Lecture #26: Plan. Cosmology: Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe. The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d)
|
|
|
- Octavia Gibbs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture #26: Plan Cosmology: The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d) Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe
2 Reminders Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review session: Monday, December 11, 6-8 pm, PHYS 1412, your TAs will be answering your questions
3 3. The Birth of our Universe [NOT ON THE FINAL!]
4 Fundamental Forces in Nature Gravitational Force Force between massive bodies Infinite in range, but weakens with distance Electromagnetic Force Force between charged bodies Infinite in range, but weakens with distance Strong Nuclear Force Force that holds atomic nuclei together Very short range meters! Weak Nuclear Force Force responsible for radioactive decay Very short range meters!
5 Relative strength of four forces depends on temperature Today 10-6 sec sec sec GUTs Grand Unified Theories
6 Decay asymmetry due to weak force caused matter / antimatter imbalance Today 10-6 sec sec sec GUTs Grand Unified Theories
7 Phase transition (e.g. water sec Release of vast amount of energy Today 10-6 sec sec sec GUTs Grand Unified Theories
8 The Epoch of Inflation ( sec) By second, the visible universe expanded from the size of a proton to the size of a basketball (x ) This rapid expansion is called inflation This coincides with the time when the strong force became distinct from the electroweak force
9 What happened before second? All forces except gravity are indistinguishable: GUT force Today 10-6 sec sec sec GUTs Grand Unified Theories
10 Planck time = 5.4 x second Gravity becomes indistinguishable from all other forces??? No good theory of quantum gravity Planck Time
11 What about t < 0??? Very uncertain! Universe created from vacuum fluctuations??? Astrophysics meets religion (take ASTR 340 to find out more about cosmology!)
12 Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings
13 Searching for Other Civilizations Searching for signals from other beings. The big problems are: is a signal artificial? where to look? what to look for?
14 What is an artificial signal? Signal with beats corresponding to prime numbers or some other mathematical theme (= universal language) Where to look? Each star one at a time can take a long time. What to look for? Searching for Other Civilizations Radio, optical, X-ray? What specific frequency of radio, optical, or X-ray?
15 What is Expected? Signal of Abnormal Behavior Codes Prime Numbers, Patterns Jodie Foster in 1997 movie Contact
16 Prime Numbers Numbers divisible only by themselves and 1 Advantage: no regular pattern, and cannot be duplicated by natural processes If signal repeats 2, 3, 5, 7,... a few times, it has to be artificial
17 Photon (Light) Strategy The Electromagnetic Spectrum
18 What is the Best Frequency / Wavelength? Frequency = (speed of light) / (wavelength) = # of crests in one second Considerations include energy to send signal and bandwidth allowed Lower-energy (longer wavelength) are more energy efficient However, shorter wavelength has higher frequency, thus higher bandwidth, thus can send more information Also, what about host star interference? Compromise is not clear
19 Consider Visible Infrared Near-infrared wavelengths cut through the dust
20 The stars disappear in the mid-to-far infrared! less interference!
21 The Power of Wavelength Conclusion: Use Long Wavelengths! But Which Ones?
22 Nature Provides A Clue Galactic Noise (Synchrotron Radiation) H OH Atmospheric Emission The Water Hole
23 Searching for Other Civilizations The water hole is a minimum in galactic emission and a pointer to our origins.
24 The Cosmic Water Hole H + OH H 2 O H 21.1 cm 1420 MHz OH 18.3 cm 1638 MHz These are in the radio region!
25 Searching for Other Civilizations The hydrogen emission line at 21 cm comes from the spin flip transition of hydrogen! best frequency? The first searches by Frank Drake were done towards stars at that frequency (21 cm! 1420 MHz = 1.4 GHz): Project Ozma
26 Project Ozma, 1960 National Radio Astronomical Observatory Green Bank, West Virginia Two Stars observed by Frank Drake during one month
27 Project Ozma, 1960 Observed at GHz Total bandwidth: 400 KHz Single-channel receiver with bandwidth of 100 Hz
28 Little Green Men? 1967, Cambridge, England Doctoral student Jocelyn Bell Constructed radio telescope (interferometer) Found super-regular signals Could these be aliens?!
29 Little Green Men? 1967, Cambridge, England Doctoral student Jocelyn Bell Constructed radio telescope (interferometer) Found super-regular signals Could these be aliens?!
30 Searching for Other Civilizations The first pulsars were called LGM 1, 2 and 3 where that stood for Little Green Men as a half-joke. The signals have extremely fast and regular periods which are very unusual we now know that this arises from the spins of pulsars.! 1974 Nobel Prize to Ryle (telescope design) & Hewish (Bell s supervisor) but not Bell!
31 Project Ozma II, National Radio Astronomical Observatory Green Bank, West Virginia 650 stars observed by B. Zuckerman & P. Palmer 4 years
32 November 15,1988
33 Today: National Radio Astronomical Observatory Green Bank Telescope, West Virginia Same observations as Ozma in under 1 sec!
34 How Many Channels in Cosmic Water Hole? 1638 MHz = 1,638,000,000 Hz (OH) 1420 MHz = 1,420,000,000 Hz (H) 0.1 Hz / channel (1,638,000,000 1,420,000,000 ) / billion channels
35 Math ~ 2 billion radio channels Modern computers measure Band ~ 250 million channels at once Examine each band for 1 sec need 8 seconds for total coverage of one star
36 ~ 2 Billion Candidates in Milky Way?
37 More Math ~ 2 billion radio channels in the Cosmic Water Hole Each star needs ~ 8 seconds for coverage For ~ 2 billion stars will need about 500 years for total coverage!
38 Computing Power Doubles every ~2 yrs Moore s Law In ~20 years, can study all candidate stars in ~ 1/2 year, not 500 years!
39 Searching for Other Civilizations The Allen Telescope Array: 42 six-meter antennae in Northern California Privately funded by Paul Allen (Microsoft co-founder; >$30M), Franklin Antoniio (QUALCOMM, $3.6M), others SETI observations as of 2016 Breakthrough Listen: In July 2015, Russian billionaire Yuri Milner has agreed to donate $100M in 10 yrs to fund SETI projects Stay tuned! Breakthrough Starshot: Milner donated another $100M to prove the principle of sending multiple tiny crafts to Alpha Centauri (planet Proxima B)
40 Searching for Other Civilizations There are no detections to date at any wavelength. The researchers are very motivated and committed to making their results public! So what does this mean? What would it mean if we continue to detect nothing for 100 years?!
41 ASTR 380 Searching for Other Civilizations Two critical questions in interpreting the lack of detections are: How likely is it that ET wants to communicate with us? -- very hard to guess this. -- perhaps our only hope is accidental emissions How long does a civilization broadcast freely into space? -- perhaps after 100 years we will use optical fibers, or something new and the Earth will be radio quiet (no losses / leakage to space).
42 The Drake Equation A Fun Exercise: the Drake Equation (simplified) where: N I = N * x f P x f L x f I N I is the number of planets in our Galaxy that contain intelligent life N * is the number of suitable stars in our Galaxy f P is the fraction ( 1) of these stars that have a habitable planet f L is the probability ( 1) of life forming on such a planet is the probability of intelligent life forming (now) given that life had formed f I What are your guesses for these factors???
43 The Drake Equation A Fun Exercise: the Drake Equation (simplified) where: N I = N * x f P x f L x f I N I is the number of planets in our Galaxy that contain intelligent life N * is the number of suitable stars in our Galaxy (~10 10 ) f P is the fraction ( 1) of these stars that have a habitable planet (~0.1) f L is the probability ( 1) of life forming on such a planet (~0.01) f I is the probability of intelligent life forming (now) given that life had formed (~0.001) N I = x 0.1 x 0.01 x ~ 10,000! Not Bad!
44 However: If one other civilization exists in our Galaxy, AND Searching for Other Civilizations 1. It started 1,000,000 years before us. 2. And does space travel 5-10 light-year distances 3. And colonizes a new stellar systems every 20,000 years 4. And is long lived.. Exponential growth! It would span every stellar system in our Galaxy with suitable Earth-like planets right now! But then where are they?! This is often called the Fermi Paradox
45 Summary Finding intelligent life probably means patiently waiting until we receive some signal No detections yet What does it mean? Fermi Paradox? (take ASTR 380 to find out more!)
Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations. SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings
 Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings Searching for Other Civilizations Searching for signals from other
Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings Searching for Other Civilizations Searching for signals from other
Lecture #25: Plan. Cosmology. The early Universe (cont d) The fate of our Universe The Great Unanswered Questions
 Lecture #25: Plan Cosmology The early Universe (cont d) The fate of our Universe The Great Unanswered Questions Announcements Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review sheet #3 was emailed to you
Lecture #25: Plan Cosmology The early Universe (cont d) The fate of our Universe The Great Unanswered Questions Announcements Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review sheet #3 was emailed to you
Search Strategies. Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons
 Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes. Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017
 Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017 Reminders Last star party of the semester tomorrow night! Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm The first three minutes
Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017 Reminders Last star party of the semester tomorrow night! Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm The first three minutes
! Communication, 2.!
 Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm. Astronomy 100. Tom Burbine
 Astronomy 100 Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Tom Burbine tburbine@mtholyoke.edu www.xanga.com/astronomy100 Schedule Today (end and beginning of the universe) May 3 (Does Life Exist Elsewhere in the Universe)
Astronomy 100 Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Tom Burbine tburbine@mtholyoke.edu www.xanga.com/astronomy100 Schedule Today (end and beginning of the universe) May 3 (Does Life Exist Elsewhere in the Universe)
Lecture 40: SETI. Astronomy Winter This lecture is about SETI, the Search for Extra- Terrestrial Intelligence.
 Lecture 40 SETI: The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture is about SETI, the Search for Extra- Terrestrial Intelligence. Searching for artificial radio signals
Lecture 40 SETI: The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture is about SETI, the Search for Extra- Terrestrial Intelligence. Searching for artificial radio signals
Chapter 22 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. The Birth of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Big Bang The Beginning of Time
 The Big Bang The Beginning of Time What were conditions like in the early universe? The early universe must have been extremely hot and dense Photons converted into particle-antiparticle pairs and vice-versa
The Big Bang The Beginning of Time What were conditions like in the early universe? The early universe must have been extremely hot and dense Photons converted into particle-antiparticle pairs and vice-versa
Search Strategies. Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons
 Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3.
 Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3)
 Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3) Key Ideas Physics of the Early Universe Informed by experimental & theoretical physics Later stages confirmed by observations
Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3) Key Ideas Physics of the Early Universe Informed by experimental & theoretical physics Later stages confirmed by observations
Chapter 27: The Early Universe
 Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
Sociological Factors. Putting it all Together: How far away? How many stars to search?
 f c = /2? Sociological Factors at least, maybe 3 intelligent species on Earth with technology for remote communication L > 75 years Longevity - how long are they detectable? leakage of VHF/UHF signals
f c = /2? Sociological Factors at least, maybe 3 intelligent species on Earth with technology for remote communication L > 75 years Longevity - how long are they detectable? leakage of VHF/UHF signals
Stellar remnants II. Neutron Stars 10/18/2010. (progenitor star 1.4 < M< 3 Msun) Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Exam #2 on Wednesday Review sheet and study guide posted by Thursday Use office hours and Astronomy Tutorial hours Covers material since Exam #1 (plus background
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Exam #2 on Wednesday Review sheet and study guide posted by Thursday Use office hours and Astronomy Tutorial hours Covers material since Exam #1 (plus background
Lecture #24: Plan. Cosmology. Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe
 Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc. Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc. Indirect searches
A100H Exploring the Universe: Big Bang Theory. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the : Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 21, 2016 Read: Chap 23 04/26/16 slide 1 Early Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at 10:30 am 12:30 pm, here! Emphasizes
A100H Exploring the : Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 21, 2016 Read: Chap 23 04/26/16 slide 1 Early Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at 10:30 am 12:30 pm, here! Emphasizes
Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1. Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017
 Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1 Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017 Reminders Star party tonight! Homework #3 due Monday Exam #1 Monday, September 25 The nature of light Look, but don t
Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1 Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017 Reminders Star party tonight! Homework #3 due Monday Exam #1 Monday, September 25 The nature of light Look, but don t
Cosmology. Big Bang and Inflation
 Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE?
 i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
A100 Exploring the Universe Big Bang Theory and the Early Universe. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100 Exploring the Universe and the Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu December 02, 2014 Read: Chap 23 12/04/14 slide 1 Assignment on Chaps 22 23, at the end of next week,
A100 Exploring the Universe and the Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu December 02, 2014 Read: Chap 23 12/04/14 slide 1 Assignment on Chaps 22 23, at the end of next week,
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online.
 Announcements HW #5 Due Wed, Dec. 10th. Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online. NOTE: Planetarium: Large dome you sit inside.
Announcements HW #5 Due Wed, Dec. 10th. Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online. NOTE: Planetarium: Large dome you sit inside.
Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy. Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017
 Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017 Reminders Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm One more lecture after today Monday
Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017 Reminders Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm One more lecture after today Monday
Chapter 22 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. The Birth of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory What were conditions like in the early universe? How did the early universe change with time?
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory What were conditions like in the early universe? How did the early universe change with time?
Chapter 23 The Beginning of Time. Agenda. Presentation Tips. What were conditions like in the early universe? 23.1 The Big Bang.
 Chapter 23 The Beginning of Time Agenda Announce: Observation April 19 Thursday 8pm APS Meeting April 17 no class (instead Fate of the Universe tutorial Presentation Tips Ch. 23 Presentation Tips Limit
Chapter 23 The Beginning of Time Agenda Announce: Observation April 19 Thursday 8pm APS Meeting April 17 no class (instead Fate of the Universe tutorial Presentation Tips Ch. 23 Presentation Tips Limit
2) On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find red giant stars? A) upper right B) lower right C) upper left D) lower left
 Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Lecture 12 Cosmology III. Inflation The beginning?
 Lecture 12 Cosmology III Inflation The beginning? Unsolved issues in the standard model Horizon problem: Why is the CMB so smooth? The flatness problem: Why is Ω~1? Why is the universe flat? The structure
Lecture 12 Cosmology III Inflation The beginning? Unsolved issues in the standard model Horizon problem: Why is the CMB so smooth? The flatness problem: Why is Ω~1? Why is the universe flat? The structure
Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway?
 Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI,
Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI,
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Alternative Standard Frequencies for Interstellar Communication. C Sivaram. Indian Institute of Astrophysics. Bangalore , India
 Running title: Alternate standard frequency Alternative Standard requencies for Interstellar Communication C Sivaram Indian Institute of Astrophysics angalore - 560 0, India Kenath Arun * Christ Junior
Running title: Alternate standard frequency Alternative Standard requencies for Interstellar Communication C Sivaram Indian Institute of Astrophysics angalore - 560 0, India Kenath Arun * Christ Junior
Chapter 27 The Early Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 27 The Early Universe Units of Chapter 27 27.1 Back to the Big Bang 27.2 The Evolution of the Universe More on Fundamental Forces 27.3 The Formation of Nuclei and Atoms 27.4 The Inflationary Universe
Chapter 27 The Early Universe Units of Chapter 27 27.1 Back to the Big Bang 27.2 The Evolution of the Universe More on Fundamental Forces 27.3 The Formation of Nuclei and Atoms 27.4 The Inflationary Universe
OUSSEP Final Week. If we run out of time you can look at uploaded slides Pearson Education, Inc.
 OUSSEP Final Week Last week hopefully read Holiday-Week 23rd November Lecture notes Hand in your Hubble Deep Field Reports today! (If not today then in my mail box @ International College.) Today we will
OUSSEP Final Week Last week hopefully read Holiday-Week 23rd November Lecture notes Hand in your Hubble Deep Field Reports today! (If not today then in my mail box @ International College.) Today we will
Part I: The Dawn of Time
 Part I: The Dawn of Time Topics within Part I. 1. Origins of the Universe: from the Infinite to the Subatomic. 2. Planets and Meteorites: Neighbors in Space 3. Birth of the Earth and Moon: a Coupled System
Part I: The Dawn of Time Topics within Part I. 1. Origins of the Universe: from the Infinite to the Subatomic. 2. Planets and Meteorites: Neighbors in Space 3. Birth of the Earth and Moon: a Coupled System
Unity in the Whole Structure
 Cosmology II Unity in the Whole Structure How is it possible by any methods of observation yet known to the astronomer to learn anything about the universe as a whole? It is possible only because the universe,
Cosmology II Unity in the Whole Structure How is it possible by any methods of observation yet known to the astronomer to learn anything about the universe as a whole? It is possible only because the universe,
Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time
 Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Future of universe depends on the total amount of dark and normal matter Amount of matter
Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Future of universe depends on the total amount of dark and normal matter Amount of matter
Young Solar-like Systems
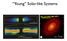 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Early (Expanding) Universe. Average temperature decreases with expansion.
 Early (Expanding) Universe Average temperature decreases with expansion. Particles & Anti-Particles Very short wavelength photons collide and form electron-positron pairs. E=mc 2 electron=matter positron=antimatter
Early (Expanding) Universe Average temperature decreases with expansion. Particles & Anti-Particles Very short wavelength photons collide and form electron-positron pairs. E=mc 2 electron=matter positron=antimatter
Mapping the Galaxy using hydrogen
 The Swedish contribution to EU-HOU: A Hands-On Radio Astronomy exercise Mapping the Galaxy using hydrogen Daniel Johansson Christer Andersson Outline Introduction to radio astronomy Onsala Space Observatory
The Swedish contribution to EU-HOU: A Hands-On Radio Astronomy exercise Mapping the Galaxy using hydrogen Daniel Johansson Christer Andersson Outline Introduction to radio astronomy Onsala Space Observatory
Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time
 Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Back to the Big Bang The early Universe was both dense and hot. Equivalent mass density of radiation (E=mc
Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Back to the Big Bang The early Universe was both dense and hot. Equivalent mass density of radiation (E=mc
AST 205. Lecture 23. December 8, 2003 SETI, Interstellar Travel and the Fermi Paradox. Assignments for week of Dec 8
 AST 205. Lecture 23. December 8, 2003 SETI, Interstellar Travel and the Fermi Paradox Evaluation of the Drake Equation SETI: Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Good news Bad news Interstellar travel
AST 205. Lecture 23. December 8, 2003 SETI, Interstellar Travel and the Fermi Paradox Evaluation of the Drake Equation SETI: Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Good news Bad news Interstellar travel
Inflationary Universe and. Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation
 Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Survey questions. Inflationary Universe and. Survey Questions. Survey questions. Survey questions
 Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Astronomy Ch. 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In a neutron star, the core
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In a neutron star, the core
2. The evolution and structure of the universe is governed by General Relativity (GR).
 7/11 Chapter 12 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe. We start with two assumptions: 1. Cosmological Principle: On a large enough scale (large compared
7/11 Chapter 12 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe. We start with two assumptions: 1. Cosmological Principle: On a large enough scale (large compared
ABCs of Space By: John Kraus
 North American AstroPhysical Observatory (NAAPO) Cosmic Search: Issue 3 (Volume 1 Number 3; Summer 1979) [Article in magazine started on page 36] ABCs of Space By: John Kraus A. Stars and Their Spectra;
North American AstroPhysical Observatory (NAAPO) Cosmic Search: Issue 3 (Volume 1 Number 3; Summer 1979) [Article in magazine started on page 36] ABCs of Space By: John Kraus A. Stars and Their Spectra;
Fate of Stars. relative to Sun s mass
 INITIAL MASS relative to Sun s mass M < 0.01 Fate of Stars Final State planet.01 < M
INITIAL MASS relative to Sun s mass M < 0.01 Fate of Stars Final State planet.01 < M
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 6. The Structure and Scale of the Universe
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 6. The Structure and Scale of the Universe
Hubble s Law. Our goals for learning. What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe?
 Hubble s Law Our goals for learning What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe? How does the universe s expansion affect our distance measurements? We measure speeds
Hubble s Law Our goals for learning What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe? How does the universe s expansion affect our distance measurements? We measure speeds
Extragalactic Astronomy
 Extragalactic Astronomy Topics: Milky Way Galaxies: types, properties, black holes Active galactic nuclei Clusters and groups of galaxies Cosmology and the expanding universe Formation of structure Galaxies
Extragalactic Astronomy Topics: Milky Way Galaxies: types, properties, black holes Active galactic nuclei Clusters and groups of galaxies Cosmology and the expanding universe Formation of structure Galaxies
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D.
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter 17-2 Cosmology ³ The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³ Key moments: ² Einstein General Theory of Relativity
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter 17-2 Cosmology ³ The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³ Key moments: ² Einstein General Theory of Relativity
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter. Olber s Paradox. Cosmology. Olber s Paradox. Assumptions 4/20/18
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter Cosmology ³The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³Key moments: ²Einstein General Theory of Relativity ²Hubble
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter Cosmology ³The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³Key moments: ²Einstein General Theory of Relativity ²Hubble
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS FINAL EXAM: THURSDAY, May 14 th, 11:15am Last Astronomy public talk, May 8 th (up to 3% Extra class credit (see Blackboard announcement for details)
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS FINAL EXAM: THURSDAY, May 14 th, 11:15am Last Astronomy public talk, May 8 th (up to 3% Extra class credit (see Blackboard announcement for details)
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. OUR Universe: Accelerating Universe
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies FINAL: Saturday, Dec 12th, 7:30pm, HERE ALTERNATE FINAL: Monday, Dec 7th, 5:30pm in Muenzinger E131 Last OBSERVING session, Tue, Dec.8th, 7pm Please check
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies FINAL: Saturday, Dec 12th, 7:30pm, HERE ALTERNATE FINAL: Monday, Dec 7th, 5:30pm in Muenzinger E131 Last OBSERVING session, Tue, Dec.8th, 7pm Please check
Light. Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation. Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays
 Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Nuclear Synthesis. PHYS 162 Lectures 10a,b 1
 Nuclear Synthesis All elements heavier than Helium are made inside stars up to Iron - fusion in Red Giants heavier than Iron (and some lighter) - Supernova explosions Stars lose matter at end of life-cycle
Nuclear Synthesis All elements heavier than Helium are made inside stars up to Iron - fusion in Red Giants heavier than Iron (and some lighter) - Supernova explosions Stars lose matter at end of life-cycle
a)! 0-10 miles b)! miles c)! miles d)! miles
 How far away from this classroom will you be for Thanksgiving? a)! 0-10 miles b)! 10-100 miles c)! 100-1000 miles d)! 1000+ miles This Class (Lecture 33): The Early Universe HW 11 due on Dec 5 th Music:
How far away from this classroom will you be for Thanksgiving? a)! 0-10 miles b)! 10-100 miles c)! 100-1000 miles d)! 1000+ miles This Class (Lecture 33): The Early Universe HW 11 due on Dec 5 th Music:
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
ASTR Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
The first 400,000 years
 The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago
 Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller hgeller@gmu.edu http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George
Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller hgeller@gmu.edu http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab
 Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th
 Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Chiara Caprini (APC)
 COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
Science advances by a combination of normal science and discovery of anomalies.
 Science advances by a combination of normal science and discovery of anomalies. Many revolutions come from long periods of normal science reinforced by exceptional science. example: accelerating universe
Science advances by a combination of normal science and discovery of anomalies. Many revolutions come from long periods of normal science reinforced by exceptional science. example: accelerating universe
ASTRONOMY 161. Introduction to Solar System Astronomy. Class 9
 ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 9 Light Monday, January 29 Look, but don t touch. - Astronomers Motto Light: Key Concepts (1) Visible light is just one form of electromagnetic
ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 9 Light Monday, January 29 Look, but don t touch. - Astronomers Motto Light: Key Concepts (1) Visible light is just one form of electromagnetic
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars
 Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09. Astronomy 101
 The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere
 Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
What is the evidence that Big Bang really occurred
 What is the evidence that Big Bang really occurred Hubble expansion of galaxies Microwave Background Abundance of light elements but perhaps most fundamentally... Darkness of the night sky!! The very darkness
What is the evidence that Big Bang really occurred Hubble expansion of galaxies Microwave Background Abundance of light elements but perhaps most fundamentally... Darkness of the night sky!! The very darkness
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006
 Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
The Science Missions of Columbia
 The Science Missions of Columbia Tools for Viewing The Universe Tools for Viewing The Universe & Columbia Shuttle Added Corrective Optics to the Hubble Space Telescope Hubble Discovers a New View of The
The Science Missions of Columbia Tools for Viewing The Universe Tools for Viewing The Universe & Columbia Shuttle Added Corrective Optics to the Hubble Space Telescope Hubble Discovers a New View of The
The Early Universe. 1. Inflation Theory: The early universe expanded enormously in a brief instance in time.
 The Early Universe The Early Universe 1. Inflation Theory: The early universe expanded enormously in a brief instance in time. 2. The fundamental forces change during the first second after the big bang.
The Early Universe The Early Universe 1. Inflation Theory: The early universe expanded enormously in a brief instance in time. 2. The fundamental forces change during the first second after the big bang.
What is the 'cosmological principle'?
 What is the 'cosmological principle'? Modern cosmology always starts from this basic assumption the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic. This idea seems strange there's empty space between me and the
What is the 'cosmological principle'? Modern cosmology always starts from this basic assumption the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic. This idea seems strange there's empty space between me and the
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
Exploring the Early Universe. Chapter Twenty-Nine. Guiding Questions. The Isotropy Problem
 Exploring the Early Universe Chapter Twenty-Nine Guiding Questions 1. Has the universe always expanded as it does today, or might it have suddenly inflated? 2. How did the fundamental forces of nature
Exploring the Early Universe Chapter Twenty-Nine Guiding Questions 1. Has the universe always expanded as it does today, or might it have suddenly inflated? 2. How did the fundamental forces of nature
HNRS 227 Lecture 18 October 2007 Chapter 12. Stars, Galaxies and the Universe presented by Dr. Geller
 HNRS 227 Lecture 18 October 2007 Chapter 12 Stars, Galaxies and the Universe presented by Dr. Geller Recall from Chapters 1-11 Units of length, mass, density, time, and metric system The Scientific Method
HNRS 227 Lecture 18 October 2007 Chapter 12 Stars, Galaxies and the Universe presented by Dr. Geller Recall from Chapters 1-11 Units of length, mass, density, time, and metric system The Scientific Method
Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
 Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. The CMB as seen by the WMAP satellite.!2
Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. The CMB as seen by the WMAP satellite.!2
Name Final Exam December 7, 2015
 Name Final Exam December 7, 015 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Name Final Exam December 7, 015 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Origin of the Universe - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin. What does it all mean?
 Origin of the Universe - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin What does it all mean? Fundamental Questions in Cosmology 1. Why did the Big Bang occur? 2. Why is the Universe old? 3. Why is the Universe made of matter?
Origin of the Universe - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin What does it all mean? Fundamental Questions in Cosmology 1. Why did the Big Bang occur? 2. Why is the Universe old? 3. Why is the Universe made of matter?
Moment of beginning of space-time about 13.7 billion years ago. The time at which all the material and energy in the expanding Universe was coincident
 Big Bang Moment of beginning of space-time about 13.7 billion years ago The time at which all the material and energy in the expanding Universe was coincident Only moment in the history of the Universe
Big Bang Moment of beginning of space-time about 13.7 billion years ago The time at which all the material and energy in the expanding Universe was coincident Only moment in the history of the Universe
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint
 Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
One of elements driving cosmological evolution is the presence of radiation (photons) Early universe
 The Frontier Matter and Antimatter One of elements driving cosmological evolution is the presence of radiation (photons) Early universe Matter and antimatter But we live in universe full of matter -- where
The Frontier Matter and Antimatter One of elements driving cosmological evolution is the presence of radiation (photons) Early universe Matter and antimatter But we live in universe full of matter -- where
Course Descriptions. Appendix F
 Appendix F Course Descriptions Seven new courses are required to implement the Space Physics program, and their course descriptions are contained in this appendix. 51 F.1 Course Description: Physics II
Appendix F Course Descriptions Seven new courses are required to implement the Space Physics program, and their course descriptions are contained in this appendix. 51 F.1 Course Description: Physics II
The 64th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places
 The 64th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places Brian Odom Fall 2006 http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 2: From the Big Bang to
The 64th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places Brian Odom Fall 2006 http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 2: From the Big Bang to
ASTR 1P02 Test 2, March 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 2: March 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02, Section 2 Number of students: 1193
 ASTR 1P02 Test 2, March 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 2: March 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02, Section 2 Number of students: 1193 Examination date: 4 March 2017 Time limit: 50 min Time of
ASTR 1P02 Test 2, March 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 2: March 2017 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02, Section 2 Number of students: 1193 Examination date: 4 March 2017 Time limit: 50 min Time of
ASTR 200 : Lecture 20. Neutron stars
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 20 Neutron stars 1 Equation of state: Degenerate matter We saw that electrons exert a `quantum mechanical' pressure. This is because they are 'fermions' and are not allowed to occupy
ASTR 200 : Lecture 20 Neutron stars 1 Equation of state: Degenerate matter We saw that electrons exert a `quantum mechanical' pressure. This is because they are 'fermions' and are not allowed to occupy
Hawking & the Universe
 Hawking & the Universe This is a supplement to the lecture given on Jan 26, 2015, by Dr. Mounib El Eid, Physics department, AUB. It may motivate the reader to explore some of the presented issues. There
Hawking & the Universe This is a supplement to the lecture given on Jan 26, 2015, by Dr. Mounib El Eid, Physics department, AUB. It may motivate the reader to explore some of the presented issues. There
Cosmic Background Radiation
 Cosmic Background Radiation The Big Bang generated photons, which scattered frequently in the very early Universe, which was opaque. Once recombination happened the photons are scattered one final time
Cosmic Background Radiation The Big Bang generated photons, which scattered frequently in the very early Universe, which was opaque. Once recombination happened the photons are scattered one final time
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Before the term black hole was coined in 1967, these
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Before the term black hole was coined in 1967, these
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008
 Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Introduction. How did the universe evolve to what it is today?
 Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
