Uranus and Neptune. Uranus and Neptune Properties. Discovery of Uranus
|
|
|
- Ronald Knight
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Uranus and Neptune Uranus and Neptune are much smaller than Jupiter and Saturn, but still giants compared to Earth Both are worlds we know relatively little about Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to visit these planets Uranus and Neptune Properties Semimajor axis Eccentricity Orbital Period Rotational Period Mass Radius Average Density Surface gravity Cloud Top Temp Atmosphere Uranus 19.2 A.U years days 8.68 x kg (14.5 x Earth) 25,559 km (4.0 x Earth) 1.27 g/cm 3 (0.23 x Earth) 8.87 m/s 2 (0.91 x Earth) 58 K hydrogen, helium Neptune 30.1 A.U years 0.67 days 1.02 x kg (17.2 x Earth) 24,766 km (3.88 x Earth) 1.64 g/cm 3 (0.30 x Earth) 11.1 m/s 2 (1.14 x Earth) 59 K hydrogen, helium Discovery of Uranus Unlike the other planet's we've discussed, Uranus is not easily visible in the night sky It's brightness is barely detectable by the human eye, and it was discovered by telescope William Herschel noticed its motion against the background stars in 1781 Image of Uranus from Earth (arrows indicate moons) 1
2 Discovery of Neptune Neptune's further distance makes it impossible to see with the naked eye After watching the orbit of Uranus, astronomers noticed the planet was being pulled by some unseen body After much searching, Neptune was finally found in 1846 Image of Neptune from Earth (arrows indicate moons) Visiting Uranus and Neptune Uranus For each of these planets, it provided the first detailed images of the planets and their moons While Uranus was relatively featureless, Neptune showed cloud bands and storms much like Jupiter Neptune Voyager 2 continues to travel out of the Solar System and is now twice the distance from the Sun as Pluto Despite their smaller size, Uranus and Neptune share many characteristic with Jupiter and Saturn The Jovian Family The slightly higher densities of Uranus and Neptune reveal that their rocky cores probably make up a significant portion of the planet 2
3 Uranus - A Planet on Its Side Uranus is the only planet in the Solar System to have a rotational axis almost perpendicular to its revolution axis Astronomer can't definitively say what caused this tilt, but it may have been a catastrophic collision early in Neptune's formation Atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune Like all the Jovian planets, both Uranus and Neptune's atmospheres are mainly hydrogen (84%) and helium (13-14%) The main difference in color between the two worlds results from different concentrations of methane _ _ Methane is very good at absorbing red and yellow light, leaving only the blues and greens to reflect off the cloud tops Weather on Uranus While no major activity is visible to the naked eye, computer enhanced images do show some storms in Uranus' atmosphere The last image is in infrared, which shows much more details in the cloud bands and Uranus' rings Uranus' colder temperatures keep the majority of the weather at much deeper layers which are hidden under a layer of haze 3
4 Weather on Neptune Neptune's weather is much more prominent and active, despite its greater distance from the Sun Unlike Uranus, Neptune does appear to have an internal heat source, though its origins are unknown _ Voyager 2 witnessed a large storm, named the Great Dark Spot, but this storm has since disappeared Hubble images revealed the weather systems are still constantly active in the atmosphere Magnetospheres for Uranus and Neptune The size of the bars indicates strength of the magnetic field The location of the bars shows the origin of the magnetic field Notice that the magnetic axis is not always aligned with the rotation axis Uranus and Neptune Interiors The fact that both Uranus and Neptune's magnetic fields are strange suggests that their interiors are much different Unlike Jupiter and Saturn, pressure and temperatures outside the cores are not high enough to change hydrogen into the liquid metallic state Current theories suggest that Uranus and Neptune have a large slushy layer of water and water ice 4
5 The Moons of Uranus Following the trend for gas giants, Uranus has many moons, the number continually increasing The five largest, are all much smaller than our Moon and have diameters around 1000 kilometers Moons of Uranus All of the moons are quite dark in color, suggesting a dirtier, older surface Recent theories suggest that ultraviolet sunlight and high energy particles cause radiation darkening on these outer worlds The high energy photons break up material on the surface and react to form a dark hydrocarbon soot Umbriel Ariel Miranda takes the prize for weirdest moon of Uranus Miranda Voyager 2 images of Miranda showed a very dramatic surface of varying terrain A large impact may have severely fractured the moon into several pieces which later reformed 5
6 Moons of Neptune Like Uranus, Neptune has many moons, though the number is smaller (around a dozen) Most of these moons are small (10's of kilometers) Proteus Triton Triton is the largest moon at 2710 km and a mass that is 0.29 times the mass of Earth's Moon Triton Geysers of nitrogen gas were seen erupting from the surface and help maintain a very thin atmosphere of nitrogen There is also evidence of past heating which created pools of frozen water on the surface Triton is the only large moon in the Solar System which has a retrograde orbit around its planet The Fate of Triton Remember that tidal forces between the Earth and Moon gradually 'push' the Moon away The opposite situation happens with Triton, and it will eventually drift inside the Roche limit of Neptune 6
7 The Rings of Uranus They were discovered in 1977 by a technique called stellar occultation Astronomers measure the light from a background star as Neptune passes in front of it Dips in the light correspond to the star being blocked by Uranus' rings The Rings of Uranus The naming scheme for Uranus' rings is a mess, with a combination of Greek letters and numbers All the rings are much more narrow and confined than Saturn's The average size of particles is also much larger, with few chunks less than a centimeter in size Ophelia Cordelia The Rings of Neptune Neptune also displays a thin, dim ring system Three of the rings are relatively narrow, while two other are much wider in size The outermost ring also appears 'clumpy', probably from interactions with moons 7
The Outermost Planets. The 7 Wanderers known since Antiquity. Uranus and Neptune distinctly Blue-ish!
 The Outermost Planets The 7 Wanderers known since Antiquity. Uranus and Neptune distinctly Blue-ish! Uranus Uranus and 3 of its moons, barely visible from Earth. Discovered by William Herschel 1781. (Accidentally!)
The Outermost Planets The 7 Wanderers known since Antiquity. Uranus and Neptune distinctly Blue-ish! Uranus Uranus and 3 of its moons, barely visible from Earth. Discovered by William Herschel 1781. (Accidentally!)
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 13. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 13 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 13 Uranus and Neptune Units of Chapter 13 13.1 The Discoveries of Uranus and Neptune 13.2 Orbital and Physical Properties
Lecture Outlines Chapter 13 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 13 Uranus and Neptune Units of Chapter 13 13.1 The Discoveries of Uranus and Neptune 13.2 Orbital and Physical Properties
Uranus & Neptune, The Ice Giants
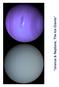 Uranus & Neptune, The Ice Giants What We Will Learn Today How & When were Uranus & Neptune discovered? How are the interiors and weather on these planets? Why is Neptune as warm as Uranus? What are their
Uranus & Neptune, The Ice Giants What We Will Learn Today How & When were Uranus & Neptune discovered? How are the interiors and weather on these planets? Why is Neptune as warm as Uranus? What are their
Astronomy. Uranus Neptune & Remote Worlds
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Uranus Neptune & Remote Worlds Uranus and Neptune Orbits and Atmospheres Internal Structure Magnetic Fields Rings Uranus's
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Uranus Neptune & Remote Worlds Uranus and Neptune Orbits and Atmospheres Internal Structure Magnetic Fields Rings Uranus's
Lecture 25: The Outer Planets
 Lecture 25: The Outer Planets Neptune Uranus Pluto/Charon Uranus and three moons Neptune and two moons 1 The Outer Planets Uranus Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, who realized that this extended
Lecture 25: The Outer Planets Neptune Uranus Pluto/Charon Uranus and three moons Neptune and two moons 1 The Outer Planets Uranus Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, who realized that this extended
Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants. Discovery of Uranus. Bode s Law. Discovery of Neptune
 Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants Discovery of Uranus Discovery of Uranus & Neptune Properties Density & Composition Internal Heat Source Magnetic fields Rings Uranus Rotational Axis by William Herschel
Uranus & Neptune: The Ice Giants Discovery of Uranus Discovery of Uranus & Neptune Properties Density & Composition Internal Heat Source Magnetic fields Rings Uranus Rotational Axis by William Herschel
Earth, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto. 14a. Uranus & Neptune. The Discovery of Uranus. Uranus Data: Numbers. Uranus Data (Table 14-1)
 14a. Uranus & Neptune The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus &
14a. Uranus & Neptune The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus &
Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Outer Worlds 4/19/07
 The : Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto Reading Assignment Finish Chapter 17 Announcements 6 th homework due on Tuesday, April 24 Quiz on Tuesday, April 24 (will cover all lectures since the last exam and Chapters
The : Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto Reading Assignment Finish Chapter 17 Announcements 6 th homework due on Tuesday, April 24 Quiz on Tuesday, April 24 (will cover all lectures since the last exam and Chapters
Earth, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto
 14a. Uranus, Neptune & Pluto The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus
14a. Uranus, Neptune & Pluto The discovery of Uranus & Neptune Uranus is oddly tilted & nearly featureless Neptune is cold & blue Uranus & Neptune are like yet dislike Jupiter The magnetic fields of Uranus
Unit 3 Lesson 5 The Gas Giant Planets. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Florida Benchmarks SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets and other astronomical bodies relative to solar system, galaxy, and universe, including distance, size, and composition.
Florida Benchmarks SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets and other astronomical bodies relative to solar system, galaxy, and universe, including distance, size, and composition.
Investigating Astronomy Timothy F. Slater, Roger A. Freeman Chapter 7 Observing the Dynamic Giant Planets
 Investigating Astronomy Timothy F. Slater, Roger A. Freeman Chapter 7 Observing the Dynamic Giant Planets Observing Jupiter and Saturn The disk of Jupiter at opposition appears about two times larger than
Investigating Astronomy Timothy F. Slater, Roger A. Freeman Chapter 7 Observing the Dynamic Giant Planets Observing Jupiter and Saturn The disk of Jupiter at opposition appears about two times larger than
The Gas Giants Astronomy Lesson 13
 The Gas Giants Astronomy Lesson 13 The four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, are much larger and more massive than Earth, and they do not have solid surfaces. Because these planets
The Gas Giants Astronomy Lesson 13 The four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, are much larger and more massive than Earth, and they do not have solid surfaces. Because these planets
The Jovian Planets (Gas Giants)
 The Jovian Planets (Gas Giants) Discoveries and known to ancient astronomers. discovered in 1781 by Sir William Herschel (England). discovered in 1845 by Johann Galle (Germany). Predicted to exist by John
The Jovian Planets (Gas Giants) Discoveries and known to ancient astronomers. discovered in 1781 by Sir William Herschel (England). discovered in 1845 by Johann Galle (Germany). Predicted to exist by John
Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets
 Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets 2-28-2018 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ASTR-101 Section 004 Bulk Properties of Terrestrial and Jovian Planets All Jovian planets have strong magnetic fields
Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets 2-28-2018 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ASTR-101 Section 004 Bulk Properties of Terrestrial and Jovian Planets All Jovian planets have strong magnetic fields
Traveler s Guide to the Planets Uranus & Neptune
 Traveler s Guide to the Planets Uranus & Neptune 1. These worlds are the ice giants. (There are two or more answers to this a. Jupiter c. Saturn b. Neptune d. Uranus 2. Uranus is the th planet in the Solar
Traveler s Guide to the Planets Uranus & Neptune 1. These worlds are the ice giants. (There are two or more answers to this a. Jupiter c. Saturn b. Neptune d. Uranus 2. Uranus is the th planet in the Solar
Lecture 11 The Structure and Atmospheres of the Outer Planets October 9, 2017
 Lecture 11 The Structure and Atmospheres of the Outer Planets October 9, 2017 1 2 Jovian Planets 3 Jovian Planets -- Basic Information Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Distance 5.2 AU 9.5 AU 19 AU 30 AU Spin
Lecture 11 The Structure and Atmospheres of the Outer Planets October 9, 2017 1 2 Jovian Planets 3 Jovian Planets -- Basic Information Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Distance 5.2 AU 9.5 AU 19 AU 30 AU Spin
Saturn. Slightly smaller 1/3 the mass density 700 kg/m 3. Interior - light elements, lack of rocky materials. Voyager 2, NASA
 Saturn Slightly smaller 1/3 the mass density 700 kg/m 3 Interior - light elements, lack of rocky materials Voyager 2, NASA 1 Saturn - Atmosphere belts - driven by rapid rotation period - 10 hrs 14 min
Saturn Slightly smaller 1/3 the mass density 700 kg/m 3 Interior - light elements, lack of rocky materials Voyager 2, NASA 1 Saturn - Atmosphere belts - driven by rapid rotation period - 10 hrs 14 min
Directed Reading B. Section: The Outer Planets
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Outer Planets 1. What is one way that gas giants differ from the terrestrial planets? a. They are much smaller. b. They are rocky and icy. c. They are made
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Outer Planets 1. What is one way that gas giants differ from the terrestrial planets? a. They are much smaller. b. They are rocky and icy. c. They are made
Similarities & Differences to Inner Planets
 Similarities & Differences to Inner Planets Jupiter Jupiter: Basic Characteristics Mass = 1.898 10 27 kg (318 x Earth) Radius = 71,492 km (11x Earth) Albedo (reflectivity) = 0.34 (Earth = 0.39) Average
Similarities & Differences to Inner Planets Jupiter Jupiter: Basic Characteristics Mass = 1.898 10 27 kg (318 x Earth) Radius = 71,492 km (11x Earth) Albedo (reflectivity) = 0.34 (Earth = 0.39) Average
The Outer Planets (pages )
 The Outer Planets (pages 720 727) Gas Giants and Pluto (page 721) Key Concept: The first four outer planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are much larger and more massive than Earth, and they do
The Outer Planets (pages 720 727) Gas Giants and Pluto (page 721) Key Concept: The first four outer planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are much larger and more massive than Earth, and they do
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Physics 1305 Notes: The Outer Solar System
 Physics 1305 Notes: The Outer Solar System Victor Andersen University of Houston vandersen@uh.edu April 5, 2004 Copyright c Victor Andersen 2004 1 The Gas Giant Planets The predominant feature of Jupiter,
Physics 1305 Notes: The Outer Solar System Victor Andersen University of Houston vandersen@uh.edu April 5, 2004 Copyright c Victor Andersen 2004 1 The Gas Giant Planets The predominant feature of Jupiter,
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 16 4 Moons SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.d, 8.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How did Earth s moon
CHAPTER 16 4 Moons SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.d, 8.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How did Earth s moon
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS. NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Io Above Jupiter s Clouds on New Year's Day, Credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
 LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section X
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section X Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section X Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of
Starting from closest to the Sun, name the orbiting planets in order.
 Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Label next 2 pages in ISN Gas Giants. Make sure the following assignments are turned in:
 Do Now: Label next 2 pages in ISN Gas Giants Make sure the following assignments are turned in: A3K Article Analysis Small Group Test Corrections Form (if applicable) Astronomical Bodies in The Solar System
Do Now: Label next 2 pages in ISN Gas Giants Make sure the following assignments are turned in: A3K Article Analysis Small Group Test Corrections Form (if applicable) Astronomical Bodies in The Solar System
The Jovian Planets. Why do we expect planets like this in the outer reaches of the solar system?(lc)
 The Jovian Planets Beyond Mars and the Asteroid belt are the Jovian or Gas Giant Planets that are totally different than the terrestrial planets: They are composed almost entirely of gas They do not have
The Jovian Planets Beyond Mars and the Asteroid belt are the Jovian or Gas Giant Planets that are totally different than the terrestrial planets: They are composed almost entirely of gas They do not have
GIANT PLANETS & PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 GIANT PLANETS & PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Problem Set 6 due Tuesday 25 October 2018 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2018 1 From last lecture INTERIOR TEMPERATURE OF A ROCKY PLANET! "# 'Λ "$ =! $ "$ + -! 1 "$ 3* + $ / "$
GIANT PLANETS & PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Problem Set 6 due Tuesday 25 October 2018 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2018 1 From last lecture INTERIOR TEMPERATURE OF A ROCKY PLANET! "# 'Λ "$ =! $ "$ + -! 1 "$ 3* + $ / "$
Earth & Space Science ~ The Solar System
 Earth & Space Science ~ The Solar System In e r Sci Uni 11 I. Sun, Earth & Moon A. The Solar System 1. the sun & the objects orbiting it a. incl. 8 planets, other stars, asteroids, meteoroids, dwarf planets,
Earth & Space Science ~ The Solar System In e r Sci Uni 11 I. Sun, Earth & Moon A. The Solar System 1. the sun & the objects orbiting it a. incl. 8 planets, other stars, asteroids, meteoroids, dwarf planets,
Chapter 3 The Solar System
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 The Solar System Section 1 Observing the Solar System (pp. 72-77) Key Concepts What are the geocentric and heliocentric systems? How did Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler contribute
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 The Solar System Section 1 Observing the Solar System (pp. 72-77) Key Concepts What are the geocentric and heliocentric systems? How did Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler contribute
Chapter 11 The Jovian Planets
 Chapter 11 The Jovian Planets The Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Using Venus transit it was possible to get a good value of the AU (1639). Knowing the AU, it is possible to calculate
Chapter 11 The Jovian Planets The Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Using Venus transit it was possible to get a good value of the AU (1639). Knowing the AU, it is possible to calculate
Page Uranus. Uranus's Structure
 Page 270 10.3 Uranus Uranus, although small compared with Jupiter and Saturn, is much larger than the Earth. Its diameter is about 4 times that of the Earth, and its mass is about 15 Earth masses. Lying
Page 270 10.3 Uranus Uranus, although small compared with Jupiter and Saturn, is much larger than the Earth. Its diameter is about 4 times that of the Earth, and its mass is about 15 Earth masses. Lying
Universe Now. 4. Solar System II: Jovian planets
 Universe Now 4. Solar System II: Jovian planets An overview of the known Solar System The Sun 4 terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, The Earth, Mars 4 Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 5
Universe Now 4. Solar System II: Jovian planets An overview of the known Solar System The Sun 4 terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, The Earth, Mars 4 Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 5
Jovian Planet Systems
 Jovian Planet Systems Reading: Chapter 14.1-14.5 Jovian Planet Systems Voyager 1 and 2 explored the outer planets in the 1970s and 1980s. The Galileo spacecraft circled Jupiter dozens of times in the late
Jovian Planet Systems Reading: Chapter 14.1-14.5 Jovian Planet Systems Voyager 1 and 2 explored the outer planets in the 1970s and 1980s. The Galileo spacecraft circled Jupiter dozens of times in the late
1781: Uranus Discovered. The Outer Worlds. 1846: Neptune Discovered. Distance Comparison. Uranus Rotates Sideways. Exaggerated Seasons On Uranus
 The Outer Worlds 1781: Discovered (accidentally!) by William Herschel using a 6 inch telescope [he thought it was a comet!] 2 Draft 12/03/2006 Updated May 05, 2011 1846: Discovered Le Verrier: proposed
The Outer Worlds 1781: Discovered (accidentally!) by William Herschel using a 6 inch telescope [he thought it was a comet!] 2 Draft 12/03/2006 Updated May 05, 2011 1846: Discovered Le Verrier: proposed
Physics Homework 4 Fall 2015
 1) How were the rings of Uranus discovered? 1) A) by Percival Lowell, who observed two "bumps" on either side of Uranus B) photometric observations of the occultation of a star made from Earth C) by Voyager
1) How were the rings of Uranus discovered? 1) A) by Percival Lowell, who observed two "bumps" on either side of Uranus B) photometric observations of the occultation of a star made from Earth C) by Voyager
Unusual Moon Information
 Saturn s Numbers Saturn is 1.35 billion km from the Sun minimum. Saturn is 1.5 billion km from the Sun maximum. One day on Saturn takes about 10.67 hours. One full rotation around the sun takes about 29.5
Saturn s Numbers Saturn is 1.35 billion km from the Sun minimum. Saturn is 1.5 billion km from the Sun maximum. One day on Saturn takes about 10.67 hours. One full rotation around the sun takes about 29.5
The Jovian Planets. The Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
 The Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Their masses are large compared with terrestrial planets, from 15 to 320 times the Earth s mass They are gaseous Low density All of them have rings
The Jovian planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Their masses are large compared with terrestrial planets, from 15 to 320 times the Earth s mass They are gaseous Low density All of them have rings
Lecture #27: Saturn. The Main Point. The Jovian Planets. Basic Properties of Saturn. Saturn:
 Lecture #27: Saturn Saturn: General properties. Atmosphere. Interior. Origin and evolution. Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Saturn) and 11.1. The Main Point Saturn is a large Jovian-class planet with a composition
Lecture #27: Saturn Saturn: General properties. Atmosphere. Interior. Origin and evolution. Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Saturn) and 11.1. The Main Point Saturn is a large Jovian-class planet with a composition
Object Type Moons Rings Planet Terrestrial none none. Max Distance from Sun. Min Distance from Sun. Avg. Distance from Sun 57,910,000 km 0.
 Mercury Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is extremely hot on the side of the planet facing the sun and very cold on the other. There is no water on the surface. There is practically no atmosphere.
Mercury Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is extremely hot on the side of the planet facing the sun and very cold on the other. There is no water on the surface. There is practically no atmosphere.
The Fathers of the Gods: Jupiter and Saturn
 The Fathers of the Gods: Jupiter and Saturn Learning Objectives! Order all the planets by size and distance from the Sun! How are clouds on Jupiter (and Saturn) different to the Earth? What 2 factors drive
The Fathers of the Gods: Jupiter and Saturn Learning Objectives! Order all the planets by size and distance from the Sun! How are clouds on Jupiter (and Saturn) different to the Earth? What 2 factors drive
ASTRO 120 Sample Exam
 ASTRO 120 Sample Exam 1) If a planet has a reasonably strong magnetic field, we know that a. It is made entirely of iron b. There is liquid nitrogen below the surface c. It can harbor life d. It has a
ASTRO 120 Sample Exam 1) If a planet has a reasonably strong magnetic field, we know that a. It is made entirely of iron b. There is liquid nitrogen below the surface c. It can harbor life d. It has a
Chapter 23. Our Solar System
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars.
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Chapter 10 The Outer Planets
 Chapter 10 The Outer Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Outer Worlds Beyond the orbit of Mars,
Chapter 10 The Outer Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Outer Worlds Beyond the orbit of Mars,
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Jupiter and Saturn. Guiding Questions. Long orbital periods of Jupiter and Saturn cause favorable viewing times to shift
 Jupiter and Saturn 1 2 Guiding Questions 1. Why is the best month to see Jupiter different from one year to the next? 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn?
Jupiter and Saturn 1 2 Guiding Questions 1. Why is the best month to see Jupiter different from one year to the next? 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn?
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 11. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 11 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 11 Jupiter Units of Chapter 11 11.1 Orbital and Physical Properties 11.2 Jupiter s Atmosphere Discovery 11.1 A Cometary
Lecture Outlines Chapter 11 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 11 Jupiter Units of Chapter 11 11.1 Orbital and Physical Properties 11.2 Jupiter s Atmosphere Discovery 11.1 A Cometary
The Outer Planets. Video Script: The Outer Planets. Visual Learning Company
 11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan November 16, 2017 I Jupiter 1. How do Jupiter s mass, size, day and year compare to Earth s? Mass: 318 Earth masses (or about 1/1000th the mass of the Sun). Radius:
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan November 16, 2017 I Jupiter 1. How do Jupiter s mass, size, day and year compare to Earth s? Mass: 318 Earth masses (or about 1/1000th the mass of the Sun). Radius:
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan December 6, 2016 I The Outer Planets in General 1. How do the sizes, masses and densities of the outer planets compare with the inner planets? The outer planets
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan December 6, 2016 I The Outer Planets in General 1. How do the sizes, masses and densities of the outer planets compare with the inner planets? The outer planets
Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets. 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal
 Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal What is a storm on Saturn like? The Giant Planets, Part 1 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal What is a storm on Saturn like? The Giant Planets, Part 1 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Inner and Outer Planets
 Inner and Outer Planets SPI 0607.6.2 Explain how the relative distance of objects from the earth affects how they appear. Inner Planets Terrestrial planets are those that are closest to the Sun. Terrestrial
Inner and Outer Planets SPI 0607.6.2 Explain how the relative distance of objects from the earth affects how they appear. Inner Planets Terrestrial planets are those that are closest to the Sun. Terrestrial
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems. Jovian Planet Composition. Are jovian planets all alike? Density Differences. Density Differences
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning:! Are jovian planets all alike?! What are jovian planets like on the inside?! What is the weather like on jovian
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning:! Are jovian planets all alike?! What are jovian planets like on the inside?! What is the weather like on jovian
Did you know that ALL Jovian Planets have rings??
 Outer Planets Did you know that ALL Jovian Planets have rings?? Jupiter: faint, dusty rings Saturn: bright, spectacular rings Uranus: dark, thin rings Neptune: dark, thin rings & ring arcs PLANET DATA
Outer Planets Did you know that ALL Jovian Planets have rings?? Jupiter: faint, dusty rings Saturn: bright, spectacular rings Uranus: dark, thin rings Neptune: dark, thin rings & ring arcs PLANET DATA
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems. Comparing the Jovian Planets. Jovian Planet Composition 4/10/16. Spacecraft Missions
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Interiors and Atmospheres How are jovian planets alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets? Do jovian
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Interiors and Atmospheres How are jovian planets alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets? Do jovian
The scientific theory I like best is that the rings of. Saturn are composed entirely of lost airline luggage. Mark Russell
 The scientific theory I like best is that the rings of Saturn are composed entirely of lost airline luggage. Mark Russell What We Will Learn Today Why does Saturn have such a low density and how does that
The scientific theory I like best is that the rings of Saturn are composed entirely of lost airline luggage. Mark Russell What We Will Learn Today Why does Saturn have such a low density and how does that
Lecture 24: Saturn. The Solar System. Saturn s Rings. First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: (where we have used Earth units)
 Lecture 24: Saturn The Solar System First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: Planet Distance Density Mass Mercury 0.4 1.0 0.06 Venus 0.7 0.9 0.8 Earth 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mars 1.5 0.7 0.1 (asteroid)
Lecture 24: Saturn The Solar System First we focus on solar distance, average density, and mass: Planet Distance Density Mass Mercury 0.4 1.0 0.06 Venus 0.7 0.9 0.8 Earth 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mars 1.5 0.7 0.1 (asteroid)
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM. James Martin. Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC
 OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
Chapter 8 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline. 8.1 The Galilean Moons of Jupiter. Moons, Rings, and Plutoids. 8.1 The Galilean Moons of Jupiter
 Lecture Outline Chapter 8 Moons, Rings, and Plutoids All four Jovian planets have extensive moon systems, and more are continually being discovered. The Galilean moons of Jupiter are those observed by
Lecture Outline Chapter 8 Moons, Rings, and Plutoids All four Jovian planets have extensive moon systems, and more are continually being discovered. The Galilean moons of Jupiter are those observed by
3. The name of a particularly large member of the asteroid belt is A) Halley B) Charon C) Eris D) Ceres E) Triton
 Summer 2013 Astronomy - Test 2 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Summer 2013 Astronomy - Test 2 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Solar System revised.notebook October 12, 2016 Solar Nebula Theory
 Solar System revised.notebook The Solar System Solar Nebula Theory Solar Nebula was a rotating disk of dust and gas w/ a dense center dense center eventually becomes the sun start to condense b/c of gravity
Solar System revised.notebook The Solar System Solar Nebula Theory Solar Nebula was a rotating disk of dust and gas w/ a dense center dense center eventually becomes the sun start to condense b/c of gravity
Human Understanding of both Earth and Space has Changed Over Time. Unit E: Topic One
 Human Understanding of both Earth and Space has Changed Over Time Unit E: Topic One 1.4 Our Solar Neighbourhood Nebular Hypothesis The theory of how solar systems are formed Evolution of solar system
Human Understanding of both Earth and Space has Changed Over Time Unit E: Topic One 1.4 Our Solar Neighbourhood Nebular Hypothesis The theory of how solar systems are formed Evolution of solar system
Unit 8. The Outer Planets
 Unit 8 The Outer Planets The Outer Worlds Beyond the orbit of Mars, the low temperatures of the solar nebula allowed condensing bodies there to capture hydrogen and hydrogen-rich gases This, together with
Unit 8 The Outer Planets The Outer Worlds Beyond the orbit of Mars, the low temperatures of the solar nebula allowed condensing bodies there to capture hydrogen and hydrogen-rich gases This, together with
Read each slide then use the red or some underlined words to complete the organizer.
 Read each slide then use the red or some underlined words to complete the organizer. 1B Did it start as a bang! 1B The Expanding Universe A. The Big Bang Theory: Idea that all matter began in an infinitely
Read each slide then use the red or some underlined words to complete the organizer. 1B Did it start as a bang! 1B The Expanding Universe A. The Big Bang Theory: Idea that all matter began in an infinitely
Physical Science 1 Chapter 16 INTRODUCTION. Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time.
 INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
Inner and Outer Planets
 Inner and Outer Planets Inner Planets Terrestrial planets are those that are closest to the Sun. Terrestrial planets are made mostly of rock and have similar characteristics to Earth. There are four terrestrial
Inner and Outer Planets Inner Planets Terrestrial planets are those that are closest to the Sun. Terrestrial planets are made mostly of rock and have similar characteristics to Earth. There are four terrestrial
Chapter 11 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Jovian Planet Systems Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian
Chapter 11 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian
known since prehistoric times almost 10 times larger than Jupiter
 Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune 40.329407-74.667345 Sun Mercury Length of rotation Temperature at surface 8 official planets large number of smaller objects including Pluto, asteroids,
Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune 40.329407-74.667345 Sun Mercury Length of rotation Temperature at surface 8 official planets large number of smaller objects including Pluto, asteroids,
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems. Jovian Planet Composition. Are jovian planets all alike? Density Differences. Density Differences
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe
 Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe The Formation of the Solar System Our Solar System includes: Planets Dwarf Planets Moons Small Solar System bodies Sun Outer portion created Planets and their
Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe The Formation of the Solar System Our Solar System includes: Planets Dwarf Planets Moons Small Solar System bodies Sun Outer portion created Planets and their
The Main Point. Planetary Ring Systems
 Lecture #31: Satellites and Rings II Ring Systems Overview of rings: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. What are rings made of? How do they form? Reading: Chapter 11.3. The Main Point All of the giant planets
Lecture #31: Satellites and Rings II Ring Systems Overview of rings: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. What are rings made of? How do they form? Reading: Chapter 11.3. The Main Point All of the giant planets
Our Sun. & the Planets. Sun and Planets.notebook. October 18, Our Sun (a quick review) Hydrogen is the main fuel source
 Sun and Planets.notebook October 18, 2016 Our Sun Our Sun (a quick review) Average size main sequence star Hydrogen is the main fuel source In about 5 billion years it will become a & the Planets red giant
Sun and Planets.notebook October 18, 2016 Our Sun Our Sun (a quick review) Average size main sequence star Hydrogen is the main fuel source In about 5 billion years it will become a & the Planets red giant
Chapter 10 Mars Friday, March 12, 2010
 Chapter 10 Mars 10.1 Orbital Properties Mars s orbit is fairly eccentric which affects amount of sunlight reaching it Mars can be either in the direction of the Sun (conjunction) or not (opposition) 10.2
Chapter 10 Mars 10.1 Orbital Properties Mars s orbit is fairly eccentric which affects amount of sunlight reaching it Mars can be either in the direction of the Sun (conjunction) or not (opposition) 10.2
Name: Date: Hour: 179 degrees celsius. 5% of Earth A 70 pound person would weigh 27 pounds on Mercury.
 Planet Exploration- http://www.kidsastronomy.com/solar_.htm Mercury 1 87.9 days 58.6 days 57 million Km 465 degrees celsius Minimum -184 degrees celsius 179 degrees celsius Moons Terrestrial or Gaseous?
Planet Exploration- http://www.kidsastronomy.com/solar_.htm Mercury 1 87.9 days 58.6 days 57 million Km 465 degrees celsius Minimum -184 degrees celsius 179 degrees celsius Moons Terrestrial or Gaseous?
Saturn and Planetary Rings 4/5/07
 Saturn and Planetary Rings Announcements Reading Assignment Chapter 15 5 th homework due next Thursday, April 12 (currently posted on the website). Reminder about term paper due April 17. There will be
Saturn and Planetary Rings Announcements Reading Assignment Chapter 15 5 th homework due next Thursday, April 12 (currently posted on the website). Reminder about term paper due April 17. There will be
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System
 Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 10 - SEARCHING FOR LIFE IN OUR SOLAR SYSTEM: THE OUTER PLANETS AND THEIR MOONS Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ JUPITER DIAMETER:
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 10 - SEARCHING FOR LIFE IN OUR SOLAR SYSTEM: THE OUTER PLANETS AND THEIR MOONS Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ JUPITER DIAMETER:
Solar System Research Teacher Notes The Sun
 The Sun G-type main sequence star (G2V), also known as a yellow dwarf Mass = 1.99 x 10 30 kg or 333,000 Earths. Volume = 1.41 x 10 18 km 3 or 1,300,000 Earths. Density (average) = 1.41 g/cm 3 or 0.255
The Sun G-type main sequence star (G2V), also known as a yellow dwarf Mass = 1.99 x 10 30 kg or 333,000 Earths. Volume = 1.41 x 10 18 km 3 or 1,300,000 Earths. Density (average) = 1.41 g/cm 3 or 0.255
Ag Earth Science Chapter 23
 Ag Earth Science Chapter 23 Chapter 23.1 Vocabulary Any of the Earth- like planets, including Mercury, Venus, and Earth terrestrial planet Jovian planet The Jupiter- like planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
Ag Earth Science Chapter 23 Chapter 23.1 Vocabulary Any of the Earth- like planets, including Mercury, Venus, and Earth terrestrial planet Jovian planet The Jupiter- like planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018
 Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018 Tidal locking We always see the same face of the Moon. This means: period of orbit = period of spin Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth Why? The tidal bulge in the solid
Moons of Sol Lecture 13 3/5/2018 Tidal locking We always see the same face of the Moon. This means: period of orbit = period of spin Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth Why? The tidal bulge in the solid
By Andrew Hartsel. and. Evelyne Ridinger
 By Andrew Hartsel and Evelyne Ridinger Time Line of Uranus 1781- Discovered 1783- Orbit Predicted 1784- Prediction fails- discover Neptune 1787- First two moons discovered- Titania and Oberon 1821- Bouvard
By Andrew Hartsel and Evelyne Ridinger Time Line of Uranus 1781- Discovered 1783- Orbit Predicted 1784- Prediction fails- discover Neptune 1787- First two moons discovered- Titania and Oberon 1821- Bouvard
Lesson 3 The Outer Planets
 Lesson 3 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 44 Content Vocabulary 45 Lesson Outline 46 MiniLab 48 Content Practice A 49 Content Practice B 50 Language Arts Support 51 Math Skills 53 School to
Lesson 3 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 44 Content Vocabulary 45 Lesson Outline 46 MiniLab 48 Content Practice A 49 Content Practice B 50 Language Arts Support 51 Math Skills 53 School to
11/11/08 Announce: Chapter 9. Jupiter. The Outer Worlds. Jupiter s Interior. Jupiter 11/11/2008. The Outer Planets
 11/11/08 Announce: Can take AST 302 for Advanced Honors credit Will be late for office hours tomorrow Thursday: Meet in Library 229 computer lab Project Part II Due Thursday Email in plain text (no Microsoft
11/11/08 Announce: Can take AST 302 for Advanced Honors credit Will be late for office hours tomorrow Thursday: Meet in Library 229 computer lab Project Part II Due Thursday Email in plain text (no Microsoft
Jupiter and Saturn: Lords of the Planets
 11/5/14 Jupiter and Saturn: Lords of the Planets Guiding Questions 1. Why is the best month to see Jupiter different from one year to the next? 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres
11/5/14 Jupiter and Saturn: Lords of the Planets Guiding Questions 1. Why is the best month to see Jupiter different from one year to the next? 2. Why are there important differences between the atmospheres
Mercury Named after: Mercury, the fast-footed Roman messenger of the gods. Mean Distance from the Sun: 57,909,175 km (35,983,093.1 miles) or 0.
 Mercury Named after: Mercury, the fast-footed Roman messenger of the gods. Mean Distance from the Sun: 57,909,175 km (35,983,093.1 miles) or 0.387 astronomical units Diameter: 4,879.4 km (3,031.92 miles)
Mercury Named after: Mercury, the fast-footed Roman messenger of the gods. Mean Distance from the Sun: 57,909,175 km (35,983,093.1 miles) or 0.387 astronomical units Diameter: 4,879.4 km (3,031.92 miles)
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
Chapter 8 Jovian Planet Systems How do jovian planets differ from terrestrials? They are much larger than terrestrial planets They do not have solid surfaces The things they are made of are quite different
TITAN MOON OF SATURN. ASTRO 101 Contributors: Duc Dinh, Spring 2016 Caroline Brandon, Fall Source:
 TITAN MOON OF SATURN ASTRO 101 Contributors: Duc Dinh, Spring 2016 Caroline Brandon, Fall 2014 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/titan_(moon) Discovered by Christiaan Huygens in 1655 Has a dense atmosphere
TITAN MOON OF SATURN ASTRO 101 Contributors: Duc Dinh, Spring 2016 Caroline Brandon, Fall 2014 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/titan_(moon) Discovered by Christiaan Huygens in 1655 Has a dense atmosphere
Edmonds Community College ASTRONOMY 100 Sample Test #2 Fall Quarter 2006
 Edmonds Community College ASTRONOMY 100 Sample Test #2 Fall Quarter 2006 Instructor: L. M. Khandro 10/19/06 Please Note: the following test derives from a course and text that covers the entire topic of
Edmonds Community College ASTRONOMY 100 Sample Test #2 Fall Quarter 2006 Instructor: L. M. Khandro 10/19/06 Please Note: the following test derives from a course and text that covers the entire topic of
Contents. Section 1: The Sun s Energy. Section 2: The Solar System. Section 3: The Moon
 Contents Section 1: The Sun s Energy 1. Earth s Powerhouse.... 3 2. Our Nuclear Furnace.... 7 3. Quiz 1.... 10 Section 2: The Solar System 4. Mercury, Venus, and Earth... 12 5. Mars and the Asteroid Belt....
Contents Section 1: The Sun s Energy 1. Earth s Powerhouse.... 3 2. Our Nuclear Furnace.... 7 3. Quiz 1.... 10 Section 2: The Solar System 4. Mercury, Venus, and Earth... 12 5. Mars and the Asteroid Belt....
12. Jovian Planet Systems Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison Wesley
 12. Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive 2. are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen compounds 3. have
12. Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive 2. are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen compounds 3. have
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems
 Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Chapter 11 Jovian Planet Systems 11.1 A Different Kind of Planet Our goals for learning: Are jovian planets all alike? What are jovian planets like on the inside? What is the weather like on jovian planets?
Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014
 1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
The Jovian Planets and Their Moons
 The Jovian Planets and Their Moons Jupiter 1 Physical Properties of Earth and Jupiter Jupiter Earth Equatorial lradius 11.2 R Earth 6378 km Mass 318 M Earth 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 1.34 g/cm 3 5.497
The Jovian Planets and Their Moons Jupiter 1 Physical Properties of Earth and Jupiter Jupiter Earth Equatorial lradius 11.2 R Earth 6378 km Mass 318 M Earth 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 1.34 g/cm 3 5.497
Astronomy I Exam 2 Sample
 NAME: Part I: Multiple Choice (2 points. ea.) Read carefully, choose the best answer 1. Which of the following occurs because of the orbital motion of the Earth about the Sun and cannot be accounted for
NAME: Part I: Multiple Choice (2 points. ea.) Read carefully, choose the best answer 1. Which of the following occurs because of the orbital motion of the Earth about the Sun and cannot be accounted for
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
