 3 total), such a rubber ball, a baseball, and a piece of roundish
Astron 104 Laboratory #5 The Orbit of Mars
 Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #5 The Orbit of Mars Section 1.3 Note: Use a pencil with a sharp point! Mark your data as accurately as possible. This table contains measurements by Tycho Brahe.
Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #5 The Orbit of Mars Section 1.3 Note: Use a pencil with a sharp point! Mark your data as accurately as possible. This table contains measurements by Tycho Brahe.
1 The Solar System. 1.1 a journey into our galaxy
 1 The Solar System Though Pluto, and the far-flung depths of the Solar System, is the focus of this book, it is essential that Pluto is placed in the context of the planetary system that it inhabits our
1 The Solar System Though Pluto, and the far-flung depths of the Solar System, is the focus of this book, it is essential that Pluto is placed in the context of the planetary system that it inhabits our
Patterns in the Solar System (Chapter 18)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Patterns in the Solar System (Chapter 18) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and meter stick.
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Patterns in the Solar System (Chapter 18) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and meter stick.
Physics Unit 7: Circular Motion, Universal Gravitation, and Satellite Orbits. Planetary Motion
 Physics Unit 7: Circular Motion, Universal Gravitation, and Satellite Orbits Planetary Motion Geocentric Models --Many people prior to the 1500 s viewed the! Earth and the solar system using a! geocentric
Physics Unit 7: Circular Motion, Universal Gravitation, and Satellite Orbits Planetary Motion Geocentric Models --Many people prior to the 1500 s viewed the! Earth and the solar system using a! geocentric
Name Class Date. Chapter 29. The Solar System. Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided.
 The Solar System Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. Ptolemy modified Aristotle s model of the universe to include a. Oort clouds. b. retrograde motion.
The Solar System Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. Ptolemy modified Aristotle s model of the universe to include a. Oort clouds. b. retrograde motion.
What is a Satellite? A satellite is an object that orbits another object. Ex. Radio satellite, moons, planets
 Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 4: Planetary Orbits
 AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 4: Planetary Orbits Name: Partners: Student number (SUID): Lab section number: 1 Introduction Objectives The Planetary Orbits Lab reviews used the Planetary Orbit
AST101: Our Corner of the Universe Lab 4: Planetary Orbits Name: Partners: Student number (SUID): Lab section number: 1 Introduction Objectives The Planetary Orbits Lab reviews used the Planetary Orbit
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system.
 1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
1. The bar graph below shows one planetary characteristic, identified as X, plotted for the planets of our solar system. Which characteristic of the planets in our solar system is represented by X? A)
ASTRONOMY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 I ASTRONOMY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Line Up Make a Model of the Solar System! Celestial bodies are natural things in the sky, such as stars (bodies made of gases that are so hot they give off light), planets
I ASTRONOMY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Line Up Make a Model of the Solar System! Celestial bodies are natural things in the sky, such as stars (bodies made of gases that are so hot they give off light), planets
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Question number Answer Notes Marks 1 correctly; (ii) Sun X should be left of the imaginary 5-7 line, reject X placed outside the orbit
 ( a) (i) omet orbit behind Sun completed Dashed or solid correctly; curved line X marked anywhere in grey area; No need to label X as Sun X should be left of the imaginary 5-7 line, reject X placed outside
( a) (i) omet orbit behind Sun completed Dashed or solid correctly; curved line X marked anywhere in grey area; No need to label X as Sun X should be left of the imaginary 5-7 line, reject X placed outside
October 19, NOTES Solar System Data Table.notebook. Which page in the ESRT???? million km million. average.
 Celestial Object: Naturally occurring object that exists in space. NOT spacecraft or man-made satellites Which page in the ESRT???? Mean = average Units = million km How can we find this using the Solar
Celestial Object: Naturally occurring object that exists in space. NOT spacecraft or man-made satellites Which page in the ESRT???? Mean = average Units = million km How can we find this using the Solar
Lab 6: The Planets and Kepler
 Lab 6: The Planets and Kepler The Motion of the Planets part I 1. Morning and Evening Stars. Start up Stellarium, and check to see if you have the Angle Tool installed it looks like a sideways A ( ) in
Lab 6: The Planets and Kepler The Motion of the Planets part I 1. Morning and Evening Stars. Start up Stellarium, and check to see if you have the Angle Tool installed it looks like a sideways A ( ) in
Assignment 1. Due Feb. 11, 2019
 Assignment 1 Due Feb. 11, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
Assignment 1 Due Feb. 11, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
How does the solar system, the galaxy, and the universe fit into our understanding of the cosmos?
 Remember to check the links for videos! How does the solar system, the galaxy, and the universe fit into our understanding of the cosmos? Universe ~ 13.7 bya First Stars ~ 13.3 bya First Galaxies ~ 12.7
Remember to check the links for videos! How does the solar system, the galaxy, and the universe fit into our understanding of the cosmos? Universe ~ 13.7 bya First Stars ~ 13.3 bya First Galaxies ~ 12.7
Astronomy Test Review. 3 rd Grade
 Astronomy Test Review 3 rd Grade Match the vocabulary word to its definition. Outer Planets The path a planet takes around the sun. Inner Planets Orbit Sun The center of our solar system. Small, rocky
Astronomy Test Review 3 rd Grade Match the vocabulary word to its definition. Outer Planets The path a planet takes around the sun. Inner Planets Orbit Sun The center of our solar system. Small, rocky
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PRACTICAL ACTIVITY HOW DO THE PANETS MOVE? One of the most important questions historically in Physics was how the planets move. Many historians consider the field of Physics to date
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PRACTICAL ACTIVITY HOW DO THE PANETS MOVE? One of the most important questions historically in Physics was how the planets move. Many historians consider the field of Physics to date
Sol o ar a r S yste t m e F o F r o m r at a i t on o The Ne N b e u b l u a a Hypothesis
 Solar System Solar system- the sun and all objects that orbit the sun due to its gravity Solar System Formation The Nebula Hypothesis Parts of the Solar System Planet- a celestial body that is in orbit
Solar System Solar system- the sun and all objects that orbit the sun due to its gravity Solar System Formation The Nebula Hypothesis Parts of the Solar System Planet- a celestial body that is in orbit
 Chapter 4 Thrills and Chills +Math +Depth Acceleration of the Moon +Concepts The Moon is 60 times further away from the center of Earth than objects on the surface of Earth, and moves about Earth in an
Chapter 4 Thrills and Chills +Math +Depth Acceleration of the Moon +Concepts The Moon is 60 times further away from the center of Earth than objects on the surface of Earth, and moves about Earth in an
Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n)
 When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS
 Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS I. Introduction The planets revolve around the Sun in orbits that lie nearly in the same plane. Therefore, the planets, with the exception of Pluto, are
Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS I. Introduction The planets revolve around the Sun in orbits that lie nearly in the same plane. Therefore, the planets, with the exception of Pluto, are
PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy
 PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy - observing sessions: Sunday Thursday, 9pm, weather permitting http://www.phys.uconn.edu/observatory - Exam - Tuesday March 20, - Review Monday 6:30-9pm, PB 38 Marek Krasnansky
PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy - observing sessions: Sunday Thursday, 9pm, weather permitting http://www.phys.uconn.edu/observatory - Exam - Tuesday March 20, - Review Monday 6:30-9pm, PB 38 Marek Krasnansky
DARE TO BE. FORMULA: e = distance between foci length of major axis VOCABULARY: ECCENTRIC. ellipse: eccentricity: focus (plural is foci): major axis:
 NAME: DATE: DARE TO BE ECCENTRIC INTRODUCTION: Have you ever heard the phrase dare to be different? Well that's what eccentricity is all about: deviating from the norm - or in other words, being different!
NAME: DATE: DARE TO BE ECCENTRIC INTRODUCTION: Have you ever heard the phrase dare to be different? Well that's what eccentricity is all about: deviating from the norm - or in other words, being different!
The Solar System. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Kepler s Laws Simulations
 Kepler s Laws Simulations Goto: http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/guidry/java/kepler/kepler.html 1. Observe the speed of the planet as it orbits around the Sun. Change the speed to.50 and answer the questions.
Kepler s Laws Simulations Goto: http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/guidry/java/kepler/kepler.html 1. Observe the speed of the planet as it orbits around the Sun. Change the speed to.50 and answer the questions.
The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS. Scientific Language. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name. Topic. K: What I Know. W: What I Want to Know. L: What I Learned. S: What I Still Want to Know
 Instructions: Write the Solar System topic you are studying on the line provided. In the first section, write what you already know about the topic. In the second section, write what you would like to
Instructions: Write the Solar System topic you are studying on the line provided. In the first section, write what you already know about the topic. In the second section, write what you would like to
1. Determine the length of the major & minor axis. List the coordinates of vertices and co-vertices of the following ellipses. Vertices: Co-Vertices:
 1. Sec 6.3 Conic Sections Ellipses Name: An ELLIPSE could be accurately described as circle that has been stretched or compressed by a constant ratio towards a diameter of a circle. A circle is actually
1. Sec 6.3 Conic Sections Ellipses Name: An ELLIPSE could be accurately described as circle that has been stretched or compressed by a constant ratio towards a diameter of a circle. A circle is actually
Early Theories. Early astronomers believed that the sun, planets and stars orbited Earth (geocentric model) Developed by Aristotle
 Planetary Motion Early Theories Early astronomers believed that the sun, planets and stars orbited Earth (geocentric model) Developed by Aristotle Stars appear to move around Earth Observations showed
Planetary Motion Early Theories Early astronomers believed that the sun, planets and stars orbited Earth (geocentric model) Developed by Aristotle Stars appear to move around Earth Observations showed
6 TH GRADE ACCURATE PLANET SIZES AND DISTANCE FROM THE SUN ACTIVITY
 6 TH GRADE ACCURATE PLANET SIZES AND DISTANCE FROM THE SUN ACTIVITY Summary: Accurate planet size and distance from the Sun is studied in this lesson. Each student constructs a correctly scaled diagram
6 TH GRADE ACCURATE PLANET SIZES AND DISTANCE FROM THE SUN ACTIVITY Summary: Accurate planet size and distance from the Sun is studied in this lesson. Each student constructs a correctly scaled diagram
Great Science Adventures
 Great Science Adventures What is the solar system? Lesson 6 Space Concepts: The planets, moons, and asteroids orbiting the Sun make up our solar system. The first four planets are the solid, inner planets:
Great Science Adventures What is the solar system? Lesson 6 Space Concepts: The planets, moons, and asteroids orbiting the Sun make up our solar system. The first four planets are the solid, inner planets:
TEKS Cluster: Space. identify and compare the physical characteristics of the Sun, Earth, and Moon
 5.8 Earth and space. The student knows that there are recognizable patterns in the natural world and among the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. 5.8(C) 5.8(D) demonstrate that Earth rotates on its axis once
5.8 Earth and space. The student knows that there are recognizable patterns in the natural world and among the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. 5.8(C) 5.8(D) demonstrate that Earth rotates on its axis once
The Sun s center is much hotter than the surface. The Sun looks large and bright in the sky. Other stars look much smaller.
 The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
The Planets and Scale
 The Planets and Scale Elementary grades Lesson Summary Students practice reading data about the planets from a table and making numerical comparisons. Prior Knowledge & Skills Comparing numbers Reading
The Planets and Scale Elementary grades Lesson Summary Students practice reading data about the planets from a table and making numerical comparisons. Prior Knowledge & Skills Comparing numbers Reading
4 A(n) is a small, rocky object that orbits the sun; many of these objects are located in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
 Name Vocabulary Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence., 6.11B 1 is the process in which energy is released as the nuclei of small atoms combine to form a larger nucleus., 6.11B
Name Vocabulary Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence., 6.11B 1 is the process in which energy is released as the nuclei of small atoms combine to form a larger nucleus., 6.11B
I. Introduction. II. An Introduction to Starry Night NAME: ORBITAL MOTION
 NAME: ORBITAL MOTION What will you learn in this Lab? You will be using some special software to simulate the motion of planets in our Solar System and across the night sky. You will be asked to try and
NAME: ORBITAL MOTION What will you learn in this Lab? You will be using some special software to simulate the motion of planets in our Solar System and across the night sky. You will be asked to try and
Class: 6 Science Date: 1/30/13 Solar System Simulator + Guide
 Class: 6 Science Date: 1/30/13 Solar System Simulator + Guide Objectives Today we will learn information about each planet and continue to familiarize ourselves with the solar system. We will learn this
Class: 6 Science Date: 1/30/13 Solar System Simulator + Guide Objectives Today we will learn information about each planet and continue to familiarize ourselves with the solar system. We will learn this
1. thought the earth was at the center of the solar system and the planets move on small circles that move on bigger circles
 Earth Science Chapter 20: Observing the Solar System Match the observations or discoveries with the correct scientist. Answers may be used more than once. Answers that cannot be read will be counted as
Earth Science Chapter 20: Observing the Solar System Match the observations or discoveries with the correct scientist. Answers may be used more than once. Answers that cannot be read will be counted as
Unit 5 Gravitation. Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion
 Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
Chapter 16 Astronomy Study Guide. VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW geocentric system meteorite meteoroid
 NAME: Period: asteroid asteroid belt comet ellipse force Galilean moons gas giants Chapter 16 Astronomy Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW geocentric system meteorite gravity meteoroid greenhouse effect
NAME: Period: asteroid asteroid belt comet ellipse force Galilean moons gas giants Chapter 16 Astronomy Study Guide VOCABULARY WORDS TO KNOW geocentric system meteorite gravity meteoroid greenhouse effect
Eclipses and Forces. Jan 21, ) Review 2) Eclipses 3) Kepler s Laws 4) Newton s Laws
 Eclipses and Forces Jan 21, 2004 1) Review 2) Eclipses 3) Kepler s Laws 4) Newton s Laws Review Lots of motion The Moon revolves around the Earth Eclipses Solar Lunar the Sun, Earth and Moon must all be
Eclipses and Forces Jan 21, 2004 1) Review 2) Eclipses 3) Kepler s Laws 4) Newton s Laws Review Lots of motion The Moon revolves around the Earth Eclipses Solar Lunar the Sun, Earth and Moon must all be
Name Class Date. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 1. terrestrial planet and gas giant 2. asteroid and comet 3. meteor and meteorite Complete
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 1. terrestrial planet and gas giant 2. asteroid and comet 3. meteor and meteorite Complete
The Law of Ellipses (Kepler s First Law): all planets orbit the sun in a
 Team Number Team Members Present Learning Objectives 1. Practice the Engineering Process a series of steps to follow to design a solution to a problem. 2. Practice the Five Dimensions of Being a Good Team
Team Number Team Members Present Learning Objectives 1. Practice the Engineering Process a series of steps to follow to design a solution to a problem. 2. Practice the Five Dimensions of Being a Good Team
The Outer Planets (pages )
 The Outer Planets (pages 720 727) Gas Giants and Pluto (page 721) Key Concept: The first four outer planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are much larger and more massive than Earth, and they do
The Outer Planets (pages 720 727) Gas Giants and Pluto (page 721) Key Concept: The first four outer planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are much larger and more massive than Earth, and they do
Yes, inner planets tend to be and outer planets tend to be.
 1. Planet Density Make some general comments about inner and outer planets density Inner Planets Density Outer Planets Density Is there a pattern or a trend in planet density? Yes, inner planets tend to
1. Planet Density Make some general comments about inner and outer planets density Inner Planets Density Outer Planets Density Is there a pattern or a trend in planet density? Yes, inner planets tend to
cosmogony geocentric heliocentric How the Greeks modeled the heavens
 Cosmogony A cosmogony is theory about ones place in the universe. A geocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes Earth to be at the center of the universe. A heliocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes
Cosmogony A cosmogony is theory about ones place in the universe. A geocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes Earth to be at the center of the universe. A heliocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes
SPI Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe.
 SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
GEMS Student Activity
 Girls in Engineering, Mathematics, and Science GEMS Student Activity HONEY, I SHRUNK THE SOLAR SYSTEM Solar System Predictions How big each of the planets would be if the sun was the size of the fitness
Girls in Engineering, Mathematics, and Science GEMS Student Activity HONEY, I SHRUNK THE SOLAR SYSTEM Solar System Predictions How big each of the planets would be if the sun was the size of the fitness
Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Write the term that matches each definition: Chapter 2 Study Guide Terms: gas giants solar system moons satellite geocentric model trajectory Big Bang Theory diameter dense heliocentric model theory terrestrial
Write the term that matches each definition: Chapter 2 Study Guide Terms: gas giants solar system moons satellite geocentric model trajectory Big Bang Theory diameter dense heliocentric model theory terrestrial
Unit 1 Astronomy: Kepler s Laws Of Planetary Motion Assessed Activity (66 marks total)
 Name: Solutions & Marking Scheme 2009 TG: PF Unit 1 Astronomy: Kepler s Laws Of Planetary Motion Assessed Activity (66 marks total) Aim: To investigate Kepler s three laws planetary motion. Apparatus:
Name: Solutions & Marking Scheme 2009 TG: PF Unit 1 Astronomy: Kepler s Laws Of Planetary Motion Assessed Activity (66 marks total) Aim: To investigate Kepler s three laws planetary motion. Apparatus:
Locating the Planets (Chapter 20) and the Moon and Sun (Chapter 22)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Locating the Planets (Chapter 20) and the Moon and Sun (Chapter 22) For this assignment, you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Locating the Planets (Chapter 20) and the Moon and Sun (Chapter 22) For this assignment, you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric
Locating the Planets (Chapter 19) and the Moon and Sun (Chapter 21)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Locating the Planets (Chapter 19) and the Moon and Sun (Chapter 21) For this assignment, you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Locating the Planets (Chapter 19) and the Moon and Sun (Chapter 21) For this assignment, you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric
The second type of conic is called an ellipse, and is defined as follows. Definition of Ellipse
 72 Chapter 10 Topics in Analtic Geometr 10.3 ELLIPSES What ou should learn Write equations of ellipses in standard form and graph ellipses. Use properties of ellipses to model and solve real-life problems.
72 Chapter 10 Topics in Analtic Geometr 10.3 ELLIPSES What ou should learn Write equations of ellipses in standard form and graph ellipses. Use properties of ellipses to model and solve real-life problems.
Motion in the Heavens
 Motion in the Heavens Most ancient cultures believed that the earth was the centre of the universe. Most felt that the planets, stars, moon and sun revolved around the earth. This is known as a geocentric
Motion in the Heavens Most ancient cultures believed that the earth was the centre of the universe. Most felt that the planets, stars, moon and sun revolved around the earth. This is known as a geocentric
KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION
 KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler culminated his analysis of the extensive data taken by Tycho Brahe and published his three laws of planetary motion, which we know
KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler culminated his analysis of the extensive data taken by Tycho Brahe and published his three laws of planetary motion, which we know
Where do they come from?
 Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 4 The Meteorite-Asteroid Connection: Orbits in the Inner Solar System Objectives In Activity A students will: draw circles and ellipses to illustrate basic shapes of
Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 4 The Meteorite-Asteroid Connection: Orbits in the Inner Solar System Objectives In Activity A students will: draw circles and ellipses to illustrate basic shapes of
What's Up In Space? In the Center. Around the Sun. Around Earth. Space Facts! Places in Space
 Non-fiction: What's Up In Space? What's Up In Space? Places in Space Space is an exciting place! Our solar system is in space. It is made up of the sun and the eight planets that travel around the sun.
Non-fiction: What's Up In Space? What's Up In Space? Places in Space Space is an exciting place! Our solar system is in space. It is made up of the sun and the eight planets that travel around the sun.
Earth s Motions. Rotation -!! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours.
 Name: Date: Period: Earth In the Solar System The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES! Rotation -! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours
Name: Date: Period: Earth In the Solar System The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES! Rotation -! Period of Rotation - amount of time to make one complete rotation Example: Earth rotates in hours
Astronomy Regents Review
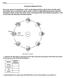 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Galaxies: enormous collections of gases, dust and stars held together by gravity Our galaxy is called the milky way
 Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
6 The Orbit of Mercury
 6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
Chapter 16 The Solar System
 Chapter 16 The Solar System Finding the Standard Time and Date at Another Location Example When it is 12 noon in London, what is the standard time in Denver, Colorado (40 N, 105 W)? Section 15.3 Finding
Chapter 16 The Solar System Finding the Standard Time and Date at Another Location Example When it is 12 noon in London, what is the standard time in Denver, Colorado (40 N, 105 W)? Section 15.3 Finding
18. Kepler as a young man became the assistant to A) Nicolaus Copernicus. B) Ptolemy. C) Tycho Brahe. D) Sir Isaac Newton.
 Name: Date: 1. The word planet is derived from a Greek term meaning A) bright nighttime object. B) astrological sign. C) wanderer. D) nontwinkling star. 2. The planets that were known before the telescope
Name: Date: 1. The word planet is derived from a Greek term meaning A) bright nighttime object. B) astrological sign. C) wanderer. D) nontwinkling star. 2. The planets that were known before the telescope
9/12/2010. The Four Fundamental Forces of Nature. 1. Gravity 2. Electromagnetism 3. The Strong Nuclear Force 4. The Weak Nuclear Force
 The Four Fundamental Forces of Nature 1. Gravity 2. Electromagnetism 3. The Strong Nuclear Force 4. The Weak Nuclear Force The Universe is made of matter Gravity the force of attraction between matter
The Four Fundamental Forces of Nature 1. Gravity 2. Electromagnetism 3. The Strong Nuclear Force 4. The Weak Nuclear Force The Universe is made of matter Gravity the force of attraction between matter
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016
 Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Total Points 50. Project grade 50
 Intro to Science Project Names: Pd: Date: 1st Nine Weeks PROJECT We are going to do an Earth Science project. You will work with a partner to make a poster of your space concept. You will have at least
Intro to Science Project Names: Pd: Date: 1st Nine Weeks PROJECT We are going to do an Earth Science project. You will work with a partner to make a poster of your space concept. You will have at least
Physical Science 1 Chapter 16 INTRODUCTION. Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time.
 INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
Our Fun Sun. Source: Measuring the Diameter of the Sun, The Educator s Reference Desk Enchanted Learning
 Our Fun Sun Subject: Science, Math Grades: 7 th 8 th Rational or Purpose: Students will develop an easy tool in which they are able to look at the sun and find out what its diameter is by a simple arithmetic
Our Fun Sun Subject: Science, Math Grades: 7 th 8 th Rational or Purpose: Students will develop an easy tool in which they are able to look at the sun and find out what its diameter is by a simple arithmetic
Voyage: A Journey through our Solar System. Grades 5-8. Lesson 5: Round and Round We Go Exploring Orbits in the Solar System
 Voyage: A Journey through our Solar System Grades 5-8 Lesson 5: Round and Round We Go Exploring Orbits in the Solar System On October 17, 2001, a one to ten billion scale model of the Solar System was
Voyage: A Journey through our Solar System Grades 5-8 Lesson 5: Round and Round We Go Exploring Orbits in the Solar System On October 17, 2001, a one to ten billion scale model of the Solar System was
Investigation: Transit Tracks
 Investigation: Transit Tracks p. 1 Students will learn what a transit is under what conditions a transit may be seen how a planet s size and distance from its star affects the behavior of transits how
Investigation: Transit Tracks p. 1 Students will learn what a transit is under what conditions a transit may be seen how a planet s size and distance from its star affects the behavior of transits how
Tycho Brahe
 Tycho Brahe 1546-1601 At the time of Shakespeare and Elizabeth I and Champlain Lost part of his nose in a duel over who was the best mathematician At 27 he measured the distance of a supernova and a comet
Tycho Brahe 1546-1601 At the time of Shakespeare and Elizabeth I and Champlain Lost part of his nose in a duel over who was the best mathematician At 27 he measured the distance of a supernova and a comet
Science Assessment Year 5: Earth and Space. The Solar System. Movements, Shape and Size. Saturn. Mars. Mercury. Earth. Neptune.
 Name: Science Assessment Year 5: Earth and Space Date: 7 total marks The Solar System. Join up these labels to the correct planet, star or satellite: Mars Earth Saturn Mercury Neptune Sun Uranus Venus
Name: Science Assessment Year 5: Earth and Space Date: 7 total marks The Solar System. Join up these labels to the correct planet, star or satellite: Mars Earth Saturn Mercury Neptune Sun Uranus Venus
Lecture #5: Plan. The Beginnings of Modern Astronomy Kepler s Laws Galileo
 Lecture #5: Plan The Beginnings of Modern Astronomy Kepler s Laws Galileo Geocentric ( Ptolemaic ) Model Retrograde Motion: Apparent backward (= East-to-West) motion of a planet with respect to stars Ptolemy
Lecture #5: Plan The Beginnings of Modern Astronomy Kepler s Laws Galileo Geocentric ( Ptolemaic ) Model Retrograde Motion: Apparent backward (= East-to-West) motion of a planet with respect to stars Ptolemy
APS 1030 Astronomy Lab 79 Kepler's Laws KEPLER'S LAWS
 APS 1030 Astronomy Lab 79 Kepler's Laws KEPLER'S LAWS SYNOPSIS: Johannes Kepler formulated three laws that described how the planets orbit around the Sun. His work paved the way for Isaac Newton, who derived
APS 1030 Astronomy Lab 79 Kepler's Laws KEPLER'S LAWS SYNOPSIS: Johannes Kepler formulated three laws that described how the planets orbit around the Sun. His work paved the way for Isaac Newton, who derived
Chapter 14 Satellite Motion
 1 Academic Physics Mechanics Chapter 14 Satellite Motion The Mechanical Universe Kepler's Three Laws (Episode 21) The Kepler Problem (Episode 22) Energy and Eccentricity (Episode 23) Navigating in Space
1 Academic Physics Mechanics Chapter 14 Satellite Motion The Mechanical Universe Kepler's Three Laws (Episode 21) The Kepler Problem (Episode 22) Energy and Eccentricity (Episode 23) Navigating in Space
Kepler s Basic Assumptions
 Theme 3.3 Kepler Kepler s Basic Assumptions Kepler wanted to use the extensive data sets provided by Tycho to work out the shapes and relative sizes of all the planetary orbits. He had to make two simplifying
Theme 3.3 Kepler Kepler s Basic Assumptions Kepler wanted to use the extensive data sets provided by Tycho to work out the shapes and relative sizes of all the planetary orbits. He had to make two simplifying
Planetary Alignment and Kepler s Law of Periods
 OZOBOT STREAM APPROVED Planetary Alignment and Kepler s Law of Periods Created by Richard Born Associate Professor Emeritus Northern Illinois University richb@rborn.org Topics Physics, Mathematics, Modeling,
OZOBOT STREAM APPROVED Planetary Alignment and Kepler s Law of Periods Created by Richard Born Associate Professor Emeritus Northern Illinois University richb@rborn.org Topics Physics, Mathematics, Modeling,
Unlocking the Solar System
 Unlocking the Solar System Grade 5 Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Unlocking the Solar System (5 th grade) DESCRIPTION What *IS* a solar system? What does it look like? What SHOULD
Unlocking the Solar System Grade 5 Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Unlocking the Solar System (5 th grade) DESCRIPTION What *IS* a solar system? What does it look like? What SHOULD
Thank you for your purchase!
 TM Thank you for your purchase! Please be sure to save a copy of this document to your local computer. This activity is copyrighted by the AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this
TM Thank you for your purchase! Please be sure to save a copy of this document to your local computer. This activity is copyrighted by the AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this
Notes: The Solar System
 Notes: The Solar System The Formation of the Solar System 1. A gas cloud collapses under the influence of gravity. 2. Solids condense at the center, forming a protostar. 3. A falttened disk of matter surrounds
Notes: The Solar System The Formation of the Solar System 1. A gas cloud collapses under the influence of gravity. 2. Solids condense at the center, forming a protostar. 3. A falttened disk of matter surrounds
History of Astronomy. PHYS 1411 Introduction to Astronomy. Tycho Brahe and Exploding Stars. Tycho Brahe ( ) Chapter 4. Renaissance Period
 PHYS 1411 Introduction to Astronomy History of Astronomy Chapter 4 Renaissance Period Copernicus new (and correct) explanation for retrograde motion of the planets Copernicus new (and correct) explanation
PHYS 1411 Introduction to Astronomy History of Astronomy Chapter 4 Renaissance Period Copernicus new (and correct) explanation for retrograde motion of the planets Copernicus new (and correct) explanation
2.4 The Birth of Modern Astronomy
 2.4 The Birth of Modern Astronomy Telescope invented around 1600 Galileo built his own, made observations: Moon has mountains and valleys Sun has sunspots, and rotates Jupiter has moons (shown): Venus
2.4 The Birth of Modern Astronomy Telescope invented around 1600 Galileo built his own, made observations: Moon has mountains and valleys Sun has sunspots, and rotates Jupiter has moons (shown): Venus
DeAnza College Winter First Midterm Exam MAKE ALL MARKS DARK AND COMPLETE.
 FAMILY NAME : (Please PRINT!) GIVEN NAME : (Please PRINT!) Signature: ASTRONOMY 4 DeAnza College Winter 2018 First Midterm Exam MAKE ALL MARKS DARK AND COMPLETE. Instructions: 1. On your Parscore sheet
FAMILY NAME : (Please PRINT!) GIVEN NAME : (Please PRINT!) Signature: ASTRONOMY 4 DeAnza College Winter 2018 First Midterm Exam MAKE ALL MARKS DARK AND COMPLETE. Instructions: 1. On your Parscore sheet
Cycles. 1. Explain what the picture to the left shows. 2. Explain what the picture to the right shows. 3. Explain what the picture to the left shows.
 Cycles 1. Explain what the picture to the left shows. 2. Explain what the picture to the right shows. 3. Explain what the picture to the left shows. Each picture above shows a cycle. The first picture
Cycles 1. Explain what the picture to the left shows. 2. Explain what the picture to the right shows. 3. Explain what the picture to the left shows. Each picture above shows a cycle. The first picture
Large and small planets
 Large and small planets Journey through the Solar System C 41 time 50 minutes. Preparation For the activity Planets show the planets under each other on the board, as shown in the table. learning outcomes
Large and small planets Journey through the Solar System C 41 time 50 minutes. Preparation For the activity Planets show the planets under each other on the board, as shown in the table. learning outcomes
