Principles of Mathematics 12: Explained!
|
|
|
- Sylvia Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 18
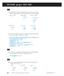
2 Part I Ferris Wheels One of the most common application questions for graphing trigonometric functions involves Ferris wheels, since the up and down motion of a rider follows the shape of a sine or cosine graph. Example: A Ferris wheel has a diameter of m, with the centre 18 m above the ground. It makes one complete rotation every 60 s. a) Draw the graph of one complete cycle, assuming the rider starts at the lowest point. Find the cosine equation of the graph. c) What is the height of the rider at 2 seconds? d) At what time(s) is the rider at m? a. When you look at a Ferris wheel it makes a circular motion. Do NOT draw 3 Midline at 18 m a circle as your graph. The graph represents the up & down motion over time. 2 In the first half of the graph, we can see the person will go up from 3 m to 33 m in seconds. In the second half, the person will go back down to 3 m. Height (m) b. a-value: We know the diameter of the wheel is m, so the radius (which is the same as amplitude) will be m Time (s) b-value: The period is 60 s, so: π b = = = P 60 c-value: There is none in the cosine pattern. d-value: The centre of the wheel is 18 m above the ground, so that will be the midline The cosine pattern is upside down, so you need to put a negative in front. π h(t) = -cos t +18 c. Method 1: Plug 2 s in for time in either the cosine equation. Simplify and calculate with your TI-83 in radian mode π ht () = cos t+ 18 π h(2) = cos h(2) = 7.96 m Method 2: Put your calculator in radian mode and graph either the cosine function. 2 nd Trace Value x = 2 This will calculate the height directly from the graph. d. To find the times the rider is at m, graph a horizontal line in your TI-83 at y =, then find the points of intersection. The rider has a height of m at 16.3 s and 43.7 s 186
3 Part I Ferris Wheels In some Ferris wheel questions, you will be given the rotational speed in units of revolutions per second or revolutions per minute. You can use these values to find the period as follows: Example: A Ferris wheel rotates at 4 rev/min. What is the period in minutes & seconds? Think of it this way: there are 60 seconds in a minute. If it completes four revolutions, each one must take only seconds. Thus, the period is s. Conversion Reminder: Minutes Seconds: Multiply by 60 Seconds Minutes: Divide by 60 Ferris Wheel Questions A Ferris wheel has a radius of 3 m and starts 2 m above the ground. It rotates once every 3 seconds. a) Determine the cosine equation of the graph, if the rider gets on at the lowest point. Sketch two complete cycles of a graph representing the height of a rider above the ground, assuming the rider gets on the Ferris wheel at the lowest point. c) What is the height of the rider at 81 seconds? d) At what time does the rider first reach a height of 1 m? 2. A Ferris wheel makes 4 revolutions in one minute. The diameter of the Ferris wheel is 28 m, and a rider boards from a platform at a height of m above the ground. The ride lasts seconds. a) Determine the cosine equation. (Hint: Think about where the rider is starting in this question.) Sketch the graph for the complete ride. c) At what times is the rider at a height of m? 187
4 Part I Ferris Wheels 3. A water wheel on a paddleboat has a radius of 1 m. The wheel rotates once every 1.46 seconds and the bottom 0.3 m of the wheel is submerged in water. (Consider the water surface to be the x-axis) a) Determine the cosine equation of the graph, starting from a point at the top of the wheel. Graph the height of a point on the wheel relative to the surface of the water, starting from the highest point. c) How long is a point on the wheel underwater? 4. The bottom of a windmill is 8 m above the ground, and the top is 22 m above the ground. The wheel rotates once every five seconds. a) Determine the cosine equation of the graph, starting from a point at the bottom of the windmill. Draw the graph of two complete cycles. c) What is the height of the point after 4 seconds? d) For how long (over the course of both cycles) is the point above 17 m?. A point on an industrial flywheel experiences a motion described by the formula: a) What is the maximum height of the point? h( t) = 13cos t At what time is the maximum height reached? c) What is the minimum height of the point? d) At what time is the minimum height reached? e) How long, within one cycle, is the point lower than 6 m above the ground? f) What is the height of the point if the wheel turns for 2 hours and minutes? 188
5 Part I Ferris Wheel ANSWERS 1. a-value: The amplitude is 3 (upside down since the rider gets on at the bottom, so use a negative in the equation) a) b-value: b = = P 3 c-value: None for cosine d-value: The lowest point is 2 m off the ground and the radius is 3 m, so the midline will be at 37 m. ht () = 3cos t d) 60 c) To find the height at 81 seconds, plug the time into the equation. ht () = 3cos t h(81) = 3cos (81) h(81) = 71.4 Or use the simpler method of 2 nd Trace Value x = 81 In your TI-83, graph the equation and also the line y = 1. The first intersection point will give the time the height first reaches 1 m. Height (m) m is first reached at 16.7 s Time (s) a) The diameter is 28 m, so the radius is 14. The period is seconds. a-value: The amplitude is 14 b-value: b = = P c-value: None for cosine d-value: The highest point is m off the ground and the radius is 14 m, so the midline will be at 16 m. ht () = 14cos t+ 16 *Use a positive since the rider gets on at the top, and therefore the cosine graph is upright. c) Height (m) 2 The rider is at a height of m at the following times: 3.06 s 11.9 s 18.1 s 26.9 s 2 Time (s) 189
6 Part I Ferris Wheel ANSWERS 3. The period is 1.46 seconds a) a-value: The amplitude is 1. c) b-value: b = = P 1.46 c-value: For the cosine graph, there is none. d-value: The midline will be at 0.7 m, since the bottom is at -0.3 m and the radius is 1 m. ht () = cos t Height (m) Time (s) Use your TI-83 to find the points of intersection with the line y=0. (In this case, it s the same as the x-intercepts) The point on the wheel is first submerged at 0.4 s, and exits the water at 0.9 s. The total time underwater is 0.37 s The period is seconds. c) To find the height at 4 seconds, a) a-value: The amplitude is 7. plug the time into your equation. max min amplitude = = = = 7 ht ( ) = 7cos t b-value: b = = h(4) = 7 cos (4) + P c-value: For the cosine graph, there is none. h(4) = 12.8m d-value: The midline is at. max+ min midline = = = = ht ( ) = 7cos t+ The cosine pattern is upside down, so we need a negative. d) Or, use 2 nd Trace Value x = 4 Height (m) 2 In the first cycle, the point is above 17 m between 1.48 s and 3.2 s, for a total of 2.04 seconds. Since the second cycle is identical to the first, the total time spent above 17 m is 4.08 s Time (s) 190
7 Part I Ferris Wheel ANSWERS. a) The midline is at m, and the radius is 13 m, so the maximum height is 28 m. The maximum occurs at the beginning of the cycle (0 s) and the end (0.7 s) c) The midline is at m, and the radius is 13 m, so the minimum height is 2 m. d) the minimum is reached exactly halfway, so 0.3 s. Height (m) Time (s) e) The point first goes under 6 m at 0.26 s, and then rises above at 0.44 s. The total time then is 0.18 s. f) We need to convert the time to seconds. 2 hours and minutes is 140 min. 140 min = 8400 s. ht () = 13cos t+ 0.7 h(8400) = 13cos (8400) h(8400) =
8 Part II Year Questions Events that are cyclic, such as seasonal variations in temperature, can be modeled with trigonometric functions. Example: The average temperature for Regina is hottest at 27 ºC on July 28, and coolest at -16 ºC on January. a) Write the cosine equation for the graph. Draw the graph that approximates the temperature curve for the year. c) What is the average temperature expected for October 4? d) The average temperature is higher than 23 ºC for how many days? a) Whenever there are questions that deal with values over an entire year, the period is 36. a-value: The amplitude is 21. max min 27 ( 16) 43 amplitude = = = = b = = P 36 b-value: c-value: We are starting the graph on January 1, so that is day zero. The maximum value (where the positive cosine graph would begin) is on July 28. So, the number of days to July 28 is: = 9 d-value: The midline is at.. max+ min 27 + ( 16) 11 midline = = = = c) To find the expected temperature on October 4, first find what day of the year it is = 277 Now use this in your equation: Td ( ) = 21.cos ( d 9) T (277) = 21.cos (277 9) T (277) = 13.9 Or, graph in your TI-83 and type: 2 nd Trace Value x = 277 d) Td ( ) = 21.cos ( d 9) Where T is temperature in ºC, and d is the number of days. Temperature (ºC) Use your TI-83 to find the intersection points of the graph and the line y=23. The first day over 23 ºC is day 173. The last day over 23 ºC is day 24. The total time is 72 days. - Time (days) 192
9 Part II Year Questions Example 2: The earliest sunset occurs at :34 PM on Dec. 21, and the latest at 11:4 PM on June 21. a) Write the cosine equation of the graph. Draw the graph approximating the sunrise times throughout the year. c) What is the sunset time on April. 6? d) The sunset time is earlier than 8 PM for what percentage of the year? a) Before anything else, we are never allowed to use time in hour/minute form when creating an equation! Convert to decimal hour form. Conversion Reminder: To get the hours, think of the 24-hour clock. Then divide the number of minutes by 60 to finish off the decimal. :34 PM PM is 17 hours on the 24-hour clock. Then, 11/60 = 0.7. So, the time we use is 17.7 Time (hours) a-value: The amplitude is 3.1 max min amplitude = = = = b = = P 36 b-value: 11:4 PM 11 PM is 23 hours on the 24-hour clock. Then, 4/60 = 0.7. So, the time we use is 23.7 More Examples: 12:00 AM = 0 hours 12: AM = 0. hours 7: PM = 19.2 hours 11: 49 PM = hours c-value: We are starting the graph on January 1, so that is day zero. The maximum value (where the cosine graph would begin) is on June 21. So, the number of days is: = 172 d-value: The midline is at max+ min midline = = = = c) To find the expected temperature on April 6, first find what day of the year it is = 96 Time (days) Now use this in your equation: Td ( ) = 3.1cos ( d 172) T (96) = 3.1cos (96 172) T (96) = = 9:28 PM Or, graph in your TI-83 and type: 2 nd Trace Value x = 96 d) Sunset is earlier than 8 PM from day 0 to 68, then again from day 276 to 36. So, the total number of days is 7. Divide by the total days in the year to get 43% Sd ( ) = 3.1cos ( d 172) S is the time of sunset (in decimal hours) d is the day number of the year
10 Part II Year Questions 1. The highest average temperature for the Edmonton region is 24 ºC, and occurs on July. The coldest average temperature is -16 ºC, and occurs on January 14. a) Write a cosine equation for the graph. Draw the graph that approximates the temperature curve for the year. c) What is the average temperature expected for November 4? d) The average temperature is below 0 ºC for how many days? 2. The average temperature for the Ottawa region is hottest at 2 ºC on July 23, and coolest at 4 ºC on January 12. a) Write a cosine equation for the graph. Draw the graph that approximates the temperature curve for the year. c) What is the average temperature expected for August 4? d) The average temperature is higher than ºC for how many days? 3. The following table gives the average recorded monthly temperature throughout the year. (Use month number for the x-axis. eg. April is x = 4). Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Temp a) What is the amplitude (Based on coldest & warmest months) and period of the function? Write a cosine equation for the graph. c) Sketch the graph that approximates the temperature curve for the year. *This question can also be completed using the trigonometric regression feature of your TI-83. d) How does the recorded temperature for September compare with the value from your equation? Note, however, that trigonometric regression is not a requirement for this course
11 Part II Year Questions 4. The latest sunrise occurs at 9: AM on December 21. The earliest occurs at 3:43 AM on June 21. a) Write the cosine equation of the graph. Draw the graph approximating the sunrise times throughout the year c) What is the sunrise time on Feb. 21? d) The sunrise time is earlier than AM for how many days?. The earliest sunset occurs at :14 PM on Dec. 21, and the latest at 11:4 PM on June. a) Write the cosine equation of the graph. Draw the sinusoidal graph approximating the sunrise times throughout the year. c) What is the sunset time on April. 6? d) The sunset time is earlier than 8 PM for what percentage of the year? 6. The following table gives the average recorded sunrise time for each month. (Use month number for the x-axis. eg. April is x = 4) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Time 8: 7:9 7: 6: 6:01 : :34 6:03 6:34 7: 7:2 8:2 a) What is the amplitude and period of the function? Write a cosine equation for the graph. c) Sketch the graph that approximates the sunrise times for the year. d) How does the recorded sunrise time for April compare with the value from your equation? 19
12 Part II Year Questions ANSWERS a) a) T( d) = cos ( d 1) c) ºC d) 9 days Td ( ) =.cos ( d 4) c) 24.8 ºC d) 118 days a) a) T( d) = 2.73cos ( 172) d c) 7.74 hours 7:44 AM d) 118 days Td ( ) = 3.34 cos ( d 171) c) 21.0 hours 9: PM d) 163 days 3. a) Amplitude is 22- (-17) =19. 2 Period is 12 months c) T( d ) = 19. cos ( d 7) d) 12.3 ºC is the answer from the equation, which is slightly off from the recorded value of ºC. This is because the equation is an approximation of the actual temperatures *Use decimal time Latest sunset = 8.0 hours Earliest sunset =.0 hours a) Amplitude is 8.. = 1. 2 Period is 12 Midline is = 7 2 Td ( ) = 1.cos ( d 6) Use a negative for the cosine pattern since it is upside down. c) d) From equation 6: AM From given data 6: AM The time from the equation is slightly off from the recorded time, but that is to be expected since the equation is only an approximation of the actual curve.
Practice Test Chapter 8 Sinusoidal Functions
 FOM 12 Practice Test Chapter 8 Sinusoidal Functions Name: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Block: _ 1. Convert 120 into radians. A. 2" 3 B.
FOM 12 Practice Test Chapter 8 Sinusoidal Functions Name: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Block: _ 1. Convert 120 into radians. A. 2" 3 B.
Section 5.1 Extra Practice. Section 5.2 Extra Practice. Chapter 5 Review. cos x. 9. Determine the amplitude & period for the graphs below.
 Chapter Review Section. Etra Practice. a) Sketch the graph of y = sin θ for 60 θ 60. Identify the key points by labelling their coordinates on the graph. b) What is the eact value of this function at?
Chapter Review Section. Etra Practice. a) Sketch the graph of y = sin θ for 60 θ 60. Identify the key points by labelling their coordinates on the graph. b) What is the eact value of this function at?
CHAPTER 8. Sinusoidal Functions
 CHAPTER 8 Sinusoidal Functions 8.1 UNDERSTANDING ANGLES Chapter 8 DEFINITIONS A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle. The unit circle is a circle whose radius is 1. Arc length
CHAPTER 8 Sinusoidal Functions 8.1 UNDERSTANDING ANGLES Chapter 8 DEFINITIONS A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle. The unit circle is a circle whose radius is 1. Arc length
Unit 3 Trigonometry. 3.4 Graph and analyze the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent to solve problems.
 1 General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. Specific Outcomes: Unit 3 Trigonometry 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. 3.2 Develop
1 General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. Specific Outcomes: Unit 3 Trigonometry 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. 3.2 Develop
Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions
 Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions 441 Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions Solving right triangles for angles In Section 5.5, we used trigonometry on a right triangle to solve
Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions 441 Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions Solving right triangles for angles In Section 5.5, we used trigonometry on a right triangle to solve
8.5. Modelling Data with Sinusoidal Functions. INVESTIGATE the Math
 8.5 Modelling Data with Sinusoidal Functions GOAL Determine the sinusoidal function that best models a set of data, and use your model to solve a problem. INVESTIGATE the Math Kelly lives in Winnipeg,
8.5 Modelling Data with Sinusoidal Functions GOAL Determine the sinusoidal function that best models a set of data, and use your model to solve a problem. INVESTIGATE the Math Kelly lives in Winnipeg,
Sunrise, Sunset and Mathematical Functions
 Teaching of Functions 13 Sunrise, Sunset and Mathematical Functions Activity #1: The table you are given reports the sunrise and sunset times for Manila, Philippines for each day of the year. Each day
Teaching of Functions 13 Sunrise, Sunset and Mathematical Functions Activity #1: The table you are given reports the sunrise and sunset times for Manila, Philippines for each day of the year. Each day
f(x)= 2x 2 +x f(x)= x 3 f(x)= x 3 +2
 Show that the following functions 1. Warm up Functions even and odd 2. Review Problems From Friday 3. Inverse Functions are even, odd or neither using function notation. f(x)= 2x 2 f(x)= 2x 2 +x f(x)=
Show that the following functions 1. Warm up Functions even and odd 2. Review Problems From Friday 3. Inverse Functions are even, odd or neither using function notation. f(x)= 2x 2 f(x)= 2x 2 +x f(x)=
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) determine an angle that is co-terminal to c) Determine the reference angle of
 1. a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) determine an angle that is co-terminal to c) Determine the reference angle of 2. Which pair of angles are co-terminal with? a., b., c., d., 3. During a routine,
1. a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) determine an angle that is co-terminal to c) Determine the reference angle of 2. Which pair of angles are co-terminal with? a., b., c., d., 3. During a routine,
13) y = - sin 2x, y = cos2(x-(3π/4)), y = cos 2(x+(π/4))
 HW: Worksheet; Test on Fri., 2/9 Aim #59: How do we model data with trigonometric functions? Kickoff: A sine curve modeled in the form y = a sin(x) +d has a maximum value of 8 and a minimum value of -2.
HW: Worksheet; Test on Fri., 2/9 Aim #59: How do we model data with trigonometric functions? Kickoff: A sine curve modeled in the form y = a sin(x) +d has a maximum value of 8 and a minimum value of -2.
Comparing Sinusoidal Functions. Relate details of sinusoidal phenomena to their graphs. LEARN ABOUT the Math. Height (m)
 Comparing Sinusoidal Functions YOU WILL NEED graphing calculator GOAL Relate details of sinusoidal phenomena to their graphs. LEARN ABOUT the Math At an amusement park, a math teacher had different students
Comparing Sinusoidal Functions YOU WILL NEED graphing calculator GOAL Relate details of sinusoidal phenomena to their graphs. LEARN ABOUT the Math At an amusement park, a math teacher had different students
Section 6.1 Exercises
 Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs 97 Section 6.1 Exercises 1. Sketch a graph of f x 3sinx 2. Sketch a graph of f x 4sinx 3. Sketch a graph of f x 2cosx 4. Sketch a graph of f x 4cosx For the graphs below,
Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs 97 Section 6.1 Exercises 1. Sketch a graph of f x 3sinx 2. Sketch a graph of f x 4sinx 3. Sketch a graph of f x 2cosx 4. Sketch a graph of f x 4cosx For the graphs below,
Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017
 Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017 1. The terminal ray of an angle drawn in standard position on the unit circle that measures 30 has 3 1 coordinates of,. Based on this information,
Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017 1. The terminal ray of an angle drawn in standard position on the unit circle that measures 30 has 3 1 coordinates of,. Based on this information,
Mathematics UNIT FOUR Trigonometry I. Unit. y = asinb(θ - c) + d. Student Workbook. (cosθ, sinθ)
 Mathematics - Student Workbook Unit 8 = 7 6 Lesson : Degrees and Radians Approximate Completion Time: Days (cos, sin) Lesson : The Unit Circle Approximate Completion Time: Days y = asinb( - c) + d Lesson
Mathematics - Student Workbook Unit 8 = 7 6 Lesson : Degrees and Radians Approximate Completion Time: Days (cos, sin) Lesson : The Unit Circle Approximate Completion Time: Days y = asinb( - c) + d Lesson
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET
 TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
6.1 Solutions to Exercises
 Last edited 3/1/13 6.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of 3, and a horizontal reflection. 3. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of. 5. Period:. Amplitude: 3.
Last edited 3/1/13 6.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of 3, and a horizontal reflection. 3. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of. 5. Period:. Amplitude: 3.
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2
 MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
Honors Precalculus Semester 1 Review
 Honors Precalculus Semester 1 Review Name: UNIT 1 1. For each sequence, find the explicit and recursive formulas. Show your work. a) 45, 39, 33, 27 b) 8 3, 16 9 32 27, 64 81 Explicit formula: Explicit
Honors Precalculus Semester 1 Review Name: UNIT 1 1. For each sequence, find the explicit and recursive formulas. Show your work. a) 45, 39, 33, 27 b) 8 3, 16 9 32 27, 64 81 Explicit formula: Explicit
Math 12 Pre-Calculus Midterm Review (Chapters 1 6)
 REVIEW SCHEDULE: Date: Topics Covered: Suggested Practice: Feb. 10/11 Chapters 1 3 Unit 1 Test : Pg. 160 161 All Feb. 12/13 Chapter 4, 5 Unit 2 Test : Pg. 328 329 # 1 6, 9, 10, 12 17, 20 Feb. 16/17 Chapter
REVIEW SCHEDULE: Date: Topics Covered: Suggested Practice: Feb. 10/11 Chapters 1 3 Unit 1 Test : Pg. 160 161 All Feb. 12/13 Chapter 4, 5 Unit 2 Test : Pg. 328 329 # 1 6, 9, 10, 12 17, 20 Feb. 16/17 Chapter
Math 30-1: Trigonometry One PRACTICE EXAM
 Math 30-1: Trigonometry One PRACTICE EXAM 1. The angle 210 is equivalent to: degrees radians degrees radians 2. The reference angle of is: radians radians radians radians 3. The principal angle of 9.00
Math 30-1: Trigonometry One PRACTICE EXAM 1. The angle 210 is equivalent to: degrees radians degrees radians 2. The reference angle of is: radians radians radians radians 3. The principal angle of 9.00
Math Review. Name:
 Math 30-1 Name: Review 1. Given the graph of : Sketch the graph of the given transformation on the same grid Describe how the transformed graph relates to the graph of Write the equation of the image of
Math 30-1 Name: Review 1. Given the graph of : Sketch the graph of the given transformation on the same grid Describe how the transformed graph relates to the graph of Write the equation of the image of
Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package. Name:
 MAT40S Unit 3 Trigonometry Mr. Morris Lesson Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package Homework 1: Converting and Arc Extra Practice Sheet 1 Length 2: Unit Circle and Angles Extra Practice Sheet 2 3: Determining
MAT40S Unit 3 Trigonometry Mr. Morris Lesson Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package Homework 1: Converting and Arc Extra Practice Sheet 1 Length 2: Unit Circle and Angles Extra Practice Sheet 2 3: Determining
Monday, October 24, Trigonometry, Period 3
 Monday, Trigonometry, Period 3 Lesson Overview: Warm Up Go over homework Writing Sinusoidal Functions to Model Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Recap: The past few classes, we ve been talking about simple harmonic
Monday, Trigonometry, Period 3 Lesson Overview: Warm Up Go over homework Writing Sinusoidal Functions to Model Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Recap: The past few classes, we ve been talking about simple harmonic
5.1: Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions
 5.1: Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Complete the table below ( we used increments of for the values of ) 4 0 sin 4 2 3 4 5 4 3 7 2 4 2 cos 1. Using the table, sketch the graph of y sin for 0 2 2. What
5.1: Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Complete the table below ( we used increments of for the values of ) 4 0 sin 4 2 3 4 5 4 3 7 2 4 2 cos 1. Using the table, sketch the graph of y sin for 0 2 2. What
GAMINGRE 8/1/ of 7
 FYE 09/30/92 JULY 92 0.00 254,550.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 254,550.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 254,550.00 AUG 10,616,710.31 5,299.95 845,656.83 84,565.68 61,084.86 23,480.82 339,734.73 135,893.89 67,946.95
FYE 09/30/92 JULY 92 0.00 254,550.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 254,550.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 254,550.00 AUG 10,616,710.31 5,299.95 845,656.83 84,565.68 61,084.86 23,480.82 339,734.73 135,893.89 67,946.95
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
Exam Review. Completion Complete each statement. 1. The maximum value of the function is. 2. The period of the function is.
 Exam Review Completion Complete each statement. 1. The maximum value of the function is. 2. The period of the function is. 3. If and, then the domain of the function is. Matching Match each equation with
Exam Review Completion Complete each statement. 1. The maximum value of the function is. 2. The period of the function is. 3. If and, then the domain of the function is. Matching Match each equation with
Math 175: Chapter 6 Review: Trigonometric Functions
 Math 175: Chapter 6 Review: Trigonometric Functions In order to prepare for a test on Chapter 6, you need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics. A. Can you sketch an
Math 175: Chapter 6 Review: Trigonometric Functions In order to prepare for a test on Chapter 6, you need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics. A. Can you sketch an
Line Graphs. 1. Use the data in the table to make a line graph. 2. When did the amount spent on electronics increase the most?
 Practice A Line Graphs Use the table to answer the questions. U.S. Personal Spending on Selected Electronics Amount Spent Year ($billions, estimated) 1994 $71 1996 $80 1998 $90 2000 $107 1. Use the data
Practice A Line Graphs Use the table to answer the questions. U.S. Personal Spending on Selected Electronics Amount Spent Year ($billions, estimated) 1994 $71 1996 $80 1998 $90 2000 $107 1. Use the data
4-10. Modeling with Trigonometric Functions. Vocabulary. Lesson. Mental Math. build an equation that models real-world periodic data.
 Chapter 4 Lesson 4-0 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions Vocabular simple harmonic motion BIG IDEA The Graph-Standardization Theorem can be used to build an equation that models real-world periodic data.
Chapter 4 Lesson 4-0 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions Vocabular simple harmonic motion BIG IDEA The Graph-Standardization Theorem can be used to build an equation that models real-world periodic data.
Honors Algebra 2 Chapter 14 Page 1
 Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Jackson County 2013 Weather Data
 Jackson County 2013 Weather Data 61 Years of Weather Data Recorded at the UF/IFAS Marianna North Florida Research and Education Center Doug Mayo Jackson County Extension Director 1952-2008 Rainfall Data
Jackson County 2013 Weather Data 61 Years of Weather Data Recorded at the UF/IFAS Marianna North Florida Research and Education Center Doug Mayo Jackson County Extension Director 1952-2008 Rainfall Data
WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities
 WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and 2001-2002 Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities Phoenix Tucson Flagstaff Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 October 0.7 0.0
WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and 2001-2002 Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities Phoenix Tucson Flagstaff Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 October 0.7 0.0
Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
(c) cos Arctan ( 3) ( ) PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER
 PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
Pre-Calc Chapter 1 Sample Test. D) slope: 3 4
 Pre-Calc Chapter 1 Sample Test 1. Use the graphs of f and g to evaluate the function. f( x) gx ( ) (f o g)(-0.5) 1 1 0 4. Plot the points and find the slope of the line passing through the pair of points.
Pre-Calc Chapter 1 Sample Test 1. Use the graphs of f and g to evaluate the function. f( x) gx ( ) (f o g)(-0.5) 1 1 0 4. Plot the points and find the slope of the line passing through the pair of points.
REVIEW, pages
 REVIEW, pages 5 5.. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio. Use eact values where possible; otherwise write the value to the nearest thousandth. a) tan (5 ) b) cos c) sec ( ) cos º cos ( ) cos
REVIEW, pages 5 5.. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio. Use eact values where possible; otherwise write the value to the nearest thousandth. a) tan (5 ) b) cos c) sec ( ) cos º cos ( ) cos
Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians
 Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians WORKBOOK MHF4U W1 4.1 Radian Measure MHF4U Jensen 1) Determine mentally the exact radian measure for each angle, given that 30 is exactly π 6 radians. a) 60
Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians WORKBOOK MHF4U W1 4.1 Radian Measure MHF4U Jensen 1) Determine mentally the exact radian measure for each angle, given that 30 is exactly π 6 radians. a) 60
Sections 01, 02, & 04 (Bressoud and Ehren) 9 October, 2015
 Math 135, Applied Calculus First Midterm Exam Sections 01, 02, & 04 (Bressoud and Ehren) 9 October, 2015 This exam is worth 100 points. Show your work. Partial credit will be given for partially correct
Math 135, Applied Calculus First Midterm Exam Sections 01, 02, & 04 (Bressoud and Ehren) 9 October, 2015 This exam is worth 100 points. Show your work. Partial credit will be given for partially correct
Grade 6 Standard 2 Unit Test Astronomy
 Grade 6 Standard 2 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. Why does the air temperature rise in the summer? A. We are closer to the sun. B. The air becomes thicker and more dense. C. The sun s rays are
Grade 6 Standard 2 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. Why does the air temperature rise in the summer? A. We are closer to the sun. B. The air becomes thicker and more dense. C. The sun s rays are
IB Mathematics HL Year 1 Unit 4: Trigonometry (Core Topic 3) Homework for Unit 4. (A) Using the diagram to the right show that
 IB Mathematics HL Year Unit 4: Trigonometry (Core Topic 3) Homework for Unit 4 Lesson 4 Review I: radian measure, definitions of trig ratios, and areas of triangles D.2: 5; E.: 5; E.2: 4, 6; F: 3, 5, 7,
IB Mathematics HL Year Unit 4: Trigonometry (Core Topic 3) Homework for Unit 4 Lesson 4 Review I: radian measure, definitions of trig ratios, and areas of triangles D.2: 5; E.: 5; E.2: 4, 6; F: 3, 5, 7,
THE LIGHT SIDE OF TRIGONOMETRY
 MATHEMATICAL METHODS: UNIT 2 APPLICATION TASK THE LIGHT SIDE OF TRIGONOMETRY The earth s movement around the sun is an example of periodic motion. The earth s tilt on its axis and corresponding movement
MATHEMATICAL METHODS: UNIT 2 APPLICATION TASK THE LIGHT SIDE OF TRIGONOMETRY The earth s movement around the sun is an example of periodic motion. The earth s tilt on its axis and corresponding movement
Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure?
 Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure? In relationship to a circle, if I go half way around the edge
Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure? In relationship to a circle, if I go half way around the edge
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Determine the trend for time series data
 Extra Online Questions Determine the trend for time series data Covers AS 90641 (Statistics and Modelling 3.1) Scholarship Statistics and Modelling Chapter 1 Essent ial exam notes Time series 1. The value
Extra Online Questions Determine the trend for time series data Covers AS 90641 (Statistics and Modelling 3.1) Scholarship Statistics and Modelling Chapter 1 Essent ial exam notes Time series 1. The value
Champaign-Urbana 2001 Annual Weather Summary
 Champaign-Urbana 2001 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: After a cold and snowy December,
Champaign-Urbana 2001 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: After a cold and snowy December,
7.3 Getting on the Right Wavelength
 7.3 Getting on the Right Wavelength A Practice Understanding Task The Ferris wheel in the following diagram has a radius of 40 feet, its center is 50 feet from the ground, and it makes one revolution counterclockwise
7.3 Getting on the Right Wavelength A Practice Understanding Task The Ferris wheel in the following diagram has a radius of 40 feet, its center is 50 feet from the ground, and it makes one revolution counterclockwise
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus. Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.. Write the equation of the line that goes through the points ( 3, 7) and (4, 5)
AP Calculus. Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.. Write the equation of the line that goes through the points ( 3, 7) and (4, 5)
Functions and their Graphs
 Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Calculations Equation of Time. EQUATION OF TIME = apparent solar time - mean solar time
 Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
AdvAlg9.7LogarithmsToBasesOtherThan10.notebook. March 08, 2018
 AdvAlg9.7LogarithmsToBasesOtherThan10.notebook In order to isolate a variable within a logarithm of an equation, you need to re write the equation as the equivalent exponential equation. In order to isolate
AdvAlg9.7LogarithmsToBasesOtherThan10.notebook In order to isolate a variable within a logarithm of an equation, you need to re write the equation as the equivalent exponential equation. In order to isolate
5.1 Arc length, area sector, vocab, coterminal, reference angles_jb A Block.notebook May 14, 2014
 Objectives: Generate vocabulary flashcards for new terms. Derive formulas for arc length and area of a circular sector. Solve application problems using the arc length and area of circular sector formulas.
Objectives: Generate vocabulary flashcards for new terms. Derive formulas for arc length and area of a circular sector. Solve application problems using the arc length and area of circular sector formulas.
Day Length Web Activity
 Day Length We Activity SAMPLE Name: Follow the directions for each section and type your answers on a separate sheet of paper. Use TI-Graph Link or TI Inter Active! to present your data and models you
Day Length We Activity SAMPLE Name: Follow the directions for each section and type your answers on a separate sheet of paper. Use TI-Graph Link or TI Inter Active! to present your data and models you
982T1S2 Assignment Topic: Trigonometric Functions Due Date: 28 th August, 2015
 HAWKER COLLEGE Faculty 42 Assignment Cover Sheet This sheet should be attached to the front of your assessment item. Read it carefully, complete the appropriate details, and sign it. Course: Specialist
HAWKER COLLEGE Faculty 42 Assignment Cover Sheet This sheet should be attached to the front of your assessment item. Read it carefully, complete the appropriate details, and sign it. Course: Specialist
5.5. Data Collecting and Modelling. Investigate
 5.5 Data Collecting and Modelling One of the real-world applications of sinusoidal models is the motion of a pendulum. A Foucault pendulum is used to measure the rotation of Earth. As Earth turns, the
5.5 Data Collecting and Modelling One of the real-world applications of sinusoidal models is the motion of a pendulum. A Foucault pendulum is used to measure the rotation of Earth. As Earth turns, the
Name: What are the landmarks for the data set above? a. maximum b. minimum c. range d. mode(s) e. median
 1. The data below shows the average daily temperature ( F) of a city. 80, 84, 84, 80, 88, 92, 80, 96, 92, 0, 92, 4, 92, 0, 4 Create a line plot of the data. 2. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 What are the landmarks
1. The data below shows the average daily temperature ( F) of a city. 80, 84, 84, 80, 88, 92, 80, 96, 92, 0, 92, 4, 92, 0, 4 Create a line plot of the data. 2. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 What are the landmarks
Using Functions in Models and Decision Making: Cyclical Functions V.B Student Activity Sheet 4: Length of Daylight
 Student: Class: V.B Student Activity Sheet 4: Daylight You may have noticed that during the winter the days are shorter and during the summer the days are longer. How much longer are days during the summer?
Student: Class: V.B Student Activity Sheet 4: Daylight You may have noticed that during the winter the days are shorter and during the summer the days are longer. How much longer are days during the summer?
What Is the Relationship Between Earth s Tilt and the Seasons?
 Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Reason for the Seasons Workbook
 Name Reason for the Seasons Workbook Clipart from the Florida Center for Instructional Technology (FCIT) Table of Contents What Causes the Seasons Factsheet and Activity............. 1 Angle of Light Rays
Name Reason for the Seasons Workbook Clipart from the Florida Center for Instructional Technology (FCIT) Table of Contents What Causes the Seasons Factsheet and Activity............. 1 Angle of Light Rays
Public Library Use and Economic Hard Times: Analysis of Recent Data
 Public Library Use and Economic Hard Times: Analysis of Recent Data A Report Prepared for The American Library Association by The Library Research Center University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign April
Public Library Use and Economic Hard Times: Analysis of Recent Data A Report Prepared for The American Library Association by The Library Research Center University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign April
DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR
 DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR LEAP AND NON-LEAP YEAR *A non-leap year has 365 days whereas a leap year has 366 days. (as February has 29 days). *Every year which is divisible by 4
DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR LEAP AND NON-LEAP YEAR *A non-leap year has 365 days whereas a leap year has 366 days. (as February has 29 days). *Every year which is divisible by 4
P7.7 A CLIMATOLOGICAL STUDY OF CLOUD TO GROUND LIGHTNING STRIKES IN THE VICINITY OF KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLORIDA
 P7.7 A CLIMATOLOGICAL STUDY OF CLOUD TO GROUND LIGHTNING STRIKES IN THE VICINITY OF KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLORIDA K. Lee Burns* Raytheon, Huntsville, Alabama Ryan K. Decker NASA, Marshall Space Flight
P7.7 A CLIMATOLOGICAL STUDY OF CLOUD TO GROUND LIGHTNING STRIKES IN THE VICINITY OF KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLORIDA K. Lee Burns* Raytheon, Huntsville, Alabama Ryan K. Decker NASA, Marshall Space Flight
Recall the following facts for the Ferris wheel Carlos is riding:
 In spite of his nervousness, Carlos enjoys his first ride on the amusement park Ferris wheel. He does, however, spend much of his time with his eyes fixed on the ground below him. After a while, he becomes
In spite of his nervousness, Carlos enjoys his first ride on the amusement park Ferris wheel. He does, however, spend much of his time with his eyes fixed on the ground below him. After a while, he becomes
Candidate Number. General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2012
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2012 Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2012 Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
7.5 Simple Harmonic Motion; Damped Motion; Combining Waves. Objectives
 Objectives 1. Build a Model for an Object in Simple Harmonic Motion. 2. Analyse Simple Harmonic Motion. 3. Analyse an Object in Damped Motion. 4. Graph the Sum of Two Functions. 30 April 2017 1 Kidoguchi,
Objectives 1. Build a Model for an Object in Simple Harmonic Motion. 2. Analyse Simple Harmonic Motion. 3. Analyse an Object in Damped Motion. 4. Graph the Sum of Two Functions. 30 April 2017 1 Kidoguchi,
Name: Math 4. a. Graph two periods of the function T(t). Helpful Numbers. Min = Max = Midline = Amplitude =
 Name: Math 4 February 3/4, 2016 Sinusoidal Application Problems Sinusoidal Application Problems Objective: Practice creating and using sinusoidal function models. 1. The temperature varies sinusoidally
Name: Math 4 February 3/4, 2016 Sinusoidal Application Problems Sinusoidal Application Problems Objective: Practice creating and using sinusoidal function models. 1. The temperature varies sinusoidally
Curriculum Map Grade 8 Math
 Curriculum Map Grade 8 Math Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. September 6 October 5 October 9 November 2 November 5 - November 30 December 3 December 21 January 2 January 16 G R A D E 8 Solving Equations: ~Solving
Curriculum Map Grade 8 Math Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. September 6 October 5 October 9 November 2 November 5 - November 30 December 3 December 21 January 2 January 16 G R A D E 8 Solving Equations: ~Solving
Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC
 Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC This threat overview relies on projections of future climate change in the Mekong Basin for the period 2045-2069 compared to a baseline of 1980-2005.
Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC This threat overview relies on projections of future climate change in the Mekong Basin for the period 2045-2069 compared to a baseline of 1980-2005.
Mountain View Community Shuttle Monthly Operations Report
 Mountain View Community Shuttle Monthly Operations Report December 6, 2018 Contents Passengers per Day, Table...- 3 - Passengers per Day, Chart...- 3 - Ridership Year-To-Date...- 4 - Average Daily Ridership
Mountain View Community Shuttle Monthly Operations Report December 6, 2018 Contents Passengers per Day, Table...- 3 - Passengers per Day, Chart...- 3 - Ridership Year-To-Date...- 4 - Average Daily Ridership
Final Exam Review Part 2
 Final Exam Review Part 2 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions and Equations Polynomial & Sinusoidal Functions Rational Expressions and Equations Exponential Functions To describe, orally and in written
Final Exam Review Part 2 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions and Equations Polynomial & Sinusoidal Functions Rational Expressions and Equations Exponential Functions To describe, orally and in written
Drought Characterization. Examination of Extreme Precipitation Events
 Drought Characterization Examination of Extreme Precipitation Events Extreme Precipitation Events During the Drought For the drought years (1999-2005) daily precipitation data was analyzed to find extreme
Drought Characterization Examination of Extreme Precipitation Events Extreme Precipitation Events During the Drought For the drought years (1999-2005) daily precipitation data was analyzed to find extreme
Carbon Career & Technical Institute
 Course: Algebra I Carbon Career & Technical Institute A1.1.1.3.1 - Simplify/evaluate expressions involving properties/laws of exponents, roots, and/or absolute values to solve problems. Aug. and Sept.
Course: Algebra I Carbon Career & Technical Institute A1.1.1.3.1 - Simplify/evaluate expressions involving properties/laws of exponents, roots, and/or absolute values to solve problems. Aug. and Sept.
Chapter 6 Resource Masters
 Chapter Resource Masters New York, New York Columbus, Ohio Woodland Hills, California Peoria, Illinois StudentWorks TM This CD-ROM includes the entire Student Edition along with the Study Guide, Practice,
Chapter Resource Masters New York, New York Columbus, Ohio Woodland Hills, California Peoria, Illinois StudentWorks TM This CD-ROM includes the entire Student Edition along with the Study Guide, Practice,
North Toronto Christian School MATH DEPARTMENT
 North Toronto Christian School MATH DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Course: Advanced Functions, Grade 12 MHF4U Teacher: D. Brooks (dbrooks@ntcs.on.ca) Course description: This course extends students experience with
North Toronto Christian School MATH DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Course: Advanced Functions, Grade 12 MHF4U Teacher: D. Brooks (dbrooks@ntcs.on.ca) Course description: This course extends students experience with
5.1 Arc length, area sector, vocab, coterminal, reference angles_jb-a Block.notebook April 03, 2014
 Objectives: Generate vocabulary flashcards for new terms. Derive formulas for arc length and area of a circular sector. Solve application problems using the arc length and area of circular sector formulas.
Objectives: Generate vocabulary flashcards for new terms. Derive formulas for arc length and area of a circular sector. Solve application problems using the arc length and area of circular sector formulas.
Champaign-Urbana 2000 Annual Weather Summary
 Champaign-Urbana 2000 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: January started on a mild note,
Champaign-Urbana 2000 Annual Weather Summary ILLINOIS STATE WATER SURVEY 2204 Griffith Dr. Champaign, IL 61820 wxobsrvr@sws.uiuc.edu Maria Peters, Weather Observer January: January started on a mild note,
Activity Sheet Counting M&Ms
 Counting M&Ms Pour a half-pound bag of M&Ms onto a paper plate so that the candies are one layer thick. You will need to spread the M&Ms to the edges of the plate. Remove all the M&Ms that have the M showing
Counting M&Ms Pour a half-pound bag of M&Ms onto a paper plate so that the candies are one layer thick. You will need to spread the M&Ms to the edges of the plate. Remove all the M&Ms that have the M showing
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Grade 12 Mathematics: Question Paper 2
 Mathematics(NSC)/Grade 12/ P2 33 Eemplar Grade 12 Mathematics: Question Paper 2 MARKS: 150marks TIME: 3hours QUESTION 1 1.1 A(0;1) ; B(-2;-3); C(8;2); D(d;6) aretheverticesoftheparalelogram ABCD. 1.1.1
Mathematics(NSC)/Grade 12/ P2 33 Eemplar Grade 12 Mathematics: Question Paper 2 MARKS: 150marks TIME: 3hours QUESTION 1 1.1 A(0;1) ; B(-2;-3); C(8;2); D(d;6) aretheverticesoftheparalelogram ABCD. 1.1.1
Chapter 4: Graphing Sinusoidal Functions
 Haberman MTH 2 Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter : Graphing Sinusoidal Functions DEFINITION: A sinusoidal function is function of the form sinw or y A t h k where A, w, h, k. y Acosw t h k,
Haberman MTH 2 Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter : Graphing Sinusoidal Functions DEFINITION: A sinusoidal function is function of the form sinw or y A t h k where A, w, h, k. y Acosw t h k,
Motions of the Sun Model Exploration
 Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
MISSION DEBRIEFING: Teacher Guide
 Activity 2: It s Raining Again?! Using real data from one particular location, students will interpret a graph that relates rainfall to the number of cases of malaria. Background The relationship between
Activity 2: It s Raining Again?! Using real data from one particular location, students will interpret a graph that relates rainfall to the number of cases of malaria. Background The relationship between
4 The Trigonometric Functions
 Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Sydney 8 The Trigonometric Functions The definitions in the previous section apply to between 0 and, since the angles in a right angle triangle can never be greater
Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Sydney 8 The Trigonometric Functions The definitions in the previous section apply to between 0 and, since the angles in a right angle triangle can never be greater
AFM Midterm Review I Fall Determine if the relation is a function. 1,6, 2. Determine the domain of the function. . x x
 AFM Midterm Review I Fall 06. Determine if the relation is a function.,6,,, 5,. Determine the domain of the function 7 h ( ). 4. Sketch the graph of f 4. Sketch the graph of f 5. Sketch the graph of f
AFM Midterm Review I Fall 06. Determine if the relation is a function.,6,,, 5,. Determine the domain of the function 7 h ( ). 4. Sketch the graph of f 4. Sketch the graph of f 5. Sketch the graph of f
January 2009 Videmus Stellae
 January 2009 January Schedule of Events Sun Mon Tu e Wed Thu Fri Sat Jan 6th: ATM Sub at Paul Lind s Garage at 1900 Jan 9th: SAC General at Grand Canyon University at 1930 in room 105 of the Fleming Bldg.
January 2009 January Schedule of Events Sun Mon Tu e Wed Thu Fri Sat Jan 6th: ATM Sub at Paul Lind s Garage at 1900 Jan 9th: SAC General at Grand Canyon University at 1930 in room 105 of the Fleming Bldg.
Lecture 8 CORRELATION AND LINEAR REGRESSION
 Announcements CBA5 open in exam mode - deadline midnight Friday! Question 2 on this week s exercises is a prize question. The first good attempt handed in to me by 12 midday this Friday will merit a prize...
Announcements CBA5 open in exam mode - deadline midnight Friday! Question 2 on this week s exercises is a prize question. The first good attempt handed in to me by 12 midday this Friday will merit a prize...
DOZENALS. A project promoting base 12 counting and measuring. Ideas and designs by DSA member (#342) and board member, Timothy F. Travis.
 R AENBO DOZENALS A project promoting base 12 counting and measuring. Ideas and designs by DSA member (#342) and board member Timothy F. Travis. I became aware as a teenager of base twelve numbering from
R AENBO DOZENALS A project promoting base 12 counting and measuring. Ideas and designs by DSA member (#342) and board member Timothy F. Travis. I became aware as a teenager of base twelve numbering from
Precalculus PreAP/D Rev A: Simple Harmonic Motion. apply the rules of trigonometry and solve using simple harmonic motion.
 4.8A: Simple Harmonic Motion I WILL apply the rules of trigonometry and solve using simple harmonic motion. Precalculus PreAP/D I. Simple Harmonic Motion A. Simple harmonic motion is a special kind of
4.8A: Simple Harmonic Motion I WILL apply the rules of trigonometry and solve using simple harmonic motion. Precalculus PreAP/D I. Simple Harmonic Motion A. Simple harmonic motion is a special kind of
1. Use a calculator to find to the nearest tenth of a degree, if 0 < < 360 and
 Practice Test 2 Numeric Response 1. Use a calculator to find to the nearest tenth of a degree, if 0 < < 360 and with in QIII 2. Use a calculator to find to the nearest tenth of a degree, if 0 < < 360 and
Practice Test 2 Numeric Response 1. Use a calculator to find to the nearest tenth of a degree, if 0 < < 360 and with in QIII 2. Use a calculator to find to the nearest tenth of a degree, if 0 < < 360 and
Dover-Sherborn High School Mathematics Curriculum Pre-Calculus Level 1/CP
 Mathematics Curriculum A. DESCRIPTION This course is an extension of Algebra II with the emphasis in Trigonometry and introductory calculus topics. All major areas covered in Algebra II are reinforced
Mathematics Curriculum A. DESCRIPTION This course is an extension of Algebra II with the emphasis in Trigonometry and introductory calculus topics. All major areas covered in Algebra II are reinforced
2.1 Inductive Reasoning Ojectives: I CAN use patterns to make conjectures. I CAN disprove geometric conjectures using counterexamples.
 2.1 Inductive Reasoning Ojectives: I CAN use patterns to make conjectures. I CAN disprove geometric conjectures using counterexamples. 1 Inductive Reasoning Most learning occurs through inductive reasoning,
2.1 Inductive Reasoning Ojectives: I CAN use patterns to make conjectures. I CAN disprove geometric conjectures using counterexamples. 1 Inductive Reasoning Most learning occurs through inductive reasoning,
STATISTICAL FORECASTING and SEASONALITY (M. E. Ippolito; )
 STATISTICAL FORECASTING and SEASONALITY (M. E. Ippolito; 10-6-13) PART I OVERVIEW The following discussion expands upon exponential smoothing and seasonality as presented in Chapter 11, Forecasting, in
STATISTICAL FORECASTING and SEASONALITY (M. E. Ippolito; 10-6-13) PART I OVERVIEW The following discussion expands upon exponential smoothing and seasonality as presented in Chapter 11, Forecasting, in
6.3 More Sine Language
 6.3 More Sine Language A Solidify Understanding Task Clarita is helping Carlos calculate his height at different locations around a Ferris wheel. They have noticed when they use their formula h(t) = 30
6.3 More Sine Language A Solidify Understanding Task Clarita is helping Carlos calculate his height at different locations around a Ferris wheel. They have noticed when they use their formula h(t) = 30
Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS
 NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
Lesson Adaptation Activity: Analyzing and Interpreting Data
 Lesson Adaptation Activity: Analyzing and Interpreting Data Related MA STE Framework Standard: 3-ESS2-1. Use graphs and tables of local weather data to describe and predict typical weather during a particular
Lesson Adaptation Activity: Analyzing and Interpreting Data Related MA STE Framework Standard: 3-ESS2-1. Use graphs and tables of local weather data to describe and predict typical weather during a particular
Modeling Periodic Phenomenon with Sinusoidal Functions Lesson 33
 (A) Lesson Objectives a. Work with the equation f x A Bx C D sin in the context of word problems using the TI-84 and graphic approaches to answering application questions. b. Use the graphing calculator
(A) Lesson Objectives a. Work with the equation f x A Bx C D sin in the context of word problems using the TI-84 and graphic approaches to answering application questions. b. Use the graphing calculator
y = sin x Chapter 9 Overview: Types and Traits of Parent Trigonometric Functions
 Chapter 9 Overview: Types and Traits of Parent Trigonometric Functions In many Precalculus courses (and in Physics), a great deal of time is spent looking at the trigonometric graphs as transformations
Chapter 9 Overview: Types and Traits of Parent Trigonometric Functions In many Precalculus courses (and in Physics), a great deal of time is spent looking at the trigonometric graphs as transformations
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) Evaluate the function for the given value of x. p(x) = x, q(x) = x - 9, (p q)(x) =? )
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) Evaluate the function for the given value of x. p(x) = x, q(x) = x - 9, (p q)(x) =? )
Mock GCSE Paper Calculator allowed for all questions
 Foundation Higher Mock GCSE Paper Calculator allowed for all questions MATHSWATCH Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Name: Question number Marks Score Question number Marks Score 1 3 14 3 2 2 15 4 3 2 16 8 4 5 17
Foundation Higher Mock GCSE Paper Calculator allowed for all questions MATHSWATCH Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Name: Question number Marks Score Question number Marks Score 1 3 14 3 2 2 15 4 3 2 16 8 4 5 17
