THE EFFECTS OF A NUCLEAR BLAST
|
|
|
- Leslie Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE EFFECTS OF A NUCLEAR BLAST A nuclear explosion releases vast amounts of energy in three forms: 1) light and heat 2) blast 3) radiation The amount of energy released depends upon the size and design of the weapon. The effects of the blast depend upon whether the weapon is exploded high in the air, or on, or near the ground. An air burst produces more fire and blast damage than a ground burst which results in a big crater and more radioactive fallout.
2 The very high temperatures attained in a nuclear explosion result in the formation of an extremely hot incandescent mass of gas called a fireball. Immediately upon formation, the fireball begins to grow rapidly and rise like a hot air balloon. Within a millisecond after detonation, the diameter of the fireball from a 1 megaton (Mt) air burst is 150 m. This increases to a maximum of 2200 m within 10 seconds, at which time the fireball is also rising at the rate of 100 m/sec. The initial rapid expansion of the fireball severely compresses the surrounding atmosphere, producing a powerful blast wave. There is an instant vapourization of all matter with the fireball. As it expands toward its maximum diameter, the fireball cools, and after about a minute its temperature has decreased to such an extent that it no longer emits significant amounts of thermal radiation. The combination of the upward movement and the cooling of the fireball gives rise to the formation of the characteristic mushroom-shaped cloud. A flash of thermal (heat) radiation is emitted from the fireball and spreads out over a large distance but with steadily decreasing intensity. The amount of heat energy received a certain distance away from ground zero depends on the power of the weapon, the terrain and the weather. People can receive flash burns, burns caused by fire, retinal burn and flash blindness. With a 500 KT nuclear detonation, 3 rd degree burns can be seen up to 10 km away; 2 nd degree burns for people km away; 1 st degree burns for people up to 15 km away from ground zero. In most places however, fog, smog, haze, clouds, buildings, trees and hills would block and reduce some of this thermal radiation.
3 The very rapid expansion of the bomb materials produces a high pressure shock wave, that moves rapidly outward from the exploding bomb. In air, this shock wave is called a blast wave because it is equivalent to and is accompanied by powerful winds of much greater magnitude than hurricanes. Much of the damage inflicted by a nuclear explosion is the result of its shock wave. There are two components to a blast s shock wave. First, there s the wall of pressure that expands outward from the explosion. It is this pressure, measured in psi (pounds per square inch), that blows away the walls from buildings. A typical two-story house subjected to 5 psi would feel the force of 180 tons on the side facing the blast. Additionally, the blast creates a 160 mile-an-hour wind. And that s only at 5 psi. The wind speed following a 20 psi blast would be 500 mph! Obviously, the bigger the weapon yield, the larger the area of damage from the blast wave. The blast wave travels more slowly than the heat flash. The damage is caused both by high overpressure of air at the front of the blast wave and by the extremely powerful winds that persist after the wave front has passed. Once again, the amount of damage caused by the blast wave is dependent on the size of the weapon, the altitude at which the bomb is detonated and the distance from ground zero (point directly under the bomb). Complete destruction of all buildings occur up to 5 km away, damage beyond repair can be seen anywhere from 5 to 8 km away; major damage to structures before they can be occupied can occur from 8 km to 17 km away; light damage to buildings ( they can be occupied while being repaired) can be see from 17 km to 25 km away. Injury to humans from the blast wave can include crushed lungs, ruptured ear-drums and ruptured hollow viscera. Due to the very powerful winds, people and other objects (wood, glass, metal) will be lunched into the air. People may be crushed by fallen buildings and/or receive penetrating trauma, blunt trauma, broken bones, severe head injuries and burns.
4 The exploding nuclear device has a unique effect it releases penetrating radiation, which is quite different from thermal radiation. When absorbed by the body, nuclear radiation can cause severe injury/death. Nuclear radiation from an explosion can be divided into 2 categories: immediate/prompt radiation and residual radiation. Prompt radiation is given off at the time of the explosion. It is dangerous only within 3-5 km. If you were near the explosion without adequate protection and managed to survive the effects of the blast and fire, you could still be seriously affected by this radiation. The nuclear fission and nuclear that occur to produce the explosion release, either directly or indirectly, neutrons, gamma rays, beta particles, and alpha particles. Neutrons are heavy particles that are released from atoms nuclei. These tiny missiles can easily penetrate solid objects. Another penetrating form of radiation is gamma rays, which are energetic photons. Both of these types of radiation can be deadly.
5 Residual radiation is given off by the radioactive particles left as fallout after the explosion. If a nuclear weapon is exploded on or near the ground, danger from radioactive fallout is the greatest. Millions of tones of pulverized earth, stones, buildings, people and other material are drawn up into the fireball and become radioactive. This radioactive material is then carred by winds until it settles to earth. The heaviest particles fall closest to ground zero and at the other extreme, the smallest particles, invisible to the naked eye can travel thousands of miles on the winds and some of it will stay suspended for decades. The radioactivity it gives off cannot be seen, felt or smelt. It can best be described as fine to coarse sand carried by winds. There are four things which determine the amount of radiation reaching your body from fallout: 1) the time that has passed since the explosion 2) the length of time you are exposed to fallout 3) the distance you are from the fallout 4) the shielding between you and the fallout. Listed below are the effects of a 1 MT nuclear blast: 1 Megaton Surface Blast: Pressure Damage Radius of destructive circle: 1.7 miles 12 pounds per square inch At the center lies a crater 200 feet deep and 1000 feet in diameter. The rim of this crater is 1,000 feet wide and is composed of highly radioactive soil and debris. Nothing recognizable remains within about 3,200 feet (0.6 miles) from the center, except, perhaps, the remains of some buildings foundations. At 1.7 miles, only some of the strongest buildings those made of reinforced, poured concrete are still standing. Ninety-eight percent of the population in this area are dead. Radius: 2.7 miles 5 psi Virtually everything is destroyed between the 12 and 5 psi rings. The walls of typical multi-story buildings, including apartment buildings, have been completely blown out. The bare, structural skeletons of more and more buildings rise above the debris as you approach the 5 psi ring. Single-family residences within this this area have been completely blown away only their foundations remain. Fifty percent of the population between the 12 and 5 psi rings are dead. Forty percent are injured. Radius: 4.7 miles 2 psi Any single-family residences that have not been completely destroyed are heavily damaged. The windows of office buildings have been blown away, as have some of
6 their walls. The contents of these buildings upper floors, including the people who were working there, are scattered on the street. A substantial amount of debris clutters the entire area. Five percent of the population between the 5 and 2 psi rings are dead. Forty-five percent are injured. Radius: 7.4 miles 1 psi Residences are moderately damaged. Commercial buildings have sustained minimal damage. Twenty-five percent of the population between the 2 and 1 psi rings have been injured, mainly by flying glass and debris. Many others have been injured from thermal radiation the heat generated by the blast. The remaining seventy-five percent are unhurt. 1 Megaton Surface Blast: Fallout Assumptions Wind speed: 15 mph Wind direction: due east Time frame: 7 days 3,000 Rem* Distance: 30 miles Much more than a lethal dose of radiation. Death can occur within hours of exposure. About 10 years will need to pass before levels of radioactivity in this area drop low enough to be considered safe, by U.S. peacetime standards. 900 Rem Distance: 90 miles A lethal dose of radiation. Death occurs from two to fourteen days. 300 Rem Distance: 160 miles Causes extensive internal damage, including harm to nerve cells and the cells that line the digestive tract, and results in a loss of white blood cells. Temporary hair loss is another result. 90 Rem Distance: 250 miles Causes a temporary decrease in white blood cells, although there are no immediate harmful effects. Two to three years will need to pass before radioactivity levels in this area drop low enough to be considered safe, by U.S. peacetime standards. *Rem: Stands for roentgen equivalent man. This is a measurement used to quantify the amount of radiation that will produce certain biological effects.
7 Besides the blast and radiation damage from individual bombs, a large scale nuclear war could conceivably have a catastrophic global effect on the climate. The nuclear winter theory states that numerous nuclear weapons being detonated would throw up enormous quantities of dust and smoke into the atmosphere. The amount could be sufficient enough to block off sunlight for several months, particularly in the northern hemisphere. This would destroy plant life and create a sub-freezing climate until the dust settled. The ozone layer might also be affected, permitting further damage. If the results were sufficiently prolonged, they could spell the virtual end of human civilization.
Questions. 1. To what altitude raises the typical mushroom cloud? 2. What overpressure generates hurricane like winds?
 Questions 1. To what altitude raises the typical mushroom cloud?. What overpressure generates hurricane like winds? 3. Why is a nuclear burst at a certain altitude more damaging than the ground burst?
Questions 1. To what altitude raises the typical mushroom cloud?. What overpressure generates hurricane like winds? 3. Why is a nuclear burst at a certain altitude more damaging than the ground burst?
Effects of Nuclear Weapons
 Effects of Nuclear Weapons Alexander Glaser WWS556d Princeton University February 12, 2007 S. Glasstone and P. J. Dolan The Effects of Nuclear Weapons, Third Edition U.S. Government Printing Office Washington,
Effects of Nuclear Weapons Alexander Glaser WWS556d Princeton University February 12, 2007 S. Glasstone and P. J. Dolan The Effects of Nuclear Weapons, Third Edition U.S. Government Printing Office Washington,
Physics of Nuclear Weapons
 Physics of Nuclear Weapons Nuclear Fission and Fusion Copy and paste into browser: https://tinyurl.com/learnnuclear What is a nuclear bomb? There are two main types of bombs which release energy from the
Physics of Nuclear Weapons Nuclear Fission and Fusion Copy and paste into browser: https://tinyurl.com/learnnuclear What is a nuclear bomb? There are two main types of bombs which release energy from the
Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Radiation sickness. Biological effects of nuclear radiation
![Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Radiation sickness. Biological effects of nuclear radiation Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Radiation sickness. Biological effects of nuclear radiation](/thumbs/77/76435546.jpg) L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
Radioactivity. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2 Einstein: a little mass goes a long way
![Radioactivity. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2 Einstein: a little mass goes a long way Radioactivity. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2 Einstein: a little mass goes a long way](/thumbs/80/81251381.jpg) L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
THE EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS John A. Auxier, PhD. CHP Auxier & Associates, Inc. Knoxville, TN 37932
 THE EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS John A. Auxier, PhD. CHP Auxier & Associates, Inc. Knoxville, TN 37932 The vast majority of what is known about the effects of nuclear weapons in an occupied urban environment
THE EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS John A. Auxier, PhD. CHP Auxier & Associates, Inc. Knoxville, TN 37932 The vast majority of what is known about the effects of nuclear weapons in an occupied urban environment
3 Severe Weather. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
Your Task: Read each slide then use the underlined red or underlined information to fill in your organizer.
 Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
L 36 Atomic and Nuclear Physics-4. Radioactivity. Nuclear reactions: E = mc 2. Hazards of radiation. Biological effects of nuclear radiation
 L 36 Atomic and Nuclear Physics- Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, half-life carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear
L 36 Atomic and Nuclear Physics- Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, half-life carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear
How Things Work II. (Lecture #32) Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434)
 How Things Work II (Lecture #32) Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434) 924-4792 email: cates@virginia.edu Course web site available through COD and Toolkit or at http://people.virginia.edu/~gdc4k/phys106/spring08
How Things Work II (Lecture #32) Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434) 924-4792 email: cates@virginia.edu Course web site available through COD and Toolkit or at http://people.virginia.edu/~gdc4k/phys106/spring08
Alpha decay usually occurs in heavy nuclei such as uranium or plutonium, and therefore is a major part of the radioactive fallout from a nuclear
 Radioactive Decay Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei. This phenomenon was first reported in 1896 by the French physicist Henri Becquerel. Marie Curie and her husband Pierre
Radioactive Decay Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei. This phenomenon was first reported in 1896 by the French physicist Henri Becquerel. Marie Curie and her husband Pierre
COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM TORNADOES
 Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Question. 1. Which natural source of background radiation do you consider as dominant?
 Question 1. Which natural source of background radiation do you consider as dominant? 2. Is the radiation background constant or does it change with time and location? 3. What is the level of anthropogenic
Question 1. Which natural source of background radiation do you consider as dominant? 2. Is the radiation background constant or does it change with time and location? 3. What is the level of anthropogenic
L 36 Modern Physics :006 FINAL EXAM. Nuclear reactions: E = mc 2. Radioactivity. Hazards of radiation. Biological effects of nuclear radiation
 9:006 FINAL EXAM The final exam is on Monday MAY 7:30 AM - 9:30 AM in W90 CB The FE is not cumulative, and will cover lectures 3 through 36. (50 questions) The last regular lecture (Lec. 36) will be given
9:006 FINAL EXAM The final exam is on Monday MAY 7:30 AM - 9:30 AM in W90 CB The FE is not cumulative, and will cover lectures 3 through 36. (50 questions) The last regular lecture (Lec. 36) will be given
Tornadoes pose a high risk because the low atmospheric pressure, combined with high wind velocity, can:
 Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
2 Energy from the Nucleus
 CHAPTER 4 2 Energy from the Nucleus SECTION Atomic Energy BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is nuclear fission? What is nuclear fusion? What
CHAPTER 4 2 Energy from the Nucleus SECTION Atomic Energy BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is nuclear fission? What is nuclear fusion? What
Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e -
 Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. radiation a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e - This can destroy the delicate balance of chemical reactions in living cells. The
Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. radiation a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e - This can destroy the delicate balance of chemical reactions in living cells. The
Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors
 King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa
King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa
Radiation Awareness Training. Stephen Price Office of Research Safety
 Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Isotopes. An isotope is an atom of the same element (same number of protons) that varies in the number of neutrons.
 Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atom of the same element (same number of protons) that varies in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atom of the same element (same number of protons) that varies in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Isotopes. An isotope is an atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that vary in the number of neutrons.
 Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that vary in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that vary in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Unit 1 Atomic Structure
 Unit 1 Atomic Structure Defining the Atom I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike 3. Individual
Unit 1 Atomic Structure Defining the Atom I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike 3. Individual
Nuclear Chemistry Unit
 Nuclear Chemistry Unit January 28th HW Due Thurs. 1/30 Read pages 284 291 Define: Radioactivity Nuclear Radiation Alpha Particle Beta Particle Gamma Ray Half-Life Answer: -Questions 1-3 -Write the symbols
Nuclear Chemistry Unit January 28th HW Due Thurs. 1/30 Read pages 284 291 Define: Radioactivity Nuclear Radiation Alpha Particle Beta Particle Gamma Ray Half-Life Answer: -Questions 1-3 -Write the symbols
Unit 1 Atomic Structure
 Unit 1 Atomic Structure 3-1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the
Unit 1 Atomic Structure 3-1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the
Physics 180. Nuclear Weapons, Nuclear War, and Arms Control
 Physics 180 Nuclear Weapons, Nuclear War, and Arms Control Frederick K. Lamb Answers to the Midterm Examination Given 1998 March 18 Name ID No. This is a closed book examination of 50 minutes duration.
Physics 180 Nuclear Weapons, Nuclear War, and Arms Control Frederick K. Lamb Answers to the Midterm Examination Given 1998 March 18 Name ID No. This is a closed book examination of 50 minutes duration.
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 21. Nuclear Chemistry. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 21, Inc. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Energy: Chemical vs. Chemical energy is associated with making and breaking chemical bonds. energy is enormous in comparison.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 21, Inc. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Energy: Chemical vs. Chemical energy is associated with making and breaking chemical bonds. energy is enormous in comparison.
Biological Agents and Nuclear Detonations
 CHAPTER 3 Biological Agents and Nuclear Detonations In a general war, US forces may be faced by an enemy capable of employing nuclear or biological weapons. The effects of weather and terrain on biological
CHAPTER 3 Biological Agents and Nuclear Detonations In a general war, US forces may be faced by an enemy capable of employing nuclear or biological weapons. The effects of weather and terrain on biological
Physics 280: Session 8
 Physics 280: Session 8 Plan for This Session Conclusion of Module 2: Nuclear Weapons Definition: Weapons of mass destruction Module 3: Effects of nuclear explosions 1 Plutonium Is Created in Nuclear Reactors
Physics 280: Session 8 Plan for This Session Conclusion of Module 2: Nuclear Weapons Definition: Weapons of mass destruction Module 3: Effects of nuclear explosions 1 Plutonium Is Created in Nuclear Reactors
Cloud formation in underwater tests
 Underwater Blasts Cloud formation in underwater tests Formation of spray dome & condensation cloud from erupted water Baker (fat man design) Bikini Atoll 1946; 23 kt First Moments Eruption through water
Underwater Blasts Cloud formation in underwater tests Formation of spray dome & condensation cloud from erupted water Baker (fat man design) Bikini Atoll 1946; 23 kt First Moments Eruption through water
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY student version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY student version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
according to and water. High atmospheric pressure - Cold dry air is other air so it remains close to the earth, giving weather.
 EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
Nuclear Chemistry. Background Radiation. Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation.
 Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry Background Radiation Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation. Most of the remaining one-fourth comes from medical irradiation such as X-rays.
Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry Background Radiation Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation. Most of the remaining one-fourth comes from medical irradiation such as X-rays.
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY teacher version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY teacher version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
The Effects of Nuclear Weapons
 The Effects of Nuclear Weapons Compiled and edited by Samuel Glasstone and Philip J. Dolan Third Edition Prepared and published by the UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE and the ENERGY RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
The Effects of Nuclear Weapons Compiled and edited by Samuel Glasstone and Philip J. Dolan Third Edition Prepared and published by the UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE and the ENERGY RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 3 EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR EXPLOSIONS SECTION I - GENERAL
 NATO UNCLASSIFIED AMedP-6(B), Part I CHAPTER 3 EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR EXPLOSIONS SECTION I - GENERAL 301. Introduction. The basic differences in the mechanisms of energy production and related characteristics
NATO UNCLASSIFIED AMedP-6(B), Part I CHAPTER 3 EFFECTS OF NUCLEAR EXPLOSIONS SECTION I - GENERAL 301. Introduction. The basic differences in the mechanisms of energy production and related characteristics
12 Moderator And Moderator System
 12 Moderator And Moderator System 12.1 Introduction Nuclear fuel produces heat by fission. In the fission process, fissile atoms split after absorbing slow neutrons. This releases fast neutrons and generates
12 Moderator And Moderator System 12.1 Introduction Nuclear fuel produces heat by fission. In the fission process, fissile atoms split after absorbing slow neutrons. This releases fast neutrons and generates
Volcanoes. Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman
 Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Activity 12 Isotopes and Radioactivity
 OUR LEARNING FIRST ABOUT IDEAS OTHER IDEAS Activity 12 Isotopes and Radioactivity Part of painting by Joseph Wright of Derby, 1734-1797: The Alchemist in Search of the Philosopher s Stone Discovers Phosphorus.
OUR LEARNING FIRST ABOUT IDEAS OTHER IDEAS Activity 12 Isotopes and Radioactivity Part of painting by Joseph Wright of Derby, 1734-1797: The Alchemist in Search of the Philosopher s Stone Discovers Phosphorus.
Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure
 Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure No. Question Answer 1 What did scientists think about atoms before the discovery of the They were tiny spheres that could not be broken up electron? 2 Which
Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure No. Question Answer 1 What did scientists think about atoms before the discovery of the They were tiny spheres that could not be broken up electron? 2 Which
Nuclear forces and Radioactivity. Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom
 Nuclear forces and Radioactivity Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom Forces act in opposing directions Electrostatic repulsion: pushes protons apart Strong nuclear force: pulls protons
Nuclear forces and Radioactivity Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom Forces act in opposing directions Electrostatic repulsion: pushes protons apart Strong nuclear force: pulls protons
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions
 Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
PS-21 First Spring Institute say : Teaching Physical Science. Radioactivity
 PS-21 First Spring Institute say 2012-2013: Teaching Physical Science Radioactivity What Is Radioactivity? Radioactivity is the release of tiny, highenergy particles or gamma rays from the nucleus of an
PS-21 First Spring Institute say 2012-2013: Teaching Physical Science Radioactivity What Is Radioactivity? Radioactivity is the release of tiny, highenergy particles or gamma rays from the nucleus of an
TORNADOES. DISPLAY VISUAL A Tornado Is... Tornadoes can: Rip trees apart. Destroy buildings. Uproot structures and objects.
 TORNADOES Introduce tornadoes by explaining what a tornado is. DISPLAY VISUAL A Tornado Is... A powerful, circular windstorm that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 250 miles per hour. Tell the participants
TORNADOES Introduce tornadoes by explaining what a tornado is. DISPLAY VISUAL A Tornado Is... A powerful, circular windstorm that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 250 miles per hour. Tell the participants
Radiation Terminology
 Radiation Terminology This section discusses the terms and concepts which are necessary for a meaningful discussion of radiation, its sources, and its risks. USNRC Technical Training Center 5-1 0703 Energy
Radiation Terminology This section discusses the terms and concepts which are necessary for a meaningful discussion of radiation, its sources, and its risks. USNRC Technical Training Center 5-1 0703 Energy
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
Tornadoes. Tornadoes COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM TORNADOES
 Tornadoes Tornadoes Tell the participants that tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms
Tornadoes Tornadoes Tell the participants that tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms
U (superscript is mass number, subscript atomic number) - radionuclides nuclei that are radioactive - radioisotopes atoms containing radionuclides
 Chapter : Nuclear Chemistry. Radioactivity nucleons neutron and proton all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, atomic number isotopes atoms with the same atomic number but different
Chapter : Nuclear Chemistry. Radioactivity nucleons neutron and proton all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, atomic number isotopes atoms with the same atomic number but different
The Atmosphere is the layer of air surrounding the Earth
 The Atmosphere is the layer of air surrounding the Earth The gases in the atmosphere are important because: They block out dangerous rays from the sun, such as UV rays They stabilize the temperature across
The Atmosphere is the layer of air surrounding the Earth The gases in the atmosphere are important because: They block out dangerous rays from the sun, such as UV rays They stabilize the temperature across
Chapter 17, Electromagnetic Waves Physical Science, McDougal-Littell, 2008
 SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum
 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum 10 4 Hz 10 6 Hz 10 8 Hz 10 12 Hz 10 14 Hz 10 16 Hz 10 18 Hz 1 million 1 trillion
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum 10 4 Hz 10 6 Hz 10 8 Hz 10 12 Hz 10 14 Hz 10 16 Hz 10 18 Hz 1 million 1 trillion
11.5 Nuclear Reactions: Fusion
 11.5 Nuclear Reactions: Fusion Nuclear fusion reactions occur in the Sun and supply the energy needed to sustain life on Earth (Figure 1). Nuclear fusion is the fusing or joining of two small nuclei to
11.5 Nuclear Reactions: Fusion Nuclear fusion reactions occur in the Sun and supply the energy needed to sustain life on Earth (Figure 1). Nuclear fusion is the fusing or joining of two small nuclei to
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Severe Weather. Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb
 Severe Weather People need to know what the weather is going to do. Sometimes severe weather can happen. Severe weather can cause property damage, injuries to people and animals, and even loss of life.
Severe Weather People need to know what the weather is going to do. Sometimes severe weather can happen. Severe weather can cause property damage, injuries to people and animals, and even loss of life.
Weather and Climate Basics
 Aims of this presentation Weather and Climate Basics To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
Aims of this presentation Weather and Climate Basics To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N a n d t h e N R C
 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N and the NRC Radiation is all around us. It is naturally present in our environment and has been since before the birth of this planet. Radiation occurs in nature,
R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N and the NRC Radiation is all around us. It is naturally present in our environment and has been since before the birth of this planet. Radiation occurs in nature,
Weather and Climate Basics
 Weather and Climate Basics Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology Aims of this presentation To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
Weather and Climate Basics Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology Aims of this presentation To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
WHAM! Toutatis Comes to Portland. Asteroid Toutatis Nears Planet Earth Image Credit & Copyright: Top: John Chumack / Bottom: Juergen Wolf
 WHAM! Toutatis Comes to Portland Asteroid Toutatis Nears Planet Earth Image Credit & Copyright: Top: John Chumack / Bottom: Juergen Wolf WHAM! Toutatis Comes to Portland R. J. Robbins On Wednesday, 29
WHAM! Toutatis Comes to Portland Asteroid Toutatis Nears Planet Earth Image Credit & Copyright: Top: John Chumack / Bottom: Juergen Wolf WHAM! Toutatis Comes to Portland R. J. Robbins On Wednesday, 29
1 Radioactivity BEFORE YOU READ. Atomic Energy. National Science Education Standards STUDY TIP
 CHAPTER 4 1 Radioactivity SECTION Atomic Energy BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are three types of radioactive decay? How does radiation
CHAPTER 4 1 Radioactivity SECTION Atomic Energy BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are three types of radioactive decay? How does radiation
Physics 10 Final Exam Physics for future Presidents December 16, 2003
 Physics 10 Final Exam Physics for future Presidents December 16, 2003 Last name First name SID Essay Questions. Choose TWO of the four. Write your essays on separate pages. with your name on the top of
Physics 10 Final Exam Physics for future Presidents December 16, 2003 Last name First name SID Essay Questions. Choose TWO of the four. Write your essays on separate pages. with your name on the top of
APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
 Former NAVWPNSTA Concord, Inland Area APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 This page intentionally left blank. Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
Former NAVWPNSTA Concord, Inland Area APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 This page intentionally left blank. Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
c) O-16 d) Pu An unstable nucleus emits. a) Atoms b) Electricity c) Plasma d) Radiation 3. Many of uranium are radioactive. a) Ions b) Isomers
 Physical Science Domain 1 Nuclear Decay Review 1. Which nucleus would be MOST likely to be radioactive? a) C-12 b) Ca-40 c) O-16 d) Pu-241 2. An unstable nucleus emits. a) Atoms b) Electricity 3. Many
Physical Science Domain 1 Nuclear Decay Review 1. Which nucleus would be MOST likely to be radioactive? a) C-12 b) Ca-40 c) O-16 d) Pu-241 2. An unstable nucleus emits. a) Atoms b) Electricity 3. Many
Name Earth Science Pd. Hurricanes. Directions: Read the information, view diagrams and answer the questions in the worksheet.
 Hurricanes Directions: Read the information, view diagrams and answer the questions in the worksheet. Hurricane Basics The ingredients for a hurricane include a pre-existing weather disturbance, warm tropical
Hurricanes Directions: Read the information, view diagrams and answer the questions in the worksheet. Hurricane Basics The ingredients for a hurricane include a pre-existing weather disturbance, warm tropical
PHYS:1200 LECTURE 36 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS (4)
 1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 36 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS (4) This last lecture of the course will focus on nuclear energy. There is an enormous reservoir of energy in the nucleus and it can be released either
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 36 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS (4) This last lecture of the course will focus on nuclear energy. There is an enormous reservoir of energy in the nucleus and it can be released either
What is Inside a Volcano?
 Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Chapter 22 - Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter - Nuclear Chemistry - The Nucleus I. Introduction A. Nucleons. Neutrons and protons B. Nuclides. Atoms identified by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 8 a. radium-8 or 88 Ra II.
Chapter - Nuclear Chemistry - The Nucleus I. Introduction A. Nucleons. Neutrons and protons B. Nuclides. Atoms identified by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 8 a. radium-8 or 88 Ra II.
Natural Disasters PASSAGE 5
 PASSAGE 5 Name Directions: Read Natural Disasters. Then answer questions 1 8. Natural Disasters Our planet can be a calm place, but weather conditions often change rapidly. Gentle breezes can blow into
PASSAGE 5 Name Directions: Read Natural Disasters. Then answer questions 1 8. Natural Disasters Our planet can be a calm place, but weather conditions often change rapidly. Gentle breezes can blow into
Weather. A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket.
 Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
TOEFL. Test of English as a Foreign Language. Reading
 TOEFL Test of English as a Foreign Language Reading For the Reading Section, you will be given 60-100 minutes to read 3 to 5 passages from academic texts and answer 36-70 questions. You have to read the
TOEFL Test of English as a Foreign Language Reading For the Reading Section, you will be given 60-100 minutes to read 3 to 5 passages from academic texts and answer 36-70 questions. You have to read the
Lecture Outlines Chapter 32. Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 32 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
Lecture Outlines Chapter 32 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
Shielding Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiation 11/08 Integrated Science 3
 Shielding Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiation 11/08 Integrated Science 3 Name Per. Introduction The term radioactivity refers to the activity of unstable atoms. Radioactive substances send out very energetic
Shielding Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiation 11/08 Integrated Science 3 Name Per. Introduction The term radioactivity refers to the activity of unstable atoms. Radioactive substances send out very energetic
College Physics B - PHY2054C
 College - PHY2054C Physics - Radioactivity 11/24/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Review Question 1 Isotopes of an element A have the same number of protons and electrons,
College - PHY2054C Physics - Radioactivity 11/24/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Review Question 1 Isotopes of an element A have the same number of protons and electrons,
REACTOR CANNOT EXPLODE LIKE A NUCLEAR BOMB
 A Reactor Cannot Explode Like a Nuclear Bomb 1 REACTOR CANNOT EXPLODE LIKE A NUCLEAR BOMB prepared by D.A. Meneley, Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, November 2000, Revision
A Reactor Cannot Explode Like a Nuclear Bomb 1 REACTOR CANNOT EXPLODE LIKE A NUCLEAR BOMB prepared by D.A. Meneley, Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, November 2000, Revision
Radiation Fundamentals. Radiation Safety Training Module 1
 Radiation Fundamentals Module 1 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the process of unstable (or radioactive) atoms becoming stable. This is done by emitting radiation. This process over a period of time is
Radiation Fundamentals Module 1 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the process of unstable (or radioactive) atoms becoming stable. This is done by emitting radiation. This process over a period of time is
Activity 11 Solutions: Ionizing Radiation II
 Activity 11 Solutions: Ionizing Radiation II 11.1 Additional Sources of Ionizing Radiation 1) Cosmic Rays Your instructor will show you radiation events in a cloud chamber. Look for vapor trails that do
Activity 11 Solutions: Ionizing Radiation II 11.1 Additional Sources of Ionizing Radiation 1) Cosmic Rays Your instructor will show you radiation events in a cloud chamber. Look for vapor trails that do
Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide. What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive?
 Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive? The nucleus of an atom is comprised of subatomic particles called protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive
Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive? The nucleus of an atom is comprised of subatomic particles called protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive
August 20, EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines th Street Golden, CO Dear EPICS 1 Teams,
 Joel G. Duncan, Ph.D. Teaching Professor Design EPICS Program GOLDEN, CO 80401-1887 USA August 20, 2013 EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines 815 15 th Street Golden, CO 80401
Joel G. Duncan, Ph.D. Teaching Professor Design EPICS Program GOLDEN, CO 80401-1887 USA August 20, 2013 EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines 815 15 th Street Golden, CO 80401
Astronomy Notes Chapter 13.notebook. April 11, 2014
 All stars begin life in a similar way the only difference is in the rate at which they move through the various stages (depends on the star's mass). A star's fate also depends on its mass: 1) Low Mass
All stars begin life in a similar way the only difference is in the rate at which they move through the various stages (depends on the star's mass). A star's fate also depends on its mass: 1) Low Mass
Finding Impact Craters with Landsat
 Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Spectrographs: instrument to separate white light into the bands of color.
 (BIG BANG PACKET 2) Name: Period: wavelength and lowest frequencies Broadcast waves and microwaves Infrared Rays Wavelength shorter than radio waves The invisible you feel Visible Light You can see The
(BIG BANG PACKET 2) Name: Period: wavelength and lowest frequencies Broadcast waves and microwaves Infrared Rays Wavelength shorter than radio waves The invisible you feel Visible Light You can see The
Available online at ScienceDirect. Nuclear power plant explosions at Fukushima-Daiichi. Takashi Tsuruda*
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 62 ( 2013 ) 71 77 The 9 th Asia-Oceania Symposium on Fire Science and Technology Nuclear power plant explosions at Fukushima-Daiichi
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 62 ( 2013 ) 71 77 The 9 th Asia-Oceania Symposium on Fire Science and Technology Nuclear power plant explosions at Fukushima-Daiichi
Chapter 18. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
Science Chapter 13,14,15
 Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Nuclear Chemistry. Chapter 24
 Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 24 Radioactivity Radioisotopes are isotopes that have an unstable nucleus. They emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay.
Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 24 Radioactivity Radioisotopes are isotopes that have an unstable nucleus. They emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay.
A. Identify the highly penetrating radioactive emission that exposed the photographic plates.
 Name Unit 3: Nuclear Chemistry Date Part 2 Questions 1. In 1896, Antoine H. Becquerel discovered that a uranium compound could expose a photographic plate wrapped in heavy paper in the absence of light.
Name Unit 3: Nuclear Chemistry Date Part 2 Questions 1. In 1896, Antoine H. Becquerel discovered that a uranium compound could expose a photographic plate wrapped in heavy paper in the absence of light.
Radioisotopes. alpha. Unstable isotope. stable. beta. gamma
 Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons Strong forces (nuclear force) hold nucleus together Protons in nucleus have electrostatic repulsion however, strong
Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons Strong forces (nuclear force) hold nucleus together Protons in nucleus have electrostatic repulsion however, strong
Physics 180B Test Points. a. 3/2c b. c c. 15/16c d. 24/25c
 Physics 180B Test 4-120 Points Name Answer 10 of the 13 Multiple Choice questions. Cross off 3 questions. 1. A rocket is traveling toward the earth at 3/4c when it ejects a missile forward at 3/4c relative
Physics 180B Test 4-120 Points Name Answer 10 of the 13 Multiple Choice questions. Cross off 3 questions. 1. A rocket is traveling toward the earth at 3/4c when it ejects a missile forward at 3/4c relative
Name Team Period. Station #1 (drawing)
 Unit 5 Notes ATMOSPHERE Name Team Period Station #1 (drawing) When done drawing, read and answer the following questions. Troposphere - layer closest to Earth s surface. Extends from surface to altitudes
Unit 5 Notes ATMOSPHERE Name Team Period Station #1 (drawing) When done drawing, read and answer the following questions. Troposphere - layer closest to Earth s surface. Extends from surface to altitudes
The Atomic Nucleus & Radioactive Decay. Major Constituents of an Atom 4/28/2016. Student Learning Outcomes. Analyze radioactive decay and its results
 The Atomic Nucleus & Radioactive Decay ( Chapter 10) Student Learning Outcomes Analyze radioactive decay and its results Differentiate between nuclear fission and fusion Major Constituents of an Atom U=unified
The Atomic Nucleus & Radioactive Decay ( Chapter 10) Student Learning Outcomes Analyze radioactive decay and its results Differentiate between nuclear fission and fusion Major Constituents of an Atom U=unified
Inner Transition Metals
 1 Inner Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals The inner transition metals are found in the f-block, usually put at the bottom of the Periodic Table. These elements were sometimes
1 Inner Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals The inner transition metals are found in the f-block, usually put at the bottom of the Periodic Table. These elements were sometimes
What happens during nuclear decay? During nuclear decay, atoms of one element can change into atoms of a different element altogether.
 When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
Light is an important form of energy for all of us
 What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
A) usually less B) dark colored and rough D) light colored with a smooth surface A) transparency of the atmosphere D) rough, black surface
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
9.5 Troposphere. Describe the characteristics and importance of the troposphere. Explain temperature inversion and its role in the troposphere.
 9.5 Troposphere Describe the characteristics and importance of the troposphere. Explain temperature inversion and its role in the troposphere. Why is the troposphere important? All of the wind, rain, and
9.5 Troposphere Describe the characteristics and importance of the troposphere. Explain temperature inversion and its role in the troposphere. Why is the troposphere important? All of the wind, rain, and
14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun
 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE? NO! Chemical energy content Luminosity ~
14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE? NO! Chemical energy content Luminosity ~
Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts)
 Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
A Nuclear Power Plant
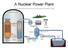 A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
Earthquakes. Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb
 Earthquakes Earthquakes cause the earth to shake! Earthquakes are caused by a fault line under the earth's crust. You do not have to be right under a fault line to feel an earthquake. You could be miles
Earthquakes Earthquakes cause the earth to shake! Earthquakes are caused by a fault line under the earth's crust. You do not have to be right under a fault line to feel an earthquake. You could be miles
Atomic & Nuclear Physics
 Atomic & Nuclear Physics Life and Atoms Every time you breathe you are taking in atoms. Oxygen atoms to be exact. These atoms react with the blood and are carried to every cell in your body for various
Atomic & Nuclear Physics Life and Atoms Every time you breathe you are taking in atoms. Oxygen atoms to be exact. These atoms react with the blood and are carried to every cell in your body for various
Radiation Safety Talk. UC Santa Cruz Physics 133 Winter 2018
 Radiation Safety Talk UC Santa Cruz Physics 133 Winter 2018 Outline Types of radiation Sources of radiation Dose limits and risks ALARA principle Safety procedures Types of radiation Radiation is energy
Radiation Safety Talk UC Santa Cruz Physics 133 Winter 2018 Outline Types of radiation Sources of radiation Dose limits and risks ALARA principle Safety procedures Types of radiation Radiation is energy
Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 8 Nuclear Chemistry 8. Discovery of radioactivity 895 Roentgen discovery of radioactivity X-ray X-ray could penetrate other bodies and affect photographic plates led to the development of X-ray
Chapter 8 Nuclear Chemistry 8. Discovery of radioactivity 895 Roentgen discovery of radioactivity X-ray X-ray could penetrate other bodies and affect photographic plates led to the development of X-ray
