Cosmic Rays, GammaRays and the Universal. Background Radiation
|
|
|
- Alicia Cameron
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Cosmic Rays, GammaRays and the Universal Background Radiation Malcolm Longair Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge
3 Celebrating Occhialini I met Occhialini only a few times, in connection with ESA projects and g-ray astronomy. The other connection is that, as a former director of the Cavendish Laboratory, his work with Blackett in the 1930s is one of the highlights of its scientific history.
4 Celebrating Occhialini My charge is to describe the current state of two areas to which he made enormous contributions and which intersect with my interests in High Energy Astrophysics and Cosmology. Cosmic ray astrophysics High energy g-rays.
5 Programme Brief Historical Notes Cosmic ray physics High energy g-rays Cosmology
6 1. Brief Historical Notes
7 The Wilson Cloud Chamber Wilson s perfected Cloud Chamber The first outstanding research involving Occhialini at the Cavendish Laboratory concerned development of the automatic Cloud Chamber. Patrick Blackett had already perfected the techniques of exploiting its capabilities.
8 Blackett s Automatic Cloud Chamber of 1928 In 1924, Blackett succeeded in taking 23,000 automatic cloud chamber photographs which contained about 270,000 tracks of aparticles. Among these were 8 tracks showing the ejection an energetic proton in the disintegration of a nitrogen nucleus.
9 Blackett s Letter to Occhialini s Father For it was certainly his (Occhialini s) arrival in Cambridge which stimulated my embarking on the field of cosmic rays which I have never left. And our work together in was a real collaboration of the happiest kind. P.M.S. Blackett Letter (1948)
10 Blackett s Nobel Prize Lecture Occhialini and I set about, therefore, the devising of a method of making cosmic rays take their own photographs, using the recently developed Geiger-Müller counters as detectors of the rays. P.M.S. Blackett Nobel Prize Speech (1948)
11 The Discovery of the Positron Occhialini had been working with Rossi using coincidence methods for detecting the arrival of cosmic rays. He arrived in Cambridge for three weeks; he stayed for three years. They combined the coincidence technique with the cloud chamber so that, whenever a high energy particle passed through the chamber, its track was photographed.
12 Blackett and Occhialini, 1933 In the key experiment, the cloud chamber was placed on its side and solenoids placed above and below it. The upper solenoid acted as a converter for the cosmic rays. P.M S. Blackett and G.P.S. Occhialini, 1933,. Proc. Roy. Soc. A139, 699
13 Blackett and Occhialini, 1933 They discovered showers of high energy electrons, accompanied by positively charged particles which were deflected by the same amount in the opposite direction. This was the discovery of the positron, the first antiparticle to be discovered. P.M S. Blackett and G.P.S. Occhialini, 1933,. Proc. Roy. Soc. A139, 699
14 COS-B g-ray Satellite As soon as space astronomy became feasible, Occhialini became a leader of European efforts, particularly in g-ray astronomy. Perhaps his greatest achievement was the success of COS-B.
15 COS-B Map of the Galaxy in g-rays
16 The Compton g-ray Observatory (CGRO)
17 Beppo-SAX Satellite The BeppoSAX satellite was a remarkable success we will discuss some of the results later.
18 The INTEGRAL Space Observatory INTEGRAL is the g-ray observatory mission of ESA launched on October on a Proton rocket. It is an ESA-led mission in collaboration with Russia and the USA.
19 SWIFT NASA project to understand the physics of g-ray bursts. Launched November
20 2. Cosmic Rays
21 The Cosmic Ray Spectrum Replot as E3 x N(E) There is encouraging agreement about the observed spectrum except at the very highest energies.
22 The Universal Mechanism Power-law energy spectra are found commonly in high energy astrophysical systems. Radio, optical, X-ray and g-ray spectra of quasars and active galaxies and g-ray bursts require N(E) de µ E-x de x ~ E-2.7 E-3.1
23 First-order Fermi Acceleration Shock front The great merit of the first order shock acceleration mechanism that it is not sensitive to the precise strength of the shock, so long as it is reasonably strong.
24 First-order Fermi Acceleration in Strong Shocks, U» vs U v2 = ¼ v1 v1 = U p2, T2, r2 p1, T1, r1 ¾U ¾U
25 First-order Fermi Acceleration In the simplest calculation for non-relativistic shocks, a power-law spectrum is found which only depends upon the shock being strong.
26 The Acceleration of Charged Particles Three Shock Acceleration mechanisms work together. First-order Fermi mechanism: scattering across the shock dominant at quasi-parallel shocks (qbn< 45o) Shock Drift Acceleration: drift along the shock surface dominant at quasi-perpendicular shocks (qbn < 45o) Second-order Fermi mechanism: Stochastic process, turbulent acceleration à add momentum diffusion term
27 Cassiopeia A A supernova which exploded about 250 years ago. This X-ray image shows the faint stellar remnant for the first time. The shell of the remnant was heated by the explosion of the star. The shock is highly supersonic. Chandra X-ray Observatory of NASA
28 Cassiopeia A A supernova which exploded about 250 years ago. This radio image shows the distribution of relativistic electrons and magnetic field in the remnant. These were accelerated in the shock. NRAO Very Large Array
29 Detecting Ultra High Energy g-rays High Energy Stereoscopic S ystem (HESS) in Namibia. The HESS telescope system and similar telescopes detect the atmospheric Cerenkov radiation resulting from electron-photon cascades induced by the incoming very high energy g-rays.
30 A Supernova Remnant Detected in Ultra High Energy g-rays The colour map shows the ultra high- energy grays. The contours show the image obtained by the Japanese ASCA X-ray Observatory. The HESS g-ray observations are interpreted as evidence for the acceleration of cosmic ray protons in the supernova remnant.
31 Notes About 50 % of shock kinetic E can be transferred to cosmic rays for strong shocks with Ms > 30. Supernova acceleration works well. A cut-off at ev is expected when the gyroradii are equal to the scale of the remnant. If the overall spectrum consists of the superposition of the spectra of protons, helium nuclei, heavy elements, this could explain the spectrum above the knee, since the gyroradii of the particles scale with atomic number.
32 Decomposing the Spectrum Is the story really as simple as this? He C,O, p E-2.7 Galactic component Nagano & Watson 00 Fe
33 The Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays
34 The Greisen, Kuzmin, Zatsepin (GKZ) Cut-off In the centre of momentum frame of reference, the ultrarelativistic protons are degraded by photo-pion and electron-positron pair production Photo-pion production Electron-positron pair production
35 The GZK Cut-off 100 Mpc As shown by Berezinsky, when the cross-sections for these processes are worked out, there is a very strong dependence of the maximum distance of propagation. This is reflected in the predicted GKZ cut-off.
36 Revised Agasa Results Energy shift ~10% at 1019 ev ~15% at 1020 ev to lower energies. Above 1020 ev 11 events è 5~6 events Teshima
37 Auger Project
38 HiRes1 and 2 Martens has reported that the HiRes data are consistent with the existence of the GZK cut-off. Key importance of the Auger observations.
39 The Berezinsky Fitting Formula Looks very convincing, but need to get the calibration of the experiments right independent of knowing the answer.
40 Tracking the Sources of the UHECRs There seems to be agreement that at the very highest energies, E > 3 x 1019 ev, the deflections due to intergalactic magnetic fields are expected to be quite small. Typical estimates of what the sky should look like at very high energies have been carried made by Dogel and others.
41 Deflection of protons with energies E > ev Trajectories of particles from within 100 Mpc.
42 The Importance of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey One of the great puzzles is that, if this story is true, we should be able to find out directly what the associated astronomical objects are from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey more that 250,000 galaxies to z ~ 0.4.
43 The Hillas Acceleration Diagram The size of the accelerating region
44 Radio Galaxies The radio emission is synchrotron radiation, the emission of extremely high energy electrons gyrating in a magnetic field. The electrons are produced by jets of relativistic material ejected from the active galactic nucleus. Scales up to 1 Mpc, magnetic fields ~10-8 T.
45 Distribution of Shock Mach Numbers in Cluster of Galaxies The Invisible Universe of Shocks Ryu and Kang
46 Velocity Field and Shocks in a Cluster Complex - simulations Lx rgas T Ms Ryu and Kang
47 Bottom-up versus Top-down My instinct is that we can explain the highest energy particles by an acceleration mechanism. But What happens if future experiments do detect significant fluxes of E > 1020 ev particles and we cannot identify their sources? I believe this is the real reason these experiments are really important.
48 3. g-rays
49 The Sky at g-ray Wavelengths g-ray sources are extremely hot objects - extremely active galaxies and emission of high energy particles
50 The Extreme g-ray source 3C279 Radio Optical X-ray g-ray The Compton g-ray Observatory discovered that the superluminal radio sources are extremely luminous g-ray sources. The emission must also be relativistically beamed because of the same gg e+e- catastrophe described by Celotti.
51 The Extreme g-ray Sources Markarian 421 and 501 These sources involve a huge range of high energy astrophysical processes, including relativistic beaming of the high energy g-ray emission.
52 Superluminal motions in 3C273 March 1978 June 1979 July The structure of the radio quasar 3C273 was observed by Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) for 3 years.
53 Superluminal motions in 3C120 The structure of the radio quasar 3C120 was observed by the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBI) for 6 years.
54 Superluminal Velocities The conventional picture is that these are associated with an optical illusion due to the fact that the jets are travelling at a speed v ~ c at an angle close to the line of sight.
55 Relativistic Beaming The result is enormous enhancements of the luminosities, typically, L µ k4 where k = g[1+(v/c) cos q]. This is primarily due to relativistic aberration effects.
56 4. Cosmology
57 g-ray Bursts These were beautifully described by Celotti this morning and so I only mention them in their cosmological context.
58 The 3-year WMAP Power-spectra These observations provide strong constraints on the epoch of reionisation. It must have occurred in the redshift interval 7< z < 15.
59 The High-Redshift IGM Period between recombination and reionization is crucial to understanding galaxy formation. Do the observed GunnPeterson troughs imply reionization? What is the re-ionisation history?
60 The Distances of g-ray Bursts g-ray bursts have turned out to be one of the most effective ways of finding very distant objects for cosmological studies. In particular, this is a way of getting beyond z = 6.
61 Background Radiation gg e+e-
62 Limiting the Extragalactic Background Radiation from g-g Interactions in Intergalactic Space Redshift = The g-g interactions result in limits to the intergalactic fluxes of UV, optical and infrared photons. The total light cannot be much greater than that already detected in deep surveys of galaxies.
63 Concluding Remark Occhialini s legacy is much more than just a sequence of outstanding experiments and discoveries, but the inspiration of his colleagues and the next generation of physicists and astrophysicists. They have built on his achievements and played a key role of astrophysical research in Italy.
> News < AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May 2nd 2:33 P.M. from NASA Kennedy space center!
 > News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
> News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A
 An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
Dr. John Kelley Radboud Universiteit, Nijmegen
 arly impressive. An ultrahighoton triggers a cascade of particles mulation of the Auger array. The Many Mysteries of Cosmic Rays Dr. John Kelley Radboud Universiteit, Nijmegen Questions What are cosmic
arly impressive. An ultrahighoton triggers a cascade of particles mulation of the Auger array. The Many Mysteries of Cosmic Rays Dr. John Kelley Radboud Universiteit, Nijmegen Questions What are cosmic
Mass Composition Study at the Pierre Auger Observatory
 OBSERVATORY Mass Composition Study at the Pierre Auger Observatory Laura Collica for the Auger Milano Group 4.04.2013, Astrosiesta INAF Milano 1 Outline The physics: The UHECR spectrum Extensive Air Showers
OBSERVATORY Mass Composition Study at the Pierre Auger Observatory Laura Collica for the Auger Milano Group 4.04.2013, Astrosiesta INAF Milano 1 Outline The physics: The UHECR spectrum Extensive Air Showers
Extensive Air Showers and Particle Physics Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware
 Extensive Air Showers and Particle Physics Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Extensive air showers are the cascades that develop in the atmosphere
Extensive Air Showers and Particle Physics Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Extensive air showers are the cascades that develop in the atmosphere
from Fermi (Higher Energy Astrophysics)
 Particle Acceleration Results from Fermi (Higher Energy Astrophysics) Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford 3 viii 2011 SLAC SSI 1 Fermi Joint NASA-DOE-Italy- France-Japan- Sweden, Germany mission Launch June
Particle Acceleration Results from Fermi (Higher Energy Astrophysics) Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford 3 viii 2011 SLAC SSI 1 Fermi Joint NASA-DOE-Italy- France-Japan- Sweden, Germany mission Launch June
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays: Observations and Analysis
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays: Observations and Analysis NOT A NEW PROBLEM, STILL UNSOLVED John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays: Observations and Analysis NOT A NEW PROBLEM, STILL UNSOLVED John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020
Dark Energy: Measuring the Invisible with X-Ray Telescopes
 Black holes, Galactic Dark Center Matter and Galactic Center Dark Energy: Measuring the Invisible with X-Ray Telescopes Christine Jones Before 1930 -- only optical observations of the sky Intro Before
Black holes, Galactic Dark Center Matter and Galactic Center Dark Energy: Measuring the Invisible with X-Ray Telescopes Christine Jones Before 1930 -- only optical observations of the sky Intro Before
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II
 Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II The March 6th lecture discussed the energy loss processes of protons, nuclei and gamma rays in interactions with the microwave background. Today I will give
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II The March 6th lecture discussed the energy loss processes of protons, nuclei and gamma rays in interactions with the microwave background. Today I will give
COSMIC RAYS DAY INTRODUCTION TO COSMIC RAYS WINDWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE - SEPTEMBER 26, 2015 VERONICA BINDI - UNIVERSITY OH HAWAII
 COSMIC RAYS DAY WINDWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE - SEPTEMBER 26, 2015 VERONICA BINDI - UNIVERSITY OH HAWAII INTRODUCTION TO COSMIC RAYS MAJOR QUESTIONS: Are there forms of matter in the Universe that do not
COSMIC RAYS DAY WINDWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE - SEPTEMBER 26, 2015 VERONICA BINDI - UNIVERSITY OH HAWAII INTRODUCTION TO COSMIC RAYS MAJOR QUESTIONS: Are there forms of matter in the Universe that do not
The Physics of Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays. Example Poster Presentation Physics 5110 Spring 2009 Reminder: Posters are due Wed April 29 in class.
 The Physics of Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays Example Poster Presentation Physics 5110 Spring 2009 Reminder: Posters are due Wed April 29 in class. 1 Introduction to Cosmic Rays References: http://www.phy.bris.ac.uk/groups/particle/pus/affo
The Physics of Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays Example Poster Presentation Physics 5110 Spring 2009 Reminder: Posters are due Wed April 29 in class. 1 Introduction to Cosmic Rays References: http://www.phy.bris.ac.uk/groups/particle/pus/affo
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park
 99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS
 STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) COSMO / CosPA 2010, Tokyo Power law flux stochastic (Fermi) acceleration in shocks cosmic ray flux Small fractional energy gain after
STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) COSMO / CosPA 2010, Tokyo Power law flux stochastic (Fermi) acceleration in shocks cosmic ray flux Small fractional energy gain after
Ultrahigh Energy cosmic rays II
 Ultrahigh Energy cosmic rays II Today we will discuss the new data on UHECR presented during the last couple of years by the Auger observatory in Argentina. These data do not match previous analyses and
Ultrahigh Energy cosmic rays II Today we will discuss the new data on UHECR presented during the last couple of years by the Auger observatory in Argentina. These data do not match previous analyses and
Chapter 0 Introduction X-RAY BINARIES
 X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
Cosmic Rays. M. Swartz. Tuesday, August 2, 2011
 Cosmic Rays M. Swartz 1 History Cosmic rays were discovered in 1912 by Victor Hess: he discovered that a charged electroscope discharged more rapidly as he flew higher in a balloon hypothesized they were
Cosmic Rays M. Swartz 1 History Cosmic rays were discovered in 1912 by Victor Hess: he discovered that a charged electroscope discharged more rapidly as he flew higher in a balloon hypothesized they were
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY. Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006
 PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
Cosmic Rays. This showed that the energy of cosmic rays was many times that of any other natural or artificial radiation known at that time.
 Cosmic Rays 1. Discovery As long ago as 1900, C. T. R. Wilson and others found that the charge on an electroscope always 'leaked' away in time, and this could never be prevented, no matter how good the
Cosmic Rays 1. Discovery As long ago as 1900, C. T. R. Wilson and others found that the charge on an electroscope always 'leaked' away in time, and this could never be prevented, no matter how good the
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation I
 Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation I Microwave background Energy loss processes for protons: - photoproduction interactions - pair production interactions - adiabatic loss due to the expansion of
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation I Microwave background Energy loss processes for protons: - photoproduction interactions - pair production interactions - adiabatic loss due to the expansion of
Cosmic Ray Astronomy. Qingling Ni
 Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Supernova Remnants as Cosmic Ray Accelerants. By Jamie Overbeek Advised by Prof. J. Finley
 Supernova Remnants as Cosmic Ray Accelerants By Jamie Overbeek Advised by Prof. J. Finley Cosmic Rays Discovered by Victor Hess in 1911 during a balloon flight through Austria He used an electroscope to
Supernova Remnants as Cosmic Ray Accelerants By Jamie Overbeek Advised by Prof. J. Finley Cosmic Rays Discovered by Victor Hess in 1911 during a balloon flight through Austria He used an electroscope to
Multi-wavelength Astronomy
 astronomy Multi-wavelength Astronomy Content What do we measure Multi-wavelength approach Data Data Mining Virtual Observatory Hands on session Larmor's formula Maxwell's equations imply that all classical
astronomy Multi-wavelength Astronomy Content What do we measure Multi-wavelength approach Data Data Mining Virtual Observatory Hands on session Larmor's formula Maxwell's equations imply that all classical
STUDY OF EXTENSIVE AIR SHOWERS IN THE EARTH S ATMOSPHERE
 STUDY OF EXTENSIVE AIR SHOWERS IN THE EARTH S ATMOSPHERE I. BACIOIU * Institute of Space Science, P.O. Box MG-23, RO-077125 Bucharest-Magurele, Romania, E-mail: iuliana.bacioiu@spacescience.ro Abstract.
STUDY OF EXTENSIVE AIR SHOWERS IN THE EARTH S ATMOSPHERE I. BACIOIU * Institute of Space Science, P.O. Box MG-23, RO-077125 Bucharest-Magurele, Romania, E-mail: iuliana.bacioiu@spacescience.ro Abstract.
Secondary particles generated in propagation neutrinos gamma rays
 th INT, Seattle, 20 Feb 2008 Ultra High Energy Extragalactic Cosmic Rays: Propagation Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Energy loss processes protons
th INT, Seattle, 20 Feb 2008 Ultra High Energy Extragalactic Cosmic Rays: Propagation Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Energy loss processes protons
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 1: introduction and overview; synchrotron radiation. Timetable. Reading. Overview. What is high-energy astrophysics?
 High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 1: introduction and overview; synchrotron radiation Robert Laing Lectures: Week 1: M 10, T 9 Timetable Week 2: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 3: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 4: M 10, T 9,
High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 1: introduction and overview; synchrotron radiation Robert Laing Lectures: Week 1: M 10, T 9 Timetable Week 2: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 3: M 10, T 9, W 10 Week 4: M 10, T 9,
Absorption and production of high energy particles in the infrared background
 Roma I, 16 March 2007 Absorption and production of high energy particles in the infrared background Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute University of Delaware Newark, DE19716 We discuss the role of
Roma I, 16 March 2007 Absorption and production of high energy particles in the infrared background Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute University of Delaware Newark, DE19716 We discuss the role of
Bright Quasar 3C 273 Thierry J-L Courvoisier. Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin
 eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2368 Bright Quasar 3C 273 Thierry J-L Courvoisier From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2368 Bright Quasar 3C 273 Thierry J-L Courvoisier From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
Gamma-ray Astrophysics
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
The Physics of Cosmic Rays
 The Physics of Cosmic Rays QuarkNet summer workshop July 23-27, 2012 1 Recent History Most natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. You can determine what these rules are by
The Physics of Cosmic Rays QuarkNet summer workshop July 23-27, 2012 1 Recent History Most natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. You can determine what these rules are by
Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics. Hang Bae Kim Hanyang University Hangdang Workshop,
 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics Hang Bae Kim Hanyang University Hangdang Workshop, 2012. 08. 22 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays Ultra High Energy Cosmic Ray (UHECR)» E 3 E & 10 18 ev Energy
Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics Hang Bae Kim Hanyang University Hangdang Workshop, 2012. 08. 22 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays Ultra High Energy Cosmic Ray (UHECR)» E 3 E & 10 18 ev Energy
COSMIC RAYS AND AGN's
 COSMIC RAYS AND AGN's RAZELE COSMICE ŞI NUCLEELE GALACTICE ACTIVE (don't worry, it is in Romanian) Sorin Roman sroman@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de We'll try to talk about: -History -Composition -CR Spectrum -Detection
COSMIC RAYS AND AGN's RAZELE COSMICE ŞI NUCLEELE GALACTICE ACTIVE (don't worry, it is in Romanian) Sorin Roman sroman@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de We'll try to talk about: -History -Composition -CR Spectrum -Detection
Active galactic nuclei (AGN)
 Active galactic nuclei (AGN) General characteristics and types Supermassive blackholes (SMBHs) Accretion disks around SMBHs X-ray emission processes Jets and their interaction with ambient medium Radio
Active galactic nuclei (AGN) General characteristics and types Supermassive blackholes (SMBHs) Accretion disks around SMBHs X-ray emission processes Jets and their interaction with ambient medium Radio
Lecture 9. Quasars, Active Galaxies and AGN
 Lecture 9 Quasars, Active Galaxies and AGN Quasars look like stars but have huge redshifts. object with a spectrum much like a dim star highly red-shifted enormous recessional velocity huge distance (Hubble
Lecture 9 Quasars, Active Galaxies and AGN Quasars look like stars but have huge redshifts. object with a spectrum much like a dim star highly red-shifted enormous recessional velocity huge distance (Hubble
Overview: UHECR spectrum and composition Arrival directions and magnetic field Method for search for UHE nuclei sources Application to the Auger data
 Overview: UHECR spectrum and composition Arrival directions and magnetic field Method for search for UHE nuclei sources Application to the Auger data Acceleration of UHECR A.G.N. GRB Radio Galaxy Lobe
Overview: UHECR spectrum and composition Arrival directions and magnetic field Method for search for UHE nuclei sources Application to the Auger data Acceleration of UHECR A.G.N. GRB Radio Galaxy Lobe
Supernova Remnants and Cosmic. Rays
 Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and the GeV-TeV Diffuse Gamma-Ray Flux
 The 4th International Workshop on The Highest Energy Cosmic Rays and Their Sources INR, Moscow May 20-22, 2008 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and the GeV-TeV Diffuse Gamma-Ray Flux Oleg Kalashev* (INR RAS)
The 4th International Workshop on The Highest Energy Cosmic Rays and Their Sources INR, Moscow May 20-22, 2008 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and the GeV-TeV Diffuse Gamma-Ray Flux Oleg Kalashev* (INR RAS)
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Cherenkov Telescope Array ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP
 Cherenkov Telescope Array A SENSITIVE PROBE OF EXTREME UNIVERSE ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP 2015 1 The CTA Observatory SST ( 4m) LST ( 23m) MST ( 12m) South North
Cherenkov Telescope Array A SENSITIVE PROBE OF EXTREME UNIVERSE ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP 2015 1 The CTA Observatory SST ( 4m) LST ( 23m) MST ( 12m) South North
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy. HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric
 Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
RECENT RESULTS FROM THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY
 RECENT RESULTS FROM THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY (Neutrino 2008, Christchurch, NZ) Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) the Auger Collaboration: 17 countries, ~100 Institutions, ~400 scientists Argentina, Australia,
RECENT RESULTS FROM THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY (Neutrino 2008, Christchurch, NZ) Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) the Auger Collaboration: 17 countries, ~100 Institutions, ~400 scientists Argentina, Australia,
The Pierre Auger Observatory
 The Pierre Auger Observatory Hunting the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays I High Energy Cosmic Rays and Extensive Air Showers March 2007 E.Menichetti - Villa Gualino, March 2007 1 Discovery of Cosmic Rays Altitude
The Pierre Auger Observatory Hunting the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays I High Energy Cosmic Rays and Extensive Air Showers March 2007 E.Menichetti - Villa Gualino, March 2007 1 Discovery of Cosmic Rays Altitude
Cosmic Rays. Discovered in 1912 by Viktor Hess using electroscopes to measure ionization at altitudes via balloon
 Cosmic Rays Discovered in 1912 by Viktor Hess using electroscopes to measure ionization at altitudes via balloon Nobel Prize in 1936 Origin of high energy cosmic rays is still not completely understood
Cosmic Rays Discovered in 1912 by Viktor Hess using electroscopes to measure ionization at altitudes via balloon Nobel Prize in 1936 Origin of high energy cosmic rays is still not completely understood
Particle acceleration in the universe
 Particle acceleration in the universe Some issues and challenges Etienne Parizot (APC Université Paris Diderot - France) Astrophysics 2 Everything we know about the universe comes from the observation
Particle acceleration in the universe Some issues and challenges Etienne Parizot (APC Université Paris Diderot - France) Astrophysics 2 Everything we know about the universe comes from the observation
Cosmic Rays: A Way to Introduce Modern Physics Concepts. Steve Schnetzer
 Cosmic Rays: A Way to Introduce Modern Physics Concepts Steve Schnetzer Rutgers CR Workshop May 19, 2007 Concepts Astrophysics Particle Physics Radiation Relativity (time dilation) Solar Physics Particle
Cosmic Rays: A Way to Introduce Modern Physics Concepts Steve Schnetzer Rutgers CR Workshop May 19, 2007 Concepts Astrophysics Particle Physics Radiation Relativity (time dilation) Solar Physics Particle
Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002
 Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002 n High Energy Astronomy Multi-Messanger Astronomy Cosmic Rays
Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002 n High Energy Astronomy Multi-Messanger Astronomy Cosmic Rays
Short Course on High Energy Astrophysics. Exploring the Nonthermal Universe with High Energy Gamma Rays
 Short Course on High Energy Astrophysics Exploring the Nonthermal Universe with High Energy Gamma Rays Lecture 1: Introduction Felix Aharonian Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin Max-Planck Institut
Short Course on High Energy Astrophysics Exploring the Nonthermal Universe with High Energy Gamma Rays Lecture 1: Introduction Felix Aharonian Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin Max-Planck Institut
Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa 2.0
 Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa. G Rastegarzade B Parvizi,, Physics Department, Semnan University, Semnan, P.O. Box 596-599, Iran Email: G_ rastegar@alum.sharif.edu Abstract
Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa. G Rastegarzade B Parvizi,, Physics Department, Semnan University, Semnan, P.O. Box 596-599, Iran Email: G_ rastegar@alum.sharif.edu Abstract
Open questions with ultra-high energy cosmic rays
 Open questions with ultra-high energy cosmic rays Pasquale Blasi INAF/Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Firenze, Italy E-mail: blasi@arcetri.astro.it Abstract. We briefly discuss three aspects related
Open questions with ultra-high energy cosmic rays Pasquale Blasi INAF/Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Firenze, Italy E-mail: blasi@arcetri.astro.it Abstract. We briefly discuss three aspects related
Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Astro 129: Chapter 1a
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Astrophysics with GLAST: dark matter, black holes and other astronomical exotica
 Astrophysics with GLAST: dark matter, black holes and other astronomical exotica Greg Madejski Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology (KIPAC) Outline:
Astrophysics with GLAST: dark matter, black holes and other astronomical exotica Greg Madejski Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology (KIPAC) Outline:
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays What we have learnt from. HiRes and Auger. Andreas Zech Observatoire de Paris (Meudon) / LUTh
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays What we have learnt from HiRes and Auger Andreas Zech Observatoire de Paris (Meudon) / LUTh École de Chalonge, Paris, Outline The physics of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays What we have learnt from HiRes and Auger Andreas Zech Observatoire de Paris (Meudon) / LUTh École de Chalonge, Paris, Outline The physics of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays
Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays: A Tale of Two Observatories
 Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays: A Tale of Two Observatories RuoYu Shang Nicholas Sherer Fei Sun Bryce Thurston Measurement of the Depth of Maximumof Extensive Air Showers above 10 18 ev,"phys. Rev. Letters104(2010)
Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays: A Tale of Two Observatories RuoYu Shang Nicholas Sherer Fei Sun Bryce Thurston Measurement of the Depth of Maximumof Extensive Air Showers above 10 18 ev,"phys. Rev. Letters104(2010)
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energy Astrophysics Introduction Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk January 2012 Today s introduction - The sky at different
High Energy Astrophysics Introduction Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk January 2012 Today s introduction - The sky at different
Lecture 11 Quiz 2. AGN and You. A Brief History of AGN. This week's topics
 Lecture 11 Quiz 2 AGN and You March 25 2003 8:00 PM BPS 1420 1. What system of time do astronomers use rather than the standard day-month-year system? 2. In that system, how long would it be between noon
Lecture 11 Quiz 2 AGN and You March 25 2003 8:00 PM BPS 1420 1. What system of time do astronomers use rather than the standard day-month-year system? 2. In that system, how long would it be between noon
GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY: IMAGING ATMOSPHERIC CHERENKOV TECHNIQUE FABIO ZANDANEL - SESIONES CCD
 GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY: IMAGING ATMOSPHERIC CHERENKOV TECHNIQUE COSMIC RAYS Discovered in 1912 by Victor Hess (Nobel Prize) Messengers from the non-thermal part of the Universe E < 15 ev: galactic E > 17
GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY: IMAGING ATMOSPHERIC CHERENKOV TECHNIQUE COSMIC RAYS Discovered in 1912 by Victor Hess (Nobel Prize) Messengers from the non-thermal part of the Universe E < 15 ev: galactic E > 17
ISAPP Gran Sasso June 28-July 9, Observations of Cosmic Rays
 ISAPP 2004 Gran Sasso June 28-July 9, 2003 Observations of Cosmic Rays Tiina Suomijärvi Institut de Physique Nucléaire Université Paris XI-Orsay, IN2P3/CNRS France Why to Study Cosmic Rays? Cosmic rays
ISAPP 2004 Gran Sasso June 28-July 9, 2003 Observations of Cosmic Rays Tiina Suomijärvi Institut de Physique Nucléaire Université Paris XI-Orsay, IN2P3/CNRS France Why to Study Cosmic Rays? Cosmic rays
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants
 Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission
 The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
Gamma-ray Bursts. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Gamma-ray Bursts At the moment, the most important application of the theory of relativistic shock waves is in explaining the radiation from Gamma-ray Burst sources. I will briefly introduce
Chapter 4 Gamma-ray Bursts At the moment, the most important application of the theory of relativistic shock waves is in explaining the radiation from Gamma-ray Burst sources. I will briefly introduce
Cosmic Rays, their Energy Spectrum and Origin
 Chapter 1 Cosmic Rays, their Energy Spectrum and Origin 1 The Problem of Cosmic Rays Most cosmic rays are not, as the name would suggest, a type of electromagnetic radiation, but are nucleonic particles
Chapter 1 Cosmic Rays, their Energy Spectrum and Origin 1 The Problem of Cosmic Rays Most cosmic rays are not, as the name would suggest, a type of electromagnetic radiation, but are nucleonic particles
Lecture 14 Cosmic Rays
 Lecture 14 Cosmic Rays 1. Introduction and history 2. Locally observed properties 3. Interactions 4. Demodulation and ionization rate 5. Midplane interstellar pressure General Reference MS Longair, High
Lecture 14 Cosmic Rays 1. Introduction and history 2. Locally observed properties 3. Interactions 4. Demodulation and ionization rate 5. Midplane interstellar pressure General Reference MS Longair, High
High-energy neutrino detection with the ANTARES underwater erenkov telescope. Manuela Vecchi Supervisor: Prof. Antonio Capone
 High-energy neutrino detection with the ANTARES underwater erenkov telescope Supervisor: Prof. Antonio Capone 1 Outline Neutrinos: a short introduction Multimessenger astronomy: the new frontier Neutrino
High-energy neutrino detection with the ANTARES underwater erenkov telescope Supervisor: Prof. Antonio Capone 1 Outline Neutrinos: a short introduction Multimessenger astronomy: the new frontier Neutrino
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical
 ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Introduction to cosmic rays
 Introduction to cosmic rays 1 COSMIC RAYS: Messages from exploding stars and even more powerful objects What are cosmic rays? How were they discovered? How do we detect them? What can we learn from them?
Introduction to cosmic rays 1 COSMIC RAYS: Messages from exploding stars and even more powerful objects What are cosmic rays? How were they discovered? How do we detect them? What can we learn from them?
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS - High Energy Astronomy From the Ground - Felix Aharonian HIGH ENERGY ASTRONOMY FROM THE GROUND
 HIGH ENERGY ASTRONOMY FROM THE GROUND Felix Aharonian Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin, Ireland and Max Planck Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany Keywords: nonthermal Universe, cosmic
HIGH ENERGY ASTRONOMY FROM THE GROUND Felix Aharonian Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin, Ireland and Max Planck Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany Keywords: nonthermal Universe, cosmic
Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful
 Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful Charged-particle astronomy coming of age How it is done The sources The signals What we have learned
Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful Charged-particle astronomy coming of age How it is done The sources The signals What we have learned
The Cosmic Microwave Background
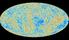 The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION. Thanassis Akylas
 X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION Thanassis Akylas Telescopes & Light Gallileo turned his telescope into the sky 400 years ago He enhanced his natural vision or the so called natural
X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION Thanassis Akylas Telescopes & Light Gallileo turned his telescope into the sky 400 years ago He enhanced his natural vision or the so called natural
On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin
 UHECR 2014 13 15 October 2014 / Springdale (Utah; USA) On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin Etienne Parizot 1, Noémie Globus 2 & Denis Allard 1 1. APC Université Paris Diderot France 2. Tel Aviv
UHECR 2014 13 15 October 2014 / Springdale (Utah; USA) On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin Etienne Parizot 1, Noémie Globus 2 & Denis Allard 1 1. APC Université Paris Diderot France 2. Tel Aviv
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
 Abstract The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Tova Yoast-Hull May 2011 The primary instrument on the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is the Large Area Telescope (LAT) which detects gamma-rays in the energy
Abstract The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Tova Yoast-Hull May 2011 The primary instrument on the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is the Large Area Telescope (LAT) which detects gamma-rays in the energy
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
X-rays Einstein. Gamma Rays
 VERY HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAY ASTRONOMY Tadashi KIFUNE Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 188-8502, Japan, tkifune@icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp Abstract Copious electrons and positrons appear
VERY HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAY ASTRONOMY Tadashi KIFUNE Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 188-8502, Japan, tkifune@icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp Abstract Copious electrons and positrons appear
Particle Acceleration in the Universe
 Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Frontiers: Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays
 Frontiers: Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays We now focus on cosmic rays with almost unimaginable energies: 10 19 ev and beyond. The very highest energy cosmic rays have energies in excess of 50 Joules(!),
Frontiers: Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays We now focus on cosmic rays with almost unimaginable energies: 10 19 ev and beyond. The very highest energy cosmic rays have energies in excess of 50 Joules(!),
Major Option C1 Astrophysics. C1 Astrophysics
 C1 Astrophysics Course co-ordinator: Julien Devriendt jeg@astro.ox.ac.uk C1 offers a total of ~40 lectures on five themes covering a broad range of topics in contemporary astrophysics. Each theme takes
C1 Astrophysics Course co-ordinator: Julien Devriendt jeg@astro.ox.ac.uk C1 offers a total of ~40 lectures on five themes covering a broad range of topics in contemporary astrophysics. Each theme takes
Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics Astroparticle Physics Lecture 5 Gamma Rays & x-rays Sept. 22, 2015 Sun Kee Kim Seoul National University Gamma ray astronomy gamma ray synchrotron radition
Special Topics in Nuclear and Particle Physics Astroparticle Physics Lecture 5 Gamma Rays & x-rays Sept. 22, 2015 Sun Kee Kim Seoul National University Gamma ray astronomy gamma ray synchrotron radition
Introduction to High Energy Astrophysics
 Introduction to High Energy Astrophysics Books 2011 2006 - for the history of the subject 1 The Sky in Different Astronomical Wavebands The context for high energy astrophysics Optical Infrared Millimetre-submillimetre
Introduction to High Energy Astrophysics Books 2011 2006 - for the history of the subject 1 The Sky in Different Astronomical Wavebands The context for high energy astrophysics Optical Infrared Millimetre-submillimetre
The Most Luminous Radio Galaxies
 The Most Luminous Radio Galaxies The physics of radio galaxies and quasars The origin of their strong cosmological evolution Where they fit into the scheme of galaxy formation and evolution How does it
The Most Luminous Radio Galaxies The physics of radio galaxies and quasars The origin of their strong cosmological evolution Where they fit into the scheme of galaxy formation and evolution How does it
Low-Energy Cosmic Rays
 Low-Energy Cosmic Rays Cosmic rays, broadly defined, are charged particles from outside the solar system. These can be electrons, protons, or ions; the latter two dominate the number observed. They are
Low-Energy Cosmic Rays Cosmic rays, broadly defined, are charged particles from outside the solar system. These can be electrons, protons, or ions; the latter two dominate the number observed. They are
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays. and
 2011 BCVSPIN Advanced Study Institute in Particle Physics and Cosmology, Huê, Vietnam, 25-30 July 2011 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays and The Pierre Auger Observatory Paolo Privitera 1 Cosmic Rays are always
2011 BCVSPIN Advanced Study Institute in Particle Physics and Cosmology, Huê, Vietnam, 25-30 July 2011 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays and The Pierre Auger Observatory Paolo Privitera 1 Cosmic Rays are always
What we (don t) know about UHECRs
 What we (don t) know about UHECRs We know: their energies (up to 10 20 ev). their overall energy spectrum We don t know: where they are produced how they are produced what they are made off exact shape
What we (don t) know about UHECRs We know: their energies (up to 10 20 ev). their overall energy spectrum We don t know: where they are produced how they are produced what they are made off exact shape
Quasars and AGN. What are quasars and how do they differ from galaxies? What powers AGN s. Jets and outflows from QSOs and AGNs
 Goals: Quasars and AGN What are quasars and how do they differ from galaxies? What powers AGN s. Jets and outflows from QSOs and AGNs Discovery of Quasars Radio Observations of the Sky Reber (an amateur
Goals: Quasars and AGN What are quasars and how do they differ from galaxies? What powers AGN s. Jets and outflows from QSOs and AGNs Discovery of Quasars Radio Observations of the Sky Reber (an amateur
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 24 Studying the Sun 24.1 The Study of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 24 Studying the Sun 24.1 The Study of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible
New physics is learnt from extreme or fundamental things
 New physics is learnt from extreme or fundamental things New physics is learnt from extreme or fundamental things The Universe is full of extremes and is about as fundamental as it gets! New physics is
New physics is learnt from extreme or fundamental things New physics is learnt from extreme or fundamental things The Universe is full of extremes and is about as fundamental as it gets! New physics is
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays. UHECRs from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai, India March 13, 2012 Outline UHECRS Chakraborti, Ray, Soderberg, Loeb, Chandra 2011 Nature
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai, India March 13, 2012 Outline UHECRS Chakraborti, Ray, Soderberg, Loeb, Chandra 2011 Nature
Radiative Processes in Astrophysics
 Radiative Processes in Astrophysics 11. Synchrotron Radiation & Compton Scattering Eline Tolstoy http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/astroa07/ Synchrotron Self-Absorption synchrotron emission is accompanied
Radiative Processes in Astrophysics 11. Synchrotron Radiation & Compton Scattering Eline Tolstoy http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/astroa07/ Synchrotron Self-Absorption synchrotron emission is accompanied
Guiding Questions. Active Galaxies. Quasars look like stars but have huge redshifts
 Guiding Questions Active Galaxies 1. Why are quasars unusual? How did astronomers discover that they are extraordinarily distant and luminous? 2. What evidence showed a link between quasars and galaxies?
Guiding Questions Active Galaxies 1. Why are quasars unusual? How did astronomers discover that they are extraordinarily distant and luminous? 2. What evidence showed a link between quasars and galaxies?
Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = solar masses
 Quasars Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = 10 6 10 9 solar masses Stars and gas fall into the black hole and shine in an accrecon disk billion
Quasars Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = 10 6 10 9 solar masses Stars and gas fall into the black hole and shine in an accrecon disk billion
MULTIMESSENGER APPROACH:Using the Different Messengers
 MULTIMESSENGER APPROACH:Using the Different Messengers PROTONS p NUCLEI (A,Z) NEUTRINOS νµ PHOTONS LECTURE PLAN: 1) COSMIC RAYS- proton interactions with photons, composition, nuclei interactions with
MULTIMESSENGER APPROACH:Using the Different Messengers PROTONS p NUCLEI (A,Z) NEUTRINOS νµ PHOTONS LECTURE PLAN: 1) COSMIC RAYS- proton interactions with photons, composition, nuclei interactions with
An Introduction to Radio Astronomy
 An Introduction to Radio Astronomy Second edition Bernard F. Burke and Francis Graham-Smith CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the second edition page x 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The role of radio
An Introduction to Radio Astronomy Second edition Bernard F. Burke and Francis Graham-Smith CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the second edition page x 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The role of radio
Study of the arrival directions of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays detected by the Pierre Auger Observatory
 Study of the arrival directions of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays detected by the Pierre Auger Observatory Piera L. Ghia*, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration * IFSI/INAF Torino, Italy, & IPN/CNRS Orsay,
Study of the arrival directions of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays detected by the Pierre Auger Observatory Piera L. Ghia*, for the Pierre Auger Collaboration * IFSI/INAF Torino, Italy, & IPN/CNRS Orsay,
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics. Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars
 Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
IceCube. francis halzen. why would you want to build a a kilometer scale neutrino detector? IceCube: a cubic kilometer detector
 IceCube francis halzen why would you want to build a a kilometer scale neutrino detector? IceCube: a cubic kilometer detector the discovery (and confirmation) of cosmic neutrinos from discovery to astronomy
IceCube francis halzen why would you want to build a a kilometer scale neutrino detector? IceCube: a cubic kilometer detector the discovery (and confirmation) of cosmic neutrinos from discovery to astronomy
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energy Astrophysics Gamma-ray Bursts Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk May 2011 Gamma-ray Bursts - Observations - Long-duration
High Energy Astrophysics Gamma-ray Bursts Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk May 2011 Gamma-ray Bursts - Observations - Long-duration
Topic 7. Relevance to the course
 Topic 7 Cosmic Rays Relevance to the course Need to go back to the elemental abundance curve Isotopes of certain low A elements such as Li, Be and B have larger abundances on Earth than you would expect
Topic 7 Cosmic Rays Relevance to the course Need to go back to the elemental abundance curve Isotopes of certain low A elements such as Li, Be and B have larger abundances on Earth than you would expect
8.2.2 Rudiments of the acceleration of particles
 430 The solar wind in the Universe intergalactic magnetic fields that these fields should not perturb them. Their arrival directions should thus point back to their sources in the sky, which does not appear
430 The solar wind in the Universe intergalactic magnetic fields that these fields should not perturb them. Their arrival directions should thus point back to their sources in the sky, which does not appear
