Powering the Universe with Supermassive Black Holes. Steve Ehlert and Paul Simeon
|
|
|
- Ezra Harris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Powering the Universe with Supermassive Black Holes Steve Ehlert and Paul Simeon
2 Overview Introduction to Galactic Nuclei Galactic Nuclear Activity Input and output energies. The aftermath of AGN flares.
3 But First... A brief primer of structure in the universe.
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 Our Own Galaxy Our story of AGN begins in our own galaxy, the Milky Way. In particular, it begins with observations at the center of our galaxy. This is in the direction of the Sagittarius constellation. Easier to observe from the Southern Hemisphere. Radio source defined as galactic center known as Sagittarius A*.
14 Sagittarius A* Image is a combination of infrared observations.
15 Sagittarius A* X-ray emission: Red 1-3 kev, Green 3-5 kev, Blue 5-8 kev
16 What is Sagittarius A*? Careful experiments show more than a dozen stars orbiting the galactic center. Central object must have mass of ~ 4 million solar within region smaller than the orbit of Uranus. This all but certainly is a super-massive black hole!
17 Tracing Stellar Orbits
18 Data Suggests a Point Source!
19 Supermassive Black Holes Black holes like the one at Sagittarius A* are observed at the center of most every galaxy. Supermassive black holes can either be Active or Inactive. Active galactic nuclei have a central region that is brighter than normal in some frequency range. Active Galaxies are among the brightest objects in the universe.
20 The Inactive Sombrero Galaxy
21 The Active Galaxy Centaurus A
22 The AGN Zoo Huge # of classifications for AGN. Based on observational history. Seyfert I/II galaxies Radio galaxy Quasi-stellar objects (Quasars) Blazars BL Lacs Optical Violently Variable (OVV)
23 Defining an AGN Key aspects spanning many different classifications: Variable emission Jets Continuum radio emission Emission lines in optical and infrared Non-thermal high energy emission Different types of AGN have different combinations of these signatures.
24 Emission at Many Frequencies ~100,000 light years across! Blue is X-ray, green is optical, and red is infrared
25 Not all to scale!
26 Outstanding Questions Does the zoo of AGN types have a common origin? If there is a common cause, why such different effects? What is the origin of such spectacular emission? Where does it originate? What are the limits to what an AGN can do? How do AGN help answer other big questions in astrophysics?
27 Cygnus A
28
29
30
31
32
33
34 Mass and Angular Momentum
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 AGN & Galaxy Formation There appears to be a very strong correlation between black hole properties and galaxy properties. Any complete galaxy formation model needs to acknowledge the influence of the AGN. The theory of supermassive black hole formation is incomplete Where are the intermediate-mass black holes
42 AGN Feedback in Galaxy Clusters In larger scale structures known as galaxy clusters, a particularly large galaxy known as a cd found at the center. A very massive galaxy means a very massive black hole and emission power. The local medium of the galaxy cluster (ICM) can be disrupted by the central AGN. The ICM is best observed in X-rays.
43 M87 in Optical, X-Ray, and Radio Jet of M87 Blue X-ray, yellow optical, and red radio
44 Temperature Map Around M87
45 Pressure Map Around M87
46 Interpreting M87 The AGN is uplifting cool gas from the center of the cluster to larger radii. We can even measure multi-temperature structure in the arms. The rings of high pressure are indicative of shocks. The nature of the jets can be constrained by the effects on the surrounding medium.
47 Inflating Cavities These jets can also inflate 'bubbles' in the local cluster medium. These bubbles have very little X-ray gas, but instead filled with radio plasma. Huge amounts of energy can go into inflating these cavities.
48 A More Powerful AGN Outburst Blue: X-ray Pink: Radio ~500,000 light years!
49 Conclusions Safe to say that super-massive black holes reside at the center of every galaxy. When an accretion disk is present, fireworks ensue. AGN directly influence the formation of large structures like galaxies and galaxy clusters. Many of the unanswered questions about AGN are being pursued by a number of people here at KIPAC.
Chapter 17. Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes
 Chapter 17 Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Guidepost In the last few chapters, you have explored our own and other galaxies, and you are ready to stretch your scientific imagination and study
Chapter 17 Active Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Guidepost In the last few chapters, you have explored our own and other galaxies, and you are ready to stretch your scientific imagination and study
Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
 ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
Lecture 9. Quasars, Active Galaxies and AGN
 Lecture 9 Quasars, Active Galaxies and AGN Quasars look like stars but have huge redshifts. object with a spectrum much like a dim star highly red-shifted enormous recessional velocity huge distance (Hubble
Lecture 9 Quasars, Active Galaxies and AGN Quasars look like stars but have huge redshifts. object with a spectrum much like a dim star highly red-shifted enormous recessional velocity huge distance (Hubble
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei
 Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Active Galaxies & Quasars
 Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Quasars: Back to the Infant Universe
 Quasars: Back to the Infant Universe Learning Objectives! What is a quasar? What spectral features tell us quasars are very redshifted (very distant)? What spectral features tell us they are composed of
Quasars: Back to the Infant Universe Learning Objectives! What is a quasar? What spectral features tell us quasars are very redshifted (very distant)? What spectral features tell us they are composed of
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
A zoo of transient sources. (c)2017 van Putten 1
 A zoo of transient sources (c)2017 van Putten 1 First transient @ first light UDFj-39546284, z~10.3 Bouwens, R.J., et al., Nature, 469, 504 Cuchiara, A. et al., 2011, ApJ, 736, 7 z=9.4: GRB 090429B, z~9.4
A zoo of transient sources (c)2017 van Putten 1 First transient @ first light UDFj-39546284, z~10.3 Bouwens, R.J., et al., Nature, 469, 504 Cuchiara, A. et al., 2011, ApJ, 736, 7 z=9.4: GRB 090429B, z~9.4
Vera Genten. AGN (Active Galactic Nuclei)
 Vera Genten AGN (Active Galactic Nuclei) Topics 1)General properties 2)Model 3)Different AGN-types I. Quasars II.Seyfert-galaxies III.Radio galaxies IV.young radio-loud AGN (GPS, CSS and CFS) V.Blazars
Vera Genten AGN (Active Galactic Nuclei) Topics 1)General properties 2)Model 3)Different AGN-types I. Quasars II.Seyfert-galaxies III.Radio galaxies IV.young radio-loud AGN (GPS, CSS and CFS) V.Blazars
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
A Unified Model for AGN. Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006
 A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
11/8/18. Tour of Galaxies. Our Schedule
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Ryan Horton, Loren Matilsky Lecture 22 Thur 8 Nov 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Ryan Horton, Loren Matilsky Lecture 22 Thur 8 Nov 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
2. Active Galaxies. 2.1 Taxonomy 2.2 The mass of the central engine 2.3 Models of AGNs 2.4 Quasars as cosmological probes.
 2. Active Galaxies 2.1 Taxonomy 2.2 The mass of the central engine 2.3 Models of AGNs 2.4 Quasars as cosmological probes Read JL chapter 3 Active galaxies: interface with JL All of JL chapter 3 is examinable,
2. Active Galaxies 2.1 Taxonomy 2.2 The mass of the central engine 2.3 Models of AGNs 2.4 Quasars as cosmological probes Read JL chapter 3 Active galaxies: interface with JL All of JL chapter 3 is examinable,
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Extragalactic Radio Sources. Joanne M. Attridge MIT Haystack Observatory
 Extragalactic Radio Sources Joanne M. Attridge MIT Haystack Observatory It all began in the 1940s... Galaxies=condensations of gas, dust and stars held together by their own gravitational potential M 87
Extragalactic Radio Sources Joanne M. Attridge MIT Haystack Observatory It all began in the 1940s... Galaxies=condensations of gas, dust and stars held together by their own gravitational potential M 87
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically faint ellipticals. Part 3. After Chandra?
 Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
The Milky Way Galaxy
 1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs): A type of AGNs: Quasars. Whatever is powering these QSO s must be very small!!
 Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs): Galaxies with lots of activity AST 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Some galaxies at high redshift (large lookback times) have extremely active centers More than 1000
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs): Galaxies with lots of activity AST 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Some galaxies at high redshift (large lookback times) have extremely active centers More than 1000
Question 1. Question 2. Correct. Chapter 16 Homework. Part A
 Chapter 16 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Following are a number of distinguishing characteristics
Chapter 16 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Following are a number of distinguishing characteristics
Galaxies. With a touch of cosmology
 Galaxies With a touch of cosmology Types of Galaxies Spiral Elliptical Irregular Spiral Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Disk component where the spiral arms are Interstellar medium Star formation Spheroidal
Galaxies With a touch of cosmology Types of Galaxies Spiral Elliptical Irregular Spiral Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Disk component where the spiral arms are Interstellar medium Star formation Spheroidal
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
4/6/17. SEMI-WARM stuff: dust. Tour of Galaxies. Our Schedule
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 22 Thur 6 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 22 Thur 6 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
Active Galactic Nuclei - Zoology
 Active Galactic Nuclei - Zoology Normal galaxy Radio galaxy Seyfert galaxy Quasar Blazar Example Milky Way M87, Cygnus A NGC 4151 3C273 BL Lac, 3C279 Galaxy Type spiral elliptical, lenticular spiral irregular
Active Galactic Nuclei - Zoology Normal galaxy Radio galaxy Seyfert galaxy Quasar Blazar Example Milky Way M87, Cygnus A NGC 4151 3C273 BL Lac, 3C279 Galaxy Type spiral elliptical, lenticular spiral irregular
Black Holes in Hibernation
 Black Holes in Hibernation Black Holes in Hibernation Only about 1 in 100 galaxies contains an active nucleus. This however does not mean that most galaxies do no have SMBHs since activity also requires
Black Holes in Hibernation Black Holes in Hibernation Only about 1 in 100 galaxies contains an active nucleus. This however does not mean that most galaxies do no have SMBHs since activity also requires
Other Galaxy Types. Active Galaxies. A diagram of an active galaxy, showing the primary components. Active Galaxies
 Other Galaxy Types Active Galaxies Active Galaxies Seyfert galaxies Radio galaxies Quasars Origin??? Different in appearance Produce huge amount of energy Similar mechanism a Galactic mass black hole at
Other Galaxy Types Active Galaxies Active Galaxies Seyfert galaxies Radio galaxies Quasars Origin??? Different in appearance Produce huge amount of energy Similar mechanism a Galactic mass black hole at
Active Galactic Alexander David M Nuclei
 d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models
 AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models Nikos Fanidakis and C.M. Baugh, R.G. Bower, S. Cole, C. Done, C. S. Frenk Physics of Galactic Nuclei, Ringberg Castle, June 18, 2009 Outline Brief introduction
AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models Nikos Fanidakis and C.M. Baugh, R.G. Bower, S. Cole, C. Done, C. S. Frenk Physics of Galactic Nuclei, Ringberg Castle, June 18, 2009 Outline Brief introduction
The X-Ray Universe. The X-Ray Universe
 The X-Ray Universe The X-Ray Universe Potsdam University Dr. Lidia Oskinova Sommersemester 2017 lida@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de ~lida/vorlesungxrayso17.html Chandra X-ray,
The X-Ray Universe The X-Ray Universe Potsdam University Dr. Lidia Oskinova Sommersemester 2017 lida@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de ~lida/vorlesungxrayso17.html Chandra X-ray,
High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 1: introduction and overview; synchrotron radiation. Timetable. Reading. Overview. What is high-energy astrophysics?
 High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 1: introduction and overview; synchrotron radiation Robert Laing Lectures: Week 1: M 10, T 9 Timetable Week 2: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 3: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 4: M 10, T 9,
High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 1: introduction and overview; synchrotron radiation Robert Laing Lectures: Week 1: M 10, T 9 Timetable Week 2: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 3: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 4: M 10, T 9,
Active Galaxies and Quasars
 Active Galaxies and Quasars Radio Astronomy Grote Reber, a radio engineer and ham radio enthusiast, built the first true radio telescope in 1936 in his backyard. By 1944 he had detected strong radio emissions
Active Galaxies and Quasars Radio Astronomy Grote Reber, a radio engineer and ham radio enthusiast, built the first true radio telescope in 1936 in his backyard. By 1944 he had detected strong radio emissions
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab
 Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Chapter 15 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline Hubble s Galaxy Classification. Normal and Active Galaxies Hubble s Galaxy Classification
 Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Spiral galaxies are classified according to the size of their central bulge. Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Type Sa has the largest central
Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Spiral galaxies are classified according to the size of their central bulge. Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Type Sa has the largest central
Supermassive Black Holes
 Supermassive Black Holes Leiden, Modern Research: Galaxy Formation and Evolution Tom van Leth & Maarten van Dijk November 25, 2005 1 Introduction Introduction Black hole theory Characteristics of SMBH
Supermassive Black Holes Leiden, Modern Research: Galaxy Formation and Evolution Tom van Leth & Maarten van Dijk November 25, 2005 1 Introduction Introduction Black hole theory Characteristics of SMBH
Introduction to AGN. General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo
 Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Galaxies. Galaxy Diversity. Galaxies, AGN and Quasars. Physics 113 Goderya
 Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics. Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars
 Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar
 Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy?
 Ch 14: Mysteries of the Milky Way How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy? The Structure of the Galaxy We know that our galaxy has
Ch 14: Mysteries of the Milky Way How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy? The Structure of the Galaxy We know that our galaxy has
IX. Stuff that's Bigger than the Solar System
 IX. Stuff that's Bigger than the Solar System Physics II 3/26/09 Leeson IX. A. Galaxies M104 Sombrero Galaxy (in Virgo) M31 A. 1. What is a Galaxy? A system of stars, planets, dust, and gas held together
IX. Stuff that's Bigger than the Solar System Physics II 3/26/09 Leeson IX. A. Galaxies M104 Sombrero Galaxy (in Virgo) M31 A. 1. What is a Galaxy? A system of stars, planets, dust, and gas held together
Active galaxies. Some History Classification scheme Building blocks Some important results
 Active galaxies Some History Classification scheme Building blocks Some important results p. 1 Litirature: Peter Schneider, Extragalactic astronomy and cosmology: an introduction p. 175-176, 5.1.1, 5.1.2,
Active galaxies Some History Classification scheme Building blocks Some important results p. 1 Litirature: Peter Schneider, Extragalactic astronomy and cosmology: an introduction p. 175-176, 5.1.1, 5.1.2,
Quasars and AGN. What are quasars and how do they differ from galaxies? What powers AGN s. Jets and outflows from QSOs and AGNs
 Goals: Quasars and AGN What are quasars and how do they differ from galaxies? What powers AGN s. Jets and outflows from QSOs and AGNs Discovery of Quasars Radio Observations of the Sky Reber (an amateur
Goals: Quasars and AGN What are quasars and how do they differ from galaxies? What powers AGN s. Jets and outflows from QSOs and AGNs Discovery of Quasars Radio Observations of the Sky Reber (an amateur
GRB history. Discovered 1967 Vela satellites. classified! Published 1973! Ruderman 1974 Texas: More theories than bursts!
 Discovered 1967 Vela satellites classified! Published 1973! GRB history Ruderman 1974 Texas: More theories than bursts! Burst diversity E peak ~ 300 kev Non-thermal spectrum In some thermal contrib. Short
Discovered 1967 Vela satellites classified! Published 1973! GRB history Ruderman 1974 Texas: More theories than bursts! Burst diversity E peak ~ 300 kev Non-thermal spectrum In some thermal contrib. Short
Lecture 11 Quiz 2. AGN and You. A Brief History of AGN. This week's topics
 Lecture 11 Quiz 2 AGN and You March 25 2003 8:00 PM BPS 1420 1. What system of time do astronomers use rather than the standard day-month-year system? 2. In that system, how long would it be between noon
Lecture 11 Quiz 2 AGN and You March 25 2003 8:00 PM BPS 1420 1. What system of time do astronomers use rather than the standard day-month-year system? 2. In that system, how long would it be between noon
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction
 The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies
 SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies 1 Symp. 324, 12-16 September, 2016 Classical view Spinning black hole Accretion disk Collimated jets of particles 2 Looking
SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies 1 Symp. 324, 12-16 September, 2016 Classical view Spinning black hole Accretion disk Collimated jets of particles 2 Looking
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy Guidepost This chapter plays three parts in our cosmic drama. First, it introduces the concept of a galaxy. Second, it discusses our home, the Milky Way Galaxy, a natural
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy Guidepost This chapter plays three parts in our cosmic drama. First, it introduces the concept of a galaxy. Second, it discusses our home, the Milky Way Galaxy, a natural
QUASARS and ACTIVE GALAXIES. - a Detective Story
 QUASARS and ACTIVE GALAXIES - a Detective Story Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, Biggest puzzle from afar. How unlike the other ones, Brighter than a trillion Suns. Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, How I wonder
QUASARS and ACTIVE GALAXIES - a Detective Story Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, Biggest puzzle from afar. How unlike the other ones, Brighter than a trillion Suns. Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, How I wonder
Astronomical Research at the Center for Adaptive Optics. Sandra M. Faber, CfAO SACNAS Conference October 4, 2003
 Astronomical Research at the Center for Adaptive Optics Sandra M. Faber, CfAO SACNAS Conference October 4, 2003 Science with Natural Guide Stars Any small bright object can be a natural guide star: Examples:
Astronomical Research at the Center for Adaptive Optics Sandra M. Faber, CfAO SACNAS Conference October 4, 2003 Science with Natural Guide Stars Any small bright object can be a natural guide star: Examples:
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution. How do we observe the life histories of galaxies?
 Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Guiding Questions. Active Galaxies. Quasars look like stars but have huge redshifts
 Guiding Questions Active Galaxies 1. Why are quasars unusual? How did astronomers discover that they are extraordinarily distant and luminous? 2. What evidence showed a link between quasars and galaxies?
Guiding Questions Active Galaxies 1. Why are quasars unusual? How did astronomers discover that they are extraordinarily distant and luminous? 2. What evidence showed a link between quasars and galaxies?
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 12: active galactic nuclei
 (Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 12: active galactic nuclei Schedule for this week Monday & Tuesday 4/21 22: ad hoc office hours for Lab # 5 (you can use the computer in my office if necessary; Sections A
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 12: active galactic nuclei Schedule for this week Monday & Tuesday 4/21 22: ad hoc office hours for Lab # 5 (you can use the computer in my office if necessary; Sections A
Outline. Supermassive Black Holes Jets Hot spots and the evolution of radio galaxies
 Active Galaxies Outline 2 Normal (boring) galaxies Active (fun) galaxies The extragalactic zoo: Quasars, Blazars, Radio Galaxies, BL Lacs, Seyferts, Optically Violent Variables, GHz Peaked Spectrum, Compact
Active Galaxies Outline 2 Normal (boring) galaxies Active (fun) galaxies The extragalactic zoo: Quasars, Blazars, Radio Galaxies, BL Lacs, Seyferts, Optically Violent Variables, GHz Peaked Spectrum, Compact
Chapter 19 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Active Galaxies. Lecture Topics. Lecture 24. Active Galaxies. Potential exam topics. What powers these things? Lec. 24: Active Galaxies
 Active Galaxies Lecture 24 APOD: M82 (The Cigar Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Active Galaxies What powers these things? Potential exam topics 2 24-1 Active Galaxies Galaxies Luminosity (L MW *) Normal < 10
Active Galaxies Lecture 24 APOD: M82 (The Cigar Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Active Galaxies What powers these things? Potential exam topics 2 24-1 Active Galaxies Galaxies Luminosity (L MW *) Normal < 10
Feeding the Beast. Chris Impey (University of Arizona)
 Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Active Galactic Nuclei-I. The paradigm
 Active Galactic Nuclei-I The paradigm An accretion disk around a supermassive black hole M. Almudena Prieto, July 2007, Unv. Nacional de Bogota Centers of galaxies Centers of galaxies are the most powerful
Active Galactic Nuclei-I The paradigm An accretion disk around a supermassive black hole M. Almudena Prieto, July 2007, Unv. Nacional de Bogota Centers of galaxies Centers of galaxies are the most powerful
Chapter 19 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
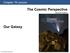 Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like? How do stars
Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like? How do stars
Spins of Supermassive Black Holes. Ruth A. Daly
 Spins of Supermassive Black Holes Ruth A. Daly Three key quantities characterize a black hole: mass, spin, and charge. Astrophysical black holes are thought to have zero net charge, and thus are characterized
Spins of Supermassive Black Holes Ruth A. Daly Three key quantities characterize a black hole: mass, spin, and charge. Astrophysical black holes are thought to have zero net charge, and thus are characterized
Tour of Galaxies. Sgr A* VLT in IR + adaptive optics. orbits. ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies VLT IR+AO
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Kyle Augustson Lecture 23 Tues 8 Apr 08 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Tour of Galaxies Briefly revisit Monster in the Milky Way
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Kyle Augustson Lecture 23 Tues 8 Apr 08 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Tour of Galaxies Briefly revisit Monster in the Milky Way
It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick, and our solar system is located 26,000 ly away from the center of the galaxy.
 The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
19.3 The History of the Milky Way. Our goals for learning: What clues to our galaxy's history do halo stars hold? How did our galaxy form?
 19.3 The History of the Milky Way Our goals for learning: What clues to our galaxy's history do halo stars hold? How did our galaxy form? What clues to our galaxy's history do halo stars hold? Halo Stars:
19.3 The History of the Milky Way Our goals for learning: What clues to our galaxy's history do halo stars hold? How did our galaxy form? What clues to our galaxy's history do halo stars hold? Halo Stars:
Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)
 Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Astronomy Summer School in Mongolia National University of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar July 21-26, 2008 Kaz Sekiguchi Hubble Classification M94-Sa M81-Sb M101-Sc M87-E0
Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Astronomy Summer School in Mongolia National University of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar July 21-26, 2008 Kaz Sekiguchi Hubble Classification M94-Sa M81-Sb M101-Sc M87-E0
1932: KARL JANSKY. 1935: noise is identified as coming from inner regions of Milky Way
 1932: KARL JANSKY Is assigned the task of identifying the noise that plagued telephone calls to Europe 1935: noise is identified as coming from inner regions of Milky Way MANY YEARS GO BY. 1960: a strong
1932: KARL JANSKY Is assigned the task of identifying the noise that plagued telephone calls to Europe 1935: noise is identified as coming from inner regions of Milky Way MANY YEARS GO BY. 1960: a strong
4/18/17. Our Schedule. Revisit Quasar 3C273. Dark Matter in the Universe. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies HST Abell 2218 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 25 Tues 18 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule Observatory Night #8 + #9 (proj
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies HST Abell 2218 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 25 Tues 18 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule Observatory Night #8 + #9 (proj
Neutron Stars. Neutron Stars and Black Holes. The Crab Pulsar. Discovery of Pulsars. The Crab Pulsar. Light curves of the Crab Pulsar.
 Chapter 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes A supernova explosion of an M > 8 M sun star blows away its outer layers. Neutron Stars The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M sun.
Chapter 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes A supernova explosion of an M > 8 M sun star blows away its outer layers. Neutron Stars The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M sun.
Powering Active Galaxies
 Powering Active Galaxies Relativity and Astrophysics ecture 35 Terry Herter Bonus lecture Outline Active Galaxies uminosities & Numbers Descriptions Seyfert Radio Quasars Powering AGN with Black Holes
Powering Active Galaxies Relativity and Astrophysics ecture 35 Terry Herter Bonus lecture Outline Active Galaxies uminosities & Numbers Descriptions Seyfert Radio Quasars Powering AGN with Black Holes
Our Galaxy. Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust. Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye
 Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = solar masses
 Quasars Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = 10 6 10 9 solar masses Stars and gas fall into the black hole and shine in an accrecon disk billion
Quasars Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = 10 6 10 9 solar masses Stars and gas fall into the black hole and shine in an accrecon disk billion
AST Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy. Lecture 20. Black Holes Part II
 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 20 Black Holes Part II 1 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Outline: Black Holes Part II Gas accretion disks around black holes, and
AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 20 Black Holes Part II 1 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Outline: Black Holes Part II Gas accretion disks around black holes, and
Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Josh Webster 4/21/2014 4/21/2014 Josh Webster 1 http://www.nasa.gov/images/content/690958main_p1237a1.jpg A Look Ahead 4/21/2014 Josh Webster 2 A Look Ahead Galaxy
Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes Josh Webster 4/21/2014 4/21/2014 Josh Webster 1 http://www.nasa.gov/images/content/690958main_p1237a1.jpg A Look Ahead 4/21/2014 Josh Webster 2 A Look Ahead Galaxy
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes
 In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera
 FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera In this presentation the different theories that can explain the formation of Supermassive Black Holes (SMBH) are presented. Before focus on
FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera In this presentation the different theories that can explain the formation of Supermassive Black Holes (SMBH) are presented. Before focus on
Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version
 Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version Introduction: The Cartwheel Galaxy Multi-Wavelength Composite The Cartwheel Galaxy is part of a group of galaxies ~five hundred
Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version Introduction: The Cartwheel Galaxy Multi-Wavelength Composite The Cartwheel Galaxy is part of a group of galaxies ~five hundred
Lecture 19: Galaxies. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 19: Galaxies Astronomy 111 Galaxies What is a galaxy? Large assembly of stars, gas and dust, held together by gravity Sizes: Largest: ~1 Trillion stars (or more) Smallest: ~10 Million stars Milky
Lecture 19: Galaxies Astronomy 111 Galaxies What is a galaxy? Large assembly of stars, gas and dust, held together by gravity Sizes: Largest: ~1 Trillion stars (or more) Smallest: ~10 Million stars Milky
X-ray variability of AGN
 X-ray variability of AGN Magnus Axelsson October 20, 2006 Abstract X-ray variability has proven to be an effective diagnostic both for Galactic black-hole binaries and active galactic nuclei (AGN). This
X-ray variability of AGN Magnus Axelsson October 20, 2006 Abstract X-ray variability has proven to be an effective diagnostic both for Galactic black-hole binaries and active galactic nuclei (AGN). This
A Shock Model for the the Outburst from the Supermassive Black Hole in M87 Bill Forman - SAO/CfA
 M87 A Shock Model for the the Outburst from the Supermassive Black Hole in M87 Bill Forman - SAO/CfA interactions galore; stripping at work, M87 outburst Low Eddington ratio accretion (like other normal
M87 A Shock Model for the the Outburst from the Supermassive Black Hole in M87 Bill Forman - SAO/CfA interactions galore; stripping at work, M87 outburst Low Eddington ratio accretion (like other normal
M31 - Andromeda Galaxy M110 M32
 UNIT 4 - Galaxies XIV. The Milky Way galaxy - a huge collection of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust, isolated in space and held together by its own gravity M110 M31 - Andromeda Galaxy A. Structure
UNIT 4 - Galaxies XIV. The Milky Way galaxy - a huge collection of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust, isolated in space and held together by its own gravity M110 M31 - Andromeda Galaxy A. Structure
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: FROM THE CENTRAL BLACK HOLE TO THE GALACTIC ENVIRONMENT
 Julian H. Krolik ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: FROM THE CENTRAL BLACK HOLE TO THE GALACTIC ENVIRONMENT PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS Princeton, New Jersey Preface Guide for Readers xv xix 1. What Are Active Galactic
Julian H. Krolik ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: FROM THE CENTRAL BLACK HOLE TO THE GALACTIC ENVIRONMENT PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS Princeton, New Jersey Preface Guide for Readers xv xix 1. What Are Active Galactic
LARGE QUASAR GROUPS. Kevin Rahill Astrophysics
 LARGE QUASAR GROUPS Kevin Rahill Astrophysics QUASARS Quasi-stellar Radio Sources Subset of Active Galactic Nuclei AGNs are compact and extremely luminous regions at the center of galaxies Identified as
LARGE QUASAR GROUPS Kevin Rahill Astrophysics QUASARS Quasi-stellar Radio Sources Subset of Active Galactic Nuclei AGNs are compact and extremely luminous regions at the center of galaxies Identified as
Exam 4 Review EXAM COVERS LECTURES 22-29
 Exam 4 Review EXAM COVERS LECTURES 22-29 Theoretically is there a center of the universe? Is there an edge? Do we know where Earth is on this? There is no center to the Universe, What kind of light we
Exam 4 Review EXAM COVERS LECTURES 22-29 Theoretically is there a center of the universe? Is there an edge? Do we know where Earth is on this? There is no center to the Universe, What kind of light we
Our Galaxy. Chapter Twenty-Five. Guiding Questions
 Our Galaxy Chapter Twenty-Five Guiding Questions 1. What is our Galaxy? How do astronomers know where we are located within it? 2. What is the shape and size of our Galaxy? 3. How do we know that our Galaxy
Our Galaxy Chapter Twenty-Five Guiding Questions 1. What is our Galaxy? How do astronomers know where we are located within it? 2. What is the shape and size of our Galaxy? 3. How do we know that our Galaxy
Tour of the Universe!
 Tour of the Universe! Andromeda: M31 (NGC 224, the famous Andromeda Galaxy) is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. It is so bright that it is easily seen by naked eye as a faint fuzzy
Tour of the Universe! Andromeda: M31 (NGC 224, the famous Andromeda Galaxy) is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. It is so bright that it is easily seen by naked eye as a faint fuzzy
Foundations of Astrophysics
 Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016
 Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Lecture11; November 1, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to stars Measuring distances Inverse square law: luminosity vs brightness Colors and spectral types, the H-R diagram
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Lecture11; November 1, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to stars Measuring distances Inverse square law: luminosity vs brightness Colors and spectral types, the H-R diagram
Astrophysical Quantities
 Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
Gravity: What s the big attraction? Dan Wilkins Institute of Astronomy
 Gravity: What s the big attraction? Dan Wilkins Institute of Astronomy Overview What is gravity? Newton and Einstein What does gravity do? Extreme gravity The true power of gravity Getting things moving
Gravity: What s the big attraction? Dan Wilkins Institute of Astronomy Overview What is gravity? Newton and Einstein What does gravity do? Extreme gravity The true power of gravity Getting things moving
Galaxies. CESAR s Booklet
 What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
Wednesday, April 19, 2017
 Wednesday, April 19, 2017 Exam 4, Skywatch 4, Friday, April 21. Review Session Tomorrow, 5 6 PM, Welch 2.308. Lectures 21 to 30 Reading for Exam 4: Chapter 8 Neutron Stars - Sections 8.1, 8.2, 8.5, 8.6,
Wednesday, April 19, 2017 Exam 4, Skywatch 4, Friday, April 21. Review Session Tomorrow, 5 6 PM, Welch 2.308. Lectures 21 to 30 Reading for Exam 4: Chapter 8 Neutron Stars - Sections 8.1, 8.2, 8.5, 8.6,
Active galactic nuclei (AGN)
 Active galactic nuclei (AGN) General characteristics and types Supermassive blackholes (SMBHs) Accretion disks around SMBHs X-ray emission processes Jets and their interaction with ambient medium Radio
Active galactic nuclei (AGN) General characteristics and types Supermassive blackholes (SMBHs) Accretion disks around SMBHs X-ray emission processes Jets and their interaction with ambient medium Radio
BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015
 BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 9 Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50
BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 9 Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy
 Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
The Milky Way: Home to Star Clusters
 Chapter 2 The Milky Way: Home to The Milky Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is something of a paradox. It is just one of the many billions of galaxies scattered throughout the Universe, a large, but quite normal
Chapter 2 The Milky Way: Home to The Milky Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is something of a paradox. It is just one of the many billions of galaxies scattered throughout the Universe, a large, but quite normal
Black Holes and Quasars
 Black Holes and Quasars Black Holes Normal and Super- massive The Schwartzchild Radius (event horizon) Normal and Super Massive Black Holes (SMBHs) The GalacAc Centre (GC) The Black Hole in Andromeda AcAve
Black Holes and Quasars Black Holes Normal and Super- massive The Schwartzchild Radius (event horizon) Normal and Super Massive Black Holes (SMBHs) The GalacAc Centre (GC) The Black Hole in Andromeda AcAve
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Pic of the day: edge-on spiral galaxy
 Friday, November 4, 2011 Exam 4, Friday, November 11 Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.1, 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10, Sections 10.1-10.6, 10.9 Astronomy in the news? The docking of the Shenzhou
Friday, November 4, 2011 Exam 4, Friday, November 11 Reading: Chapter 9, Sections 9.5.1, 9.5.2, 9.6.1, 9.6.2. 9.7, 9.8; Chapter 10, Sections 10.1-10.6, 10.9 Astronomy in the news? The docking of the Shenzhou
