What are they? Where do they come from?
|
|
|
- Jodie Maryann Wood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comets What are they? Where do they come from?
2 Lesson Objectives To distinguish between the orbits of planets and those of comets. To describe the likely origins of short-period and long-period comets. To describe the structure of a typical comet and account for its tails.
3 So what is a comet? An icy ball that travels through a Solar System When close enough to the Sun it displays a visible coma (a thin, fuzzy, atmosphere) and sometimes also a tail as the icy starts to melt. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred metres to tens of kilometres across Composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles.
4 Comets in history Comets have been observed since ancient times and have traditionally been considered bad omens. Halley's Comet depicted on the Bayeux Tapestry which shows King Harold II being told of the comet before the Battle of Hastings in The Star of Wonder that guided the Three Kings was thought to be a comet
5 Comets are thought to be the source of water on Earth Nucleus of 103P/Hartley with jets streaming out. It is ~2km in length and 400m wide at its narrowest point. Nasa develops space harpoon to take samples from comets
6 What is a comet made of? Coma Tail Nucleus made of rock, dust, water ice, and frozen gases such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane and ammonia.
7 A STORY OF 2 TAILS.. A dust tail contains small, solid particles that are about the same size found in cigarette smoke. This tail forms because sunlight pushes on these particles, gently pushing them away from the comet s nucleus. Because the pressure from sunlight is relatively weak, the dust particles end up forming a diffuse, curved tail. A gas ion tail forms when ultraviolet sunlight rips one or more electrons from gas atoms in the coma, making them into ions (a process called ionisation). The solar wind then carries these ions straight outward away from the Sun. The resulting tail is straighter and narrower
8 Material coming off Schwassmann Wachmann which broke up over three days in 1995, as seen by Hubble.
9 Kuiper Belt 30 to 55 AU from our Sun Like the asteroid belt but consisting of debris made of ices Short-period comets (less than 200 years) originate from here
10 Oort Cloud Hypothetical source of comets that stray into our Solar System 50,000 AU from the Sun Long-period comets (up to millions of years) plunge towards the Sun because of gravitational perturbations caused by the outer planets or passing stars.
11
12 Comet Shoemaker Levy 9 a comet that broke apart and collided with Jupiter in July 1994, providing the first direct observation of an extraterrestrial collision
13 METEORS
14 Lesson Objectives To distinguish between meteoroids and meteorites. To understand that meteors (shooting stars), meteor showers and fireballs are visual effects and explain the mechanisms that cause these. To relate meteor showers to comets and explain why meteors appear to diverge from a radiant point.
15 Some Definitions Asteroids (aka planetoids) are a class of small bodies in orbit around the Sun. Small rocky and metallic bodies of the inner Solar System out to the orbit of Jupiter. There are millions of asteroids, thought to be the shattered remnants of planetesimals that never grew large enough to become planets.
16 Some Definitions Meteoroid: Dust and debris left behind from a comet or asteroid floating in space before it enters the atmosphere. Small particles (no bigger than a boulder) Anything bigger is an asteroid.
17 Some Definitions Meteors: Meteoroids that enter the atmosphere and burn up. Aka shooting stars or falling stars. Most burn up and never land at the surface.
18 Some Definitions Meteorites: a portion of a meteoroid that survives its passage through the atmosphere and impacts with the ground without being destroyed.
19 The Barringer Crater, Arizona Larger rocks can sometimes generate an impact crater, though most are too small to do so. During energetic collisions, the entire impactor may be vaporized, leaving no meteorites.
20
21 Some Definitions Fireball: a meteor brighter than any of the planets Bolide: exceptionally bright fireball, particularly one that explodes creating audible sounds.
22 Why can we see Meteors? Meteors become visible between about 40 and 100 miles (65 and 120 km) above the Earth disintegrating between 30 to 60 miles (50 to 95 km). We can see meteors between 10cm to several metres due to the atmospheric ram pressure (not friction!) that heats the meteoroid so that it glows and creates a shining trail of gases and melted meteoroid particles. The gases include vaporized meteoroid material and heated atmospheric gases
23 Radiants The radiant of a meteor shower is the point in the sky, from which meteors appear to originate. An observer might see such a meteor anywhere in the sky but the direction of motion, when traced back, will point to the radiant. Cause - trails of dust and debris left in the wake of a comet. This dust continues to move along the comet's wake, and when the Earth moves through such debris, a meteor shower results. As all of the debris is moving in roughly the same direction, the meteors which strike the atmosphere all "point" back to the direction of the comet's path.
24 COLLISION COURSE!
25 Lesson Objectives To describe the orbits and nature of PHOs. To appreciate the need to monitor how PHOs move. To appreciate the potential consequences to life on Earth of a collision between a large PHO and our planet. To describe some of the evidence of past collisions within our Solar System.
26 What is a PHO? Potentially Hazardous Object! An object is considered a PHO if it comes within <0.05AU and its diameter is >150 m This will devastate human settlements unprecedented in human history or cause a major tsunami. Such impact events occur on average around once per 10,000 years.
27 4179 Toutatis Discovered in 1989, Toutatis makes frequent close approaches to Earth as small as 0.006AU (2.3 lunar distances). The next close approach will be December 12, 2012, at a distance of AU. By the middle of May 2012 the asteroid will become brighter than magnitude 19.5 The likelihood of collision is very small.toutatis is likely to be ejected from the Solar System within a few tens of thousands of years
28 The Torino Scale A method for categorizing the impact hazard associated with near-earth objects (NEOs)
29 NO HAZARD (white) 0. The likelihood of a collision is effectively zero. Also applies to small meteors that burn up in the atmosphere. NORMAL (green) 1. Passes near the Earth and poses no unusual level of danger. Chance of collision is extremely unlikely with no cause for concern. New observations will lead to re-assignment to Level 0. MERITING ATTENTION BY ASTRONOMERS (yellow) Object makes a close but not highly unusual pass near the Earth. While of interest to astronomers, there is no cause for concern as a collision is very unlikely. New observations will lead to re-assignment to Level 0. A close encounter, meriting attention by astronomers. 1% or more chance of collision causing localized destruction. New observations will lead to reassignment to Level 0. Attention by public and by public officials is merited if the encounter is less than a decade away. A close encounter, meriting attention by astronomers. Current calculations give a 1% or greater chance of collision capable of regional devastation. New observations may lead to re-assignment to Level 0. Attention by public officials is merited if less than a decade away.
30 THREATENING (orange) 5. A close encounter posing a serious, but uncertain threat of regional devastation. Critical attention by astronomers is needed to determine whether a collision will occur. If less than a decade away, governmental contingency planning may be warranted A close encounter by a large object posing a serious but uncertain threat of a global catastrophe. Critical attention by astronomers is needed to determine conclusively whether a collision will occur. If the encounter is less than 30 years away, governmental contingency planning may be warranted. A very close encounter by a large object poses an unprecedented but uncertain threat of a global catastrophe. If less than 100 years away, international contingency planning is warranted, to determine whether a collision will occur. CERTAIN COLLISIONS (red) A collision is certain, capable of causing localized destruction for an impact over land 8. or a tsunami if close offshore. Such events occur on average every 50 years to several thousand years A collision is certain, capable of causing unprecedented regional devastation for a land impact or the threat of a major tsunami for an ocean impact. Such events occur on average between once per 10,000 years and once per 100,000 years. A collision is certain, capable of causing global climatic catastrophe that may threaten the future of civilization as we know it. Such events occur on average once per 100,000 years.
31 The Spaceguard Centre The Spaceguard Centre is the only organisation in the UK addressing the hazard of NEOs. Promotes British participation in the international programme to detect Earth crossing asteroids and comets and to protect the Earth from potentially catastrophic collisions. Non-governmental and receives no external funding.
32 Impact Simulators education.down2earth.eu/ impact.ese.ic.ac.uk/impacteffects/
The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Dwarf planets Following the discovery of multiple objects similar to Pluto (and one that was even bigger than Pluto) a new classification for planets
The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Dwarf planets Following the discovery of multiple objects similar to Pluto (and one that was even bigger than Pluto) a new classification for planets
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion?
 At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Vagabonds of the Solar System
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
12/3/14. Guiding Questions. Vagabonds of the Solar System. A search for a planet between Mars and Jupiter led to the discovery of asteroids
 Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
A s t e r o i d s, C o m e t s & N E O s ( B a c k g r o u n d I n f o r m a t i o n )
 A s t e r o i d s, C o m e t s & N E O s ( B a c k g r o u n d I n f o r m a t i o n ) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Background Information Asteroids are rocky objects which
A s t e r o i d s, C o m e t s & N E O s ( B a c k g r o u n d I n f o r m a t i o n ) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Background Information Asteroids are rocky objects which
Ch. 6: Smaller Bodies in the Solar System
 Ch. 6: Smaller Bodies in the Solar System FIGURE 9-1 (Discovering the Universe) Different Classifications of Solar System Objects Some of the definitions of the different types of objects in the solar
Ch. 6: Smaller Bodies in the Solar System FIGURE 9-1 (Discovering the Universe) Different Classifications of Solar System Objects Some of the definitions of the different types of objects in the solar
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts. Chapter 12 Review Clickers
 Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids a) are rocky and small typically the size of a grain of rice or
Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids a) are rocky and small typically the size of a grain of rice or
Unit 3 Lesson 6 Small Bodies in the Solar System. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.1 Define a problem from the eighth grade curriculum using appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of
Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.1 Define a problem from the eighth grade curriculum using appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of
Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids
 Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids Bode s Law In 1772 Johann Bode, a German astronomer, created a mathematical formula now called Bode s Law. This formula determines the pattern that describes the distances
Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids Bode s Law In 1772 Johann Bode, a German astronomer, created a mathematical formula now called Bode s Law. This formula determines the pattern that describes the distances
Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19, we began our study of planetary astronomy by asking how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed, we surveyed the
Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19, we began our study of planetary astronomy by asking how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed, we surveyed the
Comets and Meteors. Sp a ce - Level 1 and 2. Concept This lesson introduces the students to comets and meteors.
 Concept This lesson introduces the students to comets and meteors. Comets From nineplanets.org Comets are a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust that did not get incorporated into planets
Concept This lesson introduces the students to comets and meteors. Comets From nineplanets.org Comets are a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust that did not get incorporated into planets
Small Bodies in our Solar System. Comets, Asteroids & Meteoroids
 Small Bodies in our Solar System Comets, Asteroids & Meteoroids * A Small Body is any object in the solar system that is smaller than a planet or moon, such as a comet, an asteroid, or a meteoroid. Compiled
Small Bodies in our Solar System Comets, Asteroids & Meteoroids * A Small Body is any object in the solar system that is smaller than a planet or moon, such as a comet, an asteroid, or a meteoroid. Compiled
23.1 The Solar System. Orbits of the Planets. Planetary Data The Solar System. Scale of the Planets The Solar System
 23.1 The Solar System Orbits of the Planets The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets are the huge gas giants
23.1 The Solar System Orbits of the Planets The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets are the huge gas giants
Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium. Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium. Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium
 Test 04 Chapters 15-20 Limited Copies Are available Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium June 4 th from 8:00 pm - 10:00 pm Covering ALL Tests Slide 1 Slide 2 Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin
Test 04 Chapters 15-20 Limited Copies Are available Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium June 4 th from 8:00 pm - 10:00 pm Covering ALL Tests Slide 1 Slide 2 Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin
Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors. By: Annette Miles
 Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors By: Annette Miles What is a comet? A comet is a small body which scientists sometimes call a planetesimal. They are made out of dust, ice rock, gas, and. They are kind of
Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors By: Annette Miles What is a comet? A comet is a small body which scientists sometimes call a planetesimal. They are made out of dust, ice rock, gas, and. They are kind of
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus,
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus,
Origin of the Solar System
 Origin of the Solar System and Solar System Debris 1 Debris comets meteoroids asteroids gas dust 2 Asteroids irregular, rocky hunks small in mass and size Ceres - largest, 1000 km in diameter (1/3 Moon)
Origin of the Solar System and Solar System Debris 1 Debris comets meteoroids asteroids gas dust 2 Asteroids irregular, rocky hunks small in mass and size Ceres - largest, 1000 km in diameter (1/3 Moon)
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
Asteroids: Introduction
 Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Chapter 25. Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19 you began your study of planetary astronomy by considering evidence about how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed
Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19 you began your study of planetary astronomy by considering evidence about how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed
Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice. Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto
 Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto 9.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our Goals for Learning Why is there an asteroid belt? How are meteorites related to asteroids? Asteroid Facts
Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto 9.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our Goals for Learning Why is there an asteroid belt? How are meteorites related to asteroids? Asteroid Facts
Smaller Bodies of the Solar System Chapter 2 continued
 Smaller Bodies of the Solar System Chapter 2 continued Small, rocky (sometimes metallic) bodies with no atmospheres. or planetoids 100,000 numbered and 12,000 named 1-1000 km in size most are small ~ 1
Smaller Bodies of the Solar System Chapter 2 continued Small, rocky (sometimes metallic) bodies with no atmospheres. or planetoids 100,000 numbered and 12,000 named 1-1000 km in size most are small ~ 1
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets
Starting from closest to the Sun, name the orbiting planets in order.
 Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Vagabonds of the Solar System. Chapter 15
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Chapter 15 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 Nov. 26, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15)
Vagabonds of the Solar System Chapter 15 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 Nov. 26, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15)
Chapter 12 Remnants of Rock and Ice. Asteroid Facts. NEAR Spacecraft: Asteroid Eros
 Chapter 12 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and the Kuiper Belt Asteroid Facts Asteroids are rocky leftovers of planet formation Largest is Ceres, diameter ~1,000 km (most smaller) 150,000 in
Chapter 12 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and the Kuiper Belt Asteroid Facts Asteroids are rocky leftovers of planet formation Largest is Ceres, diameter ~1,000 km (most smaller) 150,000 in
Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014
 1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
Table of Contents. Space Bits: Outer Space Objects
 Table of Contents Space Bits: Outer Space Objects Comet vs. Asteroid * Meteoroid vs. Meteor vs. Meteorite Crazy Craters Around the World * Halley's Comet * What is Pluto? Solar Eclipse vs. Lunar Eclipse
Table of Contents Space Bits: Outer Space Objects Comet vs. Asteroid * Meteoroid vs. Meteor vs. Meteorite Crazy Craters Around the World * Halley's Comet * What is Pluto? Solar Eclipse vs. Lunar Eclipse
Asteroids Physical Properties. Solar System Debris. Missions to Asteroids. Types of Asteroids (based on composition)
 Solar System Debris Asteroids Physical Properties Spacecraft Missions Origin Orbits Risk to Earth Tens to hundreds of km in diameter Comets History Structure Orbits Origin Missions Meteoroids & Meteor
Solar System Debris Asteroids Physical Properties Spacecraft Missions Origin Orbits Risk to Earth Tens to hundreds of km in diameter Comets History Structure Orbits Origin Missions Meteoroids & Meteor
Astronomy 3. Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets
 Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Space Notes 2. Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8
 Space Notes 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 Sun Average Size Star Sun 101 Sun s Mass almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. Most of the mass is hydrogen gas Thermonuclear Reaction Thermonuclear
Space Notes 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 Sun Average Size Star Sun 101 Sun s Mass almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. Most of the mass is hydrogen gas Thermonuclear Reaction Thermonuclear
Ag Earth Science Chapter 23
 Ag Earth Science Chapter 23 Chapter 23.1 Vocabulary Any of the Earth- like planets, including Mercury, Venus, and Earth terrestrial planet Jovian planet The Jupiter- like planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
Ag Earth Science Chapter 23 Chapter 23.1 Vocabulary Any of the Earth- like planets, including Mercury, Venus, and Earth terrestrial planet Jovian planet The Jupiter- like planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
Comets and KBO's. Comets. Halley's Comet. Far outside the orbit of Neptune are an overwhelming number of small icy bodies
 Comets and KBO's Far outside the orbit of Neptune are an overwhelming number of small icy bodies The Kuiper belt is a ring of icy material located in the plane of the Solar System Comets were known and
Comets and KBO's Far outside the orbit of Neptune are an overwhelming number of small icy bodies The Kuiper belt is a ring of icy material located in the plane of the Solar System Comets were known and
Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017
 Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017 Today: Chapter 12, Pluto and Debris March 24: Exam #2, Ch. 5-12 (9:00-9:50) March 27: Mastering Astronomy HW Chapter 11 & 12 1 Chapter 12: Meteorites, Asteroids, Comets
Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017 Today: Chapter 12, Pluto and Debris March 24: Exam #2, Ch. 5-12 (9:00-9:50) March 27: Mastering Astronomy HW Chapter 11 & 12 1 Chapter 12: Meteorites, Asteroids, Comets
Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy
 Homework Issues Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy mistakes. The speed of light is 299,792,458
Homework Issues Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy mistakes. The speed of light is 299,792,458
Chapter 23 Earth Science 11
 Chapter 23 Earth Science 11 Inner planets: Closest planets to the sun A.k.a. terrestrial planets All have a rocky crust, dense mantle layer, and a very dense core Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars Outer
Chapter 23 Earth Science 11 Inner planets: Closest planets to the sun A.k.a. terrestrial planets All have a rocky crust, dense mantle layer, and a very dense core Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars Outer
Solar System Junk however, a large number of bodies were left over as Junk or the debris of planet building
 Solar System Junk So far, we ve taken a brief look at the 8 planets of the solar system, their array of moons or natural satellites, and how we think such a system formed. Most of the material in the solar
Solar System Junk So far, we ve taken a brief look at the 8 planets of the solar system, their array of moons or natural satellites, and how we think such a system formed. Most of the material in the solar
Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids
 1 Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids Primarily found in two zones in the solar system. The Asteroid Belt (rocky, between Jupiter and Mars) The Edgeworth/Kuiper Belt (beyond Neptune) and Oort Cloud
1 Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids Primarily found in two zones in the solar system. The Asteroid Belt (rocky, between Jupiter and Mars) The Edgeworth/Kuiper Belt (beyond Neptune) and Oort Cloud
ASTRONOMY SNAP GAME. with interesting facts
 ASTRONOMY SNAP GAME with interesting facts Sun Sun The Sun is the largest object in the solar system The Sun's life expectancy is approximately 5 billion more years At its core, the Sun s temperature is
ASTRONOMY SNAP GAME with interesting facts Sun Sun The Sun is the largest object in the solar system The Sun's life expectancy is approximately 5 billion more years At its core, the Sun s temperature is
This asteroid was visited by the NEAR Shoemaker probe, which orbited it, taking extensive photographs of its
 Chapter 9 Part 1 Asteroids and Comets Why is there an asteroid belt? This asteroid was visited by the NEAR Shoemaker probe, which orbited it, taking extensive photographs of its surface, and, on February
Chapter 9 Part 1 Asteroids and Comets Why is there an asteroid belt? This asteroid was visited by the NEAR Shoemaker probe, which orbited it, taking extensive photographs of its surface, and, on February
The Solar Nebula Theory. This lecture will help you understand: Conceptual Integrated Science. Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 This lecture will help you understand: Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Overview of the Solar System The Nebular Theory The Sun Asteroids, Comets, and
This lecture will help you understand: Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Overview of the Solar System The Nebular Theory The Sun Asteroids, Comets, and
Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key
 Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of how the universe is arranged. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe Heliocentric
Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of how the universe is arranged. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe Heliocentric
CHAPTER 11. We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration
 CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids
 The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore meteor
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore meteor shooting star, falling star For the complete encyclopedic
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore meteor shooting star, falling star For the complete encyclopedic
6. (11.2) What shape are typical asteroids and how do we know? Why does Ceres not have this shape?
 SUMMARY Our Solar System contains numerous small bodies: dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. They are important astronomically because they give us information about the time of formation,
SUMMARY Our Solar System contains numerous small bodies: dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. They are important astronomically because they give us information about the time of formation,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore METEO RO ID For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore METEO RO ID For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System
 Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System The Sun The is the center of our solar system. The Sun makes up of all the mass of our solar system. The Sun s force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun.
Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System The Sun The is the center of our solar system. The Sun makes up of all the mass of our solar system. The Sun s force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun.
Illustrate It! You will need to set out colored pencil and markers at this station.
 Kesler Science Station Lab Comets, Meteors, and Asteroids Teacher Directions Explore It! I will spend much of my time at this station making sure that the students are doing the orbits correctly. I have
Kesler Science Station Lab Comets, Meteors, and Asteroids Teacher Directions Explore It! I will spend much of my time at this station making sure that the students are doing the orbits correctly. I have
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM. James Martin. Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC
 OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
Astronomy Wed. Oct. 6
 Astronomy 301 - Wed. Oct. 6 Guest lectures, Monday and today: Prof. Harriet Dinerstein Monday: The outer planets & their moons Today: asteroids, comets, & the Kuiper Belt; formation of the Solar System
Astronomy 301 - Wed. Oct. 6 Guest lectures, Monday and today: Prof. Harriet Dinerstein Monday: The outer planets & their moons Today: asteroids, comets, & the Kuiper Belt; formation of the Solar System
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 6, January 30
 Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 6, January 30 Last time: Meteors Today: Asteroids and Comets Homework: HW 1 last chance! cutoff at 5pm today. HW 2 due this Friday at 1pm http://near.jhuapl.edu/iod/20000222/20000222.jpg
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 6, January 30 Last time: Meteors Today: Asteroids and Comets Homework: HW 1 last chance! cutoff at 5pm today. HW 2 due this Friday at 1pm http://near.jhuapl.edu/iod/20000222/20000222.jpg
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts. Chapter 12 Lecture
 Chapter 12 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts
Chapter 12 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts
SPACE NOTES 2. Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8
 SPACE NOTES 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 THE SUN Average Size Star Sun 101 SUN S MASS o almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. o Most of the mass is hydrogen gas THERMONUCLEAR REACTION
SPACE NOTES 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 THE SUN Average Size Star Sun 101 SUN S MASS o almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. o Most of the mass is hydrogen gas THERMONUCLEAR REACTION
Galaxies: enormous collections of gases, dust and stars held together by gravity Our galaxy is called the milky way
 Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Notes: The Solar System
 Notes: The Solar System The Formation of the Solar System 1. A gas cloud collapses under the influence of gravity. 2. Solids condense at the center, forming a protostar. 3. A falttened disk of matter surrounds
Notes: The Solar System The Formation of the Solar System 1. A gas cloud collapses under the influence of gravity. 2. Solids condense at the center, forming a protostar. 3. A falttened disk of matter surrounds
Boardworks Ltd Asteroids and Comets
 1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids and Comets 2 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 What are asteroids? 3 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids are large rocks which normally orbit the Sun. Scientists believe that
1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids and Comets 2 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 What are asteroids? 3 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids are large rocks which normally orbit the Sun. Scientists believe that
Solar System Debris. Asteroids 11/28/2010. Large rocky debris orbiting the Sun. Ceres, the largest asteroid. Discovering Asteroids
 Solar System Debris Material leftover from the formation of the Solar System Gives important clues about its origin Composition: Asteroids and Meteoroids: rock and iron Comets: ice and dust The basic building
Solar System Debris Material leftover from the formation of the Solar System Gives important clues about its origin Composition: Asteroids and Meteoroids: rock and iron Comets: ice and dust The basic building
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
9.2 - Our Solar System
 9.2 - Our Solar System Scientists describe our solar system as the Sun and all the planets and other celestial objects, such as moons, comets, and asteroids, that are held by the Sun s gravity and orbit
9.2 - Our Solar System Scientists describe our solar system as the Sun and all the planets and other celestial objects, such as moons, comets, and asteroids, that are held by the Sun s gravity and orbit
Chapter 11. Meteors, Asteroids and Comets. YT: If a meteor hits the Earth
 Chapter 11 Meteors, Asteroids and Comets YT: If a meteor hits the Earth Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Asteroids and Comets Orbiting the
Chapter 11 Meteors, Asteroids and Comets YT: If a meteor hits the Earth Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Asteroids and Comets Orbiting the
1. Cosmology is the study of. a. The sun is the center of the Universe. b. The Earth is the center of the Universe
 Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe b. The Earth is the center of the Universe 3. The two most abundant gases
Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe b. The Earth is the center of the Universe 3. The two most abundant gases
Comets. Ancient Ideas about comets. Draft Dec 11, Edmund Halley ( ) Great Comet of 1680
 Comets Ancient Ideas about comets kometes = `the hairy one (hairy star) 550 BC Pythagoreans thought they were wandering planets. Draft Dec 11, 2006 Aristotle (350 BC) thought that, like meteors, they were
Comets Ancient Ideas about comets kometes = `the hairy one (hairy star) 550 BC Pythagoreans thought they were wandering planets. Draft Dec 11, 2006 Aristotle (350 BC) thought that, like meteors, they were
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes
 Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Brooks Observatory telescope observing
 Brooks Observatory telescope observing Mon. - Thurs., March 22 55, 8:30 to about 9:45 PM See the class web page for weather updates. This evening s session has been cancelled. Present your blue ticket
Brooks Observatory telescope observing Mon. - Thurs., March 22 55, 8:30 to about 9:45 PM See the class web page for weather updates. This evening s session has been cancelled. Present your blue ticket
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 14. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 14 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 14 Solar System Debris Units of Chapter 14 14.1 Asteroids What Killed the Dinosaurs? 14.2 Comets 14.3 Beyond Neptune 14.4
Lecture Outlines Chapter 14 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 14 Solar System Debris Units of Chapter 14 14.1 Asteroids What Killed the Dinosaurs? 14.2 Comets 14.3 Beyond Neptune 14.4
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System
 Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
The Solar System. Sun. Rotates and revolves around the Milky Way galaxy at such a slow pace that we do not notice any effects.
 The Solar System Sun Center of the solar system About 150,000,000 km from the Earth An averaged sized, yellow star Spherical in shape due to gravity Made of about ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium, both of which
The Solar System Sun Center of the solar system About 150,000,000 km from the Earth An averaged sized, yellow star Spherical in shape due to gravity Made of about ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium, both of which
What s in our solar system?
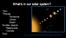 What s in our solar system? *Sun *Planets Terrestrial Jovian Dwarf Smaller objects *Meteoroids *Comets Dust http://www.techastronomy.com/userfiles/2007/7/22/solar_system4(1).jpg *Sun a. Most of mass (>99%)
What s in our solar system? *Sun *Planets Terrestrial Jovian Dwarf Smaller objects *Meteoroids *Comets Dust http://www.techastronomy.com/userfiles/2007/7/22/solar_system4(1).jpg *Sun a. Most of mass (>99%)
The History of the Solar System. From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies
 The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
Our Solar System. Lesson 5. Distances Between the Sun and the Planets
 Our Solar System Lesson 5 T he Solar System consists of the Sun, the Moon, planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, meteors and other celestial bodies. All these celestial bodies are bound to the Sun
Our Solar System Lesson 5 T he Solar System consists of the Sun, the Moon, planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, meteors and other celestial bodies. All these celestial bodies are bound to the Sun
Lecture 39. Asteroids/ Minor Planets In "Gap" between Mars and Jupiter: 20,000 observed small objects, 6000 with known orbits:
 Lecture 39 Interplanetary Matter Asteroids Meteorites Comets Oort Cloud Apr 28, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 39 1 Asteroids/ Minor Planets In "Gap" between Mars and Jupiter: 20,000 observed small objects, 6000
Lecture 39 Interplanetary Matter Asteroids Meteorites Comets Oort Cloud Apr 28, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 39 1 Asteroids/ Minor Planets In "Gap" between Mars and Jupiter: 20,000 observed small objects, 6000
The Sun. - this is the visible surface of the Sun. The gases here are very still hot, but much cooler than inside about 6,000 C.
 Name: The Sun The Sun is an average sized. Earth, Mars, Jupiter and Uranus are. A star is the only object in space that makes its own. This includes and. The sun is about million miles from Earth. This
Name: The Sun The Sun is an average sized. Earth, Mars, Jupiter and Uranus are. A star is the only object in space that makes its own. This includes and. The sun is about million miles from Earth. This
Unit 12 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System?
 Unit 12 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? The Solar System Earth, other planets, and the moon are part of a solar system. A solar system is made up of a star and the planets and other
Unit 12 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? The Solar System Earth, other planets, and the moon are part of a solar system. A solar system is made up of a star and the planets and other
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Astro 1: Introductory Astronomy
 Astro 1: Introductory Astronomy David Cohen Class 16: Thursday, March 20 Spring 2014 large cloud of interstellar gas and dust - giving birth to millions of stars Hubble Space Telescope: Carina Nebula
Astro 1: Introductory Astronomy David Cohen Class 16: Thursday, March 20 Spring 2014 large cloud of interstellar gas and dust - giving birth to millions of stars Hubble Space Telescope: Carina Nebula
Exploring Our Solar System
 Exploring Our Solar System Our Solar System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Exploring Our Solar System Our Solar System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Chapter 4 The Solar System
 Chapter 4 The Solar System Comet Tempel Chapter overview Solar system inhabitants Solar system formation Extrasolar planets Solar system inhabitants Sun Planets Moons Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Kuiper
Chapter 4 The Solar System Comet Tempel Chapter overview Solar system inhabitants Solar system formation Extrasolar planets Solar system inhabitants Sun Planets Moons Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Kuiper
GLY August, Ms. Nelda Breedt. Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth.
 Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The Structure of the Solar System Lesson 2 The Inner Planets Lesson 3 The Outer Planets Lesson 4 Dwarf Planets and Other Objects Chapter Wrap-Up NASA/JPL/USGS What kinds of
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The Structure of the Solar System Lesson 2 The Inner Planets Lesson 3 The Outer Planets Lesson 4 Dwarf Planets and Other Objects Chapter Wrap-Up NASA/JPL/USGS What kinds of
Comet Demo. Comet Demo. Supplies:
 Comet Demo Comet Demo Supplies: Apron Zip Lock Bags Beakers Bowl; Large Gloves Safety Goggles Hammer Newspaper and/or Aluminum Foil Spoons Paper Towel (To Clean Up The Mess!) Plastic Table Cover Comet
Comet Demo Comet Demo Supplies: Apron Zip Lock Bags Beakers Bowl; Large Gloves Safety Goggles Hammer Newspaper and/or Aluminum Foil Spoons Paper Towel (To Clean Up The Mess!) Plastic Table Cover Comet
The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS. Scientific Language. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
The Solar System. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
2010 Pearson Education, Inc. MAVEN launch yesterday
 MAVEN launch yesterday Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) How is Mars losing its atmosphere now? How did Mars lose its atmosphere in the past? 1. Determine the role that loss of volatiles to
MAVEN launch yesterday Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) How is Mars losing its atmosphere now? How did Mars lose its atmosphere in the past? 1. Determine the role that loss of volatiles to
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan December 6, 2016 I The Outer Planets in General 1. How do the sizes, masses and densities of the outer planets compare with the inner planets? The outer planets
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan December 6, 2016 I The Outer Planets in General 1. How do the sizes, masses and densities of the outer planets compare with the inner planets? The outer planets
Today. The Little Things. Comets. Dwarf Planets. Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then.
 Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Contents of the Solar System
 The Solar System Contents of the Solar System Sun Planets 9 known (now: 8) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars ( Terrestrials ) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ( Jovians ) Pluto (a Kuiper Belt object?) Natural
The Solar System Contents of the Solar System Sun Planets 9 known (now: 8) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars ( Terrestrials ) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ( Jovians ) Pluto (a Kuiper Belt object?) Natural
IX. Dwarf Planets A. A planet is defined to be an object that is large enough to coalesce into a sphere and to have cleared its orbit of other
 7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
Our Sun. The centre of our solar system
 Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
~15 GA. (Giga Annum: Billion Years) today
 ~15 GA (Giga Annum: Billion Years) today ~ 300,000 years after the Big Bang The first map of the Universe. Not homogeneous. Cosmic microwave background (CMB) anisotropy. First detected by the COBE DMR
~15 GA (Giga Annum: Billion Years) today ~ 300,000 years after the Big Bang The first map of the Universe. Not homogeneous. Cosmic microwave background (CMB) anisotropy. First detected by the COBE DMR
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More
 12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
Dwarf Planets and Other Objects
 Lesson 4 Dwarf Planets and Other Objects LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.1, SC.8.E.5.3, SC.8.E.5.7, SC.8.N.3.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts
Lesson 4 Dwarf Planets and Other Objects LA.8.2.2.3, SC.8.E.5.1, SC.8.E.5.3, SC.8.E.5.7, SC.8.N.3.1 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts
Chapter 11. Meteors, Asteroids and Comets. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 11 Meteors, Asteroids and Comets Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Asteroids and Comets Orbiting the Sun are numerous small bodies the
Chapter 11 Meteors, Asteroids and Comets Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Asteroids and Comets Orbiting the Sun are numerous small bodies the
Astronomy Unit Notes Name:
 Astronomy Unit Notes Name: (DO NOT LOSE!) To help with the planets order 1 My = M 2 V = Venus 3 Eager = E 4 M = Mars 5 Just = J 6 Served = Saturn 7 Us = Uranus 8 N = N 1 Orbit: The path (usually elliptical)
Astronomy Unit Notes Name: (DO NOT LOSE!) To help with the planets order 1 My = M 2 V = Venus 3 Eager = E 4 M = Mars 5 Just = J 6 Served = Saturn 7 Us = Uranus 8 N = N 1 Orbit: The path (usually elliptical)
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Midterm #4 in one week!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 in one week! 1 Previously Mass extinctions K/Pg extinction Impact theory -- evidence? Other possible causes Other extinctions 2 Where did the K/Pg impactor
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 in one week! 1 Previously Mass extinctions K/Pg extinction Impact theory -- evidence? Other possible causes Other extinctions 2 Where did the K/Pg impactor
Pluto. Touring our Solar System. September 08, The Solar System.notebook. Solar System includes: Sun 8 planets Asteroids Comets Meteoroids
 Touring our Solar System Solar System includes: Sun 8 planets Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Jan 4 5:48 PM Jan 4 5:50 PM A planet's orbit lies in an inclined orbital plane Planes of seven planets lie within
Touring our Solar System Solar System includes: Sun 8 planets Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Jan 4 5:48 PM Jan 4 5:50 PM A planet's orbit lies in an inclined orbital plane Planes of seven planets lie within
Background: (write a few things that you already know pertaining to about the question above)
 Our Solar System at a Glance Reading Introduction: When the ancients studied the night sky, they noticed that five stars moved with respect to the others. They called them planets, from the Greek word
Our Solar System at a Glance Reading Introduction: When the ancients studied the night sky, they noticed that five stars moved with respect to the others. They called them planets, from the Greek word
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 13, February 15
 Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 13, February 15 Hour Exam 1 next time, Feb 17, in class more later today Planetarium: report due Feb 24 extra show added tomorrow, Thursday Feb 16 or can
Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 13, February 15 Hour Exam 1 next time, Feb 17, in class more later today Planetarium: report due Feb 24 extra show added tomorrow, Thursday Feb 16 or can
