Titan Saturn System Mission. Jonathan Lunine Co Chair, TSSM JSDT
|
|
|
- June Wilkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Titan Saturn System Mission Jonathan Lunine Co Chair, TSSM JSDT
2 1. Overview of key processes on Titan 2. The methane cycle and its source 3. Measurements beyond Cassini 4. TSSM
3 Overview of Key Processes on Titan
4 Four worlds with atmospheres that support exploration by balloon and parachute Complete worlds whose interior, surface, atmosphere couple through volatile cyclling
5 Titan as an object is of keen interest for virtually all areas of planetary science
6 Titan s organic cycle
7 Titan s greenhouse climate
8 Titan s intriguing unknowns
9 The methane cycle and its source
10 1 cm 1 km Clockwise: Cassini ISS, RADAR; Huygens DISR 100 km 1000 km
11 Titan s rapid methane loss models the inevitable long-term loss of Earth s water as the solar constant increases over time Lunine and Atreya, 2008
12 Interaction of the interior and the surface Low 36 Ar/N 2 : Nitrogen came from ammonia. Enceladus: Ammonia is resident in Saturnian satellites (2008). 40 Ar: Titan outgasses over time. Ammonia is key for "cryo" volcanism Impact or cryovolcanic melting of the crust exposes organics to liquid water interesting prebiotic chemistry Some products of this chemistry will end up in Titan s lakes and seas Neish et al., 2009
13 Artemieva and Lunine, 2005 Impact craters exist, though many have been erased or buried. (Wood et al., in press).
14 Is the methane resupplied from the subsurface? Schaller et al 2009: Convective cloud outburst near the equator, powerful enough to trigger waves that initiated a southern secondary cloud formation. Hueso & ;Sànchez- Lavega 2006: Methane convective storm models
15 Lunine and Awal, Moist-entraining plume model of methane convective cloud Therefore the cloud outburst is circumstantial evidence for emission of methane and/or heated air from the surface in the outburst source region. (Schaller et al., Nature, 2009).
16 Measurements beyond Cassini a. Mass resolution and range b. Spatial resolution and range c. Temporal resolution and range d. Altitude resolution and range
17 Cassini INMS spectra (PI Hunter Waite) (Figure by S. Hörst and R. Yelle)
18 a. Mass resolution and range for the organics Tholin synthesis in lab much higher molecular weight compounds Figure prepared by S. Hörst from lab data of Szopa et al 2006.
19 Negative (top) and positive ion (bottom panel) data for Titan s upper atmosphere from Cassini CAPS confirm existence of heavier species but does not have the resolution to identify them. CAPS data plotted by S. Hörst. CAPS INMS
20 The plumes of Enceladus have a rich organic inventory that almost certainly goes beyond the INMS mass range Measured plume composition displayed schematically. Waite et al., 2009
21 The search for self organizing (autocatalytic) chemistry on Titan s surface or in the Enceladus plume also requires a much greater mass range than INMS/GCMS Davies et al., 2009
22 Brown et al VIMS λ, mi crons ISS Team, Ontario Lacus Lake/sea compositions/conditions require direct sampling
23 b. Spatial resolution and range Cassini ISS resolution 3 km
24 Cassini RADAR resolution 0.5 km
25 Titan s surface Huygens flyover area at 50 meters resolution
26 Titan s surface Fluvial features N of landing site at 10 meters resolution
27 Titan s surface Huygens landing site at centimeter resolution
28
29 c. Temporal resolution and range: i. Cassini was elsewhere in the Saturn system during almost the entire outburst episode. Schaller et al. 2009
30 c. Temporal resolution and range. ii: TSSM launched in 2020 meshes very well with Cassini in terms of seasonal coverage
31 d.altitude range: Thermosphere and ionosphere: not accessible to Cassini-Huygens
32 TSSM
33 Kim Reh: JPL Study Lead Christian Erd: ESA Study Lead Pat Beauchamp, Nathan Strange, Tom Spilker, John Elliot, (JPL) Mark Perry, Michael Paul (APL
34 Traceability matrix (sample page)
35 Baseline mission architecture Combining An orbiter (Titan+Enceladus) A hot-air balloon/montgolfière on Titan and one North-pole lake-landing probe Dedicated Titan orbiter would be used also for relay after several Enceladus flybys A hot-air balloon (Titan Montgolfière) would float at 10 km above the surface around the equator with some altitude control A short-lived Probe/Lander with liquid surface package would land in a northern sea
36 TSSM Phases (assumes 2020 launch)
37
38
39 TSSM orbiter maps well to decadal objectives Decadal Survey p. 138 Cassini TSSM What are the chemistry, distribution and cycling of organic materials on Titan? Is Titan internally active, producing water-rich environments with potential habitability? What are the current state and the history of Titan s surface? What drives the meteorology of Titan? Has there been climate change on Titan? Could Titan support life forms that do not require liquid water? Methane/ethane sensed at Huygens site; high altitude polymers; lakes, fluvial Spin rate evidence for ocean; radar images of cryovolcanic features; near-ir spectra of carbon dioxide patches Radar and VIMS show dearth of craters; fluvial transport at Huygens site Huygens wind and CIRS temperature data provide crude basis for GCM Fluvial erosion at desert Huygens site; extensive dunes; missing ethane High latitude lakes found, as well as environments where active fluvial flow may occur, and cryovolcanism High molecular weight mass spectroscopy; hi-res imaging at 5 µm; near-ir spectra Accelerometry-enhanced gravity; hi-res surface imaging; surface temperature monitoring in thermal IR; 5 6 µm spectra High resolution imaging; radar altimetry and sounding; near-ir spectra Sub-millimeter wind/thermal mapping; IR mapping; near-ir cloud sounding High resolution imaging; radar sounding; near-ir spectra Hi-res spectra over 5 6 µm; repeat surface coverage; high molecular weight sampling of upper atmosphere organics 39
40 The Titan mission would also offer technological firsts, including the floating lander and that undeniably romantic hot air balloon. Nature editorial 22/1/09.
41 Ground-penetrating radar on Enceladus Schubert et al Superposed arrow indicates maximum radar penetration depth (SWRI) Plume reservoirs should be accessible via the groundpenetrating radar. (Verification using detailed models to be done).
42 Waite et al., 2009
43 Waite et al., 2009
Titan Saturn System Mission: Jonathan Lunine Co Chair, TSSM JSDT
 Titan Saturn System Mission: Jonathan Lunine Co Chair, TSSM JSDT Kim Reh: JPL Study Lead Christian Erd: ESA Study Lead Pat Beauchamp, Nathan Strange, Tom Spilker, John Elliot, (JPL) Baseline mission architecture
Titan Saturn System Mission: Jonathan Lunine Co Chair, TSSM JSDT Kim Reh: JPL Study Lead Christian Erd: ESA Study Lead Pat Beauchamp, Nathan Strange, Tom Spilker, John Elliot, (JPL) Baseline mission architecture
SATELLITES: ACTIVE WORLDS AND EXTREME ENVIRONMENTS. Jessica Bolda Chris Gonzalez Crystal Painter Natalie Innocenzi Tyler Vasquez.
 SATELLITES: ACTIVE WORLDS AND EXTREME ENVIRONMENTS Jessica Bolda Chris Gonzalez Crystal Painter Natalie Innocenzi Tyler Vasquez. Areas of interest! How did the Satellites of the outer solar system form
SATELLITES: ACTIVE WORLDS AND EXTREME ENVIRONMENTS Jessica Bolda Chris Gonzalez Crystal Painter Natalie Innocenzi Tyler Vasquez. Areas of interest! How did the Satellites of the outer solar system form
Life in the Outer Solar System
 Life in the Outer Solar System Jupiter Big Massive R = 11R M = 300 M = 2.5 x all the rest Day about 10 Earth hours Year about 12 Earth years Thick Atmosphere, mostly H 2, He But also more complex molecules
Life in the Outer Solar System Jupiter Big Massive R = 11R M = 300 M = 2.5 x all the rest Day about 10 Earth hours Year about 12 Earth years Thick Atmosphere, mostly H 2, He But also more complex molecules
The Icy Moons. and the. Extended Habitable Zone
 The Icy Moons and the Extended Habitable Zone Europa Interior Models Other Types of Habitable Zones Water requires heat and pressure to remain stable as a liquid Extended Habitable Zones You do not need
The Icy Moons and the Extended Habitable Zone Europa Interior Models Other Types of Habitable Zones Water requires heat and pressure to remain stable as a liquid Extended Habitable Zones You do not need
Titan Mare Explorer: TiME for Titan
 Titan Mare Explorer: TiME for Titan Titan Mare Explorer (TiME) will: Conduct the first exploration of an extraterrestrial sea Directly sample and measure the organic constituents on another planetary object
Titan Mare Explorer: TiME for Titan Titan Mare Explorer (TiME) will: Conduct the first exploration of an extraterrestrial sea Directly sample and measure the organic constituents on another planetary object
Titan and Enceladus after 7 years of. discoveries by Cassini
 Titan and Enceladus after 7 years of 1. Titan Organic cycle Geological features Deep ocean 2. Enceladus Jets of vapor on the southern hemisphere Origin of the jets 3. New questions and future missions
Titan and Enceladus after 7 years of 1. Titan Organic cycle Geological features Deep ocean 2. Enceladus Jets of vapor on the southern hemisphere Origin of the jets 3. New questions and future missions
Planetary Surface Processes
 Planetary Surface Processes Nathan Bridges Applied Physics Laboratory (and former JPLer and ongoing coworker with many at JPL and Caltech) rippled sand in Gale Crater MSL landing ellipse HiRISE image ESP_023957_1755
Planetary Surface Processes Nathan Bridges Applied Physics Laboratory (and former JPLer and ongoing coworker with many at JPL and Caltech) rippled sand in Gale Crater MSL landing ellipse HiRISE image ESP_023957_1755
Amazing Saturn. Saturn from the ground
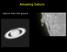 1 Amazing Saturn Saturn from the ground 2 Saturn Information Overload The Cassini Mission started orbiting Saturn in 2004. 3 Getting There Planetary pinball with passes by Venus, Venus, Earth, and Jupiter
1 Amazing Saturn Saturn from the ground 2 Saturn Information Overload The Cassini Mission started orbiting Saturn in 2004. 3 Getting There Planetary pinball with passes by Venus, Venus, Earth, and Jupiter
AST 248, Lecture 21. James Lattimer. Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University. November 15, 2018
 vi AST 248, Lecture 21 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University November 15, 2018 The Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu
vi AST 248, Lecture 21 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University November 15, 2018 The Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 29. Search for life on jovian moons. Habitability.
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 29. Search for life on jovian moons. Habitability.
TITAN MOON OF SATURN. ASTRO 101 Contributors: Duc Dinh, Spring 2016 Caroline Brandon, Fall Source:
 TITAN MOON OF SATURN ASTRO 101 Contributors: Duc Dinh, Spring 2016 Caroline Brandon, Fall 2014 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/titan_(moon) Discovered by Christiaan Huygens in 1655 Has a dense atmosphere
TITAN MOON OF SATURN ASTRO 101 Contributors: Duc Dinh, Spring 2016 Caroline Brandon, Fall 2014 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/titan_(moon) Discovered by Christiaan Huygens in 1655 Has a dense atmosphere
Jupiter & Saturn. Moons of the Planets. Jupiter s Galilean satellites are easily seen with Earth-based telescopes. The Moons
 The Moons Jupiter & Saturn Earth 1 Mars 2 Jupiter 63 Saturn 47 Uranus 27 Neptune 13 Pluto 3 Moons of the Planets Galileo (1610) found the first four moons of Jupiter. Total 156 (as of Nov. 8, 2005) Shortened
The Moons Jupiter & Saturn Earth 1 Mars 2 Jupiter 63 Saturn 47 Uranus 27 Neptune 13 Pluto 3 Moons of the Planets Galileo (1610) found the first four moons of Jupiter. Total 156 (as of Nov. 8, 2005) Shortened
Titan - What Next? Ralph D Lorenz. Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85821, USA
 Titan - What Next? Ralph D Lorenz Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85821, USA rlorenz@lpl.arizona.edu A new beginning... Artwork by Mark Robertson-Tessi and Ralph Lorenz,
Titan - What Next? Ralph D Lorenz Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85821, USA rlorenz@lpl.arizona.edu A new beginning... Artwork by Mark Robertson-Tessi and Ralph Lorenz,
Titan. PTYS 206 (from original presentation by Catherine Neish) April 1, 2014
 Titan PTYS 206 (from original presentation by Catherine Neish) April 1, 2014 Introduction Titan is Saturn s largest moon, and the second largest moon in the solar system Titan History Titan was discovered
Titan PTYS 206 (from original presentation by Catherine Neish) April 1, 2014 Introduction Titan is Saturn s largest moon, and the second largest moon in the solar system Titan History Titan was discovered
Lecture #27: Saturn. The Main Point. The Jovian Planets. Basic Properties of Saturn. Saturn:
 Lecture #27: Saturn Saturn: General properties. Atmosphere. Interior. Origin and evolution. Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Saturn) and 11.1. The Main Point Saturn is a large Jovian-class planet with a composition
Lecture #27: Saturn Saturn: General properties. Atmosphere. Interior. Origin and evolution. Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Saturn) and 11.1. The Main Point Saturn is a large Jovian-class planet with a composition
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems. Comparing the Jovian Planets. Jovian Planet Composition 4/10/16. Spacecraft Missions
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Interiors and Atmospheres How are jovian planets alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets? Do jovian
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Interiors and Atmospheres How are jovian planets alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets? Do jovian
Mission Architecture Options For Enceladus Exploration
 Mission Architecture Options For Enceladus Exploration Presentation to the NRC Planetary Science Decadal Survey Satellites Panel Nathan Strange Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Inst. Of Technology
Mission Architecture Options For Enceladus Exploration Presentation to the NRC Planetary Science Decadal Survey Satellites Panel Nathan Strange Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Inst. Of Technology
Balloon Concepts for Titan. Ralph D Lorenz, JHU-APL
 Balloon Concepts for Titan Ralph D Lorenz, JHU-APL Ralph.lorenz@jhuapl.edu http://www.lpl.arizona.edu/~rlorenz LCANS 26 April 2007 Titan is the 2 nd -largest satellite in the solar system, larger than
Balloon Concepts for Titan Ralph D Lorenz, JHU-APL Ralph.lorenz@jhuapl.edu http://www.lpl.arizona.edu/~rlorenz LCANS 26 April 2007 Titan is the 2 nd -largest satellite in the solar system, larger than
Astrobiology in the outer Solar System
 Non-habitable Astrobiological planetsrelevance of giant planets Astrobiology in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Jupiter Sagan & Salpeter (1976) investigated the potential
Non-habitable Astrobiological planetsrelevance of giant planets Astrobiology in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Jupiter Sagan & Salpeter (1976) investigated the potential
Life in the outer Solar System. AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life
 Life in the outer Solar System AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life Prospects for life on: Overview: 1. Europa (Jupiter moon) 2. Titan (Saturn s moon) 3. Enceladus (Saturn s moon) Life on Europa? NASA
Life in the outer Solar System AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life Prospects for life on: Overview: 1. Europa (Jupiter moon) 2. Titan (Saturn s moon) 3. Enceladus (Saturn s moon) Life on Europa? NASA
Terrestrial Atmospheres
 Terrestrial Atmospheres Why Is There Air? An atmosphere is a layer of gas trapped by the gravity of a planet or moon. Here s Earth s atmosphere viewed from orbit: Why Is There Air? If atoms move faster
Terrestrial Atmospheres Why Is There Air? An atmosphere is a layer of gas trapped by the gravity of a planet or moon. Here s Earth s atmosphere viewed from orbit: Why Is There Air? If atoms move faster
ESA s Cosmic Vision Programme: Outer Planet Mission Studies
 ESA s Cosmic Vision Programme: Outer Planet Mission Studies Jean-Pierre LEBRETON (ESA s EJSM and TSSM Study Scientist) Europa Lander workshop IKI, Moscow, 9-13 February 2009 ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, Pays-Bas
ESA s Cosmic Vision Programme: Outer Planet Mission Studies Jean-Pierre LEBRETON (ESA s EJSM and TSSM Study Scientist) Europa Lander workshop IKI, Moscow, 9-13 February 2009 ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, Pays-Bas
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
and the Joint Science Definition Team
 oh brave new world The in situ elements of TSSM A. Coustenis, J. Lunine, D. Matson, J-P. Lebreton, K. Reh, Ch. Erd, P. Beauchamp, N. Strange and the Joint Science Definition Team TSSM 1 H D L O 110-0 km
oh brave new world The in situ elements of TSSM A. Coustenis, J. Lunine, D. Matson, J-P. Lebreton, K. Reh, Ch. Erd, P. Beauchamp, N. Strange and the Joint Science Definition Team TSSM 1 H D L O 110-0 km
Astrobiology in the outer Solar System
 Non-habitable Astrobiological planetsrelevance of giant planets Astrobiology in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Jupiter Sagan & Salpeter (1976) investigated the potential
Non-habitable Astrobiological planetsrelevance of giant planets Astrobiology in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Jupiter Sagan & Salpeter (1976) investigated the potential
Astrobiology in the outer Solar System
 Non-habitable Astrobiological planetsrelevance of giant planets Astrobiology in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2015-2016) G. Vladilo Jupiter Sagan & Salpeter (1976) investigated the potential
Non-habitable Astrobiological planetsrelevance of giant planets Astrobiology in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2015-2016) G. Vladilo Jupiter Sagan & Salpeter (1976) investigated the potential
Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018
 Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018 Tidal locking We always see the same face of the Moon. This means: period of orbit = period of spin Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth Why? The tidal bulge in the solid
Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018 Tidal locking We always see the same face of the Moon. This means: period of orbit = period of spin Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth Why? The tidal bulge in the solid
Universe Now. 4. Solar System II: Jovian planets
 Universe Now 4. Solar System II: Jovian planets An overview of the known Solar System The Sun 4 terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, The Earth, Mars 4 Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 5
Universe Now 4. Solar System II: Jovian planets An overview of the known Solar System The Sun 4 terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, The Earth, Mars 4 Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 5
Last Class. Today s Class 11/28/2017
 Today s Class: The Jovian Planets & Their Water Worlds 1. Exam #3 on Thursday, Nov. 30 th! a) Covers all the reading Nov. 2-28. b) Covers Homework #6 and #7. c) Review Space in the News articles/discussions.
Today s Class: The Jovian Planets & Their Water Worlds 1. Exam #3 on Thursday, Nov. 30 th! a) Covers all the reading Nov. 2-28. b) Covers Homework #6 and #7. c) Review Space in the News articles/discussions.
Mission Concept Study
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Mission Concept Study Planetary Science Decadal Survey Titan Saturn System Mission Science Champion: John Spencer (spencer@boulder.swri.edu) NASA HQ POC: Curt
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Mission Concept Study Planetary Science Decadal Survey Titan Saturn System Mission Science Champion: John Spencer (spencer@boulder.swri.edu) NASA HQ POC: Curt
Topside interactions with the Titan atmosphere. Anne Wellbrock
 Topside interactions with the Titan atmosphere Anne Wellbrock Outline 1. About me 2. Introduction 3. Introducing Titan and its atmosphere 4. The UCL Titan thermosphere code 5. The interaction with Saturn
Topside interactions with the Titan atmosphere Anne Wellbrock Outline 1. About me 2. Introduction 3. Introducing Titan and its atmosphere 4. The UCL Titan thermosphere code 5. The interaction with Saturn
Jovian Planet Systems
 Jovian Planet Systems Reading: Chapter 14.1-14.5 Jovian Planet Systems Voyager 1 and 2 explored the outer planets in the 1970s and 1980s. The Galileo spacecraft circled Jupiter dozens of times in the late
Jovian Planet Systems Reading: Chapter 14.1-14.5 Jovian Planet Systems Voyager 1 and 2 explored the outer planets in the 1970s and 1980s. The Galileo spacecraft circled Jupiter dozens of times in the late
1 of 5 4/21/2015 6:40 PM
 1 of 5 4/21/2015 6:40 PM 1. Which of the following lists the outer planets in order of increasing mass?,,,,,,,,,,,, 2. The surface structure of 's largest satellite, Titan, is completely unknown because
1 of 5 4/21/2015 6:40 PM 1. Which of the following lists the outer planets in order of increasing mass?,,,,,,,,,,,, 2. The surface structure of 's largest satellite, Titan, is completely unknown because
International Workshop on Instrumentation for Planetary Missions (2012)
 TITAN SATURN SYSTEM MISSION INSTRUMENTATION A. Coustenis 1, J. Lunine 2, K. Reh 3, J.-P. Lebreton 4, C. Erd 5, P. Beauchamp 3, C. Sotin 3 and D. Matson 3, 1 LESIA, Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, 92195 Meudon,
TITAN SATURN SYSTEM MISSION INSTRUMENTATION A. Coustenis 1, J. Lunine 2, K. Reh 3, J.-P. Lebreton 4, C. Erd 5, P. Beauchamp 3, C. Sotin 3 and D. Matson 3, 1 LESIA, Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, 92195 Meudon,
ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet
 ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet JUICE - JUpiter ICy moons Explorer - is the first large-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 programme. Planned for launch in 2022 and arrival at Jupiter
ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet JUICE - JUpiter ICy moons Explorer - is the first large-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 programme. Planned for launch in 2022 and arrival at Jupiter
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Complex molecules in Titan s upper atmosphere
 Complex molecules in Titan s upper atmosphere Panayotis Lavvas GSMA/CNRS Roger V Yelle LPL, University of Arizona 52 nd ESLAB Meeting, ESTEC, 14 th May 2018 INTRODUCTION From ATOMS to MOLECULES to MACROMOLECULES
Complex molecules in Titan s upper atmosphere Panayotis Lavvas GSMA/CNRS Roger V Yelle LPL, University of Arizona 52 nd ESLAB Meeting, ESTEC, 14 th May 2018 INTRODUCTION From ATOMS to MOLECULES to MACROMOLECULES
12a. Jupiter. Jupiter Data (Table 12-1) Jupiter Data: Numbers
 12a. Jupiter Jupiter & Saturn data Jupiter & Saturn seen from the Earth Jupiter & Saturn rotation & structure Jupiter & Saturn clouds Jupiter & Saturn atmospheric motions Jupiter & Saturn rocky cores Jupiter
12a. Jupiter Jupiter & Saturn data Jupiter & Saturn seen from the Earth Jupiter & Saturn rotation & structure Jupiter & Saturn clouds Jupiter & Saturn atmospheric motions Jupiter & Saturn rocky cores Jupiter
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Presentations. Outline. ! Nicholas Langhammer esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 13): What is n p? Anna Dorn Praneet Sahgal HW 2 Nicholas Langhammer http://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/sociopolitica/ esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.htm Next Class: Life on
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 13): What is n p? Anna Dorn Praneet Sahgal HW 2 Nicholas Langhammer http://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/sociopolitica/ esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.htm Next Class: Life on
Post-Cassini Saturn Exploration. Saturn (shallow) Probes. Sushil Atreya NRC Decadal / Outer Planets Irvine, CA, 26 October 2009
 Post-Cassini Saturn Exploration Saturn (shallow) Probes Sushil Atreya www.umich.edu/~atreya NRC Decadal / Outer Planets Irvine, CA, 26 October 2009 map who needs probes? why Saturn probes; why now? what
Post-Cassini Saturn Exploration Saturn (shallow) Probes Sushil Atreya www.umich.edu/~atreya NRC Decadal / Outer Planets Irvine, CA, 26 October 2009 map who needs probes? why Saturn probes; why now? what
Lecture 11 The Structure and Atmospheres of the Outer Planets October 9, 2017
 Lecture 11 The Structure and Atmospheres of the Outer Planets October 9, 2017 1 2 Jovian Planets 3 Jovian Planets -- Basic Information Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Distance 5.2 AU 9.5 AU 19 AU 30 AU Spin
Lecture 11 The Structure and Atmospheres of the Outer Planets October 9, 2017 1 2 Jovian Planets 3 Jovian Planets -- Basic Information Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Distance 5.2 AU 9.5 AU 19 AU 30 AU Spin
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Huygens at Titan. Paul Withers Boston University Titan The big questions Huygens mission and instruments First results
 saturn.jpl.nasa.gov Huygens at Titan Paul Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Titan The big questions Huygens mission and instruments First results MIT EAPS Lunch Talk 2005.02.08 Why Titan? Atmospheric
saturn.jpl.nasa.gov Huygens at Titan Paul Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Titan The big questions Huygens mission and instruments First results MIT EAPS Lunch Talk 2005.02.08 Why Titan? Atmospheric
Lecture #11: Plan. Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets
 Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
The Fathers of the Gods: Jupiter and Saturn
 The Fathers of the Gods: Jupiter and Saturn Learning Objectives! Order all the planets by size and distance from the Sun! How are clouds on Jupiter (and Saturn) different to the Earth? What 2 factors drive
The Fathers of the Gods: Jupiter and Saturn Learning Objectives! Order all the planets by size and distance from the Sun! How are clouds on Jupiter (and Saturn) different to the Earth? What 2 factors drive
Introduction to Astrobiology. Chapter 4 Search for habitable environments, biomarkers and life outside the Earth
 Introduction to Astrobiology Chapter 4 Search for habitable environments, biomarkers and life outside the Earth Search for habitable environments and life in the Solar System Venus Examples of nonhabitable
Introduction to Astrobiology Chapter 4 Search for habitable environments, biomarkers and life outside the Earth Search for habitable environments and life in the Solar System Venus Examples of nonhabitable
Planetary Atmospheres: What do they tell us? Melissa Trainer CU Center for Astrobiology
 Planetary Atmospheres: What do they tell us? Melissa Trainer CU Center for Astrobiology Earth s atmosphere today is the end-point of an evolution that started about 4.6 billion years ago by examining other
Planetary Atmospheres: What do they tell us? Melissa Trainer CU Center for Astrobiology Earth s atmosphere today is the end-point of an evolution that started about 4.6 billion years ago by examining other
The Case for an Enceladus New Frontiers Mission
 The Case for an Enceladus New Frontiers Mission T.A. Hurford, B. Buratti, A. Coustenis, A. Dombard, R. Greenberg, H. Hussmann DRAFT: 1 September 2009 It is unlikely that a flagship mission devoted to the
The Case for an Enceladus New Frontiers Mission T.A. Hurford, B. Buratti, A. Coustenis, A. Dombard, R. Greenberg, H. Hussmann DRAFT: 1 September 2009 It is unlikely that a flagship mission devoted to the
Venus: Key Ideas: A Warm Up Exercise. Venus at a Glance -- Orbit. Venus at a Glance Planetary Data
 Venus A Warm Up Exercise Because Mercury has a high average density despite its relatively low mass, it is thought to a) Have a subsurface ocean b) Have a large iron core c) Be made largely of lead d)
Venus A Warm Up Exercise Because Mercury has a high average density despite its relatively low mass, it is thought to a) Have a subsurface ocean b) Have a large iron core c) Be made largely of lead d)
12. Jovian Planet Systems Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison Wesley
 12. Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive 2. are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen compounds 3. have
12. Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive 2. are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen compounds 3. have
Saturn. AST 101 chapter 12. Spectacular Rings and Mysterious Moons Orbital and Physical Properties Orbital and Physical Properties
 Saturn Spectacular Rings and Mysterious Moons 12.1 Orbital and Physical Properties This figure shows the solar system from a vantage point that emphasizes the relationship of the jovian planets to the
Saturn Spectacular Rings and Mysterious Moons 12.1 Orbital and Physical Properties This figure shows the solar system from a vantage point that emphasizes the relationship of the jovian planets to the
The observations. The deductions. Determine the density of the Galilean satellites. Two classes of Galilean satellites
 The Galilean satellites are easily seen Spacecraft reveal unique properties The Galilean satellites mimic a planetary system Io is covered with volcanic sulfur compounds Io s interior is affected by Jupiter
The Galilean satellites are easily seen Spacecraft reveal unique properties The Galilean satellites mimic a planetary system Io is covered with volcanic sulfur compounds Io s interior is affected by Jupiter
Satellites of giant planets. Satellites and rings of giant planets. Satellites of giant planets
 Satellites of giant planets Satellites and rings of giant planets Regular and irregular satellites Regular satellites: The orbits around the planet have low eccentricity and are approximately coplanar
Satellites of giant planets Satellites and rings of giant planets Regular and irregular satellites Regular satellites: The orbits around the planet have low eccentricity and are approximately coplanar
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Planet 2. Planet 1 Gas Giant. Planet 3. Earth
 Planet 1 Gas Giant Planet 2 The temperature at the cloud tops is 200 C while the interior temperatures reach tens of thousands of degrees. The churning of the atmosphere causes temperatures of the circulating
Planet 1 Gas Giant Planet 2 The temperature at the cloud tops is 200 C while the interior temperatures reach tens of thousands of degrees. The churning of the atmosphere causes temperatures of the circulating
Life in the outer Solar System. AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life
 Life in the outer Solar System AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life Prospects for life on: Overview: 1. Europa (Jupiter moon) 2. Titan (Saturn s moon) 3. Enceladus (Saturn s moon) Life on Europa? Europa
Life in the outer Solar System AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life Prospects for life on: Overview: 1. Europa (Jupiter moon) 2. Titan (Saturn s moon) 3. Enceladus (Saturn s moon) Life on Europa? Europa
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
SCIENCE WITH DIRECTED AERIAL DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION SAILING THE PLANETS
 : SCIENCE WITH DIRECTED AERIAL ROBOT EXPLORERS (DARE) DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION 1 NEW ARCHITECTURE FOR PLANETARY EXPLORATION KEY ELEMENTS: Long-Duration Planetary Balloon Platforms
: SCIENCE WITH DIRECTED AERIAL ROBOT EXPLORERS (DARE) DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION 1 NEW ARCHITECTURE FOR PLANETARY EXPLORATION KEY ELEMENTS: Long-Duration Planetary Balloon Platforms
Jupiter and Saturn s Satellites of Fire and Ice. Chapter Fifteen. Guiding Questions
 Jupiter and Saturn s Satellites of Fire and Ice Chapter Fifteen Guiding Questions 1. What is special about the orbits of Jupiter s Galilean satellites? 2. Are all the Galilean satellites made of rocky
Jupiter and Saturn s Satellites of Fire and Ice Chapter Fifteen Guiding Questions 1. What is special about the orbits of Jupiter s Galilean satellites? 2. Are all the Galilean satellites made of rocky
Chapter 10 The Outer Planets
 Chapter 10 The Outer Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Outer Worlds Beyond the orbit of Mars,
Chapter 10 The Outer Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Outer Worlds Beyond the orbit of Mars,
Chapter 11 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Jovian Planet Systems Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian
Chapter 11 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System
 AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System STRUCTURE OF A PLANET S ATMOSPHERE If you remember this. X-rays Ultraviolet Heating & Destruction Heating & Destruction Visible Infrared Transmission and Scattering
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System STRUCTURE OF A PLANET S ATMOSPHERE If you remember this. X-rays Ultraviolet Heating & Destruction Heating & Destruction Visible Infrared Transmission and Scattering
Mimas, moon of Saturn and Death Star impersonator responsible for several gaps in Saturn s ring system
 Last time: Gravitational signs of large outer moons in the rings Ring shepherding/gap maintenance Longer lived structures due to mean motion resonances with large satellites Example: 2:1 resonance with
Last time: Gravitational signs of large outer moons in the rings Ring shepherding/gap maintenance Longer lived structures due to mean motion resonances with large satellites Example: 2:1 resonance with
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
The methane cycle on Titan
 The methane cycle on Titan REVIEW ARTICLE Saturn s moon Titan is the second largest natural satellite in the solar system, and the only one that possesses a substantial atmosphere. With a surface temperature
The methane cycle on Titan REVIEW ARTICLE Saturn s moon Titan is the second largest natural satellite in the solar system, and the only one that possesses a substantial atmosphere. With a surface temperature
11.2 A Wealth of Worlds: Satellites of Ice and Rock
 11.2 A Wealth of Worlds: Satellites of Ice and Rock Our goals for learning: What kinds of moons orbit the jovian planets? Why are Jupiter's Galilean moons so geologically active? What is remarkable about
11.2 A Wealth of Worlds: Satellites of Ice and Rock Our goals for learning: What kinds of moons orbit the jovian planets? Why are Jupiter's Galilean moons so geologically active? What is remarkable about
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different Terrestrial planets are made principally of
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different Terrestrial planets are made principally of
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different Terrestrial planets are made principally of
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different Terrestrial planets are made principally of
Inner Planets (Part II)
 Inner Planets (Part II) Sept. 18, 2002 1) Atmospheres 2) Greenhouse Effect 3) Mercury 4) Venus 5) Mars 6) Moon Announcements Due to technical difficulties, Monday s quiz doesn t count An extra credit problem
Inner Planets (Part II) Sept. 18, 2002 1) Atmospheres 2) Greenhouse Effect 3) Mercury 4) Venus 5) Mars 6) Moon Announcements Due to technical difficulties, Monday s quiz doesn t count An extra credit problem
SPRITE: Saturn PRobe Interior and atmosphere Explorer
 SPRITE: Saturn PRobe Interior and atmosphere Explorer Thomas R. Spilker Feb. 23, 2017 2016. California Institute of Technology. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Decadal Survey Saturn Probe Science
SPRITE: Saturn PRobe Interior and atmosphere Explorer Thomas R. Spilker Feb. 23, 2017 2016. California Institute of Technology. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Decadal Survey Saturn Probe Science
Similarities & Differences to Inner Planets
 Similarities & Differences to Inner Planets Jupiter Jupiter: Basic Characteristics Mass = 1.898 10 27 kg (318 x Earth) Radius = 71,492 km (11x Earth) Albedo (reflectivity) = 0.34 (Earth = 0.39) Average
Similarities & Differences to Inner Planets Jupiter Jupiter: Basic Characteristics Mass = 1.898 10 27 kg (318 x Earth) Radius = 71,492 km (11x Earth) Albedo (reflectivity) = 0.34 (Earth = 0.39) Average
The Main Point. Basic Properties of Mars. Observations. Lecture #19: Mars
 Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
Ocean Worlds Roadmap. Jonathan I Lunine Cornell University
 Ocean Worlds Roadmap Jonathan I Lunine Cornell University 1 Key references Hand et al., 2017. Report of the Europa Lander SDT, https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/docs/europa_lander_sdt_report_2016.pdf Hendrix,
Ocean Worlds Roadmap Jonathan I Lunine Cornell University 1 Key references Hand et al., 2017. Report of the Europa Lander SDT, https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/docs/europa_lander_sdt_report_2016.pdf Hendrix,
Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere
 Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere Permafrost Permafrost Ground that is at a temperature of 0 or below for
Lithosphere: (Rocky Sphere) Solid, rocky, outer layer of the Earth. Includes the crust and part of the upper mantle. Lithosphere Permafrost Permafrost Ground that is at a temperature of 0 or below for
4.3. Clouds and Convection
 or haze occurs during the tropics near equinox, when the tropical jets appear. Current GCM models do not however resolve the details of convective systems, which occur on spatial scales much smaller than
or haze occurs during the tropics near equinox, when the tropical jets appear. Current GCM models do not however resolve the details of convective systems, which occur on spatial scales much smaller than
10/6/16. Observing the Universe with Gravitational Waves
 Lecture Outline Observing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Thursday, October 13 7:00 PM Bell Museum Auditorium This event is free and open to the public, and will be followed by telescope observing.
Lecture Outline Observing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Thursday, October 13 7:00 PM Bell Museum Auditorium This event is free and open to the public, and will be followed by telescope observing.
Chapter 4! Search for habitable environments, biomarkers and life outside the Earth!
 Introduction to Astrobiology! Chapter 4! Search for habitable environments, biomarkers and life outside the Earth! The Solar System! Search for habitable environments and life! Venus! T s =735 K! Examples
Introduction to Astrobiology! Chapter 4! Search for habitable environments, biomarkers and life outside the Earth! The Solar System! Search for habitable environments and life! Venus! T s =735 K! Examples
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Earth s Atmosphere. Atmospheric Pressure
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology.
 What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
Life in the Solar System
 Life in the Solar System Basic Requirements for Life 1. Chemical elements to make biological molecules. On Earth these are mostly C, H, O and N 2. Source of energy for metabolism. This can come from a
Life in the Solar System Basic Requirements for Life 1. Chemical elements to make biological molecules. On Earth these are mostly C, H, O and N 2. Source of energy for metabolism. This can come from a
Lecture 24: Saturn. The Solar System. Saturn s Rings. First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: (where we have used Earth units)
 Lecture 24: Saturn The Solar System First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: Planet Distance Density Mass Mercury 0.4 1.0 0.06 Venus 0.7 0.9 0.8 Earth 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mars 1.5 0.7 0.1 (asteroid)
Lecture 24: Saturn The Solar System First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: Planet Distance Density Mass Mercury 0.4 1.0 0.06 Venus 0.7 0.9 0.8 Earth 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mars 1.5 0.7 0.1 (asteroid)
Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 4: Jovian Planets Due in class Tuesday, Feb. 23, 2016
 Name: Section: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 4: Jovian Planets Due in class Tuesday, Feb. 23, 2016 The jovian planets have distinct characteristics that set them apart from the terrestrial
Name: Section: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 4: Jovian Planets Due in class Tuesday, Feb. 23, 2016 The jovian planets have distinct characteristics that set them apart from the terrestrial
Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick
 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric properties vary with altitude? Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick
10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric properties vary with altitude? Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick
The Jovian Planets (Gas Giants)
 The Jovian Planets (Gas Giants) Discoveries and known to ancient astronomers. discovered in 1781 by Sir William Herschel (England). discovered in 1845 by Johann Galle (Germany). Predicted to exist by John
The Jovian Planets (Gas Giants) Discoveries and known to ancient astronomers. discovered in 1781 by Sir William Herschel (England). discovered in 1845 by Johann Galle (Germany). Predicted to exist by John
Planetary Temperatures
 Planetary Temperatures How does Sunlight heat a planet with no atmosphere? This is similar to our dust grain heating problem First pass: Consider a planet of radius a at a distance R from a star of luminosity
Planetary Temperatures How does Sunlight heat a planet with no atmosphere? This is similar to our dust grain heating problem First pass: Consider a planet of radius a at a distance R from a star of luminosity
Locally enhanced precipitation organized by planetary-scale waves on Titan
 Locally enhanced precipitation organized by planetary-scale waves on Titan Jonathan L. Mitchell, 1 Máté Ádámkovics,2 Rodrigo Caballero, 3,4 Elizabeth P. Turtle 5 1 Earth & Space Sciences, Atmospheric &
Locally enhanced precipitation organized by planetary-scale waves on Titan Jonathan L. Mitchell, 1 Máté Ádámkovics,2 Rodrigo Caballero, 3,4 Elizabeth P. Turtle 5 1 Earth & Space Sciences, Atmospheric &
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems. Jovian Planet Composition. Are jovian planets all alike? Density Differences. Density Differences
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Galilean Moons of Jupiter
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Satellites of Jupiter & Saturn Galilean satellites Similarities and differences among the Galilean satellites How the Galilean
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Satellites of Jupiter & Saturn Galilean satellites Similarities and differences among the Galilean satellites How the Galilean
Low Cost Enceladus Sample Return Mission Concept
 Low Cost Enceladus Sample Return Mission Concept P. Tsou 1, D. E. Brownlee 2, C. P. McKay 3, A. Anbar 4, H. Yano 5, Nathan Strange 7, Richard Dissly 6, and I. Kanik 7 1 Sample Exploration Systems (Peter.Tsou@gmail.com)
Low Cost Enceladus Sample Return Mission Concept P. Tsou 1, D. E. Brownlee 2, C. P. McKay 3, A. Anbar 4, H. Yano 5, Nathan Strange 7, Richard Dissly 6, and I. Kanik 7 1 Sample Exploration Systems (Peter.Tsou@gmail.com)
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
SAILING THE PLANETS: PLANETARY EXPLORATION FROM GUIDED BALLOONS. 7 th Annual Meeting of the NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts
 SAILING THE PLANETS: PLANETARY EXPLORATION FROM GUIDED BALLOONS 7 th Annual Meeting of the NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION SAILING THE PLANETS 1 MARS
SAILING THE PLANETS: PLANETARY EXPLORATION FROM GUIDED BALLOONS 7 th Annual Meeting of the NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION SAILING THE PLANETS 1 MARS
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
TRAMS: A new dynamic cloud model for Titan s methane clouds
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L03203, doi:10.1029/2006gl028652, 2007 TRAMS: A new dynamic cloud model for Titan s methane clouds Erika L. Barth 1 and Scot C. R. Rafkin
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L03203, doi:10.1029/2006gl028652, 2007 TRAMS: A new dynamic cloud model for Titan s methane clouds Erika L. Barth 1 and Scot C. R. Rafkin
The greenhouse effect
 The greenhouse effect Visible light arrives About half reflected, half is absorbed by the ground. This absorbed energy is then reradiated, but NOT in the visible (would just go out again anyway); in the
The greenhouse effect Visible light arrives About half reflected, half is absorbed by the ground. This absorbed energy is then reradiated, but NOT in the visible (would just go out again anyway); in the
Astrobiology Research Priorities for the Outer Solar System
 Astrobiology Research Priorities for the Outer Solar System White Paper, Final Version of 12 September 2009 Primary Author: Dirk Schulze-Makuch (Washington State University) 1-509-335-1180 dirksm@wsu.edu
Astrobiology Research Priorities for the Outer Solar System White Paper, Final Version of 12 September 2009 Primary Author: Dirk Schulze-Makuch (Washington State University) 1-509-335-1180 dirksm@wsu.edu
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 8 1. Which of the following processes is not important in shaping the surface of terrestrial planets? a) Impact cratering b) Tectonism
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 8 1. Which of the following processes is not important in shaping the surface of terrestrial planets? a) Impact cratering b) Tectonism
Quiz 3 is available for pickup in front
 Quiz 3 is available for pickup in front Extra credit corrections: for up to 4 of the questions you missed: Look up or figure out the correct answer. Write a sentence or two explaining what you did wrong
Quiz 3 is available for pickup in front Extra credit corrections: for up to 4 of the questions you missed: Look up or figure out the correct answer. Write a sentence or two explaining what you did wrong
Jupiter and its Moons
 Jupiter and its Moons Summary 1. At an average distance of over 5 AU, Jupiter takes nearly 12 years to orbit the Sun 2. Jupiter is by far the largest and most massive planet in the solar system being over
Jupiter and its Moons Summary 1. At an average distance of over 5 AU, Jupiter takes nearly 12 years to orbit the Sun 2. Jupiter is by far the largest and most massive planet in the solar system being over
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
