Extreme ultraviolet spectroscopy of highly charged argon ions at the Berlin EBIT
|
|
|
- Blaze Roy Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Extreme ultraviolet spectroscopy of highly charged argon ions at the Berlin EBIT C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, G. Fussmann, F.I. Allen Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Lehrstuhl Plasmaphysik, Newtonstraße 15, 1489 Berlin and Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM Association address: Abstract. Extreme ultraviolet radiation from highly charged argon was investigated at the Berlin Electron Beam Ion Trap with a m grazing incidence spectrometer. Lines in the wavelength range 15 to 66 Å originating from C-like Ar 1+ to Li-like Ar 15+ ions have been identified and are compared with database information from solar line lists and predictions. Line ratios for the observed resonance, intercombination and forbidden lines offer important diagnostic capabilities for low density, hot plasmas. 1. Introduction The observation of radiation in the extreme-ultraviolet spectral range (EUV) from highly charged ions provides a versatile diagnostic tool for low density, hot plasmas, such as laser-produced laboratory plasmas, fusion plasmas or the plasma of astrophysical objects [1]. With the availability of data from missions like the Solar Ultraviolet Measurements of Emitted Radiation (SUMER) [] there has been an increasing need for the comparison of astrophysical database information with experimental data obtained under well-controlled laboratory conditions. Information on the plasma state, the elemental abundance or temperature and density, can be inferred by measuring wavelengths and intensities of certain EUV spectral lines. However, conclusions about the intensity of observed spectral lines can only be drawn if a relationship between the measured line ratio and the excitation and emission of these lines exists under similar plasma conditions. This dependencies requires support by a theoretical model with ab initio calculations, which, on the other hand, requires verification by well-diagnosed experiments. An Electron Beam Ion Trap (EBIT) [3] provides a controlled laboratory plasma of highly charged ions being excited by an electron beam to emit radiation which is analysed by spectrometers. The conditions in an EBIT for the excitation of radiation resemble those of the upper solar atmosphere with similar electron densities (n e = 1 1 cm -3 ) and excitation primarily by electron collisions. EBIT can produce ions of any element of the periodic table in any charge state. Here, we want to focus on the investigation of the L-shell emission of argon ions. Argon is also abundant as a minor component of the solar atmosphere at temperatures of. to 1 kev emitting EUV spectral lines which are applied for diagnostics. c 7 Ltd 1
2 There is only scarce information on the L-shell emission of argon in line lists, e.g. NIST s Atomic Spectra Database has so far no entries for highly charged argon ions like C-like Ar 1+ to Li-like Ar 15+. Some information is collected in the Kelly tables [4] from solar line lists [5-7] and theta-pinch experiments [8]. A proposal by Feldman [1] points out a few specific line ratios suitable for diagnostics with reference to wavelengths predictions by Edlén [9] and solar line lists [5-7]. Recently spectral information on Ar 1+ became available by Liang et al. [1] applying the recently developed Flexible Atomic Code. At the Berlin EBIT we have measured the EUV radiation of O-like Ar 1+ to Li-like Ar 15+ ions in the wavelength range 15 to 7 Å. In the contribution here, we present a comparison with the wavelengths available for Ar 1+ to Ar 15+ ions.. Experimental method The Berlin EBIT uses a strongly compressed monoenergetic electron beam (6 to 9 ma) to produce highly charged ions by successive electron impact ionization. The ions are trapped radially by the space charge potential and excited by collisions with electrons [3]. Axial confinement is achieved by biasing ( V) the end sections of the drift tube structure which also allows periodical (1 ms) emptying of the trap to prevent accumulation of high-z background ions. The target specie argon is injected as neutral gas continuously into the trapping region. The acceleration voltage of the electron beam is set in order to produce a particular highest charge state determined by the ionization potential of the ion species. Decreasing the acceleration voltage systematically limits the highest possible ionization stage and one observes now the radiation pattern of that ion to disappear as soon as its charge state can no longer be produced. The electron beam energy E e is determined by the acceleration potential at the drift tube assembly, taking into account corrections for the space charge of the electron beam and the ion inventory of the trap. The uncertainty in E e is ± ev originating from the estimate of the number of trapped ions and E e has a spread of about 4 ev. The EUV radiation emitted from the ions is analyzed with a high-resolution Schwob-Fraenkel grazing-incidence spectrometer [11]. A 6 m curvature grazing-incidence Au-plated mirror focuses the radiation from the 7 µm diameter, 16 mm high excitation region in the trap on the 18 µm wide entrance slit of the spectrometer, which is equipped with a 6 l/mm grating mounted at an angle of o with a blaze angle of 3.5 o. The photons are detected by a MgF -coated microchannel-plate stack followed by a Ar 13+ Ar 13+ E e = 7 ev phosphor screen image intensifier 4 viewed by a thermoelectrically cooled 6 charge-coupled device camera. The detector assembly moves with high Ar 1+ Ar 1+ Ar 1+ E e = 66 ev precision along the Rowland circle, 4 recording spectral information in the 6 range 3 to 1 Å. The wavelength scale was calibrated using the Lyman E series of He + and well-known lines in e = 6 ev first and second order diffraction from 4 C- to Li-like Neon [4] s-4p s-5p 1s-3p Wavelength [ Å ] He + 1s-6p Lyman-series Wavelength [ Å ] 1s-p FIGURE 1. EUV-emission spectra of B-like Ar 13+ and C-like Ar 1+ ions at three different electron beam energies. The bottom plate shows the Lyman series of He + used to calibrate the wavelength axis.
3 3. Spectra Figure 1 shows an example of CCD images demonstrating the technique to limit the emission of ions in EBIT to a selected charge state. While for an electron beam energy of 7 ev we can clearly see the 43 and 57 Å lines of Ar 13+, these lines vanish in the 66 ev spectrum below the ionization threshold for Ar 1+ of 686 ev. In the third image E e =6 ev is close to the ionization energy (618 ev) of Ar 11+ and the Ar 1+ EUV radiation ceases. The panel at the bottom shows the Lyman series of singly charged He-ions used for calibration of the wavelength scale, running EBIT with a very high gas injection pressure and short confinement times to increase emission from low-z lowly charged ions. TABLE 1. EUV lines of Li-, Be- and B-like argon ions. Comparison of experimental wavelengths in [Å] from the Berlin EBIT with data from solar spectra and predictions. The total uncertainty in the measured wavelength is marked as [x]. The observed strength of the line is rated as vs (very strong), s (strong), m (moderate), w (weak) and vw (very weak). The Kelly tables [4] refer to solar line lists and experiments. The numbers proposed by Feldman [1] are based on predictions by Edlén [9]. The ground state (gs) of Li-like Ar 15+ 1s s S 1/ has an ionization potential I.P. of ev, of Be-like Ar 14+ 1s s 1 S, I.P ev and of B-like Ar 13+ 1s s p P 1/, I.P ev. bl marks a blend with lines from second order reflection. Ion lower level upper level Berlin EBIT wavelength wavelength strength Kelly [4] Feldman [1] Ar 15+ 1s s S 1/ 1s p P 3/ [6] vs a Ar 15+ 1s s S 1/ 1s p P 1/ [7] s a Ar 14+ 1s s 1 S 1s s p 1 P [1] vvs 1.15 b Ar 14+ 1s s 1 S 1s s p 3 P [13] w 44.1 b 44.1 c Ar 13+ s p P 1/ s p P 3/ [63] m 18.9 d 18.9 Ar 13+ s p P 1/ s p P 1/ [54] m d Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p P 3/ [5] vs d Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p P 1/ [51] s d Ar 13+ s p P 1/ s p S 1/ [5] vs d Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p S 1/ [63] w 3.35 d Ar 13+ s p 4 P 1/ p 3 4 S 3/ 4.8 [5] vw 4.64 d Ar 13+ s p 4 P 3/ p 3 4 S 3/ 8.98 [6] vw 8.31 d 8.39 Ar 13+ s p 4 P 5/ p 3 4 S 3/ 13. [31] vw 13.4 d Ar 13+ s p P 1/ s p D 3/ [95] s d Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p D 5/ [39] m d Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p D 3/ [45] m d Ar 13+ s p P 1/ p 3 D 3/ [6] vs 376. Ar 13+ s p P 3/ p 3 D 5/ [1] s Ar 13+ s p P 1/ s p 4 P 3/ [97] vw 4.37 Ar 13+ s p P 1/ s p 4 P 1/ [44]bl w Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p 4 P 5/ [76] vw Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p 4 P 3/ [95] vw Ar 13+ s p P 3/ s p 4 P 1/ [9] vw a solar line list, Sandlin et al. [5] b Ref. [7] and solar line list, Sandlin et al. [5] c solar line list, Dere [6] d theta-pinch plasma experiment [8] 3
4 For the evaluation of accurate line positions a horizontal, central 1 pixel wide strip was binned perpendicular to the dispersion direction to circumvent the slight curvature of the slit image on the CCD blurring the wavelength information. Peaks in the binned spectra are fitted with Gaussian functions and the results are summarized in Tables 1 and. TABLE. EUV lines from C-like argon ions (Ar 1+ ), gs 1s s p 3 P, I.P ev. Comparison of experimental wavelengths from the Berlin EBIT with predictions from the Kelly data tables [4], Feldman [1] and Liang [1]. lower level upper level Berlin EBIT wavelength wavelength strength Kelly [4] Feldman [1] Liang [1] s p 3 P s p 3 3 S [7] w a s p 3 P 1 s p 3 3 S [9] w a s p 1 D s p 3 1 P [78] m a s p 3 P s p 3 3 S [54] s a s p 1 D s p 3 1 D [77] s b s p 1 S s p 3 1 P [5] w b s p 3 P s p 3 3 P [58] m 1.69 b s p 3 P 1 s p 3 3 P 5.57 [51] w 5.4 b 5.87 s p 3 P 1 s p 3 3 P [1] m 5.77 b 5.84 s p 3 P 1 s p 3 3 P [6] s 5.94 b 5.95 s p 3 P s p 3 3 P [68] vs 1.46 b s p 3 P s p 3 3 P [113] s 11. b s p 3 P s p 3 3 D [1] m 36.7 b s p 3 P 1 s p 3 3 D [79] vvw 41.9 b s p 3 P 1 s p 3 3 D [1] s 4. b 4.4 s p 3 P s p 3 3 D [9] s b s p 3 P s p 3 3 D [35] w b s p 3 P 1 s p 3 5 S [94] vvw 46.8 c d s p 3 P s p 3 5 S [7] m 49. c d s p 3 P 1 s p 1 S [89] w 657 e f a Deutschman et al. [1] b theta-pinch plasma experiment [8] c Kastner et al. [13] d predicted by Edlén [14] e Kelly tables [4] and theta-pinch plasma experiment [8] f Feldman et al. [15] 4. Comparison with database information The observed spectral lines are identified by cross-referencing to previous measurements and multichannel Dirac-Fock calculations by Edlén. The two measured Ar 15+ EUV lines connect the excited 1s p P 1/ and P 3/ levels with the ground state. These two levels can also be fed by the so-called j and k satellites of Li-like argon observed in the x-ray spectral region. The line ratio of these satellites populated by dielectronic recombination and the w-resonance line of He-like Ar 16+ serves as a temperature diagnostic for hot plasmas [16]. The accuracy of the measured EUV lines around 36 Å is improved by the fact that calibration lines could be recorded with the same spectrometer settings. 4
5 Binding energy with respect to Ar 14+ [ ev ] s s 1 S Ar Å 8.6ms M1 1s s p 194.4Å 3.4Å S 1/ 191.4Å 1s s p 1s s p 18.3Å 183.4Å 187.9Å Å 1s p Å P 1/ P 3/ 57.9Å 43.9Å 57.4Å 464.6Å D 3/ D 5/ 1s s p 484.9Å 441.1Å 4.5Å P 3/ Ar 13+ P 1/ D 5/ 3/ 436.7Å 4.3Å 4 P 1s s p 1s p 3 8.9Å 13.Å 5/ 3/ 1/ 4 S 3/ FIGURE. Energy level diagram for Ar 13+ showing transitions observed in the EUV spectral range. The first excited level decays via an M1 transition to the ground state. The wavelengths are measured values. For Be-like Ar 14+, the resonance line (s 1 S sp 1 P 1 ) at 1.16 Å and the intercombination line (s 1 S sp 3 P 1 ) at 44. Å are recorded, these being of special interest. In low density plasmas, e.g. active solar plasma regions, the sp 3 P 1 level can be depopulated significantly by electron collisions. The line ratio between the intercombination and the resonance line can therefore become sensitive to the electron density of the plasma [1]. At 1 kev EBIT beam energy and an electron density of 1 1 cm -3 a line ratio of 1.4±.4 % was estimated. A further advantage of this line ratio is the fact that for spectrometers which allow detection of second order diffracted lines, both the resonance and the intercombination line can be observed with the same spectrometer settings at nearby wavelengths. B-like Ar 13+ has a particular structure of energy levels with an excited level in near proximity of the ground state (Figure ). This sp P 3/ level decays with a radiative life time of about 9 ms via M1 emission at 441 Å to the P 1/ ground state and is used as diagnostic of the ion cloud distribution in EBIT and as a high precision test of QED [17]. All the EUV lines feeding the P 1/ ground state and the closely-lying P 3/ level have been recorded. The intercombination lines and 4.5 Å from the transitions s p P sp 4 P and the much stronger and Å lines originating from highly excited levels are considered to be valuable temperature diagnostic for plasmas. In Table we summarize the observed EUV lines for C-like Ar 1+. The weak forbidden transition s p 3 P 1 s p 1 S at 659 Å and two intercombination lines for transitions s p 3 P 1, s p 3 5 S around 48 Å have been observed in agreement with predictions by Edlén [14] and the solar line list [15]. Several lines for transitions between highly excited levels have been measured in the wavelength range 16 to 5 Å and have previously been found in theta-pinch experiments [8]. Recently these lines have been calculated with the Flexible Atomic Code. This package calculates the atomic structure; atomic radiative and collisional processes based on relativistic configuration interaction with independent particle basis wavefunctions. 5
6 References [1] U. Feldman, Phys. Scr. 63, 76 (1). [] K. Wilhelm et al., Solar Phys. 16, 189 (1995). [3] C. Biedermann, A. Förster, G. Fußmann, R. Radtke, Phys. Scr. T73, 36 (1997). [4] R.L. Kelly, Phys. Chem. Ref. Data Vol. 16 Suppl. 1 (1987). [5] G.D. Sandlin, G.E. Brueckner, V.E. Scherrer, and R. Tousey, Astrophys. J. 5, L47, (1976). [6] K.P. Dere, Astrophys. J. 1, 16 (1978). [7] K.G. Widing, Astrophys. J. 197, L33 (1975). [8] B.C. Fawcett, A.H. Gabriel and T.W. Paget, J. Phys. B 4, 986 (1971). [9] B. Edlén, Phys. Scr. 8, 483 (1983). [1] G. Liang, G. Dong, J. Zeng, At. Data and Nucl. Data Tables 88, 83 (4). [11] C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, J.L. Schwob, P. Mandelbaum, R. Doron, T. Fuchs, G. Fußmann, Phys. Scr. T9, 85 (1). [1] W.A. Deutschman and L.L. House, Astrophys. J. 149, 451 (1967). [13] S.O. Kastner, A.K. Bhatia, and L. Cohen, Phys. Scr. 15, 59 (1977). [14] B. Edlén, Phys. Scr. 31, 345 (1985). [15] U. Feldman, W. Curdt, E. Landi, and K. Wilhelm, Astrophys. J. 544, 58 (). [16] C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, K.B. Fournier, Phys. Rev. E66, 6644 (). [17] I. Draganic, J.R Crespo López-Urrutia, R. Dubois, S. Fritzsch, V.M. Shabaev, R. Soria Orts, II. Tupitsyn, Y. Zou, and J. Ullrich, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 1831 (3). 6
EUV spectra from the NIST EBIT
 EUV spectra from the NIST EBIT D. Kilbane and G. O Sullivan Atomic and Molecular Plasma Physics group, UCD, Ireland J. D. Gillaspy, Yu. Ralchenko and J. Reader National Institute of Standards and Technology,
EUV spectra from the NIST EBIT D. Kilbane and G. O Sullivan Atomic and Molecular Plasma Physics group, UCD, Ireland J. D. Gillaspy, Yu. Ralchenko and J. Reader National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Line ratios and wavelengths of helium-like argon n = 2 satellite transitions and resonance lines
 1 Line ratios and wavelengths of helium-like argon n = 2 satellite transitions and resonance lines C. Biedermann a, R. Radtke a, and K. Fournier b a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Bereich Plasmadiagnostik,
1 Line ratios and wavelengths of helium-like argon n = 2 satellite transitions and resonance lines C. Biedermann a, R. Radtke a, and K. Fournier b a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Bereich Plasmadiagnostik,
NIST Research on Spectroscopy and Collisional-Radiative Modeling of Highly-Charged Ions of Tungsten
 NIST Research on Spectroscopy and Collisional-Radiative Modeling of Highly-Charged Ions of Tungsten Yuri Ralchenko National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, USA Vienna, Austria, Dec
NIST Research on Spectroscopy and Collisional-Radiative Modeling of Highly-Charged Ions of Tungsten Yuri Ralchenko National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, USA Vienna, Austria, Dec
Investigation of M1 transitions of the ground-state configuration of In-like Tungsten
 Investigation of M1 transitions of the ground-state configuration of In-like Tungsten W Li 1,2,3, J Xiao 1,2, Z Shi 1,2a, Z Fei 1,2b, R Zhao 1,2c, T Brage 3, S Huldt, R Hutton 1, 2 * and Y Zou 1,2 * 1
Investigation of M1 transitions of the ground-state configuration of In-like Tungsten W Li 1,2,3, J Xiao 1,2, Z Shi 1,2a, Z Fei 1,2b, R Zhao 1,2c, T Brage 3, S Huldt, R Hutton 1, 2 * and Y Zou 1,2 * 1
This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract
 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-7NA27344. Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC The ITER tokamak Tungsten (W) is attractive as
This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-7NA27344. Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC The ITER tokamak Tungsten (W) is attractive as
First Experiments with the Greifswald EBIT
 First Experiments with the Greifswald EBIT B Schabinger 1, C Biedermann 2, S Gierke 1, G Marx 1, R Radtke 1,2 and L Schweikhard 1 1 Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald, Institute of Physics, Felix-Hausdorff-Str.
First Experiments with the Greifswald EBIT B Schabinger 1, C Biedermann 2, S Gierke 1, G Marx 1, R Radtke 1,2 and L Schweikhard 1 1 Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald, Institute of Physics, Felix-Hausdorff-Str.
Plasma-Related Atomic Physics with an Electron Beam Ion Trap
 Plasma-Related Atomic Physics with an Electron Beam Ion Trap Nobuyuki NAKAMURA Institute for Laser Science, The University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo 182-8585, Japan (Received 20 May 2013 / Accepted
Plasma-Related Atomic Physics with an Electron Beam Ion Trap Nobuyuki NAKAMURA Institute for Laser Science, The University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo 182-8585, Japan (Received 20 May 2013 / Accepted
Spectroscopic studies of impurities in the LHD plasmas
 Spectroscopic studies of impurities in the LHD plasmas Visitor: Zhenwei Wu (the institute of plasma physics, CAS -ASIPP) Host: Shigeru Morita (the national institute for fusion science -NIFS) Content 1.
Spectroscopic studies of impurities in the LHD plasmas Visitor: Zhenwei Wu (the institute of plasma physics, CAS -ASIPP) Host: Shigeru Morita (the national institute for fusion science -NIFS) Content 1.
Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations
 Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations S.J. McNaught, J. Fan, E. Parra and H.M. Milchberg Institute for Physical Science and Technology University of Maryland College
Laser heating of noble gas droplet sprays: EUV source efficiency considerations S.J. McNaught, J. Fan, E. Parra and H.M. Milchberg Institute for Physical Science and Technology University of Maryland College
The wavelength reconstruction from toroidal spectrometer image data
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIII 165 The wavelength reconstruction from toroidal spectrometer image data J. Blazej 1, M. Tamas 1, L. Pina 1, A. Jancarek 1, S. Palinek 1, P. Vrba
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIII 165 The wavelength reconstruction from toroidal spectrometer image data J. Blazej 1, M. Tamas 1, L. Pina 1, A. Jancarek 1, S. Palinek 1, P. Vrba
The Extreme Ultraviolet Emissions of W 23+ (4f 5 )
 The Extreme Ultraviolet Emissions of W 23+ (4f 5 ) T Pütterich, V. Jonauskas, R Neu, R Dux and ASDEX Upgrade Team Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM Association, D 85748 Garching, Germany Institute
The Extreme Ultraviolet Emissions of W 23+ (4f 5 ) T Pütterich, V. Jonauskas, R Neu, R Dux and ASDEX Upgrade Team Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM Association, D 85748 Garching, Germany Institute
Spectroscopy for planetary upper atmospheres きょくたん
 Spectroscopy for planetary upper atmospheres きょくたん Spectrum of Venus atmosphere Spectrum of Jupiter and Io Figure 1. An EUV spectrum measured by Hisaki spacecraft. The spectrograph mixes spatial and spectral
Spectroscopy for planetary upper atmospheres きょくたん Spectrum of Venus atmosphere Spectrum of Jupiter and Io Figure 1. An EUV spectrum measured by Hisaki spacecraft. The spectrograph mixes spatial and spectral
Identification and Plasma Diagnostics Study of Extreme Ultraviolet Transitions in Highly Charged Yttrium
 atoms Article Identification and Plasma Diagnostics Study of Extreme Ultraviolet Transitions in Highly Charged Yttrium Roshani Silwal 1,2,, Endre Takacs 1,2, Joan M. Dreiling 2, John D. Gillaspy 2,3 and
atoms Article Identification and Plasma Diagnostics Study of Extreme Ultraviolet Transitions in Highly Charged Yttrium Roshani Silwal 1,2,, Endre Takacs 1,2, Joan M. Dreiling 2, John D. Gillaspy 2,3 and
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
DETERMINATION OF THE FORMATION TEMPERATURE OF Si IV IN THE SOLAR TRANSITION REGION
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 477 : L119 L122, 1997 March 10 1997. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DETERMINATION OF THE FORMATION TEMPERATURE OF Si IV IN THE SOLAR
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 477 : L119 L122, 1997 March 10 1997. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DETERMINATION OF THE FORMATION TEMPERATURE OF Si IV IN THE SOLAR
arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 10 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 10 Oct 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 10 Oct 2013](/thumbs/94/118719103.jpg) Cascade emission in electron beam ion trap plasma Valdas Jonauskas a, Šarūnas Masysa, Aušra Kynienė a, Gediminas Gaigalas a arxiv:1210.5742v2 [physics.atom-ph] 10 Oct 2013 a Institute of Theoretical Physics
Cascade emission in electron beam ion trap plasma Valdas Jonauskas a, Šarūnas Masysa, Aušra Kynienė a, Gediminas Gaigalas a arxiv:1210.5742v2 [physics.atom-ph] 10 Oct 2013 a Institute of Theoretical Physics
Survey of EUV Impurity Line Spectra and EUV Bremsstrahlung Continuum in LHD )
 Plasma and Fusion Research: Regular Articles Volume 6, 2402078 (2011) Survey of EUV Impurity Line Spectra and EUV Bremsstrahlung Continuum in LHD ) Chunfeng DONG, Shigeru MORITA 1), Malay Bikas CHOWDHURI
Plasma and Fusion Research: Regular Articles Volume 6, 2402078 (2011) Survey of EUV Impurity Line Spectra and EUV Bremsstrahlung Continuum in LHD ) Chunfeng DONG, Shigeru MORITA 1), Malay Bikas CHOWDHURI
Extension of Wavelength Range in Absolute Intensity Calibration of Space-Resolved EUV Spectrometer for LHD Diagnostics )
 Extension of Wavelength Range in Absolute Intensity Calibration of Space-Resolved EUV Spectrometer for LHD Diagnostics ) Chunfeng DONG 1), Shigeru MORITA 1,2), Motoshi GOTO 1,2) and Erhui WANG 2) 1) National
Extension of Wavelength Range in Absolute Intensity Calibration of Space-Resolved EUV Spectrometer for LHD Diagnostics ) Chunfeng DONG 1), Shigeru MORITA 1,2), Motoshi GOTO 1,2) and Erhui WANG 2) 1) National
Solar UV Spectroscopy and Coronagraphy
 Solar UV Spectroscopy and Coronagraphy Werner Curdt Outline motivation the Sun s electromagnetic spectrum spectroscopic methods observational examples instrumental aspects optical design detectors others
Solar UV Spectroscopy and Coronagraphy Werner Curdt Outline motivation the Sun s electromagnetic spectrum spectroscopic methods observational examples instrumental aspects optical design detectors others
EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS
 Chapter 7 EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS Hot dense plasma lasing medium d θ λ λ Visible laser pump Ch07_00VG.ai The Processes of Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission Absorption
Chapter 7 EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET AND SOFT X-RAY LASERS Hot dense plasma lasing medium d θ λ λ Visible laser pump Ch07_00VG.ai The Processes of Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission Absorption
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
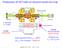 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics
 Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
Line analysis of EUV Spectra from Molybdenum and Tungsten Injected with Impurity Pellets in LHD
 Line analysis of EUV Spectra from Molybdenum and Tungsten Injected with Impurity Pellets in LHD Malay Bikas CHOWDHURI, Shigeru MORITA 1),Motoshi GOTO 1), Hiroaki NISHIMURA 2),Keiji NAGAI and Shinsuke FUJIOKA
Line analysis of EUV Spectra from Molybdenum and Tungsten Injected with Impurity Pellets in LHD Malay Bikas CHOWDHURI, Shigeru MORITA 1),Motoshi GOTO 1), Hiroaki NISHIMURA 2),Keiji NAGAI and Shinsuke FUJIOKA
Plasma Radiation. Ø Free electrons Blackbody emission Bremsstrahlung
 Plasma Radiation Ø Free electrons Blackbody emission Bremsstrahlung Ø Bound electrons (Z>2) Unresolved, multi-line emission Resolved line emission -- Single Z +n Objective Infer a thermodynamic quantity
Plasma Radiation Ø Free electrons Blackbody emission Bremsstrahlung Ø Bound electrons (Z>2) Unresolved, multi-line emission Resolved line emission -- Single Z +n Objective Infer a thermodynamic quantity
Overview of observational methods and instruments: spectrographs. Sergei Shestov
 Overview of observational methods and instruments: spectrographs Sergei Shestov 7 Feb 2018 SIDC seminar: spectrographs 2 Outline Scientific importance of spectroscopic observations Solar spectra Methods
Overview of observational methods and instruments: spectrographs Sergei Shestov 7 Feb 2018 SIDC seminar: spectrographs 2 Outline Scientific importance of spectroscopic observations Solar spectra Methods
Impurity accumulation in the main plasma and radiation processes in the divetor plasma of JT-60U
 1 EX/P4-25 Impurity accumulation in the main plasma and radiation processes in the divetor plasma of JT-6U T. Nakano, H. Kubo, N. Asakura, K. Shimizu and S. Higashijima Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Naka,
1 EX/P4-25 Impurity accumulation in the main plasma and radiation processes in the divetor plasma of JT-6U T. Nakano, H. Kubo, N. Asakura, K. Shimizu and S. Higashijima Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Naka,
Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser pulse irradiation
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 365 371 Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 365 371 Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser
The Performance of the EUV Spectroscope (EXCEED) Onboard the SPRINT-A Mission
 The Performance of the EUV Spectroscope (EXCEED) Onboard the SPRINT-A Mission K. Yoshioka, G. Murakami, A. Yamazaki, K. Uemizu, T. Kimura (ISAS/JAXA), I. Yoshikawa, K. Uji (Univ. Tokyo) F. Tsuchiya, and
The Performance of the EUV Spectroscope (EXCEED) Onboard the SPRINT-A Mission K. Yoshioka, G. Murakami, A. Yamazaki, K. Uemizu, T. Kimura (ISAS/JAXA), I. Yoshikawa, K. Uji (Univ. Tokyo) F. Tsuchiya, and
Cascade emission in electron beam ion trap plasma of W 25+ ion
 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Cascade emission in electron beam ion trap plasma of W 25+ ion V. Jonauskas a,, T. Pütterich b, S. Kučas a, Š. Masysa, A. Kynienė a, G. Gaigalas a, R. Kisielius a, L. Radžiūtė a, P. Rynkun
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Cascade emission in electron beam ion trap plasma of W 25+ ion V. Jonauskas a,, T. Pütterich b, S. Kučas a, Š. Masysa, A. Kynienė a, G. Gaigalas a, R. Kisielius a, L. Radžiūtė a, P. Rynkun
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008](/thumbs/92/108661452.jpg) New EUV Fe IX emission line identifications from Hinode/EIS P. R. Young Space Science Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 20375 arxiv:0810.5028v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008 George Mason University,
New EUV Fe IX emission line identifications from Hinode/EIS P. R. Young Space Science Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 20375 arxiv:0810.5028v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008 George Mason University,
Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga
 Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
PFC/JA Precision Measurements of the Wavelengths of Emission Lines of Mg-like and Na-like Kv in Alcator C Plasmas
 PFC/JA-86-43 Precision Measurements of the Wavelengths of Emission Lines of Mg-like and Na-like Kv in Alcator C Plasmas K. Kondo, J.L. Terry, J. E. Rice, E. S. Marmar Plasma Fusion Center Massachusetts
PFC/JA-86-43 Precision Measurements of the Wavelengths of Emission Lines of Mg-like and Na-like Kv in Alcator C Plasmas K. Kondo, J.L. Terry, J. E. Rice, E. S. Marmar Plasma Fusion Center Massachusetts
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects
 AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
Aspects and prospects of
 Equation 23 of Radiative Transfer rd Meeting of the Atomic and Molecular Data Centres Network Aspects and prospects of KAERI atomic data center Duck-Hee Kwon and Kil-Byoung Chai Nuclear Data Center Korea
Equation 23 of Radiative Transfer rd Meeting of the Atomic and Molecular Data Centres Network Aspects and prospects of KAERI atomic data center Duck-Hee Kwon and Kil-Byoung Chai Nuclear Data Center Korea
Observation of Tungsten Line Emissions in Wavelength Range of Å in Large Helical Device )
 Observation of Tungsten Line Emissions in Wavelength Range of 10-500 Å in Large Helical Device ) Yang LIU 1), Shigeru MORITA 1,2), Tetsutarou OISHI 1,2), Motoshi GOTO 1,2) and Xianli HUANG 2) 1) Department
Observation of Tungsten Line Emissions in Wavelength Range of 10-500 Å in Large Helical Device ) Yang LIU 1), Shigeru MORITA 1,2), Tetsutarou OISHI 1,2), Motoshi GOTO 1,2) and Xianli HUANG 2) 1) Department
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES
 THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black
 Report EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black S. Döring, Dr. K. Mann Laser-Laboratorium Göttingen e.v. October 28, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Setup 3 3 Measurements 4 4 Conclusion
Report EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black S. Döring, Dr. K. Mann Laser-Laboratorium Göttingen e.v. October 28, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Setup 3 3 Measurements 4 4 Conclusion
Progress at the Heidelberg EBIT
 Progress at the Heidelberg EBIT J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, J. Braun, G. Brenner, H. Bruhns, C. Dimopoulou, I. N. Draganić, D. Fischer, A. J. González Martínez, A. Lapierre, V. Mironov, R. Moshammer, R.
Progress at the Heidelberg EBIT J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, J. Braun, G. Brenner, H. Bruhns, C. Dimopoulou, I. N. Draganić, D. Fischer, A. J. González Martínez, A. Lapierre, V. Mironov, R. Moshammer, R.
Measurement and Modeling of Density-Sensitive Lines of Fe XIII in the Extreme Ultraviolet
 LLNL-JRNL-400639 Measurement and Modeling of Density-Sensitive Lines of Fe XIII in the Extreme Ultraviolet N. Yamamoto, T. Kato, P. Beiersdorfer, J. K. Lepson January 22, 2008 Astrophysical Journal Disclaimer
LLNL-JRNL-400639 Measurement and Modeling of Density-Sensitive Lines of Fe XIII in the Extreme Ultraviolet N. Yamamoto, T. Kato, P. Beiersdorfer, J. K. Lepson January 22, 2008 Astrophysical Journal Disclaimer
Study of Electron Energy and Angular Distributions and Calculations of X-ray, EUV Line Flux and Rise Times
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1987) 8, 263 270 Study of Electron Energy and Angular Distributions and Calculations of X-ray, EUV Line Flux and Rise Times Ranjna Bakaya, Sunil Peshin, R. R. Rausaria & P. N. Khosa
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1987) 8, 263 270 Study of Electron Energy and Angular Distributions and Calculations of X-ray, EUV Line Flux and Rise Times Ranjna Bakaya, Sunil Peshin, R. R. Rausaria & P. N. Khosa
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
LINE INTENSITY RATIOS IN THE EIS RANGE SENSITIVE TO ELECTRON DENSITIES IN 10 7 K PLASMAS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 679:843Y847, 2008 May 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. LINE INTENSITY RATIOS IN THE EIS RANGE SENSITIVE TO ELECTRON DENSITIES
The Astrophysical Journal, 679:843Y847, 2008 May 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. LINE INTENSITY RATIOS IN THE EIS RANGE SENSITIVE TO ELECTRON DENSITIES
Assessment of the Azimuthal Homogeneity of the Neutral Gas in a Hall Effect Thruster using Electron Beam Fluorescence
 Assessment of the Azimuthal Homogeneity of the Neutral Gas in a Hall Effect Thruster using Electron Beam Fluorescence IEPC-2015-91059 / ISTS-2015-b-91059 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International
Assessment of the Azimuthal Homogeneity of the Neutral Gas in a Hall Effect Thruster using Electron Beam Fluorescence IEPC-2015-91059 / ISTS-2015-b-91059 Presented at Joint Conference of 30th International
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
 X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Louis Scudiero http://www.wsu.edu/~scudiero; 5-2669 Fulmer 261A Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) The basic principle of the photoelectric effect
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Louis Scudiero http://www.wsu.edu/~scudiero; 5-2669 Fulmer 261A Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) The basic principle of the photoelectric effect
Application of atomic data to quantitative analysis of tungsten spectra on EAST tokamak
 Technical Meeting on Uncertainty Assessment and Benchmark Experiments for Atomic and Molecular Data for Fusion Applications, 19-21 December 2016, Vienna, Austria Application of atomic data to quantitative
Technical Meeting on Uncertainty Assessment and Benchmark Experiments for Atomic and Molecular Data for Fusion Applications, 19-21 December 2016, Vienna, Austria Application of atomic data to quantitative
Energy Dependence of Angular Momentum Capture States in Charge Exchange Collisions between Slow Highly Charged Argon Ions and Argon Neutrals
 Energy Dependence of Angular Momentum Capture States in Charge Exchange Collisions between Slow Highly Charged Argon Ions and Argon Neutrals F.I. Allen, C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, and G. Fussmann Lehrstuhl
Energy Dependence of Angular Momentum Capture States in Charge Exchange Collisions between Slow Highly Charged Argon Ions and Argon Neutrals F.I. Allen, C. Biedermann, R. Radtke, and G. Fussmann Lehrstuhl
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
 X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Louis Scudiero http://www.wsu.edu/~scudiero; 5-2669 Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) The basic principle of the photoelectric effect was enunciated
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Louis Scudiero http://www.wsu.edu/~scudiero; 5-2669 Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) The basic principle of the photoelectric effect was enunciated
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering
 X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Fusion Plasma Modelling using Atomic and Molecular Data January 2012
 2327-4 Joint ICTP- Workshop on Fusion Plasma Modelling using Atomic and Molecular Data 23-27 January 2012 Atomic Processes Modeling in Plasmas Modeling Spectroscopic Observables from Plasmas Hyun-Kyung
2327-4 Joint ICTP- Workshop on Fusion Plasma Modelling using Atomic and Molecular Data 23-27 January 2012 Atomic Processes Modeling in Plasmas Modeling Spectroscopic Observables from Plasmas Hyun-Kyung
188 L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski temperature. Some examples of the registered X-ray images are shown in Fig.1. Figure 1. X-ray pinhole images from
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 32, no. 1, March, 2002 187 Hot-Spots in Plasma-Focus Discharges as Intense Sources of Different Radiation Pulses L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski The Andrzej Soltan Institute
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 32, no. 1, March, 2002 187 Hot-Spots in Plasma-Focus Discharges as Intense Sources of Different Radiation Pulses L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski The Andrzej Soltan Institute
Relativistic Calculations for Be-like Iron
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 468 472 Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 2, August 15, 2008 Relativistic Calculations for Be-like Iron YANG Jian-Hui, 1 LI Ping, 2, ZHANG Jian-Ping,
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 468 472 Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 2, August 15, 2008 Relativistic Calculations for Be-like Iron YANG Jian-Hui, 1 LI Ping, 2, ZHANG Jian-Ping,
Estimating the plasma flow in a recombining plasma from
 Paper P3-38 Estimating the plasma flow in a recombining plasma from the H α emission U. Wenzel a, M. Goto b a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik (IPP) b National Institute for Fusion Science, Toki 509-5292,
Paper P3-38 Estimating the plasma flow in a recombining plasma from the H α emission U. Wenzel a, M. Goto b a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik (IPP) b National Institute for Fusion Science, Toki 509-5292,
Two-electron systems
 Two-electron systems Laboratory exercise for FYSC11 Instructor: Hampus Nilsson hampus.nilsson@astro.lu.se Lund Observatory Lund University September 12, 2016 Goal In this laboration we will make use of
Two-electron systems Laboratory exercise for FYSC11 Instructor: Hampus Nilsson hampus.nilsson@astro.lu.se Lund Observatory Lund University September 12, 2016 Goal In this laboration we will make use of
Construction of an extreme ultraviolet polarimeter based on highorder harmonic generation
 Construction of an extreme ultraviolet polarimeter based on highorder harmonic generation N. Brimhall *, J. C. Painter, M. Turner, S. V. Voronov, R. S. Turley, M. Ware, and J. Peatross Department of Physics
Construction of an extreme ultraviolet polarimeter based on highorder harmonic generation N. Brimhall *, J. C. Painter, M. Turner, S. V. Voronov, R. S. Turley, M. Ware, and J. Peatross Department of Physics
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 133 PROFESSOR: SHER. Atomic Spectra. Benjamin Stahl
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 133 PROFESSOR: SHER Atomic Spectra Benjamin Stahl Lab Partners: Aaron Lopez & Dillon Teal April 2, 2014 Abstract As an introduction to spectroscopy,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 133 PROFESSOR: SHER Atomic Spectra Benjamin Stahl Lab Partners: Aaron Lopez & Dillon Teal April 2, 2014 Abstract As an introduction to spectroscopy,
Bohr-Coster diagrams for multiply ionized states of light elements in the range Z--10 to 20
 Pramhn.a-J. Phys., Vol. 29, No. 3, September 1987, pp. 253-260. Printed in India. Bohr-Coster diagrams for multiply ionized states of light elements in the range Z--10 to 20 LAKSH'MI NATARAJAN, A V TANKHIWALE
Pramhn.a-J. Phys., Vol. 29, No. 3, September 1987, pp. 253-260. Printed in India. Bohr-Coster diagrams for multiply ionized states of light elements in the range Z--10 to 20 LAKSH'MI NATARAJAN, A V TANKHIWALE
Atomic structure and dynamics
 Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
PHYS General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source. c = speed of light = 3 x 10 8 m/s
 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
Detecting high energy photons. Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples)
 Detecting high energy photons Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples) Interactions of high energy photons with matter Cross section/attenution length/optical depth Photoelectric
Detecting high energy photons Interactions of photons with matter Properties of detectors (with examples) Interactions of high energy photons with matter Cross section/attenution length/optical depth Photoelectric
AG Draconis. A high density plasma laboratory. Dr Peter Young Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B.
 AG Draconis A high density plasma laboratory Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B. Ake p.r.young@rl.ac.uk Overview CHIANTI database Symbiotic Stars AG Draconis FUSE FUSE observations of AG
AG Draconis A high density plasma laboratory Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B. Ake p.r.young@rl.ac.uk Overview CHIANTI database Symbiotic Stars AG Draconis FUSE FUSE observations of AG
Problem Solving. radians. 180 radians Stars & Elementary Astrophysics: Introduction Press F1 for Help 41. f s. picture. equation.
 Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
Formation of excited states in high-z helium-like systems
 Hyperfine Interactions 127 (2000) 257 262 257 Formation of excited states in high-z helium-like systems S. Fritzsche a,th.stöhlker b,c, O. Brinzanescu c,d and B. Fricke a a Fachbereich Physik, Universität
Hyperfine Interactions 127 (2000) 257 262 257 Formation of excited states in high-z helium-like systems S. Fritzsche a,th.stöhlker b,c, O. Brinzanescu c,d and B. Fricke a a Fachbereich Physik, Universität
Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions
 Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions W. Scheid 1,A.Pálffy 2,Z.Harman 2, C. Kozhuharov 3, and C. Brandau 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik der Justus-Liebig-Universität
Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions W. Scheid 1,A.Pálffy 2,Z.Harman 2, C. Kozhuharov 3, and C. Brandau 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik der Justus-Liebig-Universität
Evaluation and Comparison of the Configuration Interaction Calculations for Complex Atoms
 Atoms 2014, 2, 1-14; doi:10.3390/atoms2010001 OPEN ACCESS atoms ISSN 2218-2004 www.mdpi.com/journal/atoms Article Evaluation and Comparison of the Configuration Interaction Calculations for Complex Atoms
Atoms 2014, 2, 1-14; doi:10.3390/atoms2010001 OPEN ACCESS atoms ISSN 2218-2004 www.mdpi.com/journal/atoms Article Evaluation and Comparison of the Configuration Interaction Calculations for Complex Atoms
Resonant Polarization Spectroscopy for Hot X-ray Plasmas
 Journal of Physical Science and Application 6 (4) (2016) 22-29 doi: 10.17265/2159-5348/2016.04.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Resonant Polarization Spectroscopy for Hot X-ray Plasmas Guo-Xin Chen Harvard-Smithsonian
Journal of Physical Science and Application 6 (4) (2016) 22-29 doi: 10.17265/2159-5348/2016.04.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Resonant Polarization Spectroscopy for Hot X-ray Plasmas Guo-Xin Chen Harvard-Smithsonian
Possibilities for a Bose-Einstein Condensed Positronium Annihilation Gamma Ray Laser
 Possibilities for a Bose-Einstein Condensed Positronium Annihilation Gamma Ray Laser Allen Mills, Jr., University of California Riverside in collaboration with David Cassidy and Harry Tom (UCR) Rod Greaves
Possibilities for a Bose-Einstein Condensed Positronium Annihilation Gamma Ray Laser Allen Mills, Jr., University of California Riverside in collaboration with David Cassidy and Harry Tom (UCR) Rod Greaves
X-ray Spectroscopy on Fusion Plasmas
 X-ray Spectroscopy on s An ongoing discussion between the two Manfreds Manfred von Hellermann for CXRS Manfred Bitter for x-ray spectroscopy G. Bertschinger for many contributers (Bitter, Kunze, Weinheimer,
X-ray Spectroscopy on s An ongoing discussion between the two Manfreds Manfred von Hellermann for CXRS Manfred Bitter for x-ray spectroscopy G. Bertschinger for many contributers (Bitter, Kunze, Weinheimer,
Extreme-ultraviolet emissivity from Xe 8+ to Xe 12+ by using a detailed line-by-line method
 Eur. Phys. J. D (21) DOI: 1.114/epjd/e21-192-6 Regular Article THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL D Extreme-ultraviolet emissivity from Xe 8+ to Xe 12+ by using a detailed line-by-line method J. Zeng a, C.
Eur. Phys. J. D (21) DOI: 1.114/epjd/e21-192-6 Regular Article THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL D Extreme-ultraviolet emissivity from Xe 8+ to Xe 12+ by using a detailed line-by-line method J. Zeng a, C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10721 Experimental Methods The experiment was performed at the AMO scientific instrument 31 at the LCLS XFEL at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The nominal electron bunch charge
doi:10.1038/nature10721 Experimental Methods The experiment was performed at the AMO scientific instrument 31 at the LCLS XFEL at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The nominal electron bunch charge
Artep, Inc., at Naval Research Laboratory, 4555 Overlook Avenue, SW, Code 7600A, Washington, DC 20375; and K. P.
 The Astrophysical Journal, 574:495 503, 2002 July 20 # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A COMPARISON BETWEEN CORONAL EMISSION LINES FROM AN ISOTHERMAL SPECTRUM
The Astrophysical Journal, 574:495 503, 2002 July 20 # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A COMPARISON BETWEEN CORONAL EMISSION LINES FROM AN ISOTHERMAL SPECTRUM
2 The solar atmosphere
 1 The solar atmosphere 1.1 Introduction The solar atmosphere may be broadly defined as that part of the Sun extending outwards from a level known as the photosphere where energy generated at the Sun s
1 The solar atmosphere 1.1 Introduction The solar atmosphere may be broadly defined as that part of the Sun extending outwards from a level known as the photosphere where energy generated at the Sun s
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018
 www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
MANIPAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SCHEME OF EVAUATION MANIPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOOGY MANIPA UNIVERSITY, MANIPA SECOND SEMESTER B.Tech. END-SEMESTER EXAMINATION - MAY SUBJECT: ENGINEERING PHYSICS (PHY/) Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 5 Note: Answer
SCHEME OF EVAUATION MANIPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOOGY MANIPA UNIVERSITY, MANIPA SECOND SEMESTER B.Tech. END-SEMESTER EXAMINATION - MAY SUBJECT: ENGINEERING PHYSICS (PHY/) Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 5 Note: Answer
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
Use of a High-Resolution Overview Spectrometer for the Visible Range in the TEXTOR Boundary Plasma
 Use of a High-Resolution Overview Spectrometer for the Visible Range in the TEXTOR Boundary Plasma Sebastijan BREZINSEK, Albrecht POSPIESZCZYK, Gennadij SERGIENKO, Philippe MERTENS and Ulrich SAMM Institut
Use of a High-Resolution Overview Spectrometer for the Visible Range in the TEXTOR Boundary Plasma Sebastijan BREZINSEK, Albrecht POSPIESZCZYK, Gennadij SERGIENKO, Philippe MERTENS and Ulrich SAMM Institut
OUTLINE: P. Kotrč (1), P. Heinzel (1) and O. Procházka (2)
 On measurements of continuum flux in solar flares. Instrument and first results. P. Kotrč (1), P. Heinzel (1) and O. Procházka (2) (1) - Astronomical Institute, AS CR, v.v.i. Ondřejov, Czech Republic (2)
On measurements of continuum flux in solar flares. Instrument and first results. P. Kotrč (1), P. Heinzel (1) and O. Procházka (2) (1) - Astronomical Institute, AS CR, v.v.i. Ondřejov, Czech Republic (2)
Multiple charge states of titanium ions in laser produced plasma
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 781 787 Multiple charge states of titanium ions in laser produced plasma M SHUKLA, S BANDHYOPADHYAY, V
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 781 787 Multiple charge states of titanium ions in laser produced plasma M SHUKLA, S BANDHYOPADHYAY, V
CONTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF MOLYBDENUM ATOM AND IONS IN ASTROPHYSICAL AND LABORATORY PLASMA AS A FUNCTION OF ELECTRON TEMPERATURE
 COTRIBUTIO FUCTIO OF MOLYBDEUM ATOM AD IOS I ASTROPHYSICAL AD LABORATORY PLASMA AS A FUCTIO OF ELECTRO TEMPERATURE A.. Jadhav Department of Electronics, Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya, anded. Affiliated to Swami
COTRIBUTIO FUCTIO OF MOLYBDEUM ATOM AD IOS I ASTROPHYSICAL AD LABORATORY PLASMA AS A FUCTIO OF ELECTRO TEMPERATURE A.. Jadhav Department of Electronics, Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya, anded. Affiliated to Swami
object objective lens eyepiece lens
 Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Highly Charged Ion Astrophysics in the Laboratory: A New User Facility at Clemson University. Chad E. Sosolik Dept. of Physics and Astronomy
 Highly Charged Ion Astrophysics in the Laboratory: A New User Facility at Clemson University Chad E. Sosolik Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Clemson s New User Facility Highly charged ion (HCI) production
Highly Charged Ion Astrophysics in the Laboratory: A New User Facility at Clemson University Chad E. Sosolik Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Clemson s New User Facility Highly charged ion (HCI) production
ATHENA / AD-1. First production and detection of cold antihydrogen atoms. ATHENA Collaboration. Rolf Landua CERN
 ATHENA / AD-1 First production and detection of cold antihydrogen atoms ATHENA Collaboration Rolf Landua CERN 1 LONG TERM PHYSICS GOALS Antihydrogen = Hydrogen? CPT Gravity But... 2 FIRST GOAL PRODUCTION
ATHENA / AD-1 First production and detection of cold antihydrogen atoms ATHENA Collaboration Rolf Landua CERN 1 LONG TERM PHYSICS GOALS Antihydrogen = Hydrogen? CPT Gravity But... 2 FIRST GOAL PRODUCTION
Discovery of Emission Lines in the X-ray Spectrum of the Perseus Cluster
 Discovery of Emission Lines in the X-ray Spectrum of the Perseus Cluster J. L. Culhane University College London Mullard Space Science Laboratory Summary Nature of the Solar Corona and properties of its
Discovery of Emission Lines in the X-ray Spectrum of the Perseus Cluster J. L. Culhane University College London Mullard Space Science Laboratory Summary Nature of the Solar Corona and properties of its
Cesium Dynamics and H - Density in the Extended Boundary Layer of Negative Hydrogen Ion Sources for Fusion
 Cesium Dynamics and H - Density in the Extended Boundary Layer of Negative Hydrogen Ion Sources for Fusion C. Wimmer a, U. Fantz a,b and the NNBI-Team a a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM
Cesium Dynamics and H - Density in the Extended Boundary Layer of Negative Hydrogen Ion Sources for Fusion C. Wimmer a, U. Fantz a,b and the NNBI-Team a a Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, EURATOM
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers
 Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Principles and Applications DAVID ATTWOOD UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
SOFT X-RAYS AND EXTREME ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Principles and Applications DAVID ATTWOOD UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
Spectral signatures of the impulsive energy release in SMM BCS spectra
 Spectral signatures of the impulsive energy release in SMM BCS spectra B. Sylwester, J. Sylwester, K.J.H. Phillips, A. Kępa, Ż. Szaforz Space Research Center of PAS, Wrocław Earth Sciences Department,
Spectral signatures of the impulsive energy release in SMM BCS spectra B. Sylwester, J. Sylwester, K.J.H. Phillips, A. Kępa, Ż. Szaforz Space Research Center of PAS, Wrocław Earth Sciences Department,
FUNDAMENTAL PARAMETER METHOD FOR THE LOW ENERGY REGION INCLUDING CASCADE EFFECT AND PHOTOELECTRON EXCITATION
 Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 511 FUNDAMENTAL PARAMETER METHOD FOR THE LOW ENERGY REGION INCLUDING CASCADE EFFECT AND PHOTOELECTRON
Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 511 FUNDAMENTAL PARAMETER METHOD FOR THE LOW ENERGY REGION INCLUDING CASCADE EFFECT AND PHOTOELECTRON
1 EX/P7-35. Spectroscopic Studies on GLAST-III Varying the Inductance and Charging Voltage of Vertical Field Coils
 1 EX/P7-35 Spectroscopic Studies on GLAST-III Varying the Inductance and Charging Voltage of Vertical Field Coils Farah Deeba, A.Qayyum, Zahoor Ahmad, S. Ahmad, R. Khan and S. Hussain National Tokamak
1 EX/P7-35 Spectroscopic Studies on GLAST-III Varying the Inductance and Charging Voltage of Vertical Field Coils Farah Deeba, A.Qayyum, Zahoor Ahmad, S. Ahmad, R. Khan and S. Hussain National Tokamak
The World s Smallest Extreme Laboratories:
 The World s Smallest Extreme Laboratories: Probing QED with Highly Charged Ions. Joan Marler Clemson University Outline About HCIs About Ion trapping Precision spectroscopy with HCIs Highly Charged Ions
The World s Smallest Extreme Laboratories: Probing QED with Highly Charged Ions. Joan Marler Clemson University Outline About HCIs About Ion trapping Precision spectroscopy with HCIs Highly Charged Ions
Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility
 2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants
 Spectroscopic Analysis and NLTE Radiative Cooling Effects in ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants I. E. Golovkin 1, J. J. MacFarlane 1, P. Woodruff 1, J. E. Bailey 2, G. Rochau 2, K. Peterson 2, T.
Spectroscopic Analysis and NLTE Radiative Cooling Effects in ICF Capsule Implosions with Mid-Z Dopants I. E. Golovkin 1, J. J. MacFarlane 1, P. Woodruff 1, J. E. Bailey 2, G. Rochau 2, K. Peterson 2, T.
Spectroscopy in Astronomy
 Spectroscopy in Astronomy History 1814 German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer sun with 600+ spectral lines; now we know more than 3000 lines 1860 German chemists Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert W. Bunsen Chemical
Spectroscopy in Astronomy History 1814 German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer sun with 600+ spectral lines; now we know more than 3000 lines 1860 German chemists Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert W. Bunsen Chemical
プラズマ光源関連イオンの EBIT による分光
 プラズマ光源関連イオンの EBIT による分光 Emission spectroscopy of multiply charged ions related to plasma light sources with an EBIT 大橋隼人, 八釼純治, 坂上裕之 *, 中村信行 レーザー新世代研究センター, 電気通信大学 * 核融合科学研究所 2012 年度原子分子データ応用フォーラムセミナー 2012
プラズマ光源関連イオンの EBIT による分光 Emission spectroscopy of multiply charged ions related to plasma light sources with an EBIT 大橋隼人, 八釼純治, 坂上裕之 *, 中村信行 レーザー新世代研究センター, 電気通信大学 * 核融合科学研究所 2012 年度原子分子データ応用フォーラムセミナー 2012
Atomic double slit: Coherence transfer through excitation and (Auger) decay processes. S. Fritzsche, Kassel University Göteborg, 3rd June 2006
 Atomic double slit: Coherence transfer through excitation and (Auger) decay processes S. Fritzsche, Kassel University Göteborg, 3rd June 2006 Experiments with double slits (Feynman-Lectures 1962) Interference
Atomic double slit: Coherence transfer through excitation and (Auger) decay processes S. Fritzsche, Kassel University Göteborg, 3rd June 2006 Experiments with double slits (Feynman-Lectures 1962) Interference
LECTURE NOTES. Ay/Ge 132 ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR PROCESSES IN ASTRONOMY AND PLANETARY SCIENCE. Geoffrey A. Blake. Fall term 2016 Caltech
 LECTURE NOTES Ay/Ge 132 ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR PROCESSES IN ASTRONOMY AND PLANETARY SCIENCE Geoffrey A. Blake Fall term 2016 Caltech Acknowledgment Part of these notes are based on lecture notes from the
LECTURE NOTES Ay/Ge 132 ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR PROCESSES IN ASTRONOMY AND PLANETARY SCIENCE Geoffrey A. Blake Fall term 2016 Caltech Acknowledgment Part of these notes are based on lecture notes from the
CYCLOTRON-RESONANCE ION SOURCE (ECRIS) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLY CHARGED IONS
 CYCLOTRON-RESONANCE ION SOURCE (ECRIS) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLY CHARGED IONS M. Schlapp'*], R. Trassl[+', P. Hathirammi[*], R. W. McCullough"], J.B Greenwood[#] and E. Salzborn'+] ['I Argonne National
CYCLOTRON-RESONANCE ION SOURCE (ECRIS) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF MULTIPLY CHARGED IONS M. Schlapp'*], R. Trassl[+', P. Hathirammi[*], R. W. McCullough"], J.B Greenwood[#] and E. Salzborn'+] ['I Argonne National
Relative intensity calibration of CDS-GIS detectors on SOHO using a plasma diagnostic technique
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS FEBRUARY II 1999, PAGE 171 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 135, 171 185 (1999) Relative intensity calibration of CDS-GIS detectors on SOHO using a plasma diagnostic
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS FEBRUARY II 1999, PAGE 171 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 135, 171 185 (1999) Relative intensity calibration of CDS-GIS detectors on SOHO using a plasma diagnostic
MT Electron microscopy Scanning electron microscopy and electron probe microanalysis
 MT-0.6026 Electron microscopy Scanning electron microscopy and electron probe microanalysis Eero Haimi Research Manager Outline 1. Introduction Basics of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron
MT-0.6026 Electron microscopy Scanning electron microscopy and electron probe microanalysis Eero Haimi Research Manager Outline 1. Introduction Basics of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron
